Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Food Chain
Uploaded by
api-3731257Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Food Chain
Uploaded by
api-3731257Copyright:
Available Formats
S.G.A.D.Govt.Girls.Sec.
School (TT)
Prepared by: - Mrs.Daljit Kaur
Guided by: - Raman Kumar
Food Chain
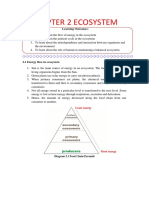
The complex energy relationship between plants
and animals often illustrate as a pyramid. The sun is the
original source of energy in virtually all ecosystems .Green
plants are called producers because they convert energy of
sun light into carbohydrate through the process of
photosynthesis.90% energy contain in the food an animals
eats is used for the animals movements, growth and repair of
tissue, or is lost as heat or in waste product just 10%
chemical energy in the food remains in the animal to be passed on the next level of pyramid.
When primary consumers (herbivores) eat the producers, the energy changes into a form that
can be stored in animal cells. Secondary consumers (carnivores) transform the energy once
again. Decomposers may occupy several positions in the pyramid, both receiving energy from
decaying plants and animals and supplying it to detrivores and fungus-eaters. With less energy
available at the top of pyramid than at the base.
⇒ Green plants, the primary producers of food in most terrestrial food webs
⇒ Herbivores, consumers of green plants
⇒ Carnivores, predators feeding upon the herbivores
⇒ Omnivores, consumers of both plants and animals
⇒ Secondary carnivores, which are predators that feed on predators, It make complete food
chain.
For example, the fungi that decompose matter in a
detrital web may sprout mushrooms that are consumed by
squirrels, mice, and deer in a grazing web. Robins are
omnivores, that is, consumers of both plants and animals, and
thus are in both detrital and grazing webs. Robins typically
feed on earthworms, which are detritivores that feed upon
decaying leaves.
References:- Microsoft Encarta Encyclopedia.
You might also like
- Exploring Ecosystems with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandExploring Ecosystems with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- The World of Food Chains with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe World of Food Chains with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Ecology The Scientific Study of The Interactions of LivingDocument3 pagesEcology The Scientific Study of The Interactions of LivingJané YongNo ratings yet
- The Food Chain vs. The Food Web - From Simple to Complex Systems | Children's Nature BooksFrom EverandThe Food Chain vs. The Food Web - From Simple to Complex Systems | Children's Nature BooksNo ratings yet
- Ecology of LifeDocument10 pagesEcology of LifePaul Jeremy MendozaNo ratings yet
- D) FEEDING RELATIONSHIPSDocument3 pagesD) FEEDING RELATIONSHIPSamarashah182No ratings yet
- Matter and Energy PresentationDocument92 pagesMatter and Energy Presentationapi-25442847475% (4)
- C H A P T e R VA IDocument8 pagesC H A P T e R VA IArnel AdinoNo ratings yet
- Interrelationship Among Plants and Animals: PresenterDocument20 pagesInterrelationship Among Plants and Animals: PresenterMicaela Kaye Margullo MontereyNo ratings yet
- Reading On Food Webs With Questions and AnswersDocument19 pagesReading On Food Webs With Questions and AnswersAmal AliyanNo ratings yet
- The Food Chain Consists of Four Main PartsDocument3 pagesThe Food Chain Consists of Four Main PartskoiaitraazNo ratings yet
- Relationships of Organisms With One Another Biology 5090 NotesDocument18 pagesRelationships of Organisms With One Another Biology 5090 NotesBalakrishnan MarappanNo ratings yet
- Ecology Bingo: Ecosystem Carnivore Consumer Producer Food Chain Energy FlowDocument18 pagesEcology Bingo: Ecosystem Carnivore Consumer Producer Food Chain Energy FlowAbdullah KhalidNo ratings yet
- Forest Ecosystem: Community Diversity and ComplexityDocument10 pagesForest Ecosystem: Community Diversity and ComplexityMateiDumitruNo ratings yet
- l14 Relationships in EcosystemsDocument20 pagesl14 Relationships in EcosystemsAriel MaganaNo ratings yet
- Producers and Consumers Are The Living Components of EcosystemsDocument6 pagesProducers and Consumers Are The Living Components of EcosystemsPaul Jeremy MendozaNo ratings yet
- Module 2.1 - Energy Flow in The EcosystemDocument8 pagesModule 2.1 - Energy Flow in The EcosystemVANDANA -IES ASPIRANTNo ratings yet
- ss1 Biology Week 4 - 10Document19 pagesss1 Biology Week 4 - 10sulaiman mohammedNo ratings yet
- Biotic Studies (Ecosystem) 1Document20 pagesBiotic Studies (Ecosystem) 1Dakarirayi MutenherwaNo ratings yet
- AksinghDocument18 pagesAksinghzehensayan275No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Ecosystem: Learning OutcomesDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Ecosystem: Learning OutcomesREKSHENA A/P PERKAS MoeNo ratings yet
- c4 InterdependenceDocument52 pagesc4 InterdependenceultrakaweNo ratings yet
- 1 in Food Chains and Webs What Trophic Level Must You Have More of Than Others 2 Each Trophic Level Has How Much Less EnergyDocument6 pages1 in Food Chains and Webs What Trophic Level Must You Have More of Than Others 2 Each Trophic Level Has How Much Less EnergyJennie KimNo ratings yet
- Interactions - Worksheets w7-8 q2Document6 pagesInteractions - Worksheets w7-8 q2Yza'sMiniClosetNo ratings yet
- The Food ChainDocument1 pageThe Food ChainAgatyxaNo ratings yet
- Food Chain and Energy FlowDocument2 pagesFood Chain and Energy FlowStephenTumulak100% (1)
- Trophic LevelsDocument4 pagesTrophic LevelsBaileyNo ratings yet
- Food ChainDocument19 pagesFood ChainSonia Sánchez Barranco100% (1)
- Food Chain VocabDocument1 pageFood Chain VocabMaas ChenNo ratings yet
- Ecosystems CambDocument20 pagesEcosystems CambarmvelNo ratings yet
- The Detritivores Play A Crucial Role in Returning Nutrients To The EnvironmentDocument2 pagesThe Detritivores Play A Crucial Role in Returning Nutrients To The EnvironmentebuezaerichNo ratings yet
- EcosystemDocument6 pagesEcosystemconnect.amairaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 5 InteractionsDocument18 pagesMODULE 5 Interactionsflorie jane macayaNo ratings yet
- What Are Three Categories of Organisms in The Ecosystem?Document3 pagesWhat Are Three Categories of Organisms in The Ecosystem?carlNo ratings yet
- Za NST 1683701260 Food Chains Cloze Procedure Activity - Ver - 1Document3 pagesZa NST 1683701260 Food Chains Cloze Procedure Activity - Ver - 1Harini NatashaNo ratings yet
- Ecology For Uce NewDocument4 pagesEcology For Uce NewHasifa KonsoNo ratings yet
- SS Tasks (biOdiversIty)Document6 pagesSS Tasks (biOdiversIty)alexandra_angel_4No ratings yet
- Year 9 Ecology Revision SolutionsDocument10 pagesYear 9 Ecology Revision SolutionsHagen SeahNo ratings yet
- 2 Ecology in GeneralDocument32 pages2 Ecology in GeneralDee MarieNo ratings yet
- Evidence 2Document7 pagesEvidence 2junso2771No ratings yet
- 16 Flow of EnergyDocument2 pages16 Flow of Energyramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Ecosystem: 8.1 The Abiotic and Biotic Component of The Environment The Abiotic ComponentDocument18 pagesDynamic Ecosystem: 8.1 The Abiotic and Biotic Component of The Environment The Abiotic ComponentMun YewNo ratings yet
- Notes - Unit 1-3Document20 pagesNotes - Unit 1-3Brian MurtaghNo ratings yet
- ECOSYSTEMSDocument8 pagesECOSYSTEMSammarahn0No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document33 pagesChapter 2Mimiento SearNo ratings yet
- Food ChainDocument4 pagesFood ChainAmara JavaidNo ratings yet
- Food ChainDocument1 pageFood ChainAlexia GheorgheNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 EcosystemDocument60 pagesChapter 2 EcosystemJu WenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Interdependence Among Living Organism andDocument13 pagesChapter 4 Interdependence Among Living Organism andNantha KumaranNo ratings yet
- How Does the Food Chain Work? - Science Book for Kids 9-12 | Children's Science & Nature BooksFrom EverandHow Does the Food Chain Work? - Science Book for Kids 9-12 | Children's Science & Nature BooksNo ratings yet
- What Is A Food ChainDocument2 pagesWhat Is A Food ChainLuzANgelaBAenaNo ratings yet
- CH7 ForgettingDocument29 pagesCH7 Forgettingapi-3731257100% (1)
- Sarojini Naidu: The Nightingale of IndiaDocument9 pagesSarojini Naidu: The Nightingale of Indiaapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Batch:-3 Phase - I Roll No.-34 Class-12 Subject: - General English Topic: - The Death of SocratesDocument13 pagesBatch:-3 Phase - I Roll No.-34 Class-12 Subject: - General English Topic: - The Death of Socratesapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Class 10+2Document5 pagesClass 10+2api-3731257No ratings yet
- Author:-J.L Nehru: JL Nehru Was 1 Prime Minister of IndiaDocument17 pagesAuthor:-J.L Nehru: JL Nehru Was 1 Prime Minister of Indiaapi-3731257No ratings yet
- GSSBANDALA English)Document14 pagesGSSBANDALA English)api-3731257No ratings yet
- Govt. High. School Jhitan KalanDocument15 pagesGovt. High. School Jhitan Kalanapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Ghsmehma Amritsar Maori VillagesDocument10 pagesGhsmehma Amritsar Maori Villagesapi-3731257No ratings yet
- A Project Report ON: Fasting As PenanceDocument10 pagesA Project Report ON: Fasting As Penanceapi-3731257No ratings yet
- General AidsDocument8 pagesGeneral Aidsapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 12 Class Topic Noun and VerbDocument18 pagesLesson Plan 12 Class Topic Noun and Verbapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Ghsguruwali ForgettingDocument7 pagesGhsguruwali Forgettingapi-3731257No ratings yet
- The Lost Child Pakharpura AmritsarDocument5 pagesThe Lost Child Pakharpura Amritsarapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Daffodils - Pandori Ran Singh - Tarn Taran (A)Document11 pagesDaffodils - Pandori Ran Singh - Tarn Taran (A)api-3731257No ratings yet
- Indian Weavers - Tarn Taran (G) - Tarn Taran (C)Document10 pagesIndian Weavers - Tarn Taran (G) - Tarn Taran (C)api-3731257No ratings yet
- Ghsmanawala - The School For SympathyDocument5 pagesGhsmanawala - The School For Sympathyapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Indian Weavers - Pandori Gola - Tarn Taran (A)Document13 pagesIndian Weavers - Pandori Gola - Tarn Taran (A)api-37312570% (1)
- No Men Are Foreign - Tarsikka - AmritsarDocument10 pagesNo Men Are Foreign - Tarsikka - Amritsarapi-3731257100% (1)
- Indian Weavers - Gaggobua) Tarn Taran (C)Document19 pagesIndian Weavers - Gaggobua) Tarn Taran (C)api-373125760% (5)
- Tolstoy's Home Sohian Khurd AmritsarDocument13 pagesTolstoy's Home Sohian Khurd Amritsarapi-3731257100% (2)
- On Saying Please Sanghana AmritsarDocument15 pagesOn Saying Please Sanghana Amritsarapi-3731257100% (2)
- Diamond Necklace Pakharpura AmritsarDocument8 pagesDiamond Necklace Pakharpura Amritsarapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Leisure Nagkalan AmritsarDocument11 pagesLeisure Nagkalan Amritsarapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Tense Nagkalan AmritsarDocument17 pagesTense Nagkalan Amritsarapi-3731257100% (1)