Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Quadratics Directed Investigation
Uploaded by
Sam AlbertonOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Quadratics Directed Investigation
Uploaded by
Sam AlbertonCopyright:
Available Formats
Quadratics Directed Investigation
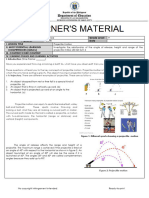
For our investigation, we are investigating the various mathematical aspects of a tennis ball being thrown into the air for a period of time.
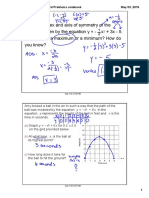
Tennis Ball Throw Height
40 35 30 25 Metres 20 (H) 15 10 5 0 0 1 2 3 Seconds (t) 4 5 6
1.) 2.) The Quadratic Equation to go along with this data is y = -4.962 + 23.65 + 6.41 which was found using the Quad Reg function on a TI-84 Plus Graphics Calculator. 3. a) The x-intercept is -0.257 and 5.025. b) The y-intercept is 6.41 c) The axis of symmetry is x = 2.36 d) The vertex is (2.36, 34.59) All of these values were found using a Graphics Calculator 4.)
5.) When the ball was released, the thrower was likely to be standing on a one story building. This is because before he threw the ball (when t was at 0) he was already 6.41m above the ground. The yintercept tells us this information. 6.) The maximum height reached by the ball was 34.59 metres. It reached this height 2.36 seconds after the ball had been thrown. This was found by using a Graphics Calculator. 7.) After 3.5 seconds, the height of the ball is at 28.425 metres. This was found by using a Graphics Calculator. 8.) After 3.347 seconds, the ball reached a height of 30 metres. This was found by using a Graphics Calculator. 9.) The ball hits the ground 5.025 seconds after it is thrown. This was found by using a Graphics Calculator. 10.) There is no significance of the left x-intercept. This is because the quadratic cannot predict what the ball was doing before it was thrown into the air. In conclusion, we found that after a certain period of time, the tennis ball starts to rapidly decrease back to ground.
You might also like
- Quadratic ApplicationsDocument2 pagesQuadratic Applicationssamuelss0229No ratings yet
- Mathematics GR 12Document1 pageMathematics GR 12reacharunkNo ratings yet
- Solutions To LEsson 5.7 Finding Equation of QuadDocument3 pagesSolutions To LEsson 5.7 Finding Equation of QuadKatheeja MusatheekNo ratings yet
- SONA RAJESH FINAL 1 PDF - SplitDocument45 pagesSONA RAJESH FINAL 1 PDF - SplitAnnumariavarkeyachanNo ratings yet
- Application Practice Vertex and Factored FormDocument2 pagesApplication Practice Vertex and Factored FormjoeyNo ratings yet
- In Class 1Document2 pagesIn Class 1Vishva OpanayakaNo ratings yet
- 3.2.4 Journal - The Distance Formula (Journal)Document5 pages3.2.4 Journal - The Distance Formula (Journal)helloelizajoyNo ratings yet
- Tugas Fisika IDocument3 pagesTugas Fisika IBenny JosephNo ratings yet
- Harshbarger/Yocco, College Algebra in Context, 5e, P. 180, #72Document2 pagesHarshbarger/Yocco, College Algebra in Context, 5e, P. 180, #72gudangworksheetNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Additional Problems With AnswersDocument5 pagesProjectile Motion Additional Problems With AnswersJanu Golez100% (1)
- Bouncing BallsDocument2 pagesBouncing BallsHiredTeenageAssassinNo ratings yet
- 2D Projectile Motion Practice IDocument2 pages2D Projectile Motion Practice IErin ChoiNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion QuestionsDocument6 pagesProjectile Motion QuestionsJabeenAhmedNo ratings yet
- CALCULUS QsDocument7 pagesCALCULUS QsDylineNo ratings yet
- Sample Problems: 111-Set #4 Projectile Motion (2-D Motion Problems)Document5 pagesSample Problems: 111-Set #4 Projectile Motion (2-D Motion Problems)Jakie UbinaNo ratings yet
- Science9 Q4 SLM6Document9 pagesScience9 Q4 SLM6Soliel RiegoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document4 pagesTutorial 1Mirnal MungraNo ratings yet
- Acceleration and Deceleration (7.4)Document5 pagesAcceleration and Deceleration (7.4)Rishi DuuNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Test Form CDocument3 pagesUnit 3 Test Form Capi-302927915No ratings yet
- L9 Application of Quadratics - Quad Formula Word Problems Worksheet F13Document1 pageL9 Application of Quadratics - Quad Formula Word Problems Worksheet F13Raymond NguyenNo ratings yet
- 2 ch06 LQ eDocument10 pages2 ch06 LQ eCHANNo ratings yet
- Math IA FinalDocument22 pagesMath IA FinalDhiman RoyNo ratings yet
- Using Parametric Equations Exercise PDFDocument1 pageUsing Parametric Equations Exercise PDFwolfretonmaths0% (2)
- 10 Examples of Projectile MotionDocument6 pages10 Examples of Projectile MotionGlaizel MorcillaNo ratings yet
- U5 L6 Applicationsof Quadratic Functions Day 1Document4 pagesU5 L6 Applicationsof Quadratic Functions Day 1jlo4uNo ratings yet
- Vertical MotionDocument17 pagesVertical MotionRhea FayeNo ratings yet
- Kinematics WorksheetDocument3 pagesKinematics WorksheetDyanie PlummerNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument19 pagesProjectile MotionJorge Rodríguez SedanoNo ratings yet
- WS 4Document1 pageWS 4Beth RankinNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Exercise PDFDocument2 pagesProjectile Motion Exercise PDFwolfretonmaths100% (2)
- LM Q4 Science G9 W2Document4 pagesLM Q4 Science G9 W2donamia quintanNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 9 Q4 SLM6 - EditedDocument7 pagesSCIENCE 9 Q4 SLM6 - Editedkerstinfsevilla777No ratings yet
- JR HSC Maths 3unit Term 2 2007Document5 pagesJR HSC Maths 3unit Term 2 2007Airfun123No ratings yet
- 9.7 × 4.16 4.7 2.9 6 6 3 2 Sin 2 A 1 2 1 Sinacosa: A+B F (X) X G (X) X F G (9) G (F (9) ), Y T X TDocument3 pages9.7 × 4.16 4.7 2.9 6 6 3 2 Sin 2 A 1 2 1 Sinacosa: A+B F (X) X G (X) X F G (9) G (F (9) ), Y T X TAnneNo ratings yet
- Worksheet: 3Document4 pagesWorksheet: 3Vivaan GandhiNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Name - DateDocument2 pagesProjectile Motion Name - DateVannyNo ratings yet
- Hawkeye3 151218061826Document28 pagesHawkeye3 151218061826keerthi GirirajNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Graphs & Bouncing Ball - Kutlwanong 2024Document60 pagesProjectile Motion Graphs & Bouncing Ball - Kutlwanong 2024ntokozomlotshwa10No ratings yet
- Quadratics - Packet 4 - Graphing and Real World ApplicationDocument13 pagesQuadratics - Packet 4 - Graphing and Real World ApplicationUmmu Fahmi FikriyantoNo ratings yet
- Homework - Intro To Quadratic Equations-1Document2 pagesHomework - Intro To Quadratic Equations-1api-368121935No ratings yet
- 253 Chapter 6. Differential CalculusDocument1 page253 Chapter 6. Differential CalculusreacharunkNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion - Solutions PDFDocument6 pagesProjectile Motion - Solutions PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- 10.10 Quad Functions Word ProblemsDocument3 pages10.10 Quad Functions Word Problemsswapnil parmarNo ratings yet
- Guia Physics, 10thDocument6 pagesGuia Physics, 10thEspinal Karla YohelyNo ratings yet
- Problems - Chapter 1 2 3Document5 pagesProblems - Chapter 1 2 3erylmaz.utkuNo ratings yet
- 4 - Quadratic EquationsDocument23 pages4 - Quadratic EquationsVince HernándezNo ratings yet
- Parametric WorksheetDocument3 pagesParametric Worksheetarghya_bi108No ratings yet
- Mini Launcher-2Document12 pagesMini Launcher-2Muhammad AsimNo ratings yet
- OxnoineaDocument40 pagesOxnoineaDaniel Barrios MaestreNo ratings yet
- The Physics of Kicking A FootballDocument5 pagesThe Physics of Kicking A Footballkc016No ratings yet
- PCH 7.5 Parametric EquationsDocument11 pagesPCH 7.5 Parametric EquationsBassem KhalidNo ratings yet
- Exercise Form 4Document3 pagesExercise Form 4ridzuan1979No ratings yet
- Physics 1 - LESSON 3 (Mid - Fall 24)Document9 pagesPhysics 1 - LESSON 3 (Mid - Fall 24)Muhammad ZayedNo ratings yet
- Asig 4Document2 pagesAsig 4api-38066150% (1)
- Tevin Sba Updated VersionDocument13 pagesTevin Sba Updated VersionAyanna HillNo ratings yet
- Class 7 - Mathematics - Yearly - Reena Krishnakumar - Reena KrishnakumarDocument6 pagesClass 7 - Mathematics - Yearly - Reena Krishnakumar - Reena KrishnakumarmuzaffaralhashmimaazmuzaffarNo ratings yet
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet