Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fractional Distillation Oral Report
Uploaded by
Paolo CoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fractional Distillation Oral Report
Uploaded by
Paolo CoCopyright:
Available Formats
Fractional Distillation
Submitted by: Co, Vian Paolo V. Comendador, Mikaela V. Cruz, Patricia Ann A. De Jesus, Cara Gabrielle A.
What is Fractional Distillation?
Fractional Distillation
is a type of distillation that involves separation of a mixture into its constituents based on the differences in their boiling point (volatility). It is practiced for those mixtures, in which the boiling point of the components differ by less than 25 ºC at one atmospheric pressure.
The component with the least boiling point is separated first, while the component with the highest boiling point is drawn off at the last. If the boiling point of the constituents differ by more than 25 ºC, then simple distillation procedure is implemented for separation.
How does Fractional Distillation Work?
In the process of fractional distillation, a specific apparatus is used for boiling the mixture and collecting a series of fractions of the constituent substances.
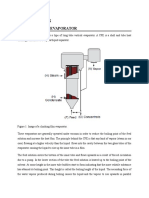
The laboratory setup for fractional distillation includes a round-bottom boiling flask, condenser, adapter (that connects boiling flask and condenser), fractionating column (within the adapter) and a collection flask. A thermometer is fixed to the adapter for monitoring the temperature.
The fractionating column is usually composed of plates arranged in a horizontal manner, which enhances the separation by allowing condensation, evaporation and recondensation of the separated components.
The vapor of the component substance after passing the fractionating column is passed to the condenser, which is fixed with a water inlet and water outlet pipe. In the water inlet pipe, cold water is constantly supplied to cool down or condense the separated vapor.
Eventually, warm water after being circulated through the condenser is removed via the outlet pipe. The component undergoes condensation in the condenser, which is then collected in the collection flask as a purified liquid.
The constituents with lower boiling point tend to collect at the top portion of the fractionating column, while those with higher boiling point settle at the bottom of the column
Though this type of distillation provides better separation of constituents, it requires more energy and longer time than the usual simple distillation.
What are the uses of fractional distillation?
Fractional Distillation
is practiced in large-scale alcoholic fermentation in order to purify alcoholic beverages.
Beer and wine produced after fermentation of grains and grapes contain less than 15 percent alcohol. It is due to the fact that a high concentration of alcohol kills the yeast that are responsible for proceeding fermentation. In such a condition, fractional distillation is practiced to purify alcohol and make stronger alcoholic drinks. In addition, fractional distillation is also used for solvent recycling, extraction of essential oils and purification of fragrances in perfume industries.
Another use of fractional distillation is in the separation of impurities contained in crude oil. In fact, fractional distillation is the most common procedure followed for separation of mixtures in petroleum refining industries and chemical industries. In petroleum refining, gasoline is separated first followed by kerosene, heating oil and lubricating oil. This technology implemented in industries is referred to as continuous fractional distillation.
Difference of Fractional from simple distillation:
fractional distillation and simple distillation
are based on the same principle, but differ in procedure.
When the substances in a mixture have boiling points which differ largely, simple distillation is the first choice.
When that isn't the case, fractional distillation is used. This process uses a fractionating column, while simple distillation doesn't.
Simple distillation cannot guarantee high purity of the separated component but
fractional distillation can provide separated chemicals with a high degree of purity.
fractional distillation is used in separating mixtures whose components have boiling points that are too close to each other, while
simple distillation is used in case of mixtures whose components have boiling points that are substantially far apart.
You might also like
- Simple distillation and fractional distillation methods explainedDocument4 pagesSimple distillation and fractional distillation methods explainedManoj KhanalNo ratings yet
- Haber Process and AmmoniaDocument2 pagesHaber Process and AmmoniaAaron HongNo ratings yet
- Final ExamDocument8 pagesFinal ExamermiasNo ratings yet
- Investigation of The Effect of Cooling Load On Cooling Tower Performance Thermodynamic Exp 6Document14 pagesInvestigation of The Effect of Cooling Load On Cooling Tower Performance Thermodynamic Exp 6hayder alaliNo ratings yet
- Total Alkalinity Determination - and Its Rule in An Aerobic Wastewater TreatmentDocument8 pagesTotal Alkalinity Determination - and Its Rule in An Aerobic Wastewater Treatmenthayder alaliNo ratings yet
- Climbing Film Evaporation Data (2016) - All GroupsDocument12 pagesClimbing Film Evaporation Data (2016) - All GroupsJuwon Jeremiah MakuNo ratings yet
- 2210 - Melting Points and Mixed Melting PointsDocument13 pages2210 - Melting Points and Mixed Melting PointsAmalia Siller0% (1)
- Lab Report InstructionsDocument13 pagesLab Report InstructionsGonzalo ElleNo ratings yet
- Acid Base TitrationDocument4 pagesAcid Base TitrationNeeta PandeyNo ratings yet
- Distillation Written ReportDocument18 pagesDistillation Written ReportMaRiz BalitaanNo ratings yet
- 07 Chapter 11Document34 pages07 Chapter 11M Zia Dogar100% (2)
- Lab Report 5 DistillationDocument6 pagesLab Report 5 DistillationMyeeka Hammond100% (1)
- Electricity and MagnetismDocument14 pagesElectricity and Magnetismhayder alaliNo ratings yet
- Sheet 5 2Document1 pageSheet 5 2IbrahimDewaliNo ratings yet
- Archimedes Principle ExperimentDocument8 pagesArchimedes Principle ExperimentMUHAMMAD AKRAMNo ratings yet
- Drying Sand in a Tray DryerDocument13 pagesDrying Sand in a Tray DryerHaziq AzliNo ratings yet
- COMSATS UNIVERSITY LAHORE DEW POINT LAB REPORTDocument5 pagesCOMSATS UNIVERSITY LAHORE DEW POINT LAB REPORTTaqqi HaiderNo ratings yet
- Chemical Formulae and Equations Part 2Document18 pagesChemical Formulae and Equations Part 2Mohd NorihwanNo ratings yet
- The Heat of Solution LabDocument4 pagesThe Heat of Solution Labapi-310957734No ratings yet
- Cooling Tower ReportDocument11 pagesCooling Tower Reportbae zazNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry (Important Notes)Document2 pagesThermochemistry (Important Notes)HenrySeowNo ratings yet
- ORG LAB Melting Point Determination2009Document8 pagesORG LAB Melting Point Determination2009Yunkai DayNo ratings yet
- Viscosity BwarDocument11 pagesViscosity BwarMUHAMMAD AKRAM100% (1)
- Chemical Reactions ExplainedDocument29 pagesChemical Reactions Explainedvv1234567No ratings yet
- Explanation Solubility Curve WorksheetDocument3 pagesExplanation Solubility Curve Worksheetapi-504044725100% (1)
- 1180 Exp 04, Density and Specific GravityDocument13 pages1180 Exp 04, Density and Specific GravityShaniCoolestNo ratings yet
- IIT Bombay Lab Manual Chemical EngineeringDocument2 pagesIIT Bombay Lab Manual Chemical EngineeringAnuj SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Lab Cracking Paraffin PDFDocument2 pagesLab Cracking Paraffin PDFJeffreyCheleNo ratings yet
- Esters OdorDocument5 pagesEsters OdortechkasambaNo ratings yet
- Errors and uncertainties in chemistry internal assessmentDocument6 pagesErrors and uncertainties in chemistry internal assessmentsarah2195No ratings yet
- Pycnometer ExperimentDocument8 pagesPycnometer ExperimentZerlyn JoebeNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Equilibria: Effect of Changing ConcentrationDocument14 pages4.2 Equilibria: Effect of Changing ConcentrationSunnyNo ratings yet
- Emissivity Guide for Common Materials Under 40 CharactersDocument1 pageEmissivity Guide for Common Materials Under 40 CharactersSinan YıldızNo ratings yet
- Experiment: 1 Parallel Flow Heat ExchangerDocument18 pagesExperiment: 1 Parallel Flow Heat ExchangerAnonymous QM0NLqZONo ratings yet
- Transition Temperature of Salt HydratesDocument2 pagesTransition Temperature of Salt HydratesDelin Shaji JohnNo ratings yet
- Balancing Chemical Equations: A Step-by-Step GuideDocument4 pagesBalancing Chemical Equations: A Step-by-Step GuideFatima Ahmed-VeriterNo ratings yet
- D and F BlockDocument30 pagesD and F BlockTS SPORTZNo ratings yet
- Experiment #2 HinchleyDocument5 pagesExperiment #2 HinchleyTalha AhmadNo ratings yet
- RI Vs Composition Methanol-Water MixtureDocument12 pagesRI Vs Composition Methanol-Water MixtureAnonymous VeJYFSMWLINo ratings yet
- Expt#3, FinalDocument3 pagesExpt#3, Finalakhtar140No ratings yet
- Determination of The Heat Capacity of A CalorimeterDocument8 pagesDetermination of The Heat Capacity of A CalorimeterVictor NyarugweNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Chemistry ConceptsDocument9 pagesQuantitative Chemistry ConceptsRizky FitriansyahNo ratings yet
- How To Use A Bunsen BurnerDocument11 pagesHow To Use A Bunsen BurnerJohn Alek NacaytunaNo ratings yet
- HeatDocument12 pagesHeatmohamedNo ratings yet
- Measurement of An Enthalpy Change: Measuring The Enthalpy Change For A Reaction Experimentally Calorimetric MethodDocument5 pagesMeasurement of An Enthalpy Change: Measuring The Enthalpy Change For A Reaction Experimentally Calorimetric MethodSunnyNo ratings yet
- Dew point measurement experimentDocument8 pagesDew point measurement experimentحامد عبد الشهيد حميد مجيدNo ratings yet
- Measure Density of LiquidsDocument6 pagesMeasure Density of LiquidsOxford NorthNo ratings yet
- Nickel Experiment XWDocument4 pagesNickel Experiment XWKhairul Anwar Abd HamidNo ratings yet
- Moles PDFDocument21 pagesMoles PDFhalvaroqNo ratings yet
- Combined Convection and Radiation Mechanical Engineering ThermoDocument15 pagesCombined Convection and Radiation Mechanical Engineering ThermoBhaggyaLakshanVidanarachchiNo ratings yet
- Partition Coefficient DeterminationDocument4 pagesPartition Coefficient DeterminationMostafa HamawandyNo ratings yet
- Experiment 14Document7 pagesExperiment 14Jc GohNo ratings yet
- Vacuum Distillation: Mir Salman 2007-Chem-53 Usama Malik 2007-Chem-11 Sheraz Hussain 2007-Chem-31 Waseem Zia 2007-Chem-15Document14 pagesVacuum Distillation: Mir Salman 2007-Chem-53 Usama Malik 2007-Chem-11 Sheraz Hussain 2007-Chem-31 Waseem Zia 2007-Chem-15Usama Malik100% (3)
- Colling Tower: Mechanical Lab / Exp. NO.Document10 pagesColling Tower: Mechanical Lab / Exp. NO.Dalal Salih100% (1)
- SI UnitsDocument24 pagesSI UnitsRenz Dela Cruz Arellano50% (2)
- 1 3 F Calculations Involving Gas VolumesDocument45 pages1 3 F Calculations Involving Gas VolumesForm 4BNo ratings yet
- Simple Distillation: Raoult's LawDocument4 pagesSimple Distillation: Raoult's LawPerry Z. ZafeNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical CellsDocument63 pagesElectrochemical CellsHoongNo ratings yet
- Official Report Practicum of Chemical Separation Principles Fracsination DestilationDocument22 pagesOfficial Report Practicum of Chemical Separation Principles Fracsination DestilationFitriyah AbidinNo ratings yet