Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Computer Repair - A Complete Illustrated Guide To PC Hardware - c2004
Computer Repair - A Complete Illustrated Guide To PC Hardware - c2004
Uploaded by
Ajay ArthurOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Computer Repair - A Complete Illustrated Guide To PC Hardware - c2004
Computer Repair - A Complete Illustrated Guide To PC Hardware - c2004
Uploaded by
Ajay ArthurCopyright:
Available Formats
A complete illustrated Guide to the PC Hardware
Karbosguide.com
Welcome t o Michael Karbo' s
Online Service. Here you will
find a modern online-
magazine wit h more t han
500 illust rat ed art icles for
t he crit ical reader!
Use our menu t o your left or
t he sit emap. You may also
follow any of t he links list ed
below. We hope t hat you
appreciat e our work!
q St art st udying t he design
of a PC mot herboard.
q Learn about harddisks
and ot her drives.
q Learn about t he PC I / O
syst em.
q Learn about t he PC video
syst em.
Sit emap
See our guest book and add
your comment .
Cor r ect i ons
Misspellings, t ypos or ot her
correct ions. Please report ! .
Kar bo' s New sl et t er :
Pent ium 4 and At hlonXP.
More t han 50 phot os of old
cars free t o download!
The MP3 art icle is re- writ t en.
Edit ing phot os wit h Phot oshop
Cleaning Windows Me for
t emporary files . . .
All modules 7 re- writ t en
Copyright ( c) 1996 - 2002 Michael B. Karbo. WWW. KARBOSGUI DE. COM.
http://www.karbosguide.com/guides/start.htm7/27/2004 4:04:12 AM
Sign up!
A complete illustrated Guide to the PC Hardware
About Michael Karbo
NEW: German
version.
Privacy politic
Software Guides
Dictionary
Photo Gallery
Search
1. About PC data
1a. About data
1b. Character tables
2. The PC system board
2a. Introduction
2b. Boot process, system
bus
2c. I/O buses
2d. Chip sets
2e. On RAM
3. About CPUs
3a. An intro to CPUs
3b. CPU improvements
3c. 5th gener. CPUs
3d. Cooling and overclocking
3e. 6th gener. CPUs
4. Drives and other
storage
4a. Drives
4b. Hard disks
4c. Optic storage media
4d. ZIP etc.
4e. Tape streamers
5. Expansion cards
and interfaces
5a. Adapters
5b. EIDE, Ultra DMA,
AGP
5c. SCSI, FireWire, USB
6. OSs and file
systems
6a. File systems
6b. Windows 95
6c. BIOS, OS, hardware
6d. The Windows 98
page
7. Graphics and sound
7a. Display basics
7b. Graphics cards
7c. About sound cards
7d. Digital music MP3,
MOD etc.
Main page
http://www.karbosguide.com/guides/sitemap.htm7/27/2004 4:04:13 AM
Support Karbosguide.com
KarbosGuide.com
Support our work
q Next page
q Previous page
Karbosguide. com a t ut orial used globally. I t is a work made "con amore". We make no profit
from it . However, j ust a lit t le economical revenue would be great . I t t akes so much t ime t o
updat e and develop t he sit e wit h high qualit y informat ion.
You can help us in several ways:
q Click on t he banners
q Regist er as a user and donat e a few dollars.
q Tell your friends an part ners about Karbosguide. com, share t he URL.
q Next page
q Previous page
http://www.karbosguide.com/info/support_01.htm7/27/2004 4:04:19 AM
KarbosGuide.com. Module 1a. About data.
KarbosGuide.com. Module 1a.
About data
q Next page
q Previous
page
Our PCs are dat a processors. The PC' s funct ion is simple: t o process dat a, and
t he processing is done elect ronically inside t he CPU and bet ween t he ot her
component s. That sounds simple, but what is dat a, and how is it processed
elect ronically in a PC? That is t he subj ect of t hese pages.
Analog data
The signals, which we send each ot her t o communicat e, is dat a. Our daily dat a have many forms:
sound, let t ers, numbers, and ot her charact ers ( handwrit t en or print ed) , phot os, graphics, film. All t his
dat a is in it s nat ure analog, which means t hat it varies in t ype. I n t his form, t he dat a- signals are
unusable in a PC. The PC can only process concise, simple dat a format s. Such dat a can be processed
very effect ively.
Digital data
The PC is an elect ric unit . Therefore, it can only deal wit h dat a, which are associat ed wit h elect ricit y.
That is accomplished using elect ric swit ches, which are eit her off or on. You can compare wit h regular
household swit ches. I f t he swit ch is off, t he PC reads numeral 0. I f it is on, it is read as numeral one.
See t he illust rat ion below:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module1a1.htm (1 of 5)7/27/2004 4:05:11 AM
KarbosGuide.com. Module 1a. About data.
Wit h our elect ric swit ches, we can writ e 0 or 1. We can now st art our dat a processing!
The PC is filled wit h t hese swit ches ( in t he form of t ransist ors) . There are lit erally millions of t hose in t he
elect ronic component s. Each represent s eit her a 0 or a 1, so we can process dat a wit h millions of 0s and
1s.
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
Bits
[ t op]
Each 0 or 1 is called a bit . Bit is an abbreviat ion of t he expression BI nary digiT. I t is called binary, since
it is derived from t he binary number syst em:
0 1 bit
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module1a1.htm (2 of 5)7/27/2004 4:05:11 AM
KarbosGuide.com. Module 1a. About data.
1 1 bit
0110 4 bit
01101011 8 bit
The binary number system
[ t op]
The binary number syst em is made up of digit s, j ust like our common decimal syst em ( 10 digit syst em) .
But , while t he decimal syst em uses digit s 0 t hrough 9, t he binary syst em only uses digit s 0 and 1.
I f you are int erest ed in underst anding t he binary number syst em, t hen here is a brief course. See if you
can follow t he syst em. See how numbers are const ruct ed in t he binary syst em, using only 0s and 1s:
Numbers, as known in t he
decimal- syst em
Same numbers in binary
syst em
0 0
1 1
2 10
3 11
4 100
5 101
6 110
7 111
8 1000
Digital data
[ t op]
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module1a1.htm (3 of 5)7/27/2004 4:05:11 AM
KarbosGuide.com. Module 1a. About data.
We have seen t hat t he PC appears capable of handling dat a, if it can receive t hem as 0s and 1s. This
dat a format is called digit al. I f we can t ranslat e our daily dat a from t heir analog format t o digit al format ,
t hey will appear as chains of 0s and 1s, t hen t he PC can handle t hem.
So, we must be able t o digit ize our dat a. Pour t ext , sounds, and pict ures int o a funnel, from where t hey
emerge as 0s and 1s:
Let us see how t his can be accomplished.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read more about t he boot process and syst em bus in Module 2b
Read more about I / O buses in module 2c
Read more about t he mot herboard chip set in module 2d
Read more about RAM in module 2e
Read about EI DE in module 5b
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module1a1.htm (4 of 5)7/27/2004 4:05:11 AM
KarbosGuide.com. Module 1a. About data.
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module1a1.htm (5 of 5)7/27/2004 4:05:11 AM
KarbosGuide.com. Module 1a. About data.
KarbosGuide.com. Module 1a2.
About Bytes
Cont ent s:
q I nt roduct ion
q ASCI I
q About t ext and code
q Dat a in files
q Next page
q Previous page
Introduction
The most basic dat a processing is word processing. Let us use t hat as an example. When we
do word processing, we work at a keyboard similar t o a t ypewrit er. There are 101 keys,
where we find t he ent ire alphabet A, B, C, et c. We also find t he digit s from 0 t o 9 and all t he
ot her charact ers we need: , . - ; ( ) : _?! "# * %&et c. .
All t hese charact ers must be digit ized. They must be expressed in 0s and 1s. Bit s are
organized in groups of 8. A group of 8 bit s is called a byt e.
8 bit s = 1 byt e, t hat is t he syst em. Then, what can we do wit h byt es? First , let us see how
many different byt es we can const ruct . A byt e is an 8 digit number. We link 0s and 1s in a
pat t ern. How many different ones can we make? Here is one: 01110101, and here is
anot her: 10010101.
We can calculat e t hat you can make 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 different pat t erns, since
each of t he 8 bit s can have 2 values.
q 2
8
( t wo in t he power of eight ) is 256. Then t here are 256 different byt es!
Now we assign a byt e t o each let t er and ot her charact ers. And since we have 256 pat t erns t o
choose from, t here is plent y of room for all. Here you see some examples of t he
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module1a2.htm (1 of 5)7/27/2004 4:05:22 AM
KarbosGuide.com. Module 1a. About data.
"t ranslat ion: "
Charact er Bit pat t ern Byt e
number
Charact er Bit pat t ern Byt e
number
A 01000001 65 10111100 188
B 01000010 66 . 00101110 46
C 01000011 67 : 00111010 58
a 01100001 97 $ 00100100 36
b 01100010 98 \ 01011100 92
o 01101111 111 ~ 01111110 126
p 01110000 112 1 00110001 49
q 01110001 113 2 00110010 50
r 01110010 114 9 00111001 57
x 01111000 120 10101001 169
y 01111001 121 > 00111110 62
z 01111010 122 10001001 137
When you writ e t he word "summer", you writ e 6 let t ers. I f t he comput er has t o process t hat
word, it will be digit ized t o 6 byt es. I n ot her words, t he word summer occupies 6 byt es in t he
PC RAM, when you t ype it , and 6 byt es on t he hard disk, if you save it .
ASCII
[ t op]
ASCI I means American St andard Code for I nformat ion I nt erchange. I t is an indust ry
st andard, which assigns let t ers, numbers, and ot her charact ers wit hin t he 256 slot s available
in t he 8 bit code.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module1a2.htm (2 of 5)7/27/2004 4:05:22 AM
KarbosGuide.com. Module 1a. About data.
The ASCI I t able is divided in 3 sect ions:
q Non print able syst em codes bet ween 0 and 31.
q "Lower ASCI I " bet ween 32 and 127. This part of t he t able originat es from older, American
syst ems, which worked on 7 bit charact er t ables. Foreign let t ers, like and were not
available t hen.
q "Higher ASCI I " bet ween 128 and 255. This part is programmable, in t hat you can
exchange charact ers, based on which language you want t o writ e in. Foreign let t ers are
placed in t his part .
Learn more about t he ASCI I t able in Module 1b
An example
Let us imagine a st ream of bit s sent from t he keyboard t o t he comput er. When you t ype,
st reams of 8 bit s are sent t o t he comput er. Let us look at a series of bit s:
001100010011001000110011
Bit s are combined int o byt es ( each 8 bit s) . These 24 bit s are int erpret ed as t hree byt es. Let
us read t hem as byt es: 00110001, 00110010, and 00110011.
When we convert t hese byt e binary numbers t o decimal numbers, you will see t hat t hey read
as 49, 50, and 51 in decimal numbers. To int erpret t hese numbers, we have t o look at t he
ASCI I t able. You will find t hat you have t yped t he numbers 1, 2, and 3.
About text and code
[ t op]
Now we have seen t he PCs user dat a, which are always digit ized. But t here are many
different kinds of dat a in t he PC. You can different iat e bet ween 2 fundament al t ypes of dat a:
q Program code, which is dat a, t hat allows t he PC t o funct ion.
q User dat a, like t ext , graphics, sound.
The fact is, t hat t he CPU must have inst ruct ions t o funct ion. You can read more about t his in
t he review of t he CPU in module 3a. An inst ruct ion is a st ring of dat a, of 0s and 1s. The CPU
is designed t o recognize t hese inst ruct ions, which arrive t oget her wit h t he user input dat a t o
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module1a2.htm (3 of 5)7/27/2004 4:05:22 AM
KarbosGuide.com. Module 1a. About data.
be processed.
The program code is t hus a collect ion of inst ruct ions, which are execut ed one by one, when
t he program runs. Each t ime you click t he mouse, or hit a key on t he keyboard, inst ruct ions
are sent from your soft ware ( program) t o t he CPU, t elling it what t o do next .
User dat a are t hose dat a, which t ells t he soft ware how t o respond. The let t ers, illust rat ions,
home pages, et c. , which you and I produce, are creat ed wit h appropriat e soft ware.
Files
[ t op]
Bot h program code and user dat a are saved as files on t he hard disk. Oft en, you can
recognize t he t ype of file by it s suffix. Here are some examples:
Cont ent File name
Program code START. EXE, WI N. COM, HELP. DLL, VMM32. VXD
User dat a LETTER. DOC, HOUSE. BMP, I NDEX. HTM
This is writ t en as an int roduct ion t o naming files. The file name suffix det ermines how t he PC
will handle t he file. You can read about t his subj ect in some of my books, e. g. "DOS - t each
yourself" ( only available in Europe.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read more about t he boot process and syst em bus in Module 2b
Read more about I / O buses in module 2c
Read more about t he mot herboard chip set in module 2d
Read more about RAM in module 2e
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module1a2.htm (4 of 5)7/27/2004 4:05:22 AM
KarbosGuide.com. Module 1a. About data.
Read about EI DE in module 5b
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module1a2.htm (5 of 5)7/27/2004 4:05:22 AM
Karbos Guide
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
Module 1b
Character tables
q Next page
q Previous
page
The ASCII tables
Here you see t he complet e ASCI I charact er t able. First t he part from ASCI I - numbers 032 t o
127:
ASCII-number Common characters
(in Windows )
Symbol Wingdings
032
033 !
! !
034 "
"
035 #
# #
036 $
$
037 %
% %
038 &
& &
039 '
'
040 (
( (
041 )
) )
042 *
*
043 +
+ +
044 ,
, ,
045 -
-
046 .
. .
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module1b.htm (1 of 9)7/27/2004 4:05:25 AM
Karbos Guide
047
/ / /
048
0 0 0
049
1 1 1
050
2 2 2
051
3 3 3
052
4 4 4
053
5 5 5
054
6 6 6
055
7 7 7
056
8 8 8
057
9 9 9
058
: : :
059
; ; ;
060
< < <
061
= =
062
> > >
063
? ? ?
064
@ @
065
A A
066
B B
067
C C
068
D D
069
E E
070
F F
071
G G
072
H H
073
I I
074
J J
075
K K
076
L L
077
M M
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module1b.htm (2 of 9)7/27/2004 4:05:25 AM
Karbos Guide
078
N N
079
O O
080
P P
081
Q Q
082
R R
083
S S
084
T T
085
U U
086
V V
087
W W
088
X X
089
Y Y
090
Z Z
091
[ [ [
092
\ \
093
] ] ]
094
^ ^
095
_ _
096
` `
097
a a
098
b b
099
c c
100
d d
101
e e
102
f f
103
g g
104
h h
105
i i
106
j j
107
k k
108
l l
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module1b.htm (3 of 9)7/27/2004 4:05:25 AM
Karbos Guide
109
m m
110
n n
111
o o
112
p p
113
q q
114
r r
115
s s
116
t t
117
u u
118
v v
119
w w
120
x x
122
z z
123
{ { {
124
| |
125
} } }
126
~ ~
127
Then t he numbers from 0128 t o 0255. Not ice t he leading zero.
ASCII-number Common characters
(in Windows )
Symbol Wingdings
0128
&eur o; &; & e u r o ;
0129
0130
0131
0132
0133
0134
0135
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module1b.htm (4 of 9)7/27/2004 4:05:25 AM
Karbos Guide
0136
0137
0138
0139
0140
0141
0142
0143
0144
0145
0146
0147
0148
0149
0150
0151
0152
0153
0154
0155
0156
0157
0158
0159
0160
0161
0162
0163
0164
0165
0166
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module1b.htm (5 of 9)7/27/2004 4:05:25 AM
Karbos Guide
0167
0168
0169
0170
0171
0172
0173
- -
0174
0175
0176
0177
t
0178
0179
0180
0181
0182
0183
0184
0185
0186
0187
0188
0189
|
0190
0191
0192
0193
0194
0195
0196
0197
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module1b.htm (6 of 9)7/27/2004 4:05:25 AM
Karbos Guide
0198
0199
0200
0201
0202
0203
0204
0314
0206
0207
0208
0209
0210
0211
0212
0213
0214
0215
0216
0217
0218
0219
0220
0221
0222
0223
0224
0225
0226
0227
0228
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module1b.htm (7 of 9)7/27/2004 4:05:25 AM
Karbos Guide
0229
0230
0231
0232
0233
0234
0235
0236
0237
'
0238
0239
0240
0241
0242
0243
0244
(
0245
0246
_
0247
0248
,
0249
1
0250
1
0251
]
0252
0253
;
0254
)
0255
q Next page
q Previous page
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module1b.htm (8 of 9)7/27/2004 4:05:25 AM
Karbos Guide
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side.
Read module 5b about AGP and module 5c about Firewire.
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
Read module 7c about sound cards, and 7d on digit al sound and music.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module1b.htm (9 of 9)7/27/2004 4:05:25 AM
An illustrated Guide to Motherboards
KarbosGuide.com. Module 2a.1
The PC and its motherboard
The cont ent s:
q I nt roduct ion t o t he PC
q The PC const ruct ion
q The mot herboard ( mot herboard)
q POST and ot her ROM ( BI OS et c. )
q Next page
q Previous
page
Please click t o support our work!
Introduction to the PC
The t echnical t erm for a PC is micro dat a processor . That name is no longer in common use. However, it places t he PC
in t he bot t om of t he comput er hierarchy:
q Supercomput ers and Mainframes are t he largest comput ers - million dollar machines, which can occupy more t han
one room. An example is I BM model 390.
q Minicomput ers are large powerful machines. They t ypically serve a net work of simple t erminals. I BM' s AS/ 400 is an
example of a minicomput er.
q Workst at ions are powerful user machines. They have t he power t o handle complex engineering applicat ions. They
use t he UNI X or somet imes t he NT operat ing syst em. Workst at ions can be equipped wit h powerful RI SC processors
like Digit al Alpha or MI PS.
q The PCs are t he Benj amins in t his order: Small inexpensive, mass produced comput ers. They work on DOS,
Windows , or similar operat ing syst ems. They are used for st andard applicat ions.
The point of t his hist ory is, t hat Benj amin has grown. He has act ually been promot ed t o capt ain! Todays PCs are j ust
as powerful as minicomput ers and mainframes were not t oo many years ago. A powerful PC can easily keep up wit h
t he expensive workst at ions. How have we advanced t his far?
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2a1.htm (1 of 7)7/27/2004 4:05:28 AM
An illustrated Guide to Motherboards
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
The PC's success [top]
The PC came out in 1981. I n less t han 20 years, it has t ot ally changed our means of communicat ing. When t he PC was
int roduced by I BM, it was j ust one of many different micro dat a processors. However, t he PC caught on. I n 5- 7 years,
it conquered t he market . From being an I BM compat ible PC, it became t he st andard.
I f we look at early PCs, t hey are charact erized by a number of feat ures. Those were inst rument al in creat ing t he PC
success.
q The PC was from t he st art st andardized and had an open archit ect ure.
q I t was well document ed and had great possibilit ies for expansion.
q I t was inexpensive, simple and robust ( definit ely not advanced) .
The PC st art ed as I BM' s baby. I t was t heir design, built over an I nt el processor ( 8088) and fit t ed t o Microsoft ' s simple
operat ing syst em MS- DOS.
Since t he design was well document ed, ot her companies ent ered t he market . They could produce funct ionable copies
( clones) of t he cent ral syst em soft ware ( BI OS) . The cent ral I SA bus was not pat ent ed. Slowly, a myriad of companies
developed, manufact uring I BM compat ible PCs and component s for t hem.
The Clone was born. A clone is a copy of a machine. A machine, which can do precisely t he same as t he original ( read
Big Blue - I BM) . Some of t he component s ( for example t he hard disk) may be ident ical t o t he original. However, t he
Clone has anot her name ( Compaq, Olivet t i, et c. ) , or it has no name at all. This is t he case wit h "t he real clones. "
Today, we different iat e bet ween:
q Brand names, PCs from I BM, Compaq, AST, et c. Companies which are so big, so t hey develop t heir own hardware
component s.
q Clones, which are built from st andard component s. Anyone can make a clone.
Since t he basic t echnology is shared by all PCs, I will st art wit h a review of t hat .
The PC construction
[ t op]
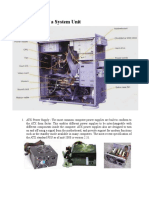
The PC consist s of a cent ral unit ( referred t o as t he comput er) and various peripherals. The comput er is a box, which
cont ains most of t he working elect ronics. I t is connect ed wit h cables t o t he peripherals.
On t hese pages, I will show you t he comput er and it s component s. Here is a pict ure of t he comput er:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2a1.htm (2 of 7)7/27/2004 4:05:28 AM
An illustrated Guide to Motherboards
Here is a list of t he PC component s. Read it and ask yourself what t he words mean. Do you recognize all t hese
component s? They will be covered in t he following pages.
Component s in t he cent ral unit - t he comput er Peripherals
The mot herboard: CPU, RAM, cache,
ROM chips wit h BI OS and st art - up programs.
Chip set s ( cont rollers) . Port s, buses and expansion
slot s.
Drives: Hard disk( s) , floppy drive( s) , CD- ROM, et c.
Expansion cards: Graphics card ( video adapt er) ,
net work cont roller, SCSI cont roller.
Sound card, video and TV card.
I nt ernal modem and I SDN card.
Keyboard and
mouse.
Joyst ick
Monit or
Print er
Scanner
Loudspeakers
Ext ernal drives
Ext ernal t ape st at ion
Ext ernal modem
So, how are t he component s connect ed. What are t heir funct ions, and how are t hey t ied t oget her t o form a PC? That
is t he subj ect of Click and Learn. So, please cont inue reading. . .
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2a1.htm (3 of 7)7/27/2004 4:05:28 AM
An illustrated Guide to Motherboards
The von Neumann Model of the PC
[ t op]
Comput ers have t heir root s 300 years back in hist ory. Mat hemat icians and philosophers like Pascal, Leibnit z, Babbage
and Boole made t he foundat ion wit h t heir t heoret ical works. Only in t he second half of t his cent ury was elect ronic
science sufficient ly developed t o make pract ical use of t heir t heories.
The modern PC has root s t hat go back t o t he USA in t he 1940s. Among t he many scient ist s, I like t o remember John
von Neumann ( 1903- 57) . He was a mat hemat ician, born in Hungary. We can st ill use his comput er design t oday. He
broke comput er hardware down in five primary part s:
q CPU
q I nput
q Out put
q Working memory
q Permanent memory
Act ually, von Neumann was t he first t o design a comput er wit h a working memory ( what we t oday call RAM) . I f we
apply his model t o current PCs, it will look like t his:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2a1.htm (4 of 7)7/27/2004 4:05:28 AM
An illustrated Guide to Motherboards
All t hese subj ect s will be covered.
Data exchange - the motherboard
[ t op]
The ROM chips cont ain inst ruct ions, which are specific for t hat part icular mot herboard. Those programs and
inst ruct ions will remain in t he PC t hroughout it s life; usually t hey are not alt ered.
Primarily t he ROM code holds st art - up inst ruct ions. I n fact t here are several different programs inside t he st art - up
inst ruct ions, but for most users, t hey are all woven t oget her. You can different iat e bet ween:
q POST ( Power On Self Test )
q The Set up inst ruct ions, which connect wit h t he CMOS inst ruct ions
q BI OS inst ruct ions, which connect wit h t he various hardware peripherals
q The Boot inst ruct ions, which call t he operat ing syst em ( DOS, OS/ 2, or Windows )
All t hese inst ruct ions are in ROM chips, and t hey are act ivat ed one by one during st art - up. Let us look at each part .
The suppliers of system software
[ t op]
All PCs have inst ruct ions in ROM chips on t he mot herboard. The ROM chips are supplied by specialt y soft ware
manufact urers, who make BI OS chips. The primary suppliers are:
q Phoenix
q AMI ( American Megat rends )
q Award
You can read t he name of your BI OS chip during st art - up. You can also see t he chip on t he syst em board. Here is a
pict ure ( slight ly blurred) of an Award ROM chip:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2a1.htm (5 of 7)7/27/2004 4:05:28 AM
An illustrated Guide to Motherboards
Here is an AMI chip wit h BI OS and st art - up inst ruct ions:
Let us look at t he different component s inside t he ROM chip.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read more about t he boot process and syst em bus in Module 2b
Read more about I / O buses in module 2c
Read more about t he mot herboard chip set in module 2d
Read more about RAM in module 2e
Read about EI DE in module 5b
I also recommend t wo books for furt her st udies. Gunnar Forst : "PC Principles", from MI T is excellent . Also "The Winn
L. Rosch Hardware Bible" from Brady covers t he same subj ect s. Also "PC I nt ern" from Abacus is fine.
Links t o BI OS informat ion:
Mr BI OS FAQ
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2a1.htm (6 of 7)7/27/2004 4:05:28 AM
An illustrated Guide to Motherboards
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2a1.htm (7 of 7)7/27/2004 4:05:28 AM
An illustrated Guide to Motherboards
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
Click & Learn. Module 2a.2
The system software on the motherboard
The cont ent s:
q The Set up program
q The POST
q The CMOS RAM
q Opening t he Set up program
q Next page
q Previous page
Art icles writ t en
by Michael B. Karbo
The Setup programs [top]
There are t hree element s in t he st art - up part of t he ROM chip:
q The I nit ializing rout ine, which set s up t he BI OS funct ions. The adapt er ROM is int egrat ed. A
t able covering all t he BI OS programs is const ruct ed. This is oft en called t he int errupt vect ors.
q The POST ( t he t est programs)
q The disk boot st rap loader, which calls upon t he operat ing syst em.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2a2.htm (1 of 7)7/27/2004 4:05:35 AM
An illustrated Guide to Motherboards
These programs are st ored in t he ROM chip, and t hey are act ivat ed one by one during t he PC st art -
up.
The POST
Power On Self Test is t he first inst ruct ion execut ed during st art - up. I t checks t he PC component s
and t hat everyt hing works. You can recognize it during t he RAM t est , which occurs as soon as you
t urn power on.
You may follow t he checks being execut ed in t his order, as t he informat ion are gat hered:
1) I nformat ion about t he graphics adapt er
2) I nformat ion about t he BI OS ( name, version)
3) I nformat ion about t he RAM ( being count ed)
As users, we have only limit ed abilit y t o manipulat e t he POST inst ruct ions. But cert ain syst em
boards enable t he user t o order a quick syst em check. Some enable t he user t o disable t he RAM
t est , t hereby short ening t he durat ion of t he POST. The durat ion of t he POST can vary considerably
in different PCs. On t he I BM PC 300 comput er, it is very slow. But you can disrupt it by pressing
[ Esc] .
Error messages
I f POST det ect s errors in t he syst em, it will writ e error messages on t he screen. I f t he monit or is
not ready, or if t he error is in t he video card, it will also sound a pat t ern of beeps ( for example 3
short and one long) t o ident ify t he error t o t he user. I f you want t o know more of t he beeps, you
can find explanat ions on t he Award, AMI and Phoenix web sit es. For inst ance you will receive error
messages if t he keyboard is not connect ed or if somet hing is wrong wit h t he cabling t o t he floppy
drive.
POST also reads t hose user dat a, which are found in t he CMOS. This is discussed in t he following
chapt er.
The bootstrap loader
The last part of t he BI OS execut ion at st art - up is t he boot st rap loader. I t is a t iny program, which
only has one t ask: t o find t he boot sect or on a disk ( hard disk, floppy or anot her boot - drive) .
The DOS Boot Record ( DBR) also holds a media descript or as well as informat ion on t he OS
version. Please read module 6a4 on t his issue. You can use DiskEdit ( included in t he "Nort on
Ut ilit ies") t o read view t he cont ent s of t he boot sect or.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2a2.htm (2 of 7)7/27/2004 4:05:35 AM
An illustrated Guide to Motherboards
When t he disk holds no boot st rap rout ine, you get an error message like "Non- syst em disk,
replace wit h syst em disk and press any key".
The boot st rap loader is t he last st ep in BI OS execut ion during st art - up. I t hands over t he cont rol t o
t he boot st rap rout ine found on t he boot disk. The OS is being loaded.
CMOS RAM [top]
CMOS st ands for Complement ary Met al Oxide Semiconduct or. I n PCs t here is a small amount of
memory in a special CMOS RAM chip. The dat a is maint ained wit h elect ric power from a small
bat t ery.
CMOS is only a medium for st orage. I t could be used for any t ype of dat a. Here, it holds import ant
syst em dat a, values t o be used during t he st art process. These informat ion t ake up maybe 100 or
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2a2.htm (3 of 7)7/27/2004 4:05:35 AM
An illustrated Guide to Motherboards
200 byt es of dat a, and st orage in t he CMOS makes t hem inst ant ly available t o t he POST and BI OS
programs ( loaded from ROM) during t he st art - up.
The values are regarding:
q Floppy and hard disk drives
q The keyboard
q The CPU, cache, chip set values, RAM t ype
q Dat e and t ime
q Much more . . .
These dat a have t o be set up correct ly, and t hey are read during t he st art - up t o make t he PC
operable.
Two types of data
CMOS dat a can be divided in t wo groups:
q Dat a, which POST cannot find during t he syst em t est .
q Dat a, which cont ain user opt ions.
For example, POST cannot by it self find sufficient informat ion about t he floppy drive( s) . Floppy
drives are so "dumb, " t hat POST cannot read whet her t hey are floppy drives or not , nor what t ype.
About t he same goes for I DE hard disks, while EI DE hard disks are a lit t le more "int elligent , "
However, POST st ill needs assist ance t o ident ify t hem 100% correct ly.
The same goes for RAM: POST can count how much RAM is in t he PC. However, POST cannot
always det ect whet her it is FPM, EDO or SD RAM. Since t he CPU and BI OS reads dat a from RAM
chips different ly, depending on t he RAM t ype, t he t ype must be ident ified t o set up t he correct
t iming.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2a2.htm (4 of 7)7/27/2004 4:05:35 AM
An illustrated Guide to Motherboards
The configuration of CMOS data
The PC must be configured, be supplied wit h t his informat ion. That is done in t he fact ory or st ore,
where it is assembled. This informat ion is st ored in CMOS, where t hey st ay. CMOS dat a only need
t o be updat ed, when different or addit ional hardware component s are inst alled. This could be a
different t ype hard disk or floppy disks or an new RAM t ype. Oft en t he user can do t his him/ herself.
Ot her dat a in CMOS cont ain various user opt ions . This is dat a, which you can writ e t o CMOS. For
example, you can adj ust dat e and t ime, which t he PC t hen adj ust s every second. You can also
choose bet ween different syst em paramet ers. Maybe you want a short syst em check inst ead of a
long one. Or if you want t he PC t o t ry t o boot from hard disk C before t rying floppy disk A, or vice
versa. These opt ions can be writ t en t o CMOS.
Many of t he opt ions are of no int erest t o t he ordinary user. These are opt ions, which regard
cont roller chips on t he mot herboard, which can be configured in different ways. Ordinarily, t here is
no need t o make such changes. The mot herboard manufact urer has already select ed t he opt imal
configurat ions. They recommend in t heir manuals, t hat you do not change t hese default set t ings.
We can conclude, t hat CMOS dat a are essent ial syst em dat a, which are vit al for operat ion of t he
PC. Their special feat ure is, t hat t hey are user adj ust able. Adj ust ment s t o CMOS are made during
st art - up.
Opening the Setup program
[ t op]
You communicat e wit h t he BI OS programs and t he CMOS memory t hrough t he so- called Set up
program. This gives us a very simple user int erface t o configuring t he PC wit h t hese vit al dat a.
Typically you reach t he Set up program by pressing [ Delet e] immediat ely aft er you power up t he
PC. That brings you t o a choice of set up menus. You leave Set up by pressing [ Esc] , and choose "Y"
t o rest art t he PC wit h t he new set t ings. Generally, you should not change t hese set t ings, unless
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2a2.htm (5 of 7)7/27/2004 4:05:35 AM
An illustrated Guide to Motherboards
you know precisely what you are doing.
Here you see t he st art menu of t he American Megat rends BI OS Set up program, which has a kind of
graphical user int erface. You are supposed t o use t he mouse:
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read more about t he boot process and syst em bus in Module 2b
Read more about I / O buses in module 2c
Read more about t he mot herboard chip set in module 2d
Read more about RAM in module 2e
Read about EI DE in module 5b
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2a2.htm (6 of 7)7/27/2004 4:05:35 AM
An illustrated Guide to Motherboards
I also recommend t wo books for furt her st udies. Gunnar Forst : "PC Principals", from MI T is
excellent . Also "The Winn L. Rosch Hardware Bible" from Brady covers t he same subj ect s. Also "PC
I nt ern" from Abacus is fine.
Links t o BI OS informat ion:
BI OS Guide
Mr BI OS FAQ
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2a2.htm (7 of 7)7/27/2004 4:05:35 AM
An illustrated Guide to Motherboards
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 2a.3
Using the system software of the motherboard
The cont ent s:
q What use of Set up program?
q Modifying t he boot sequence
q I mages from t he set up program
q Next page
q Previous page
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2a3.htm (1 of 6)7/27/2004 4:05:47 AM
An illustrated Guide to Motherboards
What can I use the Setup program for? [top]
The Set up program can do many t hings for you. However, be careful. You should not change any values
wit hin t he menus, unless you know what you are doing. Ot herwise your PC may not funct ion properly.
You have t o ent er Set up, if you inst all a different t ype or addit ional disk drive in your PC. Cert ain BI OSs
will also need adj ust ment of it s set t ings, if a CDROM drive is inst alled on one of t he EI DE channels.
The Standard values
The st andard values in t he CMOS Set up are used t o configure:
q The dat e and t ime.
q The keyboard.
q The display.
q The disket t e drive.
q EI DE unit s number 1- 4 ( t ypically hard disks and CD- ROM- drive) .
The values for dat e and t ime are st ored in t he CMOS RAM. You can always change t hem, from Set up or
from DOS, Windows or any ot her OS.
The keyboard - obviously it has t o be t here. But it is possible t o configure t he PC t o work wit hout a
keyboard. Ot herwise t he PC will error if t he keyboard is missing.
The display is always VGA. From older t imes t he Set up gives you opt ions as EGA, CGA and MDA. You
won' t need t hem!
Disket t e drive has t o be select ed. You can choose t o have A: or B: or bot h. Each drive can be of five
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2a3.htm (2 of 6)7/27/2004 4:05:47 AM
An illustrated Guide to Motherboards
t ypes or more. You probably have t he 1. 44 MB floppy drive. You choose among t he opt ions using [ PgUp]
and [ PgDn] . Modern super floppies like Zip and LS120 are not t o be inst alled as disket t e drives, t hey are
EI DE unit s.
The hard disk is t he most import ant unit t o inst all in t his part of t he Set up. Wit h t he modern
mot herboards and t he EI DE drives you may experience an aut omat ic configurat ion during t he Aut o
det ect . I n ot her sit uat ions you have t o run t he aut o det ect yourself. Wit h older drives, you have t o
ent er all t he CHS- values for t he drive ( number of cylinders, heads and sect ors.
The BIOS Feature Setup
The Feat ure Set up is t he next layer in t he CMOS set up. Here you can choose among opt ions like:
q Quick execut ion of POST ( a good t hing) .
q Choice of boot device EI DE/ SCSI . I f you have bot h t ypes of hard drives, which one is t o be boot ed?
q The boot sequence.
q . . . .
Modifying the boot sequence
You can change t he boot sequence from A: , C: t o C: , A: . That means, t hat t he PC will not t ry t o boot
from any disket t e in t he A drive. This will prot ect you from cert ain virus at t acks from t he boot sect or.
Also, t he boot process will not be blocked by any disket t e in t he A drive. I f you need t o boot from A-
drive ( for example, if you want t o inst all Windows 98) , you have t o ent er Set up again, and change t he
boot sequence t o A: , C: . That is no problem.
Power Management
You also use t he Set up program t o regulat e t he power management , which is t he power saving
feat ures in t he mot herboard. For example, you can make t he CPU shut down aft er one minut e of no
act ivit y. There are plent y of set t ings available in t his area. The power management funct ions found on
t he PCs mot herboard will cooperat e wit h t he operat ing syst em. Especially Windows 98 is very good at
using t he power management .
Password Protection
You can prot ect t he Set up program wit h a password. This is used widely in schools, where t he t eachers
do not want t he lit t le nerds t o make changes in t he set up. Please remember t he password ( writ e it down
in t he mot herboard manual) . I f you forget it you have t o remove t he bat t ery from t he mot herboard.
Then all user input t o t he CMOS is erased - including t he password.
Images from the Setup program
[top]
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2a3.htm (3 of 6)7/27/2004 4:05:47 AM
An illustrated Guide to Motherboards
Here is a scanned image from a Set up program. I t belongs a very fine board from ASUS. Here you see
t he "BI OS Feat ure Set up, " where you can select st art - up choices:
Here we are in t he special "Chip set Feat ure Set up. " These choices relat e t o t he chip set s and, most
likely, need no changes:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2a3.htm (4 of 6)7/27/2004 4:05:47 AM
An illustrated Guide to Motherboards
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Module 2b. About t he boot process and syst em bus
Read more about I / O buses in module 2c
Read more about t he mot herboard chip set in module 2d
Read more about RAM in module 2e
Read about EI DE in module 5b
I also recommend t wo books for furt her st udies. Gunnar Forst : "PC Principals", from MI T is excellent .
Also "The Winn L. Rosch Hardware Bible" from Brady covers t he same subj ect s. Also "PC I nt ern" from
Abacus is fine.
Links t o BI OS informat ion:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2a3.htm (5 of 6)7/27/2004 4:05:47 AM
An illustrated Guide to Motherboards
BI OS Guide
Mr BI OS FAQ
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Windows 98 pages]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2a3.htm (6 of 6)7/27/2004 4:05:47 AM
An illustrated Guide to Motherboards
KarbosGuide.com. Module 2a.4.
The system software of hardware
The cont ent s:
q Next page
q Previous page
The BIOS in adapter ROM
[top]
During t he st art - up process t he BI OS programs are read from t he ROM circuit s. BI OS st ands for Basic I nput
Out put Syst em and it is small program rout ines which cont rols specific hardware unit s.
For inst ance you have a BI OS rout ine which reads t he keyboard:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2a4.htm (1 of 4)7/27/2004 4:05:55 AM
An illustrated Guide to Motherboards
The BI OS is a part of t he modular design of t he I BM Compat ible PC. The OS and ot her programs access t he
hardware unit s by making request s t o t he BI OS rout ines.
BI OS t ypically occupies 64 KB, and t he programs are st ored in ROM chips on t he mot herboard.
The reserved areas
I n t he original PC design we only had 1 MB of RAM. This memory was adressed using hex numbers, so each byt e
had it s own address going from 00000h t o FFFFFh.
I mport ant part s of t he syst em soft ware is mapped int o t his range, where we also find t wo reserved areas:
Hex address Kilobyt es Occupied by
C0000-
C8000
768- 800 BI OS from t he video card
F0000 -
FFFFF
960-
1024
BI OS from t he
Mot herboard
These t wo ranges are reserved for t his special adapt er ROM. Ot her adapt ers cannot map t heir BI OS rout ines int o
t hese addresses.
I f it is set up t o shadowing ( "Shadow RAM" in t he Set up ut ilit y) , t hen t his BI OS code is copied int o RAM. I f not , it
has t o be read direct ly from t he ROM circuit . The last access is slower.
BIOS on many adapters
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2a4.htm (2 of 4)7/27/2004 4:05:55 AM
An illustrated Guide to Motherboards
There are BI OS codes on many adapt ers ( expansion cards) . The adapt ers are ext ernal hardware, which are
connect ed t o and int egrat ed wit h t he mot herboard during t he hardware configurat ion and int ernalizing.
The adapt ers hold t heir own BI OS code making t hem funct ional. This BI OS must be included during t he
configurat ion. Therefore, t he adapt er ROM is read during st art - up, and t he program code is woven t oget her
wit h ot her BI OS programs and t he CMOS dat a. I t is all writ t en int o RAM, where it is ready for t he operat ing
syst em, as you can see here:
The BI OS rout ines are not always in use. They can be regarded as basic program layers in t he PC, giving it a
simple funct ionalit y.
Many programs rout inely bypass BI OS. I n t hat case, t hey "writ e direct t o hardware", as we say. Windows
cont ains program files, which can be writ t en direct ly t o all kinds of hardware - bypassing BI OS rout ines. One
example is t he COM port s. I f you use t he BI OS rout ines connect ed wit h t hem, you can t ransmit only at max.
9600 baud on t he modem. That is insufficient . Therefore, Windows will assume cont rol over t he COM port .
BIOS update
BI OS programs can be updat ed . The modern mot herboard has t he BI OS inst ruct ions in flash ROM, which can be
updat ed. You can get new BI OS soft ware from your supplier or on t he I nt ernet , which can be read ont o t he
mot herboard. The loading is a special process, where you might need t o change a j umper swit ch on t he
mot herboard. Usually, you do not need t o do t his, but it is a nice available opt ion.
ATX motherboards [top]
The lat est PC elect ronic st andard is called ATX. I t consist s of a new t ype mot herboard wit h a specific physical
design like t he t radit ional board ( 30. 5 cm X 19 cm) . However t he board has been shift ed 90 degrees for a bet t er
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2a4.htm (3 of 4)7/27/2004 4:05:55 AM
An illustrated Guide to Motherboards
placing of t he unit s.
The I / O connect ors COM1, COM2 and LPT, keyboard, mouse and USB are mount ed direct ly on t he mot herboard.
The ATX board requires specifically designed chassises wit h an I / O access opening measuring 1 by 6 inch.
ATX is designed by I nt el, but has gained general accept ance.
The ATX mot herboard is more int elligent t han t he ordinary t ype. I n a few years, it will be wide spread. I t
includes advanced cont rol facilit ies, where t he BI OS program cont inually checks t he CPU t emperat ure and
volt ages, t he cooling fans RPM, et c. I f over heat ing occurs, t he PC will shut down aut omat ically. The PC can also
be t urned on by for example modem signals, since t he power supply is cont rolled by t he mot herboard. The on/ off
but t on will t urn t he PC "down" wit hout t urning it complet ely off.
I f you want a PC designed for t he fut ure, t he ATX layout is what you should go for.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Module 2b. About t he boot process and syst em bus
Read more about I / O buses in module 2c
Read more about t he mot herboard chip set in module 2d
Read more about RAM in module 2e
Read about EI DE in module 5b
I also recommend t wo books for furt her st udies. Gunnar Forst : "PC Principals", from MI T is excellent . Also "The
Winn L. Rosch Hardware Bible" from Brady covers t he same subj ect s. Also "PC I nt ern" from Abacus is fine.
Links t o BI OS informat ion:
BI OS Guide
Mr BI OS FAQ
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Windows 98 pages]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2a4.htm (4 of 4)7/27/2004 4:05:55 AM
An illustrated Guide to the PC System BUS
KarbosGuide.com. Module 2b1.
About the System Bus
I n t his module, you can read about t he following subj ect s, which add t o our t our of t he PC:
q The boot process
q Dat a on t he mot herboard
q Next page
q Previous page
The boot process [top]
The last st ep in t he PC st art - up is reading t he operat ing syst em. The st art - up program is inst ruct ed t o
find t he Mast er Boot Record. This is locat ed in t he very first sect or on eit her hard disk ( C) or floppy
drive A. From t he MBR it reads t he boot - st rap which point s t o t he locat ion of t he st art up files of t he
Operat ing Syst em.
By default , t he PC will look for a boot sect or in floppy drive A. That is why t he PC "drops dead" if t here is
a different disket t e in A drive. I f t here is no disket t e in A drive, t he st art - up program will search for t he
boot sect or on hard drive C. When t he boot sect or is found, a small program segment ( boot - st rap) is
read from t here. The boot - st rap t hen t akes over cont rol of t he PC. The st art - up program has done it s
j ob. Now DOS, Windows , or anot her operat ing syst em t akes cont rol.
Read more about boot sect ors, et c. in module 6a, which deals wit h file syst ems.
Here is an illust rat ion of t he st art - up process:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2b1.htm (1 of 4)7/27/2004 4:05:57 AM
An illustrated Guide to the PC System BUS
The data flow on the motherboard
[ t op]
On t he mot herboard, you will find t he CPU, which is t he "brain" of t he PC and t he buses. The buses are
t he nerve syst em of t he mot herboard. They connect t he CPU t o all t he ot her component s. There are at
least t hree buses, which you can see below. You can read more about t hose on t he following pages.
The buses are t he PC' s expressways. They are "wires" on t he circuit board, which t ransmit dat a bet ween
different component s.
One "wire" can move one bit at a t ime. I n t he following t ext , we st art from a t ypical Pent ium board. We
will look at buses, chip set s and CPUs. Here is an illust rat ion of some of t he mot herboard "logic. " You
can print it :
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2b1.htm (2 of 4)7/27/2004 4:05:57 AM
An illustrated Guide to the PC System BUS
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read more about t he mot herboards chip set in module 2d
Read more about RAM in module 2e
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2b1.htm (3 of 4)7/27/2004 4:05:57 AM
An illustrated Guide to the PC System BUS
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2b1.htm (4 of 4)7/27/2004 4:05:57 AM
An illustrated Guide to the PC System BUS
KarbosGuide.com. Module 2b2.
About the System Bus
I n t his module, you can read about t he following subj ect s, which add t o our t our of t he PC:
q PC buses, an int ro
q The syst em bus
q 66 MHz bus
q 100 MHz bus
q Next page
q Previous page
Introduction to the PC buses
[ t op]
The PC receives and sends it s dat a from and t o buses. They can be divided int o:
q The syst em bus, which connect s t he CPU wit h RAM
q I / O buses, which connect t he CPU wit h ot her component s.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2b2.htm (1 of 6)7/27/2004 4:05:59 AM
An illustrated Guide to the PC System BUS
The point is, t hat t he syst em bus is t he cent ral bus. Act ually, it
connect s t o t he I / O buses, as you can see in t his illust rat ion. I t is not
complet ely correct , since t he archit ect ure is much more complex, but
it shows t he import ant point , t hat t he I / O- buses usually derive from
t he syst em bus:
You see t he cent ral syst em bus, which connect s t he CPU wit h RAM. A bridge connect s t he I / O
buses wit h t he syst em bus and on t o RAM. The bridge is part of t he PC chip set , which will be
covered in module 2c.
3 different I/O buses
[ t op]
The I / O buses move dat a. They connect all I / O devices wit h t he CPU and RAM. I / O devices
are t hose component s, which can receive or send dat a ( disk drives, monit or, keyboard, et c. ) .
I n a modern Pent ium driven PC, t here are t wo or t hree different I / O buses:
q The I SA bus, which is oldest , simplest , and slowest bus.
q The PCI bus, which is t he fast est and most powerful bus.
q The USB bus, which is t he newest bus. I t may in t he long run replace t he I SA bus.
The t hree I / O buses will be described lat er. Here, we will t ake a closer look at t he PC' s
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2b2.htm (2 of 6)7/27/2004 4:05:59 AM
An illustrated Guide to the PC System BUS
fundament al bus, from which t he ot hers are branches from.
The system bus
[ t op]
The syst em bus connect s t he CPU wit h RAM and maybe a buffer memory ( L2- cache) . The
syst em bus is t he cent ral bus. Ot her buses branch off from it .
The syst em bus is on t he mot herboard. I t is designed t o mat ch a specific t ype of CPU.
Processor t echnology det ermines dimensioning of t he syst em bus. At t he same t ime, it has
t aken much t echnological development t o speed up "t raffic" on t he mot herboard. The fast er
t he syst em bus get s, t he fast er t he remainder of t he elect ronic component s must be. .
The following t hree t ables show different CPUs and t heir syst em buses:
Older CPUs Syst em bus widt h Syst em bus
speed
8088 8 bit 4. 77 MHz
8086 16 bit 8 MHz
80286- 12 16 bit 12 MHz
80386SX- 16 16 bit 16 MHz
80386DX- 25 32 bit 25 MHz
We see, t hat syst em bus speed follows t he CPU' s speed limit at ion. First at t he fourt h
generat ion CPU 80486DX2- 50 are doubled clock speeds ut ilized. That gives t he CPU a higher
int ernal clock frequency. The ext ernal clock frequency, used in t he syst em bus, is only half of
t he int ernal frequency:
CPUs in t he 80486 family Syst em bus widt h Syst em bus
speed
80486SX- 25 32 bit 25 MHz
80486DX- 33 32 bit 33 MHz
80486DX2- 50 32 bit 25 MHz
80486DX- 50 32 bit 50 MHz
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2b2.htm (3 of 6)7/27/2004 4:05:59 AM
An illustrated Guide to the PC System BUS
80486DX2- 66 32 bit 33 MHz
80486DX4- 100 32 bit 40 MHz
5X86- 133 32 bit 33 MHz
66 MHz bus
[ t op]
For a long t ime all Pent ium based comput ers ran at 60 or 66 MHz on t he syst em bus, which is
64 bit wide:
CPUs in t he
Pent ium family
Syst em bus widt h Syst em bus
speed
I nt el P60 64 bit 60 MHz
I nt el P100 64 bit 66 MHz
Cyrix 6X86 P133+ 64 bit 55 MHz
AMD K5- 133 64 bit 66 MHz
I nt el P150 64 bit 60 MHz
I nt el P166 64 bit 66 MHz
Cyrix 6X86 P166+ 64 bit 66 MHz
Pent ium Pro 200 64 bit 66 MHz
Cyrix 6X86 P200+ 64 bit 75 MHz
Pent ium I I 64 bit 66 MHz
100 MHz bus
The speed of t he syst em bus has increased in 1998. Using PC100 SDRAM a speed of 100 MHz
is well proven and t he use of RDRAM will give us much higher speeds.
However t he rise from 66 MHz t o 100 MHz has t he great est impact on Socket 7 CPUs and
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2b2.htm (4 of 6)7/27/2004 4:05:59 AM
An illustrated Guide to the PC System BUS
boards. I n t he Pent ium- I I modules 70- 80% of t he t raffic is inside t he SEC module, holding
bot h L1 and L2 cache. And t he module has it s own speed independent of t he syst em bus.
Wit h t he K6 t he increase of syst em bus speed gives a vast ly improved performance since t he
t raffic bet ween L1 and L2 cache crosses t he syst em bus.
133 MHz
I nt el' s 820 and 815 chipset s t o be used wit h Pent ium I I I work wit h 133 MHz RAM as well as
several VI A chipset s do.
I n AMD' s At hlon t he syst em bus archit ect ure was changed; it is not really a syst em bus any
longer. Hence At hlon chipset s may work wit h many t ypes of RAM.
Processor Chip set Syst em bus speed CPU speed
I nt el Pent ium I I 82440BX
82440GX
100 MHz 350, 400, 450 MHz
AMD K6- 2 Via MVP3ALi Aladdin V 100 MHz 250, 300, 400 MHz
I nt el Pent ium I I Xeon 82450NX 100 MHz 450, 500 MHz
I nt el Pent ium I I I i815
i820
133 MHz 600, 667 MHz and up
AMD At hlon VI A KT133 and ot hers 200 MHz 600 - 1000 MHz
Wit h t he 100 MHz bus, we dicovered t hat mot herboards have t o be well const ruct ed wit h
good power supply and many capacit ors.
Newer buses
As ment ioned under AMD At hlon, "syst em bus" is not t hat relevant a t erm looking at modern
mot herboards. The bus t o RAM becomes separat ed from t he ot her buses and t his design
opens up for bet t er bandwidt h bet ween t he CPU and t he RAM.
I nt els use of Rambus RAM working at 400 MHz as well as PC2100 RAM on non- I nt el boards
follows t his t rend.
The DDRAM operat es wit h int erfaces working at 200, 266 and 333 MHz.
q Next page
q Previous page
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2b2.htm (5 of 6)7/27/2004 4:05:59 AM
An illustrated Guide to the PC System BUS
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read more about t he mot herboards chip set in module 2d
Read more about RAM in module 2e
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2b2.htm (6 of 6)7/27/2004 4:05:59 AM
An illustrated Guide to I/O-buses
KarbosGuide.com. Module 2c.1
About the I/O buses
On t hese pages, you can read about t he import ant syst em bus derivat ives, t he different I / O
buses:
q I nt roduct ion t o t he I / O buses
q Technical and hist orical background for t he I / O buses
q Next page
q Previous page
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2c1.htm (1 of 7)7/27/2004 4:06:02 AM
An illustrated Guide to I/O-buses
Introduction to the I/O buses [top]
We have seen before, t hat t he PC' s buses are t he fundament al dat a
"highways" on t he syst em board. The "first " bus is t he syst em bus,
which connect s t he CPU wit h RAM. I n older designs it was a local bus.
I n newer designs t his bus is called t he front side bus ( FSB) .
The t ypical local bus has a speed and widt h depending on t he t ype
CPU inst alled on t he mot herboard. Typically, t he syst em bus will be
64 bit s wide and run at 66, 100 or 133 MHz. These high speeds creat e
elect rical noises and ot her problems. Therefore, t he speed must be
reduced for dat a reaching t he expansion cards and ot her more
peripheral component s.
Very few expansion cards can operat e at more t han 40 MHz. Then t he elect ronics shut down.
The chips can j ust not react fast er. Therefore, t he PC has addit ional buses.
Originally only one bus
However, t he first PCs had only one bus, which was common for t he CPU, RAM and I / O
component s:
The older first and second generat ion CPUs ran at relat ively low clock frequencies, and all
syst em component s could keep up wit h t hose speeds.
RAM on adapters
Among ot her t hings, t hat allowed addit ional RAM t o be inst alled in expansion slot s in t he PC,
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2c1.htm (2 of 7)7/27/2004 4:06:02 AM
An illustrated Guide to I/O-buses
by inst alling an adapt er in a vacant expansion slot . An adapt er, where RAM was mount ed:
This set up would be unt hinkable t oday. However it is t ruely a local bus. All unit s are unit ed
on one bus using t he same clock.
First in 1987, Compaq figured out how t o separat e syst em bus from I / O bus, so t hey could
run at different speeds. This mult i- bus archit ect ure has been indust ry st andard ever since.
Modern PCs also have more t han one I / O bus.
What does an I/O bus do?
[ t op]
I / O buses connect t he CPU t o all ot her component s, except RAM. Dat a are moved on t he
buses from one component t o anot her, and dat a from ot her component s t o t he CPU and RAM.
The I / O buses differ from t he syst em bus in speed. Their speed will always be lower t han t he
syst em bus speed. Over t he years, different I / O buses have been developed. On modern PCs,
you will usually find four buses:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2c1.htm (3 of 7)7/27/2004 4:06:02 AM
An illustrated Guide to I/O-buses
q The I SA bus, which is an old low speed bus, soon t o be excluded from t he PC design.
q The PCI bus, which is a new high speed bus.
q The USB bus ( Universal Serial Bus) , which is a new low speed bus.
q The AGP bus which solely is used for t he graphics card.
As ment ioned earlier, I / O buses are really ext ensions t o t he syst em bus. On t he
mot herboard, t he syst em bus ends in a cont roller chip, which forms a bridge t o t he I / O
buses.
All in all, t he buses have had a very cent ral placement in t he PC' s dat a exchange. Act ually, all
component s except t he CPU communicat e wit h each ot her and wit h RAM via t he different I / O
buses. Here you see a demonst rat ion of t his logic:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2c1.htm (4 of 7)7/27/2004 4:06:02 AM
An illustrated Guide to I/O-buses
The physical aspects of the I/O buses
[ t op]
Physically, t he I / O bus consist s of t racks on t he print ed circuit board. These t racks are used
as:
q Dat a t racks, which each can move one bit at a t ime
q Address t racks, which ident ify where dat a should be sent t o
q Ot her t racks for clock t icks, volt age, verificat ion signals, et c.
When dat a are sent on t he bus, t hey must be supplied wit h a receiver. Therefore, each device
on t he bus has an address. Similarly, t he RAM is divided in sect ions, each having it s address.
Prior t o sending dat a, a number is sent on t he address t rack, t o ident ify where t he dat a
should be sent t o.
The bus width
The number of dat a t racks det ermine t he dat a t ransfer capacit y. The I SA bus is slow, part ly
because it only has 16 dat a t racks. The modern PCs send 32 bit s per clock t ick. On t he I SA
bus, 32 bit s must be divided in t wo packages of 16 bit s. This delays t he dat a t ransfer.
Anot her I / O bus concept is wait st at es.
Wait states
Wait st at es are small pauses. I f an I SA adapt er cannot keep up wit h t he incoming dat a flow,
it s cont roller sends wait st at es t o t he CPU. Those are signals t o t he CPU t o "hold on for a
sec. " A wait st at e is a wast ed clock t ick. The CPU skips a clock t ick, when not occupied. Thus
t he old and slow I SA adapt er can significant ly reduce t he operat ing speed of a modern
comput er.
Anot her aspect is t he I RQ signals, which t he component s use t o at t ract at t ent ion from t he
CPU. That and t he concept s DMA and bus mast ering, are described in module 5, which deals
wit h adapt ers.
Technical and historical background for the I/
O buses [ t op]
I n modern PCs you only find t he PCI and I SA buses ( besides USB, which we do not know
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2c1.htm (5 of 7)7/27/2004 4:06:02 AM
An illustrated Guide to I/O-buses
much about yet ) . But , over t he years, t here have been ot her buses. Here is a diagram of t he
various I / O buses. Then comes a more det ailed descript ion of each of t he buses:
Bus
Year Bus widt h Bus speed
Max. t hroughput
( t heoret ical)
PC and XT 1980- 82 8 bit
Synchronous wit h CPU:
4. 77 - 6 MHz
4- 6 MBps
I SA ( AT)
Simple bus.
1984 16 bit Synchronous:
8- 10 MHz
8 MBps
MCA. Advanced,
int elligent bus by I BM.
1987 32 bit Asynchronous:
10. 33 MHz
40 MBps
EI SA.
Bus for servers.
1988 32 bit Synchronous:
max. 8 MHz
32 MBps
VL. High speed bus,
used in 486s.
1993 32 bit Synchronous:
33- 50 MHz
100- 160
MBps
PCI . I nt elligent ,
advanced high speed
bus.
1993 32 bit Asynchronous:
33 MHz
132 MBps
USB. Modern, simple,
and int elligent bus.
1996 Serial 1. 2 MBps
FireWire ( I EEE1394) .
High- speed I / O bus for
st orage, video et c.
1999 Serial 80 MBps
USB 2. 0 2001 Serial 12- 40 MBps
SCSI is anot her t ype of bus.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
5c about t he modern I / O bus called USB.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2c1.htm (6 of 7)7/27/2004 4:06:02 AM
An illustrated Guide to I/O-buses
Read module 5b about AGP and module 5c about Firewire.
Read more about chip set s on t he mot herboard in module 2d
Read about RAM in module 2e
Read Module 4b about hard disks.
Read Module 4c about opt ical media ( CDROM and DVD) .
Read Module 4d about super disket t e and MO drives.
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side.
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
Read module 7c about sound cards, and 7d on digit al sound and music.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2c1.htm (7 of 7)7/27/2004 4:06:02 AM
An illustrated Guide to I/O-buses
KarbosGuide.com. Module 2c.2
About the ISA bus and other old PC buses
The cont ent s:
q I nt roduct ion t o t he I SA bus
q MCA, Eisa and VLB buses
q Next page
q Previous page
Introduction to the ISA bus
Since about 1984, st andard bus for PC I / O funct ions has been named I SA ( I ndust ry St andard Archit ect ure) . I t is
st ill used in all PCs t o maint ain backwards compat ibilit y. I n t hat way modern PCs can accept expansion cards of t he
old I SA t ype.
I SA was an improvement over t he original I BM XT bus, which was only 8 bit wide. I BM' s t rademark is AT bus.
Usually, it is j ust referred t o as I SA bus.
I SA is 16 bit wide and runs at a maximum of 8 MHz. However, it requires 2- 3 clock t icks t o move 16 bit s of dat a.
The I SA bus works synchronous wit h t he CPU. I f t he syst em bus is fast er t han 10 MHz, many expansion boards
become flaky and t he I SA clock frequency is reduced t o a fract ion of t he syst em bus clock frequency.
The I SA bus has an t heoret ical t ransmission capacit y of about 8 MBps. However, t he act ual speed does not exceed
1- 2 MBps, and it soon became t oo slow.
Two faces
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2c2.htm (1 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:04 AM
An illustrated Guide to I/O-buses
The I SA bus has t wo "faces" in t he modern PC:
q The int ernal I SA bus, which is used on t he simple port s, like keyboard, disket t e drive, serial and parallel port s.
q As ext ernal expansion bus, which can be connect ed wit h 16 bit I SA adapt ers.
I SA slot s are t oday most ly used for t he common 16 bit SoundBlast er compat ible sound cards.
Problems
The problem wit h t he I SA bus is t wofold:
q I t is narrow and slow.
q I t has no int elligence.
The I SA bus cannot t ransfer enough bit s at a t ime. I t has a very limit ed bandwidt h. Let us compare t he bandwidt hs
of I SA bus and t he newer PCI bus:
Bus Transmission t ime Dat a volume per t ransmission
I SA 375 ns 16 bit
PCI 30 ns 32 bit
Clearly, t here is a vast difference bet ween t he capacit y of t he t wo buses. The I SA bus uses a lot of t ime for every
dat a t ransfer, and it only moves 16 bit s in one operat ion.
The ot her problem wit h t he I SA bus is t he lack of int elligence. This means t hat t he CPU has t o cont rol t he dat a
t ransfer across t he bus. The CPU cannot st art a new assignment , unt il t he t ransfer is complet ed. You can observe
t hat , when your PC communicat es wit h t he floppy drive, while t he rest of t he PC is wait ing. Quit e oft en t he whole
PC seems t o be sleeping. That is t he result of a slow and unint elligent I SA bus.
Problems with IRQs
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2c2.htm (2 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:04 AM
An illustrated Guide to I/O-buses
The I SA bus can be a t ease, when you inst all new expansion cards ( for example a sound card) . Many of t hese
problems derive from t he t uning of I RQ and DMA, which must be done manually on t he old I SA bus.
Every component occupies a specific I RQ and possibly a DMA channel. That can creat e conflict wit h exist ing
component s. Read module 5 about expansion cards and t hese problems.
The ISA bus is out
As described, t he I SA bus is quit e out dat ed and should not be used in modern pcs. There is a good chance, t hat
t his "out dat ed legacy t echnology" ( quot ing I nt el) will disappear complet ely.
The USB bus is t he t echnology t hat will replace it . I t has t aken many years t o get t his working and accept ed, but it
works now.
I nt el' s chip set 810 was t he first not t o include I SA support .
MCA, EISA and VLB [top]
I n t he 80s, a demand developed for buses more powerful t han t he I SA. I BM developed t he
MCA bus and Compaq and ot hers responded wit h t he EI SA bus. None of t hose were
part icularly fast , and t hey never became part icularly successful out side t he server market .
Please support our
sponsor.
MCA
I BM' s t op of t he line bus from 1987 is named Micro Channel Archit ect ure. The MCA bus was a mast erpiece, unifying
t he best bus t echnology from t he mainframe design wit h t he demands from t he PC. However, cont rary t o t he I SA
bus, MCA is pat ent ed, and I BM demanded high royalt y fees, when ot her PC manufact urers want ed t o use it . Thus
t he bus never became a great success, despit e it s advanced design. I t ended up being a classic example of poor
market ing st rat egy.
The MCA bus is 32 bit wide and "int elligent . " The cards configure t hemselves wit h respect t o I RQ. Thus, t hey can
be inst alled wit hout adj ust ment s of j umper swit ches or ot her feat ures. I t works const ant ly at 10. 33 MHz,
asynchronous wit h t he syst em bus.
The MCA bus is also relat ively fast wit h t ransfer rat es of up t o 40 MBps in 32 bit mode at 10. 33 MHz. MCA requires
special adapt ers. There have never been t oo many adapt ers developed, since t his bus is by and large used only in
I BM' s own PCs.
EISA
EI SA is a bus from 1988- 89. I t is designed by t he "Gang of Nine: " t he companies AST, Compaq, Epson, Hewlet t -
Packard, NEC, Olivet t i, Tandy, Wyse and Zenit h. I t came in response t o I BM' s pat ent ed MCA bus.
EI SA is built on t he I SA bus; t he connect or has t he same dimensions and old I SA cards fit int o t he slot s. To keep
t his compat ibilit y, t he EI SA bus works at maximum 8 MHz. Like I SA, t he bus bus is synchronous wit h t he CPU at a
clock frequency reduced t o a fract ion of t he syst em bus clock frequency.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2c2.htm (3 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:04 AM
An illustrated Guide to I/O-buses
EI SA is compat ible wit h I SA in t he sense t hat I SA adapt ers can be inst alled in EI SA slot s. The EI SA adapt ers hold a
second level of connect ors in t he but t on of t he slot .
However, EI SA is much more int elligent t han I SA. I t has bus mast ering, divided int errupt s and self configurat ion. I t
is 32 bit wide, and wit h it ' s compressed t ransfers and BURST modegives a highly improved performance.
But , like t he MCA, it did not have great success. The EI SA bus is st ill used in some servers.
Vesa Local Bus
This Bus called VLB for short . I t is an inexpensive and simple t echnology. This bus only achieved st at us as an
int erim phenomenon ( in 1993- 94) . VLB was widely used on 486 mot herboards, where t he syst em bus runs at 33
MHz. VLB runs direct ly wit h t he syst em bus. Therefore, dat a t ransfer is at CPU speed, synchronous and in widt h.
The problem wit h VLB was compat ibilit y. Adapt ers and syst em syst em boards would not always work t oget her.
Vesa is an organizat ion wit h about 120 members, most ly monit or and graphics card manufact urers. Therefore,
most VLB cards were video cards.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read module 5c about t he modern I / O bus called USB.
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side.
Read module 5b about AGP and module 5c about Firewire
Read more about chip set s on t he mot herboard in module 2d.
Read more about RAM in module 2e.
Read Module 4b about hard disks.
Read Module 4c about opt ical media ( CDROM and DVD) .
Read Module 4d about super disket t e and MO drives.
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
Read module 7c about sound cards, and 7d on digit al sound and music.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2c2.htm (4 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:04 AM
An illustrated Guide to I/O-buses
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2c2.htm (5 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:04 AM
An illustrated Guide to I/O-buses
KarbosGuide.com. Module 2c.3
About the PCI bus
The cont ent s:
q I nt roducing t he PCI bus
q The int ernal and ext ernal face.
q The fut ure design
q NGI O
q Next page
q Previous page
Introducing the PCI bus
[ t op]
The PCI is t he high speed bus of t he 1990s. PCI st ands for Peripheral
Component I nt erconnect . This bus is made by I nt el. I t is used t oday in
all PCs and ot her comput ers for connect ing adapt ers, such as net work-
cont rollers, graphics cards, sound cards et c.
Please support our
sponsor.
Some graphics cards however use t he AGP- bus, which is a separat e bus only int ended for
graphics.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2c3.htm (1 of 4)7/27/2004 4:06:06 AM
An illustrated Guide to I/O-buses
The PCI bus is t he cent ral I / O bus, which you find in all PCs!
A 32 bit bus
The PCI is act ually 32 bit wide, but in pract ice it funct ions like a 64 bit bus. Running at 33 MHz,
it has a maximum t ransmission capacit y of 132 MBps.
According t o t he specificat ions - not in pract ice, it can have up t o 8 unit s wit h a speed up t o
200 MHz. The bus is processor independent . Therefore, it can be used wit h all 32 or 64 bit
processors, and it is also found in ot her comput ers t han PCs.
The PCI bus is compat ible wit h t he I SA bus in t hat it can react on I SA bus signals, creat e t he
same I RQs, et c.
Buffering and PnP
The PCI bus is buffered in relat ion t o t he CPU and t he peripheral component s. This means, t hat
t he CPU can deliver it s dat a t o t he buffer, and t hen proceed wit h ot her t asks. The bus handles
t he furt her t ransmission in it s own t empo. Conversely, t he PCI adapt ers can also t ransmit dat a
t o t he buffer, regardless of whet her t he CPU is free t o process t hem. They are placed in a
queue, unt il t he syst em bus can forward t hem t o t he CPU. Under opt imal condit ions, t he PCI
bus t ransmit s 32 bit s per clock t ick. Somet imes, it requires t wo clock t icks.
Because of t his, t he peripheral PCI unit s operat e asynchronous . Therefore, t he PCI ( cont rary t o
t he VL bus) is not a local bus in a st rict sense. Finally, t he PCI bus is int elligent relat ive t o t he
peripheral component s, in t hat Plug and Play is included in t he PCI specificat ions. All adapt er
cards for t he PCI configure t hemselves. Plug and Play is abbreviat ed PnP.
PCI with two faces
On modern syst em boards, t he PCI bus ( like I SA) has t wo "faces: "
q I nt ernal PCI bus, which connect s t o EI DE channels on t he mot herboard.
q The PCI expansion bus, which t ypically has 3- 4 slot s for PCI adapt ers.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2c3.htm (2 of 4)7/27/2004 4:06:06 AM
An illustrated Guide to I/O-buses
The PCI bus is cont inuously being developed furt her. There is a PCI Special I nt erest Group,
consist ing of t he most significant companies ( I nt el, I BM, Apple, and ot hers) , which coordinat e
and st andardize t he development .
Soon we shall see PCI wit h a higher bus speed ( 66 MHz) and great er widt h ( 64 bit ) . However
alt ernat ive buses are also market ed. An example is t he high speed AGP video bus ( Accelerat ed
Graphics Port ) and t he FireWire Bus. AGP is fundament ally a 66 MHz PCI bus ( version 2. 1)
which has been enhanced wit h ot her t echnologies making it suit able for t he graphics syst em.
PCI-X
Anot her new init iat ive is t he so- called PCI - X ( also called "Proj ect One" and Fut ure I / O) .
Companies like I BM, Mylex, 3COM, Adapt ec, HP and Compaq want t o launch a special high
speed server version of t he PCI bus. This new bus ( also ment ioned as PCI X) allows a bandwidt h
of up t o 1 GB per second ( wit h a 64 bit bus running at 133 MHz) . I nt el is not cooperat ing on
t his proj ect , and neit her is Dell. I t is going t o be int erest ing t o follow.
Intel's NGIO (Next-Generation I/O)
NGI O server archit ect ure is anot her init iat ive by t he companies Dell Comput er, Hit achi, NEC,
Siemens, Sun Microsyst ems and I nt el t o produce a new archit ect ure for I / O on servers. This is
clearly an answer t o t he Proj ect One ment ioned above.
FIO to merge with NGIO
On August 31, 1999 seven of t he leading companies ( Compaq, Dell, Hewlet t - Packard Company,
I BM, I nt el, Microsoft , Sun) announced t he int ent t o merge t he best ideas of t he Fut ure I / O
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2c3.htm (3 of 4)7/27/2004 4:06:06 AM
An illustrated Guide to I/O-buses
( FI O) and Next Generat ion I / O ( NGI O) . The new open input / out put archit ect ure will find use in
servers. The bandwidt h will be up t o 6 GByt e/ sec.
The new st andard NGI O will hardly go int o product ion before 2001.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side.
Read module 5b about AGP and module 5c about Firewire.
Read about chip set s on t he mot herboard in module 2d
Read more about RAM in module 2e
Read Module 4b about hard disks.
Read Module 4c about opt ical media ( CDROM and DVD) .
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
Read module 7c about sound cards, and 7d on digit al sound and music.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2c3.htm (4 of 4)7/27/2004 4:06:06 AM
An illustrated Guide to chip sets
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 2d.01
On chip sets
Module 2d describes what chip set s are, and how t hey funct ion on t he mot herboards. This module is
subdivided int o t he following pages:
1:
2:
3:
4:
5:
6:
7:
8:
What is a chip set ?
The first chip set s for t he Pent ium boards
Non- I nt el chip set s ( most ly for Super 7 boards)
Chip set s for I nt el P6 processors
More chip set s for I nt el P6 processors
I nt el' s i810 "Whit ney"
I nt el' s i820 "Camino"
I nt el' s i815 "Solano"
q Next page
q Previous
page
I recommend t hat you read all t he pages one by one. Just follow t he links "Next page" t o get
t hrough t he t ext book. I hope you find t he informat ion useful!
What is a chip set?
[ t op]
The chip set is very import ant t o t he modern PC and it s performance. Many t echnologies meet on
t he mot herboard and are "glued" t oget her via t hese cont rollers, which we call t he "chip set ".
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d01.htm (1 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:07 AM
An illustrated Guide to chip sets
When we speak about buses and mot herboards, we are also speaking about chip set s. The chip set s
are a bunch of int elligent cont roller chips, which are on any mot herboard.
The cont rollers are closely t ied t o t he CPU, in t hat t hey cont rol t he buses around t he CPU. Wit hout
t he chip set s, neit her RAM nor I / O buses could funct ion t oget her wit h t he CPU:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d01.htm (2 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:07 AM
An illustrated Guide to chip sets
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d01.htm (3 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:07 AM
An illustrated Guide to chip sets
New technologies - new chip set [top]
Please support our
sponsor.
Therefore, t he chip set s are quit e cent ral component s on t he mot herboards. When new t echnological
feat ures are int roduced ( and t his happens cont inuously) t hey are oft en accompanied by new chip
set s. The new chip set s oft en enable:
q Higher speed on one or more buses
q Ut ilizat ion of new facilit ies ( new RAM t ypes, new buses, improved EI DE, et c. )
The vendors
There are several suppliers of chip set s for t he mot herboard:
q I nt el
q SI S
q Opt i
q Via
q ALi
I nt el has hit hert o been t he leader in supplying chip set s t o t he Pent ium mot herboard. Therefore, let
us j ust ment ion t heir chip set s, which have ast ronomical names.
The Nept une chip set ( 82434NX) was int roduced in June 1994. I t replaced t he Mercury set
( 82434LX) . I n bot h chip set s, t here were problems wit h t he PCI bus. I n January 1995 I nt el
int roduced t he first Trit on, where everyt hing worked. This chip set support s some new feat ures: it
support s EDO RAM, and it offers bus mast er int egrat ed EI DE cont rol and NSP ( Nat ive Signal
Processing - one of t he many new creat ions, which was soon forgot t en) .
However, t he following chip set s were of much higher qualit y, and wit hin very few years t hey lead t o
several new generat ions of chip set s, each of t hem more powerful and offering great new feat ures.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
I f you want t o read more about t hese and ot her chip set s, look for t he excellent web sit e Toms
Hardware Guide. Here, you will find all about t hese subj ect s.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d01.htm (4 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:07 AM
An illustrated Guide to chip sets
Read more about RAM in module 2e
Read about t he Pent ium in module 3c
Read about t he Pent ium I I ' s et c. in module 3e
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. KarbosGuide. com
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d01.htm (5 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:07 AM
An illustrated Guide to chip sets
KarbosGuide.com. Module 2d.02
The first chip sets for the Pentium boards
The cont ent s:
q Trit on first and second
q A bridge t o t he I / O syst em
q USB and EI DE
q The differences bet ween HX and VX
q The TX chip set
q Next page
q Previous page
Triton first and second [top]
The int erest in chip set s and t heir performance st art ed in lat e 1995, when t he Pent ium
processor became more popular. The Trit on cont rollers were t he first chip set s in t his t rend.
82430FX from lat e 1995 was I nt el' s next chip set and t he first Trit on. I n February 1996 t he
second generat ion of Trit on arrived. Two new chip set s were int roduced: The 82430VX and
82430HX. The last ( HX) was t he fast est one.
VX and HX
The t wo set s were similar, yet different . 430HX consist ed of t wo chips. I t was designed for
t he more professional PCs. 430VX consist ed of four chips, but t he cost was slight ly lower t han
HX. I t was aimed at t he home use PC market . Let us look at t he cont ent s of each chip set :
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d02.htm (1 of 7)7/27/2004 4:06:10 AM
An illustrated Guide to chip sets
Chip set Cont ent s
82430HX 82439HX Syst em Cont roller ( TXC)
+ 82371SB PCI I SA I DE Accelerat or
82430VX 82437VX Syst em Cont roller ( TVX)
+ t wo 82438VX Dat a Pat h Unit s ( TDX)
+ 82371SB PCI I SA I DE Accelerat or
Common t o bot h chip set s is 82371SB, which is a "PCI I SA I DE accelerat or chip". I t is also
called PI I X3, which some may recognize from t he Windows 95 device driver, which comes
wit h t he ASUS T2P4 board.
A bridge to the I/O system [top]
Please support our
sponsor.
The chip makes a bridge bet ween t he CPU, I SA and PCI bus. The news was, t hat it permit t ed
concurrent act ivit y in all t hree locat ions, t hus a new form of mult it asking. This is significant
for daily use. All dat a exchange t o and from I / O unit s cross t his int ersect ion, which now has
achieved great er widt h:
.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d02.htm (2 of 7)7/27/2004 4:06:10 AM
An illustrated Guide to chip sets
US2 and EIDE
[ t op]
New in t he chip was also t he host funct ion for USB. I t is t he Universal Serial Bus, which was
not much use at t his t ime. Finally, t he chip included a EI DE Bus Mast er cont rol. I n short t hat
means, t hat EI DE component s like hard disks, t o some ext ent can deliver t heir dat a direct ly
t o RAM wit hout t aking up CPU t ime.
Above, you see t he 82371SB chip and below, again, it s placement relat ive t o CPU and buses:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d02.htm (3 of 7)7/27/2004 4:06:10 AM
An illustrated Guide to chip sets
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
The differences between HX and VX
[ t op]
I t was generally accept ed, t hat t he HX set yielded t he best performance of t he t wo chip set s
described. But t he VX set had t wo ot her facilit ies t o offer: Capabilit y for SMBA ( Shared
Memory Buffer Archit ect ure) . That means among ot her t hings, t hat you can int egrat e t he
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d02.htm (4 of 7)7/27/2004 4:06:10 AM
An illustrated Guide to chip sets
video card on t he mot herboard wit h 1 or 2 MB st andard RAM, from t he working RAM. A
t echnology, which is used only in t he lowest cost PCs, and which soon was abandoned.
Also, t he VX set also support ed t he fast RAM t ype SD- RAM. HX did not . The VX set could
cont rol up t o 128 MB RAM, but it could not cache above 64 MB RAM.
HX cont rolled 512 MB RAM and was t he only I nt el Pent ium chip set t o cache above 64 MB
RAM.
The VX and HX chip set s are bot h out . They were replaced by t he TX chip set , which was t he
last I nt el chip set for Socket 7 mount ed CPUs. Today Ali and VI A produces chip set s for
Socket 7 mot herboards.
Intel TX chip set [top]
Please support our
sponsor.
The last chip set t o Pent ium processors were named 82430TX, which support s t wo new hot
t echnologies:
q SD- RAM
q Ult ra DMA
Ult ra DMA was also called ATA/ 33, and it is a st andard for harddisk int erface, which permit s
EI DE hard disks t o t ransfer at up t o 33 MBps.
This improved EI DE st andard is most ly market ed under t he name Ult ra DMA. Test s show t hat
Ult ra DMA result s in a speed increase of 25- 75 percent over t he t radit ional EI DE PI O mode 4.
Ult ra DMA is t he new EI DE st andard and has been vast ly enhanced since t his chip set .
The controllers in the TX chip set
Chip set Chips included
82430TX 82439TX Syst em Cont roller ( TXC)
82371AB PCI I SA I DE Accelerat or
The TX set is an updat e and improvement of t he VX set . Relat ive t o t his, t he TX first ly
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d02.htm (5 of 7)7/27/2004 4:06:10 AM
An illustrated Guide to chip sets
support s SD RAM and Ult ra DMA hard disks. Two import ant t echnologies. But t he TX- set
cannot cache above 64 MB RAM, and t hat was a problem. Please see t his art icle on t his
subj ect .
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d02.htm (6 of 7)7/27/2004 4:06:10 AM
An illustrated Guide to chip sets
Phot os t aken wit h Canon Powershot 600
The TX chip set was I nt el' s last and final set for Socket 7 mot herboards. Aft er t hat VI A and
ALi t ook over and cont inued t his work.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read more about RAM in module 2e
Read about t he Pent ium in module 3c
Read about t he Pent ium I I ' s et c. in module 3e
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. KarbosGuide. com
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d02.htm (7 of 7)7/27/2004 4:06:10 AM
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d03.htm
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d03.htm7/27/2004 4:06:10 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to SCSI, IEE1394 FireWire and USB.
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 5c2a.
About USB
The cont ent s:
q What is USB?
q Aft er a slow st art . .
On t he following page:
q Next page: The USB hub
q Next module: I EEE1394 FireWire
q Device Bay
q Next page
q Previous page
What is USB? [top]
Please support our
sponsor.
USB st ands for Universal Serial Bus. I t is a cheap and rat her slow I / O bus, running at 12 Mbit /
sec.
I t can be compared t o t he FireWire bus, which however is a lot speedier.
USB is an open and royalt y- free specificat ion. Unit s can be plugged and unplugged on t he fly
very easily. Here you see t he plugs, t he t wo small ones, number t wo from t he left :
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5c2a.htm (1 of 7)7/27/2004 4:06:13 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to SCSI, IEE1394 FireWire and USB.
There were problems wit h USB in t he beginning, since many mot herboard manufact urers
produced t heir own versions of t he port before it was fully st andardized. Hence t he nickname
Useless Serial Bus .
USB is support ed by Windows 95 OSR2. 1, Windows 98/ Me, Windows 2000 and Windows XP.
A success
USB has become a great succes. The bus simplifies PC design - giving us a simple and unified
int erface for a whole lot of PC unit s and devices like:
q Keyboard
q Mouse
q Loudspeakers, microphones, and ot her sound devices
q Print ers
q Modems and I SDN adapt ers
q Scanners and cameras
q Ext ernal drives like CD- RWs
q Card- readers and ot her adapt ers
All t hese unit s - and lot s of ot hers - will be connect ed using one single plug at t he PC. USB
holds up t o 127 unit s in one long chain.
The keyboard may hold a hub, so ot her USB unit s are connect ed here ( alt hough it more oft en is
t he monit or t o include a hub, as we shall see lat er) :
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5c2a.htm (2 of 7)7/27/2004 4:06:13 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to SCSI, IEE1394 FireWire and USB.
Each unit may hold t wo USB connect ors, so t hey all can be daisy chained.
This illust rat ion is fict ion - I never saw a set up like t his, but it shows t he int ent ions of t he serial
USB int erface:
All unit s have a firmware ident ificat ion code, t hat communicat es wit h t he OS ( i. e. Windows ) .
The unit must have a power feed ( could be minimum 100 ma) t o be recognized by t he USB
cont roller and Windows 98. I f one unit fails t his way, Windows shows an ! on yellow
background t o signalize t hat somet hing has t o be done. This could be t o unplug ot her USB
devices t o increase t he available power in t he chain.
Many hardware manufact urers t oday produce t heir modems, cameras and scanners in versions
wit h t wo- way int erfaces. These devices connect eit her t radit ionally using a COM port or using
t he USB port .
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5c2a.htm (3 of 7)7/27/2004 4:06:13 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to SCSI, IEE1394 FireWire and USB.
After a slow start ...
[ t op]
Please support our
sponsor.
Personally I always believed, t hat USB a had t o become a great renovat ion of t he PC design.
However, t hings were moving very slowly in t he beginning.
Bigger companies like Swiss Logit ech ( producing t he best mice and t rackballs available, at least
t o my opinion) moved very slowly int o USB. This probably has been due t o serious concern
over t he correct t echnical implement at ions. The COM, PS/ 2, and LPT port s represent very well-
known t echnology. Replacing t hem you have t o be very cert ain of t he consequences.
I n 1999 and 2000 t he USB product s became available in large numbers. Many of t hem are
being sold bot h t o Mac and PC. My lat est t rackball, a Kensingt on Orbit is only a Mac- product ,
j udging from t he box:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5c2a.htm (4 of 7)7/27/2004 4:06:13 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to SCSI, IEE1394 FireWire and USB.
However, t he t rackball ( which is very fine) works fine on any PC wit h USB. The Windows USB
driver inst ant ly recognizes t he t rackball.
The same goes for my great lit t le t ablet ( Wacom Graphire) :
Philips and Logitech - a private vision
[ t op]
I f I were in charge, Philips should go furt her wit h USB. Already t hey build in a USB in t heir
monit ors. Why not bundle t he monit or wit h a cordless set of keyboard & mouse. And place t he
infra- red receiver in t he monit or using USB as int erface? May I give t his idea t o Philips:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5c2a.htm (5 of 7)7/27/2004 4:06:13 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to SCSI, IEE1394 FireWire and USB.
Philips even could buy Logit ech as well. I t hink t hey would fit well t oget her - t wo fine European
vendors.
Links
You find t echnical specificat ions et c. in t hese sit es:
I nt el' s USB sit e ht t p: / / www. int el. com/ design/ usb
USB sit e: ht t p: / / www. usb. org
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Next module ( on FireWire and Device Bay)
Read Module 6a about file syst ems
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5c2a.htm (6 of 7)7/27/2004 4:06:13 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to SCSI, IEE1394 FireWire and USB.
Read about chip set s on t he mot herboard in module 2d
Read Module 4d about super disket t e and MO drives
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side
Read module 5b about AGP
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card
Read module 7c about sound cards, and 7d on digit al sound and music
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5c2a.htm (7 of 7)7/27/2004 4:06:13 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to SCSI, IEE1394 FireWire and USB.
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 5c3.
About FireWire IEEE1394
q I EEE1394 FireWire
q Device Bay
q Next page
q Previous page
FireWire is anot her int erface connect ing t he PC t o ext ernal unit s. I t does not look very much
like t he SCSI we know, but is a furt her development being a serial high speed bus. I t also a
bit like USB in t erms of hot - plugging and simple connect ions.
The int erface I EEE1394 has a bandwidt h of 400 Mbit per second, which is a lot bet t er t han
USB and comparable t o SCSI .
FireWire handles up t o 63 unit s on t he same bus. The unit s can be plugged and unplugged
hot - meaning you do not have t o power down t he PC.
The Firewire was expect ed t o replace:
q Parallel Cent ronics port ( t o some ext ent )
q I DE
q SCSI
q EI DE ( lat er on)
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5c3.htm (1 of 6)7/27/2004 4:06:15 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to SCSI, IEE1394 FireWire and USB.
However, Firewire so far has not become t he real big t hing for PCs. People wit h Macint osh
comput ers soon found great use for FireWire, especially t o connect high performance flat bed
scanners.
Today Firewire is support ed by Windows XP and it is gaining moment um. Among ot hers it is
used for:
q Connect ing DV- cameras t o video edit ing adapt ers
q High- end scanners
q Hot - plugged ext ernal harddisks from Maxt or wit h FireWire int erface.
Here is t he I EEE1394 port of a digit al video camera ( marked "DV" for Digit al Video) . I t is very
small:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5c3.htm (2 of 6)7/27/2004 4:06:15 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to SCSI, IEE1394 FireWire and USB.
FireWire for Macintosh [top]
Please support our
sponsor.
FireWire was developed by Lucent Technologies, but has ended by Apple, who claims a $1 per
port royalt y for use. I EEE1394 was conceived by Apple, who proposed it t o I EEE, who
approved it as a st andard in 1995. Firewire is Apple' s implement at ion of t he I EEE1394
st andard. Ot her companies have implement ed t heir own versions of I EEE1394. Yes, t hey are
not all t he same! ( Not e: This is t he purpose of t he I EEE - t o approve indust ry st andards, not
t o make an implement at ion. )
Hence all maj or hardware companies have adapt ed FireWire in some way. Especially t he
ent ert ainment elect ronic indust ry ( Video/ games/ t elevision) have great hopes wit h FireWire/
I EEE1394. I t will connect all t ypes of digit al elect ronics wit h t he PC and t his way open up for
a much more modular design.
Since I EEE1394 is advanced and yet claimed t o be cheap & simple, t he communicat ions
prot ocol can handle a lot of ot her unit s including:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5c3.htm (3 of 6)7/27/2004 4:06:15 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to SCSI, IEE1394 FireWire and USB.
q Net work cont rollers
q Hard disks, CDROM drives
q Print ers
Two modes
The FireWire st andard operat es wit h t wo modes.
q Asynchronous as ot her buses. This means t hat operat ions across t he bus are cont rolled
using int errupt signals. The bus report s t o t he host when a t ask is fulfilled.
q I so- synchronous . I n t his mode dat a is being t ransferred at a st eady preset speed -
cont inuously and wit hout any supervision from t he host . This opens up for dat a st reaming
useful for video or t he mult imedia present at ion. The FireWire is a peer- t o- peer int erface. This
means t hat dat a can be t ransferred bet ween t wo unit s at t ached t o t he bus wit hout
supervision from t he PC.
FireWire has a 64 bit address bus. Compared t o SCSI each unit does not need a unique I D,
t hey are dynamically configured "on t he fly". Neit her does t he bus have t o be t erminat ed. All
t oget her a lot simpler t han SCSI .
One of t he problems wit h SCSI has been t he limit at ion on dist ance bet ween t he unit s.
FireWire can hold up t o 16 unit s in t he same "st ring" and t here can be up t o 4. 5 met ers
bet ween t wo unit s.
The first implement at ions of FireWire will connect it t o t he PCI bus using t he new PI X6-
cont roller, which will be a part of one of I nt el' s new chip set s. I t hink it will be at least 2- 3
years before we really see t his new t echnology in t he market . But it will be wort h wait ing for
it , it opens up for a new world of int er connect ivit y bet ween TV, PC, video and all ot her t ypes
of elect ronic gear.
USB and FireWire - serial buses of the future
[ t op]
Soon high- end PC probably will hold bot h t hese serial I / O buses:
q USB version 2. 0 for all low speed gear.
q FireWire for high speed I / O t o Digit al Video recorders, high- end scanners et c.
Bot h int erfaces are about t o be included in t he sout h bridge of t he chipset s. I n 2002 it was
difficult t o whet her USB 2. 0 or Firewire was going t o be t he new high- speed I / O st andard.
Probably bot h of t hem will have place in t he PC archit ect ure t he coming 1- 2 years.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5c3.htm (4 of 6)7/27/2004 4:06:15 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to SCSI, IEE1394 FireWire and USB.
Device Bay
[ t op]
DeviceBay is anot her st andard which follows I EEE1394 and USB. These busses can connect
and disconnect unit s "on t he fly", t hat is while t he PC is operat ing. This abilit y t o "hot plug"
requires a new physical connect ion bet ween t he unit s. DeviceBay may be t he answer t o t his.
That is a st andard for connect ion boxes t hat can hold hard disks, CDROM drives and similar
unit s.
The mount ing frame can be inst alled wit hout t ools and while t he PC is running. Wit h t his one
can imagine a st orage unit filled wit h MP3 - files, which easily can be moved from a PC t o t he
player in t he car. Unfort unat ely, for a while it is only a fut urist ic dream.
I f DeviceBay really gains widespread usage, it could be t he end of loose ribbon cables in t he
PC cabinet . The whole PC can be made in modules, which all plug int o t he USB or t he
FireWire bus as DeviceBay unit s. The unit s can t hen freely be moved bet ween t he different
comput ers and ot her elect ronic unit s in t he home.
I t is designed for hot plugging unit s like:
q Zip drives
q Tape st reamers
q Modems
q Hard disks
q PC- card readers
These unit s will fit int o a special bay connect ed t o t he USB and FireWire buses enabling t he
hot plug. A good t hought ; however not all good t hought s end up in good hardware.
Links
You find t echnical specificat ions et c. in t hese sit es:
Apple about : FireWire
The I EEE has it s own page at ht t p: / / www. ieee. org
About DeviceBay: www. device- bay. org
q Next page
q Previous page
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5c3.htm (5 of 6)7/27/2004 4:06:15 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to SCSI, IEE1394 FireWire and USB.
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read about chip set s on t he mot herboard in module 2d
Read Module 4d about super disket t e and MO drives
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side
Read module 5b about AGP
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card
Read module 7c about sound cards, and 7d on digit al sound and music
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5c3.htm (6 of 6)7/27/2004 4:06:15 AM
An illustrated Guide to the File System
KarbosGuide.com. Module 6
About file systems: DOS formatting, FAT, etc.
The cont ent s on t his page:
q What are file syst ems?
q The file syst em and t he OS
q Limit at ions in disk size
q Next page
q Previous
page
We have seen before t hat t he PC is a big dat a processor. We have also seen t hat dat a are bit s and byt es, which
are organized in files. One of t he operat ing syst em' s maj or t asks is t o writ e t hese dat a t o a disk. Hard, floppy, and
zip disks must be format t ed before we can save files on t hem. I n t hese pages, we will review format t ing, file
syst ems, et c. We will st art wit h a general view, t hen go in dept h about FAT format t ing, which is ( st ill) t he most
common.
What are file systems?
As I wrot e in module 4a, drives are st orage media, which can hold a file syst em. When a disk is format t ed in a
drive, it becomes organized and prepared t o receive dat a. When we format a disk, it receives a file syst em .
Format t ing can be compared t o st art ing a library. You must inst all t he book shelves and t he cat alogue syst em
before any books are put in place. Once t he library is ready, bring on t he books! Similarly wit h a disk. When we
format it , we "burn in" a file syst em t o make it ready t o receive dat a ( files) .
We can format wit h any one of several different file syst ems:
FAT
File Allocat ion Table is t he original, old 16 bit DOS syst em is probably used in 90% of all PCs. I t is also called
FAT16 cont rary t o:
FAT32
This is a new addit ion t o FAT, which Microsoft int roduced wit h Windows 95 B t he December - 96 version ( OSR2) .
The performance has been even improved wit h Windows 98.
HPFS
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6a1.htm (1 of 4)7/27/2004 4:06:16 AM
An illustrated Guide to the File System
High Performance File Syst em is from OS/ 2. I t is an advanced 32 bit file syst em, which in all respect s is far
superior t o FAT, except for possible usage. I t can only be used wit h OS/ 2.
NTFS from Windows NT
A 32 bit file syst em like HPFS, but not compat ible wit h it . NTFS can only be used in Windows NT/ 2000/ XP. I f it was
available for use in Windows 95/ 98, it may be preferable t o FAT and FAT32.
NetWare
Net Ware is a server operat ing syst em from Novell. I t has it s own 32 bit file syst em. For t hat reason, t he Novell
server, cont rary t o NT or OS/ 2 servers, cannot be used as a work st at ion. The file syst em is much fast er t han FAT,
but it works only wit h Novell servers ( t ypically file servers) .
ISO 9660
This is for CDROMs and I SO 13346 for DVDs.
UDF
Universal Disk Format is for big capacit y disks like DVD RAM. UDF is not direct ly support ed by older versions of
Windows , you need a driver.
UNIX
UNI X servers have t heir own filing syst em. Here t he use of upper/ lower case in file naming is significant . Read in
t he following pages about t he concept s of t hese file syst ems.
Relationship between file system and operating system
Top
We see t hat t hat t he file syst em is an int egral part of t he operat ing syst em. An operat ing syst em can somet imes
work wit h different file syst ems:
Operat ing syst em File syst em( s)
DOS FAT16
Windows 95/ 98 FAT16, FAT32
Windows NT FAT16, NTFS
Windows 2000/ XP FAT16, FAT32, NTFS
OS/ 2 FAT16, HPFS
Novell Net Ware propriet ary file syst em
The file syst em is act ually t he int erface bet ween operat ing syst em and drives. When t he user soft ware, such as MS
Word, asks t o read a file from t he hard disk, t he operat ing syst em ( Windows 95/ 98 or NT) asks t he file syst em
( FAT or NTFS) t o open t he file:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6a1.htm (2 of 4)7/27/2004 4:06:16 AM
An illustrated Guide to the File System
The file syst em knows where files are saved. I t finds and reads t he relevant sect ors and delivers t he dat a t o t he
operat ing syst em.
Limitations in disk size
Top
Over t he years, t he PC has suffered from a long list of irrit at ing limit at ions. The hard disk indust ry has cont inuously
developed hard disks wit h increasing capacit y. However, t he syst em soft ware ( BI OS, DOS, and FAT) has set it s
limit at ions:
q DOS versions below 3. 0 could only handle hard disks up t o 16 MB.
q Versions 3. 0 t o 3. 32 could handle up t o 32 MB.
q DOS 4. 0 could handle up t o 128 MB.
q DOS version 5. 0 and t he BI OS, which cont rols I DE drives, could only accept 1024 cylinders and disks up t o 528
MB. This limit was broken wit h t he EI DE st andard.
q FAT16 can handle a maximum of 2 GB because of 16 bit calculat ions of t he clust er size.
q FAT32 accept s disks up t o 2048 GB. This st andard will probably last anot her couple of years.
Let us ret urn t o t he file syst em in next page.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6a1.htm (3 of 4)7/27/2004 4:06:16 AM
An illustrated Guide to the File System
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e Top
Read Windows t ipswit h a lit t le about Windows 95/ 98.
Read Module 6c about t he relat ionship bet ween BI OS, OS and hardware
Read Module 7a about t he videosyst em
Read about video cards in Module 7b .
Read about digit al sound in Module 7c .
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6a1.htm (4 of 4)7/27/2004 4:06:16 AM
An illustrated Guide to the File System
KarbosGuide.com. Module 6a.2
About file systems (continued)
The cont ent s:
q The format t ed disk
q About sect ors
q About clust ers
q Small clust ers wit h FAT32
q Next page
q Previous page
The formatted disk
We know t hat a disk must be format t ed wit h a file syst em , before it can accept files t o be saved:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6a2.htm (1 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:18 AM
An illustrated Guide to the File System
Now let us examine t he disk format t ing process. How does it work?
About sectors
Top
Please support our
sponsor.
All disks are divided in 512 byt e sect ors. That is t he st andard size for t he smallest disk unit . You
could easily format wit h a different sect or size, but t hat is not done. A sect or is t hen t he smallest
disk unit and it holds 512 byt es of dat a.
Sect ors are creat ed when t he circular disk is organized in concent ric t racks. Each t rack is divided
int o sect ors. Each sect or can hold 512 byt es.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6a2.htm (2 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:18 AM
An illustrated Guide to the File System
.
But , how are t hese sect ors dist ribut ed? How are t he files placed in t he sect ors? How do we handle a
file larger t han 512 byt es, which must occupy more t han one sect or? Who keeps t rack of what is in
each sect or?
This is a t ask for t he file syst em. Below, we evaluat e hard disks only and only FAT. Despit e it s age
and flaws, it is st ill by far t he most widely used file syst em. As for disket t es, read about disket t e
format t ing .
About clusters
Top
To cont inue in t he underst anding of t he file syst em, we must int roduce a new concept - clust ers .
Each sect or holds 512 byt es and a sect or is t he smallest disk unit . However, oft en a sect or is t oo
small for DOS t o handle. That is because DOS is a 16 bit operat ing syst em.
By design, DOS can only handle 2
16
disk unit s at a t ime. A disk unit ( my expression) is eit her a
sect or, or a clust er of sect ors. Thus, DOS can only handle 65, 536 of t hose!
Therefore, in FAT format t ing t he sect ors are gat hered in clust ers of 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, or 64 sect ors:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6a2.htm (3 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:18 AM
An illustrated Guide to the File System
The clust er concept is an administ rat ive invent ion. They are necessary, t o allow DOS t o handle large
disks.
They are also called allocat ion unit s . The number of sect ors gat hered in one clust er depends on t he
disk size:
Disk size ( part it ion size) Clust er size
< 255 MB 8 sect ors ( 4 KB)
< 512 MB 16 sect ors ( 8 KB)
< 1024 MB 32 sect ors ( 16 KB)
< 2048 MB 64 sect ors ( 32 KB)
I n Dos, t he dat a area of t he hard disk is divided int o a specified number of clust ers, which of
necessit y increase in size wit h t he size of t he disk. On modern hard disks, t he clust ers will usually
be 16 or 32 KB, as illust rat ed above
Small clusters with FAT32
Top
The good news is t hat FAT32, found in t he Windows 95 OSR2 and Windows 98, handles disk
format t ing much bet t er t han FAT16. Wit h FAT32 it is possible t o format hard disk part it ions of more
t han 2 GB wit h small clust er sizes:
Part it ion Clust er size
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6a2.htm (4 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:18 AM
An illustrated Guide to the File System
< 8 GB 4 KB
8 GB - 16 GB 8 KB
16 GB - 32 GB 16 KB
> 32 GB 32 KB
Somet hing else new in FAT32 is t he moveable root direct ory, which can be of variable size. I t
involves act ive use of bot h FATs ( I cannot explain how) . Alt oget her, it should make it simpler and
safer t o change part it ion sizes. But t he number of clust ers per part it ion grows enormously in large
part it ions.
FAT32 can only be inst alled in a new PC, since t he part it ion has t o be format t ed in a special manner.
The file syst em is only available in t he Windows 95 OSR2 ( OEM Service Release 2) and in Windows
98.
q Next page
q Previous page
To learn more
Top
Read Module 6b wit h a lit t le about Windows 95/ 98.
Read Module 6c about t he relat ionship bet ween BI OS, OS and hardware
Read Module 7a about t he videosyst em
Read about video cards in Module 7b .
Read about digit al sound in Module 7c .
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6a2.htm (5 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:18 AM
An illustrated Guide to the File System
KarbosGuide.com. Module 6a.3
About file systems (continued)
The cont ent s:
q Working wit h t he FAT format t ed disk
q 4 areas different on t he disk
q Next page
q Previous
page
The FAT formatted disk
Please support our
sponsor.
During format t ing, all hard disk are divided int o mult iple sect ors. The sect ors must cont ain
bot h user dat a and t he file syst em administ rat ive dat a. This is because in FAT, t he
administ rat ive dat a are st ored on t he disk also:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6a3.htm (1 of 4)7/27/2004 4:06:19 AM
An illustrated Guide to the File System
Thus, t he disk is divided in:
q Sect ors, occupied by FAT administ rat ive dat a.
q Sect ors, which are user available for dat a st orage ( t he dat a area) .
The lat t er of t he t o part s obviously is t he biggest .
The four disk areas
Top
Each disk or disk part it ion cont ains four fundament al areas:
q The boot record, which is always in t he first sect or .
q FAT areas, of which t here are usually t wo ident ical.
q The root direct ory.
q The dat a area.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6a3.htm (2 of 4)7/27/2004 4:06:19 AM
An illustrated Guide to the File System
I n t he dat a area all files and sub direct ories ( beyond t he root direct ory) are st ored. The dat a
area sect ors are gat hered in clust ers, and t his organizat ion is illust rat ed here:
q Next page
q Previous page
To learn more
Top
Read Module 6b wit h a lit t le about Windows 95/ 98.
Read Module 6c about t he relat ionship bet ween BI OS, OS and hardware
Read Module 7a about t he videosyst em
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6a3.htm (3 of 4)7/27/2004 4:06:19 AM
An illustrated Guide to the File System
Read about video cards in Module 7b .
Read about digit al sound in Module 7c .
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6a3.htm (4 of 4)7/27/2004 4:06:19 AM
An illustrated Guide to the File System
KarbosGuide.com. Module 6a.4
About file systems (continued)
The cont ent s:
q Boot record
q FAT areas
q Root direct ory and ot her direct ories
q The dat a area
q Next page
q Previous page
An example of the sectors in the four areas
Let us look at a FAT format t ed hard disk wit h 160 MB: How are t he sect ors ut ilized?
Not e: My calculat ions in t his example are NOT 100% CORRECT, as a few bright readers have not iced. I am sorry.
However, use t hem as an indicat ion of how t he disk is subdivided. One day I hope t o give t he correct pict ure. . .
The part it ion cont ains exact ly 157. 9 MB, if we calculat e correct ly. We are t alking about 165, 656, 576 byt es. The t ot al dat a
st orage area is divided in 323, 549 sect ors, 512 byt es each. I f you mult iply, t hat result s in 165, 656, 576 byt es:
323, 548 sect ors x 512 byt es = 165, 656, 576 byt es.
This equals t o 157. 9 MB as you can see from t his:
= 165, 656, 576
byt es
divided wit h 1024 =
161, 774 Kilobyt es
161, 774 Kilobyt es
divided wit h 1024
=
157. 9 Megabyt es
The file syst em now assumes cont rol over t hese 323, 548 sect ors. The boot record occupies t he first sect or . I n t he
following you find a brief descript ion of t he boot record and ot her administ rat ive areas.
Boot record
Top
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6a4.htm (1 of 6)7/27/2004 4:06:22 AM
An illustrated Guide to the File System
The first disk sect or is always reserved for t he boot record. I t cont ains informat ion about t he disk or it s part it ions. A
physical hard disk can be divided int o different part it ions. DOS, Windows 95 and NT t reat each part it ion as a separat e
drive.
The boot record informat ion enables t he file syst em t o handle t he disk. At t he same t ime, it includes a small program t o
use during syst em st art - up. Here is a summary of t hat sect or' s cont ent s ( skip, if you do not underst and) :
8086 inst ruct ion ( JUMP) .
DOS name and version number.
Byt es per sect or.
Sect ors per clust er in t he dat a area.
Number of reserved sect ors.
Max. number of ent ries in t he root direct ory.
Tot al number of sect ors.
Media descript ion ( is t his a hard disk?) .
Number of sect ors per FAT
Number of sect ors per t rack.
Number of disk read heads.
Number of hidden sect ors.
BOOT- st rap program rout ine, which reads t he hidden file ( like I O. SYS) , which st art s t he operat ing syst em.
The boot record is found on all disks, regardless of whet her t hey are FAT or ot herwise format t ed. That sect or cont ains t he
necessary descript ion of t he part it ion.
The FAT areas
Top
Aft er t he boot record, we get t o t he FAT areas. There are usually t wo ident ical FATs. FAT number 2 is simply a spare copy
of number 1, since FAT is essent ial for t he funct ion of t he disk.
The FAT file administ rat ion is act ually a very simple syst em, but it is complicat ed t o describe. Lat er, I will show some
pract ical examples. Here is t he first descript ion. Even if you do not ent irely underst and t he following, do not give up.
FAT consist s of a t able of whole numbers, which has 65, 536 16- bit ent ries . Each of t hese ent ries cont ain informat ion
about a clust er.
The cont ent of each FAT ent ry consist s of a whole number . I n t he t able below, t hey are writ t en as four digit hexadecimal
numbers, which show one of four opt ions.
Possible FAT clust er ent ry Value
The clust er is part of a file, t he last in t he file. FFFF
The clust er is part of a file. You can read t he
number of t he next clust er in t he same file.
like A8F7
The clust er is empt y, t hus free. 0000
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6a4.htm (2 of 6)7/27/2004 4:06:22 AM
An illustrated Guide to the File System
The clust er cont ains defect ive sect ors. FFF7
Example on reading a file
Top
Please support our
sponsor.
When t he file syst em has t o read a file, it follows t his rout ine. We imagine t hat t he file occupies 4 clust ers and it occupies
clust er numbers 442, 443, 444, and 448. But how does t he operat ing syst em read t hese addresses?
q Find t he file direct ory ent rance ( from it s file address) .
q Read t he first clust er, number 442 in t he direct ory ent rance.
q Look up in FAT under number 442. We find t he number of t he next clust er ( 443) .
q Look up in FAT under number 443. We find t he number of t he next clust er ( 444) .
q Look up in FAT under number 444. We find t he number of t he next clust er ( 448) .
q Look up in FAT under number 448 t o find FFFF ( indicat ing t he last clust er) .
FAT always works in t his way. Whenever a file has t o be read, it s locat ion is read in t he t able. Every t ime a file has t o be
writ t en t o a disk, vacant clust ers must be found for it , and t he informat ion is st ored in FAT, t o facilit at e ret rieval.
One of t he great advant ages of disk cache programs are, t hey always have a copy of FAT in RAM. I n t his way t he disk
clust er "map" can be read much fast er t han if t he operat ing syst em had t o read t he FAT from t he disk at each request .
The size of FAT
Top
Since each clust er has a FAT ent ry, t he size of t he FAT areas depends on t he disk size. Each ent ry occupies 16 bit s.
Let us ret urn t o t he sect or account in t he example of a disk of 160 MB size:
The maximum FAT size is 128 KB, since 2
16
files, 2 byt es each, equals 65, 536 x 2 = 131, 072 byt es or 128 KB. I n our
example, t here t urns out t o be 40, 400 clust ers , since t he disk part it ion is 160 MB.
We have t wo FATs, at 40, 400 X 2 byt es. That comes t o a t ot al of 161, 600, and t hat will occupy 316 sect ors.
The root directory and other directories
Top
The last administ rat ive area on t he disk is t he root direct ory. Since t here are always 512 file or direct ory ent rances in t he
root direct ory, it is t he same size on all hard disks. The root direct ory is unique in it s fixed size and it s locat ion in t he root .
Ot her t han t hat , it is a direct ory like any ot her.
Act ually, a direct ory is a list of files and ot her direct ories. Thus, you can read t he names of files and sub direct ories in t he
direct ory! The direct ory st ruct ure consist s of a number of direct ory ent ries.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6a4.htm (3 of 6)7/27/2004 4:06:22 AM
An illustrated Guide to the File System
Let us look at t hese direct ory ent ries, each of which occupies 32 byt es. The direct ory ent ries are ident ical, whet her t hey
are in t he root direct ory or a sub direct ory.
These ent ries, 32 byt es each, cont ain a lot of informat ion like:
q The file name ( in 8. 3 format )
q File size in byt es
q Dat e and t ime of last revision
You can see t he layout of t he file ent ry on t he illust rat ion t o t he right . The
32 byt es are grouped in sect ions. This holds t rue for all ent ries, whet her
t hey point t owards files or direct ories. This holds t rue for t he root
direct ory as well as all sub direct ories.
Not e t hat we also find t he number of t he first clust er. This is import ant ,
because t his is where t he operat ing syst em st art s t o localize t he file.
Remember t he descript ion of FAT above. You see t hat t he st art clust er
number is read in t he direct ory ent ry for t he file.
Next FAT reads t he numbers of clust er number t wo and so on, if t he file is
spread over addit ional clust ers.
The locat ion of any file is described in t his manner: The first clust er is
read in t he direct ory ent ry ( root or sub direct ory) . The following clust er
numbers are ret rieved from FAT.
On FAT16 format t ed hard disks, t he root direct ory occupies 512 ent ries,
which are 32 byt es each. Thus, it occupies 16 KB.
All sub direct ories have at least t wo ent ries. They are rat her special , in t hat t hey refer t o t he direct ory it self and t o it s
"parent " direct ory ( in which it is a sub direct ory) . The ent ries can be seen wit h t he DOS command DI R.
The ent ry for t he direct ory it self is seen as one dot . The ent ry for t he parent direct ory is seen as t wo dot s.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6a4.htm (4 of 6)7/27/2004 4:06:22 AM
An illustrated Guide to the File System
The data area
Top
The rest of t he disk cont ains t he most import ant part , t he dat a area, where all files and sub direct ories are st ored. The
dat a area is by far t he largest part of t he disk.
The sect ors in t he dat a area are allocat ed in clust ers. As ment ioned before, t he maximum number of clust ers for dat a is 2
16
= 65, 536. Our hard disk is 160 MB. That result s in 40, 400 clust ers, 8 sect ors each.
All sub direct ory ent ries in t he dat a area are organized in 32 byt e files, which cont ain t he same fields as t he root direct ory
ent ries.
Completing the account
Top
The user has a 160 MB hard disk, but t hat is a somewhat t heoret ical view. Act ually, t he disk cont ains 323, 548 sect ors, 512
byt es each. They are dist ribut ed like t his ( or rat her almost , t here are minor errors in t he calculat ions) :
Area Number of sect ors Sect or number
Boot - record 1 0
FAT 1 158 1 - 158
FAT 2 158 159 - 316
Root direct ory 32 317- 348
Dat a area wit h 40, 400 clust ers of 4 KB 323, 200 349 - 323, 548
Here is a graphic illust rat ion of t he same dist ribut ion:
q Next page
q Previous page
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6a4.htm (5 of 6)7/27/2004 4:06:22 AM
An illustrated Guide to the File System
To learn more
Top
Read Module 6b wit h a lit t le about Windows 95/ 98.
Read Module 6c about t he relat ionship bet ween BI OS, OS and hardware
Read Module 7a about t he videosyst em
Read about video cards in Module 7b .
Read about digit al sound in Module 7c .
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6a4.htm (6 of 6)7/27/2004 4:06:22 AM
An illustrated Guide to the File System
KarbosGuide.com. Module 6a.5
About file systems (continued)
The cont ent s:
q File fragment at ion
q Defragment at ion
q Windows 98 Defrag
q Next page
q Previous
page
File fragmentation
Top
Please support our
sponsor.
When we work wit h FAT format t ed disks, file fragment at ion will occur all t he t ime. One file can be several
megabyt es, t hereby occupying more t han one clust er. Maybe it requires 17 clust ers. I deally, t he 17 clust ers
should be locat ed next t o each ot her. They can t hen be read at opt imum speed, since t hat allows minimal
movement of t he read head. However, t hat is not t he way it works.
I n act ual operat ion, t he individual files are broken up in mult iple blocks, which are scat t ered across t he disk.
The problem increases wit h t ime. The more files you have on t he hard disk, t he more fragment at ion you will
experience. To begin wit h, vacant spaces appear bet ween t he files:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6a5.htm (1 of 4)7/27/2004 4:06:23 AM
An illustrated Guide to the File System
When you first writ e t o a new hard disk, t he file might occupy 17 clust ers in sequence. The same will happen t o
file number 2, 3, et c. , unt il t here are no more vacant clust ers on t he disk. Then t he file syst em must re- use
clust ers. That is done by finding empt y clust ers, where t he cont ent s have been erased. Thus, t he file could be
scat t ered in 17 clust ers, none of which are in sequence. Here you see a file split in four disconnect ed clust ers:
I n t he first DOS versions, when a new file had t o be writ t en, t he file syst em always ret urned t o t he first vacant
clust er t o st art a new file. That was done, t o get opt imum ut ilizat ion of t he disk. I t also result ed in immediat e
and t ot al file fragment at ion. Since DOS version 3. 0 t he syst em was changed t o fill t he disk, before any vacant
clust ers were re- used. That delays fragment at ion, but sooner or lat er it will occur anyway.
Defragmentation
Top
You can use t he program DEFRAG t o defragment t he files on t he disk. I f you are a heavy PC user, it needs t o
be done oft en. I usually run SCANDI SK first . That checks t he file syst em for logical errors and repairs t hem.
Scandisk will oft en find errors, so it does a good j ob.
Next defragment t he disks wit h defrag / all. Bot h programs can be st art ed wit h t he command St art - - > Run.
Type in t he command on t he window: defrag / all
Here you see t he defragment at ion:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6a5.htm (2 of 4)7/27/2004 4:06:23 AM
An illustrated Guide to the File System
Run defrag weekly - t hat will keep your hard disks in good shape. Don' t make t he int ervals t oo long. That can
cause t he disk t o get messed up, especially if it is nearly full.
Windows 98 Defrag
Top
I n Windows 98 t he defragment at ion was changed from t he way it worked in Windows 95. Windows 98/ Me
monit ors how programs are loaded. Opening Word, as an example, includes opening a large number of DLL and
ot her program files.
Wit h t he defragment at ion, all t hese files are placed in t he right posit ion t o anot her on t he disk, so t hey are
loaded wit h opt imal speed. I t works very well, t he programs are loaded 2- 3 t imes as fast as before.
However, you have t o defrag on a regular ( weekly) basis and t he process may t ake a long t ime.
q Next page
q Previous page
To learn more
Top
Read Module 6b wit h a lit t le about Windows 95/ 98.
Read Module 6c about t he relat ionship bet ween BI OS, OS and hardware
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6a5.htm (3 of 4)7/27/2004 4:06:23 AM
An illustrated Guide to the File System
Read Module 7a about t he videosyst em
Read about video cards in Module 7b .
Read about digit al sound in Module 7c .
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6a5.htm (4 of 4)7/27/2004 4:06:23 AM
An illustrated Guide to the File System
KarbosGuide.com. Module 6a.6
About file systems (continued)
The cont ent s:
q Part it ioning wit h FDI SK
q More t han one boot record
q An FDI SK example
q FDI SK / mbr
q The primary part it ion and boot ing
q Long file names wit h FAT32
q Next page
q Previous
page
Partitioning with FDISK
Hard disks can be divided in more t han one part it ion. That is done wit h t he program FDI SK, which is found in
all PCs - regardless of which version of DOS, Windows , or OS/ 2 is t he operat ing syst em. They all have FDI SK.
FDI SK can divide t he hard disk in up t o four part it ions. I n FAT16, t he individual part it ion must not exceed 2 GB.
Therefore it is oft en seen t hat t he hard disk is not ut ilized 100%. Look at t his pict ure of FDI SK, which has
part it ioned a 2 GB hard disk. The illust rat ion is in Danish, but you' ll see t he same in English:
You can clearly see, t hat t here are act ually only t wo part it ions. However, only t he upper is assigned a drive
let t er ( C: ) . The ot her part it ion consist s of 43 MB unused hard disk, which FDI SK ident ifies as Non DOS. I t is not
used, because you asked for a 2, 020 MB part it ion. The remainder is left over. The 43 MB is not enough t o
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6a6.htm (1 of 6)7/27/2004 4:06:24 AM
An illustrated Guide to the File System
bot her t o place in a new part it ion.
More than one boot record
Top
When FDI SK has part it ioned t he hard disk, t he file syst em must be able t o recognize t his part it ioning.
I nformat ion about t he locat ion of beginning and end of each part it ion is st ored in t he first sect or ( number 0) ,
which is called Mast er Boot Record ( MBR) . Then, regular boot records are st ored in t he beginning of each
part it ion on t he disk.
Here is a disk divided in t wo logical drives, which will be named C: and D: . The Mast er Boot record is in t he
first sect or of t he physical disk. I t cont ains informat ion about t he t wo part it ions. I n t he beginning of each
part it ion we find a new boot record, describing t hat part it ion.
An FDISK example
Top
You use FDI SK t o divide t he hard disk in one or more part it ions. FDI SK writ es a MBR in sect or zero. That
divides t he rest of t he disk in logical drives, each of which is regarded as a "real" drive by t he operat ing
syst em.
Let us look at t he division of an old EI DE hard disk, as it was format t ed using Windows 95. The harddisk was
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6a6.htm (2 of 6)7/27/2004 4:06:24 AM
An illustrated Guide to the File System
sold as 5. 1 GB. Act ually, it holds 4. 8 GB. Through FDI SK, t his capacit y is dist ribut ed in t hree part it ions using
FAT16. Here are t he expressions, as used in Windows 95 version of FDI SK:
First a primary part it ion is creat ed. We choose t o assign it maximum size. That is 2, 047 MB, corresponding t o
2, 146, 467, 840 byt es. That becomes our C drive, which is act ivat ed, so we can boot from t here.
We choose t o est ablish an ext ended DOS part it ion for t he rest of t he disk.
The ext ended DOS part it ion must be divided in logical DOS drives. We choose t o make t he first logical DOS
drive t he maximum allowable size. The D drive will t hen be 2, 047 MB, j ust like t he primary part it ion is.
A smaller part of t he hard disk st ill remains. We will make t hat int o anaot her logical DOS drive. That will have
813, 561, 344 byt es, or 775 MB. That becomes t he E drive.
Now FDI SK report s t hat t he disk has t hree drives. C: is t he primary part it ion, D: and E: are t wo logical DOS
drives, which are in t he ext ended part it ion.
The Physical Disk
I f we look at t he physical hard disk, we find t hat it has a t ot al of 9, 974, 720 sect ors, 512 byt es each. Aft er t he
part it ioning, t hese almost 10 million sect ors are dist ribut ed as shown below:
Physical sect or number Cont ent s
0 Mast er Boot Record, which describes t he ent ire hard disk
1 - 4, 192, 866 Drive C:
4, 192, 867 - 8, 385, 732 Drive D:
8, 385, 732 - 9, 974, 719 Drive E:
Not e, t hat each of t hree drives has it s own disk administ rat ion divided in boot record, FAT, root direct ory, and
dat a area. I f we select t he C drive from above, we can see here how t he sect ors are dist ribut ed in t he C drive
part it ion:
Physical sect or number Cont ent s
1 Boot record
2 - 513 FAT 1 + 2
514 - 545 The root direct ory
546 - 4, 192, 866 Dat a area, which is divided in 32 KB clust ers
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6a6.htm (3 of 6)7/27/2004 4:06:24 AM
An illustrated Guide to the File System
FDISK /mbr
Top
Please support our
sponsor.
Usually t he Mast er Boot Record holds read- only informat ion. I t is writ t en once by FDI SK during t he process of
part it ioning t he drive, but aft er t hat it should be left unchanged. However, some programs do change t he
cont ent of t he MBR. This goes for:
q Virus, cert ain viruses are occupying t he MBR giving t hem a safe posit ion.
q Syst em Commander and ot her mult iple boot ut ilit ies.
The mult iple boot ut ilit ies replace t he MBR wit h code belonging t o t he ut ilit y. This way a ut ilit y like Syst em
Commander t akes over t he boot process and allows t he user t o inst all several operat ing syst ems at t he same
PC. I t works fine, I can say; I have used it for a long t ime wit hout any problems.
But how do I get rid of t hese MBRs, if I want t o re- est ablish t he original MBR. One way is t o use t he command
fdisk / mbr. I t simply re- writ es t he MBR and t he ot her boot sect ors.
I have used it against a virus a few t imes, having t o boot from a floppy disk first . And I recent ly experienced a
disk, where Syst em Commander was inst alled and prot ect ed by a password! This disk was inaccessible even
aft er FDI SK' ing and format t ing unt il we used fdisk/ mbr. So please remember t his command!
The primary partition and booting
Top
There will always be one primary part it ion on t he hard disk. Boot ing must be from t he primary part it ion and t he
operat ing syst em is read from here.
The hidden system files
The core of t he operat ing syst em is st ored in t he t wo hidden syst em files, which are always found in a primary
DOS part it ion. I n t radit ional MS- DOS, t he files are named I O. SYS and MSDOS. SYS. These files have t he same
names in Windows 95/ 98, but t he cont ent s are changed slight ly compared t o t he t radit ional DOS. This review is
from t he old fashioned DOS, but t ells somet hing general about t he boot process of an operat ing syst em.
The DOS syst em format t ed disk cont ains t wo hidden syst em files. The first , I O. SYS, must be t he first ent ry in
t he root direct ory. MSDOS. SYS must be on ent ry number t wo.
Start-up on disk
When t he st art - up program has finished POST ( Power On Self Test ) and t he loading of BI OS rout ines, t he boot
process st art s. I t follows t he following st eps:
q MBR is read first . The sect or number of t he primary part it ion' s boot record is found here.
q A small boot program is read from t he primary part it ion' s boot record. That act ivat es t he loading of t he t wo
hidden files.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6a6.htm (4 of 6)7/27/2004 4:06:24 AM
An illustrated Guide to the File System
q I O. SYS is saved t o working memory. Besides creat ing an int erface "downwards" t o t he BI OS programs, I O.
SYS includes a small program called SYSI NI T. This program st art s t he next st eps of t he boot process.
q Now MSDOS. SYS is read from t he disk.
q Then SYSI NI T looks in root direct ory for a file named CONFI G. SYS. All commands in CONFI G. SYS are
execut ed, gradually configuring t he PC t o have a ready and usable DOS.
q Then SYSI NI T looks for t he command int erpret er COMMAND. COM. I f t hat is not found, we will get an error
message about t his. When it is found, AUTOEXEC. BAT, which cont ains t he last informat ion for personal
configurat ion of t he PC, is execut ed.
That was a lit t le bit about t he boot process.
OS/2 Boot Manager
Please support our
sponsor.
Wit h OS/ 2' s FDI SK edit ion, you can divide t he hard disk int o more primary part it ions. That allows use of t he
special Boot Manager, which comes wit h OS/ 2. Even if you do not use OS/ 2, you can st ill use Boot Manager let
us say t o have DOS / Windows 3. 11 on one primary part it ion and Windows 95/ 98 on anot her. They will bot h
appear as C drives, but you can only see one at a t ime. This, you cont rol wit h t he Boot Manager.
I hope you underst and t he import ance of FDI SK. I t is a good program t o be fluent in. Alt oget her, it is import ant
t o underst and t he file syst em, t he boot process, et c.
There are t wo excellent ut ilit ies - Part it ion Magic and Syst em Commander, which give furt her facilit ies t o
change t he part it ions and t he st art - up sequences, et c.
Long file names with FAT32
Top
You can st ore long file names in Windows 95/ 98, which uses t he VFAT file syst em. That is a 32 bit edit ion of
FAT. VFAT was int roduced wit h Windows 3. 11, but t he long file names did not become available unt il Windows
95.
The file syst ems in Unix, NT, and OS/ 2 have always been able t o st ore long file names, but now Windows can
do it t oo. Also VFAT is compat ible wit h regular FAT, which is smart . You can exchange files wit h ot her PCs -
regardless of whet her t hey can use long file names or not .
Act ually, t he VFAT file syst em is much like regular FAT. But in a smart way Microsoft has been able t o break
t he heavy 8. 3 file name limit at ion, which limit s regular FAT.
Physically, t he file names are st ored in a t radit ional 8. 3 file name, which VFAT creat es ( wit hout user cont rol) .
The user can assign a long file name. As an example, a file is named "Ford Escort sales. doc". That will be
t ranslat ed t o "FORDES~ 1. DOC", when t he filename is regist ered by FAT.
The long file names may be up t o 255 charact ers long, but t hey are t ranslat ed t o an "alias, " which follows t he
t radit ional 8. 3 FAT format . The t rick is, t hat t he long file name is writ t en across mult iple direct ory ent ries.
Normally, one direct ory ent ry point s t owards one file, but in t his case one file can occupy several root
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6a6.htm (5 of 6)7/27/2004 4:06:24 AM
An illustrated Guide to the File System
direct ories, each of which provides 32 byt es t o t he file name.
You should be happy about t he long file names in Windows - it makes it much easier t o ident ify saved files. The
only "danger" is, t hat you must not defragment t he hard disk wit h a DOS based applicat ion. Then t he long file
names are dest royed. The files st ill exist , but you can only find t hem under t heir 8. 3 name and t hat is an
annoying experience, especially if you have t housands of files.
However, you should not wast e memory and disk space using filenames 50 charact ers long. Usually filenames
of 15- 20 charact ers work fine.
q Next page
q Previous page
To learn more
Top
Read Module 6b wit h a lit t le about Windows 95/ 98.
Read Module 7a about t he videosyst em
Read about video cards in Module 7b .
Read about digit al sound in Module 7c .
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6a6.htm (6 of 6)7/27/2004 4:06:24 AM
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6c.htm
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6c.htm7/27/2004 4:06:24 AM
An illustrated guide to Operating Systems and the use ofhardware drivers
KarbosGuide.com. Module 6c1.
About operating systems and driver programs
The cont ent s:
q What is an operat ing syst em?
q The operat ing syst em recognizes hardware
On t he following pages:
q BI OS or driver programs
q Which operat ing syst ems?
q DOS cont rol of hardware
q 32 bit drivers and inst allat ion
q Next page
q Previous page
Click & Learn deals primarily wit h hardware. I n t hese pages I will cover t he operat ing syst em
as it connect s downward t owards hardware. The operat ing syst em is closely associat ed wit h
t he ROM BI OS program rout ines, which are described in module 2a . The t wo program layers
( operat ing syst em + BI OS) are called syst em soft ware and it is very useful t o underst and
t heir import ance for t he PC.
Let us st art by st udying what an operat ing syst em really is.
What is an operating system? [top]
Please support our
sponsor.
Tradit ionally t he operat ing syst em consist s of t hree part s:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6c1.htm (1 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:26 AM
An illustrated guide to Operating Systems and the use ofhardware drivers
Part Funct ion
Kernel The low level core being loaded aft er t he boot process.
Has many funct ions such as cont rol of t he dat a flow bet ween memory and I /
O unit s.
Shell The user int erface
File syst em A st andard for disk format t ing
The operat ing syst em can also be evaluat ed from t hese viewpoint s:
q An operat ing syst em is a number of files, which are read from t he hard disk at t he end of
t he PC st art - up rout ine.
q An operat ing syst em is a program layer. I t connect s t o t he PC hardware, t o facilit at e
opt imal execut ion of t he user programs.
The first definit ion does not say much. Let us st art wit h t he second: The operat ing syst ems
links soft ware and hardware t oget her. I t has t o enable user programs, like Works, Office,
et c. , t o funct ion wit h all possible hardware configurat ions. You can imagine t he relat ionship
bet ween hardware and user programs t hus:
q Hardware is clumpsy and dissimilar. There are unt old variat ions of PCs. They can have one
or anot her t ype hard disk, CPU, video card, et c. All of t hese various PC configurat ions behave
each in t heir own way.
q The user programs are 100% similar. They are off t he shelf product s, which expect t he PC
t o respond in a cert ain manner.
How do we make t hese t wo layers work t oget her? Can we eliminat e, t ake out , t he differences
in t he PC hardware, so a st andard product like Works j ust funct ions? Yes we can. We read in
an operat ing syst em - a syst em layer, which smoot hes out and st andardizes t he hardware:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6c1.htm (2 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:26 AM
An illustrated guide to Operating Systems and the use ofhardware drivers
You should underst and t he operat ing syst em as a necessary layer, which smoot hes out
bumps and pot holes in your PC' s hardware. This will give t he user programs a st able, even
work plat form.
The operating system recognizes hardware
[ t op]
The PC' s hardware represent s resources relat ive t o t he user program.
Think of your word processing program: You want t o print your t ext . The program issues a
print order, expect ing t hat t he document will be print ed as designed. The word processing
program dispat ches dat a according t o your commands. How t hey are t ranslat ed t o signals
underst ood by your print er - t hat is not t he word processing program' s problem. The print er
is a resource relat ive t o t he word processing program. The connect ions t o t hese resources is
via t he operat ing syst em. This holds t rue for all t he resources, which are included in t he PC
hardware:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6c1.htm (3 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:26 AM
An illustrated guide to Operating Systems and the use ofhardware drivers
As you can see, t he operat ing syst em has a very cent ral funct ion in t he PC. So wit h t hat
placement , it must be able t o recognize all forms and t ypes of hardware. There is no point in
connect ing a new mouse, if it does not work! Then what makes it work - t he operat ing
syst em. The syst em must recognize your mouse!
q Next page
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6c1.htm (4 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:26 AM
An illustrated guide to Operating Systems and the use ofhardware drivers
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Also see The Soft ware Tips
Read of module 7a and module 7b about inst allat ion monit or and video card in Windows
95/ 98!
Read about chip set s on t he mot herboard in module 2d
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6c1.htm (5 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:26 AM
An illustrated guide to Operating Systems and the use ofhardware drivers
KarbosGuide.com. Module 6c2.
About OSs and drivers - continued
The cont ent s:
q Syst em soft ware
q BI OS or driver programs
q Next page
q Previous page
System software
[ t op]
Toget her, t he operat ing syst em and t he ROM BI OS program rout ines form t he layer on which
t he user programs "rest . " When t he PC has t o work, an operat ing syst em has t o be read from
a disk. There are many different operat ing syst ems t o choose from. However, t he BI OS is
always placed firmly and cent rally in t he PC hardware.
BIOS - firmware
Please support our
sponsor.
One of t he fundament al t echniques in t he PC design is t he BI OS program layer. BI OS ( Basic
I nput Out put Syst em) is a group of small programs, furnished by t he PC manufact urer - also
called firmware .
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6c2.htm (1 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:28 AM
An illustrated guide to Operating Systems and the use ofhardware drivers
The BI OS rout ines are placed in t he hardware - in a ROM chip - and are always available.
Being st ored in t he hardware, t hey are funct ional regardless of which operat ing syst em t hey
have t o work wit h. So, in designing an operat ing syst em, one must pay close at t ent ion t o t he
BI OS. The operat ing syst em must be able t o work closely wit h t he BI OS.
BI OS cont ains some very basic program rout ines, which handle dat a t ransfer bet ween
different hardware component s. During PC st art - up, t he BI OS programs are t he only
accessible soft ware. Lat er in t he st art - up process, t he operat ing syst em is read. I t will t hen
t ake cont rol of t he PC. The operat ing syst em has t o provide a user int erface , on which t he
user programs can rest .
Thus, t he operat ing syst em has t wo "faces": One point ing up t owards t he user and his/ hers
programs and one point ing down t owards t he syst em and hardware:
As comput ers have become more and more powerful, t he user int erface has become more
graphic and user friendly. I n a few years we will be able t o address our commands direct ly t o
t he operat ing syst em ( you can do it already t oday wit h I BM' s OS/ 2) .
Thus, t he "upwards" face of t he operat ing syst em will change great ly - support ed by
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6c2.htm (2 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:28 AM
An illustrated guide to Operating Systems and the use ofhardware drivers
t echnological development . The "downwards" face - t he operat ing syst em' s int erface wit h
hardware - will change less. At least , t he fundament al principles are t he same as in t he
childhood of t he PC.
BIOS or drive programs
[ t op]
The operat ing syst em must be able t o communicat e wit h hardware. As we are going t o see,
t his can be done in t wo ways:
q The operat ing syst em communicat es direct ly wit h hardware t hrough drive programs.
q The operat ing syst em ut ilizes t he BI OS programs.
While BI OS is hardware specific program code, st ored in hardware, t he drive programs are
small hardware specific program element s read from t he disk t oget her wit h t he operat ing
syst em.
Depending on which operat ing syst em is inst alled, bot h principles are used in various
degrees. Since t he BI OS programs consist of 16 bit code, it is t ypically DOS ( a 16 bit
operat ing syst em) which ut ilizes BI OS t o a large degree. I n t he newer 32 bit operat ing
syst ems, it is not efficient t o use BI OS any more t han necessary.
Here is a model, which shows t he operat ing syst em wit h BI OS and drive programs ( usually
j ust called drivers ) :
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6c2.htm (3 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:28 AM
An illustrated guide to Operating Systems and the use ofhardware drivers
As you can see, t he driver/ BI OS funct ions are closely associat ed wit h t he operat ing syst em.
So let us look at t hat on t he following page.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Also see The Soft ware Tips
Read of module 7a and module 7b about inst allat ion monit or and video card in Windows
95/ 98!
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6c2.htm (4 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:28 AM
An illustrated guide to Operating Systems and the use ofhardware drivers
Read about chip set s on t he mot herboard in module 2d
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6c2.htm (5 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:28 AM
An illustrated guide to Operating Systems and the use ofhardware drivers
KarbosGuide.com. Module 6c3.
About OSs and drivers - continued
The cont ent s:
q Which operat ing syst ems?
q DOS cont rol of hardware
q Next page
q Previous page
Which operating systems?
[ t op]
The operat ing syst ems have undergone a t remendous development since 1981. I t all st art ed wit h DOS, which
was a 16 bit modificat ion of a simple 8 bit operat ing syst em called CP/ M.
DOS was furt her developed in t he 1980s. Since around 1990 Windows came int o t he scene. Windows st art ed as a
GUI ( Graphic User I nt erface ) for DOS.
The PC boot ed wit h DOS as operat ing syst em. Then you could choose, if you want ed mouse and graphics on t he
screen wit h Windows . Windows was a supplement t o DOS.
The Graphic User I nt erface ( GUI ) allows you t o work wit h a mouse inst ead of writ ing long command lines like
copy c: \ t ext s\ * . * d: \ t ext bak\ * . * / s/ v/ , which is t he st andard in t ext based operat ing syst ems ( like DOS) .
DOS was designed for 16 bit comput ers, which t he first PCs were. Wit h I nt el' s 80386 t he 32 bit t echnology was
knocking at t he door. Modern PCs are designed for st raight 32 bit program execut ion. So we have seen a gradual
t rend in t he PC operat ing syst ems from 16 bit t owards 32 bit and t his affect s hardware design.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6c3.htm (1 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:30 AM
An illustrated guide to Operating Systems and the use ofhardware drivers
OS/ 2 was a complet ely new- designed OS build on a 32 bit kernel ( as UNI X and LI NUX) . I t was originally
designed by I BM and Microsoft t oget her, but Microsoft abandoned t he proj ect in favour of t heir own Windows . I n
t he early 1990s many people ( including I ) were very fond of OS/ 2. But it lost moment um as Windows 95
appeared.
Wi ndow s 95 was a radical development of Windows 3. 11. Windows 95 was build on DOS, but t he 32 bit
component s made up a big part of t he OS. Toget her wit h Windows 95 came new 32 bit appliacat ions, which could
not be execut ed wit hin DOS.
Wi ndow s 98 and Me are furt her enhanced versions of Windows 95.
Windows 95 and Windows 98/ Me are most ly 32 bit OS' s, but wit h some 16 bit remnant s.
Wi ndow s NT is a pure 32 bit OS from Microsoft . I t was developed in a parallel run wit h OS/ 2.
Wi ndow s 2000 and XP are more popular versions of Windows NT. They hold t he same user int erface as
Windows 98 end ME. They include all t he Direct X t echnologies of Windows 98/ Me which enables game and ot her
mult imedia applicat ions t o run.
Protected mode
The 32 bit programs we know from Windows 95/ 98/ Me work in prot ect ed RAM sect ors, wit h t he CPU running in
prot ect ed mode . This allows t he PC t o mult it ask - more t han one program can run concurrent ly and
independent ly. That is not possible in 16 bit operat ing syst ems, where t he CPU works in real mode .
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6c3.htm (2 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:30 AM
An illustrated guide to Operating Systems and the use ofhardware drivers
A brief comparison of 16 bit and 32 bit operat ing syst ems can look like t his:
Operat ing syst em DOS 32 bit operat ing syst em ( NT, OS/ 2, UNI X)
Users Single user Mult iple users
Program execut ion 16 bit single t ask in real mode 32 bit mult it ask in prot ect ed mode
Screen appearance Most ly Text based ( poor qualit y
graphics)
Oft en GUI - graphic int erface wit h high
resolut ion graphics
Hardware handling Primarily BI OS Cust om designed 32 bit drivers for each
hardware component .
DOS control of hardware [top]
Please support our
sponsor.
DOS is quit e simple t o describe, since it principally consist s of only 4 part s:
q A boot record, which act ivat es t he operat ing syst em.
q The file I O. SYS, which is int erfaced t o ROM BI OS wit h inst allat ion of device drivers .
q The file MSDOS. SYS. That is t he core of DOS, handling t he file syst em and program execut ion.
q The file COMMAND. COM, which provides t he command line, t he t ext based user int erface.
When we t alk about hardware cont rol, it is done t hrough I O. SYS. That is a program which reads t he ROM BI OS
code and convert s it t o DOS' s own device drivers.
The smart t hing about DOS is t hat t he operat ing syst em can be expanded wit h ext ernal device drivers. I O. SYS
reads t hem via t he st art - up file CONFI G. SYS. First device drivers are read from ROM BI OS. Then any possible
addit ional drivers are read from disk. I n t hat way DOS can handle hardware unit s which did not exist when t he
PC was originally configured.
A final opt ion t o handle hardware from DOS programs is t o writ e special drivers for t he individual user program .
Many DOS games come wit h t heir own graphics drivers ( t hey have t o recognize all graphics st andards on t he
market ! ) . Anot her classic example is t he word processing program WordPerfect , which in it s prime ( version 5. 1)
came wit h drivers t o more t han 500 different print ers!
Unit Example of DOS device drivers
Hard disk BI OS
Video card BI OS
Mouse MOUSE. SYS
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6c3.htm (3 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:30 AM
An illustrated guide to Operating Systems and the use ofhardware drivers
CD- ROM ATAPI . SYS + MSCDEX. EXE
Print er I nt ernal drivers in t he user program ( like WordPerfect 5. 1)
The device drivers can be seen wit h t he program MSD. Here is a pict ure from Windows 95, where you can clearly
see t he names of t he device drivers ( CON, PRN, LPT1 et c. ) :
All t hese device drivers are in 16 bit program code.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Also see The Soft ware Tips
Read of module 7a and module 7b about inst allat ion monit or and video card in Windows 95/ 98!
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6c3.htm (4 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:30 AM
An illustrated guide to Operating Systems and the use ofhardware drivers
Read about chip set s on t he mot herboard in module 2d
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6c3.htm (5 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:30 AM
An illustrated guide to Operating Systems and the use ofhardware drivers
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 6c4.
About OSs and drivers - continued
The cont ent s:
q 32 bit drivers
q I nst allat ion of new drivers
q Next page
q Previous page
32 bit drivers
[ t op]
I n 32 bit operat ing syst ems, you use 32 bit drivers inst ead of ROM BI OS. This means t hat soft ware suppliers like Microsoft and I BM must be able t o supply drivers
t o all conceivable hardware. The advant age is, t hat once t he operat ing syst em has inst alled drivers, all user programs operat e alike relat ive t o hardware.
I t is an enormous proj ect t o supply drivers. Especially OS/ 2 has suffered problems in get t ing t he right drivers on t he market . For many years, I BM for example did
not supply OS/ 2 drivers for Canon print ers. That was part of my reason t o drop t hat operat ing syst em. Regarding driver inst allat ions, Windows 98 is
unquest ionably t he best operat ing syst em.
Windows support s plug and play. The operat ing syst em searches t he PC for hardware. Oft en all drivers ( t o CD- ROM, net work cont roller, sound card, et c. ) are
inst alled aut omat ically. The drivers can be seen under Syst em in t he cont rol panel.
Let us look at a EI DE hard disk. The hard disk operat ion is regulat ed by an EI DE cont roller on t he syst em board. Therefore, Windows must have a driver inst alled
t o t his cont roller. We can find it easily. Go t o: My comput er - > Cont rol panel - > Syst em - > Comput er. I n Windows 2000 you should click on Device manager:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6c4.htm (1 of 6)7/27/2004 4:06:33 AM
An illustrated guide to Operating Systems and the use ofhardware drivers
Then expand t he ent ries t o hardware unit s:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6c4.htm (2 of 6)7/27/2004 4:06:33 AM
An illustrated guide to Operating Systems and the use ofhardware drivers
Act ually, you can see a long list of drivers in t he pict ure above. Windows has inst alled most of t hem during Windows inst allat ion. An VI A Bus Mast er I DE cont roller,
which regulat es t he hard disk can be found:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6c4.htm (3 of 6)7/27/2004 4:06:33 AM
An illustrated guide to Operating Systems and the use ofhardware drivers
I always have t hese drivers on t he hard disk ( in t he folder C: \ Disks\ Drivers) . That makes it easy t o inst all t hem aft er an unforeseen but necessary re- inst allat ion of
Windows .
The qualit y of t he drivers is very import ant . The drivers are ext remely import ant for video cards. You oft en hear t hat a new driver has been developed for t his
video card and it improves performance by 40%. Then rush t o download it ( from t he manufact urers I nt ernet server) and inst all it . Don' t forget t o save it on disk for
fut ure use!
You also have t o be cognizant about t he syst em board chip set . Oft en Windows 98 inst alls a good st andard driver, but new chipset s may cont ain facilit ies which
require a new driver. That can be found on a disk, which comes wit h t he syst em board or on t he I nt ernet .
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6c4.htm (4 of 6)7/27/2004 4:06:33 AM
An illustrated guide to Operating Systems and the use ofhardware drivers
Installation of new drivers [top]
Please support our
sponsor.
You inst all new drivers in Windows 98/ Me/ 2000 wit h "add new hardware" found in My Comput er - > Cont rol panel: .
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6c4.htm (5 of 6)7/27/2004 4:06:33 AM
An illustrated guide to Operating Systems and the use ofhardware drivers
Don' t let Windows search for hardware. I nst ead choose yourself. Then you have t o select t he part icular hardware from t he list and in t he next screen click "Have
disket t e. . . " Learn t his t echnique if you experiment wit h your PC and want maximal benefit s from your hardware.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Also see The Windows 98 page ( module 6d)
Read of module 7a and module 7b about inst allat ion monit or and video card in Windows 95/ 98!
Read about chip set s on t he mot herboard in module 2d
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module6c4.htm (6 of 6)7/27/2004 4:06:33 AM
An illustrated Guide to Monitors and the Video System
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 7
q About t he video syst em
q About video cards
q About sound cards
q About digit al sound and music.
The cont ent s on t his and following pages:
q I nt roduct ion
q Concept s and t erminology
q Screen resolut ion, screen size et c.
q About colors, color dept h, RGB et c.
q About refresh rat es
q TCO st andards
q LCD displays
The video syst em ( of which t he monit or is a part ) is one of t he most
import ant component s in t he PC. I t affect s direct ly your pleasure of working,
and act ually also your healt h. At t he same t ime, t he video syst em shows t he
biggest variat ion bet ween different PCs. Read my coverage of t his subj ect
here in t his module, which is subdivided int o several pages.
q Next page
q Previous page
Introduction
[ t op]
All comput ers are connect ed t o some t ype of display, which usually is called t he monit or. Monit ors are
available in many different t ypes and sizes. The size generally goes from 12 t o 21 inches diagonal.
The monit or is a part of t he comput er video syst em. To underst and how t o obt ain a good screen image,
we need t o look at t he complet e video syst em. I t includes t hese t hree element s:
q The graphics card ( also called t he video card or video adapt er) . I t is an expansion card, which
generat es elect ric signals t o t he monit or.
q The monit or it self, which is connect ed by a cable t o t he video card using some kind of int erface.
q A device driver which Windows uses t o cont rol t he video card, t o make it send t he correct signals t o
t he monit or.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7a1.htm (1 of 3)7/27/2004 4:06:35 AM
An illustrated Guide to Monitors and the Video System
These t hree element s must be fit t ed and mat ched t o achieve qualit y images. Even t he finest and most
expensive monit or will only render mediocre images if it is connect ed t hrough a low qualit y video card.
All video cards depend on t he right driver and proper set t ings t o funct ion properly ot herwise t he card
will not perform well:
I n t hese pages, I will review t he complet e video syst em. First you can read about t he video image
const ruct ion, pixels. resolut ion, and refresh rat e. Those are very cent ral subj ect s. Lat er, we will look at
different monit or and video card t ypes. Finally, we put it all t oget her in Windows .
Fast development
The video syst em has developed as explosively as t he rest of t he PC since t he 1980s. These
improvement s have occurred in different areas:
q The moni t or s bot h t he t ubes and t he elect ronics cont inue t o improve, and t he flat panel monit ors
has come along. The newer monit ors render bet t er images - sharper, wit h bet t er resolut ion and bet t er
colors. Big plasma screens is a new and int erest ing t echnology.
q The v i deo car ds are get t ing fast er. They can deliver bet t er images, which t he new monit ors are
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7a1.htm (2 of 3)7/27/2004 4:06:35 AM
An illustrated Guide to Monitors and the Video System
capable of producing. The user get s more t uning opt ions. New RAM t ypes and buses will increase speed,
and new feat ures are added.
q Vi deo pr esent at i on, DVD, and 3D games are ot her areas of development , which will change t he
video card st andards.
The video syst em is a sub syst em in t he PC, wit h it s own t echnological development . At t he same t ime,
monit ors and video cards are areas, where manufact urers and dealers oft en cut corners. As an ordinary
user, you can improve your screen images significant ly wit h careful planning. That holds t rue when you
buy your PC - you must select your video syst em carefully.
I t also holds t rue for exist ing video syst ems, where bet t er drivers and soft ware opt imizing can help
produce t he opt imal screen image. We will look at t hat in t hese pages.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e Top
Read about video cards in Module 7b .
Read about sound cards in Module 7c .
Read about digit al sound and music in Module 7d .
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7a1.htm (3 of 3)7/27/2004 4:06:35 AM
An illustrated Guide to the Video Cards
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 7b.1
The video card
The cont ent s:
q An int roduct ion t o t he video card
q The video card support s t he CPU
q About RAM on t he video card
q RAMDAC or digit al?
q Heavy dat a t ransport
q Next page
q Previous
page
Three components in a videocard
The video card is j ust as import ant as t he screen and more oft en overlooked. During t he years 1999- 2001
t he overall qualit y of video adapt ers have been improved. Earlier t here was some very lousy product s in t he
market . Follow my art icles t o know more of t he video adapt er!
A video card is t ypically an adapt er, a removable expansion card in t he PC. Thus, it can be replaced!
The video card can also be an int egral part of t he syst em board This is t he case in cert ain brands of PCs and is
always t he case in lap t ops. I have a clear preference for a replaceable video card in my st at ionary PC.
However modern mot herboard may include good int egrat ed video chip set s. You j ust have t o know which ones!
Regardless of whet her it is replaceable or int egrat ed, t he video adapt er consist s of t hree component s:
q A vi deo chi p set of some brand ( ATI , Mat rox, Nvidia, S3, I nt el, t o name some of t he bet t er known) . The
video chip creat es t he signals, which t he screen must receive t o form an image.
q Some kind of RAM ( EDO, SGRAM, or VRAM, which are all variat ions of t he regular RAM) . Memory is
necessary, since t he video card must be able t o remember a complet e screen image at any t ime. Using AGP,
t he video card may use t he main memory of t he mot herboard.
q A RAMDAC - a chip convert ing digit al/ analog signals. Using Flat panel monit ors, you do not need a t he
funct ion of a RAMDAC.
The video card supports the CPU
Top
The video card provides a support funct ion for t he CPU. I t is a processor like t he CPU. However it is especially
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7b1.htm (1 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:37 AM
An illustrated Guide to the Video Cards
designed t o cont rol screen images.
You could produce a PC wit hout a video cont rolling chip and leave t his work t o t he CPU. However, t he CPU
would be const ant ly occupied running t he soft ware t hat should generat e screen images.
RAM on the video card
Top
Video cards always have a cert ain amount of RAM. This RAM is also called t he frame buffer. Today video cards
hold plent y of RAM, but before it was more import ant :
q How much RAM? That is significant for color dept h at t he highest resolut ions.
q Which t ype RAM? This is significant for card speed.
Video card RAM is necessary t o keep t he ent ire screen image in memory. The CPU sends it s dat a t o t he video
card. The video processor forms a pict ure of t he screen image and st ores it in t he frame buffer. This pict ure is a
large bit map. I t is used t o cont inually updat e t he screen image.
The amount of RAM
Older video cards were t ypically available wit h 1, 2, 4 or more MB RAM. How much is necessary? That depends
primarily on how fine a resolut ion you want on your screen. For ordinary 2D use, 16 bit colors are "good
enough. " Let us look at RAM needs for different resolut ions:
Resolut ion Bit map size wit h 16 bit colors Necessary RAM on t he video card
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7b1.htm (2 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:37 AM
An illustrated Guide to the Video Cards
640 x 480 614, 400 byt es 1 MB
800 x 600 960, 000 byt es 1. 5 MB
1024 x 768 1, 572, 864 byt es 2 MB
1152 x 864 1, 990, 656 byt es 2. 5 MB
1280 x 1024 2, 621, 440 byt es 3 MB
1600 x 1200 3, 840, 000 byt es 4 MB
Not e t hat t he video RAM is not ut ilized 100% for t he bit map. Therefore, 1 MB is not enough t o show a 800 x
600 pict ure wit h 16 bit colors, as t he above calculat ion could lead you t o believe.
Today video cards come wit h 4 MB, 8 MB or more RAM.
Using ordinary RAM, you saw speed improvement s of t he graphics card using 4 MB inst ead of 2 MB, if t he
resolut ion only was 800 x 600 or 1024 x 768. I n t his case dat a can be writ t en t o and read from t he RAM
simult aneously - using different RAM cells. Wit h only 2 MB RAM, dat a somet ime had t o wait for a free cell.
3D - lots of RAM
Support ing t he demand for high qualit y 3D performance many new cards come wit h a frame buffer of 16 or 32
MB RAM. And t hey use t he AGP int erface for bet t er bandwidt h and access t o t he main memory.
VRAM
Briefly, in principle all common RAM t ypes can be used on t he video card. Most cards use very fast edit ions of
ordinary RAM ( SDRAM or DDR) .
Some high end cards ( like Mat rox Millennium I I ) earlier used speciel VRAM ( Video RAM) chips. This was a RAM
t ype, which only was used on video cards. I n principle, a VRAM cell is made up of t wo ordinary RAM cells,
which are "glued" t oget her. Therefore. you use t wice as much RAM t han ot herwise. VRAM also cost s t wice as
much. The smart feat ure is, t hat t he double cell allows t he video processor t o simult aneously read old and
writ e new dat a on t he same RAM address. Thus, VRAM has t wo gat es which can be act ive at t he same t ime.
Therefore, it works significant ly fast er.
Wit h VRAM you will not gain speed improvement s increasing t he amount of RAM on t he graphics cont roller.
VRAM is already capable of reading and writ ing simult aneously due t o t he dual port design.
UMA and DVMT
On some older mot herboards t he video cont roller was int egrat ed. Using SMBA ( Shared Memory Buffer
Archit ect ure) or UMA ( Unified Memory Archit ect ure ) part s of t he syst em RAM were allocat ed and used as
frame buffer. But sharing t he memory was very slow and t he st andards never became very popular.
A newer version of t his is found in I nt el chip set 810 and t he bet t er 815, which also int egrat es t he graphics
cont roller and use part s of t he syst em RAM as frame buffer. Here t he syst em is called Dynamic Video Memory
Technology ( D. V. M. T. ) .
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7b1.htm (3 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:37 AM
An illustrated Guide to the Video Cards
The RAMDAC
Top
All t radit ional graphics cards have a RAMDAC chip convert ing t he signals from digit al t o analog form.
CRT monit ors work on analog signals. The PC works wit h digit ized dat a which are sent t o t he graphics adapt er.
Before t hese signals are sent t o t he monit or t hey have t o be convert ed int o analog out put and t his is processed
in t he RAMDAC:
The reccommandat ion on a good RAMDAC go like t his:
q Ext ernal chip, not int egrat ed in t he VGA chip
q Clock speed: 250 - 360 MHz.
Heavy data transport
The original VGA cards were said t o be "flat . " They were unint elligent . They received signals and dat a from t he
CPU and forwarded t hem t o t he screen, not hing else. The CPU had t o make all necessary calculat ions t o creat e
t he screen image.
As each screen image was a large bit map, t he CPU had t o move a lot of dat a from RAM t o t he video card for
each new screen image.
The graphic int erfaces, like Windows , gained popularit y in t he early ninet ies. That marked t he end of t he "flat "
VGA cards. The PC became incredibly slow, when t he CPU had t o use all it s energy t o produce screen images.
You can t ry t o calculat e t he required amount of dat a.
A screen image in 1024 x 768 in 16 bit color is a 1. 5 MB bit map. That is calculat ed as 1024 x 768 x 2 byt es.
Each image change ( wit h a refresh rat e of 75 HZ t here is 75 of t hem each second) requires t he movement of
1. 5 MB dat a. That zaps t he PC energy, especially when we t alk about games wit h cont inual image changes.
Furt hermore, screen dat a have t o be moved across t he I / O bus. I n t he early ninet ies, we did not have t he PCI
and AGP buses, which can move large volumes of dat a. The t ransfer went t hrough t he I SA bus, which has a
very limit ed widt h ( read in module 2b about t he buses) . Addit ionally t he CPUs were 386s and early 486s,
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7b1.htm (4 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:37 AM
An illustrated Guide to the Video Cards
which also had limit ed power.
q Next page
q Previous page
To learn more
Top
Read about monit ors in Module 7a.
Read about sound cards in Module 7c .
Read about digit al sound and music in Module 7d .
Read about FPU work in 3D graphics.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7b1.htm (5 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:37 AM
An illustrated Guide to the Video Cards
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 7b.2
The video card (continued)
The cont ent s:
q About accelerat or cards
q About video card and chips
q Card brands
q The video driver
q Next page
q Previous page
About the accelerator cards
Top
I n t he early ninet ies t he accelerat or video cards appeared. Today all cards are accelerat ed and t hey are
connect ed t o t he CPU t hrough high speed buses like PCI and AGP.
Wit h accelerat ed video chips, Windows ( and wit h t hat t he CPU) need not calculat e and design t he ent ire bit
map from image t o image. The video card is programmed t o draw lines, Windows , and ot her image element s.
The CPU can, in a brief code, t ransmit which image element s have changed since t he last t ransmission. This
saves t he CPU a lot of work in creat ing screen images. The video chip set carries t he heavy load:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7b2.htm (1 of 4)7/27/2004 4:06:39 AM
An illustrated Guide to the Video Cards
All video cards are connect ed t o t he PCI or t he AGP bus, t his way providing maximum dat a t ransmission. The
AGP bus is an expanded and improved version of t he PCI bus - used for video cards only.
Modern video cards made for 3D gaming use expensive high- end RAM t o secure a sufficient bandwidt h. I f you
for example want t o see a game in a resolut ion of 1280 x 1024 at 80 Hz, you may need t o move 400 MB of
dat a each second - t hat is quit e a lot . The calculat ion goes like t his:
1280 X 1024 pixels x 32 bit ( color dept h) x 80 = 419, 430, 400 byt es = 409, 600 kilobyt es = 400 megabyt es.
Cards and chips
Top
There are many manufact urers of video cards and accelerat or chips. Some produce bot h cards and chips, while
ot hers only make one or t he ot her. I have t ried a lot of different cards. The t ables below illust rat e my personal
evaluat ion. Some may disagree wit h my evaluat ion.
First t he best known video cards:
Vendor Qualit y and price
ATI High - Medium
Cirrus Logic Low
Mat rox High - Medium
NVidia High - Medium
S3 Medium
Here we see video card manufact urers:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7b2.htm (2 of 4)7/27/2004 4:06:39 AM
An illustrated Guide to the Video Cards
Vendor Qualit y and price
ATI Medium - High
Diamond Medium ( High)
Mat rox High
Creat ive Labs Medium ( High)
Orchid Medium ( High)
STB Medium - High
Brit ek/ Viewt op Low
You can use t hese t ables, when you buy a PC and/ or video card. Make sure t o st art wit h a qualit y video card!
The driver almost the most important part
Top
The difference bet ween good and mediocre cards is clearly visible in t heir soft ware. The companies ATI ,
Mat rox, and Creat ive Labs deliver excellent drivers wit h t heir cards. They allow t heir cards t o provide opt imum
screen performance.
I n cont rast I can ment ion t he ET 6000 accelerat or chip, which was int roduced in t he mid 1990s. I t had very
fine specificat ions and scored very high in various t est s. I bought a couple of cards wit h t hat chip, but I could
never get t hem t o work properly. The driver programs are poorly writ t en, for example t he refresh rat e is not
adj ust able. Such cards are all right for low qualit y monit ors, but not for monit ors wit h high specificat ions. For
t hese t he refresh rat e should be adj ust able.
Here you see a sect ion of a Mat rox video card cont rol box. The driver knows precisely which refresh rat es t he
monit or will t olerat e at different resolut ions:
Anot her problem area is in t he screen font s, which come wit h t he driver programs. Screen font s are models for
t he let t ers seen on t he screen. There are significant qualit y variat ions in t his area. Again, ATI and Mat rox are
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7b2.htm (3 of 4)7/27/2004 4:06:39 AM
An illustrated Guide to the Video Cards
wort h ment ioning.
q Next page
q Previous page
To learn more
Top
Read about video basics in Module 7a.
Read about sound cards in Module 7c .
Read about digit al sound and music in Module 7d .
Read about FPU work in 3D graphics.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7b2.htm (4 of 4)7/27/2004 4:06:39 AM
An illustrated Guide to the Video Cards
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 7b.3
The video card (continued)
The cont ent s:
q Video cards and chips, different brands
q Choosing t he right video card is hard
q Spend your money well . .
q Next page
q Previous page
Video cards and chips, different brands
Let me comment on a couple of brands:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7b3.htm (1 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:41 AM
An illustrated Guide to the Video Cards
The Canadian firm ATI was among t he first t o produce accelerat ed video cards, when t he
graphic milieus came on board in t he early ninet ies wit h Windows . One of t he company' s first
chip was called mach 8. That had an 8 bit graphic processor, which was ext remely fast
relat ive t o ot hers at t he t ime. But t hey were ext remely expensive. I bought one!
Lat er, ATI present ed mach 32 and mach 64, which were 32 bit and 64 bit graphic processors,
respect ively. The next accelerat or chip was called ATI Rage 128. I t worked wit h a 128 bit bus
connect ing t he onboard RAM and t he processor and it holds a new t ype of cache as well.
Lat er t he RADEON chip was t he t op model. All t he way, ATI has produced solid video cards
wit h good qualit y drivers. Today t hey are available in many price ranges, including low cost
edit ions. You will never go wrong wit h an ATI card ( some gamers may not agree . . . ) .
Matrox
The Mat rox company is also Canadian, founded in 1976. They make excellent cards wit h t heir
own accelerat or chips. They only make a few models. Regardless of which Mat rox card you
buy, it is an excellent product . Mat rox comes wit h good drivers. Obviously t o be
recommended. Mat rox Myst ique 220 and Millennium I I as well as G400 were excellent cards I
personally have been very sat isfied wit h.
The Mat rox Millennium G200 wit h it s 128- bit DualBus delivers high end 2D, 3D and video
performance. You find it in cards like Mat rox Millennium and Marvel ( including port s and
soft ware for Video edit ing) . Great cards for office use!
The G400 ( sixt h generat ion of t heir graphics cont rollers) support s AGP 1X, 2X, and 4X. I t has
a dual 128 bit bus bet ween t he chip and t he RAM allowing simult anously reading and writ ing.
G400 has hardware- accelerat ed Environment Bump Mapping ( ! ?! ) , which t oget her wit h
newest versions of Direct X should give a bet t er dept h perspect ive on screen. And G450 is
even improved.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7b3.htm (2 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:41 AM
An illustrated Guide to the Video Cards
Tseng has made graphic chips for many years. I n t he good old DOS days, an ET 4000 card
was one of t he best on t he market . I t was equipped wit h Tseng' s ET 4000 chip, which was
excellent for DOS usage. Since t hen came t he somewhat overlooked ET4000/ W32 chip. I had
good experiences wit h t hat on some low cost ViewTop cards. Tseng' s lat est chip was ET 6000,
which most ly sold in t he cheapest cards.
S3 was big name in graphic chips. They did not manufact ure t heir own cards, but t heir chips
are used in numerous cards. Companies like I BM, Diamond, Number Nine, and ViewTop/
Brit ek use S3s different accelerat or chips wit h widely varying result s.
A small S3 Trio 64 chip was mount ed in an old I BMs PC 300. On paper, t he cont roller is not
very powerful. Yet , it produced a very fine image. Thus, t he qualit y depends j ust as much on
ot her video card design feat ures as on t he accelerat or chip.
Choosing the right video card is hard
I t is difficult t o choose a video card, because t here is such a mult it ude of different ones. And
you can read t est report s forever. Yet , t hey may not be part icularly useful.
One of t he best cards I ever laid my hands on was I BM' s XGA graphics, which unfort unat ely
was never available separat ely. Once t hey provided a working Windows driver, t his card was
in a class by it self. This was back in t he early 1990s, where poor graphics was a big problem
on PCs. Today most graphic cont rolling chip set s work fine.
One of t he problems wit h video cards was t hat t he same graphics chip may be used in bot h
good and inferior video cards. This is especially t rue for S3 chips, which were used in fine
cards from t he vendor Number Nine and also was used in ViewTops discount cards. When a
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7b3.htm (3 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:41 AM
An illustrated Guide to the Video Cards
fundament ally good chip is found bot h in great and in mediocre cards, you cannot select t he
card based on what chip it uses!
Anot her problem was in t he t est met hods, which t he comput er magazines use. They measure
exclusively speed . Speeds are measured wit h special programs, which read how fast t he
screen image can be built , et c. That ' s fine but it does not say much about image qualit y, as
perceived by t he eye. I s it sharp, bright , not flickering, comfort able? Those are more
subj ect ive and abst ract qualit ies, which can never be evaluat ed by a t est program.
You should choose a card based on it s specificat ions. For example, can it deliver a 1024 x
768 image at 85 Hz? I t should be able t o do t hat , but not j ust in t heory. I t must also be able
t o do t hat in real life. Here is where t he driver comes in.
Spend your money well
Top
When you read all t hese t echnical explanat ions, t he choosing and buying remains. I n my
mind, t he screen image is wit hout doubt ext remely import ant for your daily work. I t is also
an area wit h vast qualit y variat ions.
Oft en PCs have been advert ised wit h a very cheap monit or and t he very cheapest video card.
Many would be happy wit h t his equipment . The PC works fine and t hey may never have seen
a high qualit y screen image.
I will st rongly recommend t hat you invest a lit t le more, t o get a bet t er video syst em.
Specifically I would recommend a 15" or 17" LCD display or a 19" Trinit ron monit or. I t lat er
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7b3.htm (4 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:41 AM
An illustrated Guide to the Video Cards
could be a Mag or ViewSonic. Bot h make excellent Trinit ron screens at reasonable prices.
Combine t he monit or wit h an ATI or maybe Mat rox video card and you will have a good video
syst em!
However, t o make a good and last ing purchase, you have t o underst and your own video
demands. Do you need:
q Office programs wit h 2D graphics?
q 3D games?
q DVD accelerat ion?
q DVI int erface?
You should get a demonst rat ion of t he card and monit or you want t o buy. Especially if it is in
t he low/ medium price group, I will st rongly recommend t hat you see it connect ed. Then
evaluat e t he screen image. How sharp is it ? Does it flicker? Ask about resolut ion, color dept h
and refresh rat e. I f t he dealer cannot answer t hese quest ions, I would not t rust him. Finally,
find out which driver t he card needs. Read on. . .
q Next page
q Previous page
To learn more
Top
Read about video basics in Module 7a
Read about sound cards in Module 7c
Read about digit al sound and music in Module 7d
Read about FPU work in 3D graphics
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7b3.htm (5 of 5)7/27/2004 4:06:41 AM
An illustrated Guide to the Video Cards
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 7b.4
The video card (continued)
The cont ent s:
q 3D graphics
q 3D accelerat ed graphics cards
q I nt el Combinat ion 2D/ 3D graphic chip set s
q The fusion of graphics cont roller and mot herboard chip set s?
q Next page
q Previous page
3D graphics
3D images, where you can move around in space, is a
t echnology, which is expanding t o t he PC world.
Ordinary PCs t oday are so powerful, t hat t hey can
act ually work wit h 3D environment s. Ordinarily, our
screen images ( such as in Windows 95/ 98) are t wo-
dimensional. But we know 3D effect s from movies and
from some comput er games.
Over t he last few years, more and more 3D st andards
have arrived in t he PC market . That includes:
Top
VRML
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7b4.htm (1 of 6)7/27/2004 4:06:49 AM
An illustrated Guide to the Video Cards
A "language" which provides 3D space on t he I nt ernet .
DirectX 3D API
A Microsoft API which enables programming of 3D games for Windows 95/ 98. This API is
especially used for flight simulat ors and racing games.
OpenGL
This is anot her API for 3D developers. OpenGL is needed for 3D- act ion games like Quake,
Unreal et c.
For games, like Quake and ot hers, it is ext remely import ant t hat t he accelerat or card has
drivers for bot h Direct X and OpenGL.
No office use
The 3D t echnologies are of no consequence for ordinary office programs. Act ually, t he
ordinary video cards are opt imized t o show 2D images. 2D cards can const ruct 3D
movement s, but it will t ake t ime t o bring t he images t o t he screen. That is because of t he
very complex calculat ions needed. Therefore, hardware accelerat ors have been designed.
They can give drast ic improvement s. Also, special funct ions are included in t he video card
chip, allowing it t o calculat e 3D movement s light ning fast .
But many 2D video cont rollers, like Mat rox G200, G400, and G450, I nt el i752, S3 Savage3D
and ATI Radeon, also have 3D accelerat ors built in - some of t hem very powerfull.
3D accelerated graphics cards
Top
All ordinary graphics cards can show 3D games. That is really no special t rick. The problem is
t o present t hem smoot hly and fast . I f t he PCs video card is made for 2D execut ion only, t he
CPU must do t he ent ire workload of geomet ric t ransformat ions et c. ! And t hat t ask can cause
even t he fast est CPU t o walk wit h a limp.
When we t alk about accelerat ing 3D programs, we are primarily t alking about games. The
t hree- dimensional games like Forsaken, Bat t lezone and Quake are very demanding for t he PC
t o execut e. The users want t o see t he games wit h good det ails in a large screen window and
wit h as many FPS ( Frames Per Second) as possible. See a descript ion of t he geomet ric
t ransformat ions which occur in a 3D environment .
I n recent years t here has been an enormous development in 3D graphics cards. Let me
briefly describe t hose here. Originally t here were t wo t ypes of graphics cards, which could be
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7b4.htm (2 of 6)7/27/2004 4:06:49 AM
An illustrated Guide to the Video Cards
used for 3D accelerat ion:
q Combinat ion 2D/ 3D cards. These are ordinary graphics cards, which have been equipped
wit h ext ra 3D power.
q The pure 3D cards, which only work as accelerat ors.
The pure 3D cards required t hat t here also is an ordinary ( 2D) graphics card in t he PC. I n
beginning t he pure 3D card yielded t he best accelerat ion, but t here soon came good
combinat ion cards int o t he market .
The real 3D card
The 3Dfx company has set t he st andard for 3D execut ion wit h t heir Voodoo accelerat or chips.
The first version was launched in 1997 and it set t he st andard for 3D accelerat ion.
The Voodoo
2
accelerat or chip came in 1998 at also became an enormous success. This card
cannot display 2D- images, so it needed t o be inst alled in combinat ion wit h an ordinary
graphics card.
The Voodoo
2
cards are special in t hat t hey do not use AGP. Many t hink t hat t his is a big flaw
in t he archit ect ure. At least t his means t hat you cannot show 32 bit color dept h ( which is 24
bit colors wit h 8 addit ional bit s for t ransparency) . However, t he difference bet ween 24 bit and
32 bit colors is not always visible - according t o expert s . . . Bundling t wo parallel Voodoo
2
cards, each wit h 12 MB RAM, working in t andem ( called SLI mode) in t he same PC, yielded
lot s of power. That gave 3D games in a resolut ion of 1024X768 in 60 FPS.
The Voodoo
2
cont roller operat ed at 95 MHz and was produced using 0. 35 micron t echnology.
I t was a chip set of t hree cont rollers ( one pixel processor and t wo t ext ure processors) .
The Voodoo
3
The lat er Voodoo
3
cont roller operat ed at up t o 183 MHz and was produced using 0. 25 micron
t echnology. I t only support ed AGP 2X, which gave a great disappoint ment wit hin t he press.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7b4.htm (3 of 6)7/27/2004 4:06:49 AM
An illustrated Guide to the Video Cards
The Voodoo
3
RAMDAC operat es at up t o 350 MHz.
Intel Combination 2D/3D graphic chip sets
Top
To relieve t he CPU, you can add cert ain 3D accelerat or charact erist ics t o t he chip on t he
graphics card. Many companies have done t hat in recent years; of t hem I nt el are int erst ing.
Intel's i740
Back in 1997 I nt el t eamed up wit h a company called Real 3D t o produce a new graphics chip.
The i740 chip was const ruct ed t o give maximum performance wit hin t wo demanding areas:
q 3D scenes
q Video playback
The processor allows parallel dat a processing and gives precise pixel int erpolat ion. Using
AGP, an i740 based cont roller will be able t o process very large amount s of dat a at a high
speed.
The i740 board works as a "normal" video card as well as 3D accelerat or. However, it never
became very popular and t oday it is out dat ed.
i752
The chip i752 ( code named "Port ola") is t he new generat ion 2D/ 3D graphics cont roller from
I nt el. I t should be 5 t imes bet t er t han t he i740. I t includes 2D graphics, 3D rendering and
digit al video accelerat ion. The i752 also feat ures AGP 2X.
According t o I nt el t he power of t he 752 set is found in:
The 3D visual qualit y being enhanced using I nt els new HyperPipelined 3D archit ect ure. The
Pixel Precise Engine includes new feat ures as a 16 t ap anisot ropic filt er, emboss bump
mapping, t ext ure compression, and t ext ure composit ing.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7b4.htm (4 of 6)7/27/2004 4:06:49 AM
An illustrated Guide to the Video Cards
Enhanced digit al video st reams from a wide variet y of input sources: VCR, camcorder, TV
t uner, MPEG- 2, and Web video st reams. Soft ware DVD is accelerat ed t hrough a high-
precision hardware- based mot ion compensat ion algorit hm.
A 128- bit 2D engine and support for high- resolut ion flat panels.
You find t he 752 graphics cont roller int egrat ed in t he I nt el chip set 810.
i754
The chip i754 ( code named "Port ola") is t he next generat ion of t his Graphics chipset ,
feat uring AGP4X.
A lat er high- end version is code named Capit ola.
The fusion of graphics controller and
motherboard chip sets? Top
Wit h t he more int ense focus on 3D graphics performance and development , it has come t o
many changes in t he indust ry t he recent years.
q I n t he summer 1999, chip manufact ure S3 fusioned wit h card and mult imedia manufact ure
Diamond.
q The chip manufact ure 3dfx fusioned wit h t he card manufact ure STB Syst ems. Hence no
ot her company will have t he Voodoo chips for card product ion.
There seems t o a t rend in all t his. The t radit ional business of graphics chips have t o re-
arrange t o survive. Many vendors want t o int egrat e t he graphics cont roller wit h ot her
processors on t he mot herboard.
Perhaps it all st art ed, when I nt el made t heir first own graphics cont roller, t he ill- fait ed i740.
Here I nt el made an at t empt t o move int o a new product ional area, and t his must have
caused some worry among t he producers of graphics cont rollers. On t he ot her hand,
int egrat ion of a graphics cont rollers wit h t he CPU or t he chip set is a logical t hought . This
disadvant ege is t he reduced flexibilit y; you cannot choose t he graphics cont roller yourself
since it is a part of t he mot herboard. The advant age is of course t he reduct ion in price.
We have seen t hese act ions support ing t he t rend:
q I nt el' s focus on t he chip set s i810 and i815 which include graphics engines.
q I n June 1999 Chip set producer SiS came wit h t he 630 chip set for Celerons and t he similar
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7b4.htm (5 of 6)7/27/2004 4:06:49 AM
An illustrated Guide to the Video Cards
SiS540 for AMD K6- I I I . These set s hold 2D/ 3D graphics engines as well as a lot of ot her
feat ures - all in j ust one chip.
q On April 11, 2000 t he company S3 announced t hat t hey had agreed t o t ransfer it s PC
graphics chip business t o t he successfull Taiwanese chip set producer VI A
q ATI ' s has also announced, t hat t hey are devoloping full chip set s int egrat ed wit h t heir own
graphics cont rollers. We have not seen t hem. ATI and Mat rox seems t o survive in t he market
by delivering high- end graphic chip set s wit hout get t ing involved wit h t he mot herboard
manufact ures. NVidia lives t hem same way serving t he market for game PCs.
q Next page
q Previous page
To learn more
Top
Read about video basics in Module 7a
Read about sound cards in Module 7c
Read about digit al sound and music in Module 7d
Read about FPU work in 3D graphics
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7b4.htm (6 of 6)7/27/2004 4:06:49 AM
An illustrated Guide to the Video Cards
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 7b.5
The video card (continued)
The cont ent s:
q About t he Windows driver
q About DDC
q About Quickres ( a smart ut ilit y)
q Next page
q Previous page
The screen image and Windows
Top
Once you buy bot h a good monit or and video card, you have t o make t hem work t oget her. That is done in Windows
t hrough driver programs. That part of t he inst allat ion is ext remely import ant , it requires at t ent ion.
I f you leave it t o Windows t o inst all t he necessary drivers, t he result may be mediocre. Windows is so smart , so along
t he road it will find your hardware. And Windows will inst all drivers, when it encount ers new soft ware. Oft en some
st andard drivers are inst alled . They will make t he soft ware work, but no more.
The Windows drivers link video card and monit or t oget her, and make t hem cooperat e wit h each ot her.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7b5.htm (1 of 9)7/27/2004 4:06:54 AM
An illustrated Guide to the Video Cards
Checking the drivers
I f you care about your screen image, you must make sure you have t he correct drivers inst alled. We are t alking about
t wo drivers:
q Driver for t he video card ( t he most import ant ) .
q Driver for t he monit or ( less import ant ) .
Bot h can be found in Windows, in My Comput er - > Cont rol Panel - > Display:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7b5.htm (2 of 9)7/27/2004 4:06:54 AM
An illustrated Guide to the Video Cards
You should choose Set t ings and click on Advanced:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7b5.htm (3 of 9)7/27/2004 4:06:54 AM
An illustrated Guide to the Video Cards
I t opens a box, which t he graphics driver may alt er. Here you see my current set t ings. The ATI Radeon cont roller has
ist alled it s own set t ings. The first five t abs are st andard ones, but ATI has added six new t abs:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7b5.htm (4 of 9)7/27/2004 4:06:54 AM
An illustrated Guide to the Video Cards
I f you check t he t abs Adapt er and Monit or, you should find t he names of your hardware and find t he opt imal drivers
are inst alled. This allows Windows t o get a full pict ure of t he video syst em. Then t he video card can deliver t he
opt imal signals t o t he screen.
I once dest royed a 17" monit or by changing t he video card. I adj ust ed t he new card t o deliver precisely t he maximum
abilit y of t he monit or - according t o t he specificat ions. However, t he monit or was a few years old. I t had always run at
a lower resolut ion and refresh rat e, t o which it must have adj ust ed it self. I t did not work out - t he elect ronics burned
out !
Adjusting the refresh rate
The st andard driver in Windows oft en cannot adj ust refresh rat es. You can check it on t he t ab Monit or:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7b5.htm (5 of 9)7/27/2004 4:06:54 AM
An illustrated Guide to the Video Cards
Oft en, a new driver has t o be inst alled t o exercise t his opt ion. Here is a Mat rox Millennium I I video card, wit h it s own
dialog boxes inst alled:
And here are t he set t ings from my not ebook, which has an adj ust able Cirrus Logic video chip:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7b5.htm (6 of 9)7/27/2004 4:06:54 AM
An illustrated Guide to the Video Cards
You need t o inst all a driver program, which works specifically wit h your video card. Ot herwise, you are guarant eed not
t o ut ilize your video card efficient ly. Very few dealers seem t o underst and t his concept . Nearly all PCs are sold wit h
Windows st andard driver inst alled and t he video syst em will render absolut e minimum performance!
DDC
Top
VESA DDC ( Display Dat a Channel) are t echnologies, which should allow t he video syst em t o find t he opt imum
adj ust ment , t hrough communicat ions wit h t he video card. I do not t hink it is quit e working yet .
QuickRes
I f you want t o experiment wit h different screen resolut ions, you can inst all t his program: QuickRes. exe. I t is a small
Windows ut ilit y applicat ion ( only found in some versions of Windows) , which you t hen have t o run ( double click on it ) .
Then, t he program will appear as a small icon in t he lower right corner of your screen ( in t he Syst ray) :
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7b5.htm (7 of 9)7/27/2004 4:06:54 AM
An illustrated Guide to the Video Cards
When you right click on t he icon, a menu will open showing all t he resolut ions
and color dept hs you can choose from on your PC:
Here you can see, t hat t he resolut ions on my PC go from 640 x 480 up t o 1600
x 1200. Color dept h goes from 8 bit ( 256 colors) t o 32 bit .
Not e t hat t he maximum color dept h at 1600 x 1200 resolut ion is 16 bit and at
1280 x 1024 it is 24 bit .
Only t he 1152 x 864 resolut ion can be seen in full 32 bit colors. This limit at ion
is because t his video card only has 4 MB RAM inst alled.
QuickRes is smart , because you can change resolut ion "on t he fly". Normally
Windows has t o be re st art ed, but here, t he screen image j ust blinks a couple
of seconds, t hen t he new resolut ion is in place.
I n some versions of Windows, you may inst all Quickres from t he screen
propert ies box, Set t ins, Advanced. Choose as here ( Danish dump - I am
sorry) :
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7b5.htm (8 of 9)7/27/2004 4:06:54 AM
An illustrated Guide to the Video Cards
Aft er clicking OK t he lit t le icon is in t he Syst ray.
q Next page
q Previous page
To learn more
Top
Read about video basics in Module 7a.
Read about digit al sound and music in Module 7d .
Read about FPU work in 3D graphics.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7b5.htm (9 of 9)7/27/2004 4:06:54 AM
A guide to sound cards and digital sound
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 7c1.
PC sound
The cont ent s:
q An int roduct ion
q The synt hesizer
q The A/ D conversion
q Sampling t he Wav files
q Next page
q Previous page
I do not claim t o be an expert in sound cards. But I will t ry t o describe what lit t le I know about t his
t echnology. The sound capabilit ies of t he PC are quit e int erest ing. I n t he lat e 1990s, new and radical
designs in sound t echnology appeared, and at t he same t ime t he MP3 wave swept t he I nt ernet societ y.
On t he first pages we shall describe t he t radit ional sound card concept ( t he Sound Blast er compat ible
sound card) . Then follows somet hing on t he newer t echnologies.
Introduction
[ t op]
Sound cards have a minimum of four t asks. They funct ion as:
q Synt hesizer
q MI DI int erface
q Analog- t o- digit al conversion during t he recording ( A/ D) .
q Digit al- t o- analog conversion during t he playback ( D/ A) . All element s are t o be explained on t hese
pages, so please read on.
The synthesizer
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7c1.htm (1 of 6)7/27/2004 4:06:57 AM
A guide to sound cards and digital sound
The synt hesizer delivers t he sound. That is, t he sound card generat es t he sounds. Here we have t hree
syst ems:
q FM synt hesis, Frequency Modulat ion
q Wave t able
q Physical modeling
FM synthesis
The cheapest sounds card use t he FM t echnology t o generat e sounds simulat ing various inst rument s.
Those are t rue synt hesizers. The sounds are synt het ic it may sound like a piano, but it is not . FM
synt hesis is and sounds like t he art ificial sounds it consist s of.
Wave tables - sampling
Wave t able is t he best and most expensive sound t echnology. This means t hat t he sounds on t he sound
card are recorded from real inst rument s. You record, for example, from a real piano and make a small
sample based on t he recording. This sample is st ored on t he sound card.
When t he music has t o be played, you are act ually list ening t o t hese samples. When t hey are of good
qualit y, t he sound card can produce very impressive sounds, where t he "piano" sounds like a piano.
Wave t able is used in Sound Blast er' s AWE card.
Physical modeling
Physical modeling synt hesis is a t hird sound producing t echnology. I t involves simulat ing sounds
t hrough programming. The process is supposed t o be rat her cumbersome, but it should yield a number
of ot her advant ages. The original Sound Blast er Gold card cont ains 14 inst rument sounds, which are
creat ed from physical models.
Testing the sound
The basic qualit y of a sound card can be t est ed by playing a MI DI file. Then you can easily hear t he
difference. There is also a difference in how many not es ( polyphony) can be played simult aneously. I f
you want t o compose your own music on your PC, you use t he sounds available on your sound card. The
great er works you want t o writ e, t he more "voices" you will need. The SB AWE64 card has 64 voices,
while SB16 only has 20 voices.
Some sound cards can import new sounds. They are simply downloaded t o t he sound card, which might
have 512 KB ( Sound Blast er AWE64) or 4 MB RAM ( Sound Blast er AWE64 Gold) available for t he user' s
own sounds.
The A/D conversion
[ t op]
You need a A/ D conversion, when analog sound signals are recorded, i. e. from a microphone. The ot her
way around, t he D/ A- convert er is used when t he digit al sounds have t o be reproduced int o a signal for
t he speakers amplifier.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7c1.htm (2 of 6)7/27/2004 4:06:57 AM
A guide to sound cards and digital sound
The acoust ic waves are collect ed by t he microphone and lead t o t he sound card. Here it is convert ed
int o series of digit al pulses, which event ually are saved in a file. This way a sampling is an analog- t o-
digit al conversion:
During t he playback, t he bit st ream from t he sample file is convert ed t o analog signals, which end in t he
loudspeaker.
When you connect a microphone t o t he sound card, you can easily record your own voice on t he PC. The
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7c1.htm (3 of 6)7/27/2004 4:06:57 AM
A guide to sound cards and digital sound
result is a small WAVE file which holds a digit al recording of t he sound, which reached t he microphone.
The sound of your voice is analog, but t he result ing t he file is digit al. The t ransformat ion from analog
signals t o digit al dat a is done in t he A/ D convert er of t he sound card.
About sampling
As ment ioned is t he basic concept of digit al recording of sound is called sampling. You can record any
sound you want int o a sample ( a Wav file) if you have a sound card and a microphone. The sampling
can be done in various qualit ies:
q 8 bit or 16 bit sampling
q 11, 22 or 44 KHz ( kilohert z)
q St ereo or mono
The number of kilohert z t ells how many t housand t imes per second t he sound will be recorded.
The quality of the sample
A sample is like a t ape recording - it can be good or less good. The recording range from low end, as
recorded on t he cheapest casset t e recorder, t o hi- fi recordings in CD qualit y. Here is an image from my
set up, where I can choose bet ween different qualit ies for recording:
You record by sampling many t imes per second. The more frequent ly it is done, t he bet t er qualit y we
get . The best would be infinit ely sampling, which is not possible.
To record audio CDs t he sampling is execut ed 44, 100 t imes per second. This we call a 44. 1 KHz
sampling.
The qualit y is measured in kilohert z ( KHz) and resolut ion ( bit widt h) as you see above. The higher t he
KHz is, t he bet t er becomes t he qualit y of t he WAV file, but it also becomes bigger in file size. 8 or 16 bit
sampling refers t o how much dat a we spent on each sample. 16 bit gives a good qualit y.
File sizes
Using 2 channels st ereo and 16 bit sampling at 44. 1 KHz, t he bit st ream can be calculat ed as t his:
2 channels X 16 bit X 44, 100 samples per second = 176, 400 byt es per second ( since 8 bit s make one
byt e) .
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7c1.htm (4 of 6)7/27/2004 4:06:57 AM
A guide to sound cards and digital sound
This gives us t he following file sizes of sampled st ereo music in CD qualit y:
Replay Number of
byt es
One minut e 10 MB
One hour 605 MB
74 Minut es 746 MB
Here you see t he set t ings in a Wave program:
St ereo sampling at 16 bit and 44 KHz gives t he best qualit y, but t he Wave files will t ake up quit e a bit
more space.
The Wav files
[ t op]
I f you look down in your PC, you will find plent y of Wav files. I did a lit t le search, and t his showed up:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7c1.htm (5 of 6)7/27/2004 4:06:57 AM
A guide to sound cards and digital sound
All t hese Wav files cont ain sounds in a digit al form - samples. They only cont ain very few seconds of
sound, because of t he file size, which must not grow t oo big.
A Wav file will sound t he same no mat t er which sound card you may have, be it a sound card using FM
Synt hesis or Wave t able. The sound is in t he file and not in t he sound card!
These samples above are used as sound effect s wit hin Windows. Similar samples are used as mat erial
on music CDs and in t he MOD format of digit al music.
AU is anot her file format for samples. MP3 files are highly compressed samples.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Also see: Module 7d - about digit al music: MP3s, MODs et c.
Read about video cards in Module 7b .
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7c1.htm (6 of 6)7/27/2004 4:06:57 AM
A guide to sound cards and digital sound
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 7c2.
PC sound - continued
The cont ent s:
q The sound card - an adapt er
q Newer sound cards
q Next page
q Previous page
The sound card - an adapter
[ t op]
I n t he previous module, we saw t he principles of PC sound. Let us here look at t he sound card, which is an
adapt er card.
The sound card used t o be a I SA card ( using t he old I SA int erface) . Here you see t he original Sound Blast er
AWE64 Gold card:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7c2.htm (1 of 4)7/27/2004 4:06:59 AM
A guide to sound cards and digital sound
The connect ors may look different on different sound cards, but as an example: I n t he back of t he AWE64 Gold
card you find connect ors t o:
q Microphone input , a j ack
q Line input , a j ack
q Two phone j acks for act ive speakers
q A DB15 j ack for MI DI or j oyst ick.
Most sound cards t ypically have a 2 Wat t amplifier built - in. I t can push a set of earphones. An except ion is t he
SB Gold card, where t he amplifier is eliminat ed. I t has no pract ical significance, since you probably want t o
at t ach it t o a pair of act ive speakers.
The new sound cards
[ t op]
For many years PC sound has been t ot ally dominat ed by t he Sound Blast er card. All sound cards had t o be
compat ible wit h Sound Blast er, or it would not sell. Obviously t hat is due t o t he numerous game programs,
which require a SB compat ible sound card.
The new sound cards break away from t he Sound Blast er compat bilit y. This break involves many facet s. Below
I will describe some of t he t endencies in t he sound t echnology.
Sound over the PCI bus
New sound cards use t he PCI bus. The SB compat ibilit y used t o require t he old I SA bus, but t his has been
overcome. Creat ive Labs produce fine PCI - based SoundBlast er cards. Wit h PCI you gain t hese advant ages:
q The I RQ problems disappear.
q Signal/ noise rat io can be improved wit h 5 dB.
q There is sufficient bandwidt h ( capacit y for dat a t ransmission) .
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7c2.htm (2 of 4)7/27/2004 4:06:59 AM
A guide to sound cards and digital sound
q The sound card workload for t he CPU is less.
q We can drop t he I SA bus, which t akes up unnecessary space on t he PC syst em board.
The problem in moving t he sound t o t he PCI bus involved t he exist ing soft ware. First of all t he old DOS games,
which expect ed and demanded t he Sound Blast er card wit h it s well- known I RQ- and DMA numbers. The games
did not work wit h t he new cards, unless special solut ions were implement ed. However, t he impact of t his
problem is gone. No more I SA- based sound cards are in product ion, and all games use t he new st andards for
Windows sound.
Onboard sound chips
Many mot herboard include sound card funct ions. This is i fine t hing, if you only need sound for ordinary use.
The qualit y is not as good as t he sound from a $80- $100 sound card, but for many users it is fine!
On- board audio is found wit hin some chip set s. For inst ance you find it in t he much used VI A KT133 chip set
for AMD processors. Here t he VT82C686B sout h bridge I / O- cont roller holds built - in AC97 digit al audio
funct ions:
A Windows report on t his:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7c2.htm (3 of 4)7/27/2004 4:06:59 AM
A guide to sound cards and digital sound
Onboard sound chips is an in- expensive an simple via t o incorporat e sound facilit ies in your PC.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read Module 6a about file syst ems
Read about chip set s on t he mot herboard in module 2d
Read Module 4d about super disket t e and MO drives
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side
Read module 5b about AGP
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card
Also see: Module 7d - about digit al music: MP3s, MODs et c.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7c2.htm (4 of 4)7/27/2004 4:06:59 AM
A guide to sound cards and digital sound
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 7c3.
PC sound - continued
The cont ent s:
q 3D sound
q Next page
q Previous page
3D sound
[ t op]
3D sound is a new hot area. You can creat e a very powerful illusion of 3D sound coming from j ust
loudspeaker. This is done using new 3D processors on t he sound card, which work wit h some very
complex mat hemat ical models. The sound comes from behind, from t he front , from side t o side -
complet ely realist ic.
The idea of 3D sound has t o come from games, which especially are designed for it . The sound syst ems
oft en include 4 or 6 loudspeakers. But t hey work fine wit h headphones t oo.
Sound Blast er Live is such a high- end, high fidelit y 3D card coming from Creat ive Labs. I t is a PCI - based
card, and t he best performance comes wit h t he Four Point Surround sound syst em. Diamond MX300 is
anot her.
SB Live!
The SoundBlast er t op model sound card is called SoundBlast er Live!
I t includes a lot of fine and powerful feat ures:
q EMU10K1 accelerat or chip
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7c3.htm (1 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:01 AM
A guide to sound cards and digital sound
q Connect ions for four speakers.
q Digit al DI N plug, which can be used for fut ure high- end sound syst ems like Dolby ProLogic.
q SP/ DI F digit al phone plug, which can be connect ed t o unit s such as DVD drives, DAT or MiniDisc for
direct digit al input .
q Plug for digit al MPEG signal.
The EMU10K1 is as powerful as a Pent ium 166 MHz CPU. I t is an accelerat or chip which relieves t he PCs
CPU when execut ing sound, such as Direct X act ivit ies t hat require a lot of processor power.
Creat ive Labs SoundBlast er Live is a phenomenal piece of hardware:
3D sound - better than stereo
I n t he 1950s st ereo was invent ed. The music is recorded using t wo channels - a left and a right channel.
Since t hen t he aim has been t o expand t he sound int o 3 dimensions.
This is possible. Only using t wo speakers you can creat e an illusion of "room". Many new sound cards
are capable of giving 3D sound effect s ( i. e. Virt ual Dolby) . This way games can achieve even more
realist ic sound.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7c3.htm (2 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:01 AM
A guide to sound cards and digital sound
Diamond MX300 is a 3D sound card. I t is const ruct ed using accelerat or chips from Aureal ( Vort ex 2 and
A3D ver. 2. 0) . The first sound chip from Aureal was very revolut ionary t o 3D sound performance. I t has
been used by many vendors ( such as Compaq) . I n 1999 t he next generat ion chip was shipping.
The Diamond card was very well received. I t should be j ust as good as t he SoundBlast er Live! product ,
which has been in a class by it self since t he int roduct ion in 1998.
SoundBlast er Live works wit h an open st andard for 3D sound called EAX ( Environment al Audio
Ext ensions) . The MX300 card is compat ible wit h t his as well as wit h t he Microsoft ' s st andard for 3D
sound.
3D environmental sound
The 3D sound card gives t he list ener an illusion of being in a landscape, where t he sounds come from
t he front and t he back. Sounds coming from up and down are difficult t o reproduce.
The illusion is best when you use a four- set speaker syst em as SoundBlast er PC Works, which gives a
very high qualit y at a modest price.
3D sound is also possible using only t wo speakers. The MX300 should be very good at t his. The spacious
sound is creat ed using advanced mat hemat ical manipulat ions, which need a good port ion of CPU power.
Hence t he accelerat or chip. This is called 3D Posit ional Sound. The best result should be achieved using
headphones.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7c3.htm (3 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:01 AM
A guide to sound cards and digital sound
Anot her 3D effect is called Environment al Sound. Here t he sound from a game is changed corresponding
t o t he physical sit uat ion of t he charact ers. I f a person ent ers a t unnel, t here may be an echo. I n a big
empt y hall t he sound is complet ely different . This way t he games can send commands t o t he sound
card, which adj ust t he feeling of t he sound t o t he environment .
q Next page
q Previous page
Learn more
[ t op]
Read Module 6a about file syst ems
Read about chip set s on t he mot herboard in module 2d
Read Module 4d about super disket t e and MO drives
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side
Read module 5b about AGP
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card
Also see: Module 7d - about digit al music: MP3s, MODs et c.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7c3.htm (4 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:01 AM
A guide to sound cards and digital sound
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 7c4.
PC sound - continued
The cont ent s:
q USB sound
q Next page
q Previous page
Sound over the USB bus
You may experience very high qualit y sound syst ems using t he USB bus.
The difference is t hat t here is no sound card in t he PC. You connect t he speakers t o a USB
port inst ead of using t he sound card.
Using t his syst em, t he sound signals are in digit al form right coming from t he harddisk or
whereever, and t hey st ay in t his form when t hey are sent out on t he USB channel and int o
t he speakers:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7c4.htm (1 of 3)7/27/2004 4:07:03 AM
A guide to sound cards and digital sound
Less noise
I nside t he PC t here is a lot of elect ric ( st at ic) int erference from many sources. That can affect
t he int egrit y of t he signals in t he sound module.
Wit h USB t he noise sensit ive digit al/ analog conversion will t ake place in t he speaker, and t his
result s in a superior qualit y. Bot h Philips and Alt ec Lansing produce USB speakers.
More CPU work
Wit h USB sound you leave all t he sound processing t o t he CPU. This "cost s" some CPU power;
however, modern CPUs are so powerful, t hat t his is OK.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7c4.htm (2 of 3)7/27/2004 4:07:03 AM
A guide to sound cards and digital sound
You find high fidelit y loudspeakers wit h built - in amplifier and convert er, which can receive
pure digit al signals ( via USB) . One could hope, t hat t hese speakers will be able t o int erpret
dat a from hi- fi equipment , PC, TV/ video and ot her sources. See t he descript ion of some of
t he finest speakers I ever have heard: A set ofPhilips USB speakers.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Also see: Module 7d - about digit al music: MP3s, MODs et c.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7c4.htm (3 of 3)7/27/2004 4:07:03 AM
A guide to sound cards and digital sound
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 7c5.
PC sound - continued
The cont ent s:
q DOS or Direct X
q Next page
q Previous page
DOS or DirectX
[ t op]
When so many games used t o be DOS based, it primarily was because of t he sound. Under
DOS t he programmer can modify and manipulat e t he sound card t o a very high ext ent . I t can
be cont rolled very precisely, sounds can be mixed wit hout int errupt ion, and all kinds of
effect s can be designed. Here DOS proves very effect ive - t he operat ing syst em permit s
direct cont rol of t he hardware.
The disadvant age wit h DOS sound is, t hat t he hardware must be t ot ally st andardized. This
gave t he Sound Blast er card it s great success.
Windows
I n Windows all program inst ruct ions t o hardware are execut ed t hrough a programming layer
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7c5.htm (1 of 3)7/27/2004 4:07:04 AM
A guide to sound cards and digital sound
( API ) .
The first mult imedia API would not allow mixing of sounds. Therefore t he music in t he
Windows- based game had t o be cut off, if t here was a need for playing such a t hing as t he
sound of an explosion. This put heavy rest raint s on programming creat ivit y. Consequent ly
DOS based game applicat ions remained long int o t he Windows era. But it changed . . .
DirectX
Direct X is a set of mult imedia API s ( applicat ion program int erface ) developed for Windows .
I t is a collect ion of programs which enable much improved low level cont rol over t he
hardware in games and ot her mult imedia applicat ions. Direct X has now reached version 6. 1
and includes:
q Direct Draw
q Direct Sound
q Diect Sound3D
q Direct Play
q Direct I nput
q Direct Set up
These programs are designed t o enable all possible image and sound effect s.
The advant age of Direct X is t hat t he applicat ions can be writ t en direct ly t o Windows and
simult aneously get maximum hardware cont rol. Hence Direct X is very import ant t o hardware
manufact ures. To make sure t hat t he new product s work t oget her wit h all soft ware, t he
drivers have support t he lat est version of Direct X.
Wit h Direct X we should finally have eliminat ed t he need for programs t o rely on Sound
Blast er compat ibilit y.
Direct X comes in new versions every year.
I n version 7. 0 you find improved 3D accelerat ion of sound as well as pict ure wit h reduced
CPU usage. The performance should be increased wit h 20% compared t o version 6. 1.
Windows 2000 was t he first NT- based version of Windows t o include Direct X.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7c5.htm (2 of 3)7/27/2004 4:07:04 AM
A guide to sound cards and digital sound
Also see: Module 7d - about digit al music: MP3s, MODs et c.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7c5.htm (3 of 3)7/27/2004 4:07:04 AM
A guide to digital music #1
KarbosGuide.com. Module 7d1.
About digital music
The cont ent s:
There are quit e a few different kinds of music format s you can
find on t he I nt ernet . A few of t hem are described on t hese pages.
q About t he player
q Next page
q Previous page
About the player
[ t op]
When you have some of t hose files, you need a player ( a plugin) t o replay it on your PC. All
versions of Windows have built - in players for t he Wav and Midi files, so you do not have t o
t hink of t hat . Just double- click on t he file, and t he sound or t une is replayed:
However, t he sound files MP3s and t he MODs are much more int erest ing format s t han Wav
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7d1.htm (1 of 2)7/27/2004 4:07:06 AM
A guide to digital music #1
and Midi. But you need plugins, a lit t le program t o replay t he t unes. These players are freely
available on t he I nt ernet - I ' ll give you t he links lat er.
Some players are only available as plugins t o browsers. This goes for t he Koan st uff. Ot hers
( MP3s and MODs) can be achieved as st and- alone players or plugins.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
q Click for Module 3b about CPU improvement s
Click for Module 3c about t he 5t h generat ions CPUs ( Pent iums et c. )
Click for Module 3d about t he clock frequencies
Click for Module 3e about 6t h generat ions CPUs ( Pent ium I I s et c. )
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7d1.htm (2 of 2)7/27/2004 4:07:06 AM
A guide to digital music #2
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 7d2.
About MIDI and sequencing
The cont ent s:
q MI DI
Next page
Previous page
Introduction
This page is about MI DI composit ions, which are "real" pieces of music, writ t en for playback wit h any
sound card. MI DI is a st andard in Windows, so any PC wit h a sound card can play t hese Midi files.
MI DI ( Musical I nst rument Digit al I nt erface) is a specificat ion, which was developed in t he 1980s t o
communicat e bet ween synt hesizers. Since t hen MI DI has also become a st andard, which allows
programs t o play music t hrough t he PC sound card.
MI DI is a comput er st andard music format . You writ e composit ions - musical event s - in t he MI DI
format . The MI DI files do not cont ain t he sounds but a descript ion of how t he music is t o be played. The
sounds are in your sound card. The MI DI file only cont ains sequencing informat ion - which inst rument it
is played how and when .
For example a MI DI sequence can describe t he hit on a piano key. The MI DI sequence describes:
q The inst rument
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7d2.htm (1 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:08 AM
A guide to digital music #2
q The not e
q The st rengt h of t he key hit
q How long t o maint ain t he not e
q Et c.
The only t hing which is not covered is t he sound of t he inst rument - t hat is creat ed in t he sound card,
and is t ot ally dependent on t he sound card qualit y:
Note level recordings
A MI DI recording is t hus a recording of music on "not e level, " wit hout sound. I t is played by a module,
such as a sound card, which can generat e t he sounds of t he inst rument . MI DI files do not occupy much
space as compared wit h t he pure sound ( WAVE files) . Therefore t hey are oft en used in PCs, on I nt ernet
et c.
You find a lot of MI DI music on t he I nt ernet . However, compared t o MP3s t he format is rat her t ame.
There is rarely more t han a few minut es of music in a MI DI file, and you soon get t ired of t he pieces,
which all sound t he same using t he limit ed number of voices wit hin your sound card.
The advant age of MI DI is t hat t he file format is so st andardized. I f you have a sound card, no mat t er
which, it will work. Depending on t he qualit y of your sound card, a MI DI can sound good or lousy. Cheap
sound cards have a chip on t hem which mimics t he sounds of different inst rument s when you play a
MI DI file. Newer sound cards use a Wave t able chip which cont ains act ual samplings of t he inst rument s.
The MI DI file is st ill limit ed t o t he around 120 inst rument s on t he sound card.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7d2.htm (2 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:08 AM
A guide to digital music #2
MIDI interface for keyboards
[ t op]
A musical keyboard can be connect ed t o t he sound card wit h a connect or. That is called a MI DI
int erface. You can buy special PC musical keyboards, or you can use one of t he keyboards which are
available in music st ores. I t will work as long as t he MI DI connect ors mat ch.
You connect your DI N connect or t o t he piano keyboard. I n t he ot her end of t he cable is a DB15
connect or t o t he sound card. Then you can play from t he piano keyboard t hrough t he sound card. Of
course it requires a program which can handle music, but it works.
I have t ried it myself. The Sound Blast er AWE64 Gold comes wit h t he program Cubasis. Once I
connect ed an old and cheap piano keyboard ( wit h built - in rhyt hm box) t o t he sound card, and
everyt hing worked t hrough Cubasis. The keyboard act ed as a "Local Synt hesizer" in t he program
set t ings.
This keyboard is especially designed for t he PC.
Links
[ t op]
Here is a link t o Anselmo Salzani, who t ries t o creat e excit ing music in t he MI DI format . His page also
includes a lot of ot her int erest ing music links: Brazilian MI DI music.
And a Dane: Anders Kornerups MI DI music
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7d2.htm (3 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:08 AM
A guide to digital music #2
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Click for Module 3b about CPU improvement s
Click for Module 3c about t he 5t h generat ions CPUs ( Pent iums et c. )
Click for Module 3d about t he clock frequencies
Click for Module 3e about 6t h generat ions CPUs ( Pent ium I I s et c. )
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7d2.htm (4 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:08 AM
A guide to digital music #3
KarbosGuide.com. Module 7d3.
MODs - digital music
The cont ent s:
q About MODs
q Links t o t he music and soft ware.
Next page
Previous page
The MODs
MODs anot her very int erest ing format . Originally made for Commodore Amiga comput ers and used for
musical demos by a company t hat sold t he music edit or SoundTracker.
The source code of t his program was cracked and illegal versions came. Today MOD is an int erest ing format
offering more t han four sound channels wit h bot h synt het ic inst rument s and samples int egrat ed.
Modules are digit al music files, made up of a set of samples ( t he inst rument s) and sequencing informat ion.
The file t ells t he mod player when t o play which sample on which t rack at what pit ch, opt ionally performing
an effect like vibrat o, for example.
Thus MODs are different from pure sample files as WAV, which cont ain no sequencing informat ion, and from
MI DI files, which do not include any samples/ inst rument s. MODs are ext remely popular in t he demo world
and offer a way of making music of an accept able level of qualit y rat her cheaply.
Wit h all t he new high qualit y sound hardware new generat ions of musicians may produce a sound qualit y
near t hat of t he professionals.
The technique
MODs' sequencing informat ion is based on "pat t erns" and "t racks". A pat t ern is a group of t racks wit h a
cert ain lengt h, usually 64 "rows". The t racks are independent of each ot her. A four t rack MOD can play four
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7d3.htm (1 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:10 AM
A guide to digital music #3
voices or not es simult aneously. The pat t erns can be repeat ed in a play list reducing t he file size.
The MOD files cont ain t he inst rument s along wit h t hem in t he form of samples. The samples are lit t le WAV
files of one not e on an inst rument , a beat on a drum kit , or perhaps a line of vocals. The MOD composer
decides what samples he includes in t he MOD file. He uses a t racker t o make t he t unes:
This way, t he song will sound t he same when played back on any comput er, because t he sounds as well as
t he sequences are included. Here is a MOD player:
And here I "look behind" one t he t unes above:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7d3.htm (2 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:10 AM
A guide to digital music #3
You can download great music in t he MOD format . The files are named . MOD or . XM. The most incredible is
t he file size. There obviously is a lot of compression in it , oft en you get more t han a minut e high qualit y
replay out of a MOD file of j ust 100 KB.
All you need is a lit t le soft ware:
Links
[ t op]
Visit t his MOD sit e where you find players and ot her MOD st uff.
Also check Great Swedish music in MOD format .
q Next page
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7d3.htm (3 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:10 AM
A guide to digital music #3
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Click for Module 3b about CPU improvement s
Click for Module 3c about t he 5t h generat ions CPUs ( Pent iums et c. )
Click for Module 3d about t he clock frequencies
Click for Module 3e about 6t h generat ions CPUs ( Pent ium I I s et c. )
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7d3.htm (4 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:10 AM
A guide to MP3
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 7d4.
The MP3s are dynamite
The cont ent s:
q I nt roduct ion t o MP3s
q Psychoacust ic algorit hms
q Ripping
q Links
q Next page
q Previous page
Introduction
Since 1998 t he MP3 st andard has become more and more import ant , and an enormous success. The pot ent ial is even bigger -
personally I believe, t hat MP3 end up being as popular as t he Compact Casset t e did in t he 20t h cent ury.
MP3 is a syst em t o give a huge compression of digit al sound files. The compression is lossy ( i. e. musical det ails are cut away) . Yet
MP3 delivers a sound qualit y ( almost ) as good as uncompressed CDs, due t o t he very int elligent psycho- acust ic algorit hm reducing
t he file size.
The MP3 format is very versat ile; it can be host ed on any st orage media and can be t ransferred on demand over t he I nt ernet . You
use a ripper t o encode MP3 files. These files can be played using a player like Winamp, MusicMat ch or Windows Media Player. The
MP3 files can also be decoded an used for CD- recording:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7d4.htm (1 of 9)7/27/2004 4:07:13 AM
A guide to MP3
German research
MP3 means MPEG Audio Layer 3. I t is an audio compression t echnology being a part of t he MPEG- 1 and MPEG- 2 specificat ions. MP3
compresses CD qualit y sound by a fact or of 8- 12, while maint aining almost t he same high- fidelit y sound qualit y.
MP3 is developed by a German research inst it ut e called Frauenhofer. The company Thomson Mult imedia has pat ent ed MP3 in USA
and in Germany.
Effective compressions
Music on CDs have a bandwidt h of 1. 4 Megabit per second. I t is calculat ed as 2 X 16 X 44100 bit / sec. This mean t hat one minut e of
music on a CD t akes up 10 MB of dat a.
Using MP3 t his bit st ream is dramat ically reduced ( by fact or 8 t o 12) . A t ypically MP3 file will need 128 per second. Hence one minut e
of music is reduced from 10 MB dat a t o only 1 MB. Great er compression rat ios are also possible for use on I nt ernet et c. but here you
will encount er a decrease in sound qualit y.
St andard MP3s hold approx. 1 minut es hi- fi music per megabyt e.
This reduct ion is only possible using a set of compressions.
Lossy compression with psychoacustic algorithms
Overall we have t o t ypes of compression:
q Compression wit hout loss
q Lossy compression
I f we want compression wit hout loss, we use syst ems like ZI P. This is very effect ive compression dat a files t hat hold plent y of
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7d4.htm (2 of 9)7/27/2004 4:07:13 AM
A guide to MP3
redundant informat ion. This could be Microsoft Word document s, t hey oft en zip very well. And when you unzip t hem, t he document
is ident ical t o t he original. You find similar compression wit hin GI F and PNG graphics files, which compress many graphic images
very well ( but not phot os) .
However you do not find much redundant informat ion in music files. A zip compression of raw music dat a ( WAV files) may only yield
10% reduct ion in file size. Therefore we use a lossy encoding t o reduce t he music files sizes.
Lossy encoding mean t hat we t ake away music informat ion ( j ust as JPEG encoding t ake away image informat ion from a phot o) . The
goal is t o remove music det ails you would not hear anyway!
Since MP3 offers variable compression you will find t hat t he more you compress t he music, more det ails are removed and lesser
fidelit y is t he result .
Many ways to MP3
The MP3 st andard t ells what design a MP3 file should have. I t does not t ell how t o produce t he file. This indicat es t hat we may
experience quit e different qualit y from different encoders.
The most import ant principle in MP3 compression is t he psychoacust ic select ion of sound signals t o cut away. Those signals, we are
unable t o hear are removed. These include weaker sounds t hat are present but are not heard because t hey are drowned out
( masked) by louder inst rument s/ sounds.
Many encoders use t he fact t hat t he human ear is most sensit ive t o midrange sound frequencies ( 1 t o 4 KHz) . Hence sound dat a
wit hin t his range is left unchanged.
An ot her compression used is t o reduce t he st ereo signal int o mono, when t he sound waves are so deep, t hat t he human ear cannot
regist er t he direct ion. Also t he cont ent s of common informat ion in t he t wo st ereo channels is compressed.
The Huffman algorit hm reduces t he file size by opt imizing t he dat a code for t he most oft en used signals. This is a lossless
compression working wit hin t he MP3 syst em.
Pirating or legal
All over t he I nt ernet you find pirat e copies of commercial music. This is not very good since it is illegal and may st op t he
development of t he t echnology. At www. mp3. com you only find legal music, but t here is lot s of it !
Napster
A great online music communit y was creat ed around downloading and sharing MP3 files. This was Napst er, and it was illegal. You
cannot give away copies of your MP3s t o anyone, unfort unat ely.
Napst er had t o close down several t imes in 2000 and 2001 due t o law suit s from t he music indust ry.
SDMI
Secure Digit al Music I nit iat ive. This st andard was developed by Sony, EMI , and t hree ot her big companies.
I t is a securit y cert ificat ion which can be used on MP3 files and ot her format s. I t should help t o prevent illegal copies of music. Wit h
SDMI a MP3 file can, as an example, be designed so it only can be copied t hree t imes.
SDMI is t o built int o MP3- players as Rio and MP3- man. Here it verifies t he SDMI - sigat ure on MP3 files. However, t he syst em allows
replay of "illegal" MP3s as well.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7d4.htm (3 of 9)7/27/2004 4:07:13 AM
A guide to MP3
The RIO player
I n Oct ober 1998 t he American organizat ion RI AA ( Recording I ndust ry Associat ion of America) t ried t o st op Diamond Mult imedia from
selling t his great lit t le t hing. I t is a MP3Man, j ust like a port able CD player:
Holding t he music in 32 MB of flash memory t he player has no moving part s. Wit hout moving part s, it could play for about 15 hours
on a single alkaline AA bat t ery.
The RI O was a revolut ionary new device. Lat er MP3 decoders have come in many ( bet t er) versions, including mobile phones and
digit al cameras as well. . .
Karbo's Player
My own favorit e device would be a Sony MiniDisc recorder holding MP3 playback soft ware and an int erface t o t he PC. Wit h t he 140
MB MiniDisc you will have a great medium for musical st orage. Of course Sony has t o prot ect t heir music division, but t he MiniDisc
could be so good in t his set up.
The Minidisc uses it ' s own compression algorit hms much similar t o MP3, but in my set up you would be able t o copy t he already-
encoded MP3 files direct ly t o t he Minidisc.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7d4.htm (4 of 9)7/27/2004 4:07:13 AM
A guide to MP3
The device should also connect t o my HI FI st ereo set as well as t o t he cars sound syst em.
Winamp
I use t he lit t le program called Winamp and replay from harddisk t hrough my PC' s loudspeakers:
Microsoft ' s Windows Media Player also plays MP3s. But I t is not as smart as Winamp is.
Microsoft t ried t o "kill" t he MP3 format int roducing t heir own Windows Media Audio ( WMA) format , which is similar t o MP3 but not
compat ible. This at t empt t o incorporat e yet anot her "digit al area" in Windows has failed - not many people prefer WMA t o MP3, and
t his pleases me. Microsoft produces great soft ware, but t hey should not monopolize everyt hing.
A good player should be able t o produce playlist s. A playlist is a lit t le t ext file, which list s a sequence of songs t hat are t o be played
cont inously. The playlist is a file wit h t he ext ension M3U. I t can be edit ed using Not epad et c.
Ripping
To produce MP3s you use a ripper. You load a music CD int o t he CDROM drive. The soft ware finds a CDDB dat abase on t he I nt ernet
and finds t he art ist name and t he t it le of t he disk and each song.
You j ust t ell t he ripper which t racks t o rip, and t he recording st art s. I use MusicMat ch:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7d4.htm (5 of 9)7/27/2004 4:07:13 AM
A guide to MP3
I used t o rip at a const ant bit rat e ( CBR) 128 kbs, which worked fine. Expert s t ell me t hat I should use a variabel bit rat e ( VBR)
set t ing of 75%. I t should produce t he best sound qualit y, using many bit s when t he music is complex and fewer when it is simple.
Here you see t he MusicMat ch set t ings for ripping:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7d4.htm (6 of 9)7/27/2004 4:07:13 AM
A guide to MP3
The MP3 format is ext remely easy t o use. Considering t he explosive development s wit hin I nt ernet and elect ronics in general, MP3
must hold a revolut ionary pot ent ial capable of t ransforming t he music indust ry quit e a lot .
We use MP3 for backup st orage of our music. When we need a copy of a CD, we "burn" it from MP3' s. Here we use Adapt ec Easy CD
Creat or, which works fine:
MP3pro
I n 2001 a new and updat ed version of t he MP3 st andard was int roduced. Using bet t er compression, it should deliver same sound
qualit y from files half t he size.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7d4.htm (7 of 9)7/27/2004 4:07:13 AM
A guide to MP3
Here you see my DVD- player which plays CD- ROMs filled wit h MP3 files:
Links
[ t op]
Get a MP3 player
You will have t o find t he MP3s yourself - st art wit h www. mp3. com
Get a ripper from MusicMat ch
Microsoft ' s new player " Windows Media Player " also plays MP3s.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Click for Module 3b about CPU improvement s
Click for Module 3c about t he 5t h generat ions CPUs ( Pent iums et c. )
Click for Module 3d about t he clock frequencies
Click for Module 3e about 6t h generat ions CPUs ( Pent ium I I s et c. )
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7d4.htm (8 of 9)7/27/2004 4:07:13 AM
A guide to MP3
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7d4.htm (9 of 9)7/27/2004 4:07:13 AM
A guide to digital music #5
KarbosGuide.com. Module 7d5.
About digital music - Koan
The cont ent s:
q Koan music.
q Links t o t he music and soft ware.
Next page
Previous page
Koan music
This somet hing ent irely different from MP3 et c. Koan is genuine comput er music, wit h much
more pot ent ial t han t he "flat " MI DI files earlier ment ioned.
Koan is an elect ronic music st andard. And t his represent s a fascinat ing t echnology developed by
t he Brit ish company SSEYO. Koan requires t he addit ion of a plug- in t o your browser t o enable
playing t he files. Koan music is writ t en t o designat ed sound cards. The Sound Blast er AWE is t he
best as far as I know. I j ust have an ordinary Sound Blast er 16, and t here is also a lot of good
Koan music for t hat .
Koan is "live" music - it changes every t ime you play it . You can compare it wit h an aeolian harp,
where t he wind and t hus t he t one is different each t ime it is used.
"I t oo t hink it ' s possible t hat our grandchildren will look at us in wonder and say:
You mean you used t o list en t o exact ly t he same t hing over and over again?
Brian Eno 1996
The Koan music consist of small files, which st art a process in t he PC where t hey work. There
may be 8 hours of music in a 12 KB file! So it is not t he music it self which is cont ained in t he file.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7d5.htm (1 of 5)7/27/2004 4:07:15 AM
A guide to digital music #5
Rat her t he files cont ain some st ruct ures, frames if you wish, about a composit ion. These frames
are act ivat ed in your PC' s mat h processor. Then t he music is generat ed wit hin your PC,
different ly each t ime you play it .
Soundcard compatibility
Koan music is writ t en specifically for a cert ain sound card. So you must have eit her Sound
Blast er 16, 32 or 64. or a few ot her makes. Here again is a good argument t o st ay wit h t he SB
sound cards. They will give t he fewest problems. The music is I nt ernet suit able, since t he files
are small. I have found music in t he cat egory ambient , t hat is long elect ronic music sequences.
They can be very quiet and medit at ive, but t hey can also be more rhyt hmic. I f you:
q Like elect ronic music la Tangerine Dream and Brian Eno
q Have a SB sound card and speakers in your PC syst em
Then you ought t o t ry some Koan soft ware. I t is really simple t o inst all and requires only a lit t le
space.
How do I do?
I writ e t his on t hree premises:
q You have a Sound Blast er sound card and speakers.
q You are on t he I nt ernet and use eit her Net scape or MS Explorer.
q You know how t o download and ext ract ( unzip) files.
My inst allat ion example is based on soft ware for Sound Blast er 16 and Net scape in 32 bit
Windows 95 edit ion ( Net scape Gold, version 3 or 4) . I t may sound complicat ed as I describe it .
However it is really quit e simple:
You want t o inst all SSEYO soft ware, so you can play t he small SKP files wit h excit ing music. First
get t he following: 32 bit Koan Soft ware for Windows 95, and SB16 . You have t o find t he file on
SSEYO home page. New versions arrive all t he t ime.
I t is a self ext ract ing Exe file about 300 KB big, which you place in some t emporary folder. That
file will be delet ed aft er inst allat ion. Run t he file ( it is called knp1032. exe) , which will inst all t he
necessary plug- in in Net scape.
Now you can go on t he net and for example ret rieve t he st art er package on t he same server,
which includes some SKP files. Each of t hose represent s hours of elect ronic music.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7d5.htm (2 of 5)7/27/2004 4:07:15 AM
A guide to digital music #5
The best result is obt ained wit h a AWE64 sound card and a pair of good speakers. I purchased a
set of Alt ec Lansing ASC45. They are t wo t iny sat ellit es wit h a heavy sub woofer, and giving
fant ast ic sound - t hat is hi- fi!
Play back of Koan music
Once you have inst alled Koan plug- I n, Net scape can play t he Koan files! I t sounds backwards.
You would t hink t hat t he filt er should work in Windows 95, but no - t he music has t o be played
t hrough an I nt ernet browser. I use navigat or for Koan ( it works t here) while I have chanced int o
I nt ernet Explorer for surfing. . . .
You save your Koan files in a folder ( in my comput er: \ web\ music) . Then, in Net scape, you press
Cont rol+ o ( for open ) . Now you have t o modify t he file t ype, t o act ivat e t he filt er:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7d5.htm (3 of 5)7/27/2004 4:07:15 AM
A guide to digital music #5
Now you j ust select t he melody, and Net scape will play it . You need not be on t he I nt ernet , you
j ust use t he browser t o play t he music. The music can run in t he background all day, while you
do somet hing else.
I f t he SKP files are associat ed wit h Net scape, you can play t hem direct ly by double clicking on
t hem.
Links
[ t op]
At t he SSEYO Koan home page you can find plugins, t unes and informat ion, including soft ware t o
let you writ e your own Koan music.
q Next page
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7d5.htm (4 of 5)7/27/2004 4:07:15 AM
A guide to digital music #5
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Click for Module 3b about CPU improvement s
Click for Module 3c about t he 5t h generat ions CPUs ( Pent iums et c. )
Click for Module 3d about t he clock frequencies
Click for Module 3e about 6t h generat ions CPUs ( Pent ium I I s et c. )
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7d5.htm (5 of 5)7/27/2004 4:07:15 AM
An illustrated Guide to Scanners and Digital Cameras
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 8
The cont ent s:
q Edit ing phot os wit h Phot oshop
q Next page
q Previous page
UNDER CONSTRUCTI ON.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e Top
Read about video cards in Module 7b .
Read about sound cards in Module 7c .
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module8a1.htm (1 of 2)7/27/2004 4:07:17 AM
An illustrated Guide to Scanners and Digital Cameras
Read about digit al sound and music in Module 7d .
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module8a1.htm (2 of 2)7/27/2004 4:07:17 AM
Karbo's Software Tips, Photoshop.
Karbosguide.com. Software Tip
Fixing photos using Photoshop
q Next page
q Previous
page
When you look at your digit al images, you' ll probably find t hat a few of t hem could benefit from some edit ing.
The fish eye
One of t he problems you may experience consist of unwant ed geomet rical dist ort ions.
The lens of t he digit al cameras is rat her "short ", it covers a wide angle. This oft en gives geomet rical dist ort ions,
especially phot ographing big obj ect s at a short dist ance. I f a square obj ect fills all t he image, you will see t hat
t he lines of t he figure no more are parallel.
You may download t he phot o by right clicking on it , t hen you can pract ise t he operat ion on your own PC, if you
have Phot oshop inst alled. We use t his phot o of St . Vict or in Marseille:
I t is not t he phot ographer, who has had t o much past is. The phot o has been t aken on a very short dist ance. That
has result ed in a significant dist ort ion in t he left part of t he image.
Too bad; ot herwise t he phot o is OK, but now it is useless. Or what ?
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/photoshop01.htm (1 of 5)7/27/2004 4:07:19 AM
Karbo's Software Tips, Photoshop.
Use Photoshop
The phot o is not t o be wast ed, it j ust has t o be correct ed. The great imaging edit or Phot oshop has t he t ools.
You open t he phot o in Phot oshop and choose Select all ( Cont rol+ a) .
Next choose Edit - - > Transformer - - > Dist ort :
Now you see eight handles in t he corners of t he image. You may drag one of t he handles, and t he image is
geomet rically dist ort ed. This is how t his t ool works.
You should apply a dist ort ion which correct s t he phot o. Somet hing like t his:
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/photoshop01.htm (2 of 5)7/27/2004 4:07:19 AM
Karbo's Software Tips, Photoshop.
You always apply a t ransformat ion by hit t ing [ Ent er] . The t he image is OK from a geomet rically point of view:
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/photoshop01.htm (3 of 5)7/27/2004 4:07:19 AM
Karbo's Software Tips, Photoshop.
You may need t o do a lit t le furt her edit ing. I n t he left corner t here is a grey are which is an unwant ed effect of
t he t ransformat ion:
I t has t o be correct ed. Eit her you crop t he phot o, so t his part disappears, or you may use t he clone brush t o edit
t he areas. All t his is described in my Phot oshop book) , which is available in many European languages ( not
English, unfort unat ely) .
Finally t he image should be saved in a high qualit y JPEG file. Delet e t he old version - you should not keep t o
versions of t he same phot o.
The Phot oshop funct ion Transformat ion is great and very versat ile. You may use for many very different t ask.
Here is t he result at of our lit t le exercise, which can be performed wit hin a minut es t ime:
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/photoshop01.htm (4 of 5)7/27/2004 4:07:19 AM
Karbo's Software Tips, Photoshop.
The original
photo:
After the
treatment:
PS: All images on t his page are heavily compressed. So t he phot o qualit y is not very good.
I f you want t o see a beaut iful phot o from same locat ion, please click here.
q Next page
q Previous page Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo.
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/photoshop01.htm (5 of 5)7/27/2004 4:07:19 AM
Karbo's Software Tips, Photoshop.
Photos taken with Canon S20 digital camera
q Next page
q Previous
page
I am very happy wit h t his phot o. Here you see a reduced version of it .
Originally t he size is 2048 x 1536 pixels. Here it only covers 850 x 638 pixels t o make it more web- friendly. The original image file is of 900 KB;
here it is reduced t o a mere 61 KB.
The phot is t aken using our lit t le Canon S20 digit al camera. I t is from t he inside of t he church St . Vict or in Marseille, Provence.
The exposure t ime was 0. 7 second og t he apert ure was f/ 2. 90. But t hese set t ings were applied aut omat ically by t he camera:
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/photoshop01b.htm (1 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:21 AM
Karbo's Software Tips, Photoshop.
I find t he phot o wery nice wit h great color t ones.
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/photoshop01b.htm (2 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:21 AM
Karbo's Software Tips, Photoshop.
I am oft en surprised by t he qualit y of t he images coming from t his lit t le camera. I t almost always produces good phot os, no mat t er what I demand
from it . Here is anot her example, t aken in Saint - Raphal by night :
The image dat a are:
q Shut t er Speed: 1/ 3. 33
q Apert ure: f/ 3. 50
I can recommend having a digit al camera t o all phot o int erest ed persons. I t is so great !
q Next page
q Previous page
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/photoshop01b.htm (3 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:21 AM
Karbo's Software Tips, Photoshop.
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo.
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/photoshop01b.htm (4 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:21 AM
Tips for Windows.
Karbosguide.com. Software Tip 18
Use MSConfig to alter the Windows start-up.
q Next page
q Previous
page
Windows 98 has a new powerful t ool called MSConfig, which a lot of people not are aware of.
I n t ip number 3 I showed how t o clean up all t he t emporary I nt ernet files including t he
subdirect ories, cookies, and ot her t emporary files. I have got several comment s on t his t ip,
which many people find very useful.
Temporary disabling commands
Somet imes it is nice t emporary t o disable t hese DOS commands, as Mr. Kokusai of Japan wrot e
me and asked how t o it .
Many programs rely on t he folder C: \ Windows\ t emp during t he inst all process. I f t hey also
include a re- boot , it may cause problems if your Aut oexec delet es all t he files in C: \ Windows
\ t emp.
The solut ion t o t his is MSConfig.
Find MSConfig
You have t o use St art - - > Run and t ype t he command msconfig like t his:
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/18.htm (1 of 5)7/27/2004 4:07:22 AM
Tips for Windows.
The program cont ains of six t abs. On t he first , you choose Select ive st art up:
The second t ab let s you enable/ disable driver or ot her calls placed in Config. sys. The same is
t he case wit h t ab number t hree Aut oexec. bat . Here I see t he t hree lines discussed earlier. Here
I disable one of t hem:
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/18.htm (2 of 5)7/27/2004 4:07:22 AM
Tips for Windows.
You can also add/ edit / disable commands t o Syst em. ini. here you see my favorit e set t ing for
disk cache:
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/18.htm (3 of 5)7/27/2004 4:07:22 AM
Tips for Windows.
The commands in Startup
A very import ant t ool is t he last t ab. Here you can disable programs, t hat normally are loaded
during t he Windows st art up. This is a very handy t ool for clearing some of t hose background
program, since many of t hem are redundant . They are inst alled by varies t ypes of soft ware, but
oft en t hey only delay t he st art up and represent a wast e of memory and ot her ressources:
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/18.htm (4 of 5)7/27/2004 4:07:22 AM
Tips for Windows.
q Next page
q Previous page
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo.
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/18.htm (5 of 5)7/27/2004 4:07:22 AM
Tips for Windows.
Karbosguide.com. Software Tip 17
Enable DMA on your harddisk
q Next page
q Previous page
I t is ext remely import ant t o act ivat e t he DMA funct ion in Windows!
A few readers have report ed problems wit h harddisk aft er enabling DMA; however I st ill
recommend it since it gives such bet t er performance. I f you experience unst abilit y, which will
happen in some cases, please disable DMA.
Some of t he combinat ions of mot herboards and HDDs are unst able in t his mode, and seems
t o be crit ical t o t he t emperat ure of t he HDD. Even 5 degrees celcius can have an impact on
st abilit y, and if t he fan of your comput er is dust y or underdimensioned, you might get t his
effect . Replacing a 40- wires HDD cable by 80- wires UDMA- 66 cable will decrease t he
elect rical noises in t he I DE channel and make your comput er more st able in DMA mode.
For example press Windows+ Break t o open t he Syst em Propert ies dialog box. Select t he
Device Manager t ab:
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/17.htm (1 of 5)7/27/2004 4:07:23 AM
Tips for Windows.
Double click on Disk drives, t hen select your hard disk and click on Propert ies:
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/17.htm (2 of 5)7/27/2004 4:07:23 AM
Tips for Windows.
Now select t he Set t ings t ab:
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/17.htm (3 of 5)7/27/2004 4:07:23 AM
Tips for Windows.
Verify t hat you have a check mark in t he DMA box:
DMA t ransfer bet ween hard disk and RAM is much more effect ive t han when t he DMA channel
is not in use. Wit h DMA a writ e or read operat ion can be execut ed in t wo t o four clock t icks.
Wit hout DMA it will cost t he CPU a minimum of 16 clock t icks per operat ion! That makes a big
difference.
Not ice t hat t his enabling of DMA for hard disks and CD- ROM is far from aut omat ic. I n some
mot herboards it is act ivat ed aut omat ically when Windows is inst alled, but t hat is probably t he
except ion. So check for yourself t hat it is act ivat ed!
OBS: Some people report t hat enabling DMA t o hard drives causes problems. On newer PCs
wit h good cooling t here should be no problems.
A tip from a reader
We never experienced problems ourselves from enabling DMA on any of our PCs. However
here is a comment , t hat might prove a useful addendum:
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/17.htm (4 of 5)7/27/2004 4:07:23 AM
Tips for Windows.
You forgot one very import ant part t hat is required t o enable DMA in Windows 98. Aft er you
check t he DMA box in t he device mamager- disk drive window, do t he following:
To make sure t hat DMA doesn' t cause any int ernal Windows conflict s ( assuming t he drive
support s DMA) , you are going t o need t o add t hese lines t o t he Mshdc. inf file at t he bot t om of
t he [ ESDI _AddReg] t ag ( if t hey aren' t already t here) :
HKR, , I DEDMADrive0, 3, 01
HKR, , I DEDMADrive1, 3, 01
HKR, , I DEDMADrive2, 3, 01
HKR, , I DEDMADrive3, 3, 01
Only add t he bot t om t wo lines ( t he bolded ones) if you have more t han t wo I DE drives ( HD/
CD devices) connect ed t o your syst em.
Wit hin t he DI SKDRV. I NF file, add t he same lines under t he [ DiskReg] ent ry. I f t he lines are
already t here, you don' t need t o cont inue on, because you are done. Ot herwise, copy t he t wo
modified files t o anot her direct ory.
I recommend creat ing a new direct ory named inf2 in your windows syst em direct ory. Then
remove all of t he it ems under t he Hard Drive Cont rollers and all of t he Hard Drives ( only hard
drives, not removable media) from under t he Disk Drives heading.
Then reboot your syst em.
When t he comput er' s Hardware Wizard pops up t o reinst all t he drives, set it so you can
choose from t he compat ible drivers list and check t he dat e on t he drivers. They should be for
t he same day you modified t hem. I f t hey are, great , use t hem, ot herwise you will need t o
point t hem at t he copies ( t he inf folder is invisible at t his point , which is why you need t he
second copies) and use t hose. Thanks guys!
David Gillespie
- - - We hope t his will be useful, and t hanks t o David!
q Next page
q Previous page
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo.
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/17.htm (5 of 5)7/27/2004 4:07:23 AM
Tips for Windows.
Karbosguide.com. Software Tip 16
Running out of space on my hard disk...
q Next page
q Previous
page
People oft en t hink t hey lack space on t heir hard disk. But j ust as oft en t he real problem is
t hat t heir dat a and programs are t erribly disorganized. The most common errors are:
Wrong partitioning of the hard disk.
I n Windows 98 you should only have one part it ion, a C drive, where all dat a are locat ed. The
subdivision in D- and E- drives will in most cases add t o wast ed space and mess.
Duplicates
I f program packages like Net scape Communicat or, I nt ernet Explorer, not t o speak of
Microsoft Office are present in different versions - no wonder you run out of space. I see t hat
in many places.
General mess
Lack of st ruct ure and disk cleaning. People inst all all kinds of programs ret rieved from t he
I nt ernet and borrow from each ot her - of course t hat is fun. But if you do not have a firm
division of t he hard disk for different kinds of dat a, it might be impossible t o clean up when
you need t o.
A model for hard disk space utilization
Your hard disk should be one big part it ion ( a C drive) , which in Windows 98 and 2000 oft en is
format t ed wit h FAT32. Then all inst allat ion and ot her dat a st orage is done according t o t hese
guide lines:
Program folders
The folder C: \ Windows cont ains what t he name implies.
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/16.htm (1 of 3)7/27/2004 4:07:24 AM
Tips for Windows.
q C: \ Program Files cont ains all program packages.
q C: \ Ut ils cont ains all small programs ( fax, cookie killers et c. ) , which do not inst all in C:
\ Program Files.
q C: \ Temp cont ains all t he t emporary st uff, what ever is in for review and t est ing et c.
q C: \ My Document s\ Download\ Program1 is t emporary and cont ains t he downloaded and
ext ract ed files for Program1.
When programs are "accept ed" as being of last ing value, t hey are moved t o C: \ Ut ils
\ Program1 et c. And t he t emporary folders are delet ed.
Program files from CD-ROM
The folder C: \ Disks cont ains inst allat ion disket t es/ CD- ROM' s for import ant programs. Though
you should keep t he CD- ROMs coming wit h t he programs, it is much more convenient t o have
a copy on t he hardisk.
Your documents
A folder like C: \ Text s cont ain all user document s set up in a dynamic st ruct ure of mult iple
sub folders. You cont inually need t o creat e new sub folders and move and delet e among t he
older ones, so your document st ruct ure fit s your work needs.
I prefer not t o use C: \ My document s for st orage of document s. This folder is involved in
many operat ions from wit hin Windows and ot her programs; hence it oft en get s clut t ered wit h
a lot of files which are of t emporary charact er. Use a folder like C: \ Text s for all your
document s, images et c. having a permanent charact er.
q D: \ Backup cont ains all backups.
You should backup your document s daily/ weekly on anot her harddisk t han where t he
originals are kept .
The point is t o maint ain t he syst em one hundred and t en percent ! ! ! And t hat is really not
hard - it j ust requires some presence of mind and careful t hought during download/
inst allat ion.
About creating folders
Always remember t o creat e new folders - you can do t hat direct ly from t he download dialog
box as well as from t he Save As dialog box. Use t his but t on:
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/16.htm (2 of 3)7/27/2004 4:07:24 AM
Tips for Windows.
Is it worth the effort?
All t his boring t rouble - like having t o plan ahead every t ime. I t pays off t en fold in st abilit y
and surplus in daily work. The alt ernat ive is repeat ed reinst allat ion of t he whole shebang,
dat a loss and wast ed t ime. That is j ust t he way it is . I speak from more t han 12 years
experience.
q Next page
q Previous page
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo.
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/16.htm (3 of 3)7/27/2004 4:07:24 AM
Tips for Windows.
Karbosguide.com. Software Tip 15
MacroExpress 98
q Next page
q Previous
page
This program is quit e smart . I t is about developing macros, which can handle t he repet it ive keyboard/ mouse
operat ions.
A small, very simple example: I f I writ e my home pages in an edit or like Composer; I have t o forever format
headings wit h t he heading 1, 2, and 3 format s. The only way I can do t hat is t hrough t he menu or t ool bar.
To grab t he mouse every t ime is not pract ical while I writ e, and menu choices require some complicat ed
keyboard ent ries. All I wish is t o make:
q [ Alt ] + 1 give heading 1
q [ Alt ] + 2 give heading 2
q [ Alt ] + 3 give heading 3
That ' s how t he st yles work in Word. But wit h MacroExpress 98 it is very easy t o add t his funct ionalit y. You
see t he screen image here:
You can select whet her t he macros will work in all programs, or whet her t hey only work in a designat ed
program. Probably t he last opt ion is t he smart est . I need t o add t hat t he program places some demands on
t he user. I t t akes a lit t le while t o underst and how it works. You see MacroExpress 98 records an image of for
example your mouse movement s. So if you for example change t he menus or program set - up, you might
risk t hat t he result s are quit e different when you play t he macro. Here is a brief descript ion:
You st art t he recording in t his screen image. Here I will add a macro t o t he keyboard command [ Alt ] + q:
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/15.htm (1 of 5)7/27/2004 4:07:26 AM
Tips for Windows.
The next image looks like t his:
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/15.htm (2 of 5)7/27/2004 4:07:26 AM
Tips for Windows.
Then t he macro is recorded t hrough t he keyboard/ mouse commands for t hat program. When you are
finished, you close by pressing [ Alt ] + q ( in t his case) .
Then t he macro works. When you are in t he given program you press [ Alt ] + q, and t he macro plays. I f you
used t he mouse during recording, you will see ( surely t o your great surprise) t he mouse work on it s own. I t
t akes a lit t le while, but t he macro works j ust like you recorded it .
Now it j ust remains t o speed it up. I do t hat by double clicking on t he macro. The first command regards t he
speed, and I set t he value t o 0. 01, t o make t he macro work at t he speed of light ning. I can also delet e all
Delays:
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/15.htm (3 of 5)7/27/2004 4:07:26 AM
Tips for Windows.
I can recommend t he t wo programs here - t hey are invaluable if you work a lot wit h your PC.
I t is even easier, when you can t ype in t he keys direct ly:
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/15.htm (4 of 5)7/27/2004 4:07:26 AM
Tips for Windows.
q Next page
q Previous page
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo.
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/15.htm (5 of 5)7/27/2004 4:07:26 AM
Tips for Windows.
Karbosguide.com. Software Tip 14
Windows Autotexts
q Next page
q Previous
page
I t is t erribly impract ical t o have t o repeat t he same operat ions over and over again. Some
programs ( like Word) gives lot s of opt ions for cust omizing t heir execut ion wit h macros,
aut ot ext s, and keyboard short cut s. You can read about t hat in "Word 97 short course, " where
I have given much emphasis on t hese opt ions.
But ot her - many ot her- Windows programs do not offer t hese macro et c. opt ions. That is t he
case wit h a program like Composer, which I use t o writ e my home pages. There is no
quest ion t hat t he program is excellent for writ ing home pages. But it s funct ionalit y is quit e
primit ive. There are hardly any keyboard short cut s, and no macros. Many Windows programs
are designed like t his, and it can really be quit e t rying t o fight your way t hrough a larger
assignment .
You can get help. I am t alking about t wo programs, which can spruce up any Windows
program. I can equip Composer wit h j ust t he same aut ot ext s and keyboard short cut s, which I
enj oy so much in Word:
q Short Keys 98
q MacroExpress 98
Bot h programs require some get t ing used t o, but t hen t hey really work. Unfort unat ely only
for 30 days, unless you pay for t hem. Let me show you some examples of how I use t hem.
First t he simplest of t he programs:
ShortKeys 98
[ t op]
Short Keys is quit e similar t o t he Aut ot ext funct ion in t he word processing program Word. The
idea is t hat you make an abbreviat ion of t hose words or expressions you use most frequent ly.
The smart t hing about Short Keys is t hat it works in all Windows programs. Look at t his
illust rat ion:
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/14.htm (1 of 2)7/27/2004 4:07:26 AM
Tips for Windows.
Every t ime I need t o writ e t he word Windows, I j ust press w. When I hit t he space bar aft er
t he w, t he abbreviat ion is replaced immediat ely and aut omat ically wit h "Windows". Likewise:
q h gives t he t ext home pages,
q ht give gives t he t ext Click & Learn: ht t p: / / www. mkdat a. dk/ english
q et c.
You j ust have t o get used t o t he program, since it somet imes may surprise you. But t hat is
soon correct ed, and it really saves you t ime. That is cert ainly wort h it s $20 - regist er it right
away!
q Next page
q Previous page
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo.
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/14.htm (2 of 2)7/27/2004 4:07:26 AM
Tips for Windows.
Karbosguide.com. Software Tip 13
The FAX program - what happened in Windows 98?
q Next page
q Previous
page
Windows FAX is t he program which enables you t o send fax using your modem. That is a
smart it em, since fax by modem can appear much more appealing t o t he receiver t han fax
from a machine. Machine fax has t o be scanned first , and t hat result s in a loss of qualit y.
The FAX funct ion was quit e simple t o inst all in Windows 95, but for some reason t hat
program has been omit t ed in Windows 98. Well it is not really gone, but you have t o look
hard for it . Then you have t o inst all it yourself. Peculiar, but here is how:
On t he Windows 98 CD- ROM you need t o ent er t he folder \ WI N98\ TOOLS\ OLDWI N95
\ MESSAGE. There you find t he Awfax program, and you need t o click on t hat :
Aft er you have accept ed t he license agreement , you can now inst all Microsoft Fax:
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/13.htm (1 of 3)7/27/2004 4:07:27 AM
Tips for Windows.
Now follows t he inst allat ion:
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/13.htm (2 of 3)7/27/2004 4:07:27 AM
Tips for Windows.
Aft er you rest art your PC, Microsoft Fax will be ready t o use. I t works by inst alling an ext ra
print er:
When you have writ t en a document in your word processor, you can print t hat t o t he fax
inst ead of your regular print er. I hope t his works ( my own I SDN modem can not work wit h
fax) .
One quest ion remains: Why all t hese capers t o hide t he program so far out of t he way in
Windows 98? God' s ways are unfat homable!
q Next page
q Previous page
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo.
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/13.htm (3 of 3)7/27/2004 4:07:27 AM
Tips for Windows.
Karbosguide.com. Software Tip 12
Tweak UI
q Next page
q Previous
page
TWEAK UI , which is found on t he 98 CD, is a program t o cust omize t he user int erface. I t is
included in t he collect ion of small programs, which is known as "Power t oys. " I n Windows 98
t hese programs have been included in t he CD- ROM, but t hey are st ill well hidden. First look
at t he inst allat ion here.
You need t o find an inst allat ion file named t weakui. inf. Right click on t hat and select I nst all:
Then t he program will be inst alled quickly, and now you can find it in t he Cont rol Panel:
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/12.htm (1 of 3)7/27/2004 4:07:28 AM
Tips for Windows.
Here you can change a lot of paramet ers concerning t he behavior of t he user int erface:
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/12.htm (2 of 3)7/27/2004 4:07:28 AM
Tips for Windows.
Enj oy yourself!
q Next page
q Previous page
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo.
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/12.htm (3 of 3)7/27/2004 4:07:28 AM
Tips for Windows.
Karbosguide.com. Software Tip 11
Single click in Explorer
q Next page
q Previous
page
I use t he single click syst em in Explorer, as you can see in some of t he screen dumps.
This causes t he folder names t o be underlined, which means t hat t hey work as links on a
home page. One click opens t hem. Try t hat .
To act ivat e it you need t o select View - > Folder Opt ions in Explorer.
On t he General t ab select :
Then click Set t ings. . . , and select :
Click OK and it works. You j ust have t o get used t o t he new int erface. You j ust select obj ect s
by let t ing t he mouse cursor rest on t hem - wit hout clicking. Give it a chance!
Moreover you can adj ust t he "react ion t ime, " t hat is t he t ime bet ween t ouching an obj ect and
select ing it . You need t o find t he program TWEAK UI , which is on t he 98 CD. There you can
adj ust "menu speed" - increase it . I t causes t he select ion t o appear fast er. Now t here is no
excuse for t he impat ient souls, who might t hink t hat t he point ing met hod is t oo slow
compared t o t he t radit ional click. Read lat er about TWEAK UI .
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/11.htm (1 of 2)7/27/2004 4:07:29 AM
Tips for Windows.
q Next page
q Previous page
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo.
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/11.htm (2 of 2)7/27/2004 4:07:29 AM
Tips for Windows.
y
Karbosguide.com. Software Tip 10
Folders with names in capital letters
q Next page
q Previous
page
A ( small) novelt y in Windows 98 is t hat you can use capit al let t ers in folder names. Not ice t he
second t o last folder in t he pict ure below:
Windows 95 did not allow t hat , but now it is accept able.
Personally I should prefer, t hat only smallcaps were allowed bot h in files and folders names.
I t would make t hings a lot easier.
You should also remember t hat on many web- servers ( Unix/ Linux- based) t here is a
difference bet ween lower cases and capit als. The file I ndex. ht m and t he file index. ht m are
not t he same. Therefore it is good only t o use lower cases, bot h in file and folder naming. I f
you mix t he cases it can be difficult t o remember whichyou have used.
q Next page
q Previous page
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo.
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/10.htm7/27/2004 4:07:29 AM
Tips for Windows.
Karbosguide.com. Software Tip 9
Change the Windows opening screen
q Next page
q Previous
page
When you t urn your PC on you see a screen like t his:
Since it a simple piece of bit map graphics, you can alt er t his image. The file is named C:
\ Logo. sys, which means it is in t he root direct ory. Open it in a graphics program, and alt er it .
Just beware t hat t his pict ure is in a special format , t hat is 320 X 400 pixels. When shown, it
is scaled up t o double widt h like 640 X 400. You must consider t hat when you modify t he
pict ure - it will be dist ort ed when shown. Here you see t he pict ure during edit ing:
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/09.htm (1 of 3)7/27/2004 4:07:30 AM
Tips for Windows.
I f you use Windows 98, you have t o creat e t he file Logo. sys yourself and place it in t he root
direct ory. I t will work t hen as well.
I n t he same manner you can change t he closing pict ure. I t is named C: \ Windows\ Logow. sys.
You can clearly see t he peculiar t all format :
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/09.htm (2 of 3)7/27/2004 4:07:30 AM
Tips for Windows.
q Next page
q Previous page
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo.
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/09.htm (3 of 3)7/27/2004 4:07:30 AM
Tips for Windows.
Karbosguide.com. Software Tip 8
Color changes in the title bar
q Next page
q Previous
page
A new det ail in t he user int erface is t hat you can select different colors for different screen
window port ions. Select Display Propert ies - > Appearance. Select Menu and color 1, t hen
select Act ive Window and color 2. as shown below:
That gives quit e a neat effect .
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/08.htm (1 of 2)7/27/2004 4:07:31 AM
Tips for Windows.
q Next page
q Previous page
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo.
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/08.htm (2 of 2)7/27/2004 4:07:31 AM
Tips for Windows.
Karbosguide.com. Software Tip 7
Choose your own start page
q Next page
q Previous
page
When you open your browser, some kind of home page is aut omat ically writ t en in. That is t rue
regardless of which browser you use. I t is not quit e unimport ant which home page you choose,
and act ually you have four opt ions:
q A blank page
q A home page saved in your PC
q Some fixed page from t he net
q The browsers default page.
I will highly recommend t hat you experiment wit h t hese opt ions. The bl ank page is t he
easiest way out . The browser st art s wit h a blank page and is ready immediat ely. A l ocal
home page is a good opt ion. You make your own home page wit h t he links you use most
frequent ly. Then t he browser will open t hat as your st art ing page. I have such a local home
page myself, but it is on my deskt op as is described elsewhere here.
The f i x ed st ar t page f r om t he net can be an excit ing ent erprise. There are really many who
like for you t o use t heir web sit e as st art page. That gives many visit s t o t heir page, which in
t urn signals success and might result in earnings t hrough advert isement s.
Finally you can choose t o let t he browser select a st art page - but t hat is least desirable
solut ion. Neit her Microsoft ' s nor Net scape' s st art pages are part icularly excit ing. Make a bet t er
choice yourself!
How do y ou do t hi s? Well, in I nt ernet Explorer you need t o select View - > I nt ernet Opt ions.
The rest is easy:
Above t he easiest is t o browse t o t he page you want as your st art page and t hen click on t he
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/07.htm (1 of 2)7/27/2004 4:07:32 AM
Tips for Windows.
but t on Use Current . I n Net scape Navigat or you similarly select Edit , Preferences. . . :
Here it is similarly easy t o browse t o t he st art page and t hen click on t he but t on Use Current
Page.
q Next page
q Previous page
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo.
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/07.htm (2 of 2)7/27/2004 4:07:32 AM
Tips for Windows.
Karbosguide.com. Software Tip 6
Fixed folder for downloading in Internet Explorer
q Next page
q Previous
page
When you are in t he I nt ernet wit h I nt ernet Explorer and look at a file, which is not a home
page, you have t he opt ion t o download t he file. But in which folder does it end up? Maybe
you have not iced t hat it appears t o be random. Or maybe you have discovered t hat it always
saves in t he last folder you downloaded t o. You see Windows saves t hat informat ion.
I want I nt ernet Explorer t o always suggest C: \ t emp for saving downloads, since I always use
t hat folder for t his purpose. So how do I make t he I nt ernet Explorer program accept t hat ?
Unfort unat ely I need t o go t o t he regist ry dat abase. That is j ust a small t hing, and here I will
show you how:
Open a new t ext document in Not epad, or what ever program you use for t hat kind of t hing.
Then writ e t hese lines, precisely as you see t hem here ( I t is easier t o copy t hem from here,
t hen you will get no errors) :
REGEDI T4
[ HKEY_USERS\ . DEFAULT\ Soft ware\ Microsoft \ I nt ernet Explorer]
"Download Direct ory"= "C: \ \ t emp"
Here you see it :
Now save t he file, for example on t he deskt op. I t MUST have t he suffix . REG. I call it
ie40download. reg. The moment you rename t he suffix, t he file will be included in t he regist ry
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/06.htm (1 of 2)7/27/2004 4:07:32 AM
Tips for Windows.
dat abase, as you can see from t he icon:
Now you j ust have t o double click on t he file t o run it . Confirm wit h OK t wice, t hen everyt hing
is in it s place. I n t he fut ure t he download folder will be C: \ t emp ( or what ever you wrot e in
t he file) . This remains t rue unt il you save in anot her folder. Then you have t o run t he file
again t o re- est ablish C: \ t emp as t he default folder.
q Next page
q Previous page
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo.
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/06.htm (2 of 2)7/27/2004 4:07:32 AM
Tips for Windows.
Karbosguide.com. Software Tip 5
Use the desktop
q Next page
q Previous
page
I f you collect all your favorit e I nt ernet addresses in an HTML document , you can select t hat
as background. St art by t urning Act ive Deskt op on:
Now creat e your HTML document . Save it in t he folder C: \ Windows\ Web\ Wallpaper:
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/05.htm (1 of 3)7/27/2004 4:07:33 AM
Tips for Windows.
Then select :
Here you need t o click on t he Background t ab and ident ify your HTML document :
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/05.htm (2 of 3)7/27/2004 4:07:33 AM
Tips for Windows.
When you click OK you will be off and running! I had t o do some manipulat ions t o get t he
links out in t he right side. I insert ed a t able wit h t wo cells ( columns) . Then I placed a
graphics it em ( t he same color as t he deskt op) in t he left cell. Then t he links came in t he right
cell.
Now it works. Here is how t he deskt op looks now. You see t he 6 links on t he right :
q Next page
q Previous page
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo.
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/05.htm (3 of 3)7/27/2004 4:07:33 AM
Tips for Windows.
Karbosguide.com. Software Tip 4
About file types
- showing only some of them!
q Next page
q Previous
page
By default Explorer does not show t he suffix t o t he name for regist ered file t ypes. However
you can add t hat you always want t o see t he suffix for cert ain t ypes of files:
I n Explorer select View Folder Opt ions. . . and select t he t ab File Types. Then find t he file
t ype in t he long list . Here I find t he MiDi files, where I always want t o see t heir suffix:
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/04.htm (1 of 2)7/27/2004 4:07:34 AM
Tips for Windows.
Then click on t he Edit . . . but t on and check as seen below:
Then click t wice on OK. From now on t his file t ype will always be ident ified including t he suffix
in Explorer.
q Next page
q Previous page
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo.
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/04.htm (2 of 2)7/27/2004 4:07:34 AM
Tips for Windows.
Karbosguide.com. Software Tip 3b
About temporary files - get rid of them (II)
q Next page
q Previous
page
Here is anot her t ip t o cleaning up Windows' t emporary files. Thank you t o Mr. Frank Fallon of Aust ralia, who has
a sit e wit h similar Windows t ips. This works wit h Windows 98 and Me:
To clean up t emporary files, you use t hese command lines:
DELTREE / Y C: \ WI NDOWS\ FF* . TMP > NUL
DELTREE / Y C: \ WI NDOWS\ COOKI E* . > NUL
DELTREE / Y C: \ WI NDOWS\ TEMP
DELTREE / Y C: \ WI NDOWS\ "Temporary I nt ernet Files"\ * . *
MD C: \ WI NDOWS\ TEMP
I prefer t o place t hem in a bat ch file. I have t he file clean. bat placed on my deskt op on my Windows 98- based
PC. I t holds t he ment ioned lines, and is easy t o execut e, being placed at t he deskt op:
When I run t he bat chfile, t he commands are execut ed one by by one:
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/03b.htm (1 of 2)7/27/2004 4:07:35 AM
Tips for Windows.
I t really cleans up - very fast and very efficient ly.
Mr. Fallon also recommended a handy t emp cleaner. I t is a lit t le program which may t ake care of t hese problems.
Download it here, if you want t o t est it .
q Next page
q Previous page
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo.
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/03b.htm (2 of 2)7/27/2004 4:07:35 AM
Tips for Windows.
Karbosguide.com. Software Tip 3a
About temporary files - get rid of them (I)
q Next page
q Previous
page
Windows cont inuously creat es t emporary files. They are t emporary files, which really need t o be delet ed.
However, t hey are never delet ed aut omat ically - cert ainly not when Windows crashes, as it somet imes
does. They are in t he folder C: \ Windows\ Temp. You ought t o check it rout inely:
I t is t o your advant age t o delet e t hese t emporary files. They j ust t ake up space and t here can be hundreds
of t hem.
However, t he problem is t hat you may not be able t o delet e all t emporary files while Windows is running -
some of t hem may be act ive. Therefore I recommend t his simple met hod: put a line in your Aut oexec. bat !
You can find t he file Aut oexec. Bat ( Aut oexec) t hrough St art - > Find. Right click on it and choose edit . Then
t ype t he line shown below and save t he file:
echo Y | del c: \ windows\ t emp\ * . *
This will cause all t emporary files t o be delet ed at any st art - up. The echo command adds a "Y" int o t he del
command, so you do not need t o confirm wit h a "Y" t o execut e t he delet e.
You may also want t o delet e t he subdirect ories using t his command:
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/03a.htm (1 of 3)7/27/2004 4:07:36 AM
Tips for Windows.
delt ree / y c: \ windows\ t emp\ * . *
Use the Autoexec.bat
Windows also has t ools for cleaning t he harddisk. However I st ill recommend t he following addit ion t o t he
Aut oexec. bat . This only works in Windows 98, since Windows Me has no Aut oexec. bat .
Aut oexec. bat is a t ext file, and it has t o be t o be edit ed. I f you worked wit h your PC t en years ago, you
would not ask what Aut oexec. bat is. We used it all t he t ime t o t weak more free memory out of t he st art -
up.
Aut oexec. bat is t he cent ral st art - up file in any DOS- based comput er. I t holds a number of "lines" ( writ t en
in simple t ext ) .
Each line in Aut oexec. bat is t o be execut ed during t he st art - up - one by one. Hence t he file t ype is BAT,
which st ands for bat ch. A bat ch file holds one or several of lines of commands. And here we add t hree lines
int o t he Aut oexec. bat .
To open Aut oexec. bat , you find Windows Explorer and highlight C: \ ( t he root direct ory) in t he left frame.
I n t he right frame you find Aut oexec. bat . Highlight it and make a right click on it . Then choose edit , and it
is opened for you in Not epad.
Make your changes and save t he file, which t hen works aft er re- boot .
Using Aut oexec. bat is smart since it cleans up every t ime you boot t he pc. The first line t o add:
delt ree / y C: \ Windows\ t emp\ * . *
This line delet es all t he t emporary I nt ernet files including t he subdirect ories, which all t he t ime is creat ed
in C: \ WI NDOWS\ Temporary I nt ernet Files:
delt ree / y C: \ Windows\ TEMPOR~ 1\ * . *
Finally add
C: \ WI NDOWS\ COMMAND\ delt ree / y C: \ Windows\ cookies\ * . *
This line clears out t he cookies, which my browser collect s all t he t ime. The PC has t o reboot for t he
Aut oexec. bat t o work. You can monit or t he delet ion on screen during t he st art up ( hit [ pause] key t o
freeze t he screen) .
Three lines
You may use t hese t hree lines in my Aut oexec. bat :
C: \ WI NDOWS\ COMMAND\ delt ree / y C: \ Windows\ t empor~ 1\ * . *
C: \ WI NDOWS\ COMMAND\ delt ree / y c: \ windows\ t emp\ * . *
C: \ WI NDOWS\ COMMAND\ delt ree / y C: \ Windows\ cookies\ * . *
The first line empt ies t he browsers cache - a good t hing. The second line cleans up aft er Windows in
general. The t hird line clears out t he cookies, which t he browser collect s all t he t ime.
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/03a.htm (2 of 3)7/27/2004 4:07:36 AM
Tips for Windows.
All use is on your own responsabilit y - you may experience some problems using t his t ip, so please t est it .
The next t ip shows anot her opt ion. Also read more about delet ing t hese files in Tip 18.
q Next page
q Previous page
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo.
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/03a.htm (3 of 3)7/27/2004 4:07:36 AM
Tips for Windows.
Software Tip 2b
About the Disk Cache
q Next page
q Previous
page
Especially in Windows versions 95 and 98 it is import ant t o underst and t he of t he relat ionship bet ween:
q Size of and cont rol of Disk cache
q The free memory
q The size of t he swap file
What is disk cache?
The cache is a port ion of RAM, reserved for cache ( buffer) for t he hard disk. The disk cache is necessary, since it speeds up t he hard
disk a lot . However, it should not be bigger t han 8 or 16 MB.
The problem is t hat t he disk cache really gobbles up RAM. I n Windows 98 it can easily eat up 20- 25% of your RAM. An t hat is a t ot al
wast e of RAM.
I n Windows 98 you can limit t he size of your cache. This is done by edit ing t he file Syst em. I ni, which is found in C: \ Windows. Double
click on it and scroll down unt il you reach t he t ext [ vcache] .
Then t ype in t he t wo lines you see below and save t he file. Do it soon. This is import ant !
[ Non Windows App]
[ vcache]
MinFileCache= 8096
MaxFileCache= 8096
[ display]
The change t akes effect when you rest art Windows. I am convinced t hat 8 MB disk cache is sufficient - at least when you use t he
FAT32 file syst em.
I f you use Windows 95 wit h t he old FAT16 file syst em, you should probably maint ain j ust 1 or 2 MB of disk cache.
I n Fat 32 t he vcache holds a permanent copy of t he whole FAT t able, which occupies full 2 MB under t he FAT32 file syst em. Wit h t his
size FAT t he Vcache has t o be 4 MB big, if t here shall be room for ot her t hings besides t he FAT.
Read about file syst ems and about t he cache copy of FAT in same module.
The System Monitor
You can wat ch your use of memory wit h t he excellent t ool resource met er . You find it by going t o: St art - > Programs - > Accessories -
> Syst em Tools - > Syst em Monit or. You can add element s in t he edit menu. That will allow you t o see available memory and t he swap
file, as illust rat ed below ( you may print t his page, alt hough t he figure is in Danish) :
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/02b.htm (1 of 2)7/27/2004 4:07:36 AM
Tips for Windows.
You should check available memory and t he size of t he swap file over a period of t ime. Do t his daily for a while and see how big t he
swap file get s.
I t is also a good idea t o check t he disk cache, so t hat it does not occupy more t han 16 MB ( or less) . I f t he disk cache only occupies 8
or 16 MB, you can easily calculat e your act ual RAM usage by keeping t rack of available memory and t he size of t he swap file.
q Next page
q Previous page
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo.
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/02b.htm (2 of 2)7/27/2004 4:07:36 AM
A complete illustrated Guide to the PC Hardware
Karbosguide.com
Sitemap
Guestbooks
Support
Photo Gallery
Hardware Guides:
Digital Data
Motherboard logic
CPU and RAM
Disks and drives
PC Interface
System Software
Monitors & Sound
Digital Imaging
Others:
Software Guides
Search
Dictionary
About us
My Super PC
Karbosguide.
com
Welcome t o Michael
Karbo' s Online
Service. Here you will
find a modern online-
magazine wit h more
t han 500 illust rat ed
art icles for t he crit ical
reader!
Use our menu t o your
left or t he sit emap.
You may also follow
any of t he links list ed
below. We hope t hat
you appreciat e our
work!
q St art st udying t he
design of a PC
mot herboard.
q Learn about
harddisks and ot her
drives.
q Learn about t he PC
I / O syst em.
q Learn about t he PC
video syst em.
Sit emap
See our guest book
and add your
comment .
Cor r ect i ons
Misspellings, t ypos or
ot her correct ions.
Please report ! .
Kar bo' s New sl et t er :
Pent ium 4 and
At hlonXP.
More t han 50 phot os of
old cars free t o
download!
The MP3 art icle is re-
writ t en.
Edit ing phot os wit h
Phot oshop
Cleaning Windows Me
for t emporary files . . .
All modules 7 re-
writ t en
http://www.karbosguide.com/index.htm (1 of 2)7/27/2004 4:07:37 AM
Sign up!
A complete illustrated Guide to the PC Hardware
Copyright ( c) 1996 - 2002 Michael B. Karbo. WWW. KARBOSGUI DE. COM.
http://www.karbosguide.com/index.htm (2 of 2)7/27/2004 4:07:37 AM
An illustrated Guide to RAM.
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 2e1.
About RAM
Here you can read about :
q What is RAM?
q About RAM t ypes
On t he following pages:
q About SI MMs
q DI MMs
q PC100 RAM and furt her
q Rambus
q DDR
q Next page
q Previous page
What is RAM? [top]
This page should be read t oget her wit h modules 2a, 2b, 2c, and 2d,
which deal wit h syst em board, syst em bus, I / O bus and chip set s.
When we t alk about mot herboard and chip set s, we cannot ignore
RAM. Warning: RAM and RAM chips is a very complicat ed, t echnical
subj ect area. I can in no way give a complet e, comprehensive
descript ion of t his subj ect .
Please support our
sponsor.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2e1.htm (1 of 6)7/27/2004 4:07:39 AM
An illustrated Guide to RAM.
RAM is our working memory st orage. All t he dat a, which t he PC uses and works wit h during
operat ion, are st ored here. Dat a are st ored on drives, t ypically t he hard drive. However, for
t he CPU t o work wit h t hose dat a, t hey must be read int o t he working memory st orage, which
is made up of RAM chips. To examine RAM, we need t o look at t he following:
q RAM t ypes ( FPM, EDO, ECC, and SD RAM)
q RAM modules ( SI MM and DI MM) in different versions
q RAM and t he syst em bus
First , let us look back in t ime. Not t oo many years ago, Bill Gat es said, t hat wit h 1 MB RAM,
we had a memory capacit y, which would never be fully ut ilized. That t urned out t o be unt rue.
Historical review
Back in t he 80s, PCs were equipped wit h RAM in quant it ies of 64 KB, 256 KB, 512 KB and
finally 1 MB. Think of a home comput er like Commodore 64. I t had 64 KB RAM, and it worked
fine.
Around 1990, advanced operat ing syst ems, like Windows , appeared on t he market , That
st art ed t he RAM race. The PC needed more and more RAM. That worked fine wit h t he 386
processor, which could address larger amount of RAM. The first Windows operat ed PCs could
address 2 MB RAM, but 4 MB soon became t he st andard. The race has cont inued t hrough t he
90s, as RAM prices have dropped dramat ically.
Today. it would be foolish t o consider less t han 32 MB RAM in a PC. Many have much more.
128 MB is in no way t oo much for a "power user" wit h Windows 95/ 98, it is import ant wit h
plent y of RAM. Click here t o read about t he swap file and RAM considerat ions. Windows 98 is
a lit t le bet t er at handling memory, but st ill a lot af RAM is a good t hing.
RAM types
[ t op]
The t radit ional RAM t ype is DRAM ( dynamic RAM) . The ot her t ype is SRAM ( st at ic RAM) .
SRAM cont inues t o remember it s cont ent , while DRAM must be refreshed every few milli
seconds. DRAM consist s of micro capacit ors, while SRAM consist s of off/ on swit ches.
Therefore, SRAM can respond much fast er t han DRAM. SRAM can be made wit h a rise t ime as
short as 4 ns. I t is used in different versions in L2 cache RAM ( for example pipe line BURST
Cache SRAM) .
DRAM is by far t he cheapest t o build. Newer and fast er DRAM t ypes are developed
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2e1.htm (2 of 6)7/27/2004 4:07:39 AM
An illustrated Guide to RAM.
cont inuously. Current ly, t here are at least four t ypes:
q FPM ( Fast Page Mode)
q ECC ( Error Correct ing Code)
q EDO ( Ext ended Dat a Out put )
q SDRAM ( Synchronous Dynamic RAM)
A brief explanation of DRAM types
[ t op]
FPM was t he t radit ional RAM for PCs, before t he EDO was int roduced. I t is mount ed in SI MM
modules of 2, 4, 8, 16, or 32 MB. Typically, it is found in 60 ns or 70 ns versions. 60 ns is t he
fast est and t he one t o use. You cannot mix different speeds on t he same Pent ium
mot herboard.
EDO ( Ext ended Dat a Out ) RAM is an improvement of FPM RAM. Dat a are read fast er. EDO
ext ends t he t ime t hat out put dat a is valid, which bet t ers t iming issues bet ween t he CPU and
RAM and t his way improves t he performance.
By swit ching from FPM t o EDO, one could expect a performance improvement of 2 t o 5
percent . EDO RAM was usually sold in 60 ns versions. A 50 ns version was available at higher
cost .
EDO has now been replaced by t he even fast er SDRAM.
ECC RAM is a special error correct ing RAM t ype. I t is especially used in servers.
SDRAM ( synchronous DRAM) ) : The replacement for DRAM, FPM, and EDO RAM t ypes. SDRAM
"locks" ( synchronizes) t he memory access t o t he CPU clock. This way we get fast er dat a
t ransfer. While one port ion of dat a is t ranport ed t o t he CPU anot her can be being prepared
for t ransfer.
SDRAM comes only in 64 bit modules ( long 168 pin DI MMs) . SDRAM has a access t ime of
only 6- 12 ns. The performance improvement over EDO RAM was a mere 5 percent running at
66 MHz. At 100 and 133 MHz it proves bet t er.
DDR RAM is clock doubled version of SDRAM, which is replacing SDRAM during 2001- 2002.
RAMBUS ( RDRAM) is a more fut urist ic RAM t ype. I nt el and ot hers had great expect at ions
from t his t ype, but it flopped in 2000- 2001.
8 or 9 bits per byte?
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2e1.htm (3 of 6)7/27/2004 4:07:39 AM
An illustrated Guide to RAM.
Normally you figure 8 bit s t o one byt e. For many years, a nint h bit has been added as parit y
bit in t he RAM blocks t o verify correct t ransmission. That way you have t o t ransmit 9 bit s, t o
st ore 8 bit s in t he old 30 pin RAM chips. And it t akes 36 bit s t o st ore 32 bit s in t he larger 72
pin chips, which increases t he cost of t he RAM chip by about 12%.
I f your mot herboard requires 36 bit modules, you must respect t hat . Fort unat ely, most
syst em boards accept s 32 bit modules, so t his creat es no problems.
RAM and motherboard
[ t op]
You cannot freely inst all your desired RAM t ype. RAM is cont rolled by t he chip set on t he
mot herboard, so you must inst all a t ype, which mat ches your mot herboard. Furt hermore,
RAM chips come in different sizes, which must mat ch t he syst em board.
On modern syst em boards, RAM is inst alled on SI MM or DI MM modules. Before, small
individual DRAMs were used. There was usually room for 36 small chips on t he syst em board.
That made it cumbersome t o inst all new RAM. Then, someone figured out t o inst all RAM chips
on cards, which are easily inst alled. First came t he SI PP modules. They had mult iple pins,
which fit in t he mot herboard. Since t hen came t he SI MM modules. They are mount ed on a
card, which has an edge connect or. They fit in socket s on t he mot herboard, and anyone can
inst all t hem.
RAM speeds
[ t op]
RAM speed is measured in ns ( nano seconds) . The fewer ns, t he fast er is t he RAM. Years ago,
RAM came in 120, 100 and 80 ns. Today, we are t alking about 60 ns and fast er.
I t becomes complicat ed t o describe t he relat ionship bet ween RAM speed and t he abilit y of t he
syst em bus t o ut ilize fast RAM. I will gloss over t hat . But here is a t able which illust rat es RAM
speed, relat ive t o clock speed:
Clock speed Time per clock
t ick
20 MHz 50 ns
25 MHz 40 ns
33 MHz 30 ns
50 MHz 20 ns
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2e1.htm (4 of 6)7/27/2004 4:07:39 AM
An illustrated Guide to RAM.
66 MHz 15 ns
100 MHz 10 ns
133 MHz 6 ns
Peak Bandwidth
[ t op]
Here you see t he maximal peak bandwidt h of t he t hree well known RAM t ypes. The figures
illust rat es t he absolut ely maximal t ransfer from RAM t o t he L2- cache - in peaks, not as
cont inuously t ransferred.
RAM t ype Max. peak bandwidt h
FPM 176 MB/ sec
EDO 264 MB/ sec
SD 528 MB/ sec
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Also see module 3. An illust rat ed Guide t o CPUs from 8086 t o t he Pent ium- I I I .
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side.
Read module 5b about AGP and module 5c about Firewire.
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
Read module 7c about sound cards, and 7d on digit al sound and music.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2e1.htm (5 of 6)7/27/2004 4:07:39 AM
An illustrated Guide to RAM.
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. KarbosGuide. com
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2e1.htm (6 of 6)7/27/2004 4:07:39 AM
An illustrated Guide to RAM.
KarbosGuide.com. Module 2e2
About SIMM RAM
The cont ent s:
q About SI MMs
q Number of chips per module
q Buswidt h 32 bit
q Next page
q Previous page
SIMMs [top]
SI MM ( Single I nline Memory Modules) were first made in 8 bit edit ions. They were small cards
wit h 1, 2 or 4 MB RAM. They were connect ed t o t he mot herboard wit h a 30 pin edge
connect or. The modules were 8 bit wide. This meant t hat 16 bit processors ( 286 and 386SX)
needed 2 SI MMs in a pair. Thus, t here was room for t wo modules in what is called a bank.
32 bit processors ( 386DX and 486) need 4 of t he small 8 bit SI MMs in a bank, since t heir banks
are 32 bit wide. So, on a t ypical 1st generat ion 486 mot herboard, you could inst all 4 X 1 MB, 4
X 2 MB, or 4 X 4 MB in each bank. I f you only had one bank ( wit h room for 4 modules) , it was
expensive t o increase t he RAM, because you had t o discard t he old modules.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2e2.htm (1 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:41 AM
An illustrated Guide to RAM.
32 bit modules
Please support our
sponsor.
Wit h t he advent of t he 486 processor, demand increased for more RAM. Then t he larger 32 bit
modules came int o use. A 486 mot herboard could st ill have 4 SI MM socket s, but when t he
modules were 32 bit wide, t hey could be inst alled one at a t ime. This was quit e ingenious.
You could add different t ypes of modules and st ill use t he old ones. Also, since t he 486
mot herboard ran at only 33 MHz on t he syst em bus, t he RAM module qualit y was not so crit ical.
You could mix 60 ns and 70 ns modules of different brands wit hout problems.
Here you see a couple of SI MM modules. On t op is a 64 bit module ( 168 pins - don' t t ry t o count
t hem) . Next is a 32 bit module wit h a 72 pin connect or. Below is an 8 bit module wit h a 30 pin
connect or:
64 bit
SDRAM:
32 bit
DRAM:
and
16 bit
DRAM:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2e2.htm (2 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:41 AM
An illustrated Guide to RAM.
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
Number of chips per module
[ t op]
Some SI MMs have more chips on t he module t han ot hers. Looking at j ust t he 32 bit modules,
we find modules wit h 2, 4, 8 or chips on each side. SI MMs wit h 2 MB, 8 MB and 32 MB are
double sided. There are chips on bot h sides of t he module, and all t hese chips are 16 Mbit ones.
The newest DI MM- modules holds 64 Mbit RAM chips. This way a 32 MB module is made of only
4 chips since 4 X 64 / 8 = 32.
Pentium motherboard with SIMMs
On t he Pent ium mot herboard, t he syst em bus is 64 bit wide. Therefore, t he 32 bit SI MMs are
inst alled in pairs. Since t he st andard mot herboard only has t wo banks wit h a t ot al of four SI MM
socket s, RAM expansion possibilit ies are limit ed. NOTE: never use different speed RAM modules
on t he Pent ium mot herboard. All modules must have t he same speed. Here you see a few
configurat ions on an old Pent ium mot herboard wit h four SI MM socket s:
Bank 1 Bank 2 Tot al RAM
16 MB + 16 MB - 32 MB
16 MB + 16 MB 32 MB + 32 MB 96 MB
32 MB + 32 MB 32 Mb + 32 MB 128 MB
Cert ain mot herboards ( like TYAN) have 6 or 8 SI MM socket s. That provides more RAM
expansion flexibilit y.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2e2.htm (3 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:41 AM
An illustrated Guide to RAM.
An illust rat ed Guide t o CPUs from 8086 t o t he Pent ium- I I I : Module 3.
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side.
Read module 5b about AGP and module 5c about Firewire.
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
Read module 7c about sound cards, and 7d on digit al sound and music.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2e2.htm (4 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:41 AM
An illustrated Guide to RAM.
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 2e3.
About new fast RAM
The cont ent s:
q DI MMs
q PC100 RAM
q PC133 and VC133
q I nt el and PC133
On t he following pages:
q Rambus
q DDR
q Next page
q Previous page
DIMMs [top]
The most used modern RAM t ype, SDRAM is made in 64 bit wide modules called DI MMs ( Dual
I nline Memory Module) .
They have a 168 pin edge connect or. Here you see one module:
Please support our
sponsor.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2e3.htm (1 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:43 AM
An illustrated Guide to RAM.
Since t he DI MM modules are 64 bit s wide, you can inst all one module at a t ime. They are
available in 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256 MB, and 512MB wit h 6, 8, 10, and 12 ns speed. There are
usually 2 - 4 DI MM socket s on a mot herboard.
The advant age of SDRAM is increased speed. That allows you t o increase syst em bus speed. Wit h 60 ns EDO- RAM, you
can run at a maximum of 75 MHz on t he syst em bus, while SDRAM speed can increase t o 133 MHz and above. Also t he
SDRAM work synchronous wit h t he syst em bus for a bet t er performance.
Most chip set s are made for SDRAM. Some mot herboards had bot h SI MM and DI MM socket s. The idea was t hat you
could reuse old EDO RAM in t he SI MM socket s, or choose t o inst all SDRAM in t he DI MM socket s. They were not
designed t o mix RAM t ypes alt hough it works at some boards.
Above: a 64 MB DI MM- module holding 32 chips each of 16 Mbit ( 32 X 16 Mbit / 8 bit = 64 MB) .
I t is bet t er t o use DI MMs made of t he new 64 Mbit chips. A 64 MB module is t his way made of only 8 chips ( 8 X 64
Mbit / 8 bit = 64 MB) .
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2e3.htm (2 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:43 AM
An illustrated Guide to RAM.
Fast RAM
[ t op]
I nt el have managed t o speed up t he processors power by fact or 200 t imes t he last t en years. That is a lot , but it is a
problem t hat RAM memory t echnology only has improved by fact or 20 in t he same period.
Today we hope and dream of new fast RAM t ypes, t hat will help us t o get t he full pot ent ial from our powerful PCs.
PC100 RAM
The first at t empt t o improving RAM speed was t he PC100 st andard. Wit h chip set s like BX t he syst em bus speed has
come up t o 100 MHz. Hence I nt el has made a new st andard called PC100. Only 8 ns SD- RAM modules t hat are
const ruct ed according t o t hese st andards are guarant eed t o work at 100 MHz. I n some art icles t his RAM is described at
125 SD- RAM.
SPD
The new DI MM- modules include a EPROM- chip holding informat ion about t he module. This lit t le 8- pin chip works as a
SPD ( Serial Presence Det ect ) - a unit st oring informat ion about t he RAM t ype. The idea is t hat BI OS can read t his
informat ion and t his way t une t he syst em bus and t he t imings for a perfect CPU- RAM performance.
You can find a program, t hat t est s t he cont ent s of t he SPD at t his c' t homepage. I t works wit h t he I nt el chip set s
holding a 82371 sout h bridge like BX and GX.
Anot her program is called DI MM_I D.
PC133
The PC133 RAM running at 133 MHz is t he lat est version of SDRAM. Specificat ions are made by VI A, Micron, NEC,
Samsung, SI S, Acer Labs and ot her vendors. The first product ion ( from Corsair, June 1999) used 7. 5 ns RAM modules
from Micron.
VI A support s t he PC133 RAM wit h t heir Apollo Pro Plus chip set ( 693A) . Lat er t hey launched support for PC266 DDR
RAM!
Also AMD' s K7 At hlon may use PC133 RAM wit h t he VI A KX133Pro chipset .
VC133
Virt ual Channel 133 is anot her flavour of t he PC133 st andard. The modules holds a small cache of superfast SRAM.
According t o t est s, t hese modules perform very well, but due t o unknown reasons, it never became popular.
Intel and PC133
Originally I nt el planned t o by- pass PC133 RAM in t heir roadmaps. They int ended t o migrat e from PC100- based chip set s
( like BX) t o Rambus- based chip set s ( like i820) .
For a period of 12 mont hs in 1999- 2000, I nt el experienced several disast rous incident s from t heir at t empt t o implement
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2e3.htm (3 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:43 AM
An illustrated Guide to RAM.
Rambus in chip set s and mot herboards. During t his period t hey were forced ( by t aiwanese mot herboard manufact ures)
t o adapt t he PC133 st andard.
The chip set i815 was t he result of t his revision of st rat egies.
I nt el' s problem is t hat t hey have "sold t heir soul" t o Rambus I nc. According t o t heir agreement , unt il 2003 I nt el can
only implement ot her RAM t ypes t han RDRAM if t he bandwidt h is less t han 1 GB/ sec. This agreement does not include
server chipset s, from what we underst and.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side.
Read module 5b about AGP and module 5c about Firewire.
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
Read module 7c about sound cards, and 7d on digit al sound and music.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2e3.htm (4 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:43 AM
An illustrated Guide to RAM.
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 2e4
About Rambus RAM
The cont ent s:
q Rambus
q High clock rat es
q Next page
q Previous page
Rambus RDRAM
[ t op]
While t he CPUs has become around 200 t imes fast er in t en years, t he RAM
performance has only gone up 20 t imes. So we need new RAM t ypes. But which?
Many vendors decided t o go for DDR RAM as described in . Where DDR RAM is a
development of t he exist ing SDRAM t echnology, I nt el choose RDRAM, which
represent s a much more revolut ionary change in RAM design.
Please support our
sponsor.
Intel and RDRAM without succes
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2e4.htm (1 of 5)7/27/2004 4:07:45 AM
An illustrated Guide to RAM.
I nt el is comit t ed t o t he Rambus RAM, which also is called RDRAM ( Rambus Direct RAM) , nDRAM, or
RI MM ( Rambus I nline Memory Modules) .
RDRAM is an advanced t echnology pat ent ed by a company, who sells t he t echnology t o ot her chip
manufact ures for a 2% in license. I n 1997 I nt el signed a cont ract t hat apparent ly commit s t hem t o
support RDRAM only in all new chipset up t o 2002.
Originally AMD also expect ed t o support t he Rambus RAM for it s At hlon processor. But having seen all
I nt el' s problems wit h t he t echnology, AMD is not so keen on t he Rambus anymore. However, RDRAM is
already used in Sony PlaySt at ion 2 and in Nint endo64 machines. I n t he Sony PlaySt at ion 2 you find 32
MB of RDRAM delivering a bandwidt h of 3. 2 GB/ sec.
During 1999 and 2000, Rambus was not very successful. I n fact , I nt el has suffered a serious set - back
due t o t heir commit ment t o t he Rambus design. The chip set i820 "Camino" became a lit t le disast er.
I nt el failed t o produce a reliable way t o int erface SDRAM t o t he 820 chipset . The MTH ( Memory
Translat or Hub - which t ranslat ed RDRAM bus t o SDRAM modules) had some t iming or noise issues t hat
caused unreliable operat ion. I nt el replaced CC820 boards wit h VC820 boards ( wit h 128MB RDRAM
included) as t he CC820 use t he MTH and SDRAM while t he VC820 used RDRAM.
But , on t he paper, Rambus sounds great :
Intelligent Rambus design
RDRAM is developed from t he t radit ional DRAM, but t he archit ect ure is complet ely new. I t has been
st reamed and opt imized t o yield new performance.
The RAMBUS- design gives a more int elligent access t o t he RAM, meaning t hat unit s can "prefet ch" dat a
and t his way free t he CPU some work. The idea is t hat dat a is read in small packet s at a very high clock
speed.
The RI MM modules are only 16 bit wide compared t o t he t radit ional 64 bit SDRAM DI MMs, but t hey work
at a much higher clock frequency:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2e4.htm (2 of 5)7/27/2004 4:07:45 AM
An illustrated Guide to RAM.
The Rambus modules work on 2. 5 volt s, which int ernally is reduced down t o 0. 5 volt when possible. This
helps t o reduce heat and radio signals.
The RI MMs hold cont rolling chips t hat t urns off t he power t o sect ions not in use. They can also reduce
t he memory speed if t hermal sensors report of overheat ing.
CRIMMs
All RAM slot s have t o be full; t his is new, wit h RAMBUS we have t o fill in blank modules in slot s which
are not in use. The blank modules are called CRI MMs ( wit h a ' C' for cont inuit y) .
The RI MM modules hold 184 pins.
The RDRAM chips have t o be placed very close t o t he CPU t o reduce radio noise. This indicat es, t hat
RI MM t echnology is rat her sensit ive; I nt el seems t o have made t hat discovery as well.
High clock rates
As ment ioned, t he modules are only 16 bit wide, but t hey work at 600, 700 and 800 MHz. Act ually a
PC800 RI MM runs on a 400 MHz clock using bot h rising and falling edges, being clockdoubled j ust as
DDR RAM.
More confusing t he PC600 RI MM act ually runs on a 266/ 532 MHz clock, and t he PC700 works at
366/ 712 MHz.
PC800 800/ 400
MHz
PC700 712/ 366
MHz
PC600 532/ 266
MHz
This gives t he bandwidt h of up t o 1. 6 GB per second - compared t o t he 500- 800 MB/ sec of PC100
SDRAM - of a single Rambus channel. You may find a chart comparing t he bandwit hs of different RAM
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2e4.htm (3 of 5)7/27/2004 4:07:45 AM
An illustrated Guide to RAM.
t ypes in t he next page.
Multichannel memory design
You may bundle four channels t o a 64 bit wide RAM bus giving 6. 4 GB/ sec:
This is not possible using t he exist ing RAMBUS- based chip set s like i820. They only operat e wit h one
RAMBUS channel onboard. The high- end chip set i840 operat es wit h dual RDRAM channels, as t he up-
coming i850 will.
RIMM in the future, says Intel
GigaHert z versions of Rambus RAM will probably follow, so t he t echnology has pot ent ial for much higher
bandwidt hs.
I n 1999 it seemed t hat I nt el was having big problems wit h t he Rambus t echnology in t he ill- fait ed i820
chip set ( t he so- called "Caminogat e" t ragedy) . Hence t hey were forced t o support PC133 RAM as seen in
t he i815 chipset .
Poor performance so far
Unfort unat ely it was soon obvious t hat t he i815 chip set wit h it s PC133 RAM was performing slight ly
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2e4.htm (4 of 5)7/27/2004 4:07:45 AM
An illustrated Guide to RAM.
bet t er t han t he i820 chip set wit h it s st ill very expensive RDRAM. You have t o use dual Rambus channels
( as in upcomming I nt el chip set i850 "Tehema") t o benefit from a higher bandwidt h. But t his doubling is
also possible from using DDR RAM.
A t est bet ween a i840- based dual Rambus PC and a Micron DDR- based PC gave t he same result ; all
benchmarks were bet t er on t he DDR syst em.
So far Rambus RAM is of no big int erest . I t is t oo expensive, and t here is not hing t o gain from it .
However t he Rambus t echnology st il is quit e promising, but t he prices has t o come down, and it bet t er
be soon. DDR RAM is closing in.
I nt el claims t hat DDR is t o slow for t he new Pent ium 4 processor. I t would require dual channel DDR
RAM t o get t he required bandwidt h. And dual channel DDR RAM meens a 128 bit wide bus, which is no
good solut ion. The nort h bridge and t he mot herboard would be loaded wit h hundreds of signal lines.
I n 2001 RDRAM is being used wit h great success on t he GB850 Pent ium 4 board and RDRAM prices are
t umbling st eadily.
RDRAM 2.0
Rambus plans t o speed up t he bandwit h a fact or t wo using a Quad Rambus Signaling Level. This should
happen wit hout any increase in clock frequency.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side.
Read module 5b about AGP and module 5c about Firewire.
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
Read module 7c about sound cards, and 7d on digit al sound and music.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2e4.htm (5 of 5)7/27/2004 4:07:45 AM
An illustrated Guide to DDR RAM.
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 2e5
About DDR RAM
The cont ent s:
q DDR RAM
q PC2100 RAM
q I nt el not allowed
q Comparing bandwidt h
q Next page
q Previous page
DDR RAM
A very int erest ing RAM t ype is t he DDR RAM, which is expect ed t o hit t he market in 2001.
DDR st ands here for Double Dat a Rat e. I t is a t echnology t hat t ransmit s dat a on bot h sides of
a t act signal.
This way t he performance has been doubled; a 133 MHz SDRAM chip can very easy become
alt ered t o a 266 MHz DDR chip:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2e5.htm (1 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:47 AM
An illustrated Guide to DDR RAM.
I t should be pret t y easy for t he market t o change for DDR RAM. The modules look like and
operat e quit e similar t o exist ing SDRAMs. We j ust need new chipset s t o st art t he migrat ion.
However, t he modules hold 16 pins more t han SDRAM do, so t hey do not fit int o t he same
socket s.
Please support our
sponsor.
PC2100
The Taiwanese company VI A, which produces chip set s and CPUs and who are fight ing I nt el,
is fully support ing t he DDR RAM st rat egy. Soon we shall see 266 MHz moduls ( being
"overclocked"133 MHz SDRAM modules) . The 266 MHz modules reaches a 2. 1 GB/ sec
bandwidt h. Hence t hey are t o be sold as PC2100 RAM.
Ot her t erms used are:
q DDR200 ( 200 MHz)
q DDR266 ( 266 MHz)
q DDR333 ( 333 MHz)
VI A expect s DDR t o be used in all segment s of t he pc market . I nt el, who is behind t he
Rambus t echnology, only expect s t o use DDR in large servers, where you find several
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2e5.htm (2 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:47 AM
An illustrated Guide to DDR RAM.
Gigabyt es of RAM inst alled, and where RAM price really mat t ers.
No Intel here
I nt el is dedicat ed t o t he Rambus t echnology. I n t he summer 2000 it was revealed t hat I nt el
has comit t ed it self t o t he RAMBUS t echnology so t hey cannot implement DDR! This goes for
all fut ure deskt op PCs unt il 2003, according t o t heir agreement wit h Rambus I nc. Only t he 64
bit server I t anium processor and it succesors Fost er and McKinley are using DDR RAM.
We hope t hat I nt el will change t heir st rat egy. We expect DDR- SDRAM t o be cheaper t han
Rambus RAM for quit e some t ime; yet it should give t he same performance. Rambus
represent s a sophist icat ed t echnology, but wit h prices 5 t imes higher it is not a low- end
product . I nt el produces great chipset s for deskt op PCs like i815E, and it would be sad if t hey
abandoned t his market . We want I nt el and PC2100!
Report s in t he summer 2000 t old t hat I nt el has licensed VI A t o develop DDR- enabled chip
set s for Pent ium 4.
Evolutionary changes of design
Where RDRAM requires complet ely new product ion plant s, DDR represent s an evolut ionary
progress. The chip manufact ures may re- use t heir SDRAM fabs for t he product ion wit hout
many problems.
Hence it seems quit e nat ural and in t une wit h t he previous changes in RAM t echnology t hat
we use t he DDR st andard for a couple of years. Before Rambus ( or somet hing even bet t er)
ent ers t he market .
Comparing bandwidth
Below you see t he t heoret ical bandwidt s of different RAM t ypes. However, SDRAM does not
perform as good as t he figures show. This is due t o lat encies; t he CPU and ot her unit s cannot
read t he dat a at t hese speeds; t hey have t o wait some clock circles in bet ween each reading
before t he dat a t ransfers st art . The same goes for DDR RAM.
RAM t ype Theoret ical max. bandwidt h
SDRAM 100 MHz 100 MHz X 64 bit = 800 MB/ sec
SDRAM 133 MHz 133 MHz X 64 bit = 1064 MB/ sec
DDRAM 200 MHz ( PC1600) 2 X 100 MHz X 64 bit = 1600 MB/ sec
DDRAM 266 MHz ( PC2100) 2 X 133 MHz X 64 bit = 2128 MB/ sec
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2e5.htm (3 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:47 AM
An illustrated Guide to DDR RAM.
DDRAM 366 MHz ( PC2600) 2 X 166 MHz X 64 bit = 2656 MB/ sec
RDRAM 600 MHz 600 MHz X 16 bit = 1200 MB/ sec
RDRAM 700 MHz 700 MHz X 16 bit = 1400 MB/ sec
RDRAM 800 MHz 800 MHz X 16 bit = 1600 MB/ sec
DDR-II
A new version of DDR RAM is scheduled for 2003. Using anot her t echnique, it should be
possible t o double t he performance!
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side.
Read module 5b about AGP and module 5c about Firewire.
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
Read module 7c about sound cards, and 7d on digit al sound and music.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2e5.htm (4 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:47 AM
An illustrated Guide to CPUs from 8086 to Pentium-III
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 3a1.
About CPUs
To underst and t he dat a processing met hodology, an underst anding of t he design and funct ion
of t he CPU is essent ial. The following subj ect s will be covered on t hese pages.
The cont ent s:
q What is a CPU?
q I nt ro t o CPUs from 1st t o 7t h generat ion
q Next page
q Previous page
The module is divided in several sub modules, which all t oget her
ought t o be read as a unit . Please support our
sponsor.
What is a CPU?
[ t op]
The CPU is cert ainly t he most import ant PC component . CPU st ands for Cent ral Processing
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3a1.htm (1 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:50 AM
An illustrated Guide to CPUs from 8086 to Pentium-III
Unit . Let us briefly st udy t hat name:
q I t is a processor, because it processes ( moves and calculat es) dat a.
q I t is cent ral, because it is t he cent er of PC dat a processing.
q I t is a unit , because it is a chip, which cont ains millions of t ransist ors.
Speed, speed, speed
Wit hout t he CPU, t here would be no PC. Like all ot her hardware component s, t he CPUs are
cont inually undergoing furt her development . You can see t he explosive t echnological
development in dat a processing most clearly in t he development of newer and fast er CPUs.
The CPUs have for years doubled t heir performance about every 18 mont hs ( Moore' s Law) ,
and t here are no indicat ions t hat t his t rend will st op.
When we now look at all t he CPUs from a broader perspect ive, we can see t hat :
q The CPU hist ory is closely t ied t o t he companies I BM and especially I nt el.
q The CPUs have t heir root s back t o I nt el' s chip 4004 from 1971.
q You can ident ify seven or eight CPU generat ions up t ill t oday.
q The compat ibilit y concept has been import ant t hroughout t he development .
CPUs - brief review
[ t op]
CPU hist ory st art s in 1971, when a small unknown company, I nt el, for t he first t ime
combined mult iple t ransist ors t o form a cent ral processing unit - a chip called I nt el 4004.
However, it was 8 years before t he first PC was const ruct ed.
PCs are designed around different CPU generat ions. I nt el is not t he only company
manufact uring CPUs, but by far t he leading one. The following t able shows t he different CPU
generat ions. They are predominant ly I nt el chips, but in t he 5t h generat ion we see
alt ernat ives:
PC CPUs Year Number
of t ransist ors
1st . Generat ion 8086 and 8088 1978- 81 29, 000
2nd. Generat ion 80286 1984 134, 000
3rd. Generat ion 80386DX and 80386SX 1987- 88 275, 000
4t h. Generat ion 80486SX, 80486DX,
80486DX2 and 80486DX4
1990- 92 1, 200, 000
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3a1.htm (2 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:50 AM
An illustrated Guide to CPUs from 8086 to Pentium-III
5t h. Generat ion Pent ium
Cyrix 6X86
AMD K5
I DT WinChip C6
1993-
95
1996
1996
1997
3, 100, 000
- -
- -
3, 500, 000
I mproved
5t h. Generat ion
Pent ium MMX
I BM/ Cyrix 6x86MX
I DT WinChip2 3D
1997
1997
1998
4, 500, 000
6, 000, 000
6, 000, 000
6t h. Generat ion Pent ium Pro
AMD K6
Pent ium I I
AMD K6- 2
1995
1997
1997
1998
5, 500, 000
8, 800, 000
7, 500, 000
9, 300, 000
I mproved 6t h. Generat ion Mobile Pent ium I I
Mobile Celeron
Pent ium I I I
AMD K6- 3
Pent ium I I I CuMine
1999 27, 400, 000
18, 900, 000
9, 300, 000
?
28, 000, 000
7t h. Generat ion AMD original At hlon
AMD At hlon Thunderbird
Pent ium 4
1999
2000
2001
22, 000, 000
37, 000, 000
42, 000, 000
Please not ice t hat t he mobile CPUs as well as Pent ium I I I CuMine include very large on- die L2-
caches. These caches consist of millions of t ransist ors.
We will now see what t he CPU really does.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Click for Module 3b about CPU improvement s
Click for Module 3c about t he 5t h generat ions CPUs ( Pent iums et c. )
Click for Module 3d about t he clock frequencies
Click for Module 3e about 6t h generat ions CPUs ( Pent ium I I s et c. )
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3a1.htm (3 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:50 AM
An illustrated Guide to CPUs from 8086 to Pentium-III
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3a1.htm (4 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:50 AM
An illustrated Guide to CPUs from 8086 to Pentium-III
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 3a2.
About CPUs - continued
The cont ent s:
q How does a CPU work?
q 8086 compat bilit y
q CI SC, RI SC and VLI W inst ruct ions
q Next page
q Previous page
Please support our
sponsor.
How does a CPU work?
[ t op]
The CPU is cent rally locat ed on t he mot herboard. Since t he CPU carries out a large share of t he
work in t he comput er, dat a pass cont inually t hrough it . The dat a come from t he RAM and t he
unit s ( keyboard, drives et c. ) . Aft er processing, t he dat a is send back t o RAM and t he unit s.
The CPU cont inually receives inst ruct ions t o be execut ed. Each inst ruct ion is a dat a processing
order. The work it self consist s most ly of calculat ions and dat a t ransport :
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3a2.htm (1 of 5)7/27/2004 4:07:52 AM
An illustrated Guide to CPUs from 8086 to Pentium-III
Dat a have a pat h t o t he CPU. I t is kind of a dat a expressway called t he syst em bus. You can
read more about t he syst em bus in module 2b.
Two types of data
[ t op]
The CPU is fed long st reams of dat a via t he syst em bus. The CPU receives at least t wo t ypes of
dat a:
q I nst ruct ions on how t o handle t he ot her dat a.
q Dat a, which must be handled according t o t he inst ruct ions.
What we call inst ruct ions is program code. That includes t hose messages, which you
cont inuously send t o t he PC from t he mouse and keyboard. Messages t o print , save, open, et c.
Dat a are t ypically user dat a. Think about t he let t er, which you are writ ing t o Aunt Karen. The
cont ent s, let t ers, images, et c. , are user dat a. But if you click "print , " you are t hen sending
program code ( inst ruct ions) :
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3a2.htm (2 of 5)7/27/2004 4:07:52 AM
An illustrated Guide to CPUs from 8086 to Pentium-III
8086 compatible instructions
[ t op]
The biggest j ob for t he CPU consist s of decoding t he inst ruct ions and localizing dat a. The
calculat ions t hemselves are not heavy work.
The decoding consist s of underst anding t he inst ruct ions, which t he user program sends t o t he
CPU. All PC CPUs, are "8086 compat ible. " This means t hat t he programs communicat e wit h t he
CPU in a specific family of inst ruct ions.
These inst ruct ions, originally writ t en for t he I nt el 8086 processor, became t he blueprint for t he
"I BM compat ible PC" concept . The 8086 from 1978 received it s inst ruct ions in a cert ain format .
Since t here was a desire t hat subsequent CPU generat ion should be able t o handle t he same
inst ruct ions which t he 8086 could, it was necessary t o make t he inst ruct ion set s compat ible.
The new CPUs should underst and t he same inst ruct ions. This backwards compat ibilit y has been
an indust ry st andard ever since. All new processors, regardless of how advanced, must be able
t o handle t he 8086 inst ruct ion format .
Thus, t he new CPUs must use much effort t o t ranslat e t he 8086 inst ruct ion format t o int ernal
inst ruct ion codes:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3a2.htm (3 of 5)7/27/2004 4:07:52 AM
An illustrated Guide to CPUs from 8086 to Pentium-III
CISC, RISC, and VLIW instructions and their
handling [ t op]
The first CPUs had a so called Complex I nst ruct ion Set Comput er ( CI SC) . This means t hat t he
comput er can underst and many and complex inst ruct ions. The X86 inst ruct ion set , wit h it s
varying lengt h from 8 t o 120 bit , was originally developed for t he 8086 wit h it s mere 29000
t ransist ors.
More inst ruct ions have been added wit hin new generat ions of CPUs. The 80386 had 26 new
inst ruct ions, t he 486 added 6 and t he Pent ium anot her 8 new inst ruct ions. This meant , t hat
programs had t o be rewrit t en t o use t hese new inst ruct ions. This happened for example wit h
new versions of Windows . Hence, some programs require a 386 or a Pent ium processor t o
funct ion.
You should also see module 3e09 on MMX, 3DNow! and ot her ext ensions t o t he set of
inst ruct ions.
Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC)
The RI SC inst ruct ions are brief and t he same lengt h ( for example 32 bit long, as in Pent ium
Pro) , and t hey process much fast er t han CI SC inst ruct ions. Therefore, RI SC is used in all newer
CPUs. However, t he problem is t hat t he inst ruct ions arrive t o t he CPU in 8086 format . Thus,
t hey must be decoded.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3a2.htm (4 of 5)7/27/2004 4:07:52 AM
An illustrated Guide to CPUs from 8086 to Pentium-III
For every new CPU generat ion, t he inst ruct ion set has been expanded. The 386 came wit h 26
new inst ruct ions, t he 486 wit h 6 new inst ruct ions, and Pent ium wit h 8 new inst ruct ions. These
changes mean t hat some programs require at least a 386 or a Pent ium processor t o work.
VLIW
A Very Long I nst ruct ion Word processor uses inst ruct ion t hat are long. The idea is t o put many
inst ruct ions t oget her in one. Then t he processor can fet ch several inst ruct ions in one operat ion
and be more effecient . Normal non- VLI W processors only receive one inst ruct ion per word . A
word is an amount of dat a t ransmit t ed t o t he processor, and t he VLI W processor receives
several inst ruct ions in each word.
To re- order t he inst ruct ions you use a soft ware compiler. This principle works fine in more
special processors such as DSPs. These chip perform t he same operat ions over and over again.
A CPU is a general- purpose processor, and t he VLI W design becomes ext remely complex in t his
case. Hence, I nt el has had many problems wit h t heir 64 bit I t anium processor, which comes in
VLI W design. Anot her company t o use VLI W is TransMet a wit h t heir port able Crusoe processor.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Click for Module 3b about CPU improvement s
Click for Module 3c about t he 5t h generat ions CPUs ( Pent iums et c. )
Click for Module 3d about t he clock frequencies
Click for Module 3e about 6t h generat ions CPUs ( Pent ium I I s et c. )
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3a2.htm (5 of 5)7/27/2004 4:07:52 AM
An illustrated Guide to CPUs from 8086 to Pentium-III
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 3a3.
About modern CPUs
The cont ent s:
q Dual pipeline
q Float ing point unit - FPU
q Graphic overview of t he processors
q Next page
q Previous page
Dual pipeline: More work per clock stroke
There is also a cont inuous opt imizing of t he inst ruct ion handling process. One is t hat t he clock frequency increases, as we
will see lat er - t he fast er, t he bet t er. But what can t he CPU do in one clock t ick. That is crit ical t o it s performance. For
example, a 386 needed 6 clock t icks t o add a number t o a sub t ot al. A j ob which t he 486 manages in only t wo clock t icks,
because of more effect ive inst ruct ion decoding.
5t h and 6t h generat ion CPUs can execut e more t han one of t hose operat ions in one clock t ick, since t hey cont ain more
processing lines ( pipelines) , which work parallel:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3a3.htm (1 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:54 AM
An illustrated Guide to CPUs from 8086 to Pentium-III
Please also read t he sect ion about MMX, about 3DNow! , and Kat mai inst ruct ions.
Floating point unit - FPU
[ t op]
The first CPUs could only work wit h whole numbers. Therefore, it was necessary t o add a mat hemat ical co- processor
( FPU) , when bet t er mat h power was needed. Lat er, t his FPU was built int o t he CPU:
CPU FPU
8086 8087
80286 80287
80386 80387
80486DX Built in
80486SX None
Pent ium and t hereaft er Built in
I t is said t hat I nt el' s CPUs have by far t he best FPU unit s. Processors from AMD and Cyrix definit ely have a reput at ion for
providing sub st andard performance in t his area. But , you may not ut ilize t he FPU. That depends on t he applicat ions ( user
programs) you are using. Common office programs do not use t he float ing point operat ions, which t he FPU can handle.
However, 3D graphics programs like Aut oCad do. And all 3D- games like Quake rely heavily on FPU perfomance! Read
more of t his subj ect here.
Therefore, if you use your PC in advanced design applicat ions, t he FPU performance becomes significant . For some users,
it is only of limit ed import ance.
Graphic overview of the processors
[ t op]
There are CPUs of many brand names ( I BM, Texas, Cyrix, AMD) , and oft en t hey make models which overlap t wo
generat ions. This can make it difficult t o keep of t rack of CPUs. Here is an at t empt t o ident ify t he various CPUs according
t o generat ion:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3a3.htm (2 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:54 AM
An illustrated Guide to CPUs from 8086 to Pentium-III
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3a3.htm (3 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:54 AM
An illustrated Guide to CPUs from 8086 to Pentium-III
Click for Module 3c about t he 5t h generat ions CPUs ( Pent iums et c. )
Click for Module 3d about t he clock frequencies
Click for Module 3e about 6t h generat ions CPUs ( Pent ium I I s et c. )
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3a3.htm (4 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:54 AM
An illustrated Guide to CPU improvements
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 3b1.
The CPU developments and improvements
The cont ent s:
q Clock frequency and - doubling
q Next page
q Previous page
Intro
I f you have t o improve a CPU and t hat happens all t he t ime it is not only a mat t er of
t echnical development . There are many bot t lenecks in and around t he CPU, which are
cont inually being bet t ered.
To underst and t hese t echnological improvement s, one must remember t hat t he CPU is a dat a
processing gadget , mount ed on a print ed circuit board ( t he mot herboard) . Much of t he dat a
processing t akes place inside t he CPU. However, all dat a must be t ransport ed t o and from t he
CPU via t he syst em bus. But what det ermines t he speed of t he CPU?
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3b1.htm (1 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:56 AM
An illustrated Guide to CPU improvements
Clock frequency
[ t op]
We know t his from t he ads: "A Celeron 466 MHz. " The 466 MHz is t he clock frequency.
Act ually, t here is a small cryst al on t he mot herboard. which cont inually t icks t o t he CPU at a
st eady number of clock t icks per second. At each clock t ick somet hing happens in t he CPU.
Thus, t he more t icks per second t he more dat a are processed per second.
The first CPUs worked at a frequency of 4. 77 MHz. Subsequent ly t hen, clock frequencies rat es
rose t o 16, 25, 50, 66, 90, 133 and 200 MHz t o t he best t oday, which operat e at almost 2000
MHz. Clock frequencies are st ill being increased. I n a few years we will have CPUs operat ing
at 3 GHz and more.
To reach t hese very high clock frequencies, one has t o employ a t echnique called clock
doubling.
Clock doubling in the CPU
[ t op]
The problem wit h t he high clock frequencies is t o ensure t hat ot her elect ronic component s
keep up wit h t he pace. I t is rat her simple t o make dat a move very fast inside a chip where
t he print t racks are microscopic. But when we move out side t he chip, ot her problems appear.
The ot her component s must be able t o keep up wit h t he pace. When t he frequency get s t oo
high, t he circuit board print t racks st art act ing as ant ennae and various forms of "radio noise"
appears. Briefly, it becomes expensive t o make t he rest of t he hardware t o keep up wit h
t hese high frequencies.
The solut ion t o t his problem was t o split t he clock frequency in t wo:
q A high int ernal clock frequency, which governs t he pace of t he CPU.
q A lower ext ernal clock frequency, which governs t he pace on t he syst em bus.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3b1.htm (2 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:56 AM
An illustrated Guide to CPU improvements
I nt el' s 80486DX2 25/ 50 MHz was t he first chip wit h clock doubling. I t was int roduced in 1992
wit h great pot ent ial. For a lower price you could acquire a chip, which provided 90% of t he
486DX50 performance. The DX50 ran at 50 MHz bot h int ernally and ext ernally. The DX2 ran
at j ust 25 MHz on t he syst em bus. This enabled lower cost mot herboards. Also RAM speed
demands were lower.
Clock doubling occurs inside t he CPU. I f t he mot herboard cryst al works at 25 MHz, t he CPU
will receive a signal every 40 nanosecond ( ns) . I nt ernally in t he CPU, t his frequency is
doubled t o 50 MHz. Now t he clock t icks every 20 ns inside t he CPU. This frequency governs
all int ernal t ransact ions, including int eger unit , float ing point unit , and all memory
management unit operat ions as well as ot hers. The only area st ill working at 25 MHz are
ext ernal dat a t ransfers. That is t ransfers t o RAM, BI OS and t he I / O port s.
RAM speeds
The speed of t he CPU is also connect ed t o t he RAM. The ordinary FPM RAM and EDO RAM can
funct ioned at a maximum of 66 MHz ( possibly 75 MHz) . Therefore, Pent ium and similar CPUs
were "clocked up" wit h fact ors from 2 t o 5 int ernally.
I n 1998 t he PC100 RAM was int roduced t oget her wit h new mot herboards and chip set . This
RAM works at 100 MHz, and using t he clock fact ors 3. 5, 4 and 4. 5 we had CPUs running at
350, 400 and 450 MHz. The I nt el CPUs Pent ium I I , Celeron, and Pent ium I I I can operat e wit h
clock fact ors of up t o 8.
Wit h chip set designs like i815 t he int ernal clock frequency operat es independent ly of t he FSB
( front side bus) connect ing t he CPU t o t he nort h bridge of t he chip set . Hence we do not need
t o t alk about clock doubling anymore, and t he clock frequencies of t he CPU reaches 1700
MHz and above.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Also see Module 3c about t he 5t h generat ions CPUs ( Pent iums et c. )
Click for Module 3d about t he clock frequencies
Click for Module 3e about 6t h generat ions CPUs ( Pent ium I I s et c. )
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3b1.htm (3 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:56 AM
An illustrated Guide to CPU improvements
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3b1.htm (4 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:56 AM
An illustrated Guide to CPU improvements
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 3b2.
The CPU developments and improvements
The cont ent s:
q Cache RAM
q Cache overview
q Next page
q Previous page
Please support our
sponsor.
About CPU cache RAM
[ t op]
The CPU must deliver it s dat a at a very high speed. The regular RAM cannot keep up wit h
t hat speed. Therefore, a special RAM t ype called cache is used as a buffer - t emporary
st orage. To get t op performance from t he CPU, t he number of out going t ransact ions must be
minimized. The more dat a t ransmissions, which can be cont ained inside t he CPU, t he bet t er
t he performance. Therefore, t he I nt el 80486 was equipped wit h a built in mat hemat ical co-
processor, float ing point unit and 8 KB L1- cache RAM. These t wo feat ures help minimize t he
dat a flow in and out of t he CPU.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3b2.htm (1 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:57 AM
An illustrated Guide to CPU improvements
Cache RAM becomes especially import ant in clock doubled CPUs, where int ernal clock
frequency is much higher t han ext ernal. Then t he cache RAM enhances t he "horsepower" of
t he CPU, by allowing fast er receipt or delivery of dat a. Beginning wit h 486 processors, t wo
layers of cache are employed. The fast est cache RAM is inside t he CPU. I t is called L1 cache.
The next layer is t he L2 cache, which are small SRAM chips on t he mot herboard. See t he
illust rat ion below of a t radit ional Pent ium PC:
How much RAM
The L2 cache can cache a cert ain amount of RAM. How much is det ermined by t he chip set
and t he so- called TAG- RAM, t he circuit cont rolling t he cache.
One of t he most popular chip set s for t he original Pent ium was I nt el s 82430TX. it worked
very well - except for det ail. it could not cache more t han 64 MB RAM. I f you added more
RAM t o t he PC, it was not cached by t he L2 cache. Hence, using more t han 64 MB of RAM on
a TX- based mot herboard decreased t he performance.
This sit uat ion has caused a lot of rumors about Windows not being able t o use more t han 64
MB RAM. However: Windows 98 can use up t o 2 GB RAM! The only problems wit h t he amount
of RAM has come from poorly designed chip set s as t he TX.
Cache overview
[ t op]
L1- cache first appeared in I nt el' s 80486DX chip. Today, bigger and bet t er CPU cache is a
nat ural st ep in t he development of new CPUs. Here we only see t he int ernal caches, i. e.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3b2.htm (2 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:57 AM
An illustrated Guide to CPU improvements
cache int egrat ed t o t he CPU and working at t he full clock speed.
CPU Cache size in t he CPU
80486DX and DX2 8 KB L1
80486DX4 16 KB L1
Pent ium 16 KB L1
Pent ium Pro 16 KB L1 + 256 KB L2
( some 512 KB L2)
Pent ium MMX 32 KB L1
AMD K6 and K6- 2 64 KB L1
Pent ium I I and I I I 32 KB L1
Celeron 32 KB L1 + 128 KB L2
Pent ium I I I Cumine 32 KB L1 + 256 KB L2
AMD K6- 3 64 KB L1 + 256 KB L2
AMD K7 At hlon 128 KB L1
AMD Duron 128 KB L1 + 64 KB L2
AMD At hlon Thunderbird 128 KB L1 + 256 KB L2
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3b2.htm (3 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:57 AM
An illustrated Guide to CPU improvements
Also see Module 3c about t he 5t h generat ions CPUs ( Pent iums et c. )
Click for Module 3d about t he clock frequencies
Click for Module 3e about 6t h generat ions CPUs ( Pent ium I I s et c. )
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3b2.htm (4 of 4)7/27/2004 4:07:57 AM
An illustrated Guide to CPU improvements
KarbosGuide.com. Module 3b3.
The CPU developments and improvements
The cont ent s:
q Areas of development
q The CPU speed measurement
q CPU changes - hist orical review
q 80486DX4
q Next page
q Previous page
Please support our
sponsor.
Areas of development
[ t op]
I n t he following t able, you see some of t he t echnologies, which can be improved in t he CPU
design. Not e t hat int ernal means inside t he CPU. Ext ernal speed, et c. refers t o feat ures
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3b3.htm (1 of 6)7/27/2004 4:07:59 AM
An illustrated Guide to CPU improvements
immediat ely out side t he CPU on t he mot herboard.
Development area Significance Example
I nt ernal clock frequency speed of dat a processing inside
t he CPU.
800 MHz
Ext ernal clock frequency Speed of dat a t ransfer t o and
from t he CPU via t he syst em bus
( or Front Side Bus) .
133 MHz
Clock doubling That t he CPU works x t imes
fast er int ernally t han ext ernally.
6. 0 t imes ( like above)
I nt ernal dat a widt h How many dat a bit s can t he CPU
process simult aneously.
32 bit s
Ext ernal dat a widt h How many dat a bit s can t he CPU
receive simult aneously for
processing
64 bit s
I nt ernal cache ( Level 1 cache) Large and bet t er L1 cache, which
is a small fast RAM. I t works as a
buffer bet ween CPU and regular
RAM.
64 KB
Ext ernal cache ( Level 2
cache)
Larger and bet t er implement ed
L2 cache, place on- die in same
chip as CPU.
256 or 512 KB
I nst ruct ion set Can t he inst ruct ion set be
simplified, t o speed up program
processing? Or can it be
improved?
RI SC code
More pipelines
MMX inst ruct ions
3DNow! or SSE
The CPU speed measurement
[ t op]
When we look at a CPU, it s speed is t he most significant feat ure. All newer CPUs can do t he
same. You can run Office 2000 in Windows 98 on a 486 CPU. I t would be quit e slow, but it is
possible.
Speed is t he primary difference bet ween newer CPUs. Speed improvement is a product of t he
above ment ioned t echnologies ( such as clock frequency and bus widt h) .
The old Speed Index
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3b3.htm (2 of 6)7/27/2004 4:07:59 AM
An illustrated Guide to CPU improvements
There are many, many ways t o measure CPU speed. The subj ect is boundless. For years,
Nort on' s Speed I ndex was used. That is a t est , which can be run on any PC wit h t he Nort on
Ut ilit ies Sysinfo program.
I n t he t able below, you see a number of t he most common older CPUs. You can see how t hey
are designed regarding clock speed and bus widt h. The last column shows t heir Nort on Speed
I ndex ( SI ) . That is a relat ive number, which can be used t o compare different CPUs. I t is not
used for modern CPUs.
CPU CPU speed Clock
doubling
Syst em bus
speed
Dat a widt h SI
8086 4. 77 MHz 1 4. 77 MHz 16 bit 1
80286 12 MHz 1 12 MHz 16 bit 8
80386DX 25 MHz 1 25 MHz 32 bit 40
486 DX2- 66 66 MHz 2 33 MHz 32 bit 142
5x86- 133 133 MHz 4 33 MHz 32 bit 288
Pent ium 75 75 MHz 1. 5 50 MHz 64 bit 235
Pent ium 90 90 MHz 1. 5 60 MHz 64 bit 278
Pent ium 100 100 MHz 1. 5 66 MHz 64 bit 305
Pent ium 133 133 MHz 2 66 MHz 64 bit 420
Pent ium 166 166 MHz 2. 5 66 MHz 64 bit 527
Pent ium 200 200 MHz 3 66 MHz 64 bit 629
Newer CPUs are compared by t heir clock frequency or by more more sophist icat ed rat ings.
CPU changes - historical review
[ t op]
This describes briefly t he changes t hroughout t he early CPU generat ions:
8088 and 8086
The 8086 from 1978 was t he first 16 bit CPU from I nt el using a 16 bit syst em bus. However
16 bit hardware such as mot herboards were t oo expensive and even non exist ing at t his
t ime, where t he 8 bit microcomput ers were t he st andard.
I n 1979 I nt el reengineered t he CPU so it fit wit h exist ing 8 bit hardware. The first PC ( in
1981) had t his 8088 CPU. The 8088 is a 16 bit CPU, but only int ernally. The ext ernal dat a bus
widt h is only 8 bit giving compat ibilit y wit h exist ing hardware.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3b3.htm (3 of 6)7/27/2004 4:07:59 AM
An illustrated Guide to CPU improvements
Act ually t he 8088 is a 16/ 8 bit CPU. Logically it could have been named 8086SX. The 8086
was t he first t ot al 16 bit CPU in t his family.
80286
The 286 from 1982 was also a 16 bit processor. I t gave a big advance relat ive t o t he first
generat ion chips. The clock frequency was increased, but t he maj or improvement was in
opt imizing inst ruct ion handling. The 286 produced much more per clock t ick t han 8088/ 8086
did.
At t he int roduct ory speed ( 6 MHz) it performed four t imes bet t er t han t he 8086 at 4. 77 MHz.
Lat er it was int roduced wit h 8, 10 and 12 MHz clock speed being used in t he I BM PC- AT from
1984.
Anot her innovat ion was t he abilit y t o run in prot ect ed mode - a new work mode wit h a "24 bit
virt ual address mode", which point ed t owards t he lat er shift from DOS t o Windows and
mult it asking. However you could not change from prot ect ed back t o real mode wit hout
reboot ing t he PC, and t he only operat ing syst em t o use t his was OS/ 2.
80386
The change t o t he 386s came Oct ober t he 17t h 1985. The 80386 was t he first 32 bit CPU.
From t he t radit ional DOS PC' s point of view, t his was not a revolut ion. A good 286 ran as fast
as t he first 386SXs - despit e t he implement at ion of 32 bit mode.
I t could address up t o 4 GB of memory and had a bet t er addressing ( in bigger chunks) t han
t he 286. The 386 ran at clock speeds of 16, 20 and 33 MHz. Lat er Cyrix and AMD made
clones working at 40 MHz.
The 386 int roduced a new working mode besides t he real and t he prot ect ed modes of t he
286. The new mode called virt ual 8086 opened for mult it asking since t he CPU could generat e
several virt ual 8086s running in each t heir own memory space.
The 80386 was t he first CPU t o perform well wit h t he early versions of Windows .
80386SX
This chip was a very popular discount edit ion of 386DX. I t has only 16 bit ext ernal dat a bus
cont rary t o t he DX 32 bit . Also, t he SX has only 24 address lines, Therefore, it can only
address a maximum of 16 Mb RAM. I t is not really a t rue 386, but t he cheaper mot herboard
layout made it very popular.
80486
The 486 was released April t he 10t h 1989. Generally speaking, t he 486 runs t wice as fast as
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3b3.htm (4 of 6)7/27/2004 4:07:59 AM
An illustrated Guide to CPU improvements
it s predecessor - all t hings being equal. That is because of bet t er implement at ion of t he x86
inst ruct ions. They are handled fast er, more in RI SC mode. At t he same t ime bus speed is
increased, but bot h 386DX and 486DX are 32 bit chips. A novelt y in t he 486 is t he built in
mat h co- processor. Before, t hat had t o be inst alled as a separat e 387 chip. The 486 also held
8 KB of L1 cache.
80486SX
This was a new discount chip. The mat h co- processor was simply omit t ed.
Cyrix 486SLC: Cyrix and Texas I nst rument s have made a series of 486SLC chips. They used
t he same set of inst ruct ions as did t he 486DX, and t hey run at 32 bit int ernally, like t he DX.
However, ext ernally t hey run at only 16 bit ( like a 386SX) . Therefore, t hey can only handle
16 MB RAM. Furt hermore, t hey only have 1 KB int ernal cache and no mat hemat ical co-
processor. Act ually t hey are j ust improved 286/ 386SXs. They are not cloned chips. There are
subst ant ial differences in t heir archit ect ure compared t o t he I nt el chips.
I BM 486SLC2: I BM had t heir own 486 chip product ion. The series was named SLC2 and
SLC3. The lat t er was also known as Blue Light ning. These chips could be compared t o I nt el' s
486SX, since t hey did not have a built - in mat hemat ical co- processor. However, t hey had 16
KB int ernal cache ( compared t o I nt el' s 8) . What reduced t heir performance was t he bus
int erface, which was from t he 386 chip. SLC2 runs at 25/ 50 MHz ext ernally and int ernally,
while t he SLC3 chip runs at 25/ 75 and 33/ 100 MHz. I BM manufact ured t hese chips for t heir
own PCs in t heir own facilit ies, licensing t he logic from I nt el. The chips were not sold
separat ely.
DX4: Further 486 developments
[ t op]
I nt el' s DX4 processors represent ed an improvement on t he 80486 series. The clock speed
was t ripled from 25 t o 75 MHz and from 33 t o 100 MHz. Anot her DX4 chip was speeded up
from 25 t o 83 MHz.
Cont rary t o what you might t hink, t he DX4 were not named for a quadrupling. They were
named t his way because of t he regist ry of I nt el' s 80486 and 80586 names. The DX4 name is
separat ed from t hat cont ext , so it could be pat ent ed. I f DX3 referred t o a t ripling, t his would
not work. The same t ype of problem caused t he next generat ion chip t o be named Pent ium,
rat her t han 80586.
The DX4 has 16 KB int ernal cache and operat es on 3. 3 volt ( t hey will t olerat e 5 volt , t o
accommodat e exist ing syst em boards) . DX and DX2 have only 8 KB cache and require 5 volt
wit h inherent heat problems.
5X86: AMD has made a series of so called 5X86 CPUs. Those are improved 486s, which
approach t he 5t h generat ion chips, hence t heir name. Their 120 MHz model is not ewort hy. I t
could easily be t uned t o run at 160 MHz.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3b3.htm (5 of 6)7/27/2004 4:07:59 AM
An illustrated Guide to CPU improvements
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Click for Module 3d about t he clock frequencies
Click for Module 3e about 6t h generat ions CPUs ( Pent ium I I s et c. )
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3b3.htm (6 of 6)7/27/2004 4:07:59 AM
An illustrated Guide to Pentiums
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. .
Module 3c. About the 5th generations CPUs
Wit h I nt el' s Pent ium from 1993, a new era began in t he cont inued CPU development . I n t hese pages, we will look
at different variat ions and furt her development of 5t h. generat ion CPUs.
q The original Pent ium
q Next page
q Previous page
Please support our
sponsor.
Pentium Classic (P54C)
[ t op]
This chip was developed by I nt el in Haifa, I srael and was released on March t he 22t h 1993.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3c1.htm (1 of 3)7/27/2004 4:08:01 AM
An illustrated Guide to Pentiums
The Pent ium processor is super scalar, meaning t hat it can execut e more t han one inst ruct ion per clock t ick.
Typically, it handles t wo inst ruct ions per t ick. I n t his respect , we can compare it t o a double 486.
At t he same t ime, t here have been big changes in t he syst em busses. The widt h has doubled t o 64 bit , and t he
speed has increased t o 60 or 66 MHz.
This has result ed in a subst ant ial improvement from t he 486 t echnology.
Two versions to start with
Originally, Pent ium came in t wo versions: a 60 MHz and a 66 MHz. Bot h operat ed on 5 Volt . This produced a lot of
heat ( it was said t hat you could fry an egg on t hem! ) .
The next Pent ium ( P54C) generat ion worked wit h an int ernal clock doubling of 1. 5 t imes. These chips ran at 3
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3c1.htm (2 of 3)7/27/2004 4:08:01 AM
An illustrated Guide to Pentiums
Volt . This t ook care of t he heat problem. However, heat coming from t he CPU has been a problem ever since.
Wit h t hese t he first P5 processors, I nt el carried t wo Pent ium lines; some running at 60 MHz on t he syst em bus
( The P90, P120, P150, and P180) and ot hers wit h 66 MHz syst em bus ( t he P100, P133, P166 and P200) .
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Or cont inue wit h t he 6t h generat ion CPUs. Click for Module 3e.
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side.
Read module 5b about AGP and module 5c about Firewire.
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
Read module 7c about sound cards, and 7d on digit al sound and music.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3c1.htm (3 of 3)7/27/2004 4:08:01 AM
An illustrated Guide to Pentiums
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. .
Module 3c2. About the 5th generations CPUs - continued
q The Cyrix 6x86
q The AMD K5
q Next page
q Previous page
Please support our
sponsor.
Cyrix [ t op]
This is a low cost alt ernat ive t o Pent ium. The chip from t he Cyrix company, which was
int roduced February 5, 1996, is a cheap Pent ium copy.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3c2.htm (1 of 5)7/27/2004 4:08:03 AM
An illustrated Guide to Pentiums
The chip was Pent ium compat ible, since it fit t ed int o a Socket 7. When Cyrix suggest ed a 6t h
generat ion in t heir naming, it was because t he 6X86 employed advanced t echniques, which
were not found in I nt el' s Pent ium. Thereby Cyrix got improved performance from t heir chip
wit h t he same clock speed.
The Cyrix 6X86 was market ed using a comparison t o I nt el' s clock frequency.
The 6x86 chips had lower int ernal speed t han model name st at ed. Below, you can see t he
dat a for t he different models:
Cyrix model CPU speed Clock doubling Syst em bus speed
P120+ 100 MHz 2 50 MHz
P133+ 110 MHz 2 55 MHz
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3c2.htm (2 of 5)7/27/2004 4:08:03 AM
An illustrated Guide to Pentiums
P166+ 133 MHz 2 66 MHz
P200+ 150 MHz 2 75 MHz
An int erest ing det ail was, t hat t he 6X86 P200+ was t he first CPU t o run a syst em bus speed
above 66 MHz. However it was difficult t o find mot herboards wit h chip set s capable of t his, so
t he chip never achieved an import ant posit ion in t he market .
Cyrix 6X86s were known for poor performance regarding float ing point operat ions. There also
were problems wit h Cyrix and NT 4. 0.
I n my experience, t he 6x86 did quit e a good j ob wit h common office programs in Windows
95. I was very sat isfied wit h t he P166+ I had. Of course I would prefer a genuine Pent ium
166, but I was not willing t o pay t hree t imes t he price at t hat t ime.
The 6X86 was lat er improved wit h Dual Volt age ( like Pent ium P55C) . This reduced power
consumpt ion and heat generat ion.
Also see t he art icle on Cyrix M3. The company Cyrix was in 1999 t aken over by Taiwanese
chip producer VI A.
[ t op]
AMD is anot her CPU brand, which has become very import ant . Their Pent ium like chips
offered I nt el t ight compet it ion. AMD used t heir own t echnologies, and hence t hey are not
clones. They had t hese series:
q K5, corresponding t o t he classic Pent iums ( wit h 16 KB L1 cache and no MMX)
q K6, K6- 2, and K6- 3 which compet e wit h Pent ium MMX and Pent ium I I
q K7 At hlon, from August 1999, which is not Socket 7 compat ible.
K5
K5 was Pent ium copy. The old K5 was for example sold as PR133. This means, t hat t he chip
should perform like a Pent ium P133. However, it only runs 100 MHz int ernally. I t st ill has t o
be inst alled in t he mot herboard like a P133.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3c2.htm (3 of 5)7/27/2004 4:08:03 AM
An illustrated Guide to Pentiums
AMD' s K5 also exist ed as PR166. As t he name suggest s, it was int ended t o compet e wit h
I nt el' s P166. I t operat ed at j ust 116. 6 MHz int ernally ( 1. 75 X 66 MHz) . According t o t he
highly respect ed German magazine c' t , issue 3. 97 page 20, it act ually ran at least as fast as
t he P166.
This was due t o an opt imized cache and ot her new development s. The only feat ure on which
it could not mat ch t he P166 was in float ing point operat ions. These are t ypically necessary in
3D calculat ions in Aut oCAD and similar applicat ions.
PR133 and PR166 cost far less t han t he similar Pent ium models, and t hey were very popular
in low budget machines.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Or cont inue wit h t he 6t h generat ion CPUs. Click for Module 3e.
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side.
Read module 5b about AGP and module 5c about Firewire.
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
Read module 7c about sound cards, and 7d on digit al sound and music.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3c2.htm (4 of 5)7/27/2004 4:08:03 AM
An illustrated Guide to Pentiums
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3c2.htm (5 of 5)7/27/2004 4:08:03 AM
An illustrated Guide to Pentiums
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. .
Module 3c3. The 5th generations CPUs - continued
q The P55C - MMX
q I DT WinChip
q Volt ages - dual volt age
q Next page
q Previous page
Please support our
sponsor.
Pentium MMX (P55C)
[ t op]
The P55C Pent iums were int roduced January 8, 1997. MMX is a new set of inst ruct ions ( 57
new int eger inst ruct ions, four new dat a t ypes, and eight 64 bit regist ers) , which expand t he
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3c3.htm (1 of 6)7/27/2004 4:08:06 AM
An illustrated Guide to Pentiums
capabilit ies of t he CPU. I t is an addit ion t o t he original Pent ium set of inst ruct ions.
The MMX inst ruct ions were designed for mult imedia programs. The programmers can ut ilize
t hese inst ruct ions in t heir programs. These allow t he Pent ium t o provide improved program
execut ion.
Bot h Cyrix and AMD use MMX in t heir 6t h generat ion CPUs ( K6 and M2) . Programs, which are
writ t en wit h MMX inst ruct ions, can st ill be run on, for example, a Pent ium wit hout MMX.
However, execut ion is slower wit h t he t radit ional inst ruct ions.
Please, READ MORE ON MMX HERE.
More L1 cache and higher clock frequency
Compared t o t he Pent ium Classic, t he Pent ium MMX were furt her improved wit h 32 KB L1
cache ( t he old one had 16 KB) . There were also ot her improvement s in t he CPU. These
improvement s t oget her meant 10- 20% bet t er performance at similar clock speeds. The clock
frequency of t he new processors were 166, 200 and 233 MHz.
Dual voltage
The P55C required a new mot herboard. Not because of MMX - t hat is pure soft ware, but
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3c3.htm (2 of 6)7/27/2004 4:08:06 AM
An illustrated Guide to Pentiums
because of changes in t he power supply. The P55C operat ed wit h dual volt age t echnology. To
reduce heat generat ion, t his chip requires t wo different volt ages: 2. 8 Volt t o t he nucleus and
3. 3 Volt t o t he I / O sect ion. The old mot herboards for t he P54Cs have only one volt age t o t he
CPU. Thus, t he new CPU requires a new mot herboard.
Tillamook
For use in lapt ops I nt el has a special power- saving version of t he Pent ium MMX. The so- called
Tillamook processor is manufact ured using 0. 25 micron t echnology, and you find it in 266
and 300 MHz versions.
IDT Winchip
[ t op]
I DT was anot her smaller company t o produce low- priced Pent ium MMX- like CPUs. Their first
WinChip C6 was int roduced in May 1997. The company want ed t o deliver 200 MHz Pent ium
MMXs for $50.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3c3.htm (3 of 6)7/27/2004 4:08:06 AM
An illustrated Guide to Pentiums
About the IDT WinChip C6 CPU
q 5. 4 million t ransist or
q 0. 35 micron, 4- layer met al CMOS t echnology
q Socket 7 compat ible
q 200 MHz
About the WinChip 2 3D, released May 19, 1998
q Socket 7 processors running at 266 MHz and 300 MHz
q 0. 25- micron process t echnology
q 2. 5- volt I BM Blue Logic t echnology
q 6 million t ransist ors
q Die size only 88mm
2
making it t he smallest x86 processor in t he world
q Superscalar MMX and 3DNow!
q Fully pipelined float ing point unit
q 100 MHz bus support I DT expect ed t o cont inue t he development of t heir WinChips. They
want ed t o double up t he L1 cache for bet t er performance and t o int roduce a superpipeline
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3c3.htm (4 of 6)7/27/2004 4:08:06 AM
An illustrated Guide to Pentiums
t echnology, which also will speed up t he whole t hing.
We never saw many I DT chips in my count ry.
I n 1999 t he company was t aken over by VI A who int egrat es t he I DT t echnology in t heir Cyrix
processor line.
Voltages - dual voltage
[ t op]
One of t he most import ant CPU t echnologies is t he cont inually t hinner wires inside t he chip.
Wit h t hinner wires, t he CPU can operat e at lower volt age. That result s in a smaller CPU
generat ing less heat and wit h t he abilit y t o operat e at higher speeds. A st ep in t his
development is t he design of dual volt age chips:
q The int erface t o t he I / O bus, which always requires 3. 3 volt .
q I n int ernal CPU part s, it is advant ageous t o reduce t he volt age as much as possible. This
can be done because of t he ext remely t hin wires in t he CPU. The Socket 7 mot herboards
have a t wo part volt age regulat or t o mat ch t he needs of t he CPU. Here are some select ed
CPUs and t heir volt age requirement s:
CPU I nt ernal volt age I / O volt age
Pent ium MMX 2. 8 Volt 3. 3 Volt
AMD K6 2. 8/ 2. 9 Volt 3. 3 Volt
Cyrix 6X86MX 2. 8 Volt 3. 3 Volt
Pent ium I I "Klamat h" 2. 8 Volt 3. 3 Volt
AMD K6- 2 2. 2 Volt 3. 3 Volt
Pent ium I I and I I I 2. 0 Volt 3. 3 Volt
Pent ium I I I "CuMine" 1. 6 Volt 3. 3 Volt
q Next page
q Previous page
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3c3.htm (5 of 6)7/27/2004 4:08:06 AM
An illustrated Guide to Pentiums
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Or cont inue wit h t he 6t h generat ion CPUs. Click for Module 3e.
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side.
Read module 5b about AGP and module 5c about Firewire.
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
Read module 7c about sound cards, and 7d on digit al sound and music.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3c3.htm (6 of 6)7/27/2004 4:08:06 AM
An illustrated Guide to Pentiums
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
www.karbosguide.com
Module 3c4. The 5th generations CPUs - continued
q Chip product ion
q Moore' s Law
q Various not es about CPUs
q Next page
q Previous page
Please support our
sponsor.
Chip production
[ t op]
I t t akes a long t ime t o manufact ure a CPU. 5 t o 50 million t ransist ors must be placed on a
t iny silicon wafer. Act ually, it required 90 workdays 24 hours round- t he- clock t o produce a
Pent ium CPU.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3c4.htm (1 of 6)7/27/2004 4:08:08 AM
An illustrated Guide to Pentiums
CPUs are manufact ured in large wafers cont aining maybe 140 t o 150 CPUs. Usually 110 t o
120 of t hese perform perfect ly. The rest are discarded. The wafers are burned, et ched, and
t reat ed in hour long processes - layer by layer. I n t he CPU t here are up t o 20 layers of silicon
wafers wit h millions of micro t ransist ors.
Process technology
The CPUs are processed using CMOS t echnology wit h smaller and smaller "wires". The result
is smaller "dies" ( t he lit t le area inside t he chip holding all t he t ransist ors) wit h more and
more t ransist ors. The power consumpt ion goes down, and t he clock frequency goes up.
CPU Process t echnology Number of t ransist ors die size
486 1. 0 micron 1, 200, 000
79 mm
2
I nt el Pent ium 0. 5 micron 3, 100, 000
161 mm
2
Cyrix 6X86 0. 5 micron 3, 100, 000
392 mm
2
I nt el Pent ium MMX 0. 35 micron 5, 500, 000
128 mm
2
AMD K6 0. 25 micron 8, 000, 000
68 mm
2
I nt el Pent ium I I 0. 35 micron
0. 25 micron
7, 500, 000
131 mm
2
I nt el Celeron 0. 25 micron 7, 500, 000
131 mm
2
155 mm
2
Cyrix MI I 0. 25 micron 6, 500, 000
119 mm
2
I DT
WinChip 2 3D
0. 25 micron 6, 000, 000
88 mm
2
AMD K6- 2 0. 25 micron 9, 300, 000
81 mm
2
AMD K6- 3 0. 25 micron ?
118 mm
2
AMD ATHLON 0. 25 micron 22, 000, 000
184 mm
2
I nt el Pent ium I I I CuMine 0. 18 micron 28, 000, 000
106 mm
2
AMD ATHLON "Thunderbird" 0. 18 micron 37, 000, 000
( 22 mil. + 15 mil. )
117 mm
2
I nt el Pent ium 4 0. 18 micron 42, 000, 000
217 mm
2
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3c4.htm (2 of 6)7/27/2004 4:08:08 AM
An illustrated Guide to Pentiums
I nt el Pent ium 4 Nort hwood 0. 13 micron 42, 000, 000
116 mm
2
At hlon T 0. 13 micron 37, 000, 000
80 mm
2
Here you see t he I nt el process generat ions:
Process generat ion Year Gat e lengt h
P648 1989 1. 0 micron
P650 1991 0. 8 micron
P852 1993 0. 5 micron
P854 1995 0. 35 micron
P856 1997 0. 25 micron
P858 2000 0. 18/ 0. 13 micron
Moore's Law
The CPUs have doubled t heir calculat ing capacit y every 18 mont hs. This is called "Moore' s
Law" and was predict ed in 1965 by Gordon Moore. He was right for more t han 30 years. The
lat est CPUs use int ernal wiring only 0. 25 microns wide ( 1/ 400 of a human hair) . But if
Moore' s Law has t o be valid int o t he next cent ury, more t ransist ors have t o be squeezed ont o
silicon layers.
I BM succeeded as t he first in making copper conduct ors inst ead of aluminum. Copper is
cheaper and fast er, but t he problem was t o isolat e it from t he silicon. The problem has been
solved wit h a new t ype of coat ing, and now chips can be designed wit h 0. 13 micron
t echnology. The t echnology is expect ed lat er t o work wit h j ust 0. 05 micron wiring!
Texas I nst rument s announced on August 27t h 1998 t hat t hey expect 0. 07 micron CMOS
processing in t he year 2001.
AMD was t he first company t o mass- produce copper- wired CPU' s. This happened in t heir fab
30 in Dresden, April 2000.
Chip errors
[ t op]
The following miscalculat ions occur in 386, 486, and Pent ium, when running Excel, Works, or
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3c4.htm (3 of 6)7/27/2004 4:08:08 AM
An illustrated Guide to Pentiums
Pascal, wit h t he numbers 49 and 187:
All CPUs have fault y inst ruct ions. Recent ly flaws have been discovered wit hin t he Pent ium I I
and Cyrix 6x86MX.
The Pentium scandal
[ t op]
Pent ium was hit by a scandal in lat e 1994, when an error in t he mat hemat ical co- processor
( FPU) became publicly known. I t simply miscalculat ed at a given division. I nt el knew of t he
error from early t hat summer but more or less kept it secret .
I nt el insist ed t hat t he error would occur ext remely rarely. Compaq immediat ely modified t heir
product ion t o disable t he FPU. Short ly t hereaft er, I BM announced t hat t hey would st op t he
product ion of Pent ium based PCs. I BM had calculat ed t hat t he error would occur every 24
days. At t he t ime, I BM was working t o ext ricat e t hemselves from t he I nt el CPU monopoly.
They were moving t owards Power PC, Cyrix, and NexGen based PCs. Thus t he scandal played
right int o t heir hands. You see t he error here, where A3 should be equal t o A1:
I nt el underest imat ed t he significance of t he miscalculat ions, cert ainly regarding users
employing complex mat hemat ical calculat ions. I BM over dramat ized t he error for polit ical
reasons. This all happened in December 1994, while I nt el was running t heir big TV campaign
for Pent ium.
That gave birt h t o a number of j okes: How many Pent ium programmers are needed t o screw
in a bulb? ( answer: 1. 9990427) . Why is Pent ium not named 586? Because it would have t o
be called 585. 999983405! I n a different vein: How many Apple employees does it require t o
change a bulb? 7! One t o hold t he bulb and 6 t o design T- shirt s. And: how many I BM
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3c4.htm (4 of 6)7/27/2004 4:08:08 AM
An illustrated Guide to Pentiums
employees does it require t o change a bulb? None! I BM simply announces a new feat ure
called "black bulb. "
Intel Owner's Club site
[ t op]
This sit e is good if you are int erest ed in t he CPUs. Find t he I nt el Owner' s Club, which is a
free, easy way for members t o:
q get t he scoop on t he lat est I nt el t echnologies
q get info on hot new soft ware and t echnologies
q int eract wit h I nt el & t echnology expert s
q download free soft ware and games
q ent er cont est s.
My membership has helped me t o learn how t o use t he I nt el web sit e, which holds a lot of
informat ion. Only I nt el' s servers can be t errible slow, so you easily get t ired from t hem.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Or cont inue wit h t he 6t h generat ion CPUs. Click for Module 3e.
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port
side.
Read module 5b about AGP and module 5c about Firewire.
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
Read module 7c about sound cards, and 7d on digit al sound and music.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3c4.htm (5 of 6)7/27/2004 4:08:08 AM
An illustrated Guide to Pentiums
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3c4.htm (6 of 6)7/27/2004 4:08:08 AM
An illustrated Guide to Over-clocking.
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com.
Module 3d.1 About Cooling and Over clocking
The cont ent s:
q About cooling
q A clean cooler. .
q Next page
q Previous page
Cooling
[ t op]
All modern CPUs share a common need for cooling. Make sure t o include a good cooler. I t has t o be mat ched t o
t he size of t he CPU.
q I t has t o be at t ached properly, eit her wit h glue or a clamp, which fit s t he CPU.
q I t must have a subst ant ial size heat sink - t he bigger t he bet t er.
q The fan must be mount ed in roller bearings, t o minimize noise.
The bigger t he fan and heat sink, t he bet t er it is. The CPU will operat e more reliably. I t will have a longer life
span, and it can possibly be over clocked. I f you buy I nt el CPUs, buy t hem "in a box". I t is a special package,
priced slight ly higher t han j ust t he CPU. They always include a good fan and a t hree year warrant y.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3d1.htm (1 of 7)7/27/2004 4:08:10 AM
An illustrated Guide to Over-clocking.
Pent ium wit h fan. Phot o t aken wit h Canon Powershot 600. JPG- file 1: 30, 32 KB.
What is a cooler?
[ t op]
A cooler consist s of t wo part s:
q A fan t hat needs power supply.
q A cooling element , usually made of met al ribs. The fan is placed on t he t op of t he cooling element , which is
fast ened very t ight t o t he t op of t he CPU:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3d1.htm (2 of 7)7/27/2004 4:08:10 AM
An illustrated Guide to Over-clocking.
The power supply can be connect ed t wo ways:
q From t he main power supply of t he PC. This is t he case in most PCs and all older ones.
q From t he mot herboard. This way t he rot at ion can be monit ored by t he BI OS soft ware which t hen can cont rol
t he t emperat ure of t he CPU. This syst em is implement ed on many ATX- boards. Here you see t he BI OS program
monit oring t he t emperat ure ( 29 C on my board, right now) :
Some coolers use pelt ier element s which give an ext ra cooling. Look at t his one below where you see t he whit e
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3d1.htm (3 of 7)7/27/2004 4:08:10 AM
An illustrated Guide to Over-clocking.
pelt ier- t hing at t he bot t om. Not ice t he t wo- fold power supply:
Cleaning the cooler
[ t op]
Anot her import ant t hing t o t ake care of is vacuum cleaning t he fan on a regular basis. My old Pent ium Pro has
a very big fan on it . I t began giving error messages wit hin Windows . I really could not find out why. Unt il I
discovered t hat t he heat ing sink was ext remely hot . The fan was rot at ing as it should, but a large amount of
dust had gat hered j ust beneat h it , so t he air did not cool t he sink at all!
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3d1.htm (4 of 7)7/27/2004 4:08:10 AM
An illustrated Guide to Over-clocking.
You should separat e t he fan from t he cooling element t o clean it properly. Here is t he cooling element alone on
t he t op of t he CPU:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3d1.htm (5 of 7)7/27/2004 4:08:10 AM
An illustrated Guide to Over-clocking.
What t o be learned: Check your CPU fan once a year. Perhaps you have t o disconnect t he CPU t o clean it
t horoughly. Take t he CPU in your hand and hold t he vacuum cleaner close t o t he sink.
Here you see a powerful cooling device for ( over clocking) Pent ium I I s. I t cont ains t hree fans ( t he t hird being
difficult t o see, it ' s in t he middle of t he device) plus a pelt ier element :
q Next page
q Previous page
Learn more
[ t op]
Read Module 3e - about t he lat est CPUs.
Read more about t he boot process and syst em bus in Module 2b
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3d1.htm (6 of 7)7/27/2004 4:08:10 AM
An illustrated Guide to Over-clocking.
Read more about I / O buses in module 2c
Read more about t he chip set s in module 2d
Read more about RAM in module 2e
Read about EI DE in module 5b
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3d1.htm (7 of 7)7/27/2004 4:08:10 AM
An illustrated Guide to Over-clocking.
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 3d.2
About Cooling and Over clocking (continued)
The cont ent s:
q What is clocking?
q Two frequencies t o clock on. .
q What is over clocking?
q Next page
q Previous page
Please support our
sponsor.
What is clocking?
[ t op]
All Pent ium CPUs run wit h clock doubling. That ' s t he way t hey are built . The PC works wit h t wo
frequencies, which t he user can adj ust . The clock doubling is set on small j umpers on t he
mot herboard. You simply set a clock doubling fact or, t o make t he CPU work but who says t hat
you must use t he fact or list ed in t he manual?
I f you are brave, you t ry t o set your CPU t o run fast er t han it is designed t o run. Oft en it works. I f
you "cheat " t he CPU in t his manner t o work fast er, it is called over clocking. Over clocking is kind
of a PC t uning, which can be fun t o fool wit h if you are int erest ed in t he t echnicalit ies of PC-
hardware. Ot herwise - skip it ! .
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3d2.htm (1 of 8)7/27/2004 4:08:13 AM
An illustrated Guide to Over-clocking.
I f you are lucky, you can make a medium speed CPU run as fast as t he t op of t he line version!
Please not e, I accept no responsibilit y for t he result of your experiment s. I will now t ry t o explain
t he t echnologies in t he over clocking phenomenon. The int erest ing part is t hat , like much of t he
t heory I t ried t o describe in in t he modules 3a, 3 b and 3c, it all comes t oget her here in t he clock
doubling t echnology.
Two frequencies to clock
[ t op]
The CPU works on t wo frequencies: An int ernal and an ext ernal.
q The ext ernal clock frequency ( t he bus frequency) is t he speed bet ween t he CPU and RAM. I n t he
Pent ium CPUs it is act ually t he speed bet ween L1 and L2 cache. I n t he Pent ium I I it is t he speed
bet ween L2 cache and RAM.
q The int ernal clock frequency is t he speed inside t he CPU, t hat is bet ween L1 cache and t he
various CPU regist ers.
For pract ical reasons you let t hese t wo frequencies depend on each ot her. I n pract ice you choose a
given bus frequency ( bet ween 60 and 153 MHz) and double it up a number of t imes ( bet ween 3
and 8) . The lat t er frequency become t he CPU int ernal work frequency.
Here I show a number of t heoret ical CPU frequencies, result ing form different clock doublings:
Many of t hese frequencies will act ually never be used, but t hey are possible because of t he syst em
st ruct ure:
Bus
frequencies
Clock
doubling
fact ors
Examples of result ing CPU frequencies
60 MHz
66 MHz
75 MHz
83 MHz
100 MHz
117 MHz
133 MHz
153 MHz
1,
3,
4,
4,
5,
5,
6
6,
7
7,
8
233 MHz, 266 MHz, 333 MHz
333 MHz, 366 MHz, 400 MHz,
433 MHz, 466 MHz, 500 MHz,
300 MHz, 338 MHz, 375 MHz,
375 MHz, 416 MHz, 458 MHz,
468 MHz, 527 MHz, 585 MHz
533 MHz, 600 MHz, 667 MHz,
612 MHz, 688 MHz, 765 MHz
Not e an import ant point : The CPU frequency is t he result of t he t he bus frequency mult iplied wit h a
fact or. I f you increase t he bus frequency, it affect s t he CPU frequency, which is also increased.
Look here at a page from t he manual t o a ASUS P2L97 mot herboard. I t has a clear inst ruct ion
about how t o set t he t wo values ( bus frequency and clock fact or) . This ( old) mot herboard accept s
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3d2.htm (2 of 8)7/27/2004 4:08:13 AM
An illustrated Guide to Over-clocking.
bus frequencies up t o 83 MHz wit h a clock fact or up t o 5:
What is over clocking?
[ t op]
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3d2.htm (3 of 8)7/27/2004 4:08:13 AM
An illustrated Guide to Over-clocking.
Since clock doubling and bus speed can be freely adj ust ed on t he mot herboard according t o your
desires, you can in principle make t he CPU run at 600 MHz. You set t he bus t o 133 MHz and t he
clock fact or t o 4. Then t he CPU runs at 600 MHz if it runs. The quest ion is whet her t he chip will
t olerat e t hat - and if it will give a st able performance, since clock doubling means more t han added
heat .
We have now seen t hat t here are t wo frequencies which can be manipulat ed, if you want t o re-
clock t he CPU:
q The bus frequency can be increased, let ' s say from 133 t o 153 MHz.
q The CPU frequency can be increased. That can happen as a result of an increased bus speed,
which also affect s t he CPU frequency, or it can happen by using a great er clock fact or. The lat est is
not possible anymore.
Bot h t echniques result in a fast er PC. I f t he bus frequency is increased, it affect s all dat a t ransport
t o and from RAM. I t will work fast er, t o t he j oy of all work done on t he PC. However, t he RAM has
t o cope wit h t he increased speed.
When t he CPU int ernal frequency is increased, many applicat ions will be happily affect ed.
More cooling
The t uning will oft en work, but it requires good cooling of t he CPU, t he more cooling t he higher you
can have t he clock frequency. CPUs are built in CMOS t echnology. That is a t ype chip which works
bet t er t he cooler it is. See t his relat ionship bet ween t emperat ure and performance:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3d2.htm (4 of 8)7/27/2004 4:08:13 AM
An illustrated Guide to Over-clocking.
You can see t hat t he performance drops drast ically wit h increased CPU t emperat ure.
This problem caused t he Kryot ech company t o manufact ure coolers ut ilizing t he Danish Danfoss
compressors, j ust like in refrigerat ors. See t his cooling unit on a CPU:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3d2.htm (5 of 8)7/27/2004 4:08:13 AM
An illustrated Guide to Over-clocking.
I t is fed from t he compressor in t he bot t om of t he cabinet :
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3d2.htm (6 of 8)7/27/2004 4:08:13 AM
An illustrated Guide to Over-clocking.
This form of cooling is ext reme, but it works. Kryot ech can make a st andard CPU work at 400- 700
MHz! But it requires t hat it is kept const ant ly cooled t o - 40 degrees F or C. ( it is t he same) . The
Kryot ech set up is efficient , but it is expensive, noisy and power consuming.
I f you like, look at Kryot ech' s Home Page ht t p: / / www. kryot ech. com/
Anot her company in t his business is Aset ek.
This was t o demonst rat e t hat over clocking can be a serious issue. . . .
However, t he CPU speed has become less import ant . To most users it really does not mat t er
whet her you have a CPU running at 300 or at 600 MHz.
q Next page
q Previous page
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3d2.htm (7 of 8)7/27/2004 4:08:13 AM
An illustrated Guide to Over-clocking.
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Also see Module 3e - about t he lat est CPUs.
Read more about t he boot process and syst em bus in Module 2b
Read more about I / O buses in module 2c
Read more about t he mot herboard chip set in module 2d
Read more about RAM in module 2e
Read about EI DE in module 5b
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3d2.htm (8 of 8)7/27/2004 4:08:13 AM
An illustrated Guide to Over-clocking.
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 3d.3
About Cooling and Over clocking (continued)
The cont ent s:
q Which CPUs can be over clocked?
q Risks in over clocking?
q Next page
q Previous page
Please support our
sponsor.
Which CPUs can be over clocked?
[ t op]
The first CPUs which were dramat ically over clocked were AMD' s 5x86 series. That was a 486
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3d3.htm (1 of 5)7/27/2004 4:08:15 AM
An illustrated Guide to Over-clocking.
CPU, which could be forced up t o an excellent performance at 160 MHz.
Since t hen especially I nt el' s Pent ium CPUs have been over clocked. Many of t hose seem t o be
sold wit h specs far from t heir opt imum performance. Act ually it was so easy t hat as a result
many P133s were sold in 1996 as fake P166s. They worked fine, and t he users did not know
it . But Pent ium MMX and Pent ium I I can also be re- clocked.
I t appeared t hat I nt el were aware of t his act ivit y, and t hey don' t seem t o care. Unfort unat ely
t heir CPUs came in t wo groups:
q Clock doubling works.
q Clock doubling does not work - it is disabled by t he manufact urer.
You cannot guarant ee t hat it always will work. But let me show a couple of examples, which I
have made work wit h good result s:
CPU Manufact urers spec Tuning result
I nt el Pent ium 2 X 60 MHz = 150 MHz 3 X 66 MHz = 200 MHz
I nt el Pent ium Pro 3 X 66 MHz = 200 MHz 3 X 66 MHz = 233 MHz
I nt el Pent ium I I 3 X 66 MHz = 233 MHz 4 X 75 MHz = 300 MHz
I nt el Pent ium I I 4 X 100 MHz = 450 MHz 4 X 117 MHz = 527 MHz
Looking at t he t hree examples, number 1 and 3 show t he best result s, where bot h bus
frequency and clock fact ors are increased. That simply moved t he CPU up one class in
performance.
Here is a t able of t he clock fact ors, which t he CPU' s t heoret ically can accept ( according t o my
st udies) :
CPU Clock fact or
I nt el Pent ium ( P54C) 1, 2, 2, 3
I nt el Pent ium Pro 2, 3, 3, 4
Cyrix 6x86 2, 3
Cyrix 6x86MX ( M2) 2, 2, 3, 3
I nt el Pent ium MMX ( P55C) 2, 2, 3, 3
AMD K5 PR75 - PR133 1, 1
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3d3.htm (2 of 5)7/27/2004 4:08:15 AM
An illustrated Guide to Over-clocking.
AMD K5 PR150 and PR166 2
AMD K6- 2 and K6- 3 4, 4, 5
I nt el Pent ium I I , Celeron and Pent ium I I I Up t o 8 and 12 ( lat est models)
Some AMD and Cyrix chips were special, in t hat t hey did not always respond t o mot herboard
set t ings. I t is like t hey det ermined t heir own frequencies.
All modern I nt el processors are locked at fixed clock fact ors ( Mult iplier Locking) . They only
operat e wit h one specific mult iply fact or.
The Celeron
The original Celeron was a Pent ium I I wit hout L2 cache. This CPU was very overclocking
friendly. There are several report s about 300 MHz Celerons working at 504 MHz wit hout any
problems at all.
The Celeron A
The I nt el Celeron line st art ing wit h models 300A and 333 ( bot h wit h 128 KB L2 cache on-
chip) are bot h prot ect ed against overclocking. They hold a "Mult iplier Locking", which locks
t hem t o t he clockfact ors 4. 5 and 5. 0 respect ively.
The Celeron 533 will only work wit h clockfact or 8, so if you want t o overclock it , you have t o
go for a mot herboard wit h adj ust able syst em bus frequencies. This could be 8 X 100 MHz
inst ead of 8 X 66 MHz increasing t he CPU speed from 533 MHz t o 800 MHz. Many users have
found t his in- expensive way t o get a higher performance.
Disadvantages and risks in over-clocking?
[ t op]
Many fact ors need t o be considered, when you st art t ampering wit h t hese syst em set t ings.
Wat ch out for:
q Heat . Can t he CPU dissipat e t he heat ?
q The L2 cache RAM of old Pent ium I I , I I I or At hlon cart ridges - how fast can it work?
q RAM speed. Can it keep up wit h t he syst em bus?
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3d3.htm (3 of 5)7/27/2004 4:08:15 AM
An illustrated Guide to Over-clocking.
q The I / O bus. Can PCI and EI DE unit s keep up?
q Will t he soft ware st ill work?
The last t wo problems are associat ed wit h increased syst em bus speed. This kind of over
clocking gives t he best result s. However t hose also creat e t he biggest problems, at least in
my experience.
The CPU gets hot
First of all t he higher CPU frequency causes more wear on t he chip. I t is said t hat a CPU can
last 10 years. However do not count on t hat if you over clock it . Act ually I am less concerned
about t he wear. Of course you should not allow t he chip t o over heat , but I have never heard
about burnt out CPUs. I n news groups you can read about various monst er fans used for
cooling of t ot ally over clocked CPUs.
RAM speed
Anot her problem is in t he relat ionship wit h t he bus frequency. Here we are t alking about t he
syst em bus, which connect s RAM wit h t he CPU. I f you increase t his speed, RAM must be able
t o keep up. Here is a guideline t able for t he maximum bus frequencies wit h different RAM
t ypes:
RAM t ype Speed Maximum bus frequency
FPM 60 ns 66 MHz
EDO 50 ns 75 MHz
SD 10 ns 100 MHz
SD 7 ns 133 MHz
Finally you could say t hat wit h cheap CPUs running at 900 MHz and above - you really do not
need any overclocking. Most users will not experience any benefit from shift ing from say 700
MHz t o 1000 MHz.
q Next page
q Previous page
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3d3.htm (4 of 5)7/27/2004 4:08:15 AM
An illustrated Guide to Over-clocking.
Lear n mor e [ t op]
See Module 3e - about t he lat est CPUs.
Read more about t he boot process and syst em bus in Module 2b
Read more about I / O buses in module 2c
Read more about t he mot herboard chip set in module 2d
Read more about RAM in module 2e
Read about EI DE in module 5b
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3d3.htm (5 of 5)7/27/2004 4:08:15 AM
An illustrated Guide to Over-clocking.
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 3d.4
About Cooling and Over clocking (continued)
The cont ent s:
q I / O speed and experiment s wit h t hat
q Side effect s
q Fake Pent ium I I s
q Jumpers.
q Next page
q Previous page
Please support our
sponsor.
Experimenting the I/O speed
[ t op]
The area which has given me t he most problems is t he increased PCI speed. At 66 MHz t he PCI bus runs at half t he syst em bus
frequency. At 100 MHz it runs at one t hird and at 133 MHz one quart er of t his frequency. Thus if we increase t he syst em bus, it
also affect s t he PCI bus:
Syst em bus speed Bus fact or Result ing PCI speed
66 MHz The half 33 MHz
75 MHz The half 37. 5 MHz
83. 3 MHz The half 41. 6 MHz
100 MHz One t hird 33. 3 MHz
112 MHz One t hird 37. 3 MHz
133 MHz One quart er 33. 3 MHz
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3d4.htm (1 of 4)7/27/2004 4:08:17 AM
An illustrated Guide to Over-clocking.
153 MHz One quart er 38. 25 MHz
Side effects
When we increase t he PCI bus speed, a number of unit s are affect ed. They may not always agree wit h t he fast er pace. This
includes:
q The EI DE hard disk
q The video card
q The net work cont roller and ot her I / O cards.
My own experiment with Pentium II
I n 1997 I experiment ed wit h a very early Pent ium I I , which was bought as a 233 MHz model.
First I made it run at 3 X 75 MHz. I t worked fine wit h CPU, RAM ( 10 ns SD) and hard disk ( I BM DHEA) . But t he net card ( a cheap
10/ 100 Et hernet card) refused. When I copied large volumes of files on t he net , it froze up - st opped. I t was quit e obvious t hat t he
problem was in t he net card.
I had t o accept t he t radit ional 66 MHz. But t o soot he t he pain, it t urned out t o run excellent ly wit h a clock fact or of 4 - t hus at 266
MHz.
Wit hin a couple of weeks I was in t he mood t o experiment again. I now found an adj ust ment in t he set up program. I t is called PCI
lat ency. I t is not explained anywhere, but it has a default value of 32. I increased it t o 36 and increased t he bus frequency t o 75
MHz it works. Now t he net card runs wit hout problems.
Then I hoped t o speed t he syst em bus up t o 83 MHz, which should give a significant performance improvement for all RAM
t ransport . My 10 ns SD RAM can cert ainly handle 83 MHz. But no, it did not work. Regardless of t he PCI lat ency, t he PC would not
st art . This indicat es t hat t he PCI lat ency set t ing does not work like I expect ed. Maybe it has not hing t o wit h t his - I do not know.
My explanat ion is, t hat t he video card could not t olerat e t he 41. 5 MHz PCI frequency. Not hing appeared on t he screen.
Now t he PC runs fine at 4 X 75 = 300 MHz. There can be an occasional unexplained break- down in Windows 95 ( t hat happens
under ot her circumst ances also) , which I blame on t he drast ic over clocking. However, t he advant ages of t he significant
performance improvement far exceed t he annoyance of t hese small int errupt ions, which happen far from daily.
Problems with NT 4.0
Windows NT 4. 0 does not inst all wit h over clocked CPU. The program t est s for "genuine I nt el", and seems t o regist er t he change in
clock frequency. And t hen it will not work. But if you inst all NT first , t hen you can over clock aft erwards and NT will work. Act ually
NT is quit e sensit ive. One of my friends experienced some peculiar errors. The solut ion t urned out t o be moving t he RAM module
from one socket t o anot her!
Fake Pentium IIs
[ t op]
Since some Pent ium I I - 233 perform very well at 300 MHz, t hey have been sold as such ones. To t est your own Pent ium I I , you can
download t his t est program from C' t , which can check your Pent ium I I . Here is t he int erface of t he Windows 95 version, which
correct ly det ect ed my CPU t o be over clocked:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3d4.htm (2 of 4)7/27/2004 4:08:17 AM
An illustrated Guide to Over-clocking.
Jumpers on the motherboard
[ t op]
To set t he clock doubling, some small swit ches ( called j umpers) have t o be reset . They are locat ed on t he mot herboard, as you see
here:
You can read in t he mot herboard manual how t o set t hem. Or you can look at t he mot herboard! I n t he pict ure below you can see
some of t he print ed informat ion on t he mot herboard ( t his is an ASUS TX97 wit h a Socket 7) .
Here you can read which j umpers t o set t o select clock doubling 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3 and 4 for 6 t ypes of processors:
q P54C and K5
q P55C, K6 and M2 ( Cyrix 6x86MX)
q M1 ( Cyrix 6x86)
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3d4.htm (3 of 4)7/27/2004 4:08:17 AM
An illustrated Guide to Over-clocking.
On modern mot herboards you may find a soft ware solut ion t o t he set t ings, and t hat is a lot bet t er.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Also see: Module 3e - about t he lat est CPUs.
Read more about t he boot process and syst em bus in Module 2b
Read more about I / O buses in module 2c
Read more about t he mot herboard chip set in module 2d
Read more about RAM in module 2e
Read about EI DE in module 5b
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3d4.htm (4 of 4)7/27/2004 4:08:17 AM
An illustrated Guide to Over-clocking.
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 3d.5
About Cooling and Over clocking (continued)
The cont ent s:
q An example of overclocking
q The SDRAM speed
q Feat ures of t he Abit BX6 mot herboard.
q Next page
q Previous page
Please support our
sponsor.
An over-clocked Pentium II
[ t op]
I n t he previous pages you can read about t he t heory behind over clocking. Here I describe a pract ical case.
I n April 1999 we needed a new workst at ion. I t was t o used for graphics work and somet imes video edit ing, so it had t o be
speedy. We decided t o t ry some over clocking.
Over clocking with Intel - earlier results
[ t op]
I nt el CPUs have always been good for over clocking.
Back in 1997 we had a Pent ium Pro designed for 200 MHz. I t ran ( and st ill runs) at 233 MHz wit hout any problem at all.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3d5.htm (1 of 7)7/27/2004 4:08:20 AM
An illustrated Guide to Over-clocking.
Lat er we got one of t he first Pent ium I I s. These processors were very friendly t o over clocking, bot h t he frequency of t he
syst em bus as well as t he clock fact or could be changed. A modest 233 MHz version ran ( and st ill does) at 300 MHz.
The Deschut es kernel of second generat ion Pent ium I I and Celeron was changed, so every CPU only could work wit h a
specific clock fact or. This means t hat you only can over- clock by increasing t he bus frequency. This has been t he sit uat ion
wit h all lat er I nt el processors.
You see our over clocking result s as described are not ext reme. This has a reason; all our PCs funct ion in a net work and t hey
are heavily used for various demanding t asks. So t hey have t o be complet ely st able, which t hey also have been. Furt her over
clocking would aggravat e t he inherent un- st abilit y.
The first attempt
[ t op]
We st art ed up wit h t he cheapest solut ion. A 300 MHz Celeron should be doing fine at 450 MHz if t he syst em bus was
increased from 66 MHz t o 100 MHz. We even added ext ra cooling, a fan placed above t he SEC module:
I t never worked. But t he mot herboard was int erest ing, so we went for anot her approach.
Pentium II and Abit BX6
[ t op]
We t hen purchased a Pent ium I I - 450 MHz. This processor was t he clock fact or 4. 5 model of t he Pent ium I I you could say.
The mot herboard was t he newest version ( 2. 0) of t he pret t y well- known Abit BX6. I t is a BX- based board wit h is capable of
delivering a lot of different frequencies. The clock mult iplier goes up t o fact or 8, but since t he Pent ium I I only works wit h
clock fact or 4. 5, we had t hese opt ions:
Bus frequency
( SDRAM speed)
Clock
fact or
Result ing
CPU frequency
L2 Cache
speed
66 MHz 4. 5 300 MHz 150 MHz
75 MHz 4. 5 338 MHz 169 MHz
83 MHz 4. 5 375 MHz 188 MHz
100 MHz 4. 5 450 MHz 225 MHz
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3d5.htm (2 of 7)7/27/2004 4:08:20 AM
An illustrated Guide to Over-clocking.
112 MHz 4. 5 504 MHz 252 MHz
117 MHz 4. 5 527 MHz 263 MHz
124 MHz 4. 5 558 MHz 229 MHz
129 MHz 4. 5 581 MHz 290 MHz
133 MHz 4. 5 599 MHz 300 MHz
138 MHz 4. 5 621 MHz 310 MHz
143 MHz 4. 5 644 MHz 322 MHz
148 MHz 4. 5 666 MHz 333 MHz
153 MHz 4. 5 689 MHz 344 MHz
Of course I could not expect my Pent ium I I t o run at 689 MHz. The values are t heoret ical.
When you increase t he bus frequency it affect s a lot of unit s wit hin t he PC. This is due t o t he archit ect ure, where t he syst em
bus so t o say is a local bus, wit h ot her at t ached buses and unit s working synchronously. I ncreasing t he bus frequency
influences:
q The CPU clock frequency. Oft en I nt el CPUs are capable of working at a higher frequency t han what t hey are sold for.
However, improved cooling is import ant .
q The L2 Cache of t he Pent ium I I module. I t has an upper speed limit as all ot her RAM t ypes do. Cooling is import ant for t he
L2 cache RAM chips.
q The SDRAM speed. The RAM modules have t o fast enough t o cope wit h t he increased bus frequency.
q The PCI unit s. The graphics cont roller, EI DE cont roller and net work cont roller all have t o work at around 33 MHz, ot herwise
un- st abilit y is t he result ( at least t hat is our experiences) .
q The AGP bus speed.
Over clocking a PC is not t hat simple. All t he ment ioned unit s have t o be t uned, so t hey work at right frequencies.
Testing and trying
[ t op]
One of t he biggest problems is t o cont rol t he speed of t he PCI unit s. Our net work ( LAN) is a very good t ool for t est ing t his. I
make a backup of all my document s ( > 10. 000 files) across t he net work from harddisk t o harddisk, and if t his works i am
pret t y sure t hat everyt hing is all right wit h t he new PC.
Wit h t he Pent ium I I , I st art ed increasing t he bus frequency. Of course everyt hing worked fine at 100 MHz. I t should. 112 MHz
was complet ely st able. 117 MHz as well, but at 124 MHz t he problems came. Here you see t he Soft Menu set t ing, which is an
ext remely nice feat ure of t he BX6 board:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3d5.htm (3 of 7)7/27/2004 4:08:20 AM
An illustrated Guide to Over-clocking.
The PC seemed t o work at 558 MHz, but t he file copy- t est could not be performed. The PC froze. This probably was due t o
"slow" SDRAM. Wit h bet t er RAM it might have worked.
SDRAM speeds
[ t op]
Here is an t heoret ical calculat ion of t he required SDRAM speed:
Bus frequency SDRAM speed
( Nano seconds)
66 MHz 15. 02
75 MHz 13. 33
83 MHz 12. 00
100 MHz 10. 00
112 MHz 8. 93
117 MHz 8. 55
124 MHz 8. 03
129 MHz 7. 75
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3d5.htm (4 of 7)7/27/2004 4:08:20 AM
An illustrated Guide to Over-clocking.
133 MHz 7. 52
138 MHz 7. 25
143 MHz 6. 99
148 MHz 6. 76
153 MHz 6. 54
The RAM was of PC100 t ype. But t his may be 10, 8 or 7 ns. I n our case it was 8 ns, so t he 124 MHz set t ing should have been
working, it j ust didn' t .
Two versions of 117 MHz
At 117 MHz I had t wo opt ions. I could go for a PCI bus at 39 or 29 MHz. These values come out as one t hird or one quart er of
t he 117 MHz bus frequency. Unfort unat ely 39 MHz was t oo much for my PCI unit s:
Soft Menu set t ing: PCI 1/ 3 Soft Menu set t ing: PCI 1/ 4
PCI frequency: 39 MHz PCI frequency: 29 MHz
Syst em st abilit y: not good Syst em st abilit y: 100% all right
So we ended up wit h a complet ely st able Pent ium I I syst em running at 527 MHz. That ' s absolut ely OK.
Features of the Abit BX6
[ t op]
The Abit board seems pret t y cool t o me. The manual is OK but not overwhelming impressive. The board has 5 PCI slot s which
I like. But especially t he Soft Menu I I is great - a brilliant t ool for over- clockers. You do not have t o move a simple j umper on
t he BX6 board, so it is ext remely simple t o t est your CPU and syst em at various frequencies.
You also get t hermist or t o det ect t he CPU t emperat ure:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3d5.htm (5 of 7)7/27/2004 4:08:20 AM
An illustrated Guide to Over-clocking.
I t is t aped t o t he heat sink and connect ed t o t he mot herboard.
You get some soft ware, among ot hers t his diagnost ic t ool:
More over clocking?
Wit h bet t er RAM we might t weak t he full 689 MHz out of t he Pent ium I I processor. Running wit h a bus frequency of 153 MHz,
t he PCI unit s have t o work on 38, 25 MHz which I very much doubt t hey can.
My realist ic guess would be t hat t his configurat ion using 7 ns SDRAM might work:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3d5.htm (6 of 7)7/27/2004 4:08:20 AM
An illustrated Guide to Over-clocking.
Bus
frequency
CPU
frequency
SDRAM
speed
PCI
frequency
138 MHz 621 MHz 7, 25 ns 34, 5 MHz
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read more about t he boot process and syst em bus in Module 2b
Read more about I / O buses in module 2c
Read more about t he mot herboard chip set in module 2d
Read more about RAM in module 2e
Read about EI DE in module 5b
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3d5.htm (7 of 7)7/27/2004 4:08:20 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 3e
Module 3e describes t he development of 6t h generat ion CPU' s. The module is subdivided int o
t he following pages:
01:
02:
03:
04:
05:
06:
07:
08:
09:
10:
11:
12:
13:
14:
The Pent ium Pro, fat her of all P6s
The first Pent ium I I
The "Deschut es" and t he Celerons
The P6- like processors: AMD' s K6, K6- 2, and Cyrix
The K6- 3
The Pent ium Xeon
The Pent ium I I I
The Great At hlon
On MMX, 3DNow! , and Kat mai
On socket s and roadmaps
On I nt el I t anium ( codename "Merced") and I A- 64
On VI A Joshua
AMD Duron
I nt el Pent ium 4
I recommend t hat you read all t he pages one by one. Just follow t he links "Next page" t o get
t hrough t he t ext book. I hope you find t he informat ion useful!
Introduction to the 6th generation of CPUs
The first 6t h generat ion CPU was I nt el' s Pent ium Pro from 1995. However, first from 1997
wit h bot h AMD' s K6 and t he Pent ium I I t he 6t h generat ion performances have been available
for us all.
The cont ent s:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e01.htm (1 of 4)7/27/2004 4:08:22 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
q Pent ium Pro
q A giant chip
q No DOS wit h PPro
q Pent ium Pro versus Pent ium I I
q The next module 3e
Pent ium Pro was an import ant CPU, since it became t he fat her t o t he Pent ium I I , t he Celeron,
t he Pent ium I I I and made t he ground ot her P6- like processors as K6- 2.
Pentium Pro
[ t op]
Pent ium Pro development st art ed in 1991, in Oregon. I t was int roduced on November 1,
1995.
The Pent ium Pro is a pure RI SC processor, opt imized for 32 bit processing in Windows NT or
OS/ 2. The new hot feat ure was t hat t he L2 cache is built - in. This is like t wo chips in one. The
new feat ures were:
q Built in opt imized L2 cache wit h 256 KB or 512 KB. This is connect ed t o t he CPU it self wit h
a 64 bit back side bus. Thus, t he L2 cache runs synchronous wit h t he CPU speed.
q Mult iple branch predict ion, where t he CPU ant icipat es t he next inst ruct ion. Dat a Flow
Analysis, which should reduce dat a dependence. Speculat ive Execut ion, where t he CPU
at t empt s t o ant icipat e inst ruct ion result s.
q 5. 5 million t ransist ors in t he CPU, 15 million for t he 256 KB SRAM L2 cache. ( 6 t ransist ors
per bit ) .
q 4 pipelines for simult aneous inst ruct ion execut ion.
q RI SC inst ruct ions wit h concurrent x86 CI SC code t o MicroOps RI SC inst ruct ions decoding.
q 2. 9 Volt 4 layer BiCMOS processor t echnology.
q Pat ent ed prot ocol. Thus, ot her CPU manufact urers cannot use t he Pent ium Pro Socket and
chip set . This was not t o t he user' s advant age.
A giant chip
Here you see a rect angular chip. The CPU and L2 cache are separat e unit s inside t his chip:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e01.htm (2 of 4)7/27/2004 4:08:22 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
I t is mount ed in a huge Socket 8:
Pentium Pro was not for DOS...
Pent ium Pro was primarily opt imized t o 32 bit program execut ion. Oft en you heard about it s
poor performance execut ing 16 bit programs. I used a PPro 200 MHz ( at 233 MHz) and
experienced t remendous power in my Windows 95 environment . However t he CPU was aimed
at use in servers.
PPro versus Pentium II
Aft er t he int roduct ion of Pent ium I I , t he int erest in t he PPro has declined, and by t he end of
1998 it was out of product ion. However it sold awhile aft er t he int roduct ion of t he Pent ium I I .
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e01.htm (3 of 4)7/27/2004 4:08:22 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
Compared t o t he first generat ions of t his one, t he PPro had advant ages when used in cert ain
servers:
CPU Pent ium Pro 1. generat ion
Pent ium I I
Max. RAM 4 GB 512 MB
L2 cache speed 200 MHz 150 MHz
Max. number CPU 4 2
I nt el also supplied a Pent ium Pro- Overdrive Kit running at 333 MHz. However, wit h t he I nt el
Xeon CPU t he end came t o t he Pent ium Pro.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read about chip set s on t he mot herboard in module 2d
Read more about RAM in module 2e
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side.
Read module 5b about AGP and module 5c about Firewire.
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
Read module 7c about sound cards, and 7d on digit al sound and music.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e01.htm (4 of 4)7/27/2004 4:08:22 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 3e.02
The Pentium II
The second 6t h generat ion CPU was I nt el' s Pent ium I I from 1997.
The cont ent s:
q Pent ium I I
q L2 cache out of chip
q The SEC module
q L2 cache speeds compared
q Next page
q Previous page
Pentium II
[ t op]
Pent ium Pro "Klamat h" was t he code name for I nt el' s t op processor. I t ended up as a part ially
reduced and part ially improved Pent ium Pro model.
I nt roduced May 7, 1997, t he const ruct ion of Pent ium I I was a lit t le cont roversial. The feat ures
include:
q A CPU mount ed t oget her wit h 512 KB L2 in a SECC ( Single Edge Cont act Cart ridge) module
q Connect ion t o t he mot herboard using t he slot one connect or and t he P6 GTL+ bus.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e02.htm (1 of 6)7/27/2004 4:08:24 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
q MMX inst ruct ions.
q I mproved 16 bit program execut ion ( j oy for Windows 3. 11 users) .
q Doubled and improved L1 cache ( 16 KB + 16 KB) .
q New increased int ernal speed: from 233 MHz t o 300 MHz ( lat er version much higher) .
q L2 cache working at half CPU speed.
L2 cache out of chip [top]
Please support our
sponsor.
The most int erest ing change was t he separat ion of CPU and L2 cache. I nt el found it t oo cost ly
t o combine t hem in one chip as in Pent ium Pro. To facilit at e mass product ion, cache RAM of a
different brand ( Toshiba) was used. The cache RAM is marked 7 ns allowing a clock frequency
of maximum 150 MHz.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e02.htm (2 of 6)7/27/2004 4:08:24 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
The SEC module
[ t op]
Pent ium I I is a large rect angular plast ic box, which cont ains t he CPU and cache. There is also a
small cont roller ( S82459AB) and a well dimensioned cooling fan. All are mount ed on a card.
This card wit h chips weighs about 380 g ( 13 ounces) . I t fit s in a new 242 pin Single Edge
Connect or on t he mot herboard:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e02.htm (3 of 6)7/27/2004 4:08:24 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
Here you see t he SEC module mount ed in my ASUS board. Not e t he cooling element s on t he
cache RAM chips on bot h sides of t he CPU:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e02.htm (4 of 6)7/27/2004 4:08:24 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
L2 cache speeds compared
[ t op]
Wit h it s special design, t he L2 cache has it s own bus. I t runs at half t he CPU speed, like 133
MHz or 150 MHz. This is clearly a ret rogression from t he Pent ium Pro, which can run at 200
MHz bet ween t he CPU and L2 cache. I t is count ered by t he improved L1 cache, which really zips
along! Here you see a comparison:
CPU L1 t ransfer rat e L2 clock speed L2 t ransfer rat e
Pent ium 200 777 MB/ sec. 66 MHz 67 MB/ sec.
Pent ium 200 MMX 790 MB/ sec. 66 MHz 74 MB/ sec.
Pent ium Pro 200 957 MB/ sec. 200 MHz 316 MB/ sec,
Pent ium I I 266 MHz 1, 175 MB/ sec. 133 MHz 221 MB/ sec.
Pent ium I I is and has been available in 233, 266, 300, 333, 350, 400, 450, and 500 MHz
edit ions. Wit h t he 82440BX and i810 chip set s Pent ium I I was an excellent performer. Read on
for more informat ion on Pent ium I I I .
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read about chip set s on t he mot herboard in module 2d
Read more about RAM in module 2e
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side.
Read module 5b about AGP and module 5c about Firewire.
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
Read module 7c about sound cards, and 7d on digit al sound and music.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e02.htm (5 of 6)7/27/2004 4:08:24 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e02.htm (6 of 6)7/27/2004 4:08:24 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 3e.03
The second generation of Pentium II
The cont ent s:
q The Deschut es
q 100 MHz Front Side Bus
q The Original Celeron
q The Over- clocking
q The Good Celeron ( t he Mendocino)
q The New Great Socket 370
q Dual Celeron configurat ion
q Next page
q Previous page
The next Pentium II, the Deschutes
[ t op]
The t hird P6 CPU was I nt el' s Pent ium I I code named "Deschut es". This new core also lead t o t he
Celerons in various brands.
On January t he 26t h 1998 I nt el int roduced t he new 333 MHz model of Pent ium I I .
I t was t he first of a second generat ion Pent ium I I s known under t he code name "Deschut es". The chips
are produced wit h 0. 25 micron t echnology, which reduces t he power consumpt ion by more t han 50 %
compared t o t he original Pent ium I I "Klamat h" wit h it s 0. 35 micron t echnology. The core volt age is
down from 2. 8 t o 2. 0 Volt
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e03.htm (1 of 7)7/27/2004 4:08:26 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
Please support our
sponsor.
100 MHz Front Side Bus
[ t op]
On April t he 15t h, 1998 I nt el released t he next line of Deschut es. The syst em bus had been increased t o
100 MHz. This will int ernally be mult iplied by t he clock fact ors 3. 5, 4. 0 and ( June 1998) 4. 5, making t he
CPU run at 350, 400 and 450 MHz. These CPUs use t he new chip set : 82440BX.
So t hese Deschut es chips use t wo different mot herboards:
q LX- based for t he 333 MHz version ( 5 X 66 MHz)
q BX- based for t he 350, 400, 450, and 500 MHz versions
( wit h clock mult ipliers of: 3. 5, 4. 0, 4. 5, and 5. 0 X 100 MHz) .
Fast L2 cache RAM
The L2 cache RAM has t o be cooled down and it has t o be fast :
CPU Clock RAM t ype Cont roller
333 and 350 MHz 5. 5 ns S82459AC
400 MHz 5. 0 ns S82459AD
450 MHz 4. 4 ns S82459AD
The Original Celeron
[ t op]
Early 1998 I nt el was having a hard t ime wit h t he Pent ium I I which was pret t y expensive. Many users
bought t he AMD K6- 233, which offered very good performance at a moderat e price.
So I nt el creat ed a brand new CPU called Celeron. I t is a Pent ium I I cart ridge except for t he L2 cache,
which has been chopped away. I t uses a ' Covingt on' core, and we could j ust as well have called it t he
Pent ium I I - SX. I n 1998 I nt el replaced t heir Pent ium MMX wit h t he first Celerons. Lat er t he design was
improved a lot , and Celeron became a very successful product .
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e03.htm (2 of 7)7/27/2004 4:08:26 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
This first inexpensive Celeron cart ridge fit t ed int o Slot 1 and it ran on a 66 MHz syst em bus. The int ernal
clock ran at 266 or 300 MHz and delivered good performance for float ing point and MMX heavy
programs such as cert ain games. Concerning office applicat ions, t he lack of L2 cache was a great
disadvant age.
Over-clocking
[ t op]
The first Celeron were ext remely good for over- clocking, since much of t he problem here arises from t he
onboard L2 cache. The L2 cache RAM cannot funct ion at high clock frequencies, but wit hout L2 cache
RAM t his problem did not occur wit h t he first Celerons.
The Celeron 266 and 300 ran at speeds of 412 MHz and 464 MHz wit hout any problems. However, for
non- overclocking purposes t he Celeron cart ridge could not be recommended. I t s lack of L2 cache was
t oo big a disadvant age.
Celeron with L2 cache - the Mendocino
[ t op]
The next variant of Celeron got t he code name Mendocino. First it came in 300 and 333 MHz versions.
The int erest ing part is t hat t he new cart ridge holds 128 KB L2 cache inside t he CPU it self. This gives
very good performance, since t he L2 cache runs at full CPU speed. Here you see a Celeron 300A. A chip
on a card:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e03.htm (3 of 7)7/27/2004 4:08:26 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
Integrated L2 cache
The manufact uring price was increased by less t han 10%, adding t he 128 KB int egrat ed L2 cache, while
t he performance probably increased 30- 40%. The number of t ransist ors were increased from 7. 5 million
t o 19 million due t o t he L2 cache.
However, on- chip L2 cache is a good t echnology. I n t he first 0. 25- micron t echnology, t he Mendocino' s
128K cache t ook up about 35 mm2 of die area. I t added $10 t o t he manufact uring cost s, but t hese
numbers decreased going int o 0. 18 micron process t echnology. And t hen it is cheaper t o produce a big
int egrat ed L2 cache t han t o add t he chips t o an expensive Slot 1 or 2 module.
These early "Mendocino" cart ridges were j ust as good as t he t radit ional 66 MHz Pent ium I I s. The
Mendocino- based Celeron cart ridge running at 300 MHz was named wit h an A as suffix t o dist inguish it
from t he Celeron 300 wit hout L2 cache.
Also good for over-clocking
Hence, t he first t wo models were t he Celeron 300A and 333. They did very well, being priced very low
compared t o t he equivalent Pent ium I I s.
I n t erms of over- clocking t hey proved successful as well. Here it appears t hat t he 300A was t he best . I t
works fine wit h a clock doubling of 4. 5 X 103 MHz giving 464 MHz. The 333A model "only" runs at 416
MHz ( 5 X 83 MHz) .
Faster with Celeron
On January 4t h 1999, I nt el int roduced a 366 MHz version and a 400 MHz version bot h working t he RAM
on a 66 MHz bus. The clock mult iplier wit hin t he new Celerons goes up t o 8. 0.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e03.htm (4 of 7)7/27/2004 4:08:26 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
March 15, 1999. The 433 MHz version of t he Celeron was launched. A 466 MHz version was released
lat e April.
July 31, 1999. The 500 MHz version of Celeron was launched.
Lat er 1999 t he Celeron came in a 533 MHz version. I n 2000 came 566 MHz Celerons produced wit h 0. 18-
micron process t echnology.
New Socket 370 for the Celeron
[ t op]
The 400 and 366 MHz processors were as all successors available in a plast ic pin grid array ( P. P. G. A. )
form fact or.
This PGA370 socket looks quit e like a t radit ional Socket 7. I t holds 370 pins:
Bot h are ZI F ( Zero I nsert ion Force) socket s cont aining a lever so you can open and close t he socket .
This makes it very easy t o insert t he CPU.
However, t he PGA uses a different bus prot ocol ( GTL+ ) t han t he Socket 7, which also only holds 238
pins. The GTL+ bus is t he same prot ocol as all Pent ium I I ' s. Hence, t hey use t he same chip set s.
The socket 370 is cheaper t o produce t han Slot 1 cart ridges, so all I nt els mainst ream processors will
come in t his design.
The roadmap for t he Celeron looks like t his:
q 66 MHz bus versions up t o 800 MHz.
q 100 MHz bus versions int roduced in 2001, bringing t he chip up t o 1200 MHz.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e03.htm (5 of 7)7/27/2004 4:08:26 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
Dual Celeron configuration
Using t wo Celerons on one mot herboard could be a great idea. I t would enable people t o produce very
inexpensive high- powered workst at ions. Windows NT is capable of using bot h processors.
During 1998 I heard of several privat e persons, who made t he Celerons work in dual SMP ( symmet ric
mult iprocessing) configurat ions. But in July 1999 t wo companies produce mot herboards for dual Celeron
configurat ion.
Here is a lit t le pict ure of such a board. You see t wo socket 370' s:
See Abit s own homepage on t he BP6 board. And see QDI .
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read about chip set s on t he mot herboard in module 2d
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e03.htm (6 of 7)7/27/2004 4:08:26 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
Read more about RAM in module 2e
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side.
Read module 5b about AGP and module 5c about Firewire.
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7bon graphics card.
Read module 7c about sound cards, and 7d on digit al sound and music.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e03.htm (7 of 7)7/27/2004 4:08:26 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
KarbosGuide.com. Module 3e.04
About P6-like processors from AMD and Cyrix
The cont ent s:
q AMD' s powerfull K6
q AMD' s K6- 2
q Cyrix 6x86MX
q Pure CI SC
q Two brands of 6X86MX
q K6- 2
q Next page
q Previous page
K6
[ t op]
I nt el' s Pent ium I I soon got compet it ion from AMD and Cyrix. Bot h companies have launched
several good processors, somet imes giving I nt el a hard compet it on.
AMD' s K6 is from April 2, 1997. I n 1996 AMD produced t he K5 processor which was not very
impressive, however very cheap. The company was put back t o business by Mr. At iq Raza,
who brought in t he t echnology from NexGen. This lead t o t he very successful model K6,
which saved AMD from ruin.
The market soon discovered t hat t he K6 performed a lot bet t er t han Pent ium MMX, which it
shared t he Socket 7 mot herboards wit h. Here are t he dat a:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e04.htm (1 of 8)7/27/2004 4:08:29 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
q Equipped wit h 32+ 32 KB L1 cache and MMX.
q Cont aining 8. 8 million t ransist ors.
K6 is ( like K5) compat ible wit h Pent ium. Thus, it can be mount ed in a Socket 7 on a regular
Pent ium mot herboard, and t his soon made t he K6 very popular.
BIOS and voltage
On t he older mot herboards, it is possible t hat t he BI OS has t o be updat ed t o make it work.
K6 performs best when t he BI OS recognizes t he chip, so it s full pot ent ial can be ut ilized. That
requires a dual volt age mot herboards. The K6- 200 requires 2. 9 volt for it s core. The ot her
models require 2. 8 volt as t he Pent ium MMX.
[top]
Please support our
sponsor.
The K6 model 7 ( Lit t le Foot ) was running at 300 MHz. These high performance K6s were sold
at very reasonable prices. The problem seemed in t he beginning t o be t o produce enough
chips. The K6 was followed by t he K6- 2 ( and lat er t he At hlon) , which gave AMD an enormous
success in t he lat e 1990' s.
Cyrix 6X86MX (MII)
[ t op]
Cyrix was a
company wit h anot her high performance chips, placed somewhere bet ween 5t h and 6t h
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e04.htm (2 of 8)7/27/2004 4:08:29 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
generat ion. The first models were posit ioned against t he Pent ium MMX chip from I nt el. Lat er
models can be compared t o t he K6. I have t o admit , t hat I quit e seldom saw t hese
processors in my count ry, but t hey did exist .
Cyrix powerful P6- classed processor was announced as t he "M2". I nt roduced on May 30,
1997 t he name became 6X86MX. Lat er it has been named MI I again. There has always been
some confusion about t he ident ificat ion of t he Cyrix CPUs.
MMX
This 6X86MX chip is compat ible wit h t he Pent ium MMX. This gives addit ional possibilit ies t o
assemble PCs on ordinary Socket 7 mot herboards.
The 6X86MX has 64 KB int ernal L1 cache, which is very impressive. Cyrix also ut ilizes
t echnologies which are not found in Pent ium MMX. These chips are named t o compare t hem
wit h genuine Pent iums, alt hough t heir int ernal clock speed is lower t han corresponding I nt el
processors.
Pure CISC
[ t op]
The 6x86MX was unique compared t o t he ot her 6. generat ion CPUs ( Pent ium I I and Pro and
K6) since it does not work upon a RI SC kernel. 6x86MX execut es t he original CI SC
inst ruct ions as does t he Pent ium MMX.
The 6x86MX has plent y of int ernal regist ers placing it in company wit h ot her 6t h generat ion
CPU' s:
CPU Number of
32 bit CPU regist ers
Pent ium MMX 8
6x86MX 32
Pent ium Pro 40
K6 48
The 6x86MX had - as all processors from Cyrix - a problem concerning t he FPU unit .
However, only using st andard office applicat ions, t his is of no concern. The problem arises
when you play 3D games.
Poor performance
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e04.htm (3 of 8)7/27/2004 4:08:29 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
The 6X86MX is quit e a powerful chip - on t he paper. However, t here are problems wit h t he
supply of t hem, and also t he syst em bus speed caused t roubles. I t was difficult t o find a
mot herboard t hat accept s t hese speeds. They also lacked good FPU and MMX performance.
They did not incorporat e t he 3DNow! t echnology. Hopefully t his will change as Cyrix has been
t aken over by VI A.
6X86MX I nt ernal speed Ext ernal speed
PR166 150 MHz 60 MHz
PR200 166 MHz 66 MHz
PR233 188 MHz 75 MHz
PR266 225 MHz 75 MHz
PR300 233 MHz 66 MHz
PR333 255 MHz 83 MHz
PR433 285 MHz 95 MHz
PR466 333 MHz 95 MHz
I t was evident t hat Cyrix int ended t o cont inue t his line of processors, and t his definit ely was a
posit ive t rend. I nt el got compet it ion, and it keept t he well t est ed and inexpensive Socket 7
mot herboards in t he market . I n 2000 t he VI A Joshua processor will hold designs originat ing
from Cyrix - port ed int o socket 370 design.
Two brands of 6x86MX and MII
[ t op]
The 6x86MX processor was produced by Nat ional/ Cyrix as well as by I BM. The archit ect ure
were t he same, but t he chips were built at different plant s.
On April 14, 1998 t he Cyrix MI I ( M- t wo) version was launched. I t was exact ly t he same chip
as t he 6X86MX j ust running at higher clock frequencies. Lat er t he volt age will be reduced t o
2. 2 Volt s.
I BM used a new t echnology for t heir PR333 chip. I t is pat ent ed and called Flip- Chip. The die is
soldered direct ly t o t he ceramic casing and t his causes less induct ion.
Cyrix MIII
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e04.htm (4 of 8)7/27/2004 4:08:29 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
I n t he year 2000 we were expect ing t he 3rd generat ion of t he 6X86MX ( code name Jalapeno
and Moj ave) . This CPU was t o be named MI I I , and t o come in> 600 MHz flavors. The MXi was
int ended Socket 7 compat ible, wit h a core running on a 133 MHz syst em bus. I t also should
include 3DNow! inst ruct ions and improved FPU. Read more on t his.
AMD K6-2
[ t op]
The next AMD "model 8" version of t he K6 had t he code name "Chomper".
This processor of May 28, 1998 was market ed as K6- 2, and like t he model 7 version of t he
original K6, it is manufact ured wit h 0. 25 micron t echnology. These chips run on j ust 2. 2
Volt age. They became an immense succes, in many sit uat ions compet ing very successfully
wit h I nt el' s Pent ium I I .
Super 7 motherboards and better MMX
The K6- 2 is made for a front side bus ( syst em bus) at t he speed of 100 MHz. This is t o be
found wit h t he so- called Super 7 mot herboards. AMD made ot her vendors like VI A produce
new chipset s for t he t radit ional socket 7 mot herboards, aft er I nt el in 1997 had given up t he
plat form.
K6- 2 is also improved wit h an MMX performance t wofold bet t er compared t o t he original K6.
3DNow!
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e04.htm (5 of 8)7/27/2004 4:08:29 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
The K6- 2 holds a new 3D plug- in ( called 3DNow! ) for bet t er game performance. I t consist s of
21 new inst ruct ions t hat can be used by soft ware developers giving a bet t er 3D- performance.
To benefit from it , you need a graphics driver or a game, which deals direct ly wit h t he new
commands.
The good t hing is, t hat games do not have t o include special programming t o benefit from
3DNow! . Support is included in Direct X 6. 0 ( and newer) for Windows . Direct X is a so- called
mult imedia API ( in fact a hardware abst ract ion layer) for Windows . I t is some programs t hat
can enhance t he mult imedia performance wit hin all Windows programs.
3DNow! is not compat ible wit h MMX, but t he K6- 2 holds MMX as well as t he 3DNow! . Also
Cyrix and I DT launch CPUs wit h 3DNow! . Read more on 3DNow!
Good and inexpensive power
The K6- 2 gave very, very good performance. You can compare t he models t o t he Pent ium
I I s. A K6- 2 350 MHz performed very similar t o a Pent ium I I - 350, but was sold a lot cheaper.
And you even saved more because of t he cheaper mot herboard.
100 MHz bus
Not all K6- 2s ran wit h a 100 MHz bus. Here you see some of t he versions, which require
mot herboards wit h cryst als capable of t hese configurat ions:
K6- 2 Bus Clock
266 MHz 66 MHz 4. 0 X 66 MHz
266 MHz 88 MHz 3. 0 X 88 MHz
300 MHz 100 MHz 3. 0 X 100 MHz
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e04.htm (6 of 8)7/27/2004 4:08:29 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
333 MHz 95 MHz 3. 5 X 95 MHz
350 MHz 100 MHz 3. 5 X 100 MHz
380 MHz 95 MHz 4. 0 X 95 MHz
400 MHz 100 MHz 4. 0 X 100 MHz
Two of t he CPU' s in t he t able must be t he same. AMD calls it a 350 MHz version, but in
Denmark e. g it was sold as a 380 MHz version.
K6-2/400 and above
November 15, 1998. The K6- 2/ 400 was int roduced. This chip worked on a new core, which
should be slight ly improved. Hence t he performance mat ched a Pent ium I I - 400.
April 6, 1999. A 475 MHz version of t he K6- 2 was int roduced. The lat est version is 533 MHz.
AMD had 39% of t he market wit h K6- 2 in 1999!
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read about chip set s on t he mot herboard in module 2d
Read more about RAM in module 2e
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side.
Read module 5b about AGP and module 5c about Firewire.
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
Read module 7c about sound cards, and 7d on digit al sound and music.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e04.htm (7 of 8)7/27/2004 4:08:29 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. . Click & Learn .
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e04.htm (8 of 8)7/27/2004 4:08:29 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 3e.05
The AMD K6-3
The cont ent s:
q K6- 3
q K6- 2+
q Next page
q Previous page
K6-3 [top]
Please support our
sponsor.
AMD announced t he very powerful K6- 3 for quit e a long t ime. I t was delayed quit e a while,
should have been released February 22nd 1999. During t he delay I nt el had t ime est ablish it s
Socket 370 version of Celeron. But finally it arrived in t he summer of 1999.
Using t he next version of t his chip - model 9 code name "Sharpt oot h" - you may have t hree
levels of cache!
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e05.htm (1 of 4)7/27/2004 4:08:31 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
I n t he K6- 3 you find:
q A slight ly improved K6- 2 unit .
q An in- chip L2 cache of 256 KB.
q TriLevel Cache design.
q New 133 MHz Front side bus.
q Clock speeds of 400 MHz and 450 MHz.
TriLevel Cache design
Bot h t he 64 KB L1 cache and t he 256 KB L2 cache are int egrat ed wit h t he chip. This L2 on-
die cache works at full processor speed j ust like it did in t he Pent ium Pro, and as it does in
t he Celeron A and in t he Xeon processors from I nt el. This will definit ely speed up t he K6 quit e
a bit !
Since t he K6- 3 is t o be used in a Super 7 mot herboard t here is room for anot her level of
cache, t he L3 cache. The TriLevel Cache design is const ruct ed t o use t he exist ing
mot herboards wit h up t o 2 MB of cache on- board. This used- t o- be L2 cache ( on t he
mot herboard) is used as t he t hird level of cache. This happens aut omat ically, and t he bigger
cache seems t o increase performance a lot !
High performance
Test s show performance from t he K6- 3 450 MHz comparable t o t he Pent ium I I I 500 MHz
processor. This is coming from a Socket 7 mot herboard! My predict ion is t hat t he K6- 3 will be
an excellent CPU at a very good price. The problem was t o find it , t he K6- 3 never became
very popular.
Still weaknesses in the FPU
Tradit ionally only I nt el can produce a powerful FPU ( Float ing Point Unit ) . Test confirms t hat
t he K6- 3 has t he same FPU as t he K6- 2 does. At same clock frequencies it performs 40%
under t he Pent ium I I I . However t he 3DNow! t echnology, which is support ed by t he Microsoft
Direct X soft ware layer, makes up for t he weak t radit ional FP- performance. I n t est it ends up
15% under t he equaling Pent ium I I I .
The die size
The K6- 3 obviously is bigger t han t he K6- 2, due t o t he int egrat ed L2 cache. However it is a
lot smaller t han t he At hlons :
Chip Die size
K6- 2 81 mm2
K6- 3 118 mm2
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e05.htm (2 of 4)7/27/2004 4:08:31 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
K7 At hlon 0. 25 micron 184 mm2
K7 At hlon 0. 18 micron 100 mm2
I nt el Pent ium I I I Cumine 106 mm2
K6-2+
I n 2000 t he K6- 3 is expect ed t o disappear from t he market . I t never became a success.
However, t he K6- 2 has been a great seller, so AMD will launche new versions of t he K6- 3 as
K6- 2+ .
This new chip will have following feat ures:
q 0. 18 micron process t echnology
q I nt egrat ed 256 KB L2 cache
q Addit ional 3DNow! inst ruct ions ( from At hlon)
q 550 MHz
The maximum speed from t his design is expect ed t o be 750 MHz. Hence one can expect t he
Socket 7 plat form soon t o die out .
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read about chip set s on t he mot herboard in module 2d
Read more about RAM in module 2e
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side.
Read module 5b about AGP and module 5c about Firewire.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e05.htm (3 of 4)7/27/2004 4:08:31 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
Read module 7c about sound cards, and 7d on digit al sound and music.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e05.htm (4 of 4)7/27/2004 4:08:31 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 3e.06
Intel Xeon for servers
The cont ent s:
q Xeon
q A product for servers
q Next page
q Previous page
Pentium II Xeon [top]
Please support our
sponsor.
I nt el always had an import ant market supplying CPU' s for servers. The original Pent ium Pro
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e06.htm (1 of 4)7/27/2004 4:08:32 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
was for several years used for t his purpose. Xeon is a line of CPUs for use in servers.
On July 26t h, 1998 I nt el int roduced t he Pent ium I I cart ridge named Xeon. Aimed at servers
and perhaps high- end users.
The Xeon is a Pent ium I I in a new cart ridge fit t ing int o a new connect or called Slot Two. The
module is t wice as t all as t he current Pent ium I I , but t here are ot her import ant innovat ions
and improvement s:
q New t ype L2 cache RAM chips: CSRAM ( Cust om SRAM) , which runs at full CPU speed.
q Different L2 cache sizes: 512, 1, 024, or 2, 048 KB L2 RAM.
q Up t o 8 GB RAM can be cached.
q Up t o four or even eight Xeons in one server.
q Support for clust ered servers.
q New chip set s 82440GX and 82450NX.
The new ( huge) cart ridge fit s int o a new Slot Two wit h t hree layers of edge connect ors. The
large L2 caches running high speed will use a lot of power, so cooling will be very import ant .
The cart ridge is about t wice t he size of t he well known Pent ium I I .
A server product
[ t op]
The Xeon chip is for high performance servers. The first t op model will hold 2 MB L2 cache on
t he cart ridge, running at full 450 MHz. This chip cost s $4, 500!
Performance gain from L2 cache at full speed
The L2 cache of t he Xeon runs at full CPU clock speed. One could t hink, t hat t his would have
t he same performance as t he L1 cache. However t he int erface from L1 t o L2 cost s some clock
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e06.htm (2 of 4)7/27/2004 4:08:32 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
t icks in t he beginning of each t ransmission, so t here is some lat ency. But when dat a is
t ransferred, it runs at full clock speed.
Pract ical t est s only show an increase in t he performance of 5- 8% comparing Pent ium I I and
Xeon/ 512 KB, bot h running at 450 MHz.
Personally, I find t he Xeons t oo expensive. I know companies who have been advised t o and
bought t he modules wit h 2 MB cache for use in web- servers. Obviously t he price does not
mat t er in t hose cases, and I nt el makes a good profit from t hat . I do not t hink t he
performance mat ches t he price.
Tanner
I n 1999 t he code name Tanner chip became known as t he Pent ium I I I Xeon.
Lat er might follow t he processor code named "Fost er" which should int egrat e 2 MB of L2
cache in- chip.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read about chip set s on t he mot herboard in module 2d
Read more about RAM in module 2e
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side.
Read module 5b about AGP and module 5c about Firewire.
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
Read module 7c about sound cards, and 7d on digit al sound and music.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e06.htm (3 of 4)7/27/2004 4:08:32 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e06.htm (4 of 4)7/27/2004 4:08:32 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 3e.07a
The Pentium III - Katmai and SSE
The cont ent s:
q Kat mai New I nst ruct ions ( KNI )
q Two new feat ures
q The I D number panic, panic
q SSE
q New regist ers
q Program support wit h Direct X 6. 1
q My conclusion
q Next page
q Previous
page
The first P6 CPU from I nt el was t he Pent ium Pro. Lat er we got t he Pent ium I I in various
flavours ( including t he popular Celeron) . I n 1999 t he t ime came for t he Pent ium I I I .
Katmai New Instructions (KNI)
[ t op]
I n March 1999 I nt el int roduced t he new enhanced MMX2 set of graphics inst ruct ions ( 70 of
t hem) . These are called Kat mai New I nst ruct ions ( KNI ) or SSE. They are int ended t o speed
up 3D gaming performance - j ust like AMD' s 3DNow! t echnology. Kat mai includes "double
precision float ing point single inst ruct ion mult iple dat a" ( or DPFS SI MD for short ) running in
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e07a.htm (1 of 5)7/27/2004 4:08:34 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
eight 128 bit regist ers.
Kat mai New I nst ruct ions ( KNI ) was int roduced wit h t he 450 and 500 MHz Pent ium I I I . I t was
processors very similar t o t he old Pent ium I I s, using Slot 1.
The only new feat ure was t he implement at ion of Kat mai and SSE, which I shall t ry t o
describe in t his page.
Two new features [top]
Please support our
sponsor.
I n fact t he Pent ium I I I cont ained t wo rat her different news it ems, one small and one
somewhat bigger. I nt el' s new t op processor is a Pent ium I I in principle. I t is mount ed in a BX
based mot herboard wit h Slot 1. This processor has some built - in feat ures:
q A rat her problemat ic I D numbering.
q New regist ers and 70 new inst ruct ions.
Finally t he clock speed was raised t o 500 MHz wit h room for furt her increases. Pent ium I I I
Xeon ( code name Tanner) was int roduced March 17t h, 1999. I t was a Xeon chip updat ed wit h
all t he new feat ures from Pent ium I I I . To ut ilize it I nt el has t he 840 chipset .
The ID number panic, panic
[ t op]
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e07a.htm (2 of 5)7/27/2004 4:08:34 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
The I D number PSN ( Processor Serial Number) , which is unique for each CPU, has caused lot s
of securit y discussions. I t is a 96 bit value t hat is elect ronically programmed int o each chip.
Act ually it was meant as a very sensible init iat ive, which could make elect ronic t rade and
encrypt ing on t he I nt ernet more secure and effect ive.
The advocat es see t he I D number as "t he permanent cookie. "However it t urns out t hat
hackers and crackers can easily access t he number, which makes t he securit y dubious. At t he
same t ime t he syst em is proposing a global regist ry of I nt ernet users, which can easily be
misused for market ing, et c. That will be invasion of privacy, if you no longer can remain
anonymous on t he I nt ernet .
SSE etc.
[ t op]
The somewhat bigger news it em is a real change in t he basic processor archit ect ure. I t is
act ually t he first change since 1985, where t he x86 archit ect ure was expanded from 16 t o 32
bit ( compared wit h t he 386 processor) .
q New 128 bit regist ers, which each can handle four float ing- point numbers.
q St reaming SI MD Ext ensions ( SSE) . 50 new inst ruct ions, which enable simult aneous,
advanced calculat ions of more float ing- point numbers wit h a single inst ruct ion.
q New Media I nst ruct ions. 12 new inst ruct ions in t his cat egory, which include ot her
inst ruct ions for float ing- point decimal calculat ions besides inst ruct ions t hat are designed for
coding and decoding of MPEG- 2 video st reams "on t he fly. "
q St reaming Memory. Here are 8 new inst ruct ions, which improve t he int eract ion bet ween L2-
cache and RAM. Wit h opt imum ut ilizat ion of t he inst ruct ions, it could result in a 20%
improvement of t he bandwidt h on t he syst em bus. These inst ruct ions require newly- compiled
programs, so it may be some t ime before we see t he effect of t his.
The combined new inst ruct ions are called KNI ( Kat mai New I nst ruct ions) or SSE. The Pent ium
I I I const ruct ion is an at t empt at improving t he FPU performance in t he processor. The
regist ers are used by t he new Kat mai inst ruct ions.
New registers
[ t op]
The new 128 bit regist ers can pot ent ially speed up 3D- graphics and mult imedia handling,
since t he regist ers can cont ain four of t he import ant 32 bit float ing- point decimal numbers.
Since t he regist ers are a new physical creat ion wit hin t he CPU, t hey require support in t he
operat ing syst em t o ut ilize t hem. Such support is expect ed soon in Windows 98.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e07a.htm (3 of 5)7/27/2004 4:08:34 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
Program support with DirectX
[ t op]
Microsoft ' s Direct X program layer is opt imized relat ive t o Kat mai. Wit h t hat , a large number
of exist ing programs should benefit from t he addit ional power of Pent ium I I I ( when Direct X
6. 1 or bet t er is inst alled) . However t he drivers for sound and graphics cards need t o be re-
writ t en, t o enable ut ilizat ion of t he new Direct X edit ion. Games t hat are not based on Direct X
need t o be re- writ t en or expanded wit h pat ches, which ut ilize Kat mai. Finally, a pat ch has
been announced for t he operat ing syst em it self, Windows 98, which should support t he new
inst ruct ions. Whet her it will support all or only part of t hem is yet unknown.
Problems
I n April 1999 came report s of heat problems wit h t he 550 MHz version. I t should be very very
hot , so big fans are t he issue here. . .
July 31, 1999. The 600 MHz version was launched. Lat er t he "Coppermine" version was
int roduced wit h Socket 370, as you will see in t he following page.
A provisional evaluation
[ t op]
I t is difficult t o evaluat e t he significance of Pent ium I I I s new regist ers and inst ruct ions.
However, it seems t hat most programs, drivers, et c. are being t uned for t he new inst ruct ions.
Then t here is no doubt t hat t he mult imedia capabilit ies have received a great boost . There
could be a doubling of t heir performance. So far Adobe have included support for SSE in
version 5. 5 of Phot oshop. This works very well, some very t ime- consuming processes has
been short ened wit h approx. 40%.
The quest ion is, if AMD will be forced t o work in SSE et c. in t heir t op processors or if t hey will
cont inue t he development of 3DNow! . I n t hat case we' ll have t wo syst ems t o work wit h.
Perhaps t his is not a problem.
Please read about Cumine and ot her new chips following Pent ium I I I in t he next module.
q Next page
q Previous page
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e07a.htm (4 of 5)7/27/2004 4:08:34 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read about chip set s on t he mot herboard in module 2d
Read more about RAM in module 2e
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side.
Read module 5b about AGP and module 5c about Firewire.
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
Read module 7c about sound cards, and 7d on digit al sound and music.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e07a.htm (5 of 5)7/27/2004 4:08:34 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 3e.07b
Pentium III CuMine
The cont ent s:
q CuMine
q Many models
q But no copper
q Next page
q Previous page
Coppermine - CuMine..
[ t op]
Here we shall look at t he furt her development of Pent ium I I I .
600 MHz
31, July 1999 t he Pent ium I I I was released in a 600 MHz version. This chip is working on a
100 MHz bus.
27, Sept ember 1999, I nt el launched t wo new chips, t he 533 and t he 600 MHz versions of
Pent ium I I I . These chips are bot h running on a 133 MHz syst em bus. Unfort unat ely t he new
chip set , i820, which was t o be launched t he same day, was pulled back in t he last minut e.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e07b.htm (1 of 4)7/27/2004 4:08:36 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
The int erest ing point is t hat t he 820 set wit h Pent ium I I I Coppermine is supposed t o be
I nt el' s answer t o t he t he very successful AMD At hlon.
Some good news: Adobe has updat ed t he graphics program Phot oshop 5. 5 wit h support for
t he SSE set of inst ruct ions. I t should be very succesfull.
Coppermine
25, Oct ober 1999 t he next generat ion of Pent ium I I I processors was released. The new t hing
here is t he process t echnology and t he int egrat ed L2 cache.
The headlines:
q 0. 18 process t echnology wit h 28 million t ransist ors
q 6 layer aluminium product ion
q Reduced die size and 1, 65 core volt age
q I nt egrat ed L2 cache of 256 KB
q New L2 t o CPU bus of 256 bit s widt h
The elect ronic "wires" insides t he chip has been reduced from a widt h of 0. 25 micron t o0. 18,
which is 1/ 500 of a human hairs widt h. . . The impact of 0. 18 process t echnology is t hat t he
required volt age can be lowered from 2. 2 Volt t o 1. 6 Volt . Hence, t he Coppermine chip is
developing less heat at t he same clock frequency, and it can be produced for higher speeds.
The launched t opmodel was running at 733 MHz.
I nside t he CPU, t he archit ect ure has not changed a lot . The die size has decreased, and t his
way t here has become room for an int egrat ed 256 KB of L2 cache. This cache now works at
full CPU speed and at a 256 wide bus. This gives a solid increase in performance.
The 28 millions of t ransist ors are loaded int o 106 squaremillimet ers, which is quit e small; t he
old Pent ium I I I wit hout int egrat ed L1 cache and only 9. 3 million t ransist ors t ook up 128
squaremillimet ers.
Many models
Please support our
sponsor.
The new chips produced wit h 0. 18 micron process t echnology are labeled wit h an "E" t o
dist inguish t hem from older models.
But since t he new process t echnology is also used for Pent ium I I I ' s running at t radit ional 100
MHz, t he models wit h 133 MHz are labeled wit h a "B". This way we will ( for a while) have four
flavours of 600 MHz Pent ium I I I s:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e07b.htm (2 of 4)7/27/2004 4:08:36 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
Model Process Clock frequency
600 0. 25 6 x 100 MHz
600E 0. 18 6 x 100 MHz
600B 0. 25 4. 5 x 133 MHz
600EB 0. 18 4. 5 x 133 MHz
Obviously, I nt el plans t o skip t he chips produced in 0. 25 micron. But meanwhile bot h process
t echnologies will be sold side by side.
Lat e we shall have Celerons at 800 MHz and more based on t he new CuMine kernel.
But no copper
I t was expect ed t his new generat ion of chips t o produced using copper. The name "CuMine"
also indicat es t his. But t he first of t hese Cumines are produced wit h t radit ional aluminium
wiring in 0. 18 microns widt h. First in 2001 I nt el plans t o st art using copper ( in t he P860
kernel) , and t his should lead t o much higher levels of speed.
AMD launched GigaHerz version of t he At hlon using copper in 2000. I nt el also launched
GigaHert z versions of Pent ium I I I , but t hey were only sold in few numbers in 2000.
SpeedStep
I nt el launched a new series of chips for not ebooks. The first models are 500 MHz versions of
Pent ium I I I running on a 100 MHz bus. Producing t hem in 0. 18 t echology, I nt el has been able
t o work wit h t he power consumpt ion.
The new chips can work in a "light " mode when t he not ebook is on bat t eries. The core
volt age is reduced from 1. 6 t o 1. 1 Volt , and t he power usage goes down t o j ust 50%! The
CPU performance only decreases wit h 20%.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e07b.htm (3 of 4)7/27/2004 4:08:36 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
Read about chip set s on t he mot herboard in module 2d
Read more about RAM in module 2e
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side.
Read module 5b about AGP and module 5c about Firewire.
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
Read module 7c about sound cards, and 7d on digit al sound and music.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e07b.htm (4 of 4)7/27/2004 4:08:36 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 3e.07c
The further development of Pentium III
The cont ent s:
q Pent ium I I I
q The Pent ium 4
q Next page
q Previous page
CuMine in year 2000
[ t op]
Here we shall look at t he furt her development of Pent ium I I I .
Athlon was not not good for Intel
I n t he first mont hs of 2000 it was obvious t hat I nt el had a hard t ime wit h Pent ium I I I . From unknown
reasons, t hey were not capable of producing t he CPUs t he market want ed. I n Denmark we could get all
t he At hlons needed in February, but only very few Pent ium I I I s.
At t he same t ime AMD showed up wit h fast er and cheaper versions of t he At hlon - all put t ing a heavy
pressure on I nt el.
I nt el on t heir side launched a lot of new models. On Jan 11t h, 2000 t he 800 MHz version was launched
running 6 x 133 MHz. I n February t he company showed a Pent ium I I I running at 1 Ghz wit hout special
cooling.
The 850 and 866 MHz were scheduled for February 27/ 28, 2000. The 933 MHz model came May 27,
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e07c.htm (1 of 4)7/27/2004 4:08:38 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
2000. This way I nt el t ried t o prove, t hat t hey are keeping up wit h AMD. However in t he real world, t hey
were not , being unable t o supply t he market wit h processors. I n t he same period t housands of t he
compet ing 650 and 700 MHz AMD At hlons were sold every week.
I n t he summer 2000, a 1, 113 MHz version of Pent ium I I I was t aken out of t he market due t o unst abilit y,
and it appears t hat 1000 MHz is going t o be t he t opmodel of Pent ium I I I . Pent ium 4 is heading for 2 GHz
in 2001.
The last Pentium III
The int erest ing issue is, which version of Pent ium I I I t o be t he last one. I f we look at t he scheme, we
see t hat Pent ium I I I is bulding on pret t y old t echnology, namely t he P6 core:
I t was expect ed, t hat t he P6 line of processors would end wit h CuMine. However, I nt el seems t o have
decided t o cont inue t he line one more year:
The "Tualatin" core
Please support our
sponsor.
I n August 2001 I nt el launched t he 0. 13 micron version of Pent ium I I I , which has been known as
codename "Tualat in" ( I nt el' s codenames is from rivers in t he pacific Nort hwest of t he USA) . This
processor uses copper int erconnect s.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e07c.htm (2 of 4)7/27/2004 4:08:38 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
The new processor is a Pent ium I I I "Cumine" wit h 256 or 512 KB L2 cache int egrat ed. Hardware dat a
prefect h is a new feat ure, which gives an 8- 10% increase in performance.
I t runs on 1. 475 Volt and is mount ed in a Socket 370. The Tualat in comes in 1. 2 and 1. 13 GHz versions,
bot h using a 133 MHz Front Side Bus.
The I nt el i815EEA chipset is designed t o t his processor as well as VI A Apollo Pro 266T. The lat est gives
support for DDR RAM.
Marketing ...
This t he last Pent ium I I I processor has not been advert ised very much. Probably I nt el does not want it
t o compet e wit h t he 1. 4 GHz Pent ium 4. Many people was looking forward t o t he 1. 2 GHZ model wit h
512 KB cache. However t his one is only sold for use in servers and in mobile PCs - not for deskt op use!
The Pentium 4
The roadmap I nt el made several years ago was t o abandon t he P6 core in favour of a complet ely new
core. The processor codenamed "Willamet t e" should be t he first of a new line of I A32 processors, which
should be market ed side- by- side t o t he I A64 I t anium ( "Merced") :
Read about t he Pent ium 4 in a following module.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
The Pent ium 4
Read about chip set s on t he mot herboard in module 2d
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e07c.htm (3 of 4)7/27/2004 4:08:38 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
Read more about RAM in module 2e
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side.
Read module 5b about AGP and module 5c about Firewire.
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
Read module 7c about sound cards, and 7d on digit al sound and music.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e07c.htm (4 of 4)7/27/2004 4:08:38 AM
An illustrated Guide AMD K7 Athlon.
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 3e.08a
AMD "The Great" Athlon.
The cont ent s:
q An int roduct ion t o K7 At hlon
q The background
q No syst em bus
q Next page
q Previous page
An overview of Athlon
[ t op]
The At hlon is a powerful CPU, t he first 7t h generat ion CPU in my opinion. I t was expect ed June 1999 but
was delayed unt il August 1999. I nt el' s response ( code name Willamet t e) was scheduled Oct ober 2000.
At hlon was designed using t echnologies from DEC Alpha 21064 and 2162 RI SC processors. Their "fart her"
Dirk Meyer came t o AMD and brought in an engineering t eam who succesfully developed t he At hlon, which
ended up being an enormous success t o AMD.
Wit hin t he first mont hs, t he market s response t o t he At hlon was very posit ive. I t seemed ( as expect ed) t o
out perform t he Pent ium I I I at same clock frequency.
Let us look at what At hlon has t o offer:
Raw data
q Mount ing in a Pent ium I I like module, which is ent irely AMDs own design. The socket is called slot A.
q A clock speed of 500 MHz in t he first versions.
q Up t o 8 MB L2- cache ( minimum 512 Kb, wit hout ext ra TAG- RAM) .
q 128 KB L1- cache.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e08a.htm (1 of 5)7/27/2004 4:08:41 AM
An illustrated Guide AMD K7 Athlon.
q 22 million t ransist ors ( t he original Pent ium I I I had 9. 3 million) .
New bus type
q A brand new syst em bus t ype, which in t he first versions will work at 200 MHz. An increase t o 400 MHz is
expect ed lat er. The bus is ready for new fast RAM t ypes.
q I ndependent backside bus, which connect s t he L2 cache. Here t he clock speed can be 1/ 4, 1/ 3, 2/ 5 or
ident ical wit h t he int ernal CPU frequency. That is t he same syst em which is used in t he P6 syst ems where
t he L2 speed is eit her half ( Pent ium I I and I I I Kat mai) or full CPU frequency ( at Celeron, Xeons and Pent ium
I I I CuMine) .
Heavy decoding and FPU
q Three inst ruct ion decoders, which t ranslat e t he X86 program' s CI SC inst ruct ions t o t he effect ive RI SC
inst ruct ions, ROPs, where up t o 9 can be execut ed simult aneously. The first t est show a decoding of 2. 8
CI SC- inst ruct ion per clock cycle. This is roughly 30% bet t er t han Pent ium I I and I I I .
q Can handle and rearrange up t o 72 inst ruct ions ( ROP out of order) simult aneously ( Pent ium I I I can do 40,
K6- 2 only 24) .
q Enormous FPU performance wit h t hree simult aneous inst ruct ions and one GFLOP at 500 MHz ( 1 billion
float ing- point number operat ions per second) wit h 80 bit float ing- point numbers. Two GFLOP wit h MMX and
3DNow! inst ruct ions. That at least equals Pent ium I I I s performance wit h full ut ilizat ion of Kat mai. The
3DNow! engine has even been improved comparing t o t he K6- 3.
The first t est s show t his FPU performance:
Processor FPU
Winmark
I nt el Pent ium I I I / 500
MHz
2562
AMD At hlon / 500 MHz 2767
The background [top]
Please support our
sponsor.
AMD has no license t o use t he Slot 1 archit ect ure, so t he cont rolling logic comes from Digit al Equipment
Corp. I t is called EV6 and was designed for t he 21264 Alpha CPU. AMD developed t he first chip set s ( 750)
t hemselves, but t he archit ect ure is royalt y free t o use. I t will be AMD' s first processor using a mot herboard
and chip set specially designed by t hemselves. VI A has developed a series of chip set s for t he At hlon.
The use of t he EV6 bus gives a lot more bandwidt h t han t he I nt el GTL+ . This means t hat t he At hlon has t he
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e08a.htm (2 of 5)7/27/2004 4:08:41 AM
An illustrated Guide AMD K7 Athlon.
capacit y t o work wit h new RAM t ypes such as RDRAM. Also t he use of 128 KB L1 cache is pret t y heavy. The
L1 cache is import ant when t he clock speed increases and 128 KB is t wice t he size in Pent ium I I ' s.
The At hlon came in several versions. The "slowest " ones will have t he L2 cache running at one t hird of t he
CPU speed, where t he best ones ( like "Thunderbird") work at full CPU speed ( as t he Xeons do) . The At hlon
was int ended t o give I nt el compet it ion in all segment s including servers, where t he t opmodels are being
compareable wit h t he best I nt el Xeon processors.
No system bus
[ t op]
Since t he At hlon is not inst alled in t he same way as Pent ium I I and I I I , AMD could develop a brand new
archit ect ure. This means t hat t here really is no syst em bus. The At hlon module is connect ed direct ly t o
chipset ' s "Nort h bridge" in t he first edit ion t hrough a 200 MHz dat a channel. I n a mult i- processor syst em,
each CPU will have it s own 200 MHz channel.
That channel connect s only t wo unit s: t he CPU and t he chipset . I n t he P6 syst ems t he CPU, L2- cache, RAM,
PCI unit s, t he AGP unit and t he chipset are all connect ed t o t he syst em bus. I n At hlon t he t raffic is split .
Nort h bridge comes first , t hen come RAM, AGP, t he PCI unit s and t he Sout h bridge.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e08a.htm (3 of 5)7/27/2004 4:08:41 AM
An illustrated Guide AMD K7 Athlon.
Better bandwidth
By eliminat ing t he syst em bus and replacing it wit h t he new syst em, At hlon achieves access t o a much
bigger bandwidt h. I n t heory t he bandwidt h in a 200 MHz connect ion is:
200, 000, 000 x 64 bit / bit / second = 1. 6 GB per second.
That was significant ly bet t er t han I nt el' s present syst ems:
Syst em Maximum t ot al bandwidt h
I nt el 100 MHz 800 MB/ sec.
I nt el 133 MHz 1064 MB/ sec.
AMD At hlon, 200 MHz 1600 MB/ sec.
AMD At hlon, 400 MHz 3200 MB/ sec.
The new archit ect ure opens up for new RAM int erfaces. We will see support for 100 and 133 MHz SDRAM,
for DDR SDRAM and for RDRAM.
I t is also likely t hat we lat er can choose from 64, 128 or 256 bit wide RAM access.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e08a.htm (4 of 5)7/27/2004 4:08:41 AM
An illustrated Guide AMD K7 Athlon.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read about chip set s on t he mot herboard in module 2d
Read more about RAM in module 2e
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side.
Read module 5b about AGP and module 5c about Firewire.
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
Read module 7c about sound cards, and 7d on digit al sound and music.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e08a.htm (5 of 5)7/27/2004 4:08:41 AM
An illustrated Guide AMD K7 Athlon.
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 3e.08b
AMD K7 "The Great" Athlon.
The cont ent s:
q The At hlon Tbird
q The Sledgehammer
q Next page
q Previous
page
The Thunderbird Athlons
[ t op]
The At hlon processor has a very large pot ent ial. Back in 1999 some analyt ics believed t hat
At hlon will be t he most import ant and dominant processor in 2001. And t hey were almost
right . All maj or vendors - except Dell - are using At hlons in high- end PCs.
The At hlon has an enormous bandwidt h t hat obviously not will be needed in t he immediat e
fut ure.
The point is t hat t he archit ect ure is looking ahead. There is lot s of room for t echnological
advances in t he coming years, such as significant ly fast er RAM, hard disk et c.
At t he same t ime AMD signals t hat t his is t he fut ure server archit ect ure, since especially
larger net work servers will have a need for t he large bandwidt h.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e08b.htm (1 of 5)7/27/2004 4:08:43 AM
An illustrated Guide AMD K7 Athlon.
The Thunderbird core
AMD has a new fabricat ion unit ( fab 30) in Dresden, Germany. From t his t he new
"Thunderbird" core was shipping June 2000.
The first Thunderbirds:
q 750 MHz t o 1 GHz versions using 0. 18 micron copper t echnology.
q 256 KB L2 cache int egrat ed.
q New 462 pin socket A.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e08b.htm (2 of 5)7/27/2004 4:08:43 AM
An illustrated Guide AMD K7 Athlon.
q Bot h copper and aluminium chips available.
The Thunderbird is a very powerful chip wit h it s 37 million t ransist ors. I t compet es direct ly
wit h t he Pent ium I I I "Cumine".
The "old" At hlon design using a Slot A- based cart ridge suffered from poor L2 cache
performance. The 512 KB of L2 cache was placed out side t he CPU. This gave a connect ion t o
t he CPU working at only a half or a t hird of t he processors clockspeed.
I nt egrat ing t he L2 cache wit h t he processor, t he 256 KB is accessed at full processor speed,
as it should. On- die cache gives t he best performance. The reduct ion in t he L2 size from 512
t o 256 KB is of less import ance; t he full clockspeed has an enormous effect .
The Thunderbird chip performs j ust as good as or slight ly bet t er t han Pent ium I I I running at
t he same clock frequencies. Wit h t he new on- die L2 cache of 256 KB in combinat ion wit h t he
original 128 KB L1 cache, AMD indeed has a very powerful product .
Narrow L2 cache to CPU pipeline
St ill Pent ium I I I Cumine has one advant age t o t he Thunderbird. When I nt el decided t o
int egrat e t he 256 KB of L2 cache wit h t he processor, t hey gave it a 256 bit wide bus t o work
wit h.
When t he L2 resides out side t he CPU you have t o st ick t o a 64 bit bus bet ween CPU and L2.
This rest rict ion comes from t he number of CPU pins you want t o allocat e t o t he L2
connect ion.
I f t he L2 cache is int egrat ed wit h t he CPU t here is no need for t his limit at ion. I nt el wisely
went from 64 t o 256 bit s widt h. This AMD has not done. For some reason, t he Thunderbird
core st ill only connect t o t he L2 cache on a 64 bit wide bus.
Copper or alu?
The new Thunderbirds are being produced t wo fabs:
q At fab25 in Aust in, Texas ( 0. 18 micron aluminium)
q At fab30 in Dresden, Germany ( 0. 18 micron copper)
AMD t old t hat t here should be no difference bet ween t he t wo chips.
Copper is t he most sophist icat ed mat erial since it opens up for much higher clock frequencies
t han aluminium, due t o t he bet t er elect rical conduit . However, at sub- GigaHert z frequencies
aluminium works fine, and t here should be no difference bet ween t he chips coming from
different fabs.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e08b.htm (3 of 5)7/27/2004 4:08:43 AM
An illustrated Guide AMD K7 Athlon.
Chip sets
Please support our
sponsor.
The original At hlon chip set AMD 750 works fine wit h t he Thunderbird processor. However,
AMD is soon int roducing t he 760 chipset for use wit h Thunderbird. I t is expect ed t o support
DDR RAM.
The popular VI A KX133 chip set had problems wit h Thunderbird. Therefore VI A produced t he
KT133 chipset specially designed for Thunderbirds and Durons. This chipset was at first
int roduced as "KZ133" which was a very unwise choice in naming. KZ was t he Nazi- German
abbreviat ion for concent rat ion camp - t he camps in which millions of Jews and ot her
Europeans were murdered. VI A wisely renamed t he chip set when t he hist orical significance
of t he t wo let t ers KZ came t o t heir minds.
Anot her brand of At hlon is t he "Spit fire" core, which was launched as "Duron" for cheaper PCs
- Celeron- killer so t o say. Please see module3e13 on t his chip.
Sledgehammer
Please support our
sponsor.
The successor t o At hlon is codenamed "Sledgehammer". I t sounds int erest ing:
q Mult i- core t echnology wit h several complet e microprocessors working parallel wit hin t he
same CPU.
q The I A32 set of inst ruct ions are beeing ext ended t o include a 64 bit mode.
q More powerfull FPU.
The value of 64 bit inst ruct ions is disput eable. We already have 64 bit and even 128 bit
inst ruct ions wit hin SSE and 3DNow! . Here it means new 64 bit inst ruct ions, regist ers, busses
and memory addresses. To benefit fully from t his 64 bit power, all soft ware have t o be
recompiled. But AMD claims t hat t he processor will run all exist ing 32 bit soft ware at full
speed as well.
From my humble viewpoint , "Sledgehammer" ( what a name) sounds far more int erest ing
t han I nt el' s I t anium. Backward compat ibilit y has always been ext remely import ant .
Lots of RAM
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e08b.htm (4 of 5)7/27/2004 4:08:43 AM
An illustrated Guide AMD K7 Athlon.
One of t he limit at ions of t he 32 bit archit ect ure is t he amount of RAM. A 32 bit processor can
"only" address 4 Gb of RAM. This is not enough for t he biggest syst ems.
Wit h 64 bit addressing you can use 18 Exebyt es of RAM. That ' s a lot .
Sledgehammer will be int roduced in 2002.
Please also see t he art icle on die sizes here.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read about chip set s on t he mot herboard in module 2d
Read more about RAM in module 2e
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side.
Read module 5b about AGP and module 5c about Firewire.
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
Read module 7c about sound cards, and 7d on digit al sound and music.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e08b.htm (5 of 5)7/27/2004 4:08:43 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 3e.09
On MMX, 3DNow!, and Katmai
The cont ent s:
q An int roduct ion
q The FPU
q Working wit h 3D graphics
q MMX
q 3DNow!
q Kat mai
q Next page
q Previous page
Multimedia, MMX and Katmai
[ t op]
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e09.htm (1 of 6)7/27/2004 4:08:45 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
Wit h t he Pent ium MMX we had t he first of several improvement s of t he microprocessor' s set
of inst ruct ions. Lat er, we got 3DNow! and Kat mai. What does all t his mean?
I n 1995 t he Pent ium processor was expanded wit h t he so- called MMX inst ruct ions. That was
announced as a mult imedia expansion wit h 57 new inst ruct ions.
Today t he emphasis in mult imedia is especially in 3D graphics. Here t he most import ant
operat ion is t he so- called geomet ric t ransformat ions, which deal wit h float ing- point numbers.
Let us t ake a look at t hese issues.
FPU
[ t op]
FPU st ands for Float ing- point Unit . That is t he unit in t he processor, t hat handles float ing-
point numbers. I t is difficult for t he CPU t o manipulat e float ing- point numbers, since it
requires lot s and lot s of bit s t o perform an accurat e calculat ion. Mat h wit h int egers is much
simpler, and is done wit h hundred percent accuracy each t ime.
The FPU works wit h float ing - point numbers of various bit lengt h, depending on t he desired
degree of accuracy. The most accurat e t ype has a bit lengt h of 80!
All t he modern P6 processors have 8 FP regist ers, each of which has a bit lengt h of 80. So
t here is room inside t he CPU it self for 8 numbers each of 80 bit lengt h or, for example, 16
numbers each of 32 bit lengt h. Read more. . .
Working with 3D graphics [top]
Please support our
sponsor.
When you draw people and landscapes, which are alt ered in 3D graphics, t he figures are built
up from small polygons ( usually t riangles or rect angles) .
A figure in a PC game can t ypically be built from 200- 1500 such polygons. For each change in
t he pict ure t hese polygons have t o be re- drawn in a new posit ion. This means t hat each
corner ( vert ex) in every polygon has t o be recalculat ed.
Floating-point number operations
To calculat e t he placement of t he polygons, you need t o use float ing- point numbers. I nt eger
calculat ions ( 1, 2, 3, 4 et c. ) are not nearly precise enough. I nst ead, you use decimal
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e09.htm (2 of 6)7/27/2004 4:08:45 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
numbers such as 4. 347. These numbers are single precision. They are 32 bit s long. There are
also 64 bit numbers ( having more decimal places) . They are called double precision numbers,
which are useful for even more demanding calculat ions.
However t he 32 bit s numbers are sufficient t o design 3D obj ect s. When t he figures in a 3D
landscape move, you need t o make a so- called mat rix mult iplicat ion t o calculat e t he new
vert ices. I f a figure consist s of 1000 polygons, it requires up t o 84, 000 mult iplicat ions, each
wit h t wo 32 bit float ing- point numbers.
I t is quit e a heft y piece of mat h, for which t he t radit ional PC is not well equipped. Act ually,
t he largest spreadsheet available t o t he finance minist ry is a drop in t he bucket compared t o
Quake I I , as far as number crunching abilit y is concerned.
What assists the 3D execution?
The CPU can easily run out of breat h when it comes t o work wit h 3D movement s across t he
screen. So what assist ance can it get ? That can be provided in different ways:
q Generally speaking, t he fast er t he CPU, t he higher t he clock speed, t he fast er t he
t radit ional FPU performance will be.
q I mprovement s in t he CPUs FPU wit h pipelines and ot her accelerat ion. We see t hat in each
new CPU generat ion.
q New inst ruct ions for more effect ive 3D performance. I nst ruct ions which can be called by
t he programs, 3DNow! and SSE, are examples of t his.
q 3D accelerat ed graphics cards.
MMX
[ t op]
The Pent ium MMX processor was a big success. However, t hat was not because of t he MMX
inst ruct ions. Many regard t hem as a flop.
The point is t hat MMX only works wit h int egers. Furt hermore t he syst em is so weak, t hat it
can only work wit h eit her MMX or wit h FPU, not bot h simult aneously. That is because t he t wo
set s of inst ruct ions share regist ers.
The MMX inst ruct ions can be of assist ance in ot her t asks in t he redrawing of 3D landscapes
( t he surface et c. ) , but for all t he geomet ry you need much more umph!
Here you see t he MMX enabling in a program. I t is "Paint er Classic" a great drawing program,
which is bundled wit h Wacoms drawing t ablet s. The program ut ilizes MMX:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e09.htm (3 of 6)7/27/2004 4:08:45 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
3DNow!
[ t op]
During t he summer of 1998 AMD int roduced a new collect ion of CPU inst ruct ions, which
improve t he 3D execut ion.
q 21 new inst ruct ions.
q SI MD inst ruct ions, which enable handling of more dat a port ions wit h j ust one inst ruct ion.
q I mproved handling of numbers, especially t he 32 bit numbers, which are used widely in 3D
games. 3DNow! became a big success, since t he inst ruct ions soon became int egrat ed in
Windows , in different games ( and ot her programs) and in t he driver programs from t he
hardware producers.
The inst ruct ions use t he same regist ers, as do MMX and t radit ional FPU. So t hey have t o
share t hem. Since t he regist ers are 80 bit s wide, t hey can hold t wo 32 bit numbers
simult aneously.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e09.htm (4 of 6)7/27/2004 4:08:45 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
Katmai [top]
Please support our
sponsor.
Kat mai ( SSE) is I nt el' s way t o improve 3D execut ion in Pent ium I I I . Read also t he descript ion
in module 3e7. The problem wit h Kat mai is t hat t he inst ruct ions require soft ware support ,
and t hat will t ake some t ime t o get in place.
I n principle Kat mai is significant ly more powerful t han 3DNow! The 8 new 128 bit regist ers
can act ually hold four 32 bit numbers at a t ime. But t o t ake advant age of t his, t he FPU
pipeline should also have been doubled, so each mult iplicat ion or addit ion pipeline could
receive four numbers at a t ime.
However t hat was not done in Pent ium I I I , since it would have delayed it s int roduct ion. So
t he pipelines can st ill handle t wo 32 bit numbers at a t ime. I n t hat way t he full pot ent ial of
Kat mai is not reached wit hin t he act ual Pent ium I I I design.
Wit h t he current FPU unit Pent ium I I I can perform t wice as many 32 bit number operat ions
per clock t ick as can t he ot her P6 processors ( Pent ium I I and Celeron) . That is t he same
performance as we find in t he 3DNow! processors. But Pent ium I I I is scheduled for fut ure
edit ions wit h a four- fold increase in FPU performance as far as t he 32 bit numbers are
concerned.
SIMD
SI MD st ands for Single I nst ruct ion Mult iple Dat a. This t echnique was int roduced in t he MMX
processors, where more t han one int eger could be processed simult aneously. I n Pent ium I I I
t his t echnique was given anot her lift , so now it can handle more t han one float ing- point
number. Mult imedia handling especially will benefit from t his, since many float ing- point
number operat ions are handled in sound and video programs.
Wit h t he int roduct ion of Pent ium 4, t he SI MD inst ruct ion set was furt her improved wit h144
new inst ruct ions.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e09.htm (5 of 6)7/27/2004 4:08:45 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
Read about chip set s on t he mot herboard in module 2d
Read more about RAM in module 2e
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side.
Read module 5b about AGP and module 5c about Firewire.
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
Read module 7c about sound cards, and 7d on digit al sound and music.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e09.htm (6 of 6)7/27/2004 4:08:45 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 3e.10
On CPU sockets
The cont ent s:
q The CPU Socket s and chip set s
q Pent ium I I road map
q Three lines of I nt el CPUs
q Next page
q Previous page
The CPU Sockets and chip sets [top]
Please support our
sponsor.
To get an overview on all t he different I nt el CPUs, you may t ake a look at t he various
socket s, t hat are used t o mount t he CPU. Each socket is working t oget her wit h specific chip
set s. Let us finally also look int o t he fut ure. . .
There are many different CPU socket s in use for t he various CPUs. Here you see a handfull of
t hem:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e10.htm (1 of 5)7/27/2004 4:08:47 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
Socket Fit s CPU I nt el Chip set Number of pins
Socket 7 Pent ium, MMX, K5, 6x86, K6, I DT WinChip,
6x86MX, K6- 2
82430TX 321
Socket 8 Pent ium Pro 82440FX 387
Slot One Pent ium I I 82440FX
82440LX
242
Slot One Pent ium I I ( 100 MHz syst em bus) ,
Pent ium I I I ( 100 and 133 MHz)
82440BX
82440JX
242
Slot One Celeron 82440EX 242
PGA370 Socket ed Celeron
Pent ium I I I
82440BX
82440LX
82440EX
82440EZ
i810
i815
370
Slot Two Pent ium I I Xeon, Tanner 82440GX
82450NX
330
PGA423 Pent ium 4 i850 423
Slot M Merced ? ?
Only Socket 7 may be copied freely. The ot her ones are I nt el' s pat ent s. They may be
manufact ured by ot hers on license from I nt el. Cyrix is expect ed t o produce Slot 1- compat ible
modules.
A road map to Intel CPUs
[ t op]
Put t ing all t he 6t h generat ion' s CPUs from I nt el t oget her, we get a pict ure like t his:
CPU name/
code name
Year CPU/ bus
MHz
L2
cache
Socket Process
t echno- logy
Ext ra
inst ruct ions
Pent ium Pro 1995 233/ 66 512-
1024
full
speed
Socket 8 0. 35 None
Pent ium I I
"Klamat h"
1997 300/ 66 512 KB
half
speed
Slot 1 0. 35 MMX
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e10.htm (2 of 5)7/27/2004 4:08:47 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
Pent ium I I
"Deschut es
first "
1998 300/ 66 512 KB
half
speed
Slot 1 0. 25 MMX
Pent ium I I
" Deschut es
second"
1998 400/ 100
450/ 100
512 KB
half
speed
Slot 1 0. 25 MMX
Celeron 1998 266/ 66
300/ 66
No Slot 1 0. 25 MMX
Celeron A
"Mendocino"
1998/
1999
300/ 66
333/ 66
366/ 66
400/ 66
128 KB
full
speed
( on-
die)
Slot 1 0. 25 MMX
Celeron
socket ed
1999 366/ 66
400/ 66
433/ 66
466/ 66
500/ 66
533/ 66
128 KB
full
speed
( on-
die)
Socket
370
0. 25/ 0. 18 MMX
Xeon 1998 400/ 100 512-
2048
full
speed
Slot 2 0. 25 MMX
Pent ium I I I 1999-
2000
500/ 100
533/ 133
600/ 100
600/ 133
650/ 100
700/ 100
733/ 133
. . .
1133/ 133
256
Half
speed
Slot 1/
PGA370
0. 25/ 0. 18 MMX SSE
Pent ium I I I
Xeon
( Tanner)
1999 550/ 100 512-
2048
full
speed
Slot 2 0. 25 MMX SSE
Coppermine 1999/
2000
733/ 133 256 KB
full
speed
( on-
die)
Slot 1 and
PGA370
0. 18 MMX SSE
Pent ium 4 2000 1400 256 KB
full
speed
( on-
die)
PGA423 0. 18/ 0. 13 SI MD2
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e10.htm (3 of 5)7/27/2004 4:08:47 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
"Nort hwood" 2001 1600 512
full
speed
( on-
die)
PGA478 0. 13 ?
"Tualat in" 2001 1500 512
full
speed
( on-
die)
Socket
370
0. 13 ?
Celeron 2 2001 900 -
1200
128
full
speed
( on-
die)
Socket
370
0. 13 ?
Three lines of Intel CPUs
[ t op]
I f you st udy t he scheme above, you see t he development from I nt el coming in t hree "lines".
Each line will be developed independent ly:
Market segment Processor line CPU speed Bus Speed/
Front Side Bus
speed
Number of CPUs
in syst em
The consumer
Socket ed Celeron
566- 1200 66/ 100 MHz 1
The professional
Pent ium I I I
Pent ium 4
733- 1400
MHz
100/ 133 MHz
or 400 MHz
1 or 2
The server
Xeon
Tanner
( Cascades)
600 - 1200
MHz
100/ 133 MHz
or 400 MHz
4
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e10.htm (4 of 5)7/27/2004 4:08:47 AM
An illustrated Guide to 6th generation CPUs
Read about drives in module 4a
Read about chip set s on t he mot herboard in module 2d
Read more about RAM in module 2e
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side.
Read module 5b about AGP and module 5c about Firewire.
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
Read module 7c about sound cards, and 7d on digit al sound and music.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e10.htm (5 of 5)7/27/2004 4:08:47 AM
A guide to Intel Itanium
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 3e.11
A guide to Intel Itanium.
The cont ent s:
q An int roduct ion t o I nt el' s I t anium/ Merced
q The specs
q The perspect ive for I A 64
q Next page
q Previous page
The Itanium/Merced
[ t op]
Merced was t he code name for a complet ely new CPU, which I nt el has developed t oget her
wit h HP, who has a vast experience in t he manufact ure of high end CPUs ( RI SC) . The chip is
due 2000 and will be launched under t he name I t anium.
The chippen will cost around $4000.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e11.htm (1 of 4)7/27/2004 4:08:53 AM
A guide to Intel Itanium
I t anium is a I A- 64 processor. This means t hat it is t arget ed for a complet ely different t ype of
programs t han t hose we are used t o.
Please support our
sponsor.
The specs
This is what I know of t he I t anium:
q A 64 bit CPU wit h I A- 64 archit ect ure.
q St art ing clock frequency: 800 MHz.
q 25. 4 million t ransist ors.
q "Massive hardware unit s": 128 int eger and 128 float ing point regist ers wit h mult iple
int eger and float ing point unit s all working in parallel.
q 0. 18 micron t echnology at 1. 8 Volt .
q Slot M cart ridge.
q 4 MB of Level 3 cache, holding 320 millions of t ransist ors.
q The L3 cache runs on a 12. 3 GB per second bus.
q VLI W design
The first chip set for I t anium should become 460GX, which allows four I t aniums on t he same
mot herboard and 64 GB of RAM.
Lat er it should be possible t o const ruct super comput ers holding 512 I t aniums ( in clust ers of
four) .
DDR RAM
The I t anium chip set s should be designed t o use DDR RAM and not Rambus
Problems with heating
Heat ing problems have been report ed. The I t anium is ext remely power hungry and runs very
hot . I t has been using up t o 130 wat t s in some t est s, and t his appears t o be a really serious
problem. The problems should arise from t he choice of VLI W design, which should not be
suit able for a general- purpose CPU as I t anium as some art icles indicat e. I am no expert on
t hese issues, and it sounds weird if I nt el should choose t hewrong archit ect ure.
The perspective for IA 64
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e11.htm (2 of 4)7/27/2004 4:08:53 AM
A guide to Intel Itanium
There is no doubt t hat t he I t anium is going t o be a heavy processor. But it will not end up on
many deskt ops. I t is t oo expensive, and t he design is 100% int ended t he server market .
There have been speculat ions about a lousy I A- 32 performance. All t he programs we use
( including Windows 2000) are of 32bit s design. This corresponds wit h t he P6 processors ( like
Pent ium I I I et c. ) which also are of 32 bit s archit ect ure.
Now I nt el comes wit h a 64 bit processor. I t has t o emulat e t he 32 bit inst ruct ions, t o execut e
32 bit programs like Windows . An emulat ion is cost ly, it t akes power from t he processor.
This is also t he case wit h t he I t anium; it has t o t ranslat e each of t he I A- 32 inst ruct ion. Some
magazines have claimed t hat t he I t anium will be t errible slow execut ing I A- 32 programs.
Some art icles even claim t hat I nt el want s t o dump t he I t anium and go for t he successor
' McKinley' .
Anyway, t he I t anium will require a new 64 bit operat ing syst em - could it be Windows 2064?
Linux 64 and NT 64 should be upcoming.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read about drives in module 4a
Read about chip set s on t he mot herboard in module 2d
Read more about RAM in module 2e
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side.
Read module 5b about AGP and module 5c about Firewire.
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
Read module 7c about sound cards, and 7d on digit al sound and music.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e11.htm (3 of 4)7/27/2004 4:08:53 AM
A guide to Intel Itanium
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e11.htm (4 of 4)7/27/2004 4:08:53 AM
An illustrated Guide VIA "Joshua" processor
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 3e.12
The VIA "Joshua" processor
The cont ent s:
q An int roduct ion
q Compared t o At hlon
q Next page
q Previous page
Joshua or Cyrix MIII [top]
Please support our
sponsor.
Cyrix was working on a brand new processor nucleus ( code name Jalapeo) before t he
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e12.htm (1 of 3)7/27/2004 4:08:55 AM
An illustrated Guide VIA "Joshua" processor
company was sold t o VI A. The processor was expect ed t o be market ed in t he MI I I in t he
middle of year 2000, but I do not know what happened t o t he design.
The feat ures were:
q Clock frequencies st art ing at 533 MHz ( PR533) .
q Built in 64 KB L1 cache, which works at full clock speed.
q Built in 256 KB L2 cache, which works at full clock speed.
q Built in 3DNow! 3D graphics accelerat ion.
q Socket 370 wit h 133 MHz bus for RAM.
From t he original MI I I design t he following rest s: Built in hardware coder for MPEG. Use of
Direct RDRAM ( Rambus RAM) . Powerful memory cont roller, which should permit t ransmission
at 3. 2 GB per second.
VI A3 lat er int roduced a Cyrix I I I processors based on I DT' s WinChip t echnology.
Compared to Athlon
Joshua was not a high end processor like AMDs K7 At hlon. However it is int ended t o be a
powerful low price CPU wit h int egrat ed sound and graphics cont roller. I f we compare t he
design wit h t he At hlon, we see a slight ly lower performance:
Joshua At hlon
Number of program inst ruct ions
which can be execut ed superscalar
( simult aneously)
2 3
Number of int ernal
operat ions per clock cycle
6 9
Pipelines t o float ing- point number
operat ions
( FP, MMX, 3DNow! )
2 3
q Next page
q Previous page
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e12.htm (2 of 3)7/27/2004 4:08:55 AM
An illustrated Guide VIA "Joshua" processor
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read about chip set s on t he mot herboard in module 2d
Read more about RAM in module 2e
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side.
Read module 5b about AGP and module 5c about Firewire.
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
Read module 7c about sound cards, and 7d on digit al sound and music.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e12.htm (3 of 3)7/27/2004 4:08:55 AM
An illustrated Guide AMD "Duron" processor
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 3e.13
The AMD "Duron" processor
The cont ent s:
q An int roduct ion
q Compared t o Celeron
q Next page
q Previous page
The Duron [top]
Please support our
sponsor.
I n t he summer 2000 AMD int roduced a new and very powerful low- end chip, formerly known
as codename "Spit fire".
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e13.htm (1 of 3)7/27/2004 4:08:56 AM
An illustrated Guide AMD "Duron" processor
The Duron is a At hlon in new design:
q 64 KB L2 cache on- die
q 128 KB L1 cache on- die
q Exclusive L2 cache design
q Socket A for in- expensive mot herboard design
q Clock frequencies from 600 t o 950 MHz
The Duron is t he first CPU t o have an int ernal L2 cache smaller t han t he L1 cache.
The exclusive cache design means t hat you never find t he same dat a in L1 as in L2 cache.
This increases t he efficiency of t he cache.
A Celeron killer
The Duron processor is designed for t he lower end of t he market . Here we find t he I nt el
Celeron processor an AMD' s own K6- 2, which is on it s way out of product ion.
Compared t o t he Celeron, Duron has a more powerful layout :
q Bigger cache
q Choice of PC100 or PC133 RAM
q A bet t er processor archit ect ure
The Morgan Kernel
Lat e in 2001 new 1200 MHz versions of t he Duron processor was int roduced. This processor
holds a new kernel of same generat ion as t he Palomino kernel in At hlonXP.
Here you find SSE support and ot her news similar t o t hose in t he At hlonXP.
The first t est s of t he new 1200 MHz Duron showed a very convincing performance almost
compareable t o a Pent ium 4 working at 1500 MHz!
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e13.htm (2 of 3)7/27/2004 4:08:56 AM
An illustrated Guide AMD "Duron" processor
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read about chip set s on t he mot herboard in module 2d
Read more about RAM in module 2e
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side.
Read module 5b about AGP and module 5c about Firewire.
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
Read module 7c about sound cards, and 7d on digit al sound and music.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e13.htm (3 of 3)7/27/2004 4:08:56 AM
An illustrated Guide Intel Pentium 4 processors
KarbosGuide.com. Module 3e.14
The Intel Pentium 4 processor
The cont ent s:
q An int roduct ion t il Pent ium 4
q SSE2
q The Execut ion Trace Cache
q "Nort hwood"
q Next page
q Previous
page
The Pentium 4 [top]
Please support our
sponsor.
I n November 2000 I nt el int roduced t he new and very powerful high- end chip Pent ium 4, formerly known as codename
"Willamet t e". I t was ( as expect ed) delayed.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e14.htm (1 of 7)7/27/2004 4:08:59 AM
An illustrated Guide Intel Pentium 4 processors
The Pent ium 4 is a complet ely new processor holding several new designs. Here is a highlight :
q 400 MHz Front Side Bus of 128 bit widt h
q Execut ion Trace Cache
q 20 KB L1 cache and 256 KB L2
q The ALU ( Arit hmet ical Logic Unit ) runs at t wice t he clock speed
q A new socket for simple mot herboard design
q Clock frequencies from 1500 MHz
q 20 st ages pipeline
q SSE2 and 128 bit MMX
q 42 millions of t ransist ors
q A new 423 pins socket design
q Dual Rambus memory channel wit h i850 chipset
q Only single processor mode available.
NetBURST
I nt el uses t he t erm Net BURST t o describe some feat ures in Pent ium 4:
q Advanced Dynamic Execut ion
q The Rapid Execut ion Engine
Advanced Dynamic Execut ion means t hat t he processor may execut e up t o 6 inst ruct ions simult anously.
Using Rapid Execut ion Engine cert ain inst ruct ions may be execut ed at t wice t he normal speed.
20 stages of pipeline
The pipeline is a execut ion unit which t akes in decoded micro- inst ruct ions. The X86 inst ruct ions are first decoded and
t hen sent t o t he pipeline. The longer t he pipeline is, t he quicker an inst ruct ion can be execut ed. Each st age execut es a
minor part of t he work and by spreading t he work on "more hands", t he efficiency is increased.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e14.htm (2 of 7)7/27/2004 4:08:59 AM
An illustrated Guide Intel Pentium 4 processors
I n Pent ium I I I t he pipeline was of 10 st ages. I n Pent ium 4 it has been increased t o 20 st ages.
The problem wit h t he long pipeline is, t hat it t akes t o longer t ime load t he inst ruct ion. And if t he inst ruct ion should not
have been loaded at all, t he error is most cost ly ( in t ime) t he longer t he pipeline becomes.
Wit h many inst ruct ions being execut ed simult anously you cannot avoid loading t he wrong inst ruct ion ( called
mispredict ion) from t ime t o t ime. And a short er pipeline is quicker t o recover t his error - fewer st ages has t o be cleared
and reloaded.
The analyt ic work prevent ing mispredict ions is done by t he Branch Predict ion Unit . This has, according t o I nt el, been
improved wit h a 30% bet t er performance compared t o t he Pent ium I I I .
St alling is anot her phenomen. Normally t he dat a t o be used is locat ed in t he cache. But if, for some reason, t he dat a is
missing in t he cache, it has t o be loaded from RAM. This t akes a lot of t ime, and t he longer t he pipeline is t he longer t ime
it t akes. .
The benefit from a pipeline increased from 10 st ages t o 20, is t o open up for new higher clock frequencies. When each
inst ruct ion is execut ed in more st ages, it can be done a lot quicker.
At lower frequencies t his gives no advant age. I n fact all report s indicat e t hat a 2000 MHz Pent ium 4 is slower t han a 1600
MHz At hlonXP. This is due t o t he difficult predict ion of t he order of t he inst ruct ions. Wrong predict ions gives wast ed clock
cycluses and a poorer performance.
However, a longer pipeline is required for processor speeds above 2 GHz. I nt el expect s t his new Net Burst core t o live
t hree t o five years. Hence we may expect Pent ium 4 successors t o reach 5 GHz or more.
SSE2
The St reaming SI MD ( Single I nst ruct ion Mult iply Dat a) Ext ensions known from Pent ium I I I has been improved. The dat a
widt h has doubled from 64 t o 128 bit .
Also 144 new inst ruct ions in SSE2 gives more parallel execut ion. Now four I nt ernet / Mult imedia- based operat ions can be
execut ed simult anously. The new design appears t o have been accept ed by soft ware developers, and it will probably be
very useful wit hin programs like Phot oshop.
The Execution Trace Cache
The Pent ium 4 is t he first CPU t o have a "code cache". All inst ruct ions are t ranslat ed inside t he CPU. This happens in all
modern x86 processors. They receive x86 inst ruct ions from t he soft ware. These inst ruct ions are "crunched" int o smaller
inst ruct ions which t hen are execut ed nat ively.
The new t hing in Pent ium 4 is t hat t hese t ranslat ed inst ruct ions are cached and reused. The logic of t his set up may look
like t his:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e14.htm (3 of 7)7/27/2004 4:08:59 AM
An illustrated Guide Intel Pentium 4 processors
This new cache, being a part of t he L1 cache holds 12 KB. Toget her wit h 8 KB of dat a cache, t he L1 cache consist s of 20
KB.
Heavy hardware
The first Pent ium 4s were giant chips wit h a die size of 247 mm
2
. The 42 millions of t ransist ors uses 60 wat t s and
requires heavy cooling. However, I nt el has done a lot t o provide sufficient cooling using new mat erials and design.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e14.htm (4 of 7)7/27/2004 4:08:59 AM
An illustrated Guide Intel Pentium 4 processors
The sockets
The first Pent ium 4s came wit h a 423 pin design. These CPUs could only use RDRAM, which only requires few pins
int erface.
Lat er came a 478 pin design wit h support for SDRAM.
The chipsets
The chip set i850 ( "Tehama") is using a dual RDRAM bus. This is also heat ing up t he MCH ( nort h bridge) chip, so
addit ional cooling is required.
The I nt el i845 chipset was int roduced August 2001. I t gives an int erface t o st andard 133 MHz SDRAM. This chipset is
found in many cheap Pent ium 4 comput ers.
Support for 266 MHz DDR RAM is found in t he VI A P4X266 and P4X266A chipset s t o be used wit h Pent ium 4 ( against
I nt els will; t hey don' t like VI A at all) .
SI S 645 is a chipset for Pent ium 4 wit h support for bot h 266 and 333 MHz DDR RAM.
The i845D chipset
December 2001 I nt el suddenly int roduced a new flavour of t he 845 chipset . I t is designed t o use wit h DDR- RAM!
There was no press releases about t his product . Searching I nt el' s web for info on t his chipset gave no result ( December
27t h 2001) :
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e14.htm (5 of 7)7/27/2004 4:08:59 AM
An illustrated Guide Intel Pentium 4 processors
However t he i845D chipset was found in comput ers from Dell and ot hers.
I nt el has been under a hard pressure from AMD, VI A, and t he Taiwanese mot herboard companiess in all 2001, and it was
fine t o see, t hat t hey finally had t o adapt t o common sense. DDR is t he RAM t ype t o use - almost nobody want s RAMBUS!
And I nt el' s dominat ing posit ion in t he market will promot e bet t er DDR RAM product s.
Northwood
On January 7t h 2002 I nt el int roduces a new 2. 2 GHz version of t he Pent ium 4.
This processor comes wit h t he new Nort hwood kernel:
q L2 cache doubled from 256 KB t o 512 KB
q 0. 13- micron process
New t echniques should also improve t he clock circle/ inst ruct ion execut ion rat io.
Due t o t he new design, t he performance of t his Pent ium 4 was increased wit h 30% compared t o t he 2 GHZ version -
where one should expect only 10%.
q Next page
q Previous page
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e14.htm (6 of 7)7/27/2004 4:08:59 AM
An illustrated Guide Intel Pentium 4 processors
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read about chip set s on t he mot herboard in module 2d
Read more about RAM in module 2e
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side.
Read module 5b about AGP and module 5c about Firewire.
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
Read module 7c about sound cards, and 7d on digit al sound and music.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. Click & Learn
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module3e14.htm (7 of 7)7/27/2004 4:08:59 AM
An illustrated Guide to disk drives - storage media.
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 4a.
Drives are storage media
q Next page
q Previous page
A drive is t he name for several t ypes of st orage media. There are also st orage media, which
are not drives ( RAM, Tape St reamers) , but on t hese pages, we will discuss t he drives.
Common t o drive medium is:
q A file syst em can be assigned t o t hem.
q They are recognized by t he operat ing syst em and t hey are assigned a drive let t er.
During st art up, drives are t ypically recognized by t he PC syst em soft ware ( ROM BI OS +
operat ing syst em) . Thus, t he PC knows which drives are inst alled. At t he end of t his
configurat ion, t he appropriat e drive let t er is ident ified wit h each drive. I f a drive is not "seen"
during st art up, it will not be accessible t o t he operat ing syst em. However, some ext ernal
drives cont ain special soft - ware, allowing t hem t o be connect ed during operat ion.
Some examples of drives
[ t op]
St orage media Drive let t er
Floppy disks A: B:
Hard disk C: D: E:
CDROM/ DVD F:
MO drive G:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module4a.htm (1 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:00 AM
An illustrated Guide to disk drives - storage media.
Net work drive M:
RAM disk O:
On t his and t he following pages, I will describe t he various drive t ypes, t heir hist ory and
t echnology. The last t wo drive t ypes in t he above t able will not be covered.
Storage principles
[ t op]
St orage: Magnet ic or opt ic. Dat a on any drive are digit ized. That means t hat t hey are
expressed as myriads of 0s and 1s. However, t he st orage of t hese bit s is done in any of t hree
principles:
The physical
drive principle
Disk t ypes
Magnet ic Floppy disks
Hard disk
Syquest disks
Zip drive
LS- 120 disks
Opt ic CD- ROM
DVD
Magnet o opt ic High end drives
Interface
[ t op]
I ndividual drives are connect ed t o ot her PC component s t hrough an int erface. The hard disk
int erface is eit her I DE or SCSI , which in modern PCs is connect ed t o t he PCI bus. Cert ain
drives can also be connect ed t hrough a parallel port or t he floppy cont roller:
I nt erface Drive
I DE and EI DE Hard disks ( current ly up t o 40 GB)
CD- ROM
SCSI Hard disks ( all sizes) and CD- ROM
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module4a.htm (2 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:00 AM
An illustrated Guide to disk drives - storage media.
I SA ( int ernal) Floppy drives
CDROM and super floppies connect ed t hrough parallel port
Let us st art evaluat ing t he drives from t he easy side:
The traditional floppy drive
[ t op]
We all know disket t es. Small flat disks, irrit at ingly slow and wit h t oo limit ed st orage capacit y.
Yet , we cannot live wit hout t hem. Very few PCs are wit hout a floppy drive.
Disket t es were developed as a low cost alt ernat ive t o hard disks. I n t he 60s and 70s, when
hard disk prices were exorbit ant , I t was unt hinkable t o use t hem in anyt hing but mainframe
and mini comput ers.
The first disket t es were int roduced in 1971. They were 8" diamet er plast ic disks wit h a
magnet ic coat ing, enclosed in a cardboard case. They had a capacit y of one megabyt e. The
disket t es are placed in a drive, which has read and writ e heads. Conversely t o hard disks, t he
heads act ually t ouch t he disk, like in a casset t e or video player. This wears t he media.
Lat er, in 1976, 5. 25" disket t es were int roduced. They had far less capacit y ( only 160 KB t o
begin wit h) . However, t hey were inexpensive and easy t o work wit h. For many years, t hey
were t he st andard in PCs. Like t he 8" disket t es, t he 5. 25" were soft and flexible. Therefore,
t hey were named floppy disks.
I n 1987 I BM' s revolut ionary PS/ 2 PCs were int roduced and wit h t hem t he 3" hard disket t es
we know t oday. These disket t es have a t hinner magnet ic coat ing, allowing more t racks on a
smaller surface. The t rack densit y is measured in TPI ( t racks per inch) . The TPI has been
increased from 48 t o 96 and now 135 in t he 3. 5" disket t es.
Here you see t he st andard PC disket t e configurat ions:
Disket t e size Name Tracks per side Number of sect ors
per t racks
Capacit y
5. 25" Single side SD8 40 8 40 X 8 X 512 byt es
= 160 KB
5. 25" Double side DD9 40 9 2 X 40 X 9 X 512
byt es = 360 KB
5. 25" Double side
High Densit y
DQ15 80 15 2 X 80 X 15 X 512
byt es = 1. 2 MB
3. 5" DD DQ9 80 9 2 X 80 X 9 X 512
byt es = 720 KB
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module4a.htm (3 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:00 AM
An illustrated Guide to disk drives - storage media.
3. 5" HD DQ18 80 18 2 X 80 X 18 X 512
byt es = 1. 44 MB
3. 5" XD ( I BM only) DG36 80 36 2 X 80 X 36 X 512
byt es = 2. 88 MB
Disket t e drives t urn at 300 RPM. That result s in an average search t ime ( revolut ion) of 100
ms.
The super floppy drives are described in module 4d.
The floppy controller
[ t op]
All disket t e drives are governed by a cont roller. The original PC cont roller was named NEC
PD765. Today, it is included in t he chip set , but funct ions like a 765. I t is a programmable
chip. I t can be programmed t o handle all t he various floppy drive t ypes: 5. 25" or 3. 5" drives,
DD or HD et c.
The cont roller has t o be programmed at each st art up. I t must be t old which drives t o
cont rol. This programming is performed by t he st art up programs in ROM ( read module 2a) .
So you don' t have t o ident ify available drive t ypes at each st art up, t hese drive paramet ers
are saved in CMOS RAM.
The floppy cont roller reads dat a from t he disket t e media in serial mode ( one bit at a t ime.
like from hard disks) . Dat a are delivered in parallel mode ( 16 bit s at a t ime) t o RAM via a
DMA channel. Thus, t he drives should be able t o operat e wit hout CPU supervision. However,
in realit y t his does not always work. Dat a t ransfer from a disket t e drive can delay and
somet imes freeze t he whole PC, so no ot her operat ions can be performed simult aneously.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Module 4b about hard disks.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module4a.htm (4 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:00 AM
An illustrated Guide to disk drives - storage media.
Read Module 4c about opt ical media ( CDROM and DVD) .
Read Module 4d about super disket t e and MO drives.
Read Module 4e about t ape st reamers ( which are not drives) .
Read Module 5c about SCSI .
Read Module 6a about file syst ems.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module4a.htm (5 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:00 AM
An illustrated Guide toZip, LS120, HiFD and MO-drives
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 4d.
Other drives
Here we look at ot her drive t ypes not previously ment ioned:
q Super floppies
q Zip
q LS 120
q Sony HI FD
q MO- drives
q Next page
q Previous page
Super floppies
Please support our
sponsor.
Wit h t he increasing performance in magnet ic hard disks you may expect a similar development
in t he product ion of t he floppy drives. However, it t ook many years t o get alt ernat ives t o t he
1. 44 MB floppy disk. Now we have t hree drives t o choose from, all using special 3 inch
media.
All of t hem perform very well and are st able and pret t y fast :
Drive Capacit y Comment s
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module4d.htm (1 of 8)7/27/2004 4:09:03 AM
An illustrated Guide toZip, LS120, HiFD and MO-drives
I omega Zip 100 MB 10 million sold unit s makes it t he most
compat ible drive
LS120 120 MB Read and writ e on 1. 44 MB floppies as well
Sony HiFD 200 MB Read and writ e on 1. 44 MB floppies as well
Use t he Zip, t he LS120 or t he HiFD in new PCs - t hey are cheap and good for backup. You also
find port able PC Card versions of t hese drives.
The Zip drive
[ t op]
The Zip drive uses a kind of disket t e, which can hold 100 MB. I n my opinion, t he Zip drive
works excellent ly. They are st able, inexpensive, and easy t o work wit h. The drives are not t he
fast est .
I and many ot hers have used Zip drives since t hey came on t he market . This provides us wit h
a common st andard t o move large files and t o make back- ups. For example, you can use t his
drive t o inst all Windows 95/ 98 on a comput er wit hout a CDROM and avoid having t o insert
numerous floppy disks.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module4d.htm (2 of 8)7/27/2004 4:09:03 AM
An illustrated Guide toZip, LS120, HiFD and MO-drives
The 100 MB Zip disk is borderline size. However, compared t o t he work I had t o do previously,
compressing files wit h PKZI P ont o mult iple disket t es, t hese are very pract ical.
Two types of interface
The Zip drive exist s in different versions:
q I nt ernal and ext ernal
q For SCSI and t o floppy/ parallel port
The SCSI model is by far t he fast est . That is really good. I f your SCSI cont roller is inst alled
wit h Windows 95/ 98, you j ust have t o inst all t he drive wit h t wo screws and t wo cables and you
are in business.
The parallel port version is good, because it can be connect ed t o any PC. I have a boot
disket t e, which includes a driver plus t he program GUEST. EXE. I connect t he drive t o a parallel
port , and boot wit h t he disket t e. Then it is ready t o run.
I have t he quit e fast SCSI version inst alled in my st at ionary PC. I use t he somewhat slower
parallel port version "in t he field. "
My lat est informat ion is t hat almost 20 million Zip drives have been sold ( Oct ober ' 98) and t hat
t hey sell 1 mill. a mont h. This speaks for it self and makes it a de fact o st andard.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module4d.htm (3 of 8)7/27/2004 4:09:03 AM
An illustrated Guide toZip, LS120, HiFD and MO-drives
The BI OS manufact urers AMI and Phoenix include t he floppy version of t he drive in t heir
programs as a boot device. That will eliminat e t he need for ot her drivers, and you will be able
t o boot from t he Zip disk.
LS120
[ t op]
Since 1993, we have heard about t he LS120 drive and now it is available. I t is a 120 MB
st andard designed by t he company I mat ion. LS120 is supposed t o replace t he regular floppy
drives. At t he same t ime, t hey read t he t radit ional 3" floppy disket t es ( DD and HD) much
fast er t han t he ordinary floppy drives.
The LS120 ought t o have become t he new floppy st andard, but it has come t oo lat e wit h all t he
inst alled Zip drives.
The drives, coming from I mat ion, use EI DE int erface, and t hey are comparable t o t he Zip
drives.
However t he SCSI - version of Zip is several t imes fast er t han t he LS120 drive.
HiFD
[ t op]
Sony has a super disket t e drive called HiFD ( High Floppy Disk) holding 200 MB on a 3" floppy
disk.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module4d.htm (4 of 8)7/27/2004 4:09:03 AM
An illustrated Guide toZip, LS120, HiFD and MO-drives
Like t he LS120, t he HiFD disk drives can read and writ e old 1. 44 MB floppy disks in addit ion t o
t he new high densit y disks. However, it should be a lot fast er t han t he LS120 drive.
q 3. 6 MB/ s maximum t ransfer rat e ( read)
q 1. 2 MB/ s maximum t ransfer rat e ( writ e)
q 3, 600 rpm rot at ional speed wit h dual discret e gap head ( flying head t ype) and a high speed
head act uat or wit h VCM ( voice coil mot or)
q Recording Capacit y: 200 MB ( format t ed) , 240 MB ( unformat t ed) .
q Disk Diamet er: 86 mm
q Track Densit y: 2822 TPI ( 111 t / mm)
The HiFD drive is t he best performing of t he t hree super floppies ment ioned in t his art icle.
However, compat ibilit y is oft en more import ant t han performance. I n t hat case Zip is t he
winner.
MO drives
[ t op]
Magnet ic Opt ic drives represent an excit ing t echnology. The medium is magnet ic, yet very
different from a hard disk. You can only writ e t o it , when it is heat ed t o about 300 degrees
Celsius ( The Curie point )
This heat ing is done wit h a laser beam. The advant age is t hat t he laser beam can heat a very
minut e area precisely. I n t his manner t he rat her unprecise magnet ic head, can writ e in
ext remely small spot s. Thus, writ ing is done wit h a laser guided magnet . The laser beam reads
t he media. I t can det ect t he polarizat ion of t he micro magnet s on t he media.
MO disks are fast , inexpensive, and ext remely st able. They are regarded as almost wear proof.
They can be writ t en over and over again forever, wit hout signs of wear. The dat a life span is
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module4d.htm (5 of 8)7/27/2004 4:09:03 AM
An illustrated Guide toZip, LS120, HiFD and MO-drives
said t o be at least 30 years. There are many MO drive variat ions, but all are very expensive.
The only mainst ream use of t he MO- t echnology is found in Sony' s recordable MiniDisc.
All ot her drives are very expensive ( > $2000) . For example:
Sony SMO-F551 MO Drive
q Cont inuous/ Composit es ( I SO/ I EC 15286) format
q Direct overwrit e magnet o opt ical drive wit h 5. 25- inch double sided disk
q 5. 2 GB ( 2, 048 Byt es/ sect or) , 4. 8 GB ( 1, 024 Byt es/ sect or) , 4. 1 GB ( 512 Byt es/ sect or)
q 3, 600 rpm/ 3, 300 rpm
Maxoptix T6-5200
HI GH CAPACI TY, MULTI - PURPOSE 5. 2 GB READ/ WRI TE OPTI CAL DI SC DRI VE
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module4d.htm (6 of 8)7/27/2004 4:09:03 AM
An illustrated Guide toZip, LS120, HiFD and MO-drives
Near-field recording
A new magnet o opt ical t echnology wit h flying heads and solid immersion opt ical lenses is called
near- field recording. I t promises 20 GB high densit y magnet ic st orage on 5. 25" plast ic media.
Check www. t erast or. com for furt her informat ion.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Module 4e about t ape st reamers ( which not are drives) .
Module 5c about t he SCSI int erface
Module 6a about t he file syst ems.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module4d.htm (7 of 8)7/27/2004 4:09:03 AM
An illustrated Guide toZip, LS120, HiFD and MO-drives
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module4d.htm (8 of 8)7/27/2004 4:09:03 AM
An illustrated Guide to tapestreamers..
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 4e.
About tape streamers
This subj ect is not very int erest ing, and t he t ext in t his
module reflect s t his point of view. Tape st reamers are used
for dat a backup. They come in different t ypes and price
ranges, but have t his in common:
q The t ape st reamer does not work like a drive. You cannot
ret rieve any part icular file. The dat a must be read using
special back- up soft ware.
q Dat a are st ored sequent ially on t he t ape. This means t hat
you can not , cont rary t o disks or CDROMs, read in random
fashion. You must wind t he t ape t o t he desired locat ion.
The advant age of Tape st reamers is t heir low cost . They
cont ain lot s of dat a on inexpensive t apes. They are available
in different t ypes:
q Next page
q Previous page
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module4e.htm (1 of 4)7/27/2004 4:09:05 AM
An illustrated Guide to tapestreamers..
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module4e.htm (2 of 4)7/27/2004 4:09:05 AM
An illustrated Guide to tapestreamers..
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Module 5a about adapt ers.
Read Module 5c about SCSI .
Read Module 6a about file syst ems.
Last revised: February 20, 1997.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module4e.htm (3 of 4)7/27/2004 4:09:05 AM
An illustrated Guide to tapestreamers..
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo . . Click & Learn visit ed
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module4e.htm (4 of 4)7/27/2004 4:09:05 AM
A Guide to Adapters and I/O units.
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 5a1a.
About the PC I/O system. Expansion cards. Adapters, etc.
The cont ent s:
q I nt ro t o I / O
q A model
q Next page
q Previous page
Intro to I/O [top]
Please support our
sponsor.
This page should preferably be read t oget her wit h module 2c, 2d, 5b and 5c. The first t wo describe t he I /
O buses and t he chip set s. Here we will look at t he ot her end of t he I / O buses, t he "exit . "
There are four I / O buses in t he modern PC archit ect ure and each of t hem has several funct ions. They
may lead t o int ernal and ext ernal port s or t hey lead t o ot her cont rolling buses. The four buses are:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5a1a.htm (1 of 4)7/27/2004 4:09:06 AM
A Guide to Adapters and I/O units.
q I SA, which is old, slow, and limit ed, compared t o t he alt ernat ives list ed below. We hope t hat it is
replaced by t he following int erfaces:
q PCI , which is t he newer high speed mult ifunct ion I / O bus.
q AGP, which only is used for graphics adapt er.
q USB, which is t he new low speed I / O bus t o replace I SA.
The I SA and t he PCI bus bot h end up having t o exit s:
q I nt ernal I / O port s ( LPT, KBD, COM1, COM2, EI DE et c. )
q Expansion slot s in t he syst em board, in which we can insert adapt ers.
I f you look at t his illust rat ion you will see t he overview of t his archit ect ure:
A model
I f we focus on t he right end of t he illust rat ion we approach t he I / O unit s. Here you get a closer look at
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5a1a.htm (2 of 4)7/27/2004 4:09:06 AM
A Guide to Adapters and I/O units.
t hat :
As you see, t here is room for a lot of unit s t o be connect ed t o t he PC.
The PCI bus is t he most loaded of all t he buses. I t is used for so many purposes t hat t he out put for t he
graphics adapt er has been isolat ed on it s own AGP- bus.
But st ill t he PCI bus is heavyly loaded, connect ing t he syst em bus t o t he net work cont roller and t he
various EI DE- and SCSI drives. Because of t he high bandwidt h of t he FireWire bus, overall t hroughput of
bot h int erfaces would be improved by separat ing t hese. We hope t o see a separat e FireWire int erface in
fut ure mot herboard archit ect ures.
q Next page
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5a1a.htm (3 of 4)7/27/2004 4:09:06 AM
A Guide to Adapters and I/O units.
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read: Module 5b about EI DE, Ult ra DMA and AGP.
Read Module 5c about SCSI , USB et c.
Read A lit t le about Windows 95/ 98.
Read Module 6c about t he relat ionship bet ween BI OS, OS and hardware
Read Module 7a about t he videosyst em
Read about video cards in Module 7b.
Read about digit al sound in Module 7c.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5a1a.htm (4 of 4)7/27/2004 4:09:06 AM
A Guide to Adapters and I/O units.
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 5a1b.
About I/O units, continued
The cont ent s:
q The I nt ernal I / O port s and unit s
q The serial port s
q Next page
q Previous page
The internal I/O ports [top]
Please support our
sponsor.
As ment ioned, t he USB is going t o become t he main bus for low speed devices. But so far we st ill use t he int ernal "face"
of t he I SA bus for a range of purposes. At any PC mot herboard you find t hese:
q The floppy cont roller
q The serial port s
q The parallel port ( s)
q The keyboard cont roller
They all occupy I RQs which is a cent ral part of I SA archit ect ure and a pain in t he a. . . Let us t ake a moment t o look at
t hese port s and cont rollers.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5a1b.htm (1 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:08 AM
A Guide to Adapters and I/O units.
The serial ports
Serial t ransmission means t o send dat a from one unit t o anot her one bit at t he t ime. The PC archit ect ure t radit ionally
holds t wo RS232 serial port s. The RS- 232 st andard describes an asynchronous int erface. This means t hat dat a are
t ransmit t ed only when t he receiving unit is ready t o receive t hem:
Synchronous/asynchronous
I n t he synchronous t ransmission you need t wo seperat e cables. Wit h every clock pulse ( i. e. t he posit ive going edge of t he
clock) one dat a bit is t ransferred.
I n t he asynchronous t ransmission clock and dat a are t ransferred wit h only one cable.
The clock has t o be reconst ruct ed from t he mixed signal in t he receiver: Aft er a "1" st art bit come 8 dat a bit s and t hen a
"0" st op bit ( or t wo "0" st op bit s) and so on.
The UART chip
The serial port s are cont rolled by an UART chip ( Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmit t er) like 16550 AFN. This chip
receives byt es from t he syst em bus and chops t hem up int o bit s. The most common package is called 8/ N/ 1 meaning t hat
we send 8 bit s, no parit y bit and finally one st op bit . This way one byt e occupies 9 bit s:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5a1b.htm (2 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:08 AM
A Guide to Adapters and I/O units.
The serial t ransfer is limit ed t o a speed of 115, 200 bit s per second. The cable can be up t o 200 met er long. The serial
port s can be used t o connect :
q The mouse and digit izers
q Modems
q I SDN adapt ers
q Print ers wit h serial int erface
q Digit al cameras
q . . . .
These unit s are connect ed t o t he serial port s using eit her DB9 or DB25 plugs.
I n modern PCs most of t hese devices connect t o t he USB bus inst ead. This gives a much higher t ransfer speed.
The parallel port
Parallel t ransmission means t hat dat a are conduct ed t hrough 8 separat e wires - t ransmit t ing a full byt e in one operat ion.
This way t he parallel t ransmission is speedier t han t he serial, but t he cabling is limit ed t o 5- 10 met ers. The cable is fat
and unhandy, holding up t o 25 wires and t he t ransmission is cont rolled according t o t he Cent ronics st andard.
Most print er manufact ures use a 36- pins Amphenol plug, where t he PC' s parallel port holds a 25- pinned connect or. Hence
t he special print er cable. To t he left you see t he 25 pin connect or, t o t he right t he 36- pin:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5a1b.htm (3 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:08 AM
A Guide to Adapters and I/O units.
Please support our
sponsor.
Then parallel port represent s t he most uncomplicat ed int erface of t he PC. I t is always used t o connect t he print er, but
wit h t he bi- direct ional parallel port ( EPP/ ECP) , ot her devices have found t heir way t o t his int erface. Today you find:
q ZI P drives
q Port able CD- ROM drives
q SCSI adapt ers
q Digit al cameras
q Scanners all using t he parallel port t o connect t o t he syst em bus.
The EPP/ECP ports
Today we operat e wit h Enhanced Parallel Port / Enhanced Capabilit y Port s. This met hod for bi- direct ional ( half duplex)
parallel communicat ion offers higher rat es of dat a t ransfer ( up t o 1 megabyt e per second) t han t he original parallel
signaling met hod. EPP is used for non- print er peripherals, where ECP is for print ers and scanners. You find t he set t ings for
t he print er port in t he set up program on t he mot herboard.
Bot h port t ypes are part s of t he I EEE1284 st andard, which also includes Cent ronics.
To get t he best result s all t he involved hardware and t he operat ing syst em has t o be EPP/ ECP compat ible. Windows
support s I EEE1284 in it s parallel plug- and- play feat ure. I t also support s ECP if you have a print er and a parallel port wit h
ECP. The print er cable has t o be complet e wit h all 25 wires connect ed.
The keyboard
Tradit ionally t he keyboard is connect ed using a DI N or PS/ 2 mini DI N plug. Soon we shall have USB keyboards but t he old
ones connect t o t he int ernal I SA bus occupying an I RQ.
The keyboard operat es wit h scan codes, which are generat ed each t ime a key is pressed and released. The scan codes are
t ranslat ed int o ASCI I values, which are t ranslat ed according t o t he code pages ( see module 1a and 1b) . Here you see a
simple illust rat ion of t he syst em:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5a1b.htm (4 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:08 AM
A Guide to Adapters and I/O units.
This syst em is quit e flexible because it allows for arbit rary remapping of t he keyboard codes. This is especially useful if
you find t he placement of t he Caps Lock and Cont rol keys awkward. I t ' s a simple mat t er t o remap t hem t o swap places.
Each key generat es a unique scan code. This happens complet ely independent of t he t ypeface t hat is print ed on t he
plast ic key.
At t he ot her end, t he code pages represent s a programmable int erpret at ion of t he key press; you can assign any t ype t o
any key as you want it . Languages like German and French use different keyboard layout s as well as many ot her
languages.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read: Module 5b about EI DE, Ult ra DMA and AGP.
Read Module 5c about SCSI , USB et c.
Read A lit t le about Windows 95/ 98.
Read Module 6c about t he relat ionship bet ween BI OS, OS and hardware
Read Module 7a about t he videosyst em
Read about video cards in Module 7b.
Read about digit al sound in Module 7c.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5a1b.htm (5 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:08 AM
A Guide to Adapters and I/O units.
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 5a2.
About adapters
The cont ent s:
q Adapt ers
q The modular PC design
q Next page
q Previous page
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5a2.htm (1 of 6)7/27/2004 4:09:10 AM
A Guide to Adapters and I/O units.
Adapters
I n a st at ionary PC, adapt ers are t ypically print ed circuit
boards called expansion boards or expansion cards. They
form a link bet ween t he cent ral PC unit and various
peripherals. This is t he so- called open archit ect ure.
[top]
Please support our
sponsor.
q Typically, adapt ers provide funct ions, which are separat ed from t he syst em board.
q Adapt ers provide expansion capabilit y t o t he PC.
There are PCs wit hout expansion slot s. I n t hat case all funct ions must be built int o t he
syst em board. You could easily include chips for graphics, et hernet , SCSI , and sound on t he
syst em board. This is not common in st at ionary PCs. Port able, lapt op PCs have nearly all
elect ronics on t he syst em board. This is called closed archit ect ure.
A t radit ional PC has a syst em board which cont ains all st andard funct ions ( except t he
graphics chip) . To t his syst em board you can add various expansion cards, which cont rol one
or more peripheral unit s:
The syst em board Expansion boards
St andard funct ions
incl. cont rol of
keyboard,
COM and LPT port s. and
four EI DE unit s.
Video card
Net work cont roller
Sound card
SCSI card
3D graphics cont roller ( for 3D games)
Ot her expansion board t ypes:
q I nt ernal modem ( in lieu of ext ernal modem)
q I SDN adapt ers
q Ext ra parallel port s
q Video edit ing boards
q Special graphics cards, which supplement t he usual ( 3D and MPEG)
q TV and radio receivers.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5a2.htm (2 of 6)7/27/2004 4:09:10 AM
A Guide to Adapters and I/O units.
The integrated hard disk controller [top]
Please support our
sponsor.
I n t he Pent ium based PC, t he hard disk is connect ed t o an EI DE cont roller, which is
int egrat ed on t he syst em board. Likewise, t he serial and parallel port s are connect ed direct ly
t o t he syst em board. This is new. On t he 386 PCs, you had t o inst all special cont roller cards
( I / O cards) t o handle t hese funct ions. They are included in t he modern chip set s on t he
syst em board. Ot her funct ions are not int egrat ed. That includes:
The video controller
[ t op]
You have t o inst all a video card t o make t he PC funct ion. I t would be illogical t o assemble a
PC wit hout a video card. You would not be able t o see what you are doing, since t he video
card governs dat a t ransmission t o t he monit or.
The advant age of t his design is, t hat t he user can choose bet ween numerous video cards in
various qualit ies. A discount st ore may offer a complet e Pent ium based PC ( wit hout print er)
and wit h t he cheapest video card for $669. - . I f t he buyer is qualit y orient ed, he would want
t o spend an addit ional $40 t o get a much bet t er video card.
The modular PC design
[ t op]
I n t his way, various expansion boards provide flexibilit y in assembling a cust omized PC. At
t he same t ime, various elect ronics manufact urers are specializing t heir product ion:
ASUS and Tyan are good at making syst em boards. Ot hers, like S3, Mat rox, and ATI
specialize in making graphics chips and expansion boards. Olicom make only net boards.
Adapt ec make only SCSI cont rollers and Creat ive Labs make SoundBlast er sound boards.
This variet y of manufact urers offers t he consumer wide choices. Your PC can be cust omized
and configured according t o your needs and wallet size.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5a2.htm (3 of 6)7/27/2004 4:09:10 AM
A Guide to Adapters and I/O units.
About the electronics
[ t op]
The adapt er is a print ed circuit board. They have an edge connect or, so t hey can be insert ed
in expansion slot s in t he syst em board. The expansion slot s connect t o t he I / O buses. Since
t he Pent ium syst em board has t wo I / O buses, it has t wo t ypes of expansion slot s:
q I SA slot s
q PCI slot s
Typically, on a regular Pent ium syst em board t here are t hree or four of each t ype. That gives
a t ot al of 7 expansion slot s. One expansion board can be inst alled in each of t hese. You
simply press t he edge connect or of t he expansion board int o t he expansion slot . Now it is
connect ed t o t he bus.
Here you see t wo PCI slot s open for video cards, net work cont rollers and ot hers:
Below, you see a net work adapt er. I t is an et hernet card wit h PCI int erface, so it fit s in a PCI
slot in t he Pent ium. This inexpensive board allows your comput er t o j oin a net work wit h ot her
net board equipped PCs. Please compare t he edge connect or at t he but t on of t he card wit h
t he socket s above. They fit t oget her!
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5a2.htm (4 of 6)7/27/2004 4:09:10 AM
A Guide to Adapters and I/O units.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read: Module 5b about EI DE, Ult ra DMA and AGP.
Read Module 5c about USB.
Read Module 6b wit h a lit t le about Windows 95/ 98.
Read Module 6c about t he relat ionship bet ween BI OS, OS and hardware
Read Module 7a about t he videosyst em
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5a2.htm (5 of 6)7/27/2004 4:09:10 AM
A Guide to Adapters and I/O units.
Read about video cards in Module 7b.
Read about digit al sound in Module 7c.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5a2.htm (6 of 6)7/27/2004 4:09:10 AM
A Guide to Adapters and I/O units.
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 5a3.
About IRQs, DMA, bus mastering etc.
The cont ent s:
q I RQ
q DMA
q Bus mast ering
q Next page
q Previous page
IRQs
When you inst all an expansion board in a slot , it get s
connect ed t o t he I / O bus. Now t he board can send and receive
dat a. But who regulat es t he t raffic? Who gives clearance t o t he
new cont roller t o send dat a? I t would appear t hat dat a t raffic
could soon be chaot ic.
[top]
Please support our
sponsor.
To cont rol dat a t raffic on t he I / O bus, t he concept of I RQ ( I nt errupt ReQuest ) was creat ed.
I nt errupt s are a fundament al principle in t he PC design. There are t wo t ypes of int errupt s: Soft ware
I nt errupt s are used t o call any number of BI OS rout ines. Hardware I nt errupt s are t he subj ect of t his
page.
Hardware Interrupts
[ t op]
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5a3.htm (1 of 9)7/27/2004 4:09:13 AM
A Guide to Adapters and I/O units.
The adapt er or unit on t he I / O bus uses t he int errupt t o signal request t o send or receive dat a. An
int errupt signal is like a door bell. The unit signals by applying a volt age t o one of t he wires in t he
bus - an I RQ. When t he CPU acknowledges t he signal, it knows t hat t he unit want s send or receive
dat a, or is finished.
The advant age of I RQs is t hat t he CPU can manage ot her t asks, while an adapt er "massages" it s
dat a. When t he adapt er has finished it s t ask, it will report t o t he CPU wit h a new I RQ.
As an example, let us see how keyboard dat a are handled. The keyboard send bit s, serially, t hrough
t he cable t o t he keyboard cont roller. The cont roller organizes t hem in groups of 8 ( one byt e) . Every
t ime it has a byt e, it sends an I RQ t o t he I / O bus. The I RQ cont roller asks t he CPU permission t o
use t he bus, t o send t he byt e t o wherever. The I RQ cont roller report s back t o t he keyboard
cont roller, giving clearance t o send t he next charact er ( byt e) :
IRQ wires
[ t op]
Physically, t he I RQ is a wire on t he bus. This wire connect s t o all expansion slot s. Therefore,
regardless of in which slot you inst all an adapt er, t he adapt er can communicat e wit h an I RQ.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5a3.htm (2 of 9)7/27/2004 4:09:13 AM
A Guide to Adapters and I/O units.
I n t he prist ine PC design ( t he original PC/ XT bus) you found 8 I RQ' s. The more recent PC is "born"
wit h 16 I RQs, but five of t hem are int ernal, and cannot be used wit h I / O cards, and one of t hem
connect s t he lower I RQ' s wit h t he higher ( I RQ2/ 9) .
We find 10 accessible I RQs on t he I / O buses. Each of t hose consist of a circuit board wire, which
goes t hrough t he ent ire bus. When you inst all an expansion card in a vacant slot , one of t he I RQs is
assigned t o it .
When a signal arrives on an I RQ channel, t hat is a message t o t he CPU. I t is t old t hat a unit want s
t o get on t he bus. Which unit is t o be ident ified t hrough t he I RQ number.
Next t he unit is admit t ed t o t he bus, t o send or receive dat a. When t he t ransact ion is complet ed,
anot her signal is t ransmit t ed t o t he CPU t o indicat e t hat t he bus is vacant .
The I RQs have different priorit ies, so t he CPU knows which I RQ have priorit y, if t wo signals are sent
simult aneously.
The I RQ syst em is guided by a cont roller chip, like I nt el 8259. I t can handle 8 I RQ signals and
couple t wo of t hem t oget her, via I RQ 2 or 9. All PCs wit h I SA bus include t wo 8259 chips.
MSD (Microsoft Diagnose System)
[ t op]
Let me show an image of t he MSD diagnost ic program, which you can run in Windows 95/ 98. I t
shows t he use of I RQs on a PC:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5a3.htm (3 of 9)7/27/2004 4:09:13 AM
A Guide to Adapters and I/O units.
MSD shows t he I RQs of t he PC, where t he program is run. There are a t ot al of 15 I RQ channels and
each I RQ is assigned t o a unit . However, it is not always possible t o ut ilize I RQ 9. I t funct ions like a
bridge bet ween t wo part s in t he I RQ syst em.
I n t he above illust rat ion, I RQ numbers 5, 10, 11, 12, and 15 appear vacant .
I RQ numbers 2 and 9 show t he linking bet ween t hose t wo I RQ cont rollers.
Some I RQs are reserved for various int ernal unit s, which must also be able t o disconnect t he CPU.
Those are I RQ numbers 0, 1, 2, 8, and 13, as you can see in t he illust rat ion above. They are not
available for ot her unit s. I n principle, t he remainder are available for expansion boards and EI DE
unit s.
I RQs are assigned during t he PC st art - up. An I SA expansion board is assigned a given I RQ during
st art - up. That I RQ is used every t ime t hat expansion board uses t he bus.
Shared IRQs
The modern I / O buses MCA, EI SA and PCI permit shared I RQs. Thus, t wo adapt ers can share one
I RQ. When t he I RQ is act ivat ed, t he drive programs for t he t wo adapt ers are checked, t o ident ify
which is on t he bus.
IRQ and conflicts on the ISA bus
[ t op]
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5a3.htm (4 of 9)7/27/2004 4:09:13 AM
A Guide to Adapters and I/O units.
The I RQ syst em can cause some problems on t he unint elligent I SA bus. When bus and adapt ers are
referred t o as unint elligent , it implies t hat t hey are unable t o organize t he I RQ dist ribut ion on t heir
own.
I n order t o funct ion, an I SA net work cont roller must be assigned an I RQ. The manufact urer could
preset it t o work wit h I RQ 9, 10, 11, or 12. One of t hese values, let us say I RQ 11, is preset as t he
default value. When t he cust omer inst alls t hat board, during st art - up it will t ry t o access t he bus as
I RQ 11. I f no ot her unit s are connect ed t o I RQ 11, it should work. I f I RQ 11 is occupied, we have a
problem. Those t wo unit s would get in a conflict . Oft en, t he PC will not st art at all and panic erupt s.
The solut ion is t o change t he I RQ of t he adapt er. The manufact urer has designed t he board t o work
on I RQ 9, 10, 11, or 12. Number 11 was t he default . I f t hat does not work, you must adj ust t o
anot her. This can be done wit h t he accompanying soft ware, or by reset t ing a lit t le j umper - an
elect ric cont act on t he board, which has t o be reset . The manual for t he board will include
inst ruct ions about how t o do t his.
These I RQ problems can be a t errible nuisance. I f bot h sound and net boards had t o be inst alled in
I SA slot s in t he same PC, somet imes I had t o give up.
I n Windows 95 ( Syst em, Comput er, Propert ies) you can find an excellent overview of t he I RQs.
Here it is from my Danish version:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5a3.htm (5 of 9)7/27/2004 4:09:13 AM
A Guide to Adapters and I/O units.
DMA
[ t op]
I RQs are only one of t he problems wit h I SA boards. The ot her one is DMA ( Direct Memory Access) .
That is a syst em which allows an adapt er t o t ransfer dat a t o RAM wit hout CPU involvement .
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5a3.htm (6 of 9)7/27/2004 4:09:13 AM
A Guide to Adapters and I/O units.
Normally, t he CPU cont rols all bus act ivit ies. Wit h DMA, t his "int elligence" is assigned t o a DMA
cont roller on t he syst em board. This special cont roller chip ( I nt el 8237) has clearance t o move dat a
t o and from RAM, via t he I / O bus, wit hout burdening t he CPU.
You can implement a number of DMA channels, which can be used by t he I SA boards. Each channel
has it s own number and one cont roller can be in charge of four channels. Each I SA unit can occupy
one of t hese channels, if so designed. Disket t e drives ut ilize DMA.
The DMA syst em can result in conflict s bet ween t wo unit s on t he bus, if t hey have request ed t he
same DMA channel. As an example, on I SA sound boards you have t o reset bot h I RQ and DMA
number.
I t is import ant t o enable DMA for your harddisk in Windows . See how in t his Windows t ip.
Bus mastering
[ t op]
There are no DMA channels on t he PCI bus. I nst ead bus mast ering is employed. I t is a similar
syst em, where special cont roller funct ions allow adapt ers t o cont rol t he bus. Thus, t hey can deliver
t heir dat a direct ly t o RAM, minimizing t he workload on t he CPU. I t does not need t o keep t rack of
t he t ransact ions, t he bus mast er t akes care of t hat .
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5a3.htm (7 of 9)7/27/2004 4:09:13 AM
A Guide to Adapters and I/O units.
This allows t he PC t o mult it ask, handle more t han one t ask at a t ime. The hard disk can pour
st reams of dat a t o RAM, while t he CPU handles some ot her t ask. The bus mast ering syst em works
fairly well wit h EI DE hard disks. However in t his part icular area, t he SCSI cont roller is far more
advanced. EI DE bus mast ering is rat her new and we will see furt her development s in t his area.
Bus mast ering version Chip set Year
DMA mode 2 82430FX 1995
Ult ra DMA 82430TX 1997
The lat est version Ult ra DMA/ 66 is described in module 5b.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read: Module 5b about EI DE, Ult ra DMA and AGP.
Read Module 5c about SCSI , USB et c.
Read Module 6b wit h a lit t le about Windows 95/ 98.
Read Module 6c about t he relat ionship bet ween BI OS, OS and hardware
Read Module 7a about t he videosyst em
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5a3.htm (8 of 9)7/27/2004 4:09:13 AM
A Guide to Adapters and I/O units.
Read about video cards in Module 7b.
Read about digit al sound in Module 7c.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5a3.htm (9 of 9)7/27/2004 4:09:13 AM
A Guide to Adapters and I/O units.
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 5a4.
About I/O port, Plug and Play, and PC Cards.
The cont ent s:
q I / O addressing
q Plug and Play ( PnP)
q The physical connect or on adapt ers
q Next page
q Previous page
I/O addresses
Finally, we need t o ment ion how t he CPU finds all t hese unit s - adapt ers, port s.
et c. They all have an address - an I / O port number.
Each unit can be reached t hrough one of many I / O port s. Each port is a byt e
port . That means t hat 8 bit s ( one byt e) can be t ransmit t ed simult aneously -
parallel mode.
[top]
Please support our
sponsor.
I f t he unit is on t he I SA bus, it handles 16 bit s at a t ime ( words) . Then you link t wo consecut ive port s t oget her, t o
make a 16 bit channel. I f we t alk about a 32 bit PCI unit , we link four byt e port s t oget her t o get 32 bit s widt h
( called dword) .
The PC has a built in list ing of all I / O unit s, each of which has t heir own "zip code" - a port address. Since t he PC is
basically a 16 bit comput er, t here are 2 at t he 16t h power possible addresses ( 65, 536) - from 0000 t o FFFFH. They
are described in t he hexadecimal number syst em as 5 digit numbers. Hexadecimal is a 16 digit number syst em.
Digit s go from 0 t o 9 and cont inue wit h 6 let t ers A - F. Let me show you some examples of I / O addresses:
Unit I / O port s
CMOS RAM 0070H
Keyboard 0060H . . . 0063H
Serial port 1 ( COM 1) 03F8H . . . 03FFH
Parallel port 1 ( LPT1) 0378H . . . 037FH
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5a4.htm (1 of 3)7/27/2004 4:09:14 AM
A Guide to Adapters and I/O units.
Fort unat ely, you do not have t o adj ust port addresses t oo oft en. Some adapt ers give room t o adj ust t o user opt ion I /
O addresses, but you have t o have bad luck t o encount er any conflict in t his area.
Plug and Play
[ t op]
Plug and play ( PnP) is an indust ry st andard for expansion boards. I f t he board conforms t o t he PnP st andard, t he
inst allat ion is very simple. The board configures it self aut omat ically. These are t he minimum requirement s:
q The PC syst em board must be PnP compat ible.
q The operat ing syst em must be capable of ut ilizing PnP, as Windows is.
q The adapt er must be able t o inform t he I / O bus which I / O addresses and I RQs it can communicat e wit h.
q The adapt er must be able t o adj ust t o use t he I / O address and t he I RQ, which t he I / O bus communicat es t o t he
adapt er.
The physical connector
[ t op]
The different I / O cards each fit wit h a part icular I / O bus. The different buses each have t heir own syst em board slot
configurat ion. That is a socket in t he syst em board, in which you press in t he expansion board. Here you see t hree
different edge connect ors fit t ing int o each t heir own t ype of socket . The I SA bus has a t ot al of 98 prongs ( 31+ 18 on
each side) .
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5a4.htm (2 of 3)7/27/2004 4:09:14 AM
A Guide to Adapters and I/O units.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Module 5b about EI DE, Ult ra DMA and AGP.
Read Module 5c about SCSI , USB et c.
Read Module 6b wit h a lit t le about Windows 95/ 98.
Read Module 6c about t he relat ionship bet ween BI OS, OS and hardware
Read Module 7a about t he videosyst em
Read about video cards in Module 7b.
Read about digit al sound in Module 7c.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5a4.htm (3 of 3)7/27/2004 4:09:14 AM
A Guide to PC Cards
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 5a5
About PC Cards.
The cont ent s:
q PC Card
q PC Card I I
q Next page
q Previous
page
The PC Card
I n port able PCs, t he adapt er is usually a PC Card. This is
a lit t le t iny box which fit s int o a special slot . The PC Card
used t o be called a PCMCI A card, but t his obviously was
a lit t le difficult t o remember.
The first generat ion of PC Cards were t echnically
connect ed t o t he I SA bus. The newer ones are PC
Card32 working wit h t he CardBus. They are int ernally
connect ed t o t he 32 bit PCI bus.
Here you see a net work cont roller, as a PC Card. I t is about t he size of a credit card, but
slight ly t hicker:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5a5.htm (1 of 4)7/27/2004 4:09:16 AM
A Guide to PC Cards
The PC Card is placed in a special socket , where it can be insert ed or removed, while t he PC
is operat ing. Act ually, each socket act s like an I / O unit , regardless of whet her t here is a PC
Card in it or not . When t he card is insert ed, it is aut omat ically configured wit h I / O address,
I RQ, et c. Windows 98 provides by far t he best support for PC Cards.
I use t wo PC Cards myself: The net work cont roller you see above connect s my lapt op t o my
net work. And my digit al camera ( Canon Powershot 600) uses a PC Card wit h 4 MB Flash
RAM. Having t aken t he phot os I j ust move t he PC Card from t he camera t o t he lapt op. Here it
inst ant ly becomes a D- drive and I use Explorer t o move t he phot os t o a folder on t he server.
The operat ion t akes less t han a minut e.
Please support our
sponsor.
PC Card II
The lat est st andard ( PC Card I I ) makes it possible t o use harddisks wit hin t he PC card. The
I BM Microdrive is very handy when using digit al cameras. All modern cameras of good qualit y
can hold such a harddisk of 340 MB. This gives room for more t han 300 pict ures in a very
high qualit y.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5a5.htm (2 of 4)7/27/2004 4:09:16 AM
A Guide to PC Cards
The PC card, holding Compact Flash Card, SSFDC ( Smart Media) or a MicroDrive, can be read
by a USB- connect ed reader like t hese:
I f you use PC Card, you should invest in a reader for USB. I t is very handy and speedy.
CardX
The new high speed serial port s USB and FireWire will also become available for port able PC
users. CardX is a new PC Card int erface built on FireWire and allowing t ransfers of up t o 400
megabit per second.
Two function adapters
[ t op]
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5a5.htm (3 of 4)7/27/2004 4:09:16 AM
A Guide to PC Cards
I nt egrat ed adapt ers wit h more t han one funct ion are space savers. Especially, t he ASUS
company has int roduced dual funct ion boards t o st at ionary PCs, since t hey ut ilize bot h t he
I SA and PCI bus t o share a slot :
q Graphics + sound
q SCSI + sound There are also t wo funct ion PC Cards for port able PCs:
q Et hernet net work cont roller + modem
q Token Ring net work cont roller + modem
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Module 5b about EI DE, Ult ra DMA and AGP.
Read Module 5c about SCSI , USB et c.
Read Module 6b wit h a lit t le about Windows 95/ 98.
Read Module 6c about t he relat ionship bet ween BI OS, OS and hardware
Read Module 7a about t he videosyst em
Read about video cards in Module 7b.
Read about digit al sound in Module 7c.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5a5.htm (4 of 4)7/27/2004 4:09:16 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the EIDE, Ultra DMA and AGP interfaces. For teachers, students and self-study.
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 5b1.
About the interfaces EIDE, Ultra DMA and AGP
The cont ent s:
q What is EI DE?
q Four unit s cont rolled by t he mot herboard
On t he following pages:
q The EI DE cable
q The Promise Fast Track EI DE cont roller
q Transfer speeds and prot ocols
q What does Ult ra DMA offer?
q Looking at a good harddisk
q ATA/ 66
q Configuring your EI DE hard disk
q What is AGP?
q Next page
q Previous page
What is EIDE? [top]
Please support our
sponsor.
EI DE is t he current st andard for inexpensive, high performance hard disks used in PCs.
EI DE st ands for Enhanced I DE and it is regist ered name own by harddisk manufact ure
West ern Digit al. They also own t he name "I DE".
Ot her companies like Seagat e, I BM, Quant um and Maxt or Uses t he t erm ATA, which st ands
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b1.htm (1 of 4)7/27/2004 4:09:18 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the EIDE, Ultra DMA and AGP interfaces. For teachers, students and self-study.
for Advanced Technology At t achment . But it is all t he same. However t here are many
differant prot ocols behind t he t erms.
You can t hink of EI DE as a bus - which is a host cont roller - which cont rols it , and you can
connect up t o four unit s. Here you see t he cont roller and it s t wo channels:
All Pent ium syst em boards since 1995 have t his EI DE cont roller built int o t he chip set . That
allows t he hard disk and ot her EI DE unit s t o be connect ed direct ly t o t he syst em board.
Improvements
The EI DE st andard is a great improvement over t he old I DE. Here are some examples:
q The hard disk can exceed t he 528 MB I DE limit . Current ly t he largest EI DE disks are of 37
GB and t his number keeps increasing. I BM has promised harddisks of more t han 100 GB
before year 2001.
q The hard disk' s int erface is moved from t he I SA bus t o t he high speed PCI bus.
q Four unit s can be connect ed t o t he syst em board, which has t wo EI DE channels. Each
channel can be connect ed t o a mast er and a slave unit .
The most import ant feat ure is t he int erface direct ly on t he PCI bus. This has given EI DE
t ransfer speeds and disk capacit ies, which far exceed older cont roller principles. Concurrent ly,
t here is a cont inual development of t he prot ocols, which are needed for t he connect ion
bet ween t he unit s and t he EI DE bus.
Four units controlled by the motherboard
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b1.htm (2 of 4)7/27/2004 4:09:18 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the EIDE, Ultra DMA and AGP interfaces. For teachers, students and self-study.
The EI DE int erface is not designed for hard disks only. There are four channels, which can be
connect ed t o four independent unit s:
q Hard disks
q CD- ROM drives
q CR- RW drives
q DVD drives
q LS 120, Zip or HiFD drive
q Tape st reamers
EI DE is t hus designed as an inexpensive all- round int erface, which can be connect ed t o all
kinds of st orage media.
Auto detect
The BI OS on t he syst em board has a neat aut o det ect feat ure, which oft en allows EI DE unit s
t o be connect ed direct ly and work immediat ely. The PC st art up program aut omat ically finds
t he necessary informat ion about t he drive via t he aut o det ect funct ion.
Somet imes you have t o assist t he hard disk inst allat ion by act ivat ing t he aut o det ect in t he
CMOS Set up program, but oft en it runs by it self. You definit ely do not have t o key in
informat ion about cylinders, et c. , as you had t o wit h earlier I DE unit s.
q Next page
q Previous page
To learn more
[ t op]
Read more t he boot process and syst em bus in Module 2b
Read about file syst ems in module 6a
Read about I / O buses in module 2c
Read about t he mot herboard chip set in module 2d
Read about RAM in module 2e
Read Module 5c about SCSI , USB et c.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b1.htm (3 of 4)7/27/2004 4:09:18 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the EIDE, Ultra DMA and AGP interfaces. For teachers, students and self-study.
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
Click for Module 7d about digit al music, MP3s
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b1.htm (4 of 4)7/27/2004 4:09:18 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the EIDE, Ultra DMA and AGP interfaces. For teachers, students and self-study.
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 5b2a.
About the EIDE interface - continued
The cont ent s:
q The EI DE cable
q Problems wit h assigning t wo EI DE harddisks
q The Promise Fast Track EI DE cont roller
q Next page
q Previous page
The EIDE cable
Here you see a t ypical EI DE cable:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b2a.htm (1 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:21 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the EIDE, Ultra DMA and AGP interfaces. For teachers, students and self-study.
These cables are diffficult t o handle, if you want t o make a nice PC. The are so big, t hat t hey dist urb t he
air circulat ion and hence t he cooling inside t he PC cabinet .
Since each channel can handle t wo unit s, t here are t wo of t hese connect ors on t he syst em board. Not e t he
blind hole in t op cent er. Not e also t he st ripe ( it is red) in t he far right edge of t he cable. I t t ells you t hat
lead number one is on t his edge. Bot h of t hese feat ures help prevent incorrect inst allat ion of t he cable.
Using primary and secondary channels
The syst em board has socket s for t wo EI DE cables. Each EI DE cable ( primary and secondary) has socket s
for t wo unit s ( mast er and slave) .
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b2a.htm (2 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:21 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the EIDE, Ultra DMA and AGP interfaces. For teachers, students and self-study.
Settting up four units
I f we have t o use all four connect ions, it causes some problems. The set up may look like t his:
Primary, mast er Hard disk 1
Primary, slave Hard disk 2 or CD- ROM
Secondary, mast er CD- RW DVD drive
Secondary, slave ZI P/ LS120 disket t e drive
Typically, a PC has t wo EI DE unit s connect ed: t he hard disk and t he CDROM drive. However, as you can
see, ot her unit s can be connect ed as well. The hard disk must must be on t he primary EI DE channel. On
some syst em boards, t his has t he great est t ransfer capacit y.
Please support our
sponsor.
Using two EIDE harddisk
I n t he t able above I indicat e t hat it is not good t o assign t wo harddisks t o t he primary channel. They
should be assigned t o t he mast ers of t he primary and t he secondary channel.
This is due t o t he fact , t hat t he t wo main cont rollers ( primary and secondary) are capable of mult it asking.
The t wo channels can process dat a simult aneously and independent ly, at t he same t ime.
The t wo sub- channels ( slave and mast er) do not mult it ask; here only one operat ion is processed at t he
t ime, be it on t he mast er or on t he slave channel.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b2a.htm (3 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:21 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the EIDE, Ultra DMA and AGP interfaces. For teachers, students and self-study.
So for best performance, t he t wo harddisk have t o be assigned one at t he primary EI DE channel and t he
ot her at t he secondary EI DE channel. This leaves us wit h t he problem of t he CD- ROM drives, which also
have t o be placed on EI DE channels.
My conclusion is t hat if you have t o use t wo EI DE harddisks ( and many of us do) , t he mot herboard should
be enhanced wit h furt her EI DE channels. Please cont inue t he reading. . .
q Next page
q Previous page
To learn more
[ t op]
Read more t he boot process and syst em bus in Module 2b
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b2a.htm (4 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:21 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the EIDE, Ultra DMA and AGP interfaces. For teachers, students and self-study.
Read about file syst ems in module 6a
Read about I / O buses in module 2c
Read about t he mot herboard chip set in module 2d
Read about RAM in module 2e
Read Module 5c about SCSI , USB et c.
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b2a.htm (5 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:21 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the EIDE, Ultra DMA and AGP interfaces. For teachers, students and self-study.
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 5b2b.
RAID/EIDE controllers
The cont ent s:
q The Promise Fast Track EI DE cont roller
q Adapt ec UDMA RAI D
q Highpoint UDMA RAI D onboard
q Next page
q Previous page
The Promise FastTrack EIDE controller
You may expand your syst em wit h a lit t le PCI - based EI DE- cont roller from Promise.
This cont roller can be connect ed t o t wo or four EI DE hard disks. And it works side by side wit h t he exist ing
EI DE- cont roller on t he mot herboard! I have t est ed it , and it works fine:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b2b.htm (1 of 7)7/27/2004 4:09:24 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the EIDE, Ultra DMA and AGP interfaces. For teachers, students and self-study.
The card is very powerfull. You can use it in mult iple set ups:
q Connect ing four EI DE hard disk t o your PC; t he onboard EI DE- cont roller can be used for CD- ROMs, ZI P or
ot her ATA- based drives.
q I ncreased performance ( 2X or 4X) by using t he RAI D 0 funct ionalit y.
q I ncreased capacit y since t wo or four disks can be assigned t o one big virt ual drive.
q I ncreased securit y using RAI D 1 mirroring.
The most impressive t hing is t hat t he cont roller holds it s own BI OS. I t works complet e independent of t he
host ing PC.
Please support our
sponsor.
Striping
The Fast Trak cont roller can double or quadruple t he t ransfer speed if you want it .
Using RAI D 0 st riping, t he dat a are st riped over more t han one drive. You use t wo or four ident ical drives,
which all are unified int o one big volume.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b2b.htm (2 of 7)7/27/2004 4:09:24 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the EIDE, Ultra DMA and AGP interfaces. For teachers, students and self-study.
When you writ e dat a t o t he drive, it is simult aneously writ t en t o all t wo or four drives in t he array. This is t he
principle of st riping: int erleaving during t he read/ writ e process.
The st ripe size ( blocks t o be st riped) can be set from 1 KB t o 1024 KB. The default value for business
applicat ion use is st ripe size 8 KB. For working wit h bigger files ( for inst ance sound and video edit ing) t he
recommendat ion is 64KB.
Mirroring
Using RAI D 1 mirroring, t he dat a are duplicat ed t o several drives. This gives an increased securit y. The syst em
is fault t olerant ; if one drive is damaged, t he dat a can be read from anot her.
My own use
I was very glad t o use t he Fast Track PCI RAI D cont roller. I used it j ust t o improve t he capacit y of t he EI DE
syst em.
The PC looked like t his regarding EI DE unit s:
q Mot herboard primary EI DE, mast er: A 28 GB Seagat e hard disk, 7200 RPM.
q Mot herboard primary EI DE, slave: Not hing.
q Mot herboard secondary EI DE, mast er: A 40X CD- ROM drive.
q Mot herboard secondary EI DE, slave: A HP 8100plus CD- RW drive.
q Fast Track primary EI DE, mast er: A 30 GB Maxt or hard disk.
The t wo hard disks ( each format t ed int o j ust one big part it ion) cooperat ed very well. I could copy bet ween
t hem at 10 MB/ sec.
Wit h t he syst em described, I had room for expansion, since I could add anot her disk t o t he Fast Track
secondary mast er. I could also have opt ed for st iping, if I ' d want ed t o - it only requires t wo ident ical disks. I
have t ried it , and it works fine.
The Fast Track adapt er can st ripe disks for bet t er performance, but as described here, it is also great j ust for
adding versat ilit y t o your PC syst em!
Adaptec UDMA RAID
The name Adapt ec has for many years been synonymous wit h SCSI and SCSI - based RAI D.
The AAA- UDMA RAI D cont roller support s up t o 4 ATA/ 66 hard disks in RAI D 0, 1, 0/ 1 and RAI D 5 ( fault
t olerance) arrays. The RAI D 5 array is int erest ing for use in servers, giving t he opt ion of hot - plugging a
subst it ut e disk in case of diskfault s. All dat a is reconst ruct ed on t he fly.
This is t he first t ime t hat t his is possible using EI DE disks, and it shows how t he qualit y of t he EI DE/ ATA
st andards is improving nowadays.
The maximum out put of t he RAI D cont rollers is 66 MB per second due t o t he limit at ion of t he ATA/ 66 prot ocol.
Wit h ATA/ 100 and lat er Serial ATA we shall see much more powerful syst ems!
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b2b.htm (3 of 7)7/27/2004 4:09:24 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the EIDE, Ultra DMA and AGP interfaces. For teachers, students and self-study.
RAID controllers on the motherboard
I n 2001 we saw several mot herboards including ATA/ 100- based RAI D cont rollers onboard.
I bought an Epox 8KTA3+ board for my 900 MHz AMD processor. Overall, it is a very nice board, but t he best
feat ure is t he ATA/ 100- based RAI D cont roller which is int egrat ed.
The RAI D cont rolling logic comes from HighPoint ; t heir HPT370 chip is locat ed on t he mot herboard:
Here it cooperat es wit h t he t radit ional "sout h bridge" from VI A:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b2b.htm (4 of 7)7/27/2004 4:09:24 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the EIDE, Ultra DMA and AGP interfaces. For teachers, students and self-study.
Toget her t hey cont rol four EI DE- channels all ATA66/ 100 compat ible:
This way you are free t o assign up t o 8 I DE unit s t o t he mot herboard. Most people would probably have t wo
hard disks and t wo CD drives. Wit h t his board t hey can be mount ed as mast er on each channel. That is really
good!
Wit h Windows , you always get RAI D cont rollers recognized as SCSI cont rollers. This is also t he case here.
I nst alling Windows 2000 or XP using t he HighPoint cont roller, you have t o use t he driver disket t e included wit h
t he board. I t ' s a lit t le bit weird why t hese Windows NT- based OS' s cannot det ect a RAI D cont roller and inst all a
driver aut omat ically.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b2b.htm (5 of 7)7/27/2004 4:09:24 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the EIDE, Ultra DMA and AGP interfaces. For teachers, students and self-study.
However t he driver inst allat ion works perfect ly. You see t he cont roller under SCSI / RAI D cont rollers:
q Next page
q Previous page
To learn more
[ t op]
Read more t he boot process and syst em bus in Module 2b
Read about file syst ems in module 6a
Read about I / O buses in module 2c
Read about t he mot herboard chip set in module 2d
Read about RAM in module 2e
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b2b.htm (6 of 7)7/27/2004 4:09:24 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the EIDE, Ultra DMA and AGP interfaces. For teachers, students and self-study.
Read Module 5c about SCSI , USB et c.
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b2b.htm (7 of 7)7/27/2004 4:09:24 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the EIDE, Ultra DMA and AGP interfaces. For teachers, students and self-study.
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 5b3.
About the EIDE interface - continued
The cont ent s:
q Transfer speeds and prot ocols
q I mproving PI O prot ocol
q The max. disk size
q Next page
q Previous page
Transfer speeds and protocols [top]
Please support our
sponsor.
EI DE exist s wit h different prot ocols, like PI O ( Programmed I npu/ Out put ) 3, PI O 4, UDMA/ 33,
and UDMA/ 66. They are backwards compat ible, t herefore always choose t he lat est .
The prot ocol is significant t o t he t ransfer speed, since it set s t he st andard for t he drives
ext ernal speed. The prot ocol cont rols t he int erface bet ween drive and mot herboard.
An overview
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b3.htm (1 of 4)7/27/2004 4:09:26 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the EIDE, Ultra DMA and AGP interfaces. For teachers, students and self-study.
Each EI DE unit communicat e according t o a specific prot ocol. Here you see t he four best
known:
Prot ocol for
EI DE int erface
Year Maximum t heoret ical t ransfer
PI O 3 or
Mult i- word DMA Mode 1
1993 13. 3 MB/ second
PI O 4 or
Mult i- word DMA Mode 2
1994 16. 6 MB/ second
Ult ra DMA ( ATA/ 33) 1997 33. 0 MB/ second
Ult ra DMA ( ATA/ 66) 1999 66. 0 MB/ second
Ult ra DMA ( ATA/ 100) 2000 100. 0 MB/ second
Improving PIO
Tradit ionally PI O dat a t ransfers rely heavily on t he CPU t o do all t he work, processing each
and every lit t le t ask of reading or writ ing dat a.
Wit h t he ATA- 2 specificat ion, including DMA- support solved t his problem. Hence dat a are
t ransport ed bet ween RAM and hard disk wit hout t he supervision of t he CPU.
ATA- 2 was t o be known as EI DE.
The max. disk size
[ t op]
Anot her problem solved by t his new prot ocol was t he 2 GB limit of disk size. LBA ( Logical
Block Addressing) was t he new set up. LBA is an addressing and t ranslat ing scheme t hat
replaces t he CHS syst em ( Cylinder Head Sect or) . This new scheme enables t he BI OS t o
address up t o 8. 4 GB hard disk using 24 bit long addresses.
The 8. 4 GB limit was lat er broken by t he new FAT32 file syst em.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b3.htm (2 of 4)7/27/2004 4:09:26 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the EIDE, Ultra DMA and AGP interfaces. For teachers, students and self-study.
Only one protocol per channel?
The t wo main channels ( primary and secondary EI DE) can work wit h each one prot ocol. As an
example, t he primary channel may host UDMA/ 66 drives, while t he secondary channel host s
PI O4 based CD- ROMs.
However, somet imes t he slave/ mast er channels only have room for one prot ocol. Be aware of
t his pot ent ial problem. I s t here only room for one common prot ocol? I n t hat case t he
"winner" will invariably be t he slowest of t he ones connect ed.
Harddisks always on the best protocol
[ t op]
I t is import ant t hat you connect your hard disk t o an EI DE channel, which runs ATA/ 100 ( or
bet t er) .
Ult ra DMA requires t he inst allat ion of drivers. Windows 95 before OSR2, due t o age, did not
recognize Ult ra DMA, while Windows 98 nat urally does.
The mot herboard vendor ASUS ( as well as ot hers) provides an excellent , simple pat ch
program on CD. You run it j ust once. Then t he drivers are st ored in t he right locat ions. Aft er
one or t wo re- boot s everyt hing works.
Big disks
Anot her problem can arise if you connect t wo hard disks t o t he syst em board. Despit e t he
suppliers assurance t hat "it is very simple, " it does not always work. Therefore, it is
import ant t o st art wit h one sufficient ly large hard disk.
Please also read t he art icle Problems wit h assigning t wo EI DE harddisks
q Next page
q Previous page
To learn more
[ t op]
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b3.htm (3 of 4)7/27/2004 4:09:26 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the EIDE, Ultra DMA and AGP interfaces. For teachers, students and self-study.
Read more t he boot process and syst em bus in Module 2b
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
Read about file syst ems in module 6a
Read about I / O buses in module 2c
Read about t he mot herboard chip set in module 2d
Read about RAM in module 2e
Read Module 5c about SCSI , USB et c.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b3.htm (4 of 4)7/27/2004 4:09:26 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the EIDE, Ultra DMA and AGP interfaces. For teachers, students and self-study.
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 5b4.
About the EIDE interface - continued
The cont ent s:
q What does Ult ra DMA offer?
q Looking at a good harddisk
q Next page
q Previous page
What does Ultra DMA offer? [top]
Please support our
sponsor.
The real EI DE improvement was accomplished wit h t he int roduct ion of t he Ult ra DMA or Ult ra ATA
( UDMA) . I t is an int erface pat ent ed by Quant um but support ed by all mot herboard and disk drive
manufact urers.
New protocol
The t echnology involves an improvement of t he int erface - t he governing elect ronics which deliver t he
hard disk dat a t o t he syst em board. Quant um succeeded in eliminat ing t he bot t le neck in exist ing
elect ronics t o deliver dat a t o t he EI DE hard disks.
The UDMA hard disk is no fast er it self, but t he dat a pat hs have been opt imized. Wit hin t he new
prot ocol, t he speed is doubled by allowing t wice t he dat a t ransfer per clock cycle.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b4.htm (1 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:28 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the EIDE, Ultra DMA and AGP interfaces. For teachers, students and self-study.
Is 33 MB per second realistic?
I nt roducing ATA/ 33, it sounded great but exaggerat ed t o t alk about a 33 MB per second t ransfer rat e,
well knowing t hat no EI DE hard disk at t his t ime could deliver more t han 7 MB per second. Then PI O4,
which can move 16 MB per second, should suffice? No, not so - t he secret is in t he EI DE host cont roller.
Overheads
The host cont roller, among ot her t hings, must ret rieve dat a from t he drive and deliver t hem t o t he PCI
bus. Or it must ret rieve dat a from t he bus and deliver t hem t o t he disk.
The host cont roller has cert ain administ rat ive dut ies t o handle bet ween reading t o/ from t he disk. And
t hey t ake some t ime. One clock cycle in t he EI DE cont roller last s 400 micro seconds. Of t hese, 275 are
spent on "administ rat ive overhead" - handling prot ocol commands, et c. The remaining 125 micro
seconds are used t o read from t he hard disk. Therefore, a maximum t ransfer rat e of 33 MB per second
is necessary t o keep up wit h t he hard disk' s capacit y.
40% better
Act ual measurement s show t hat Ult ra DMA disks yield up t o 40% bet t er performance t han comparable
PI O 4 disks. That was a clear improvement - even t hough t he disks could not deliver t he advert ised 33
MB per second.
Anot her new feat ure in Ult ra DMA was t he CRC ( Cyclical Redundancy Check) - aut omat ic error
correct ion for bet t er dat a prot ect ion and verificat ion.
EIDE on the motherboard
The syst em board and wit h t hat t he chip set , must be set up for Ult ra DMA in order for you t o ut ilize
such a disk. As always, check t he chip set , when you buy a new PC. Since it provides solid performance
improvement at no ext ra cost , it is import ant t hat it support s Ult ra DMA.
Not e: Wit h t he increasing magnet ic densit y on harddisk plat t ers, we use t he bandwidt h of t he UDMA
ATA/ 66 or Serial ATA int erface.
Conclusion
For t he EI DE hard disk t o funct ion in t he Ult ra DMA prot ocol, t he following condit ions must be met :
q The hard disk must be t he Ult ra DMA t ype.
q The syst em board must have a chip set which support s Ult ra DMA wit h t he lat est prot ocol.
q BI OS must "log on" t he hard disk wit h Ult ra DMA prot ocol. You can verify t hat in t he st art up screen.
q Drivers for t he chip set must be inst alled in Windows .
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b4.htm (2 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:28 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the EIDE, Ultra DMA and AGP interfaces. For teachers, students and self-study.
A good Ultra DMA disk
[ t op]
Here you see my ( old) Maxt or harddisk ( Diamond Max 91728D8 from 1998/ 99) . I t holds 17 GB. I t
rot at es wit h a modest 5400 RPM, which makes it noise- free and it does not produces a lot of heat .
Yet it is quit e fast due t o t he magnet ic densit y, which is 4. 32 GB per plat t er. This t hing holds 4 plat t ers:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b4.htm (3 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:28 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the EIDE, Ultra DMA and AGP interfaces. For teachers, students and self-study.
The harddisk is configured as a slave unit on t he primary EI DE channel as described lat er.
More modern harddisks from Maxt or t ake exact ly t he same physical dimensions; int ernally, t hey j ust
hold 30, 45 or 60 GB.
q Next page
q Previous page
To learn more
[ t op]
Read more t he boot process and syst em bus in Module 2b
Read about file syst ems in module 6a
Read about I / O buses in module 2c
Read about t he mot herboard chip set in module 2d
Read about RAM in module 2e
Read Module 5c about SCSI , USB et c.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b4.htm (4 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:28 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the EIDE, Ultra DMA and AGP interfaces. For teachers, students and self-study.
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b4.htm (5 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:28 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the EIDE, Ultra DMA and AGP interfaces. For teachers, students and self-study.
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 5b5.
About the UDM/66 interface
The cont ent s:
q Ult ra DMA ATA/ 66
q Chipset support t o UDMA/ 66
q ATA/ 100
q Serial ATA
q Next page
q Previous page
Ultra DMA ATA/66 [top]
Please support our
sponsor.
I n 1997- 98 I nt el and Quant um creat ed t he new Ult ra DMA st andard called ATA/ 66. This gives
a t heoret ical bandwidt h of 66 MB/ sec.
The new syst em requires a new cable wit h 80 conduct ors. The 40 new conduct ors are used
for grounding. I n t he old version, only 7 cables were used for grounding. The new and very
effect ive grounding removes t he so- called crosst alk ( i. e. noise remaining in t he cable aft er a
t ransmission) .
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b5.htm (1 of 6)7/27/2004 4:09:31 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the EIDE, Ultra DMA and AGP interfaces. For teachers, students and self-study.
I n ATA/ 66 t he cont roller had t o wait for noise in t he cable t o disappear before t he next
t ransmission. Wit h t he new cables t he noise is dramat ically reduced, t he t ransmissions can
follow one by one wit hout delay, and t he bandwidt h goes up.
The ATA/ 66 prot ocol is fully compat ible wit h ATA/ 33. You may use bot h t ype of drives on
mot herboards eit her wit h ATA/ 33 or ATA/ 66. Of course you only get ATA/ 33 performance using
a ATA/ 66 drive on a ATA/ 33 mot herboard. You may upgrade your mot herboard wit h an PCI -
based ATA/ 66 adapt er. This is quit e cheap.
The new cables also use t he same old 40- pin plugs:
I f you use a ATA/ 66 syst em wit h a 40- pin cable, t he prot ocol will aut omat ic swit ch t o ATA/ 33.
What is required?
According t o West ern Digit al ( who had some of t he fast est UDMA/ 66 drives) , t o use t he ATA/ 66
t echnology a PC syst em must have:
q Ult ra ATA/ 66 compat ible logic eit her on t he syst em mot herboard, or on an adapt er card
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b5.htm (2 of 6)7/27/2004 4:09:31 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the EIDE, Ultra DMA and AGP interfaces. For teachers, students and self-study.
q Ult ra DMA compat ible BI OS
q DMA- aware device driver for t he operat ing syst em
q Ult ra ATA/ 66- compat ible I DE device such as a hard drive or CDROM drive
q 40- pin 80- conduct or cable
See t his whit e paper from WD
ATA/ 66 was very neccessary for furt her development of t he EI DE harddisks. Wit h t he
increasing dat a densit y t he media dat a t ransfer rat es are going up and up. Therefore t he host
dat a t ransfer rat es also must increase. All t he t ime t he cont rolling logic must have a bet t er
t ransfer rat e t han t he media or else performance is reduced. The new EI DE disks coming out
from I BM and ot her vendors delivered such a powerful dat a out put t hat t he old UDMA ATA/ 33
st andard could not cope wit h it .
Chipset support to UDMA/66
VI A' s Apollo Pro+ chipset fully support s UDMA/ 66. The best performance should be gained from
t he T82C686A super sout h bridge cont roller.
I nt el support s it wit h t he 810 ( Whit ney) , 820 ( Camino) and 840 ( Carmel) chip set s.
Ot her set ups include special logic chips t o includefull UDMA/ 66 performance t ofor inst ance a BX-
based mot herboard.
Promise FastTrak66
Promise produces a PCI - based cont roller called Fast Trak66 t hat does t he j ob. I t cont rols
UDMA/ 66 disks at full speed, and it even allows doubling or quadroubling t he speed using RAI D
t echniques. See t he descript ion of t he older Promise Fast Trak cont roller.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b5.htm (3 of 6)7/27/2004 4:09:31 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the EIDE, Ultra DMA and AGP interfaces. For teachers, students and self-study.
ATA/100
I n spring 2000 t he new I BM disks became so fast , t hat ATA/ 66 was out of business. The disks
use a new prot ocol called ATA/ 100, being developed by Quant um, who holds t he Ult ra ATA
pat ent s.
The ATA int erface st art ed in 1996 wit h ATA/ 33, which in 1998 was upgraded t o ATA/ 66. Two
years lat er t he ATA/ 100 was released.
A kind of ATA/66 Second Edition
Where ATA/ 33 gave a very powerful boost in t he bandwidt h bet ween cont roller and harddisk,
t he ATA/ 66 gives a minor gain in performance. On t he ot her hand it solves a lot of compat ibilit y
problems by improving t imings and ot her paramet ers in t he specificat ion.
As a result , t he ATA/ 100 is report ed being more simple t o implement in t he chipset logic. I t is
cheaper t o produce and fully compat ible wit h bot h ATA/ 33 and ATA/ 66.
There is an upper limit of disksizes at 137 GB in t he ATA/ 100 int erface. However t here has
been made some workarounds t o t his problem in some comt rollers.
100 Megabyte per second
The ATA/ 100 int erface have t heoret ical bandwidt h of 100 MB/ sec. This is more t han any
harddisk can deliver at present . However t he harddisk t echnology is improving in very high
speed, so t he disk soon will reach t his limit . Hence t he Serial ATA will be needed.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b5.htm (4 of 6)7/27/2004 4:09:31 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the EIDE, Ultra DMA and AGP interfaces. For teachers, students and self-study.
Anot her t echnology we will see more and more is ATA- based RAI D. Using t wo or four cheap
ATA- disks you can have a very powerfull disk syst em wit h doubled bandwidt h. This requires a
RAI D- cont roller like t he Promise Fast Trak or a mot herboard wit h onboard cont roller.
Theserequires higher bandwit hs in t he ATA prot ocols t o show real powerful performances.
ATA/133
I n 2001 some hardware vendors int roduced ATA/ 133 as new version of t he int erface.
Serial ATA
Anot her more int erest ing new t echnology is t he Serial ATA. I nt el, Dell, I BM, Maxt or, Quant um
and Seagat e and ot her part ners are about t o replace ATA/ 100 wit h a fast er drive int erface.
The new Serial ATA int erface, can pump out 160 MB per second in t he first version ( Serial ATA
1x or SA1X) . Lat er version promises bandwit hs up t o 528 MB per second. This will give us
headroom for t he next five years of harddisk t echnology improvement s.
Even more promising is t he new cable design of Serial ATA. I nst ead of 40/ 80 conduct ers t he
cables only holds four conduct ors. This t hinner cabling is great news for everyone put t ing
t oget her his own PC. I also expect t he number of onboard ATA- channels t o increase from 4 t o
8.
Serial ATA probably will kill t he remaining hope for generel use of t he I EEE 1394/ FireWire
int erface for PC' s harddisks. This was never really support ed by I nt el.
Hopefully t he new int erface will operat e wit h a command queue, which has been a great lack in
ATA- design compared t o SCSI .
q Next page
q Previous page
To learn more
[ t op]
Read more t he boot process and syst em bus in Module 2b
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b5.htm (5 of 6)7/27/2004 4:09:31 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the EIDE, Ultra DMA and AGP interfaces. For teachers, students and self-study.
Read about file syst ems in module 6a
Read about I / O buses in module 2c
Read about t he mot herboard chip set in module 2d
Read about RAM in module 2e
Read Module 5c about SCSI , USB et c.
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b5.htm (6 of 6)7/27/2004 4:09:31 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the EIDE, Ultra DMA and AGP interfaces. For teachers, students and self-study.
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 5b6.
Practical hints to setting up a harddisk
The cont ent s:
q Set t ing up t he disk
q The BI OS
q Next page
q Previous page
Configuring your EIDE hard disk [top]
Please support our
sponsor.
Oft en set t ing up a hard disk is very easy. But somet imes it t eases you - somet imes even a lot . Let me here describe a few
checkpoint s:
q The cabling. Your hard disk has t o be connect ed t o t he mast er EI DE channel, and t he connect ion has t o be ensured.
q The j umpers - is t he drive a slave or a mast er? Read below.
q The BI OS set up has t o be configured. Read below.
q Run FDI SK t o part it ion t he hard disk. Boot from a disket t e wit h fdisk. exe on it . Read about file syst ems in module 6a.
Slave or master
I f you connect EI DE harddisk number 2, you probably have t o connect as a slave unit on t he primary EI DE channel. This is not
very good, as I describe it in t he art icle Please also read t he art icle "Problems wit h assigning t wo EI DE harddisks".
Anyway, I ' ll use t his set up as example. You have t o make sure t he j umper set t ing is correct . Here is t he t ext from a Maxt or
manual, which t ells how t o set t he unit up as a mast er or a slave. I t is very easy - and it works:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b6.htm (1 of 4)7/27/2004 4:09:34 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the EIDE, Ultra DMA and AGP interfaces. For teachers, students and self-study.
The j umpers are on t he back side of t he drive, bet ween t he cable and power connect ors:
The BIOS
BI OS is a low- level layer of syst em soft ware. The BI OS has t o ident ify t he hard disk at t he St art - up. I f BI OS does not have t he
proper values for t he specific hard disk, it will not funct ion. There will be no access t o t he hard disk.
The hard disk is recognized by BI OS on cert ain paramet ers like number of cylinders, number of heads, sect ors et c. These values
are t o be st ored in t he CMOS memory. But oft en t he PC cannot ident ify t hese values wit hout a helping hand. I here describe t he
inst allat ion as I know it ( t he ROM soft ware is from Award) . I t is not complicat ed at all, but it involves t wo menus from t he Set up
ut ilit y.
I f you have mount ed your hard disk and ensured t hat t he cabling is correct , it is t ime t o boot t he PC. Then you hit t he [ Delet e] - key
t o ent er t he Set up program. First you choose "I DE HDD AUTO DETECTI ON" as here:
Then you have t o let t he program det ect each of t he four EI DE channels. On t he first one you should find your hard disk. I f not -
t hen somet hing definit ely is wrong.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b6.htm (2 of 4)7/27/2004 4:09:34 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the EIDE, Ultra DMA and AGP interfaces. For teachers, students and self-study.
When you find t he hard disk you usually get t hree opt ions concerning t he prot ocol assigned t he drive. Here we find t he harddisk on
Primary Mast er channel. Choose t he prompt ed one, here it is number 2 ( LBA) :
Cont inue wit h ot her channels. Here I inst all harddisk number 2:
Somet imes a CDROM drive is ident ified here, ot her t imes it isn' t , but it funct ions anyway.
When t he hard disk and ot her EI DE unit s are ident ified by t he aut o det ect ut ilit y, you ret urn t o t he main menu of t he Set up
program. Choose "STANDARD CMOS SETUP" as here:
Here you should find t he hard disk list ed. I n my case it looks like t his, using t wo harddisks:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b6.htm (3 of 4)7/27/2004 4:09:34 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the EIDE, Ultra DMA and AGP interfaces. For teachers, students and self-study.
Be aware t hat t he list above has t o correspond direct ly t o t he physically inst alled unit s - especially if you reconfigure your syst em.
Ot herwise it won' t work. This has t eased me when I inst alled hard disk number t wo and changed t he mast er/ slave set up. I t is not
enough t o run t he aut o det ect , also t he st andard CMOS set up menu has t o be updat ed.
When all t his is in place, you have t o save t he changes and reboot .
q Next page
q Previous page
To learn more
[ t op]
Read more t he boot process and syst em bus in Module 2b
Read about file syst ems in module 6a
Read about I / O buses in module 2c
Read about t he mot herboard chip set in module 2d
Read about RAM in module 2e
Read Module 5c about SCSI , USB et c.
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b6.htm (4 of 4)7/27/2004 4:09:34 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the AGP interface. For teachers, students and self-study.
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 5b7.
About the interface AGP
The cont ent s:
q I nt roducing AGP?
q The t echnology
q Next page
q Previous page
What is AGP?
A new bus was int roduced in 1997. I t is called AGP ( Accelerat ed
Graphics Port ) , and it is exclusively designed for video cards.
Introduction
AGP was designed wit h t wo purposes:
[top]
Please support our
sponsor.
q To relieve t he PCI bus of work wit h graphics dat a. Hence, it can concent rat e on ot her demanding
t ransport dut ies, like t ransfer t o and from net work adapt er and disk drives.
q To have bet t er bandwidt h wit hin t he video syst em.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b7.htm (1 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:36 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the AGP interface. For teachers, students and self-study.
AGP was int roduced wit h t he Pent ium I I processor and I nt el 82440LX chip set . I nt el hoped t o lift more
of t he CPU market away from t he Socket 7 compat ible CPUs by designing a complet ely new
mot herboard layout and including a new powerful bus for t he graphics card. However bot h Ali and VI A
soon int roduced chip set s for Socket 7 mot herboards including AGP. So t oday AGP is found on most
mot herboards.
The technology
AGP includes several t echniques:
PCI
The PCI bus in version 2. 1 is t he basis. I t runs wit h 66 MHz bus frequency. That gives a doubling of
t ransfer speed compared t o t radit ional PCI , from 133 t o 266 MB/ sec.
Clockdoubling
A kind of clock doubling in t he 2X mode, where t he bandwidt h is expanded t o 533 MB/ sec.
Texture cache
This is a met hod t o ut ilize syst em board RAM for t ext ure cache. A t echnology t hat expands t he memory
used by t he graphics card, ut ilizing t he ordinary RAM in t he PC.
The dat a for t ext ure ( backgrounds) need not be processed by t he graphics cont roller, so it is j ust being
loaded from t he RAM. This t echnology is called DI ME by I nt el ( for Direct Memory Execut e) .
Here you see t he archit ect ure involving chip set , main memory and AGP:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b7.htm (2 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:36 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the AGP interface. For teachers, students and self-study.
The socket
Below you see t he AGP socket at t he bot t om. I t looks like a PCI socket , but it has been placed in a
different posit ion on t he board.
I n t he t op you see t wo ( black) I SA socket s. Then four ( whit e) PCI socket s, and t hen t he brown AGP
socket :
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b7.htm (3 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:36 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the AGP interface. For teachers, students and self-study.
At a first hand glance, t he AGP socket very much look like a PCI socket . But it is placed in a different
posit ion, so you cannot plug an AGP card int o a PCI socket .
AGP 4X and above
I n 2000 we saw first AGP4X chip set s ( like i820) and mot herboards implement ing t his feat ure, which
many graphics cont rollers already have been made for. Wit h AGP t he bandwidt h t o t he video subsyst em
is up at 1066 MB per second.
Lat e in 2001 t he AGP 8X st andard is expect ed t o hit t he market . I t will increase t he bandwidt h t o more
t han 2 GB/ sec. To use t his power, we have t o have more powerfull chipset s wit h high- speed RAM. I nt els
i850 wit h dual Rambus channels will deliver t he necessary RAM bandwidt h.
Try www. agpforum. org for more info.
q Next page
q Previous page
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b7.htm (4 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:36 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to the AGP interface. For teachers, students and self-study.
To learn more
[ t op]
Read more t he boot process and syst em bus in Module 2b
Read about file syst ems in module 6a
Read about I / O buses in module 2c
Read about t he mot herboard chip set in module 2d
Read about RAM in module 2e
Read Module 5c2 about USB.
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5b7.htm (5 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:36 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to SCSI, IEE1394 FireWire and USB.
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 5c1a.
About SCSI
The cont ent s:
q The host adapt er
q 7 unit s in a chain On t he following page:
q SCSI is int elligent
q About t he SCSI st andards
q What do you gain wit h SCSI ?
q Next module: USB
q I EEE1394 FireWire
q Device Bay
q Next page
q Previous page
Introduction [top]
Please support our
sponsor.
SCSI ( Small Comput er Syst em I nt erface) is high end t echnology. I t is a t echnology which provide
means for dat a exchange among hardware devices such as drives, t ape st reamers and scanners. SCSI is
especially used in high end PCs such as net work servers or j ust powerful workst at ions.
SCSI might be compared t o t he EI DE int erface, which also uses a host adapt er cont rolling drives.
However SCSI has t wo maj or advant ages over EI DE:
q A SCSI host cont rols 7 or 15 devices ( using only one I RQ) .
q The SCSI syst em holds it s own comput er power, t hus freeing t he CPU from workload.
I f you are crit ical about your PC power, t he SCSI would be wort h considering.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5c1a.htm (1 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:38 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to SCSI, IEE1394 FireWire and USB.
The host adapter
[ t op]
A SCSI syst em is built around a cent ral, int elligent cont roller called t he host adapt er . A host adapt er
can cont rol several SCSI unit s:
q Many unit s on t he same host adapt er.
q Many t ypes of drives : Hard disks, CD and DVD drives, Zip drives, MO drives, et c.
q Tape st reamers ( DAT and ot hers) .
q Scanners.
The host adapt er has it s own BI OS separat e from t he PC' s. When you boot t he PC, you will see t he
adapt er communicat ing wit h connect ed SCSI devices.
The adapt er is rat her expensive. Current ly, t he best for ordinary use is called Adapt ec 2940 U2W ( priced
at around $200) . I t is PCI based, so you could use it in your next PC t oo. I have had good experiences
wit h ASUS mot herboards in versions wit h onboard SCSI cont roller. That is t he most easy solut ion - t o
have t he cont roller onboard.
7 units in a chain
[ t op]
The regular SCSI 2 syst em can handle 8 devices including t he adapt er it self. SCSI Wide handles 15
devices. Each device has t o be assigned a unique number going from I D 0 t o I D 7. The SCSI devices can
be int ernal ( inst alled inside t he PC cabinet ) or ext ernal . The host adapt er is a device it self. Typically,
t he host adapt er will occupy I D 7.
Here is an illust rat ion of a SCSI st ring wit h host adapt er ( I D 7) and five unit s ( I D numbers 0, 1, 2, 4,
and 5) :
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5c1a.htm (2 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:38 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to SCSI, IEE1394 FireWire and USB.
Here you see t he BI OS report of a found SCSI chain:
Terminators in both ends
The last unit in bot h ends of t he SCSI chain must be t erminat ed. This means t hat t here must be
resist ors ( j umpers or swit ches) at t ached t o t wo of t he unit s.
I f you only use t wo devices, you do not have t o worry about it . The host adapt er is one end of t he chain
and t he ot her device is t he ot her end. Wit h t hree or more unit s you have t o t ake care of t erminat ion:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5c1a.htm (3 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:38 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to SCSI, IEE1394 FireWire and USB.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read about FireWire in module 5c3
Read about chip set s on t he mot herboard in module 2d
Read Module 4d about super disket t e and MO drives.
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side.
Read module 5b about AGP
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
Read module 7c about sound cards, and 7d on digit al sound and music.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5c1a.htm (4 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:38 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to SCSI, IEE1394 FireWire and USB.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5c1a.htm (5 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:38 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to SCSI, IEE1394 FireWire and USB.
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 5c1b.
About SCSI - continued
The cont ent s:
q SCSI is int elligent
q About t he SCSI st andards
q What do you gain wit h SCSI ?
q Next page
q Previous page
SCSI is intelligent [top]
Please support our
sponsor.
SCSI is remarkable in having an int elligent prot ocol, which assures maximum ut ilizat ion of t he dat a t ransfer. The
basis of SCSI is a set of commands . Each individual device holds it s own cont roller, which int erpret s t hese
commands.
All commands wit hin t he SCSI syst em are handled int ernally, meaning t he CPU does not have t o cont rol t he
process:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5c1b.htm (1 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:40 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to SCSI, IEE1394 FireWire and USB.
While t he read/ writ e head moves across a SCSI disk, t he host adapt er as well as t he CPU can handle ot her j obs.
Therefore SCSI is well suit ed for mult it asking environment s.
About the SCSI standard
[ t op]
SCSI st ands for Small Comput er Syst em I nt erface. I t is int ended as a universal int erface, defined and designed
in 1982 by NCR and Shugart Associat es. I t exist s in numerous variat ions. Here you see some of t he more
significant edit ions:
St andard Year Bus speed Bus widt h Max. bandwidt h
St andard SCSI 1986 5 MHz
( Asynchronous)
8 bit 5 MB/ sec
Fast SCSI
Narrow
1990 10 MHz
( Synchronous)
8 bit 10 MB/ sec
Fast SCSI
Wide
1992 10 MHz
( Synchronous)
16 bit 20 MB/ sec
Ult ra SCSI 1994 20 MHz
( Synchronous)
16 bit 40 MB/ sec
LVD Ult ra2 1996 40 MHz 16 bit 80 MB/ sec
Today t here are many SCSI st andards. Among ot hers, you can come across SCSI - 20 and SCSI - 40, which refers
t o t he bus speed. The SCSI st andard seem t o have it s own life wit h plent y of new development .
LVD Ultra2
The lat est version of SCSI is called LVD ( Low Volt age Different iale) . You also find t he t erm SCSI Ult ra 2 - t here
have always been so many t erms. . . LVD is an improvement t o SCSI - 3.
LVD gives t wice t he bandwidt h of t he ordinary SCSI - 3. Anot her improvement is t he cabling which works up t o 12
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5c1b.htm (2 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:40 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to SCSI, IEE1394 FireWire and USB.
met ers. Tradit ional SCSI only works wit hin 3 met ers. LVD has t o compet e wit h FireWire, which also has a
powerful bandwidt h.
Adapt ec have a SCSI - cont roller delivering up t o 160 MB/ sec. This unit called Adapt ec SCSI Card 3950U2 uses t wo
independent Ult ra2 SCSI buses in one card. I t connect s up t o 30 SCSI devices!
What do you gain with SCSI?
[ t op]
Expensive but good. SCSI makes t he PC a more expensive, but more versat ile. The advant ages are, t hat on t he
same PC you have free access t o use many and good unit s:
q I t is easy t o add accessories as DAT st reamers, CD- ROM recorders, MO drives, scanners, ZI P- and DVD- drives
et c.
q You can use SCSI hard disks.
q You can use CDROM drives on SCSI , which may give a bet t er performance.
The advantages of SCSI hard disks
SCSI hard disk are generally of higher qualit y t han ot her disks. Typically, good SCSI disks come wit h a 5 year
warrant y. Tradit ionally t hey are fast er t han t he EI DE disks. At 10, 000 or 14, 000 RPM t hey have short er seek
t imes. They also have a bigger cache.
Anot her advant age is t he large number of accessories, which can be at t ached. I f you buy a 18 GB SCSI disk
t oday, you will guarant eed need addit ional disk st orage in a few years. Then you j ust add disk number t wo t o t he
SCSI chain, and lat er number t hree. The syst em is more flexible t han EI DE, where you can have a maximum of
four unit s incl. CD- ROM.
The SCSI hard disks can also adj ust t he sequence in t he PC' s disk read commands. This allows reading t he t racks
in an opt imal sequence, enabling minimal movement s of t he read/ writ e head. Quant um calls t his t echnology
ORCA ( Opt imized Reordering Command Algorit hm ) . I t should improve performance by 20%.
Finally, t he SCSI cont roller can mult it ask, so t he CPU is not locked up during hard disk operat ions, which you can
experience wit h I DE.
SCSI hard disks can achieve subst ant ially larger t ransfer capacit y t han t he I DE drives, but t hey have t he same
bot t le necks: t he serial handling of bit s in t he read/ writ e head, where t he capacit y is highly dependent on t he
rot at ion speed.
SCSI is for servers
However, t oday t he import ance of SCSI is decreasing except for use in dedicat ed servers. Modern CD- ROM and
CD- RW drives work j ust as good on EI DE as on SCSI . USB has t aken over when it comes t o cont rolling unit s like
scanners, cameras and Zip drives.
Finally, modern EI DE- based harddisks have an ext remely high qualit y compared t o t he product s we had five
years ago. Hence, t here is no reason t o prefer SCSI - based harddisk t o t he more inexpensive EI DE drives.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5c1b.htm (3 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:40 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to SCSI, IEE1394 FireWire and USB.
But for servers SCSI st ill has a market .
Booting from SCSI disk
I f t he hard disk has t o be boot ed, t radit ionally it has t o be assigned I D 0. I f t he SCSI cont roller has t o cont rol t he
hard disk, t hen t he PC CMOS set up must be modified, so t he ( I DE) hard disk is not inst alled if not bot h t ypes of
hard disks are inst alled.
The operat ing syst em will find t he host adapt er aft er st art up and BI OS will be read from t he hard disk t hrough
t he adapt er. New BI OSs allow a choice of boot ing from eit her I DE or SCSI disk.
Fast and Ultra Wide
The newest generat ion of SCSI hard disks are bot h fast , ult ra and wide. Therefore, t he best advice is t o buy an
adapt er like Adapt ec 2940UW2, which can handle t he newest disks.
IBM disks
Allow me t o advert ise I BM' s SCSI disks. They are fant ast ically good. Unfort unat ely, not many people know about
t hem. I have had a few of t hem. They excel in high qualit y at reasonable prices. The physical const ruct ion is very
appealing: The elect ronics are int egrat ed in very few component s. Everyt hing exudes qualit y! And t hey are very
quiet . You simply cannot hear t hem.
32 bit problems in Windows 3.11
Windows 32 Bit Disk Access has given problems wit h SCSI disks. For a long while, it was impossible t o inst all a
32 bit driver in Windows 3. 11 t o t he SCSI disk. This was solved in 1995 and t here have been no problems wit h
Windows and SCSI since t hen.
Links
About SCSI : SCSI Pro and DPT offer some informat ion.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read about FireWire in module 5c3
Read about chip set s on t he mot herboard in module 2d
Read Module 4d about super disket t e and MO drives.
Read module 5a about expansion cards, where we evaluat e t he I / O buses from t he port side.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5c1b.htm (4 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:40 AM
An easy-read and illustrated Guide to SCSI, IEE1394 FireWire and USB.
Read module 5b about AGP
Read module 7a about monit ors, and 7b on graphics card.
Read module 7c about sound cards, and 7d on digit al sound and music.
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5c1b.htm (5 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:40 AM
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5a1.htm
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module5a1.htm7/27/2004 4:09:40 AM
Karbo's Software Tips
Karbosguide.com
A Few Software Tips
The cont ent s:
Which are t he advant ages of Windows 98?
About t he swap files and RAM.
About t he disk cache.
About t emporary files ( 1) .
About t emporary files ( 2) .
About file t ypes - show only some of t hem!
Use t he deskt op for favorit e I nt ernet addresses.
Permanent folder for download in I nt ernet Explorer.
Choose a st art page.
Color changes in menus - a opt ion in Windows 98.
Replace opening screen in Windows.
Upper case let t ers in folder names.
Single click in Explorer - smart idea.
TWEAK UI - t he hidden t ool in Windows 98.
FAX program - what happened t o t hat ?
Windows - aut ot ext s in any program wit h Short Keys.
Windows - permanent , global and local macros. .
Running out of space on my hard disk. . .
Enabling DMA on t he harddisk. . .
Use MSConfig t o alt er t he Windows st art - up.
q Next page
q Previous page
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/start.htm7/27/2004 4:09:41 AM
Tips for Windows.
Karbosguide.com. Software Tip 1
What are the advantages of Windows 98?
q Next page
q Previous
page
I n my opinion and experience Windows 98 was an
excellent operat ing syst em when int roduced. At it s
int roduct ion in t he spring of 1998, some papers
made t he comment "it is not wort h t he money"
and "t here is not much new compared t o Windows
95. " I did not agree wit h t hem.
Please support our
sponsor.
Here are some of t he advant ages compared t o earlier versions of Windows:
Generally better performance
Generally Windows 98 ut ilizes t he PC resources bet t er:
q Memory management has been complet ely changed. I t finally works.
q The file syst em is bet t er int egrat ed int o t he operat ing syst em, which gives new
funct ionalit y.
q Program loading can be up t o four t imes as fast .
q Hardware support is significant ly improved wit h a new driver model, and all new chipset s
et c. are support ed. However t hese condit ions may change.
These improvement s are sufficient ly significant t o j ust ify an upgrade.
Better user interface
[ t op]
Superficially t he Windows 95 user int erface has not changed much. But you need not dig
down very deep t o see many novelt ies. I am t alking about small it ems wit h bet t er
adapt at ions in t he St art menu, new t ool bars, et c. But t hese small it ems are really very smart
when you need t o set t he user int erface.
Better system tools
The syst em t ools are significant for t he more demanding user, who really want s t o know and
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/01.htm (1 of 2)7/27/2004 4:09:42 AM
Tips for Windows.
be in command of t he PC. A number of new t ools have been added t o Windows 98. They
improve surveillance facilit ies. All of t his will be t horoughly described in my upcoming
"Windows 98 and hardware" booklet ( or what ever t he t it le will be) .
Stability
Many will experience t hat previous inst abilit y is j ust gone. The PC can be left on for weeks on
end wit hout going down a single t ime. Many may laugh at t his - "why should we pay t o
correct Windows 95 errors. " That may be t rue, but consider t he wast ed t ime wit h PC' s which
fail and need t o be rest art ed, et c. Cut t he must ard and get 98 on your machines - t hen it
works. Life is t oo short for lousy soft ware!
Windows 98 is not good enough
I n t he years aft er t he int roduct ion of Windows 98, we saw new and fast er hardware coming
ext remely frequent . We got fast er CPU' s, t he clock frequency increasing 3 t o 5 t imes in few
years. Also harddisks became fast er and RAM as well.
Having a moderne PC wit h plent y of fast hardware, Windows 98 or Me ( t he lat er version) is
not good enough. You need Windows 2000 or XP t o benefit from t he hardware. This is a fact .
Just look at t he way Windows 98 manages memory - it does not work using more t han 128
MB of RAM. And t hat is a pet t y. I f yOut lookwork wit h graphical applicat ions like Phot oshop or
FireWorks, you will see a great performance using 512 MB RAM or more - but not wit h
Windows 98/ Me.
q Next page
q Previous page
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo.
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/01.htm (2 of 2)7/27/2004 4:09:42 AM
Tips for Windows.
Software Tip 2a
About RAM and swap file
q Next page
q Previous
page
I n Windows 95 and 98 it is import ant t o underst and t he of t he relat ionship bet ween:
q Amount of RAM in t he PC
q Size of and cont rol of Disk cache
q Free memory
q Size of t he swap file
Windows are in all versions ( as all Microsoft soft ware) a very resource demanding operat ing
syst em. Then you might ask, why bot her t o use Windows? We all know t he answer: The
Microsoft Office packages are undoubt edly t he finest , most user friendly and most t horoughly
planned office programs on t he market - no quest ion about t hat . They can work sat isfact orily
on your PC, but it requires some hardware. A lot of hardware indeed.
The processor should be fast , as all modern processors are. Plent y of RAM and a roomy and
fast hard drive is also very desirable for running Windows.
The need for RAM
Windows gobbles up memory. Therefore, sufficient memory is essent ial for it s sat isfact ory
performance. Try t o check how much you really need - you will be surprised. The memory
comes from t wo locat ions:
q The inst alled RAM
q The swap file, which is creat ed aut omat ically, when you run out of RAM.
Windows is clever using t he swap file . I t "ext ends" it s RAM t o t he hard disk. I f you only have
64 MB RAM in your PC, you can be assured t hat you have a sizable swap file on your disk.
Controlling the swap file
You may choose which drive, you place t he swap file. Some expert s prefer t o place t he
swapfile on a separat e part it ion, which only is used for t he swap file. That way, t he swapfile
does not int erfere wit h t he ot her disk dat a, which become more easy t o defragment .
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/02a.htm (1 of 3)7/27/2004 4:09:42 AM
Tips for Windows.
You deside t he placement and size of t he swapfile using t he Syst em Propert ies dialogue box.
Here you see it from Windows 2000:
We recommend t hat you limit t he swapfile t o a size of 512 MB using Windows 98/ Me. I f you
use Windows 2000 ( which is working a lot bet t er t han 98/ Me) you should leave Windows t o
deside t he size of t he swap file.
Anyway, you need t o keep an eye on t he swap file. I n Windows 95 many breakdowns
originat ed in swap file use. But luckily Windows have improved a lot ; Windows 98 is is bet t er
at cont rolling RAM and swap file t han Windows 95 is.
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/02a.htm (2 of 3)7/27/2004 4:09:42 AM
Tips for Windows.
Windows 98 has a bet t er algorit hm t o cont rol RAM et c. The swap file is st ill t here, and it is big
- but t hat does not have t o be a problem. Windows only reads t o and from t he swap file,
while no work is done on t he PC. I n t hat way we do not even not ice t hat t here is a swap file.
I n t he Windows versions 2000 and XP t here is no need t o worry about memory management ,
it works fine ( but please use 512 MB RAM) .
No swap file?
Some expert s recommend if possible t o eliminat e t he swap file in Windows 98. I t sounds
great but is not not very smart in pract ice. The problem arises from t he ext remely lousy
memory management you find in Windows 98. Any onboard RAM above 256 MB find no use!
Even upgrading from 128 t o 256 MB gives almost no benefit ; Windows st ill runs out of
memory all t he t ime.
q Next page
q Previous page
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo.
http://www.karbosguide.com/software/02a.htm (3 of 3)7/27/2004 4:09:42 AM
A complete illustrated Guide to the PC. Index.
Index:
3D graphics
3DNow!
5X86
6X86
6X86MX ( M2)
8086- compat ibilit y
810 chip set
815 chip set
820 chip set
820E chip set
82430HX
82430TX
82430VX
82440BX
82440EX
82440FX
82440LX
82440GX
82450NX
82440ZX
Adapt ers
AGP
AMD K5 and K6
ASCI I
ATA/ 66, ATA/ 100
At hlonXP
ATI
ATX
BI OS
Bit s & Byt es
Boot record
Boot sequence
Bus mast ering
buses
EPP/ ECP
EI DE
EDO- RAM
EI SA bus
FAT16
FAT32
FDI SK
FireWire
Fost er
FPU
G400
Hard drives
HiFD
i740
I DE
I EEE1394 FireWire
I BM drives ( Deskst ar
et c. . )
I BM compat ibilit y
I nt roduct ion t o Click &
Learn
I RQs
I SA bus
K6
K6- 2
K6- 3
K7 At hlon
Kat mai
LCD display
LS120
Neumann, John von
Over- clocking CPUs
( t uning)
PC100 RAM
PC133 RAM
PC- Card
PCI bus
Pent ium
Pent ium I I
Pent ium I I I
Pent ium 4
Pent iumPro
Pipelines
Plug and Play ( PnP)
POST ( t est s)
Powersafe, in BI OS
RAI D 1, 2.
RAMDAC
RDRAM
RI SC inst ruct ions
ROM chips
S3
SCSI
SDRAM
Set up program
SiS ( Chip set s)
SI MD
SI MMs
Slot One
SPD
SSE2
Syst em bus
http://www.karbosguide.com/guides/search01.htm (1 of 2)7/27/2004 4:09:43 AM
A complete illustrated Guide to the PC. Index.
Camino
Celeron
CD- ROM
CD- RW
Chip set
CI SC inst ruct ons
CMOS
CPU- cache ( L1 and
L2)
CuMine
Cyrix DDR RAM
Direct X
Diskcache in W95
Disket t e drive
Dixon
DMA
Drives
Drives, I nt erface
Dolby AC- 3
Drivers
Dual Volt age
DVD drives
DX4
LVD
M3 ( Cyrix CPU)
Mat rox
MCA bus
Merced
MI DI
MMX
MO- drives
MPC- 3
MP3
Mot herboard
Mult i- read CD- drives
Tapest reamers
. Tmp files
TNT2
Trinit ron
Tseng
USB
Ult ra DMA
VC133 RAM
Vesa Local Bus
VI A chip set
VI A Apollo MVP3
VI A Apollo+
Wave t able
Wait st at es
Willamet t e
Windows opt imizing
Xeon
ZI F
Zip- drives
http://www.karbosguide.com/guides/search01.htm (2 of 2)7/27/2004 4:09:43 AM
An illustrated Guide to the latest chip sets for Intel's P6 processors
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 2d.06
Intel's i810
The cont ent s:
q I nt roduct ion
q The Accelerat ed Hub Archit ect ure
q The Graphics Memory Cont roller Hub of 810
q The AC97
q Karbo' s conclusion
q Next page
q Previous page
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d06.htm (1 of 7)7/27/2004 4:09:46 AM
An illustrated Guide to the latest chip sets for Intel's P6 processors
Intro to Intel 810
[ t op]
Wit h i810, I nt el has launched t he first chip set of a new generat ion.
I n lat e April 1999 t he 810 "Whit ney" chip set was int roduced. This set is new in several
aspect s.
q A new t ype of memory cont roller wit h built - in graphics t echnology.
q Support for up t o 512 MB SDRAM.
q Built - in audio- codec cont roller.
q No I SA bus!
810 is an inexpensive chip set built on t he BX t echnology. However, t he new memory bus will
come in ot her chip set s as well. The built - in audio- codec cont roller enables soft ware audio and
modem implement at ions. This meens t hat no sound card or modem is required. And finally we
see t he first at t empt t o produce modern PC' s wit hout t he old I SA bus.
Chips in 810
The chip set consist s of t hree chips:
82810 Graphics Memory Cont roller Hub 421 Ball Grid Array ( BGA)
82801 I nt egrat ed Cont roller Hub 241 Ball Grid Array ( BGA)
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d06.htm (2 of 7)7/27/2004 4:09:46 AM
An illustrated Guide to the latest chip sets for Intel's P6 processors
82802 Firmware Hub 32- pin PLCC or 40- pin TSOP
The Accelerated Hub Architecture [top]
Usually we t alk about nort h and sout h bridges in chip set s. These refer
t o t he t wo cont rollers a chip set usually consist s of. I nt el replaces t hese
t erms wit h "hubs".
The new t hing in t his hub archit ect ure is, t hat t he t wo cont rollers not
are connect ed by t he PCI bus. I nst ead t hey connect via a new I nt erlink
dedicat ed bus. This is a high speed bus, current ly wit h t wice t he
bandwidt h of t he PCI bus. This archit ect ure resembles t he new K7
At hlon point t o point channel.
Please support our
sponsor.
266 MB/sec
The int erlink bus operat es at 133 MHz in 2X mode. Being 64 bit wide t his gives a bandwidt h of
266 MB/ sec ( 2 X 133. 000. 000 X 8 byt e) .
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d06.htm (3 of 7)7/27/2004 4:09:46 AM
An illustrated Guide to the latest chip sets for Intel's P6 processors
Also see t he MCH below.
Graphics Memory Controller Hub
The 82810 Graphics Memory Cont roller Hub ( GMCH) is a MCH "nort h bridge" including a
graphics cont roller and using Direct AGP ( int egrat ed AGP, where t he graphics cont roller is
direct ly connect ed t o t he syst em RAM) operat ing at 100 MHz.
The 82810 chip feat ures a "Hardware Mot ion Compensat ion" t o improve soft DVD video and
digit al video out port for digit al flat panel monit ors. The graphics cont roller is a version of
I nt el' s new model 752. Opt ional, t he chip set can be equipped wit h a display cache of 4MB RAM
t o be used for "Z- buffering".
Dynamic Video Memory Technology ( D. V. M. T. ) is an archit ect ure t hat offers good performance
for t he Value PC segment t hrough efficient memory ut ilizat ion and "Direct AGP". A new
improved version of t he SMBA ( Shared Memory Buffer Archit ect ure) used in earlier chip set s as
VX. I n t he 810 chip set 11 MB syst em RAM is allocat ed t o be used by t he 3D- graphics cont roller
as frame buffer, command buffer and Z- buffer.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d06.htm (4 of 7)7/27/2004 4:09:46 AM
An illustrated Guide to the latest chip sets for Intel's P6 processors
82801 I/O Controller Hub
This "sout h bridge", t he 82801 ( I CH) , employs an accelerat ed hub t o give a direct connect ion
from t he graphics and memory t o t he int egrat ed AC97 ( Audio- Codec) cont roller, t he I DE
cont rollers, t he dual USB port s, and t he PCI bus. This promises increased I / O performance.
82802 Firmware Hub (FWH)
The 82802 Firmware Hub ( FWH) st ores syst em BI OS and video BI OS in a 4 Mbit EEPROM. I n
addit ion, t he 82802 cont ains a hardware Random Number Generat or ( RNG) , which ( perhaps
and in t ime) will enable bet t er securit y, st ronger encrypt ion, and digit al signing in t he I nt ernet .
AC97
The I nt egrat ed Audio- Codec 97 cont roller enables soft ware audio and modem by using t he
processor t o run sound and modem soft ware. I t will require soft ware, but using t his you need
no modem or soundcard.
This feat ure is smart if you do not use audio or modem on a regular basis. I t adds a heavy
work t o t he CPU, which has t o act as a modem and as a sound card beside it s regular t asks.
Karbo's conclusion
[ t op]
The 82810 cont roller represent a new generat ion of low- priced chip set s. I find t hese aspect s
int erest ing:
Integration of a powerful graphics accelerator
The RAMDAC is of 230 MHz giving a max. 2D- resolut ion of 1280 X 1024 pixels wit h 24 bit color
dept h and a refresh rat e of 85 Hz. The graphics cont roller offers 3D accelerat ion wit h bot h
Dirext X and OpenGL support .
I found t he performance t o be quit e OK for non- game use. The visual qualit y of t he screen
images seemed t o mat ch t he out put from mid- range graphics adapt ers from ATI and Mat rox. I
could live wit h t his graphics wit hout any problems.
Here you see a dump from t he Windows - driver t hat goes wit h t he chip set :
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d06.htm (5 of 7)7/27/2004 4:09:46 AM
An illustrated Guide to the latest chip sets for Intel's P6 processors
Many users will not like t hat you cannot disable t he graphics cont roller. So for gamers t his chip
set is no good. I t was never really accept ed by t he mot herboard manufact ures, nor by t he
press. However, I liked it . . .
The new support for software-based sound and modem
Will t his work, and what are t he consequences going t o be?
No I SA bus. This is good. we shall soon see a lot more USB- based devices. And it will become
very easy t o built small, inexpensive, and elegant PCs using all t he int egrat ed hardware and
only connect ing ext ernal unit s using t he very handy USB cabling.
100 MHz support
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d06.htm (6 of 7)7/27/2004 4:09:46 AM
An illustrated Guide to the latest chip sets for Intel's P6 processors
The 810 chip set is made for I nt el Celeron processors. But so far t hese processors only work
wit h a syst em bus frequency of 66 MHz. Why does t he chip set t hen support 100 MHz? The
obvious reason is t hat I nt el planed t o move t he Pent ium I I I processors t o a Socket 370
plat form. And t he Celerons comes operat ing at a 100 MHz bus frequency. This is good news,
and it all happened in 2000 and 2001.
Go for i815E
Aft er t he arrival of i815E in June 2000, t hat is t he chip set t o go for. I t holds all t he nice
feat ures from i810 plus a lot of great news.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read about t he Pent ium in module 3c
Read about t he Pent ium I I ' s et c. in module 3e
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. KarbosGuide. com
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d06.htm (7 of 7)7/27/2004 4:09:46 AM
An illustrated Guide to the i820 chip set
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 2d.07
The intel i820 "Camino" chip set
The cont ent s:
q I nt roduct ion
q The chips in i820
q Next page
q Previous page
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d07.htm (1 of 3)7/27/2004 4:09:48 AM
An illustrated Guide to the i820 chip set
Intro to Intel 820
[ t op]
I n 1999 t he new generat ion of high- end I nt el chip set was code named "Camino".
This i820 "Camino" chip set s was originally set for debut in May or June, but were delayed.
The Rambus t echnology was problemat ic.
The i820 chip set was finally t o be launched Sept ember 27t h, 1999 but was delayed again.
This t ime mot herboards wit h more t han t wo SDRAM socket s did not work. And t here have
been so many problems wit h t his chip set , which soon became a night mare for I nt el. I n t he
press t he sit uat ion was described as "Caminogat e"
Anyway, we have t o look int o t he archit ect ure. We find:
q New hub- based archit ect ure
q 133 MHz FSB
q Rambus
q Up t o 1GB RAM
q AGP4X
q ATA66
The chipset was designed for high- end use wit h Pent ium I I I processors.
Please support our
sponsor.
The chips in i820
The chip set consist s of t wo main cont rollers:
q The 82820 Memory Cont roller Hub.
q The 82801 I / O Cont roller Hub ( I CH)
The ( MCH) provides t he CPU int erface, DRAM int erface, and AGP int erface. This chip is found
in t wo versions: A single processor ( 82820) or a dual processorchip ( 82820DP) .
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d07.htm (2 of 3)7/27/2004 4:09:48 AM
An illustrated Guide to the i820 chip set
The I CHmakes a direct connect ion from t he graphics and memory t o t he int egrat ed AC97
cont roller, t he ATA66 cont roller, dual USB port s, and PCI add- in cards.
Besides t he t wo main cont rollers you also find:
q 82380AB PCI - I SA Bridge
q 82802 Firmware Hub
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read about t he Pent ium in module 3c
Read about t he Pent ium I I ' s et c. in module 3e
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. KarbosGuide. com
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d07.htm (3 of 3)7/27/2004 4:09:48 AM
An illustrated Guide to the i820 chip set
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 2d.08
Intel i820 "Camino", continued
The cont ent s:
q The 82802 Firmware Hub and BI OS updat es
q The Memory Cont roller Hub ( MCH)
q Next page
q Previous page
The 82802 Firmware Hub and BIOS updates
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d08.htm (1 of 4)7/27/2004 4:09:50 AM
An illustrated Guide to the i820 chip set
The 82802 Firmware Hub ( FWH) st ores mot herboard BI OS in a 4 Mbit EEPROM. I n addit ion, t he 82802
cont ains a hardware Random Number Generat or ( RNG) , which ( perhaps and in t ime) will enable bet t er
securit y, st ronger encrypt ion, and digit al signing on t he I nt ernet .
I nt el has succeeded in set t ing up a fine syst em for BI OS updat es, using t he FWH. Tradit ionally BI OS was
updat ed using a boot disket t e, but since many modern PC syst ems do not have a floppy disk, it has
become a problem t o updat e BI OS on new machines.
I nt el choose t o place t heir BI OS- Updat e- Pat ch on t he I nt ernet . You download t he 1. 2 MB file "Express
BI OS Updat e" and execut e it under Windows . Aft er re- boot , your i820- based mot herboard is updat ed
wit h new BI OS. This is really smart !
The new BI OS include a much- want ed feat ure: Rapid BI OS Boot ( RBB) . I t speeds up t he POST sequency
radically, hence reducing t he boot t ime wit h some 15 - 30 seconds. This is especially designed t o work
wit h Windows ME.
However, t he first versions of new BI OS was a failure - soundscards did not funct ion aft er t he updat e . . .
I nt el really has had a hard t ime wit h t his chip set .
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d08.htm (2 of 4)7/27/2004 4:09:50 AM
An illustrated Guide to the i820 chip set
The Memory Controller Hub (MCH)
Please support our
sponsor.
Cent ral in t he chip set is t he Memory Cont roller Hub. This device cont rols t he dat a flow t o and from
RAM. The idea is t o assign maybe t wo or four RAM channels for higher bandwidt h.
Here is my early guess on t he design:
The idea of using a Memory Translat or Hub as you see above, was t hat it would enable I nt el t o produce
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d08.htm (3 of 4)7/27/2004 4:09:50 AM
An illustrated Guide to the i820 chip set
boards using PC133 RAM as well as RDRAM. A sound idea, indeed. DDR was never planned, since I nt el
is not allowed using t his t ype of RAM, according t o t heir agreement wit h Rambus ( covering t he years
2000- 2002) .
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read about t he Pent ium in module 3c
Read about t he Pent ium I I ' s et c. in module 3e
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. KarbosGuide. com
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d08.htm (4 of 4)7/27/2004 4:09:50 AM
An illustrated Guide to the i820 chip set
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 2d.09
Intel i820 "Camino" continued
The cont ent s:
q Caminogat e: No PC133 RAM, no MTH
q The hub- based archit ect ure
q Next page
q Previous page
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d09.htm (1 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:52 AM
An illustrated Guide to the i820 chip set
Caminogate: No PC133 RAM, no MTH
Today we know t he i820 chip set is used only wit h RDRAM; I nt el failed t o produce a reliable
MTH ( or Memory Conversion Hub ( MCH) , as it lat er was named) .
One of t he problems appeared t o be t hat t he Serial Presence Det ect ( SPD) chip included on
SDRAM DI MMS was missing in some modules. This SPD was crucial t o t he MCH. A solut ion
was t o add a 150 ohm resist or bet ween t he Memory Translat or Hub and t he SDRAM . . .
Wisely I nt el finally gave up all t his business. I n t he end t hey had t o recall a million of I nt el
mot herboards and had t o give away RDRAM in large numbers t o unlucky cust omers among
buyers of ot her mot herboard brands using t he ill- fait ed i820 chip set . Here t he I TH caused
sudden reboot s when PC133 RAM was inst alled.
However you may say t hat wit hout support for eit her PC133 or PC2100 RAM, t here is no big
use for t he i820 chip set .
The hub-based architecture
Please support our
sponsor.
I n earlier designs ( like BX) you had t he t wo cont rollers unit ed by t he PCI channel:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d09.htm (2 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:52 AM
An illustrated Guide to the i820 chip set
This design but a heavy st rain on t he PCI bus, having a 133 MB/ sec bandwidt h. All dat a t o
bet ween RAM and disks, net work adapt ers and ot her I / O boards such as PCI - based graphics
cont rollers had t o pass t hrough t he PCI bus.
I n t he new design, we first saw wit hin t he i810 chip set , we have "hubs" inst ead of "bridges":
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d09.htm (3 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:52 AM
An illustrated Guide to the i820 chip set
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read about t he Pent ium in module 3c
Read about t he Pent ium I I ' s et c. in module 3e
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d09.htm (4 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:52 AM
An illustrated Guide to the i820 chip set
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. KarbosGuide. com
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d09.htm (5 of 5)7/27/2004 4:09:52 AM
An illustrated Guide to the i820 chip set
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 2d.10
Intel i820 "Camino" continued
The cont ent s:
q The I nt erlink channel
q AGP4X
q RDRAM
q Next page
q Previous page
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d10.htm (1 of 4)7/27/2004 4:09:54 AM
An illustrated Guide to the i820 chip set
Interlink
The t wo cont rollers are unit ed by a new "I nt erlink" channel. I t runs at 266 MB/ sec:
The int erlink bus operat es at 133 MHz in a 2X mode making it 128bit wide. This gives a
bandwidt h of 266 MB/ sec ( 133. 000. 000 X 128 / 8) .
The 4X AGP
I nt el was one of t he first companies t o implement AGP 4X in t he chip set . Using AGP 4x, t he
bandwidt h t o t he graphics subsyst em has doubled from 533 MB/ sec in AGP 2X t o more t han 1
GB/ sec:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d10.htm (2 of 4)7/27/2004 4:09:54 AM
An illustrated Guide to the i820 chip set
This is good for all gamers. 3D gaming needs a powerfull channel t o RAM t o produce high
qualit y screen frames.
The RDRAM channel
Please support our
sponsor.
The use of Rambus should provide t he memory opt imal bandwidt h. The RDRAM support s
PC600, PC700, and PC800, delivering 1. 6 GB/ s of memory bandwidt h in t he PC800 - t wice
t he peak memory bandwidt h of 100MHz SDRAM syst ems.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d10.htm (3 of 4)7/27/2004 4:09:54 AM
An illustrated Guide to the i820 chip set
However t he price of RDRAM was ext remely high in t he first year of i820. Therefore, i820
never became popular.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read about t he Pent ium in module 3c
Read about t he Pent ium I I ' s et c. in module 3e
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. KarbosGuide. com
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d10.htm (4 of 4)7/27/2004 4:09:54 AM
An illustrated Guide to the i820 chip set
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 2d.11
Intel i820 "Camino" continued
The cont ent s:
q The 133 MHz FSB
q Karbo' s conclusion
q Next page
q Previous page
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d11.htm (1 of 3)7/27/2004 4:09:56 AM
An illustrated Guide to the i820 chip set
The 133 MHz FSB
The Front Side Bus is t he bus connect ing t he CPU t o t he MCH. I n older syst ems t his bus was t he
syst em bus. The FSB is dependant on t he CPU; t he older Pent ium I I I s ran on a 100 MHz FSB. But
t he i820 chip set was int ended t o be used wit h t he newer Pent ium I I I "Coppermine", which operat es
at a mult iply of 133 MHz.
The increase from a 100 t o a 133 MHz FSB is not as import ant as it sounds. This is due t o t he fact
t hat t he great est work is performed inside t he CPU and bet ween it s L1 and L2 cache, where a
powerfull bandwidt h really is essent ial.
The dat a int ensit y bet ween CPU and RAM is less demanding. However a 133 MHz FSB will give
bet t er performance when working wit h lagre dat a amount s ( using Phot oshop for inst ance) .
A conclusion
Please support our
sponsor.
We have not t est ed a 820- based board ourselves. However, we did like t he 810- based board we
used for a while earlier. Not for gaming - but office use, it was and it is a fine lit t le chip set .
The i820 t hing has been a disast er for I nt el. First it was discovered, t hat you only could use 2 out of
3 RI MM- socket s. Then t he MTH did not work. Today some analyst s believe, t hat I nt el will st op
producing chip set s aft er all t his chaos. I underst and t hem, but it will be a pit y. I nt el used t o
produce excellent chip set s, and t hey should cont inue.
The i820 chip set should have been brought out of circulat ion a long t ime ago. The new i815 chip
set could probably t ake over, so t he venerable BX set could ret ire.
We see t wo point s in which I nt el has failed, and t his could easily have been avoided:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d11.htm (2 of 3)7/27/2004 4:09:56 AM
An illustrated Guide to the i820 chip set
First of all t he company should not commit t hemselves t o an uncert ain t echnology like RAMBUS as
t hey did. I nt el produces great CPUs. The cust omers might use t hem wit h Rambus or SDRAM or
DDRRAM or EXP3RAM or what ever t he indust ry might come up wit h.
We believe t hat I nt el t rust ed t o much in own powers; t hey want ed t o "force" t he market int o a
cert ain behavior. We do not like t hat ; it is against t he free will and int elligence of users all over t he
world. Last t ime I nt el t ried t his at t it ude was in 1997 when skipping Socket 7 in favour of Slot 1. A
clupmsy design, which t hey now have abandoned t hemselves.
The second lesson is t hat I nt el never again should market unt est ed product s. We have seen t his
several t imes during t he "Caminogat e" affair. Maybe I nt el has felt t hreat hend by AMD' s succesfull
At hlon proj ect . But t here is no excuse for market ing lousy unt est ed product s. Bot h I nt el and
Microsoft should learn from t his.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read about t he Pent ium in module 3c
Read about t he Pent ium I I ' s et c. in module 3e
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. KarbosGuide. com
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d11.htm (3 of 3)7/27/2004 4:09:56 AM
An illustrated Guide to the i820 chip set
KarbosGuide.com. Module 2d.12
Intel i820E "Camino II"
The cont ent s:
q I 820E
q Next page
q Previous page
820e
I n June 2000 I nt el' s revamped i820E chipset st art ed shipping.
Feat uring a brand new I CH2 I / O cont roller hub ( i82801BA) , t he new chip set holds:
q Four USB port s using dual cont rollers
q I nt egrat ed LAN cont roller
q Dual Ult ra ATA/ 100 I DE cont rollers
q Dolby surround- capable six- channel audio.
The i820e uses t he same RDRAM Memory Cont roller Hub ( MCH) found on t he original 820.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d12.htm (1 of 3)7/27/2004 4:09:58 AM
An illustrated Guide to the i820 chip set
This indicat es t hat t here will st ill be a maximum of t wo RI MM slot s on t he mot herboards.
However ot her report s ment ion 4 RI MMs
The new I CH2 offers a bandwidt h of 2, 4 MB/ sec across four USB port s. This is a good t hing as
t he ATA/ 100 support is!
The enhanced AC' 97 int erface should support 6 channelsfull surround- sound for DVD Dolby
Digit al audio.
A future for this set?
Please support our
sponsor.
I t is t oo early t o see if t here should be a hope for t he 820E chipset . I f you have read all t he
previous pages, you know about t he t roubles I nt el and millions of users have had wit h t he
I 820 set . We doubt t hat t he market will forget t his.
Our advise should be t o forget 820 and go for t he lat er i815! However, I nt el have planned a
new version, "Camino I I I ", scheduled t o launch early in 2001.
Anot her chipset t o come aft er i820 is t he i850 "Tehama" which is t o be used wit h Pent ium 4.
This is also a RAMBUS- only solut ion, using dual RI MM channels for bet t er bandwidt h.
q Next page
q Previous page
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d12.htm (2 of 3)7/27/2004 4:09:58 AM
An illustrated Guide to the i820 chip set
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read about t he Pent ium in module 3c
Read about t he Pent ium I I ' s et c. in module 3e
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. KarbosGuide. com
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d12.htm (3 of 3)7/27/2004 4:09:58 AM
An illustrated Guide to the i815E chip set
KarbosGuide.com. Module 2d.13a
Intel i815E "Solano"
The cont ent s:
q I nt roduct ion
q The chips in i815
q The feat ures
q Next page
q Previous page
Intro to Intel 815
The I nt el 815/ 815E chipset s from June 2000 are great product s. Aft er all t he t roublesome
affairs wit h i820 it seemed t hat I nt el finally was back in t he chip set business.
I nt el i815/ 815E is an updat e of t he succesfull 810 chip set . I t holds an int egrat ed graphics
adapt er as well as a lot of new funct ions. I t is int ended t o replace t he workhorse BX chip set ,
which is t o be phased out lat e in 2000. I n i815 I nt el finally support s PC133 RAM!
The only t hing I do not underst and is why I nt el come up wit h t wo flavours of t he chip set .
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d13a.htm (1 of 4)7/27/2004 4:10:00 AM
An illustrated Guide to the i815E chip set
The i815E is t he only one, t hey should sell. Why market bot h a fine and a lousy product ?
The chips in i815
Please support our
sponsor.
The chip set is designed using t he same hub- based layout as t he former i810 and i820 chip
set s.
As in i810 we find a memory cont rolling hub wit h int egrat ed graphics ( GMCH: "Graphics and
AGP Memory Cont roller Hub") and an I / O- hub ( t he I CH2) :
q 82815 ( GMCH) 544 Ball Grid Array ( BGA)
q 82801BA ( I CH2) 360 Enhanced Ball Grid Array ( EBGA)
The I CH2 is a chip also used in t he I 820E chipset . Here you see t he t wo chips:
The features
The main idea wit h t he 82815 Graphics and AGP Memory Cont roller Hub ( GMCH) is t o give an
rat her inexpensive mot herboard wit h int egrat ed graphics and high power memory
management . The I CH2 on t he ot her hand is fully updat ed wit h t he lat es improvement s
forming a sophist icat ed I / O hub. Tot ally we see:
q I nt egrat ed VGA graphics
q Up t o 512 MB of PC100 or PC133 SDRAM
q Asynchronous FSB
q ATA/ 100 int erface
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d13a.htm (2 of 4)7/27/2004 4:10:00 AM
An illustrated Guide to the i815E chip set
q Dual USB root hub
The graphics part
We have not t est ed t he chip set . However we were ( cont rary t o many ot hers) very pleased
wit h t he 2D graphics performance of t he i810 chipset . I t works very well, and we expect t he
same t o be t he case wit h t his chip set .
One big improvement has been made compared t o t he i810; you can choose t o disable t he
graphics engine and inst all your own adapt er in t he AGP slot . The chip set also support s TV
out and digit al out for flat panels:
You may choose t o upgrade t he int egrat ed graphics by adding more RAM using a AI MM ( AGP
I nline Memory Module) . However, do not expect t o do 3D- gaming using t he int egrat ed
graphics of i815. Test s shows t hat high- end graphics boards work at 6- 8 t imes speedier t han
t his one!
The enhanced 82801BA I/O Controller Hub (ICH2)
This chips is also found in t he i820E chipset . I t delivers t wice t he I / O bandwidt h as t radit ional
bridge archit ect ure, using an int erlink connect ion t o t he GMCH chip as in i810.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d13a.htm (3 of 4)7/27/2004 4:10:00 AM
An illustrated Guide to the i815E chip set
The t wo USB cont rollers double t he bandwidt h t o 2. 4 MBps across four USB port s.
AC97 audio support s full surround sound wit h up t o 6 channels and a soft modem
implement at ion.
The int egrat ed LAN is used for t hree net working environment s ( 1Mbps, 10/ 100Mbps LAN and
managed 10/ 100Mbps LAN) . This means t hat we do not need an et hernet adapt er, it is all in
t he chipset ! s
ATA/ 100 is a great new int erface giving a not iceable improvement t o disk performance if t he
disk is build t o ATA/ 100. Ot herwise t he int erface is fully downwards compat ible.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read about t he Pent ium in module 3c
Read about t he Pent ium I I ' s et c. in module 3e
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. KarbosGuide. com
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d13a.htm (4 of 4)7/27/2004 4:10:00 AM
An illustrated Guide to the i815E chip set
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 2d.13b
Intel i815E "Solano", continued ...
The cont ent s:
q Asynchronous FSB
q A conclusion
q Next chip set : "Almador"
q Next page
q Previous page
The Asynchronous FSB
A nice new det ail in t he i815E chip set is t hat t he clocks of t he FSB and t he RAM can operat e
independent ly.
This way you can use PC133 RAM t oget her wit h a Celeron wit h it s mere 66 MHz bus:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d13b.htm (1 of 4)7/27/2004 4:10:02 AM
An illustrated Guide to the i815E chip set
You may also reuse old PC100 RAM for a while before updat ing it t o PC133 RAM.
Overclocking
We do not overclock our PCs anymore in t his company. However, looking at t he asynchronit y
of FSB and RAM, it brings int o one' s mind, t hat t his must be very fancy for overclocking.
Wit h a i815- based mot herboard, you can heat up t he FSB wit hout any impact on RAM ( or
PCI ) speed. Wit h proper cooling I am pret t y sure t hat a socket ed Pent ium I I I - 933 CPU will
funct ion at 1. 05 GHz:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d13b.htm (2 of 4)7/27/2004 4:10:02 AM
An illustrated Guide to the i815E chip set
A conclusion
From t he det ails described here, we firmly believe t hat I nt el is on t he right t rack wit h t he
i815 chip set .
The BX set is worn out , and det ails like ATA/ 100 and asynchronous FSB/ RAM will be very
much appreciat ed!
I t appears t hat I nt el have t o do a revision of t he graphics drivers. I n t he first version, no
monit or would work at higher refresh rat e t han 60 Hz, if t he monit or did not have it s driver
inst alled in Windows ! This is complet ely nut s. Oft en a monit or works fine wit h t he st andard
Super VGA driver wit hin Windows .
PC133 RAM is a good product at t he t ime, and t he first t est s show t hat i815 wit h SDRAM
performs bet t er t han i820 wit h RDRAM!
We st rongly hope t hat I nt el will redirect t heir st rat egy int o using DDR in a fut ure revision of
t his chip set ( be it code name "Almador" or what ever) .
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d13b.htm (3 of 4)7/27/2004 4:10:02 AM
An illustrated Guide to the i815E chip set
The "Almador" set
Please support our
sponsor.
The successor t o i815 is codenamed "Almador" ( maybe i817?) . The int erst ing issue is t hat
I nt el has announced support for SDRAM.
Using DDR RAM, I nt el will have a very powerfull plat form for Pent ium I I I . Also t he int egrat ed
3D graphics engine will benefit from t he bet t er RAM bandwidt h.
The sout h bridge of t his set will be t he new I CH3 chip wit h t hese feat ures:
q ATA/ 100
q Six USB port s of version 2. 0
q I nt egrat ed LAN et c. like t he I CH2 of i815.
q Next page
q Previous page
Lear n mor e [ t op]
Read about t he Pent ium in module 3c
Read about t he Pent ium I I ' s et c. in module 3e
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. KarbosGuide. com
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module2d13b.htm (4 of 4)7/27/2004 4:10:02 AM
An illustrated Guide to Monitors and the Video System
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 7a.4
Refreshing the screen image
The cont ent s:
q Elect ronic beams
q High refresh rat e
q The horizont al scan frequency
q Next page
q Previous page
Electronic beams
I n t radit ional CRT monit ors, t he elect ron gun cont inually sends out very precisely aimed beams
of elect rons, moving from pixel t o pixel. The beam act ually flickers, as it sweeps t he screen.
Each dot on t he screen receives a quick flash of elect rons, before t he beam moves on t o t he
next dot . And t he beam int ensit y is varied from dot t o dot .
The phosphor coat ing on t he screen has t he peculiar abilit y t o light up, when hit by elect rons.
But t he light quickly fades away. I n pract ice, t he elect ron beam "visit s" again, before t here is
any visible fading of t he light .
The result is t hat t he it looks t o us as a st eady screen image. But act ually t he pixels of t he
image flickers every t ime t he elect ron beam hit s t he phosphor coat ed dot s.
The screen works overtime
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7a4.htm (1 of 7)7/27/2004 4:10:04 AM
An illustrated Guide to Monitors and the Video System
Typically, each pixel is hit 60, 70, 75, or 80 t imes per second. Thus, t he elect ron gun must
move ext remely fast t o make 18 million or more hit s per second. I f t he image is refreshed 75
t imes per second, we t alk about a refresh rat e of 75 Hz.
The video card issues t he refresh signals, t hus cont rolling t he refresh rat e. Thus, t he video card
has t o mat ch t he monit or, so t he t wo unit s can int erface wit h a suit able elect ronical signal.
Let us t hink of a monit or wit h a resolut ion of 1280 x 1024 and a refresh rat e of 75 Hz. That
requires t he elect ron gun t o make 98 million pixel hit s per second! That screen works at a very
hect ic pace which can somet imes result in beam cont aminat ion.
High refresh rate
Top
The screen image appears more st eady, t he higher t he refresh rat e. You see t he same in TV,
where t radit ional set s have a refresh rat e of only 50 Hz. Some manufact urers now produce TV
set s wit h 100 Hz refresh rat e. Some claim t hat t hey cannot not ice t he difference. However,
once you have been used t o 100 Hz refresh rat e, it is uncomfort able t o ret urn t o 50 Hz.
Similarly wit h PC monit ors, only here we have more opt ions.
Older and inferior screens can only work at 60 Hz, which produces a low qualit y, flickering
image which is not suit able for Windows . The general consensus is t hat 70 Hz produces an
accept able image.
I find 75 Hz accept able, but 80 or 85 Hz may be bet t er when you have t o work many hours
daily in front of t he screen. You have t o t ry t hese rat es t o find t he best on your gear. Not
unoft en 75 Hz is t he best refresh rat e.
Here you see a dump from set t ings of a ATI Radeon graphics cont roller. I t can deliver 11
different refresh rat es ( from 43 Hz t o 160 Hz) in t he t he 1280 x 1024 resolut ion:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7a4.htm (2 of 7)7/27/2004 4:10:04 AM
An illustrated Guide to Monitors and the Video System
Not e: refresh rat e is also called vert ical frequency or vert ical refresh rat e, but I have chosen t o
use t he t erm refresh rat e.
The higher t he refresh rat e, t he bet t er qualit y monit or you need. I f you want bot h high
resolut ion and high refresh rat e, you will need bot h a high qualit y monit or and a high qualit y
video card. The bigger t he screen, t he more it must be able t o produce.
Screens can always run wit h higher refresh rat es in lower resolut ions. Here are t hree examples,
showing how t he screen performance drops wit h resolut ion.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7a4.htm (3 of 7)7/27/2004 4:10:04 AM
An illustrated Guide to Monitors and the Video System
CRT Screen 800 x 600 1024 x 768 1280 x 1024 1600 x 1200
St andard 15" 75 HZ 70 Hz 60 Hz -
15" Trinit ron 90 Hz 80 Hz 75 Hz -
17" Trinit ron 110 Hz 100 Hz 90 Hz 85 Hz
For t he screen t o deliver images at t he desired refresh rat e, bot h screen and video card must be
mat ched t o t he correct specificat ions. Normally t he CRT monit ors have a feat ure called
mult isync. This means, t hat t hey aut omat ically adapt t o t he signal coming from t he video
cont roller.
A good monit or usually is expensive. Cheap monit ors may funct ion at high refresh rat es, but
t he image may not be good. Always check a new monit or visually before buying it .
And please remember: You will have t he monit or for an average of 5 years. I t will serve more
t han one PC, so buy qualit y!
More about screens
Top
Let us t ake a closer look at t he monit ors. I f you read ads for monit ors, you might see many
hard t o underst and t echnical t erms. They may ment ion many frequencies and dot s and pit ch?
Not e: I n many ads, t hese t erms ( frequencies, et c. ) can appear mixed and unclear. Therefore,
be crit ical when you read monit or dat a.
Trinitron or Invar
Top
When we t alk about t radit ional CRT monit ors, t here are t wo primary t ypes of t ubes. The best
use t he so called Trinit ron t ube. That is a t echnological principle, which was pat ent ed by t he
Sony company. Since t he pat ent has expired, t here are now some clones ( ChromaClear,
SonicTron et c. ) .
I n t he Trinit ron screens, t he light sensit ive pixels on t he inside of t he t ube are placed in a
vert ical grid, while t radit ional screens have round masks for t he color dot s. Wit h t he grid mask,
you can achieve denser coverage and t hus more color sat urat ed images. Here is an at t empt t o
illust rat e t he difference bet ween t hose masks:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7a4.htm (4 of 7)7/27/2004 4:10:04 AM
An illustrated Guide to Monitors and the Video System
The Trinit ron screens are generally very high qualit y. Since t he Trinit ron t ube is more expensive
t han t he t radit ional I nvar t ubes, manufact urers also include bet t er cont rol elect ronics in t he
Trinit ron t ubes. That increases t heir price somewhat , but t hat money is well spent !
The only disadvant age of t he Trinit ron ( besides price) is t he t hin lines, which run across t he
screen. They are visible wires, which cont ain a grid. I n daily work, you will not not ice t hem, but
rat her enj oy t he pleasure of an ext remely fine and sharp image.
Invar for contrast
The t radit ional screen can provide more cont rast t han t he Trinit ron screens, which is import ant
in some t echnical applicat ions. But for ordinary use in home and offices, where you would
t ypically choose 17" or 19" screens t he Trinit ron screens are an obvious choice. Of course,
t hey cost a lit t le more t han t radit ional t ypes, but t here is a marked difference in t he visible
qualit y. You will experience a much bet t er screen image wit h a Trinit ron t ube, no doubt about
t hat ! But t he best is a TFT display, as I ' ll show you lat er.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7a4.htm (5 of 7)7/27/2004 4:10:04 AM
An illustrated Guide to Monitors and the Video System
The horizontal scan frequency
Top
The most import ant fact ors are maximum resolut ion and refresh rat e. The screen must be able
t o deliver an image in a suit able resolut ion ( depending on screen size) and at a good refresh
rat e ( 75 Hz or more) . The screen can display many different image t ypes in various
resolut ions and refresh rat es. The int erest ing point is t he maximum refresh rat e at different
resolut ions.
These dat a are oft en report ed t oget her in a number, called t he horizont al scan frequency. The
number is measured in KHz and it is very import ant . Basically, t he horizont al scan frequency is
calculat ed from resolut ion and refresh rat e. As an example, an 800 x 600 resolut ion at 75 Hz
gives a horizont al scan frequency of 60 KHz. You cannot calculat e t he number yourself. Also it
varies slight ly from screen t o screen.
Here are examples of horizont al scan frequency. As I said, t he numbers can vary slight ly from
screen t o screen, but t hey are st ill in t he same ball park:
Resolut ion Refresh rat e Horizont al scan frequency
640 x 480 60 Hz 31. 5 KHz
640 x 480 72 Hz 37. 8 KHz
800 x 600 75 Hz 46. 9 KHz
800 x 600 85 Hz 53. 7 KHz
1024 x 768 75 Hz 60. 0 KHz
1024 x 768 85 Hz 68. 8 KHz
1152 x 864 85 Hz 77. 6 KHz
1280 x1024 75 Hz 80. 0 KHz
1280 x 1024 85 Hz 91. 2 KHz
Ususally you get t he best performance using t he highest refresh rat e available. The resolut ion
depends on screen size and user habit s. I n all cases, it would be foolish t o run t he screen at
31. 5 KHz.
NOTE: Using a digit al int erface for a TFT monit or, t here is no horizont al scan frequency t o
concern about !
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7a4.htm (6 of 7)7/27/2004 4:10:04 AM
An illustrated Guide to Monitors and the Video System
q Next page
q Previous page
To learn more Top
Read about video cards in Module 7b .
Read about sound cards in Module 7c .
Read about digit al sound and music in Module 7d .
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7a4.htm (7 of 7)7/27/2004 4:10:04 AM
An illustrated Guide to Monitors and the Video System
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 7a.5
Adjusting the monitor
The cont ent s:
q Mult i Sync
q Color adj ust ment s
q Screen savers
q Environment al st andards
q Next page
q Previous page
The multisync screen with digital control
Top
All modern screens are of t he mult isync t ype. This means, t hat t he screen adj ust s it self t o t he
signals received. The individual model has a minimum and maximum horizont al scan
frequency. As long as t he signals are received wit hin t hat spect rum, it adj ust s it self t o t he
signals.
When t he screen receives signals at any given frequency, t hese signals must be adj ust ed t o
fill t he screen 100%. That is done t hrough t he digit al cont roller found in modern screens.
Older screens would show a clear black border surrounding t he image, whenever t he
resolut ion was changed t o, let s say 800 x 600 and t hat is very irrit at ing.
To enable adj ust ment t o maximum screen ut ilizat ion, t he screen must have digit al cont rols
elect ronics. These adj ust ment s are made on t he screen cont rol panel. We are t alking about :
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7a5.htm (1 of 5)7/27/2004 4:10:07 AM
An illustrated Guide to Monitors and the Video System
q Horizont al and vert ical size, t o have t he image fill t he maximum usable screen area.
q Horizont al and vert ical posit ioning, t o cent er t he image.
q Compensat ion for t rapezoid and pin cushioning.
q Colors and light int ensit y.
The adj ust ment s can look like t his:
Adj ust ment s Sy mbol s
Hor i zont al
and ver t i cal posi t i on
Hor i zont al
and ver t i cal si ze
Tr apezoi d
and pi n cushi oni ng
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7a5.htm (2 of 5)7/27/2004 4:10:07 AM
An illustrated Guide to Monitors and the Video System
Oft en screens are preset t o a choice of different possible adj ust ment s. I n t hese preset
condit ions, t he image will immediat ely appear perfect .
However, when you set up a monit or t o work under non preset condit ions you have t o adj ust
t he image yourself. Once t hat is done t he monit or will remember your set t ings.
There are no int ernat ional st andards for t he design of t hese digit al cont rollers. They are quit e
different from monit or t o monit or and not all easy t o work wit h. However, working wit h
adj ust ment s is a minor problem, relat ive t o ot her monit or qualit ies.
Color adjustments
Top
The screen can show t he colors in different heat ranges. The bet t er screens wit h digit al
cont rollers usually have at least t wo t emperat ure ranges t o choose from. I prefer 6500
degrees. 9300 is somewhat colder.
Similarly, some video cards can adj ust t he screen color t emperat ure like Mat rox here:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7a5.htm (3 of 5)7/27/2004 4:10:07 AM
An illustrated Guide to Monitors and the Video System
You should t ry t he different color t emperat ures. They have a significant effect on t he image
appearance.
Aperture grill pitch
Top
Oft en you see t he t erm dot pit ch or apert ure grill pit ch. I t is measured in millimet ers. The
numbers indicat e t he average dist ance bet ween individual screen dot s. The smaller t he
bet t er. That provides a finer grain screen. For large CRT monit ors ( 21") , t he dot pit ch can be
0. 31 mm or 0. 28 mm.
Ot herwise, a dot pit ch of 0. 28 mm or 0. 25 mm is considered sufficient ly good for ordinary
15" and 17" screens. A few monit ors offer 0. 22 mm dot pit ch.
Screen savers
Top
Early monit ors had low qualit y phosphor coat ings. That could cause a screen image t o "burn-
in" if left unat t ended. You could clearly see t hat in work places, where t he PC was used for
only one program. That program image remained clearly on t he screen, aft er t he PC was shut
down.
That led t o screen savers. I n my recollect ion, Nort on' s Commander was one of t he first of t his
kind. Aft er a select ed number of minut es wit hout act ivit y, t he screen swit ches t o moving
st ars, as if you were flying t hrough space. This prevent s t he regular image from burning in.
CRT monit ors have improved a lot since t hen - t he screen image will not "burn in" in a
modern CRT. At t he same t ime, screen savers have developed int o an art form of t heir own.
Windows is born wit h a number of choices in screen savers. Also, many programs include a
screen saver or t wo as an ext ra feat ure . Some provide a series of images, such as "celebrit y
cars, " showing movie celebrit ies wit h t heir fancy cars.
Use t he screen savers. They can spice up day- t o- day work. And please always use a screen
saver wit h your TFT monit or!
Environmental standards
Top
Screen radiat ion is a pollut ant . There is no concret e evidence t hat screen radiat ion can cause
illness. However, art ificially generat ed radiat ion must be unwelcome in our environment .
Consequent ly, indust ry st andards have been developed for accept able radiat ion levels.
Since t he early ninet ies, t he Swedish MPR- 2 st andard est ablished limit s for monit or
elect rost at ic radiat ion.
Since t hen came t he st rict er TCO- 92. I t limit s t he permit t ed amount of low level radiat ion and
est ablishes st andards for elect rical and fire safet y. Usually TCO means Tot al Cost of
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7a5.htm (4 of 5)7/27/2004 4:10:07 AM
An illustrated Guide to Monitors and the Video System
Ownership but here it refers t o t he Swedish Confederat ion of Professional Employees
( Tj nst mnnens Cent ral Organisat ion) . They defined st rong st andards for emissions.
Finally, we have TCO- 95, which is t he st rict est st andard. Similar t o TCO- 92, it also includes
regulat ions on ergonomics ( including refresh rat es) , maximum energy consumpt ion,
environment ally friendly product ion and recycling facilit ies. The best screens comply wit h t his
st andard. Screens adhering t o t he TCO st andards are more expensive. Obviously since t hey
are bet t er screens.
The flat TFT screens do not emit any radiat ion at all and t hey consume considerably less
energy t han t he radiat ing screens. This is anot her indicat ion t hat TFT may be t he st andard
screen of t he fut ure.
The VESA DPMS syst em is an energy saving t echnology, which includes bot h screen and
video card. A modern 17 screen consumes about 100 wat t in normal use. Wit h DPMS t he
screen swit ches t o t wo energy saving modes. First , power consumpt ion drops t o 25 wat t s and
finally again drops t o 8 wat t .
q Next page
q Previous page
To learn more
Top
Read about sound cards in Module 7c.
Read about digit al sound and music in Module 7d .
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7a5.htm (5 of 5)7/27/2004 4:10:07 AM
An illustrated Guide to Monitors and the Video System
Please click t he banners t o support our work!
KarbosGuide.com. Module 7a.6
The flat panel monitors
The cont ent s:
q I nt roduct ion t o flat panel monit ors
q Eye Ergonomics
q The Digit al I nt erface
q Next Generat ion Monit ors?
q Next page
q Previous page
The Digital Flat Panel Monitors
Top
The big, heavy t radit ional CRT monit ors will event ually be phased out . To day we see t hem replaced by t he
flat andLCD ( Liquid Cryst al Display) monit ors, also known from labt ops.
I t may be a few years before t his t echnology will be dominat ing, but it is bound t o happen. The t he flat
panel monit ors are excellent , and t hey are available; t he prices have gone down. Today a 17. 3" LCD cost s
as much as a 21" CRT monit or did 4 years ago.
The LCD screen is flat , since it cont ains no cat hode ray t ube ( CRT) . I nst ead t he screen image is generat ed
on a flat plast ic disk, where millions of t ransist ors creat e t he pixels.
Here you see a Siemens Nixdorf 3501T. I t was my first TFT monit or ( from 1997) , and it produces a sharp
high resolut ion image - bet t er t han any ot her I had ever seen:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7a6.htm (1 of 9)7/27/2004 4:10:10 AM
An illustrated Guide to Monitors and the Video System
Eye Ergonomics
Top
The digit al flat panel monit ors are also called "soft " screens, since t heir images seems t o have a "soft er"
qualit y t han t hose from t radit ional CRT monit ors. The image does not flicker t hus causing less eye st rain.
People, like myself, who have become accust omed t o t hese soft images will not ret urn t o t he t radit ional
monit ors. I cannot express t his wit h enough emphasis: The flat display is t he best monit or available. I t is so
good t o your eyes!
Modern research has shown t hat a st eadily illuminat ed screen image is a very import ant element in a good
work environment . The eye responds t o all light impressions, and t he brain int erpret s all light impressions
cont inually. When a mediocre monit or flickers, t he brain will cont inually receive superfluous light
impressions "noise" t o sort out . Thus t he brain works permanent overt ime int erpret ing t he screen flicker.
No wonder t hat people get t ired from wat ching t heir monit ors.
At t he same t ime t he LCD screen is by far t he most environment ally safe product . These flat screens emit
zero radiat ion, and t hey consume significant ly less power t han t he t radit ional monit ors. Anot her reason t o
expect LCD screens t o become t he monit ors of t he fut ure.
No refresh rate
A big advant age in t he LCD screen is t hat it does not flicker. Tradit ional CRT monit ors flicker all t he t ime
which is not ideal. Of course t he best CRT monit ors have a high refresh rat e ( 85 Hz or more) , which
provides a very st able image wit h no not iceable flicker. But t he LCD screen does not flicker at all ( when
digit ally connect ed) . They have a refresh rat e of 0 Hz!
Please not ice t hat looking at LCD displays, you may read informat ion like:
q Pixel Frequency 65MHz
q Horizont al 30 ~ 50KHz
q Vert ical: 55 ~ 70Hz
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7a6.htm (2 of 9)7/27/2004 4:10:10 AM
An illustrated Guide to Monitors and the Video System
This indicat es t hat t here is a refresh rat e. There is, but it is only working when t he screen image is
changing. So if you move a window across t he screen, t he changes will be updat ed wit h a refresh rat e of 60
Hz or what ever you choose.
To many users t his does not really mat t er; using Office programs, most of t he t ime t he screen image does
not change, hence it does not flicker. Obviously it is a problem if you expect t o use your flat panel monit or
t o show full mot ion videos or games.
The digital interface
Top
The most import ant t hing about t he flat panel monit or is t hat it is connect ed t o a digit al graphics port .
Unfort unat ely, t his is not always t he case.
Back in 1997, when I got my first flat panel monit or ( t he Siemens 3501T ment ioned above) it was only
available wit h a ( t ot al propriet ary) digit al graphics adapt er. This was a 1st generat ion flat panel monit or.
Lat er t he manufact ures found out t o add an analog port in t he displays. This way people could buy a flat
panel monit or and reuse t heir exixt ing graphics adapt er. I t is a market ing st unt , which should not be
followed!
The only way t o benefit from a flat panel monit or is t o feed it digit ally.
Our latest monitor
I n spring 2001 I bought a new flat panel monit or; it is a Dell model 1701FP. A nice 17. 3" monit or, which I
paid around $900 for ( t he price have decreased lat er) . The monit or holds bot h an analog ( VGA- ) port and a
digit al port ( DVI ) .
A 17. 3" flat panel monit or has a visible area much bigger t han t hat from a t radit ional 17" CRT monit or - you
can compare it t o a 19" CRT. The 17. 3 inches is t he visible diamet er.
I was t old, t hat it should work fine using t he analog port wit h my exist ing Mat rox G400 graphics cont roller.
The manual emphased t hat one should use t he 60Hz mode. I inst alled t he hardware, and it worked fine.
Only t he image was t errible! I t was flickering and very unsharp, kind of "dirt y".
The weird t hing is, t hat t he Dell manual holds almost not hing on t hese issues. But t hrough t est ing we found
out t hat t he 75 Hz analog mode was t he best possible. But it was not sat isfact ory, not at all. Having paid
quit e a lot of money, we decided t o go for a digit al graphigs cont roller. We found an ATI Radeon VE, which
t urned out t o be a great card at a reasonable price:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7a6.htm (3 of 9)7/27/2004 4:10:10 AM
An illustrated Guide to Monitors and the Video System
From t he box, t he product seems t o be aimed gamers. To t hose I am sure, t hat t he RADEON chipset and
t he 32 MB of DDR RAM is fine. To us, t he very import ant issue was, t hat t here is a DVI connect or on t he
board:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7a6.htm (4 of 9)7/27/2004 4:10:10 AM
An illustrated Guide to Monitors and the Video System
Wit h t he DVI connect or in use, t he DELL flat panel monit or works absolut ely perfect ly. Thinking about it , it
is incredible, t hat t he company does not t ell t his in t he manual. Wit h digit al int erface t he image is ext remely
sharp and complet ely flicker free.
A flat panel monit or is digit al by nat ure. There is no analog elect ronics included, and t hat is t he big
advant age of t his t echnology. Hence, t he monit or should not be connect ed t hrough an analog int erface. I n
fact , using t he analog int erface, you get t o conversions, which bot h add noise t o t he final image. First t he
graphics adapt er has t o convert t he digit al dat a of t he PC t o analog elect ronical signals. Then t hese analog
signals have t o be convert ed back t il digit al informat ion t o feed t he display.
Using t he digit al int erface, each pixel consist s of t hree t ransist ors, which each is mapped t o t he
corresponding memory cell holding t he image info. A purely digit al t o digit al t ransmission wit h no
elect ronical noise involved - t hat is t he way t o produce a st unning image!
Here you see an illust rat ion of t he differences bet ween t he t wo set ups:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7a6.htm (5 of 9)7/27/2004 4:10:10 AM
An illustrated Guide to Monitors and the Video System
The A/ D ( analog t o digit al, t he RAMDAC of t he video card) and D/ A ( digit al t o analog) conversions only
reduce image qualit y on a flat panal monit or - not hing else! Hence, t he digit al int erface by- pass t he
RAMDAC of t he graphics cont roller:
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7a6.htm (6 of 9)7/27/2004 4:10:10 AM
An illustrated Guide to Monitors and the Video System
Panel Quality
I t is difficult t o produce a flat panel display wit hout flaws. Most panels sold have a few defect pixels, where
one or more t ransist ors are gone.
The bigger t he panel get s, t he more flaws you find ( due t o t he increasing number of t ransist ors) . This helps
keeping up t he prices - t he manufact ures have t o t hrow away a large percant age of t he product ion - you
cannot repair flawed pixels.
All vendors have some kind of qualit y policy in t his area. Some only accept up t o 3 or 5 pixel flaws per
panel. Ot hers accept up t o 15, if t hey are not sit uat ed in t he middle of t he display. When you buy a flat
panel display you should make sure t hat you can ret urn it if t he number of pixel- flaws is t o big. This can be
hard t o achieve.
I n t he summer 2001, a German survey showed t hat some vendors t ake advant age of t he consumers
ignorance in t his area. More t han 30% of t he flat panel monit ors were of second range qualit y and should
not have been brought t o t he shops. Obviously it has been t empt ing t o some companies t o sell some of t he
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7a6.htm (7 of 9)7/27/2004 4:10:10 AM
An illustrated Guide to Monitors and the Video System
displays, which should have been dismissed.
Screen savers
Using a LCD display, you should remember t o inst all t he Windows screen saver. I use "Black screen" aft er 5
minut es. Like in t he "old days", t he monit or may get damaged from longer periods of showing t he same
image.
Next Generation Monitors?
Top
The monit or t echnology is advancing very rapidly. An int erest ing development comes from a Brit ish
invent ion LEP - Light Emit t ing Plast ic . I t is an ordinary t hin, flexible plast ic ( polymer) , which is sandwiched
t oget her wit h a t hin film of indium t in oxide and aluminum. Thin- film t ransist ors cont rol t he oxide layer,
causing t he huge plast ic polymer molecules t o become light emit t ing.
These LEP screens should have t hese advant ages:
q They are complet ely flat and light weight .
q They consume only small amount s of elect ric power.
q They do not require background illuminat ion, which t he LCD cryst als do.
q They emit light , which is visible from all angles of view.
These screens was expect ed t o be available in year 2002/ 2003, but lat ely t here have been no much
indicat ion t hat t hey will come. Current ly work is being done wit h prot ot ypes, which have a resolut ion of 200
dpi. That corresponds t o a resolut ion of 2200 X 1600 pixels in a 15" screen. So maybe we can look forward
t o an ext remely high screen resolut ion.
I would like t o fant asize about fut ure Coca- Cola bot t les wit h a built - in video display in t he plast ic bot t le! By
t he way, t hese polymer plast ic mat erials are finding t heir way int o ot her part s of t he dat a processing
t echnology. Work is being done on developing different st orage media, hard disks in t erabyt es size and RAM
modules based on polymers. These "organic" st orage media should also be significant ly cheaper t o produce
t hat t he t radit ional product s.
See Cambridge Display Technology web .
q Next page
q Previous page
To learn more
Top
Read about sound cards in Module 7c.
Read about digit al sound and music in Module 7d .
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7a6.htm (8 of 9)7/27/2004 4:10:10 AM
An illustrated Guide to Monitors and the Video System
[ Main page] [ Cont act ] [ Karbo' s Dict ionary] [ The Soft ware Guides]
Copyright ( c) 1996- 2001 by Michael B. Karbo. www. karbosguide. com.
http://www.karbosguide.com/hardware/module7a6.htm (9 of 9)7/27/2004 4:10:10 AM
Karbo's Dictionary.
Karbo's Dictionary. Please choose a letter:
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X -
Click Here
http://www.karbosguide.com/dictionary/index.htm7/27/2004 4:10:11 AM
You might also like
- Apple Laptop Computer - Repair Video TutorialDocument3 pagesApple Laptop Computer - Repair Video TutorialAkhlaq HussainNo ratings yet
- Laptop Chip Level Course PDFDocument2 pagesLaptop Chip Level Course PDFMukesh YadavNo ratings yet
- COM216 Week2Document8 pagesCOM216 Week2Suopriye Hart100% (1)
- Toner Refilling CourseDocument5 pagesToner Refilling CourseKailash KandiyalNo ratings yet
- Computer - Hardware - Diagnosing & Fixing Motherboard FaultsDocument4 pagesComputer - Hardware - Diagnosing & Fixing Motherboard Faultsscribdraza786No ratings yet
- Easy Technical Guide To Understand PC Motherboard, Troubleshoot Problems and Its Repair: PART - IIIDocument3 pagesEasy Technical Guide To Understand PC Motherboard, Troubleshoot Problems and Its Repair: PART - IIIAnonymous lPvvgiQjRNo ratings yet
- Hardware and Networking Course - Dead Problem Trouble ShootingDocument15 pagesHardware and Networking Course - Dead Problem Trouble ShootingCreative Laptop SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Computer Repair Student Part.1 (DOS)Document52 pagesComputer Repair Student Part.1 (DOS)Hendra Nugraha100% (2)
- Bios Motherboard TroubleshootingDocument14 pagesBios Motherboard TroubleshootingAfdoal Al Bimani50% (2)
- The PC Doctor's Fix-It-Yourself GuideDocument370 pagesThe PC Doctor's Fix-It-Yourself GuideS'peed100% (1)
- Dictionary For Phone RepairingDocument104 pagesDictionary For Phone RepairingJean Paul Muvara Kabiligi100% (1)
- LCD Panel Basic ConceptsDocument16 pagesLCD Panel Basic ConceptsshafiuddinkagziNo ratings yet
- TV SamsungDocument88 pagesTV Samsunggledyson gueNo ratings yet
- Electronic ComponentsDocument385 pagesElectronic ComponentsSeaworks Company67% (3)
- PC Troubleshooting Tips #2Document10 pagesPC Troubleshooting Tips #2Roger EmbalsadoNo ratings yet
- Apple Ipad Take Apart GuideDocument2 pagesApple Ipad Take Apart GuideАлександрNo ratings yet
- Laptop ShemaDocument104 pagesLaptop ShemamustapmaNo ratings yet
- Hard Ware Note BookDocument22 pagesHard Ware Note BookSrini VasuluNo ratings yet
- Multifunction Peripherals for PCs: Technology, Troubleshooting and RepairFrom EverandMultifunction Peripherals for PCs: Technology, Troubleshooting and RepairNo ratings yet
- DFL WD Cracked PDFDocument2 pagesDFL WD Cracked PDFRaj KishoreNo ratings yet
- Eight Steps To Successful Troubleshooting: Step 1. Identify The Exact IssueDocument8 pagesEight Steps To Successful Troubleshooting: Step 1. Identify The Exact IssueabebeNo ratings yet
- How To Check Battery of A Cell Phone With Multimeter in 2021Document7 pagesHow To Check Battery of A Cell Phone With Multimeter in 2021ชยุต ธรรมรัตน์No ratings yet
- Computer Hardware Servicing Basic Computer Troubleshooting GuideDocument4 pagesComputer Hardware Servicing Basic Computer Troubleshooting Guidejanray1988No ratings yet
- Electronic Schematic DiagramDocument28 pagesElectronic Schematic DiagramnureyzzNo ratings yet
- Apple 27 LED Display Manual ServiceDocument117 pagesApple 27 LED Display Manual ServiceWaqass0% (1)
- Samsung Galaxy S4 Mini GT-I9195 - Schematic DiagarmDocument135 pagesSamsung Galaxy S4 Mini GT-I9195 - Schematic DiagarmFernando OrdóñezNo ratings yet
- ST2132 Mobile Phone TrainerDocument84 pagesST2132 Mobile Phone TrainerKhan RockyNo ratings yet
- How To Bypass or Remove A BIOS PasswordDocument3 pagesHow To Bypass or Remove A BIOS Passwordeu5okNo ratings yet
- Saleem Hardware Notes 5Document40 pagesSaleem Hardware Notes 5Prince Saleem91% (11)
- Computer Hardware Repairing Institute - Computer Hardware Repairing InstituteDocument4 pagesComputer Hardware Repairing Institute - Computer Hardware Repairing Institutesahil kumarNo ratings yet
- INAND e MMC 4 41 If Data Sheet v1 0Document29 pagesINAND e MMC 4 41 If Data Sheet v1 0ntc_mobileNo ratings yet
- Computer Repair With Diagnostic FlowchartsDocument17 pagesComputer Repair With Diagnostic FlowchartsOpin NetNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Components... CSEDocument28 pagesMotherboard Components... CSEAtulay Mahajan50% (2)
- Motherboard Flow Chart TroubleshootingDocument1 pageMotherboard Flow Chart TroubleshootingKubeta AkihiroNo ratings yet
- APC UPS RepairedDocument6 pagesAPC UPS Repairedcarlos16702014No ratings yet
- Laptop Components IdentifyDocument4 pagesLaptop Components IdentifyTanishsadan ANo ratings yet
- Computer Monitor RepairDocument53 pagesComputer Monitor RepairraveensanjeewaNo ratings yet
- Components of LaptopDocument7 pagesComponents of LaptopMa Michelle Nica DmNo ratings yet
- BGA Rework - Hand Soldering - IPC CertificationDocument10 pagesBGA Rework - Hand Soldering - IPC CertificationKaty RadcliffNo ratings yet
- Computer HardwareDocument75 pagesComputer HardwareIfLah IToo100% (1)
- Card Level Laptop DesktopDocument2 pagesCard Level Laptop DesktopJawad Anwar100% (1)
- Components of System UnitDocument8 pagesComponents of System UnitIvan Louie Cruto100% (1)
- Basic Electronics - College Algebra Course ManualDocument157 pagesBasic Electronics - College Algebra Course ManualJed Tedor100% (10)
- Troubleshooting Common Laptop Problem1Document41 pagesTroubleshooting Common Laptop Problem1Teddy Worku100% (2)
- Common Windows Error Codes and How To Fix Them!Document10 pagesCommon Windows Error Codes and How To Fix Them!Md. ROman MiahNo ratings yet
- Determine If Your Motherboard Is DeadDocument8 pagesDetermine If Your Motherboard Is DeadSasi DharanNo ratings yet
- Computer Support Technician: Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandComputer Support Technician: Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Simple iOS Troubleshooting: A Guide to the Most Common Issues with the iPhone, iPad and iPod TouchFrom EverandSimple iOS Troubleshooting: A Guide to the Most Common Issues with the iPhone, iPad and iPod TouchNo ratings yet
- Linux Kernel A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandLinux Kernel A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- How To Recover Deleted Files: Your Step-By-Step Guide To Recovering Deleted FilesFrom EverandHow To Recover Deleted Files: Your Step-By-Step Guide To Recovering Deleted FilesNo ratings yet