Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Air Sublimate Evapotranspiration Transpired: Processes
Air Sublimate Evapotranspiration Transpired: Processes
Uploaded by
Shanny Blink BlinkOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Air Sublimate Evapotranspiration Transpired: Processes
Air Sublimate Evapotranspiration Transpired: Processes
Uploaded by
Shanny Blink BlinkCopyright:
Available Formats
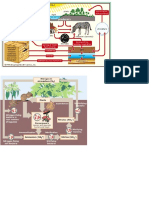
Description The sun, which drives the water cycle, heats water in oceans and seas.
Water evaporates as water vapor into the air. Ice and snow can sublimate directly into water vapor.Evapotranspiration is water transpired from plants and evaporated from the soil. Rising air currents take the vapor up into the atmosphere where cooler temperatures cause it to condense into clouds. Air currents move water vapor around the globe, cloud particles collide, grow, and fall out of the sky as precipitation. Some precipitation falls as snow or hail, sleet, and can accumulate as ice caps and glaciers, which can store frozen water for thousands of years. Most water falls back into the oceans or onto land as rain, where the water flows over the ground as surface runoff. A portion of runoff enters rivers in valleys in the landscape, with streamflow moving water towards the oceans. Runoff and groundwater are stored as freshwater in lakes. Not all runoff flows into rivers, much of it soaks into the ground as infiltration. Some water infiltrates deep into the ground and replenishes aquifers, which store freshwater for long periods of time. Some infiltration stays close to the land surface and can seep back into surface-water bodies (and the ocean) as groundwater discharge. Some groundwater finds openings in the land surface and comes out as freshwater springs. Over time, the water returns to the ocean, where our water cycle started. Processes
Many different process lead to movements and phase changes in water Precipitation Condensed water vapor that falls to the Earth's surface . Most precipitation occurs as rain, but also includes snow, hail, fog drip, graupel, and sleet.[1] Approximately 505,000 km3 (121,000 cu mi) of water falls as precipitation each year, 398,000 km3 (95,000 cu mi) of it over the oceans.[2]
Canopy interception
The precipitation that is intercepted by plant foliage, eventually evaporates back to the atmosphere rather than falling to the ground. Snowmelt The runoff produced by melting snow. Runoff The variety of ways by which water moves across the land. This includes both surface runoff andchannel runoff. As it flows, the water may seep into the ground, evaporate into the air, become stored in lakes or reservoirs, or be extracted for agricultural or other human uses. Infiltration The flow of water from the ground surface into the ground. Once infiltrated, the water becomes soil moisture or groundwater.[3] Subsurface flow The flow of water underground, in the vadose zone and aquifers. Subsurface water may return to the surface (e.g. as a spring or by being pumped) or eventually seep into the oceans. Water returns to the land surface at lower elevation than where it infiltrated, under the force of gravityor gravity induced pressures. Groundwater tends to move slowly, and is replenished slowly, so it can remain in aquifers for thousands of years. Evaporation The transformation of water from liquid to gas phases as it moves from the ground or bodies of water into the overlying atmosphere.[4] The source of energy for evaporation is primarilysolar radiation. Evaporation often implicitly includes transpiration from plants, though together they are specifically referred to as evapotranspiration. Total annual evapotranspiration amounts to approximately 505,000 km3 (121,000 cu mi) of water, 434,000 km3 (104,000 cu mi) of which evaporates from the oceans.[2] Sublimation The state change directly from solid water (snow or ice) to water vapor.[5] Advection The movement of water in solid, liquid, or vapor states through the atmosphere. Without advection, water that evaporated over the oceans could not precipitate over land.[6] Condensation The transformation of water vapor to liquid water droplets in the air, creating clouds and fog.[7] Transpiration The release of water vapor from plants and soil into the air. Water vapor is a gas that canno
BAHAYA NARKOBA BAGI REMAJA POSTED BY ZALDY MUNIR JANUARI 11, 2009 17 KOMENTAR FILED UNDER ARTIKEL, BERITA, BUDAYA, FOKUS KAJIAN, INFO, INFORMASI, OPINI Oleh : Zaldy Munir NARKOBA atau NAPZA adalah bahan / zat yang dapat mempengaruhi kondisi kejiwaan / psikologi seseorang (pikiran, perasaan dan perilaku) serta dapat menimbulkan ketergantungan fisik dan psikologi. Yang termasuk dalam NAPZA, yaitu Narkotika, Psikotropika dan Zat Adiktif lainnya. Masalah pencegahan penyalahgunaan NAPZA bukanlah menjadi tugas dari sekelompok orang saja, melainkan menjadi tugas kita bersama. Upaya pencegahan penyalahgunaan NAPZA yang dilakukan sejak dini sangatlah baik, tentunya dengan pengetahuan yang cukup tentang penanggulangan tersebut. Peran orang tua dalam keluarga dan juga peran pendidik di sekolah sangatlah besar bagi pencegahan penaggulangan terhadap NAPZA. Narkotika menurut UU RI No 22 / 1997, Narkotika, yaitu zat atau obat yang berasal dari tanaman atau bukan tanaman baik sintetis maupun semisintetis yang dapat menyebabkan penurunan atau perubahan kesadaran, hilangnya rasa, mengurangi sampai menghilangkan rasa nyeri, dan dapat menimbulkan ketergantungan. PENYEBABNYA SANGATLAH KOMPLEKS AKIBAT INTERAKSI BERBAGAI FAKTOR 1. Faktor individual Kebanyakan dimulai pada saat remaja, sebab pada remaja sedang mengalami perubahan biologi, psikologi maupun sosial yang pesat. Ciri-ciri remaja yang mempunyai resiko lebih besar menggunakan NAPZA, seperti kurang percaya diri, mudah kecewa, agresif, murung, pemalu, pendiam dan sebagainya. 2. Faktor Lingkungan Faktor lingkungan meliputi faktor keluarga dan lingkungan pergaulan kurang baik sekitar rumah, sekolah, teman sebaya, maupun masyarakat, seperti komunikasi orang tua dan anak kurang baik, orang tua yang bercerai, kawin lagi, orang tua terlampau sibuk, acuh, orang tua otoriter dan sebagainya. Faktor-faktor tersebut di atas memang tidak selalu membuat seseorang kelak menjadi penyalahguna NAPZA. Akan tetapi, makin banyak faktor-faktor di atas, semakin besar kemungkinan seseorang menjadi penyalahguna NAPZA. GEJALA KLINIS PENYALAHGUNAAN NAPZA 1. Perubahan Fisik
Pada saat menggunakan NAPZA : jalan sempoyongan, bicara pelo (cadel), apatis (acuh tak acuh), mengantuk, agresif. Bila terjadi kelebihan dosis (Overdosis) : nafas sesak, denyut jantung dan nadi lambat, kulit teraba dingin, bahkan meninggal. Saat sedang ketagihan (Sakau) : mata merah, hidung berair, menguap terus, diare, rasa sakit seluruh tubuh, malas mandi, kejang, kesadaran menurun. Pengaruh jangka panjang : penampilan tidak sehat, tidak perduli terhadap kesehatan dan kebersihan, gigi keropos, bekas suntikan pada lengan. 2. Perubahan sikap dan perilaku Prestasi di sekolah menurun, tidak mengerjakan tugas sekolah, sering membolos, pemalas, kurang bertanggung jawab. Pola tidur berubah, bergadang, sulit dibangunkan pagi hari, mengantuk di kelas atau tempat kerja. Sering berpergian sampai larut malam, terkadang tidak pulang tanpa ijin. Sering mengurung diri, berlama-lama di kamar mandi, menghidar bertemu dengan anggota keluarga yang lain. Sering mendapat telpon dan didatangi orang yang tidak dikenal oleh anggota keluarga yang lain. Sering berbohong, minta banyak uang dengan berbagai alasan, tapi tidak jelas penggunaannya, mengambil dan menjual barang berharga milik sendiri atau keluarga, mencuri, terlibat kekerasan dan sering berurusan dengan polisi. Sering bersikap emosional, mudah tersinggung, pemarah, kasar, bermusuhan, pencurigaan, tertutup dan penuh rahasia. UPAYA PENCEGAHAN PENYALAHGUNAAN NAPZA Upaya pencegahan meliputi 3 hal : mengenali remaja resiko tinggi penyalahgunaan NAPZA dan melakukan intervensi. Upaya ini terutama dilakukan untuk mengenali remaja yang mempunyai resiko tinggi untuk menyalahgunakan NAPZA, setelah itu melakukan intervensi terhadap mereka agar tidak menggunakan NAPZA. Upaya pencegahan ini dilakukan sejak anak berusia dini, agar faktor yang dapat menghabat proses tumbuh kembang anak dapat diatasi dengan baik. Komunikasi dua arah, bersikap terbuka dan jujur, mendengarkan dan menghormati pendapat anak. Memperkuat kehidupan beragama. Yang diutamakan bukan hanya ritual keagamaan, melainkan memperkuat nilai moral yang terkandung dalam agama dan menerapkannya dalam kehidupan sehari-hari. Orang tua memahami masalah penyalahgunaan NAPZA agar dapat berdiskusi dengan anak.***
You might also like
- Hydrological CycleDocument17 pagesHydrological CycleSakshi TalmaleNo ratings yet
- Science 4 Q4 Week 3 Day 1 4Document64 pagesScience 4 Q4 Week 3 Day 1 4LigieNo ratings yet
- Evaporation, Transpiration and Precipitation | Water Cycle for Kids | Children's Water BooksFrom EverandEvaporation, Transpiration and Precipitation | Water Cycle for Kids | Children's Water BooksNo ratings yet
- HydrologyDocument264 pagesHydrologyKent Xyrell100% (1)
- Topic 1Document33 pagesTopic 1Nur HananiNo ratings yet
- Let's Check (Pertimos)Document3 pagesLet's Check (Pertimos)HAROLD KING PERTIMOSNo ratings yet
- Hydro Logic CycleDocument12 pagesHydro Logic CycleGaurav YadavNo ratings yet
- PDF 1702478694358Document19 pagesPDF 1702478694358vashishth.sharma96No ratings yet
- HYDROLOGYDocument9 pagesHYDROLOGYFernel HabonNo ratings yet
- PM 211 Module 6Document19 pagesPM 211 Module 6Louray JeanNo ratings yet
- Science Project Don by Ansh YadavDocument21 pagesScience Project Don by Ansh YadavIsha YadavNo ratings yet
- Inquiry Paper FORMATDocument7 pagesInquiry Paper FORMATrachelsarifNo ratings yet
- Hydrological CycleDocument18 pagesHydrological CyclerenuNo ratings yet
- The Water CycleDocument14 pagesThe Water Cyclearme76No ratings yet
- Explanation Text - PassiveDocument12 pagesExplanation Text - Passivepd9hw7qzm9No ratings yet
- The Water CycleDocument11 pagesThe Water CycleGemlyn de CastroNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Week 11&12 OCRDocument6 pagesEarth Science Week 11&12 OCRARNOLD TEODORONo ratings yet
- Finish Line & BeyondDocument8 pagesFinish Line & BeyondAjay AnandNo ratings yet
- Hydrological CycleDocument6 pagesHydrological CyclesurajNo ratings yet
- The HydrosphereDocument14 pagesThe HydrosphereEstela Garcia AnayaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Rain, Thunder and LightningDocument3 pagesChapter 13 Rain, Thunder and Lightningbittuchintu100% (1)
- HydrologyDocument40 pagesHydrologyNimalanNo ratings yet
- Water CycleDocument11 pagesWater Cycleanika tahsinNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 01: Environmental ManagementDocument6 pagesAssignment # 01: Environmental ManagementUsama AhmadNo ratings yet
- Earth's Water Resources TopicDocument4 pagesEarth's Water Resources TopicJanine RoceroNo ratings yet
- Explanation 2 (Mazaya & Selvy)Document3 pagesExplanation 2 (Mazaya & Selvy)Mazaya HakimNo ratings yet
- HydrologyDocument19 pagesHydrologyMarc Rizo JoseNo ratings yet
- Finish Line & Beyond: WWW .E X Ce LLDocument9 pagesFinish Line & Beyond: WWW .E X Ce LLrakeshkyNo ratings yet
- Hydrology - Activity 1Document4 pagesHydrology - Activity 1Renderizzah FloraldeNo ratings yet
- Hydrologic Cycle: by - N.G.PalitDocument17 pagesHydrologic Cycle: by - N.G.PalitEngr.Hamid Ismail CheemaNo ratings yet
- Hydrologic Cycle: by - N.G.PalitDocument17 pagesHydrologic Cycle: by - N.G.PalitEngr.Hamid Ismail CheemaNo ratings yet
- VRB JishaDocument35 pagesVRB Jishaupendra1616No ratings yet
- Lecture 06 Hydrologic CycleDocument4 pagesLecture 06 Hydrologic CycleClow NNo ratings yet
- WCM Unit 1 PDFDocument12 pagesWCM Unit 1 PDFAYESHA SIDDIQANo ratings yet
- Water Study Mat1Document13 pagesWater Study Mat1Suvam DasguptaNo ratings yet
- Topic HydrologyDocument6 pagesTopic HydrologyvictorNo ratings yet
- Environmental StudiesDocument30 pagesEnvironmental StudiesMuskan NarulaNo ratings yet
- MSC WaterDocument317 pagesMSC Wateralimakbar100% (1)
- Phosphorus CycleDocument6 pagesPhosphorus CycleMarlyn P LavadorNo ratings yet
- Activity 2Document1 pageActivity 2cure213No ratings yet
- Water ResourcesDocument25 pagesWater ResourcesZay SalazarNo ratings yet
- Four Main Stages in Water CycleDocument6 pagesFour Main Stages in Water CycleJadeNo ratings yet
- Temperature Climate: InterceptionDocument3 pagesTemperature Climate: Interceptionela afrinNo ratings yet
- Hydrological Cycle by Yuvraj SinghDocument17 pagesHydrological Cycle by Yuvraj SinghZeeshan AnsariNo ratings yet
- Hydrologic Cycle and Its Human ImpactDocument3 pagesHydrologic Cycle and Its Human ImpactXsy MarcosNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere of EarthDocument41 pagesAtmosphere of EarthMa. Rowena FloresNo ratings yet
- Hydrologic CycleDocument5 pagesHydrologic CyclesupermaneditNo ratings yet
- Title /course Code Introduction To Environment (1421)Document7 pagesTitle /course Code Introduction To Environment (1421)M Noaman AkbarNo ratings yet
- Group 1 ReportDocument19 pagesGroup 1 ReportKimmy Jane FloresNo ratings yet
- Sanitation, Plumbing Design, and InstallationDocument12 pagesSanitation, Plumbing Design, and InstallationHaRriet De Guzman VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Water: Omar Khayat Faisal Al-Amoudi Abdulaziz Abuldouh Abdullah SejeniDocument7 pagesWater: Omar Khayat Faisal Al-Amoudi Abdulaziz Abuldouh Abdullah Sejenioak-606No ratings yet
- The Basic Hydrologic (Water) CycleDocument9 pagesThe Basic Hydrologic (Water) CycleMiguel ContrerasNo ratings yet
- WaterDocument7 pagesWaterkarleepsingh1438No ratings yet
- Earth Science Week 4 What You Are Expected To Learn:: Chapter 4: Water ResourcesDocument11 pagesEarth Science Week 4 What You Are Expected To Learn:: Chapter 4: Water ResourcesHannah RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Processes of The Hydrologic Cycle: HydrometeorologyDocument3 pagesProcesses of The Hydrologic Cycle: Hydrometeorologykatrinajen ferrerNo ratings yet
- The Water CycleDocument10 pagesThe Water Cycledenivo2904No ratings yet
- Water Cycle: DescriptionDocument3 pagesWater Cycle: Descriptionrotsacrreijav123No ratings yet