Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Con Analysis Flow Chart
Con Analysis Flow Chart
Uploaded by
kdyer1232Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Con Analysis Flow Chart
Con Analysis Flow Chart
Uploaded by
kdyer1232Copyright:
Available Formats
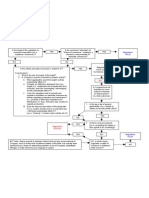
FIRST QUESTION = STATE OR FEDERAL ACTION?
IF STATE GOVERNMENT IS THE ACTOR: (including municipalities)
Dont have to show authority if its the state acting Does law violate a provision of the Constitution? 14th Amendment - Need to show state action before 14th applies!!!! Equal Protection Clause (1) Suspect Classification Racial Discrimination (see attached) Gender Discrimination (see attached) Others = just rational basis test (but rational basis with bite?) physically or mentally disabled homosexuals wealth (2) Fundamental Right voting, travel, SDP, (not education, not welfare)
Substantive Due Process (1) Does the state action prohibit/interfere with an individual liberty interest? IF NO: move on. IF YES: go to (2) (2) Is there a fundamental right deprivation? Consider how you frame the issue (Romer, Michael H.) Consider Harlans concurrance in Griswold (the dissent in Poe v. Ullman): Fundamental rights are implicit in the concept of ordered liberty Balances liberty of the individual v. needs of the society. Looks at history, but focuses on the living tradition. Consider Scalias test in Michael H, VMI.: Is the right on that is historically protected by law. Looks at the legal tradition narrowly. This is a minority view of the court. NO Rational Basis applies = a legitimate state interest, reasonably related. YES Strict Scrutiny applies = Narrowly tailored to a compelling state interest. (Narrowly tailored: Are the implemented means necessary? Can the ends be achieved in a less burdensome way?) *** Also consider Caseys undue burden test. We dont know yet if that test applies to abortion only, or to privacy rights in general. Is the obstacle to the fundamental right significant? Procedural Due Process (1) Do you have an interest which triggers PDP? (life, liberty, property) Liberty includes Bill of Rights, SDP rights, equal protection
Property = a statutory right/entitlement created by positive law (Roth)
if the laws which grant the right are repealed, then the right disappears also (ex: welfare benefits)
(2) Once you have a triggering interest, what process is due? Apply Matthews balancing test: Private interest affected by official action V. Government interest in efficiency and reducing financial/administrative burdens
Risk of erroneous deprivation of such interest must also be considered high risk weighs in favor of the individual Pre-emption (Gade Test) Look for 1 of 3 types: (1) Express = fed statute says no state shall pass a law covering (2) Implied (field) = fed legislation is so pervasive that it occupies the entire field of law; no place left for state to act (3) Implied (conflict) = compliance with fed and state statutes is impossible (Gade falls here) In all cases federal law trumps! Dormant Commerce Clause First, need to identify that there is a commerce issue (1) Does statute facially discriminate against out-of-state interests? (Philadelphia v. NJ) or Is statute economically protectionist*? (Is there a disproportionate impact on out-of-state interests?) (Carbone) *Protectionism laws that would excite those jealousies and retaliatory measures the Constitution was designed to prevent. If YES: Invalidity of statute assumed per se would need to be an overwhelming justification (ex: need for quarantine) and would need to be the only means of addressing the problem (narrowly tailored) (2) If neither Is statute unduly burdensome? Apply Pike Balancing Test: (a) legitimate state interest (benefits of statute/regulation) v (b) burden on interstate commerce Determining factor will be how much this looks like protectionism overall. Any other way to achieve the ends?
1st Amendment Balancing Test: fundamental right to engage in free speech v. (can only be overridden by) compelling state interest unrelated to suppression of ideas (Brandenburg, Dale)
IF FEDERAL GOVERNMENT IS THE ACTOR:
1. What is source of Congressional authority?
5 of 14th Amendment
Only gives Congress authority to remedy action by a state, not action by individuals if theres
no state action, then Congress has to use CC (Morrison, Civil Rights Cases) Boerne Test = must have: (1) violation of the 14th Amendment by the state Congress cant make up rights which havent been recognized by the cts (and cant use 5 to overrule SC holdings) AND (2) remedy which is congruent and proportional (a) has Congress picked the appropriate means to achieve its ends (b) cant be overbroad if it passes a nationwide law, must be remedying a nationwide problem (Boerne) Commerce Clause 3 categories which Congress can regulate: (Lopez) channels = OK roads, rivers, rails, hotels (Darby, Heart of Atlanta Motel) instrumentalities or persons/things in interstate commerce = OK this is true even if the threat comes from intrastate activities includes trucks, planes, etc.(Darby) activities substantially affecting interstate commerce = depends: Is activity economic or non-economic? (Lopez) Economic = OK Money changing hands (Katzenbach v. McClung, Wickard) If intrastate commerce, does it have a cumulative effect on interstate commerce? (McClung, Wickard, NLRB) If means are w/i CC, doesnt matter what Congress real goal is; pretext = OK (Darby) Non-economic = not OK $ flow isnt Congress real concern (Morrison) tends to look like police power Doublecheck: Has Congress enacted a statute of general application or is it commandeering the states? (10th Amendment issue)
Factors which indicate commandeering (Printz, NY v. US ) = not OK statute requires action by the state requires state to enact or enforce specific federal laws to avoid penalty (NY) makes state an agent of the federal govt requires state officials or agencies to enforce federal policy (Printz) singles out only state institutions requires state to base licensing or other regs on federal guidelines Analysis continues on next page.
If not commandeering, then its a statute of general application (Garcia) = OK if statute only requires inaction by the state (ex: dont discriminate, dont disclose info Condon) if statute not specific and directive, can try to distinguish it from NY v. US money incentives = ok (NY)
nding Taxation 2. Once Congressional authority established, are there constitutional limitations which apply?
5th Amendment Equal Protection Clause (incorporates 14th Amendment equal protection analysis Case=?) Racial Discrimination (see attached) Gender Discrimination (see attached) Others = just rational basis (but rational basis with bite?) physically or mentally disabled (Cleburne, Garrett) homosexuals (Romer) wealth Substantive Due Process - See page 1.
Procedural Due Process See page
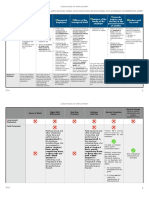
10th Amendment commandeering cases (Printz, NY v. US) see Commerce Power above. RACIAL DISCRIMINATION CASES 1. Is there State Action? Look for: Source and destination of $ Judicial enforcement of private discrimination (Shelley) Heavy hand of the state = coercive power (Rendall-Baker) Nominally private actor providing an exclusive traditional function of the state (RB) Symbiotic relationship between actor and the state (RB) Entwinement (Brentwood) = basically same as RB factors See Brentwood for more factors 2. Assuming theres State Action, is statute/policy facially discriminatory? YES: Strict Scrutiny applies! (even if reverse discr. Croson) = Compelling state interest which is narrowly tailored Congruence = same standard applies to feds as to states (Adarand)
A. Is there a compelling state interest? (i) Is it remedial? If so, majority would hold that its compelling To justify remediation, must have Past Prior Discrimination by the state To have PPD, must have past facial discrimination or past discrimination with invidious intent Past disparate impact alone is not enough (ii) If not remedial, is there any other justification? Diversity = maybe not a compelling state interest in education (Hopwood) still up in the air, though Probably no compelling interests other than remedial which will be upheld B. Is statute narrowly tailored? (i) If remedial: Is person receiving remedy the one who was originally deprived? Is remedy the thing of which they were originally deprived? (ii) If not remedial: Is statute narrowly tailored to achieve compelling govt interest NO: (only disparate impact) Is there showing of intent? 2 Problems: (1) What is the applicable standard of intent? Dominant Rule = But for test (Feeney) = would not have enacted statute but for motivation to discriminate by race Alternate standard = predominant factor(Miller) = easier to show, but not yet extended beyond voting context (2) Whose intent do you look at?
For factual analysis use factors in Arlington Heights (see outline) Consistency = no difference in Cts treatment of benign v. invidious intent (Croson) If INTENT: Strict Scrutiny applies If NO INTENT: Rational Basis Test applies (Washington v. Davis) = rational purpose reasonably related Almost everything passes under rational basis Filled milk and Williamson v. Lee Optical examples GENDER DISCRIMINATION CASES 1. Is there State Action? = same analysis as with race 2. Assuming theres State Action, is statute/policy facially discriminatory? Note: Discrimination based on pregnancy is not gender discrimination (Geduldig) YES: Intermediate Scrutiny applies = Important state interest which is substantially related or VMIs exceedingly persuasive justification test Separate but equal is sometimes ok for gender A. Is there an important state interest? (i) Is it remedial? If so, majority would hold that its important To justify remediation, must have Past Prior Discrimination by the state To have PPD, must have (1) past facial discrimination or past discrimination with invidious intent; or
(2) past disparate impact (Schlesinger, Califano v. Webster) (ii) If not remedial, is there any other justification? B. Is statute substantially related? (i) If remedial: Is person receiving remedy the one who was originally deprived? Is remedy the thing of which they were originally deprived? (ii) If not remedial: Is statute narrowly tailored to achieve important govt interest NO: (only disparate impact) Is there showing of intent? 2 Problems: (1) What is the applicable standard of intent? Dominant Rule = But for test (Feeney) = would not have enacted statute but for motivation to discriminate by gender (2) Whose intent do you look at?
For factual analysis use factors in Arlington Heights Consistency = no difference in Cts treatment of benign v. invidious intent (Croson) If INTENT: Intermediate Scrutiny applies If NO INTENT: Rational Basis Test applies (Washington v. Davis) = rational purpose reasonably related Almost everything passes under rational basis Filled milk and Williamson v. Lee Optical examples
You might also like
- PRINT 216396833 Con Law Attack SheetDocument24 pagesPRINT 216396833 Con Law Attack SheetAnnsley Oakley89% (37)
- Con Law Flow ChartsDocument6 pagesCon Law Flow Chartsbiferguson100% (48)
- Con Law Flow Chart (EPC & DPC)Document2 pagesCon Law Flow Chart (EPC & DPC)Ali Ammoura100% (10)
- 1A Flowchart (Need To Print)Document1 page1A Flowchart (Need To Print)Alexandra HoffmanNo ratings yet
- Con Law First Amendment ChecklistDocument1 pageCon Law First Amendment Checklistferndog45No ratings yet
- Con Law I Attack Sheet - GW Prof. Cheh 2009 - Text BarronDocument5 pagesCon Law I Attack Sheet - GW Prof. Cheh 2009 - Text BarronCaitlin Elizabeth100% (6)
- Commerce Clause FlowchartDocument1 pageCommerce Clause Flowchartmimiandnini100% (2)
- Commerce Clause Flowchart (Mate) PDFDocument2 pagesCommerce Clause Flowchart (Mate) PDFBrady WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Law ChecklistDocument3 pagesConstitutional Law Checklistbdittman2975% (4)
- Leg Reg Pre WriteDocument19 pagesLeg Reg Pre WriteashleyamandaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Civil Service Systems in The 21st Century (2015, Palgrave Macmillan UK) Frits M. Van Der Meer, Jos C. N. Raadschelders, Theo A. J. Toonen (Eds.) PDFDocument384 pagesComparative Civil Service Systems in The 21st Century (2015, Palgrave Macmillan UK) Frits M. Van Der Meer, Jos C. N. Raadschelders, Theo A. J. Toonen (Eds.) PDFSajid IqbalNo ratings yet
- Con Law Attack SheetDocument6 pagesCon Law Attack SheetBree Savage100% (8)
- Con Law OutlineDocument25 pagesCon Law OutlineNader80% (5)
- Con Law Attack SheetDocument20 pagesCon Law Attack Sheetelizabeth67% (3)
- 1st A - Speech Flowchart # CasesDocument2 pages1st A - Speech Flowchart # Casessmuldersam100% (1)
- Constitutional Law - Essay OpenersDocument4 pagesConstitutional Law - Essay OpenersMissPardis100% (5)
- State ActionsDocument1 pageState ActionsKatie Lee WrightNo ratings yet
- Erie Flow ChartDocument1 pageErie Flow ChartDhvanil Zaveri100% (2)
- Con Law I - Case Cheat SheetDocument22 pagesCon Law I - Case Cheat SheetPriscilla Quansah100% (1)
- Con Law II OutlineDocument44 pagesCon Law II OutlineCharlene Soleimani100% (10)
- Con Law ChecklistDocument15 pagesCon Law Checklistzoti_lejdi91% (11)
- Con Law FlowDocument12 pagesCon Law FlowBrian Palmer100% (7)
- Chart - Constitutional Law - Preemption, DCC, PICDocument1 pageChart - Constitutional Law - Preemption, DCC, PICSean Williams100% (3)
- Con Law II OutlineDocument59 pagesCon Law II OutlineHenry ManNo ratings yet
- Con Law ChecklistDocument2 pagesCon Law ChecklistAshli Braggs100% (1)
- Dormant Commerce Clause FCDocument1 pageDormant Commerce Clause FCslbernstein100% (1)
- Constitutional Law ChecklistDocument18 pagesConstitutional Law ChecklistClaudia Galan100% (2)
- Con Law Template - Commerce ClauseDocument3 pagesCon Law Template - Commerce ClauseVictor FrancoNo ratings yet
- Complete Criminal Law Bennett For MyersDocument15 pagesComplete Criminal Law Bennett For MyersDewey Bennett100% (2)
- Intro: Legal Knowledge Skill Thoroughness PreparationDocument2 pagesIntro: Legal Knowledge Skill Thoroughness PreparationHaifaNo ratings yet
- Crim Law ATK OutlineDocument10 pagesCrim Law ATK Outlinegialight100% (4)
- Answering Con Law Questions 1Document6 pagesAnswering Con Law Questions 1Andrew Welsh100% (1)
- Con Law II OutlineDocument29 pagesCon Law II OutlineLangdon SouthworthNo ratings yet
- EPC, DPC Attack PlansDocument6 pagesEPC, DPC Attack PlansEl100% (3)
- Constitutional Law StepsDocument24 pagesConstitutional Law StepsRoss 'the-hair' DeSandersNo ratings yet
- Con Law II Mentor OutlineDocument10 pagesCon Law II Mentor OutlineLALANo ratings yet
- My Con Law I Outline (Charts & Bones)Document13 pagesMy Con Law I Outline (Charts & Bones)Priscilla QuansahNo ratings yet
- Con LawDocument34 pagesCon LawNathan Breen100% (1)
- Con Law AttackDocument6 pagesCon Law Attackthisfadednight100% (2)
- Con Law OutlineDocument19 pagesCon Law Outlinesammeehan88No ratings yet
- Constitutional Law Outline Swartzwelder Standards of Review Intro Issue: RuleDocument37 pagesConstitutional Law Outline Swartzwelder Standards of Review Intro Issue: RuleKylee Colwell100% (2)
- Con Law Outline - CasesDocument2 pagesCon Law Outline - CasesJosh Hutton100% (1)
- Conlaw OpeningpsDocument4 pagesConlaw OpeningpsKaran MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Modern Constitutional Law DoctrineDocument20 pagesModern Constitutional Law DoctrineKatherine McClintock100% (1)
- Con Law ChecklistDocument1 pageCon Law ChecklistekfloydNo ratings yet
- Commerce Clause Flow ChartDocument1 pageCommerce Clause Flow Chartbanucci100% (2)
- Commerce Clause TestsDocument10 pagesCommerce Clause Testsmdaly102483No ratings yet
- Good Con Law OutlineDocument91 pagesGood Con Law OutlineJordan WoodsNo ratings yet
- Leg Reg ChecklistDocument5 pagesLeg Reg ChecklistChristopher Pedro100% (1)
- To The States, Are Reserved To The States Respectively, or To The People."Document1 pageTo The States, Are Reserved To The States Respectively, or To The People."Brat WurstNo ratings yet
- Con Law Model Answer 04Document15 pagesCon Law Model Answer 04superxl2009No ratings yet
- Tiff's Crim Law OutlineDocument37 pagesTiff's Crim Law Outlineuncarolinablu21No ratings yet
- Business Organizations: Outlines and Case Summaries: Law School Survival Guides, #10From EverandBusiness Organizations: Outlines and Case Summaries: Law School Survival Guides, #10No ratings yet
- Law School Survival Guide (Volume II of II) - Outlines and Case Summaries for Evidence, Constitutional Law, Criminal Law, Constitutional Criminal Procedure: Law School Survival GuidesFrom EverandLaw School Survival Guide (Volume II of II) - Outlines and Case Summaries for Evidence, Constitutional Law, Criminal Law, Constitutional Criminal Procedure: Law School Survival GuidesNo ratings yet
- 101 Bar Exam Affirmations: Bar Exam Booklets, #1From Everand101 Bar Exam Affirmations: Bar Exam Booklets, #1Rating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (4)
- Con Law Ocd (Afternoon) Class OutlineDocument6 pagesCon Law Ocd (Afternoon) Class OutlineXi ZhaoNo ratings yet
- Constitutional LawDocument12 pagesConstitutional Lawpv balayanNo ratings yet
- MBE Notes and StrategiesDocument16 pagesMBE Notes and StrategiesMrZee27100% (1)
- Constitutional ExamDocument4 pagesConstitutional ExamflorinaNo ratings yet
- MBE Notes and StrategiesDocument16 pagesMBE Notes and StrategiesMrZee2788% (16)
- Costume and Dress 3Document46 pagesCostume and Dress 3Nicole JeonNo ratings yet
- FootballDocument2 pagesFootballNunoricNo ratings yet
- CASE SOLUTION - VadilalDocument13 pagesCASE SOLUTION - VadilalRohan KhullarNo ratings yet
- TTL-21ST CenturyDocument8 pagesTTL-21ST CenturyYasmin G. BaoitNo ratings yet
- BankDocument3 pagesBankmastermind_asia9389No ratings yet
- Resume MelissaWoodsDocument3 pagesResume MelissaWoodspulpculchureNo ratings yet
- 385 493043 5770Document2 pages385 493043 5770Haseeb AhmadNo ratings yet
- Eight-Scale Tool For Mapping Cultural Differences by Erin MeyerDocument4 pagesEight-Scale Tool For Mapping Cultural Differences by Erin MeyerShreya Sharma100% (1)
- Technical Solutions Analyst Req. 5274Document3 pagesTechnical Solutions Analyst Req. 5274Javier Fraguela-RiosNo ratings yet
- Law On Obligations Bullet Review Part 1Document4 pagesLaw On Obligations Bullet Review Part 1randyi100% (1)
- Percent Problems Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesPercent Problems Lesson Planapi-249323843No ratings yet
- 35 Entrepreneurship and Innovation - Sep 2020 (CBCS - F + R - 2016-17 - Onwards)Document23 pages35 Entrepreneurship and Innovation - Sep 2020 (CBCS - F + R - 2016-17 - Onwards)Utkarshani RajNo ratings yet
- Concepcion CBDRRM, Cca and BDRRM PlanDocument42 pagesConcepcion CBDRRM, Cca and BDRRM PlanZyron Criste67% (3)
- Right of Way Act (RA 10752) of 2016Document21 pagesRight of Way Act (RA 10752) of 2016Elimer Teves EspinaNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Methods-Chapter-6Document32 pagesQualitative Methods-Chapter-6Siddhant AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Small v. United StatesDocument2 pagesSmall v. United StatesEarl NuydaNo ratings yet
- Individual Sport: Arnis: Physical Education 7 - 1 Quarter - Lesson 5Document43 pagesIndividual Sport: Arnis: Physical Education 7 - 1 Quarter - Lesson 5Eric Jordan ManuevoNo ratings yet
- Gen. Instructions For AP-Guest FacultyDocument4 pagesGen. Instructions For AP-Guest Facultykirti vithaniNo ratings yet
- Learning Block 1: Supply Management and Procurement OverviewDocument64 pagesLearning Block 1: Supply Management and Procurement OverviewMacy AndradeNo ratings yet
- Manual En-UsDocument191 pagesManual En-UsTimothy Cruse100% (1)
- Article XXIV Reference To CasesDocument4 pagesArticle XXIV Reference To CasesNickyta UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Conditions of EmploymentsssDocument12 pagesConditions of Employmentsssinsert nameNo ratings yet
- Narrative Report About Servant LeadershipDocument1 pageNarrative Report About Servant LeadershipNhie Jay BualanNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Environmental Value Systems Case Study 2Document3 pages1.1 Environmental Value Systems Case Study 2Vedant Patil0% (1)
- Sustainability 12 00166Document24 pagesSustainability 12 00166syedNo ratings yet
- Personal SWOT Analysis: DME Mentoring Cell Activity 1Document4 pagesPersonal SWOT Analysis: DME Mentoring Cell Activity 1Ankit KumarNo ratings yet
- Schriften Fandrych 2016 05Document8 pagesSchriften Fandrych 2016 05tomasgouchaNo ratings yet
- Hontiveros-Baraquel v. TRBDocument18 pagesHontiveros-Baraquel v. TRBjoshmagiNo ratings yet
- Const RiskDocument7 pagesConst RiskAnchal SinghNo ratings yet