Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nitroglycerin
Uploaded by
Vain VanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nitroglycerin
Uploaded by
Vain VanCopyright:
Available Formats
Cardiac Medication
Nitroglycerine
Nitroglycerin (Nitrostat)
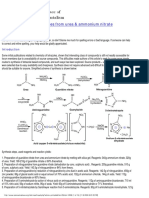
Type: Vasodilator Mechanism of Action (What the drug does in the body): Nitroglycerin dilates both arteries and veins, but it has a more pronounced effect on the venous side. By increasing the venous capacitance the preload is reduced, which serves to decrease the work of the heart. A decrease in the arteries results in a decreased afterload further reducing the workload. Nitroglycerin may also produce coronary vasodilation in arteries that are not significantly calcified. Pain relief during an acute myocardial infarction (AMI) is due to the reduced workloadnot by directly acting on pain receptors. Indications (When to give the drug):
Cardiac Medication Chest pain secondary to angina or AMI Pulmonary edema Contraindications (When not to give the drug): Viagra use within 24 hours Hypotension (systolic <90 mm/Hg) Increased intracranial pressure
Nitroglycerine
Side Effects (Undesirable things that happen in addition to the therapeutic benefit): Reflex tachycardia Flushing Dizziness Supplied: Tablet or spray 0.4 mg per dose (1/150th of a grain) Precautions: Nitroglycerin is inactivated by heat, light air and moisture and must be stored in a brown bottle or opaque metered spray device The shelf life is 3 months after opening the bottle Alcohol increases the vasodilation associated with nitroglycerin. Be alert for the development of hypotension and treat accordingly. Dosage and Route: Adults: 1 tablet or spray sublingually. May be repeated in 3 5 minutes to a maximum of 3 doses. Headache
Nausea/Vomiting
You might also like
- Dragon Fireworks 2008Document5 pagesDragon Fireworks 2008leachuaNo ratings yet
- Standard Flash, Concussion, Concussion XL, Super Sparkle Silver, Super Sparkle Gold Instructions For Use WARNING! Not For Consumer UseDocument1 pageStandard Flash, Concussion, Concussion XL, Super Sparkle Silver, Super Sparkle Gold Instructions For Use WARNING! Not For Consumer UseWayne LundNo ratings yet
- Charge Block Demolition TNTDocument1 pageCharge Block Demolition TNTBlentica FlajicNo ratings yet
- Intro25MM Pneumatic Sniper RifleDocument63 pagesIntro25MM Pneumatic Sniper Riflezaion08No ratings yet
- HMTDDocument2 pagesHMTDIain Chilliemeister KingNo ratings yet
- Electric Detonators: N I S ABDocument9 pagesElectric Detonators: N I S ABDinoYancachajllaNo ratings yet
- Pentaerythritol TetranitrateDocument8 pagesPentaerythritol TetranitrateFrancesco Maniscalco100% (1)
- Lovex Reloading GuideDocument56 pagesLovex Reloading GuideDavid LegatNo ratings yet
- Strobe StarsDocument3 pagesStrobe StarsMuthu KumarNo ratings yet
- Chlorate Explosives Tenney DavisDocument9 pagesChlorate Explosives Tenney DavisDoug OlsonNo ratings yet
- High Explosives Index PDFDocument9 pagesHigh Explosives Index PDFCivil WarNo ratings yet
- Explosives 2Document90 pagesExplosives 2ROBERT100% (1)
- Flash PowderDocument2 pagesFlash Powderelvergonzalez1No ratings yet
- ExeplosiveDocument11 pagesExeplosivekamalNo ratings yet
- Triacetone Triperoxide (TATP)Document1 pageTriacetone Triperoxide (TATP)Beaune V. VillarazaNo ratings yet
- Explosive Materials: Composition C4 (Plastic Explosives)Document4 pagesExplosive Materials: Composition C4 (Plastic Explosives)GerbenNo ratings yet
- General, Organic, and Improvised Chemistry Page 3 PDFDocument117 pagesGeneral, Organic, and Improvised Chemistry Page 3 PDFCivil WarNo ratings yet
- Smoke ScreensDocument3 pagesSmoke ScreensGaryoNo ratings yet
- Ammonium Nitrate Explosives For CivilDocument6 pagesAmmonium Nitrate Explosives For CivilIvan Katchanovski falsifier100% (1)
- TNT Equivalents For Various Explosives and Fuel-Air MixturesDocument1 pageTNT Equivalents For Various Explosives and Fuel-Air MixturesMallamaxNo ratings yet
- TrinitroanisolDocument2 pagesTrinitroanisolsilviaNo ratings yet
- Explosive Plastic PHF-89 Technical DataDocument2 pagesExplosive Plastic PHF-89 Technical DatahorscriNo ratings yet
- Picric AcidDocument3 pagesPicric Acidashokrann0% (1)
- The Trouble With TNT EquivalenceDocument25 pagesThe Trouble With TNT Equivalencepamos1111No ratings yet
- Elek Tro Detonator I EngDocument3 pagesElek Tro Detonator I Engnilton cardonaNo ratings yet
- Easy To Make and Safer To Breathe NapalmDocument8 pagesEasy To Make and Safer To Breathe NapalmjumpupdnbdjNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen TriiodideDocument8 pagesNitrogen Triiodidesharklaser009No ratings yet
- Homemade Smoke Bomb RecipeDocument2 pagesHomemade Smoke Bomb RecipeMax FrielNo ratings yet
- Synthetic Tetrazole Route from Ammonium NitrateDocument16 pagesSynthetic Tetrazole Route from Ammonium Nitratehaker10100101100% (1)
- Chemistry - How To Make TNTDocument1 pageChemistry - How To Make TNTKarthik ChallaNo ratings yet
- BB003 Parts ListingDocument9 pagesBB003 Parts ListingKeetykatNo ratings yet
- Koch-2008-Propellants, Explosives, Pyrotechnics PDFDocument12 pagesKoch-2008-Propellants, Explosives, Pyrotechnics PDFmien nam100% (1)
- Expedient Antibiotics ProductionDocument213 pagesExpedient Antibiotics ProductionJames Gray100% (1)
- Pyrotechnic Chemical ListingDocument11 pagesPyrotechnic Chemical Listingjesse1361No ratings yet
- Sparkler Composition GuideDocument3 pagesSparkler Composition GuideMuthu KumarNo ratings yet
- 6in White Elephant Pattern ShellDocument2 pages6in White Elephant Pattern Shellkrstas774No ratings yet
- Basic Guide To Explosives.Document8 pagesBasic Guide To Explosives.Seng BoucherNo ratings yet
- NitrocelluloseDocument2 pagesNitrocelluloseRomel LeoNo ratings yet
- Towards The Miniaturization of Explosive Technology: University of Illinois, Urbana, IL 61801, USADocument13 pagesTowards The Miniaturization of Explosive Technology: University of Illinois, Urbana, IL 61801, USAtempest2sNo ratings yet
- FentanylDocument2 pagesFentanylMulayam Singh YadavNo ratings yet
- How to Make a Smoke Bomb at HomeDocument4 pagesHow to Make a Smoke Bomb at HomeMurali Krishna GbNo ratings yet
- Homemade Lead AcetateDocument2 pagesHomemade Lead AcetatetrupinaNo ratings yet
- Explosives-Whistles - Pyrotechnica XIDocument6 pagesExplosives-Whistles - Pyrotechnica XIhwelch5792No ratings yet
- Chemical reactions that release energy quicklyDocument35 pagesChemical reactions that release energy quicklyChetan SuranaNo ratings yet
- CHE132 CPI REPORT ON EXPLOSIVES, PROPELLANTS AND TOXIC CHEMICAL AGENTSDocument9 pagesCHE132 CPI REPORT ON EXPLOSIVES, PROPELLANTS AND TOXIC CHEMICAL AGENTSEunice Flores100% (1)
- Effect of Shaped Charge Liner Surface Finish on Jet Break-UpDocument10 pagesEffect of Shaped Charge Liner Surface Finish on Jet Break-Upwarrior_2008No ratings yet
- Thermite ReactionDocument4 pagesThermite ReactionRenato BenintendiNo ratings yet
- Explosives & PropellantsDocument18 pagesExplosives & PropellantsLatasha Ameen100% (1)
- Semiautomatic Rifle SharacDocument3 pagesSemiautomatic Rifle SharacOlegValNo ratings yet
- TNP Synthese23Document10 pagesTNP Synthese23singhns16100% (1)
- Tipes of BulletsDocument5 pagesTipes of BulletslisandropelNo ratings yet
- Potassium Chlorate SynthesisDocument3 pagesPotassium Chlorate SynthesisJohn RhodesNo ratings yet
- Explosives PDFDocument9 pagesExplosives PDFuttamksrNo ratings yet
- Cheap Way To Prepare Betaine Explosives (: Required ChemicalsDocument4 pagesCheap Way To Prepare Betaine Explosives (: Required Chemicalsasdsa asdsdNo ratings yet
- PyroData - Pyrotechnics data for your hobbyDocument2 pagesPyroData - Pyrotechnics data for your hobbyProvat mondalNo ratings yet
- Hints on the Use and Handling of Firearms Generally, and the Revolver in ParticularFrom EverandHints on the Use and Handling of Firearms Generally, and the Revolver in ParticularRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Anti - Anginal MedicationDocument41 pagesAnti - Anginal MedicationShine StephenNo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives: 1. Relationship Between High Blood Glucose and HyperlipidemiaDocument12 pagesLearning Objectives: 1. Relationship Between High Blood Glucose and HyperlipidemiaDiedreNo ratings yet
- Nitroglycerin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesNitroglycerin Drug StudyNasrah N. Musa100% (6)