Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Basic Computer
Uploaded by
Yzza Veah EsquivelOriginal Title
Copyright
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
The Basic Computer
Uploaded by
Yzza Veah EsquivelCopyright:
CENGO309 LEC 092411 THE BASIC COMPUTER All computers consists of basic functional blocks that include a CPU,
memory and input/output ports. These functional blocks are connected together with 3 internal buses, these are the DATA BUS, the ADDRESS BUS, and the CONTROL BUS. Input and output devices are connected through the input/output ports. PORT - A physical interference on a computer through which data are passed to and from peripherals. BASIC COMPUTER BLOCK DIAGRAM MEMORIES/STORAGE RAM, ROM, CACHE, HARD DISK
INPUT/OUTPUT PORTS
CPU P
NOTE: Instructions and data are stored in memory in specific locations determined by the program.
PROGRAM - A list of instructions designed to solve a specific problem. CPU -
Central Processing Unit The brain of the computer A P (microprocessor) with associated circuits that control the running of the computer software programs. Oversees everything that the computer does.
NOTE: Basically, the CPU obtains (fetches) each program instructions from memory and carries out (executes) the instruction.
MEMORIES AND STORAGE
ROM BIOS -
Read Only Memory Stores a permanent system program called the BIOS (Basic Input / Output System) and certain locations of system programs in memory Non volatile Sometimes referred to as firmware because it is permanent software for a given system.
Is the lowest level of computers operating system. It contains instructions that tell the CPU what to do when power is first applied; the first instruction executed is in the BIOS. It controls the computers base start up functions that include a self test and a disk self-loader to bring up the rest of the operating system.
BIOS stores locations of the system programs that handle certain requests from peripherals called INTERUPTS, which cause the current processing to be temporarily stopped.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Civil Service Exam ReviewerDocument103 pagesCivil Service Exam ReviewerPatrick Hel O. Laurito78% (18)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- MSA Civil Service Reviewer PDFDocument79 pagesMSA Civil Service Reviewer PDFAhMy Endaya82% (77)
- English Reviewer (Reading Comprehension, Vocabulary)Document6 pagesEnglish Reviewer (Reading Comprehension, Vocabulary)Yzza Veah Esquivel92% (36)
- Philippine Constitution - Civil Service Exam ReviewerDocument41 pagesPhilippine Constitution - Civil Service Exam ReviewerYzza Veah Esquivel50% (2)
- Noise FigureDocument4 pagesNoise FigureYzza Veah EsquivelNo ratings yet
- COMMUNICATIONDocument6 pagesCOMMUNICATIONYzza Veah EsquivelNo ratings yet
- RA 6713 - Code of Conduct and Ethical Standard For Public Officials and EmployeesDocument12 pagesRA 6713 - Code of Conduct and Ethical Standard For Public Officials and EmployeesCrislene Cruz83% (12)
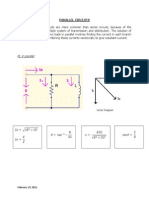
- Superposition TheoremDocument4 pagesSuperposition TheoremYzza Veah EsquivelNo ratings yet
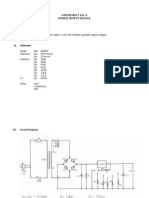
- Experiment No. 6 - Power Supply DesignDocument7 pagesExperiment No. 6 - Power Supply DesignYzza Veah EsquivelNo ratings yet
- Modulation (Am/fm)Document15 pagesModulation (Am/fm)Yzza Veah Esquivel94% (17)
- Noise and CommunicationDocument5 pagesNoise and CommunicationYzza Veah EsquivelNo ratings yet
- Nodal AnalysisDocument2 pagesNodal AnalysisYzza Veah EsquivelNo ratings yet
- Thevenin's TheoremDocument5 pagesThevenin's TheoremYzza Veah Esquivel100% (2)
- Experiment No.1 Series-Parallel Resistive CircuitsDocument4 pagesExperiment No.1 Series-Parallel Resistive CircuitsYzza Veah EsquivelNo ratings yet
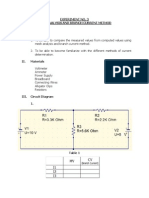
- Experiment No.3 Mesh Analysis and Branch Current MethodDocument3 pagesExperiment No.3 Mesh Analysis and Branch Current MethodYzza Veah EsquivelNo ratings yet
- Branch Current Method 1Document2 pagesBranch Current Method 1Yzza Veah Esquivel0% (1)
- Experiment No.4 Nodal AnalysisDocument2 pagesExperiment No.4 Nodal AnalysisYzza Veah EsquivelNo ratings yet
- Branch Current Method2Document2 pagesBranch Current Method2Yzza Veah Esquivel0% (1)
- Sine Wave 3Document5 pagesSine Wave 3Yzza Veah EsquivelNo ratings yet
- R-C Parallel CircuitsDocument5 pagesR-C Parallel CircuitsYzza Veah EsquivelNo ratings yet
- Sine Wave 2Document2 pagesSine Wave 2Yzza Veah EsquivelNo ratings yet
- Phasor AlgebraDocument5 pagesPhasor AlgebraYzza Veah Esquivel100% (1)
- Sine Wave 1Document2 pagesSine Wave 1Yzza Veah EsquivelNo ratings yet
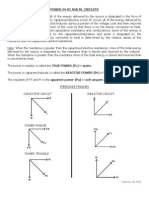
- Power in RC and RL CircuitsDocument4 pagesPower in RC and RL CircuitsYzza Veah Esquivel100% (1)
- Book 4: Alternating Current Electric CircuitDocument566 pagesBook 4: Alternating Current Electric CircuitMAT JIBRUD100% (3)
- Series-Parallel RC CircuitDocument29 pagesSeries-Parallel RC CircuitYzza Veah Esquivel80% (5)
- Polyphase SystemDocument2 pagesPolyphase SystemYzza Veah EsquivelNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 4 - The RC-RL Lead-Lag NetworksDocument4 pagesExperiment No. 4 - The RC-RL Lead-Lag NetworksYzza Veah EsquivelNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 2 - Ac Voltage MeasurementsDocument3 pagesExperiment No. 2 - Ac Voltage MeasurementsYzza Veah EsquivelNo ratings yet