Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biodiesel
Biodiesel
Uploaded by
Arun MalviyaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biodiesel
Biodiesel
Uploaded by
Arun MalviyaCopyright:
Available Formats
Biodiesel
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This article is about transesterified lipids. For hydrogenated alkane renewable diesel, see Vegetable oil refining. For biomass and organic waste-to-fuel production, seeBiomass to liquid. For unmodified vegetable oil used as motor fuel, see Vegetable oil used as fuel.
Bus run by biodiesel Space-filling model of methyl linoleate, or linoleic acid methyl ester, a common methyl ester produced from soybean or canola oil and methanol Space-filling model of ethyl stearate, or stearic acid ethyl ester, an ethyl ester produced from soybean or canola oil and ethanol
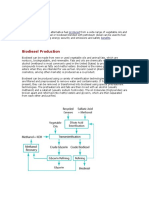
Biodiesel refers to a vegetable oil- or animal fat-based diesel fuel consisting of long-chainalkyl (methyl, propyl or ethyl) esters. Biodiesel is typically made by chemically reacting lipids(e.g., vegetable oil, animal fat (tallow)) with analcohol producing fatty acid esters. Biodiesel is meant to be used in standard diesel engines and is thus distinct from the vegetable and waste oils used to fuelconverted diesel engines. Biodiesel can be used alone, or blended with petrodiesel. Biodiesel can also be used as a low carbon alternative to heating oil. The National Biodiesel Board (USA) also has a technical definition of "biodiesel" as a mono-alkyl ester.[1]
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biodiesel
You might also like
- Data Biodiesel PosterDocument4 pagesData Biodiesel PosterAnonymous 2WwOlzfuyNo ratings yet
- What's The Difference Between Biodiesel and Renewable (Green) DieselDocument14 pagesWhat's The Difference Between Biodiesel and Renewable (Green) DieselRobert GilmoreNo ratings yet
- BiodiesalDocument2 pagesBiodiesalfleur99No ratings yet
- What Is BiodieselDocument3 pagesWhat Is BiodieselErlynne Carla SantosNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document20 pagesPresentation 2Kerolos RafeekNo ratings yet
- Biodiesel Refers To A Vegetable Oil-Or Animal Fat-Based Diesel Fuel Consisting of Long-Chain AlkylDocument12 pagesBiodiesel Refers To A Vegetable Oil-Or Animal Fat-Based Diesel Fuel Consisting of Long-Chain AlkylClaroslava FrancoNo ratings yet
- Biodiesel Methyl EsterDocument10 pagesBiodiesel Methyl EsterCiobanu MihaiNo ratings yet
- Biodiesel Definition of BiodieselDocument3 pagesBiodiesel Definition of BiodieselSivakumar AsokanNo ratings yet
- Abishek Thirumal (Dace) - Bio DieselDocument14 pagesAbishek Thirumal (Dace) - Bio Dieselஉலகலாவிய தமிழன்No ratings yet
- Biodiesel Production Principles and Processes: Oil + Alcohol Biodiesel + GlycerinDocument2 pagesBiodiesel Production Principles and Processes: Oil + Alcohol Biodiesel + GlycerinGabriel ArghiriadeNo ratings yet
- Bio DieselDocument12 pagesBio DieselMahalakshmi SahasranamanNo ratings yet
- Biodesel - Conversion of Oil Into FuelDocument13 pagesBiodesel - Conversion of Oil Into FuelpravinsankalpNo ratings yet
- BiodIesel 08ME067Document13 pagesBiodIesel 08ME067sarangwankhadeNo ratings yet
- Biodiesel Refers To A Vegetable Oil-Or Animal Fat-Based DieselDocument7 pagesBiodiesel Refers To A Vegetable Oil-Or Animal Fat-Based DieselM CHANDRA PRABHANo ratings yet
- Transesterification of Oil TBGDocument6 pagesTransesterification of Oil TBGSNo ratings yet
- BiodieselDocument17 pagesBiodieselJason SinghNo ratings yet
- Biodiesel Refers To A Vegetable Oil-Or Animal Fat-Based Diesel Fuel Consisting of LongDocument1 pageBiodiesel Refers To A Vegetable Oil-Or Animal Fat-Based Diesel Fuel Consisting of LongAdi HDNo ratings yet
- Introduction: What Is Biodiesel?: Gerhard KnotheDocument3 pagesIntroduction: What Is Biodiesel?: Gerhard KnotheIAMANDU COSTANo ratings yet
- Biofuels: Chemistry of Alcohols - EthanolDocument2 pagesBiofuels: Chemistry of Alcohols - EthanolMustufa KhalilNo ratings yet
- Biodiesel - A Fuel of FutureDocument5 pagesBiodiesel - A Fuel of FutureYashad JoshiNo ratings yet
- Palm OilDocument17 pagesPalm OilanantNo ratings yet
- BiofuelsDocument6 pagesBiofuelsChristine Yaco DetoitoNo ratings yet
- Biodiesel Production101: Homebrew Edition: A Do It Yourself Guide to Produce Biodiesel on Your BackyardFrom EverandBiodiesel Production101: Homebrew Edition: A Do It Yourself Guide to Produce Biodiesel on Your BackyardNo ratings yet
- What Is Biodiesel ?Document18 pagesWhat Is Biodiesel ?yogendra sahuNo ratings yet
- Biodiesel From Coconut Oil: A Renewable Alternative Fuel For Diesel EngineDocument5 pagesBiodiesel From Coconut Oil: A Renewable Alternative Fuel For Diesel EngineAde HadyNo ratings yet
- Chapter # 1: 1.1) What Is Biodiesel?Document125 pagesChapter # 1: 1.1) What Is Biodiesel?saqib sulmanNo ratings yet
- Formation of BiodieselDocument8 pagesFormation of BiodieselParshwa ShahNo ratings yet
- Biodiesel: An Alternative Fuel and Its Emission Effect: Yogendra Prasad Upadhyay, R.B.SharmaDocument4 pagesBiodiesel: An Alternative Fuel and Its Emission Effect: Yogendra Prasad Upadhyay, R.B.SharmaInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)No ratings yet
- A Clean Burning Alternative Fuel From Renewable ResourcesDocument36 pagesA Clean Burning Alternative Fuel From Renewable ResourcesBhavesh NethaNo ratings yet
- Demir Bas 2009Document6 pagesDemir Bas 2009hansham.dewal3No ratings yet
- Bio DieselDocument9 pagesBio DieselMohan MaheshawariNo ratings yet
- BiodieselDocument15 pagesBiodieselJason KnightNo ratings yet
- Production of Biodiesel From Used Vegetable OilDocument4 pagesProduction of Biodiesel From Used Vegetable OilEmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Biodiesel ProcessorDocument26 pagesBiodiesel ProcessorAleem MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Learn About BiodieselDocument20 pagesLearn About BiodieselH.J.PrabhuNo ratings yet
- The BiodieselDocument3 pagesThe BiodieselAbdou SaiNo ratings yet
- Ecent Trends in Non-Conventional Energy SourcesDocument14 pagesEcent Trends in Non-Conventional Energy Sourcesprathmesh238No ratings yet
- Seminar On: Preparation of Biodiesel From Waste Cooking Oil and Study Its Effects On Performance of Diesel EngineDocument19 pagesSeminar On: Preparation of Biodiesel From Waste Cooking Oil and Study Its Effects On Performance of Diesel EngineSourabh Makham0% (1)
- Chapter-1: 1.1 BackgroundDocument32 pagesChapter-1: 1.1 BackgroundTanjina azadNo ratings yet
- Project: Members: - Maricielo Olano - Paul Torrejon Teacher: José FajardoDocument11 pagesProject: Members: - Maricielo Olano - Paul Torrejon Teacher: José Fajardofrank torrejon chachiNo ratings yet
- Process DescriptionDocument4 pagesProcess DescriptionShayan KashifNo ratings yet
- SadagobanDocument48 pagesSadagobanSolomon DurairajNo ratings yet
- Biofuel: Biofuels Are A Wide Range of Fuels Which Are in Some Way Derived FromDocument16 pagesBiofuel: Biofuels Are A Wide Range of Fuels Which Are in Some Way Derived Fromsuniyoti100% (1)
- Biodiesel Feed Stock, Production TechnologyDocument27 pagesBiodiesel Feed Stock, Production Technologyboyongo313100% (1)
- 55 487 PDFDocument16 pages55 487 PDFIkhlas AmalNo ratings yet
- 29 Kapilan Natesh 1-3 (278-282)Document5 pages29 Kapilan Natesh 1-3 (278-282)Fitriani Indah LestariNo ratings yet
- Reactor Design and Production of Biodiesel: Concept TitleDocument5 pagesReactor Design and Production of Biodiesel: Concept TitleArun Kumar Arun KumarNo ratings yet
- III (ForDocument6 pagesIII (ForChristine Yaco DetoitoNo ratings yet
- Biodiese LDocument12 pagesBiodiese LNishikNo ratings yet
- Lab Report SBV 3023 Issue in Biology and EnvironmentDocument6 pagesLab Report SBV 3023 Issue in Biology and EnvironmentSaya Redha100% (1)
- Biofuel and BiodieselDocument16 pagesBiofuel and Biodieseljoe100% (3)
- Chemistry Class 12 ProjectDocument18 pagesChemistry Class 12 ProjectVaibhav GalaNo ratings yet
- Short PPT On BiodieselDocument15 pagesShort PPT On BiodieselAnkur SinghNo ratings yet
- Biodiesel Production - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument6 pagesBiodiesel Production - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaGowtham D'Night FoxNo ratings yet
- BiodieselDocument12 pagesBiodieselbasildrehman14No ratings yet
- Biodiesel Production From Euphorbia Tirucalli L.: Full Length Research PaperDocument6 pagesBiodiesel Production From Euphorbia Tirucalli L.: Full Length Research PaperMáximo Décimo MeridioNo ratings yet
- TransesterificationDocument14 pagesTransesterificationElilisya MarooskinNo ratings yet
- FL - Course 6Document22 pagesFL - Course 6Fianu AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Biodiesel Production from Used Cooking Oil: Business Advice & Training, #4From EverandBiodiesel Production from Used Cooking Oil: Business Advice & Training, #4No ratings yet
- Trait-Modified Oils in FoodsFrom EverandTrait-Modified Oils in FoodsFrank T. OrthoeferNo ratings yet