Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Respiration - The Exchange of Gases
Respiration - The Exchange of Gases
Uploaded by
Ahmed Oraby0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views19 pagesOriginal Title
5. Respiration- The Exchange of Gases
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views19 pagesRespiration - The Exchange of Gases
Respiration - The Exchange of Gases
Uploaded by
Ahmed OrabyCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 19
Respiration:
The Exchange of Gases
Respiration (gas exchange): the interchange
between an animaI and its environment
echanisms of Gas Exchange
Three phases of gas exchange:
1) Breathing
- gas exchange with environment
2) Gas transport
- circuIatory system
- bIood vesseIs
3) Servicing body tissues
- gas exchange with tissues
- O
2
uptake - ceIIuIar respiration
- CO
2
reIease - waste product
echanisms of Gas Exchange
Respiratory surface - the part of the animaI where O
2
diffuses
into the animaI and CO
2
diffuses out to
the environment.
- covered by Iiving ceIIs (singIe Iayer, moist)
Outer skin
- "skin breathers"
- capiIIaries beIow skin
smaII, Iong, fIat organisms
high surface to voIume ratio
e. g. earthworm and hydra
echanisms of Gas Exchange
ost animaIs require specific adaptations for gas exchange
GiIIs
- feather-Iike extensions body surface
- very high surface area
- in contact with environment
- must aIways be moist!!
e.g. fish, amphibians, crabs and
moIIusca
echanisms of Gas Exchange
In most terrestriaI organisms, the respiratory surfaces are
FoIded into the body.
TracheaI system
- extensive system of internaI tubes
- exchange gases with the ceIIs
- no assistance from the circuIatory
system.
e. g. insects
echanisms of Gas Exchange
ost terrestriaI organisms have Iungs
Lungs
- internaI sacs Iined with moist
epitheIium
- inner surfaces branch extensiveIy
- Iarge surface area!!
- gases carried between Iungs and
body ceIIs by the circuIation.
e.g. amphibians, reptiIes, birds and
mammaIs.
Fish GiIIs
GiIIs are adapted for gas exchange in aquatic environments
Water - Iow dissoIved O
2
VentiIation
- mechanism to increase
contact between respiratory
surface (giIIs or Iungs)
and the environment.
- fish ventiIate their giIIs
to maintain the fIow of
O
2
rich water.
Fish GiIIs
Countercurrent fIow in giIIs enhances O
2
transfer
Countercurrent exchange
- the transfer of something from a
fIuid moving in one direction to
another fIuid moving in the
opposite direction.
- opposite fIows maintain a diffusion
gradient.
GiIIs
- water (O
2
-rich) fIows one way
- bIood (O
2
-poor) fIows the other way
* can remove 80% of water O
2
TracheaI System
Insect tracheae are tubes that branch throughout the body
air sacs - contraction of muscIes around them controI air movement
tracheoIes - narrowest tubes that extend to the ceIIs; contain fIuid
Lungs - terrestriaI vertebrates
Lungs
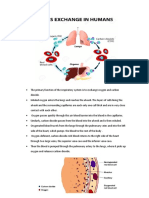
The aIveoIi are the site of gas exchange with the circuIation.
AIveoIi
- tiny sacs Iined with a thin Iayer
of epitheIiaI ceIIs; the exchange
surface with bIood
- each Iung contains miIIions
- O
2
dissoIves in the fiIm of
moisture Iining the epitheIiaI
ceIIs and diffuses across to the
bIood
- CO
2
moves the opposite way
Lungs - Breathing
Breathing - the aIternation of inhaIation and exhaIation.
Lungs - Breathing
Breathing in birds invoIves a one-way fIow of air rather than
an in-and-out fIow in humans.
ControI of Breathing
Breathing is automaticaIIy controIIed
Breathing controI centers
- in brain (pons and meduIIa)
- nerves from meduIIa signaI diaphragm
and rib muscIes to contract (inhaIe)
- pons smooths out rhythm of breathing.
- pH sensing - controI of CO
2
reIease
- decrease in pH causes an increase
in breathing rate.
HyperventiIation - deep, rapid breathing.
Gas Transport
BIood transports the respiratory gases
Heart has two divisions:
1) Ieft side handIes O
2
-rich bIood from
the Iungs (pumps bIood to body)
2) right side handIes O
2
-poor bIood
from the rest of the body
- pumps bIood to aIveoIar capiIIaries
(gas exchange)
PartiaI pressure
- the portion of a mixed gas that a
particuIar pure gas accounts for
- gradients determine movement
Gas Transport
HemogIobin - the moIecuIe in red bIood ceIIs that carries O
2
- four poIypeptide chains and a heme group
containing iron
- can carry up to 4 moIecuIes of O
2
Gas Transport
HemogIobin heIps transport CO
2
and buffer the bIood
Gas Transport
The human fetus exchanges gases with the mother's bIoodstream
Fetus
- Iungs are fuII of fIuid and
non-functionaI
- capiIIaries from the umbiIicaI
cord fan out into the pIacenta
- gas exchange occurs with the
maternaI bIood in the pIacenta
- countercurrent exchange of
fetaI and maternaI bIood
- fetaI hemogIobin has a higher
affinity for O
2
.
SUARY
- echanisms of gas exchange
(skin, giIIs, tracheaI system, Iungs)
- Breathing in water
- countercurrent exchange
- Breathing in air
- tracheaI system (insects)
- Iungs (humans)
- Breathing (controI by brain)
- Gas transport (circuIation, bIood, hemogIobin)
You might also like
- Gas Exchange in AnimalsDocument29 pagesGas Exchange in AnimalsShanice CabrilesNo ratings yet
- Respiratory - Gas ExchangeDocument3 pagesRespiratory - Gas ExchangeChris P. BeaconNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsDocument60 pagesLesson 5 - Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsBeng QuinnNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument25 pagesRespirationfacultyfisheriesNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System-11 By:-Dr. Hazim AL-RawiDocument12 pagesThe Respiratory System-11 By:-Dr. Hazim AL-RawiDrAli Al-FendiNo ratings yet
- 9 Tetrapod's AMPHIBIADocument8 pages9 Tetrapod's AMPHIBIAkahiauNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in Animals PDFDocument4 pagesGas Exchange in Animals PDFmunzarin100% (1)
- Gaseous Exchange A LevelDocument33 pagesGaseous Exchange A LevelemmanuelkeetoNo ratings yet
- 11 Resp Alveoli and Gas Exchange 24Document9 pages11 Resp Alveoli and Gas Exchange 24Shehbaaz SinghNo ratings yet
- 2 RespirationDocument86 pages2 RespirationAkwa ManNo ratings yet
- Note-Respiratory StructureDocument3 pagesNote-Respiratory StructureWONG LI KING MoeNo ratings yet
- 6) Gaseous ExchangeDocument32 pages6) Gaseous ExchangeDizzy DeeNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange Written ReportDocument11 pagesGas Exchange Written ReportEllanny GloriaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Gas ExchangeDocument19 pagesRespiratory Gas ExchangeRahul MeenaNo ratings yet
- Animal Physiology and Physiological Chemistry Paper Mzo503 Paper Mzo503Document19 pagesAnimal Physiology and Physiological Chemistry Paper Mzo503 Paper Mzo503Abhishek Singh ChandelNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in Animals3Document47 pagesGas Exchange in Animals3Ashley JibrielleNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System PDFDocument25 pagesThe Respiratory System PDFbilly sauraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 30 AnswersDocument8 pagesChapter 30 AnswersJuan SandovalNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument6 pagesScience ReviewerSherra Mariel PintorNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System NotesDocument4 pagesRespiratory System NotesFlare FlareonNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange: of GasesDocument10 pagesBreathing and Exchange: of GaseshellohelloworldNo ratings yet
- Respiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4Document90 pagesRespiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4edain84No ratings yet
- Respiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4Document90 pagesRespiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4Faida Hamid87% (23)
- Internal RespirationDocument9 pagesInternal RespirationRhose ReyesNo ratings yet
- 2.5 Gaseous Exchange in AnimalsDocument28 pages2.5 Gaseous Exchange in AnimalsCarol JamesNo ratings yet
- General Biology II Q4 Week 2Document19 pagesGeneral Biology II Q4 Week 2Alex BlancoNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System: ASTIKA NUR ROHMAH, S.Kep., NS., M.BiomedDocument43 pagesThe Respiratory System: ASTIKA NUR ROHMAH, S.Kep., NS., M.BiomedAdek KhazeliaNo ratings yet
- Bio 3RD Q LQ 1Document5 pagesBio 3RD Q LQ 1ytheresetiuNo ratings yet
- GENERAL BIOLOGY 2 Learning Activity Sheet Q4 W1 v. 2Document12 pagesGENERAL BIOLOGY 2 Learning Activity Sheet Q4 W1 v. 2Pearl Lee MetiamNo ratings yet
- Life Science Study NotesDocument28 pagesLife Science Study Notes36050245No ratings yet
- Resumen Primera Parte. FisiologíaDocument4 pagesResumen Primera Parte. FisiologíaFatima AzaleansNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument53 pagesRespiratory SystemRotan CirebonNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Respiration - Reference Material - Shared in GCDocument7 pagesUnit 1 - Respiration - Reference Material - Shared in GCTarunNo ratings yet
- Gaseous ExchangeDocument23 pagesGaseous ExchangenikitaNo ratings yet
- 2.1 (I) Know The Properties of Gas Exchange Surfaces in Living Organisms 15Document29 pages2.1 (I) Know The Properties of Gas Exchange Surfaces in Living Organisms 15YEUNG WAN CHUEN ANGELIQUENo ratings yet
- 2.1 (I) Know The Properties of Gas Exchange Surfaces in Living Organisms 2Document16 pages2.1 (I) Know The Properties of Gas Exchange Surfaces in Living Organisms 2YEUNG WAN CHUEN ANGELIQUENo ratings yet
- 6454f627e4b0ad3aaf22e06b OriginalDocument13 pages6454f627e4b0ad3aaf22e06b OriginalSuprit JainNo ratings yet
- Biology 11 BODY SYSTEMSDocument13 pagesBiology 11 BODY SYSTEMSkatwal09No ratings yet
- Respiratory: Keyword: Respiration, Respiratory, OxygenDocument8 pagesRespiratory: Keyword: Respiration, Respiratory, Oxygensiti syahirahNo ratings yet
- Breathing & Exchange of Gases NotesDocument7 pagesBreathing & Exchange of Gases NotesKankana Biswas100% (1)
- Lesson 2.1 The Need To RespireDocument35 pagesLesson 2.1 The Need To RespireAdrianne OrtizNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System: Cellular Respiration ATPDocument15 pagesThe Respiratory System: Cellular Respiration ATPAajy BgavaharNo ratings yet
- (A) Sistem Respirasi Katak. Kedua Paru (B) Dasar Mulut Ditekan Kebawah DanDocument27 pages(A) Sistem Respirasi Katak. Kedua Paru (B) Dasar Mulut Ditekan Kebawah DanRunoffNo ratings yet
- Pastel Illustration Computer UI English Class Education PresentationDocument30 pagesPastel Illustration Computer UI English Class Education PresentationElaiza marie VenusNo ratings yet
- Gaseous Exchange NotesDocument8 pagesGaseous Exchange NotesMonique RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Gas ExchangeDocument7 pagesLesson 3 Gas ExchangeBrent PatarasNo ratings yet
- Oxygen 6-Vise o DisanjuDocument12 pagesOxygen 6-Vise o DisanjuSnezana JosicNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System of Frog: External RespirationDocument3 pagesRespiratory System of Frog: External RespirationShaira CogollodoNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in AnimalDocument3 pagesGas Exchange in AnimalAaron Dave CanteroNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in AnimalDocument3 pagesGas Exchange in AnimalAaron Dave CanteroNo ratings yet
- This Is All of My Notes On The Afterschool RevisionDocument4 pagesThis Is All of My Notes On The Afterschool Revisionemretunc4654No ratings yet
- L - Life Processes - Respiration Notes and Questions For Note Book WorkDocument7 pagesL - Life Processes - Respiration Notes and Questions For Note Book WorkNotImmortalNo ratings yet
- Gas ExchangeDocument15 pagesGas Exchangeneill arcaNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Respiratory SystemDocument22 pages2.4 Respiratory SystemAnonymous u7cQyr3QYNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument31 pagesRespiratory SystemMark Jhosua Austria GalinatoNo ratings yet
- Biology Lecture NotesDocument56 pagesBiology Lecture NotesMaisonette MichNo ratings yet
- Achievement: Gas Exchange in Animals InsectsDocument8 pagesAchievement: Gas Exchange in Animals Insectssimon chanNo ratings yet
- Deciphering nCoV19, Quest for Cure, Prophylaxis, and VaccineFrom EverandDeciphering nCoV19, Quest for Cure, Prophylaxis, and VaccineNo ratings yet
- أ.د. نبيل على خليلDocument133 pagesأ.د. نبيل على خليلAhmed OrabyNo ratings yet
- لمحاضرة الاولى نقص العناصرDocument40 pagesلمحاضرة الاولى نقص العناصرAhmed OrabyNo ratings yet
- الدرس العملى الاول بساتين دولى1Document11 pagesالدرس العملى الاول بساتين دولى1Ahmed OrabyNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomic Theory1Document23 pagesMacroeconomic Theory1Ahmed OrabyNo ratings yet
- Org Chem 10Document41 pagesOrg Chem 10Muhammad Javed IqbalNo ratings yet
- Practices of Field Crop ProductionDocument77 pagesPractices of Field Crop ProductionAhmed OrabyNo ratings yet
- 7.osmoregulation and Excretion in Invertebrates - FinalDocument58 pages7.osmoregulation and Excretion in Invertebrates - FinalAhmed Oraby81% (16)
- Subkingdom Metazoa 2 (DR - Nagwa)Document28 pagesSubkingdom Metazoa 2 (DR - Nagwa)Ahmed OrabyNo ratings yet
- 8.introduction To EmbryologyDocument63 pages8.introduction To EmbryologyAhmed OrabyNo ratings yet
- Phylum Annelida 4Document22 pagesPhylum Annelida 4Ahmed OrabyNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة السادسة Chordata المختصرةDocument28 pagesالمحاضرة السادسة Chordata المختصرةAhmed OrabyNo ratings yet
- Subkingdom Metazoa 2Document28 pagesSubkingdom Metazoa 2Ahmed OrabyNo ratings yet
- 2.animal TissuesDocument50 pages2.animal TissuesAhmed OrabyNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom 1Document24 pagesAnimal Kingdom 1Ahmed OrabyNo ratings yet