Professional Documents
Culture Documents
In The 80386 Microprocessor and Later
Uploaded by
Ankit BhatnagarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
In The 80386 Microprocessor and Later
Uploaded by
Ankit BhatnagarCopyright:
Available Formats
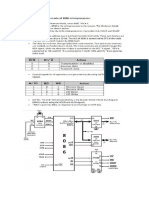
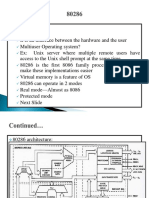
In the 80386 microprocessor and later, virtual 8086 mode (also called virtual real mode, V86mode or VM86)
allows the execution of real mode applications that are incapable of running directly in protected mode while the processor is running a protected mode operating system. VM86 mode uses a segmentation scheme identical to that of real mode (for compatibility reasons) which creates 20-bit linear addresses in the same manner as 20-bit physical addresses are created in real mode, but are subject to protected mode's memory paging mechanism. x86 processor modes Mode First supported Real mode, also called real address Real mode mode, is an operating mode of 80286 Intel 8086 and later x86-compatible CPUs. Real Protected mode mode is characterized by a 20 bit Intel 80286 segmented memory address space (giving exactly 1 MB of addressable Virtual 8086 mode Intel 80386 memory) and unlimited direct software access to all memory and Unreal mode Intel 80386 I/O addresses and peripheral hardware. Real mode provides no System Management Mode support for memory protection, Intel 386SL multitasking, or code privilege levels. Long mode 80186 CPUs and earlier, back to the AMD Opteron original 8086, have only one operational mode, which is equivalent to real mode in later chips. All x86 CPUs in the 80286 series and later start in real mode when reset.
,
You might also like
- Mega Drive Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #3From EverandMega Drive Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #3No ratings yet
- Real ModeDocument3 pagesReal Modeharsimranjeet1No ratings yet
- Master System Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #15From EverandMaster System Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #15No ratings yet
- and Pentium MicroprocessorsDocument37 pagesand Pentium Microprocessorsgayathrishiv91100% (1)
- ARM Microcontrollers Programming for Embedded SystemsFrom EverandARM Microcontrollers Programming for Embedded SystemsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Comparison of 80286 and 80386Document14 pagesComparison of 80286 and 80386Charan SinghNo ratings yet
- PlayStation 2 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #12From EverandPlayStation 2 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #12No ratings yet
- MPMC M-2 U-4Document21 pagesMPMC M-2 U-4Krishna BoreddyNo ratings yet
- Practical Reverse Engineering: x86, x64, ARM, Windows Kernel, Reversing Tools, and ObfuscationFrom EverandPractical Reverse Engineering: x86, x64, ARM, Windows Kernel, Reversing Tools, and ObfuscationNo ratings yet
- Prepared by Shikha Agrawal: Initialization of 80386DX, Debugging and Virtual 8086 ModeDocument14 pagesPrepared by Shikha Agrawal: Initialization of 80386DX, Debugging and Virtual 8086 Modeshikhamailme84No ratings yet
- Microprocessors & their Operating Systems: A Comprehensive Guide to 8, 16 & 32 Bit Hardware, Assembly Language & Computer ArchitectureFrom EverandMicroprocessors & their Operating Systems: A Comprehensive Guide to 8, 16 & 32 Bit Hardware, Assembly Language & Computer ArchitectureRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Advanced Microprocessors: 5.1 80286 MICROPROCESSORDocument16 pagesAdvanced Microprocessors: 5.1 80286 MICROPROCESSORDECS STUDENTSNo ratings yet
- Features of Micro-ProcessorDocument15 pagesFeatures of Micro-ProcessornobodyNo ratings yet
- Advanced Microprocessors-80286Document12 pagesAdvanced Microprocessors-80286Aaron BrooksNo ratings yet
- Mod 3 - 80386 and PentiumDocument7 pagesMod 3 - 80386 and PentiumAlenNo ratings yet
- Advanced Microprocessors: Dr. Hetal PatelDocument29 pagesAdvanced Microprocessors: Dr. Hetal PatelAnasNo ratings yet
- Features of 80186, 80286, 80386, 80486 and Pentium Family ProcessorsDocument32 pagesFeatures of 80186, 80286, 80386, 80486 and Pentium Family ProcessorsRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- 80286, 80386, 80486 and Pentium MicroprocessorDocument9 pages80286, 80386, 80486 and Pentium Microprocessoramit mahajan91% (11)
- Advanced MicroprocessorsDocument19 pagesAdvanced MicroprocessorsAyush DusejaNo ratings yet
- MP 13rdDocument14 pagesMP 13rdakashsin583No ratings yet
- 8086 Third Term TopicsDocument46 pages8086 Third Term TopicsgandharvsikriNo ratings yet
- The 80386 MicroprocessorsDocument24 pagesThe 80386 MicroprocessorsSourcecode BeeNo ratings yet
- Lab Assignment 1Document8 pagesLab Assignment 1Jason MurphyNo ratings yet
- Protected Mode TutorialDocument20 pagesProtected Mode TutorialfinitebookNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor 80286Document4 pagesMicroprocessor 80286xorxorxorNo ratings yet
- Microprocessors & Interfacing - (Ch3-Sec3A) - 80 X 86 Processor ArchitectureDocument24 pagesMicroprocessors & Interfacing - (Ch3-Sec3A) - 80 X 86 Processor ArchitectureSainadh PolavarapuNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument21 pagesNotesShinisg Vava50% (2)
- Different ModesDocument3 pagesDifferent ModessoravzNo ratings yet
- Features of 80186, 80286, 80386, 80486 and Pentium Family Processors Ee Vi Sem Amit ThakurDocument23 pagesFeatures of 80186, 80286, 80386, 80486 and Pentium Family Processors Ee Vi Sem Amit Thakuritsanshika555No ratings yet
- 32 - Bit Microprocessor-Intel 80386Document35 pages32 - Bit Microprocessor-Intel 80386Kartik BinagekarNo ratings yet
- Advanced ProcessorDocument85 pagesAdvanced ProcessorRenit AntoNo ratings yet
- The X86 Microprocessor: ObjectivesDocument32 pagesThe X86 Microprocessor: Objectivespapikhu36100% (4)
- Microprocessor Architectures: 1.1 Intel 1.2 MotorolaDocument14 pagesMicroprocessor Architectures: 1.1 Intel 1.2 MotorolabharadwajrohanNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - 80386DXDocument34 pagesModule 4 - 80386DXKEVINNo ratings yet
- Assignment (Chapter1 To Chapter4)Document15 pagesAssignment (Chapter1 To Chapter4)Jac ChanchalNo ratings yet
- Advanced Microprocessors: Presented by Ashish Kumar Singh Pranav Gautam Guide Mrs. Nayanica SrivastavaDocument20 pagesAdvanced Microprocessors: Presented by Ashish Kumar Singh Pranav Gautam Guide Mrs. Nayanica SrivastavaPranav GautamNo ratings yet
- Document 3Document2 pagesDocument 3Abdulrafay SaimNo ratings yet
- The Complete Understanding of Microprocessors and Intro To ARMDocument56 pagesThe Complete Understanding of Microprocessors and Intro To ARMasimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Virtual 8086 Mode: Intel 80386 Programmer'S Reference Manual 1986Document14 pagesChapter 15 Virtual 8086 Mode: Intel 80386 Programmer'S Reference Manual 1986Hussein Ali AljuburiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Protected ModeDocument1 pageIntroduction To Protected ModeRohan VaidyaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 NotesDocument53 pagesModule 1 Notesnethranagesh2013No ratings yet
- 2205 80x86 - FeaturesDocument23 pages2205 80x86 - Featuresnirmal23No ratings yet
- SegmentaionDocument14 pagesSegmentaionRohinNo ratings yet
- Architecture of 80386Document39 pagesArchitecture of 80386Raj KumarNo ratings yet
- Internal Architecture 8086Document3 pagesInternal Architecture 8086firoz83% (6)
- Architecture of 80386Document39 pagesArchitecture of 80386Satish KedarNo ratings yet
- Architecture of 80386 MicroproDocument39 pagesArchitecture of 80386 Microproompa13No ratings yet
- Architecture of 80386Document39 pagesArchitecture of 80386Imran KhanNo ratings yet
- MP-MC R16 - Unit-4Document14 pagesMP-MC R16 - Unit-4satyanarayana12No ratings yet
- and 80486Document28 pagesand 80486sangeetaranjan0% (1)
- FEATURES OF 80386:: 3) Address 4GB of Memory 3) 16 MB ofDocument39 pagesFEATURES OF 80386:: 3) Address 4GB of Memory 3) 16 MB ofSorabh ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Architecture of 80386 MicroproDocument39 pagesArchitecture of 80386 MicroproDeepthiNo ratings yet
- Intel Microprocessor Chapter 01Document86 pagesIntel Microprocessor Chapter 01Muhammad AwaisNo ratings yet
- Document 2Document4 pagesDocument 2Abdulrafay SaimNo ratings yet
- Intel 30836Document16 pagesIntel 30836banay.marynegeangaNo ratings yet
- Unit - Iv: Advanced Microprocessors: Salient Features of 80386Document14 pagesUnit - Iv: Advanced Microprocessors: Salient Features of 80386Swamy NallabelliNo ratings yet
- Features of 80386Document13 pagesFeatures of 80386Aswathy CjNo ratings yet
- 80386DX-Basic Programming Model and Applications Instruction SetDocument126 pages80386DX-Basic Programming Model and Applications Instruction SetNIRAJ CHORDIANo ratings yet
- 80286Document16 pages80286Umang RajNo ratings yet
- 8086 Family Users ManualDocument208 pages8086 Family Users ManualPriji PillaiNo ratings yet
- CR Chapter 7 PDFDocument8 pagesCR Chapter 7 PDFAnkit BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- Indian Villages: ConsiderationsDocument18 pagesIndian Villages: ConsiderationsAnkit BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- CorporatePpt Q2 2014Document9 pagesCorporatePpt Q2 2014Ankit BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- Corporate Presentation TemplateDocument6 pagesCorporate Presentation TemplateAnkit BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- SCD Type-1 Implementation in Informatica Using Dynamic LookupDocument9 pagesSCD Type-1 Implementation in Informatica Using Dynamic LookupMegha MittalNo ratings yet
- A Seminar On Virtual KeyboardDocument30 pagesA Seminar On Virtual KeyboardAnkit BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- 1.1 ControllerDocument35 pages1.1 ControllerAnkit BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- Important QuestionsDocument3 pagesImportant QuestionsRaja RawatNo ratings yet
- A Seminar On Fractional Order Pid TuningDocument11 pagesA Seminar On Fractional Order Pid TuningAnkit BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- HCL Placement Papers6Document37 pagesHCL Placement Papers6aishwarya_venkatNo ratings yet
- Packet SwitchingDocument4 pagesPacket SwitchingAnkit BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- A. Nagoor Kani - 8086 Microprocessors and Its Applications-Mc Graw Hill India (2013)Document498 pagesA. Nagoor Kani - 8086 Microprocessors and Its Applications-Mc Graw Hill India (2013)saloni100% (6)
- Operating Systems NotesDocument6 pagesOperating Systems Notesishtiaq hussainNo ratings yet
- Gigabyte GA-970A-UD3 Motherboard ManualDocument100 pagesGigabyte GA-970A-UD3 Motherboard Manuald_corsoNo ratings yet
- Ata 45Document10 pagesAta 45Guntur EkoNo ratings yet
- CoE115 1s01920 Lecture 03Document57 pagesCoE115 1s01920 Lecture 03Pao YapNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller Selector Guide: Quarter 1, 2001Document16 pagesMicrocontroller Selector Guide: Quarter 1, 2001Tomi OzzyNo ratings yet
- Sc1602D (16 Characters X 2 Lines) : Features Electrical CharacteristicsDocument1 pageSc1602D (16 Characters X 2 Lines) : Features Electrical CharacteristicsjoelpalzaNo ratings yet
- Bios Settings ReadDocument8 pagesBios Settings ReadLe Huu CanhNo ratings yet
- Digital Visual InterfaceDocument27 pagesDigital Visual InterfaceAbhishek VrNo ratings yet
- CCP105Document22 pagesCCP105api-3849444No ratings yet
- Special Study Report (1811019)Document15 pagesSpecial Study Report (1811019)Utkarsh SinghNo ratings yet
- Tabela 08-12Document9 pagesTabela 08-12Joao AmancioNo ratings yet
- Synopsis Online EducationDocument23 pagesSynopsis Online Educationsunny60% (5)
- Convert The Instructions To The Machine Code and Fill in The Content ofDocument1 pageConvert The Instructions To The Machine Code and Fill in The Content ofShri KumaranNo ratings yet
- C6140-0060 - Control Cabinet Industrial PC: VariantsDocument2 pagesC6140-0060 - Control Cabinet Industrial PC: Variantsdarinel88No ratings yet
- Telemecanique TSX Def 812Document12 pagesTelemecanique TSX Def 812ميلادالنعيريNo ratings yet
- DC16 Ch06Document36 pagesDC16 Ch06Alvin SanjayaNo ratings yet
- Gallaugher TIF Ch05 0Document11 pagesGallaugher TIF Ch05 0c3570892No ratings yet
- Verilog Program For Dual RomDocument27 pagesVerilog Program For Dual RomhareeshNo ratings yet
- Esprit MACDocument60 pagesEsprit MACAime HarmonyNo ratings yet
- Numark Mixstream Pro Serato DJ Pro Quick-Start GuideDocument6 pagesNumark Mixstream Pro Serato DJ Pro Quick-Start GuideBruce TobinNo ratings yet
- ARM Programs For BeginersDocument38 pagesARM Programs For BeginersNoobs PlayNo ratings yet
- TetraFlex SB421Document2 pagesTetraFlex SB421ciguthotabNo ratings yet
- Canon IR2270 UserguideDocument28 pagesCanon IR2270 UserguideMark Partington100% (1)
- 20DELL 7559 - AM9A (HM170 6 úCPU)Document57 pages20DELL 7559 - AM9A (HM170 6 úCPU)Nguyen LuongNo ratings yet
- SRS485 Option Card For Lon Star Coupler RER 111: Technical Reference ManualDocument16 pagesSRS485 Option Card For Lon Star Coupler RER 111: Technical Reference ManualSarah FrazierNo ratings yet
- Software and Hardware Interaction: Learning Outcomes Words To KnowDocument8 pagesSoftware and Hardware Interaction: Learning Outcomes Words To KnowArjay BacsalNo ratings yet
- Bocina Instrucciones)Document3 pagesBocina Instrucciones)Fernanda RivasNo ratings yet
- Tatsuno SetupDocument11 pagesTatsuno SetupPurnama Jati Permana100% (2)
- PT VX610Document6 pagesPT VX610reedNo ratings yet
- CompTIA Security+ All-in-One Exam Guide, Sixth Edition (Exam SY0-601)From EverandCompTIA Security+ All-in-One Exam Guide, Sixth Edition (Exam SY0-601)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Computer Science: A Concise IntroductionFrom EverandComputer Science: A Concise IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- Chip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyFrom EverandChip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (227)
- Chip War: The Fight for the World's Most Critical TechnologyFrom EverandChip War: The Fight for the World's Most Critical TechnologyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (82)
- CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102From EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- iPhone X Hacks, Tips and Tricks: Discover 101 Awesome Tips and Tricks for iPhone XS, XS Max and iPhone XFrom EverandiPhone X Hacks, Tips and Tricks: Discover 101 Awesome Tips and Tricks for iPhone XS, XS Max and iPhone XRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Hacking With Linux 2020:A Complete Beginners Guide to the World of Hacking Using Linux - Explore the Methods and Tools of Ethical Hacking with LinuxFrom EverandHacking With Linux 2020:A Complete Beginners Guide to the World of Hacking Using Linux - Explore the Methods and Tools of Ethical Hacking with LinuxNo ratings yet
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) Interview Questions and AnswersFrom EverandAmazon Web Services (AWS) Interview Questions and AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- iPhone 14 Guide for Seniors: Unlocking Seamless Simplicity for the Golden Generation with Step-by-Step ScreenshotsFrom EverandiPhone 14 Guide for Seniors: Unlocking Seamless Simplicity for the Golden Generation with Step-by-Step ScreenshotsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- How to Jailbreak Roku: Unlock Roku, Roku Stick, Roku Ultra, Roku Express, Roku TV with Kodi Step by Step GuideFrom EverandHow to Jailbreak Roku: Unlock Roku, Roku Stick, Roku Ultra, Roku Express, Roku TV with Kodi Step by Step GuideRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Programming with STM32: Getting Started with the Nucleo Board and C/C++From EverandProgramming with STM32: Getting Started with the Nucleo Board and C/C++Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- iPhone Unlocked for the Non-Tech Savvy: Color Images & Illustrated Instructions to Simplify the Smartphone Use for Beginners & Seniors [COLOR EDITION]From EverandiPhone Unlocked for the Non-Tech Savvy: Color Images & Illustrated Instructions to Simplify the Smartphone Use for Beginners & Seniors [COLOR EDITION]Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- CompTIA A+ Complete Practice Tests: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102From EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Practice Tests: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102No ratings yet
- Patterns in the Machine: A Software Engineering Guide to Embedded DevelopmentFrom EverandPatterns in the Machine: A Software Engineering Guide to Embedded DevelopmentRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Windows 10 Mastery: The Complete User Guide to Learn Windows 10 from Beginner to ExpertFrom EverandWindows 10 Mastery: The Complete User Guide to Learn Windows 10 from Beginner to ExpertRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (6)
- Amazon Echo Manual Guide : Top 30 Hacks And Secrets To Master Amazon Echo & Alexa For Beginners: The Blokehead Success SeriesFrom EverandAmazon Echo Manual Guide : Top 30 Hacks And Secrets To Master Amazon Echo & Alexa For Beginners: The Blokehead Success SeriesNo ratings yet
- CompTIA A+ Certification All-in-One Exam Guide, Eleventh Edition (Exams 220-1101 & 220-1102)From EverandCompTIA A+ Certification All-in-One Exam Guide, Eleventh Edition (Exams 220-1101 & 220-1102)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- How To Market Mobile Apps: Your Step By Step Guide To Marketing Mobile AppsFrom EverandHow To Market Mobile Apps: Your Step By Step Guide To Marketing Mobile AppsNo ratings yet
- Raspberry Pi | 101: The Beginner’s Guide with Basics on Hardware, Software, Programming & ProjecFrom EverandRaspberry Pi | 101: The Beginner’s Guide with Basics on Hardware, Software, Programming & ProjecNo ratings yet



















































































































![iPhone Unlocked for the Non-Tech Savvy: Color Images & Illustrated Instructions to Simplify the Smartphone Use for Beginners & Seniors [COLOR EDITION]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/audiobook_square_badge/728318688/198x198/f3385cbfef/1714732402?v=1)








