Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Oxidation
Uploaded by
MThana BalanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Oxidation
Uploaded by
MThana BalanCopyright:
Available Formats
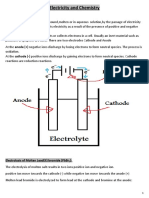
Oxidation: loss of electrons Reduction: gain of electrons Oxidant (oxidising agent): causes another species to be oxidised Oxidant: gains
electrons (oxidant is reduced) Reductant (Reducing Agent): causes another species to be reduced Reductant: loses electrons (reductant is oxidised) Redox Reactions: one species (reductant) provides electrons for another species
Examples Oxidation : Na -----> Na+ + e Sodium atom loses an electron to produce a positively charged sodium ion (cation) Sodium has been oxidised.
Reduction : F + e -----> F Fluorine atom gains an electron to form the negatively charged fluoride ion (anion) Fluorine has been reduced.
REDOX (electron transfer) Reaction : Na + F -----> Na+ + F An electron has been transferred from the sodium atom to the flourine atom. Sodium has lost an electron, it has been oxidised Sodium is the reductant as it has caused the fluorine to be reduced to the fluoride ion. Fluorine has gained an electron, it has been reduced. Fluorine is the oxidant as it has caused the sodium to be oxidised to the sodium ion.
Uses of REDOX Reactions Generation of electricity () Recharging rechargable Electrolytic extraction of metals Electroplating Quantitative analysis ()
You might also like
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Redox Reactions ExplainedDocument40 pagesRedox Reactions ExplainedMohamad HanifNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IGCSE Biology Revision NotesDocument66 pagesEdexcel IGCSE Biology Revision NotesHei Yin Sin100% (7)
- Electrolysis. Olevel ChemistryDocument53 pagesElectrolysis. Olevel ChemistrySaraYasinNo ratings yet
- Oxidation ReductionDocument7 pagesOxidation ReductionZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Oxidation and ReductionDocument28 pagesOxidation and ReductionCharlene LowNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument83 pagesElectrolysismoizbadri100% (3)
- Kinetics of CorrosionDocument50 pagesKinetics of Corrosionnani198350% (2)
- Redox Reactions Grade 11Document69 pagesRedox Reactions Grade 11RahulNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- The Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionsDocument35 pagesThe Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionsZulaikha NurafifiNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument32 pagesElectrolysischong5683% (6)
- SPM Chemistry Revision Module On The BasicsDocument64 pagesSPM Chemistry Revision Module On The BasicsMThana BalanNo ratings yet
- Redox Reactions ExplainedDocument80 pagesRedox Reactions ExplainedShashwatNo ratings yet
- Oxidation & Reduction: Redox ReactionsDocument5 pagesOxidation & Reduction: Redox ReactionsVenusCrazy 550No ratings yet
- Oxidation ReductionDocument8 pagesOxidation Reductionmaryjoy cacaldoNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-06-19 at 3.39.23 PMDocument47 pagesScreenshot 2022-06-19 at 3.39.23 PMWalaa AdelNo ratings yet
- Oxidation and ReductionDocument12 pagesOxidation and Reductionmuhsin94No ratings yet
- Class XI Chemistry Unit-8 Redox Reactions: TopicDocument60 pagesClass XI Chemistry Unit-8 Redox Reactions: TopicBaljit Singh100% (1)
- Redox Reactions and Oxidation NumbersDocument76 pagesRedox Reactions and Oxidation NumbersRabbi 08No ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument24 pagesElectrolysisstudent purposesNo ratings yet
- Class 11 - Chapter 08 - Redox Reaction NotesDocument14 pagesClass 11 - Chapter 08 - Redox Reaction NotesaasifNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Chemical Reactions and Quantities: Oxidation-Reduction ReactionsDocument13 pagesChapter 5 Chemical Reactions and Quantities: Oxidation-Reduction ReactionsJill GenuinoNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - CHEM Notes: Chemistry (Higher School Certificate (New South Wales) )Document7 pagesModule 3 - CHEM Notes: Chemistry (Higher School Certificate (New South Wales) )norbetNo ratings yet
- Oxidation-Reduction: General ChemistryDocument13 pagesOxidation-Reduction: General ChemistryBeatrice AgustinNo ratings yet
- Notes PDFDocument91 pagesNotes PDFjoyce heahNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1679932480278 7046147521763878353Document13 pagesOrca Share Media1679932480278 7046147521763878353Endelyn Salva SajorgaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Fe2+ and Fe3+Document10 pagesChemistry Fe2+ and Fe3+Khor Eu May100% (1)
- Oxidation ReductionDocument7 pagesOxidation ReductionWalu BNNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument22 pagesElectrolysisDebbie BerriesNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistr Y: Chemistry Notes GCE Study BuddyDocument30 pagesElectrochemistr Y: Chemistry Notes GCE Study BuddyHaya SweetNo ratings yet
- Unit 7Document3 pagesUnit 7api-282526559No ratings yet
- CH 6,7 NotesDocument18 pagesCH 6,7 NotesAishi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Explanation Text: By: Dwiyanti Octaviani Farrah Nabila F Malik Farhan Nazhara Ardhan Roikhan Azhari Syifa FauziahDocument28 pagesExplanation Text: By: Dwiyanti Octaviani Farrah Nabila F Malik Farhan Nazhara Ardhan Roikhan Azhari Syifa Fauziahsyifa fauziahNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis 090618180154 Phpapp01Document20 pagesElectrolysis 090618180154 Phpapp01jiivi87No ratings yet
- Chap 5Document11 pagesChap 5Tun Lin AungNo ratings yet
- 121 CH 07Document27 pages121 CH 07Thanh LanNo ratings yet
- Bab 12 - Nota A+Document7 pagesBab 12 - Nota A+Azemi AhmadNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument30 pagesElectrolysisZarrar Hamza KhanNo ratings yet
- Oxidation and Reduction Reactions Always Take Place SimultaneouslyDocument29 pagesOxidation and Reduction Reactions Always Take Place SimultaneouslyRen H. RoxasNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis: Term MeaningDocument22 pagesElectrolysis: Term MeaningYeen ChengNo ratings yet
- Experiment RustingDocument17 pagesExperiment RustingSaadiah MohammadNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRY WorksheetDocument83 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRY WorksheetbhargavintnaiduNo ratings yet
- Electricity and ChemistryDocument5 pagesElectricity and Chemistrymohamed komiNo ratings yet
- ppt6 REDOX PDFDocument17 pagesppt6 REDOX PDFOscar Kelvin NsituNo ratings yet
- A Chemistry Electrolysis ProjectDocument10 pagesA Chemistry Electrolysis ProjectLij WynterNo ratings yet
- Curian Science Tutors Chem NotesDocument6 pagesCurian Science Tutors Chem NotesMunashe BinhaNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRYDocument14 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRYmohamed komiNo ratings yet
- R2 6lA5NCDocument7 pagesR2 6lA5NCIsa ShahidNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument16 pagesElectrochemistryitsshaunboteNo ratings yet
- Electricity and ChemistryDocument13 pagesElectricity and Chemistrysalman ahsanNo ratings yet
- RedoxDocument2 pagesRedoxtmoatshe96No ratings yet
- Lecture 9_ ElectrochemistryDocument91 pagesLecture 9_ Electrochemistryteodoruunona609No ratings yet
- ELECTROLYSI1Document10 pagesELECTROLYSI1jpkaomeNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Industries' ImpactsDocument4 pagesElectrochemical Industries' ImpactsSally ChewNo ratings yet
- SS2 Note ElectrolysisDocument7 pagesSS2 Note ElectrolysisIbukun OlaitanNo ratings yet
- As Chapter 6a ElectrochemistryDocument68 pagesAs Chapter 6a ElectrochemistryNazil HaziqNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond Valence: Df8f7rf6f56d5dDocument91 pagesChemical Bond Valence: Df8f7rf6f56d5dfitradikojerdsswNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - ElectrolysisDocument51 pagesChemistry - Electrolysisjoannavera2020No ratings yet
- Chapter 16 - Oxidation and ReductionDocument50 pagesChapter 16 - Oxidation and ReductionGeorgeNo ratings yet
- Std.8 Module.7 Semester.2Document56 pagesStd.8 Module.7 Semester.2Md ZayedNo ratings yet
- 1-4 Introduction To Electrochemistry - RedoxDocument24 pages1-4 Introduction To Electrochemistry - RedoxCtstrphyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Carbon Compounds - HandoutDocument18 pagesChapter 2 Carbon Compounds - HandoutMThana BalanNo ratings yet
- Observing Science Process Skills in SPM QuestionsDocument17 pagesObserving Science Process Skills in SPM QuestionsMThana BalanNo ratings yet
- Observing Science Process Skills in SPM QuestionsDocument17 pagesObserving Science Process Skills in SPM QuestionsMThana BalanNo ratings yet
- 6 ElectrochemistryDocument24 pages6 ElectrochemistryMThana BalanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Thermochemistry - ModuleDocument14 pagesChapter 4 Thermochemistry - ModuleMThana BalanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Answer)Document4 pagesChapter 1 (Answer)MThana BalanNo ratings yet
- c03qp Chemical Formulae Equations Latest PDF August 17 2011-5-48 Am 852kDocument32 pagesc03qp Chemical Formulae Equations Latest PDF August 17 2011-5-48 Am 852kKazariyah KasaNo ratings yet
- c03qp Chemical Formulae Equations Latest PDF August 17 2011-5-48 Am 852kDocument32 pagesc03qp Chemical Formulae Equations Latest PDF August 17 2011-5-48 Am 852kKazariyah KasaNo ratings yet
- SMK Sultan Abdul Samad, Petaling Jaya: Exercise 1: Find The Number of Mole in Each QuestionDocument4 pagesSMK Sultan Abdul Samad, Petaling Jaya: Exercise 1: Find The Number of Mole in Each QuestionMThana BalanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 4 Lesson 11Document8 pagesChemistry Form 4 Lesson 11MThana BalanNo ratings yet
- C04as Periodic Table of Elements PDF August 17 2011-5-48 Am 687kDocument46 pagesC04as Periodic Table of Elements PDF August 17 2011-5-48 Am 687kMThana Balan0% (1)
- 1 Introduction To ChemistryDocument46 pages1 Introduction To ChemistryMThana BalanNo ratings yet
- 8 Natural RubberDocument18 pages8 Natural RubberMThana BalanNo ratings yet
- c03qp Chemical Formulae Equations Latest PDF August 17 2011-5-48 Am 852kDocument32 pagesc03qp Chemical Formulae Equations Latest PDF August 17 2011-5-48 Am 852kKazariyah KasaNo ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan (Chemistry F5)Document10 pagesYearly Lesson Plan (Chemistry F5)MThana BalanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Perfect Score X A Plus Module 2013Document152 pagesChemistry Perfect Score X A Plus Module 2013MThana BalanNo ratings yet
- Enabling Macro in Access 2007Document4 pagesEnabling Macro in Access 2007zharifd26No ratings yet
- Trial08 TRG Chem P123Document58 pagesTrial08 TRG Chem P123MThana BalanNo ratings yet
- Pahang JUJ 2012 SPM ChemistryDocument285 pagesPahang JUJ 2012 SPM ChemistryJeyShida100% (1)
- 9 TransformerDocument7 pages9 TransformerMThana BalanNo ratings yet
- SPM Kimia Jul12 PDFDocument49 pagesSPM Kimia Jul12 PDFSyazwani RadziNo ratings yet
- Ulangkaji Akhir Menjelang SPMDocument32 pagesUlangkaji Akhir Menjelang SPMMThana BalanNo ratings yet
- Annual Scheme of Work f4Document3 pagesAnnual Scheme of Work f4MThana BalanNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: Ions, Cells and ReactionsDocument62 pagesElectrochemistry: Ions, Cells and Reactionshanifzainol100% (1)