Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LM Q4 Science G9 W2
Uploaded by
donamia quintanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
LM Q4 Science G9 W2
Uploaded by
donamia quintanCopyright:
Available Formats
Learning Area Science Grade Level 9
W2 Quarter Fourth Date
I. LESSON TITLE Projectile Motion
II. MOST ESSENTIAL LEARNING Investigate the relationship of the angle of release, height and range of the
COMPETENCIES (MELCs) projectile (MELC 20) Q4 SLM 6
III. CONTENT/CORE CONTENT
IV. LEARNING PHASES AND LEARNING ACTIVITIES
I. Introduction (Time Frame: ________)
Have you experienced throwing or kicking a ball? So, what have you observed? Can you describe the path of the ball?
Those questions will lead you to the key concepts of projectile motion. Projectile motion is the motion of an object in
which the only force acting is gravity. The object moving in projectile motion is known as projectile and the path it takes
is its trajectory. There are different examples of projectiles. These are as follows:
1. An object dropped from rest or free fall is a special kind of
projectile. (a)
2. An object that is thrown vertically upward. (b)
3. An object that is projected upward at an angle to the
horizontal. (c)
a b c
. . .
Projectile motion can apply to sports like basketball, volley
ball and football. These sports involve throwing and
kicking a ball. And they are all making a curved path in midair.
This curved path made by the ball is called a projectile, a motion
with two-dimensions; the horizontal (range or distance) and
vertical (height) components.
Figure 1: Different sports showing a projectile motion
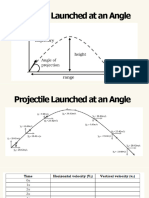
The angle of release affects the range and height of a
projectile. The maximum range is achieved if the projectile is fired at
an angle of 45º with respect to the horizontal as shown in figure 2. An
object launched at an angle of 30º will also be the same if it is
launched at 60º. The angles 30º and 60º are called complementary
angles because they add up to 90º.
Figure 2: Projectile motion
No copyright infringement intended. Ready-to-print
D. Development (Time Frame: ________)
Sample Problems:
1. A baseball player leads off the game and hits along home run. The ball leaves the bat at an
angle of 25º with a velocity of 30 m/s.
a. What is the maximum height reached by the ball?
b. What is the horizontal displacement (range) of the ball?
Given:
𝑣𝑜 = 30 m/s sin θ = 0.423 θ = 25º cos θ = 0.906
Find:
a. max. height (𝑑𝑦) = ? Solve for t (time):
b. Range (𝑑𝑥) = ? t = 𝑣𝑜 sin 𝑔 θ
(30 m/s)(0.423)
t= 9.8 𝑚/𝑠2
Solution: t = 1. 29 s
Equation:
a. 𝑑𝑦 = 𝑣𝑜 sin θ t – ½ g 𝑡2
𝑑𝑦 = (30 m/s) (0.423) (1.29 s) – ½ (9.8 m/s2 ) (1.29 𝑠)
𝑑𝑦 = 16.370 m – 8.154 m
𝒅𝒚 = 8.22 m
b. 𝑑𝑥 = 𝑣𝑜 cos θ t t = 2t
𝑑𝑥 = (30 m/s) (0.906) ( 2.58 s) t = 2 (1.29 s)
𝒅𝒙 = 70.12 m t = 2.58 s
2. A soccer ball is kicked 35º above with an initial velocity of 23.0 m/s and reaches
a maximum height of 1.27 m at 0.10 second. Determine the horizontal displacement (range)
of the ball.
Given:
𝑣𝑜 = 23 m/s sin θ = 0.574 θ = 35º cos θ = 0.819 t = 0.10 s
Find:
Range (𝑑𝑥) = ?
Solution:
Equation:
𝑑𝑥 = 𝑣𝑜 cos θ t t = 2t
𝑑𝑥 = (23 m/s) (0.819) (0.20 s) t = 2 (0.10 s)
𝑑𝑥 = 3.77 m t = 0. 20 s
Let us now do the activities below. Use a separate paper for your answer.
Activity 1: It’s My Flight!!!
Learning Competency:
Use examples derived from sports to show that the angle of release affects the range and height of a
projectile;(S9FE-IVa-35.4)
Objective:
Investigate the relationship between the projection angle, the height and range of the
projectile.
Materials: plastic spoon, cardboard, rubber band, protractor, ruler, small object, and watch
1. Make a simple catapult using the given materials, as shown in figure 3.
2. Launch the small stone in your catapult at an angle. Use the protractor to measure the angle.
3. Get the time of flight of the object, using the stopwatch.
4. Measure the distance traveled and the height achieved by the object using the ruler.
Figure 3: Improvised catapult
Angle of projection Time of flight Height achieved Distance traveled
150
No copyright infringement intended. Ready-to-print
300 5. Record your data
on the table below.
450
600
750 Questions:
1. What is the
distance traveled by the object at 150? 300? and 450?
2. At what angle of projection did the object travel farthest?
3. Compare the distance travelled by the object at 15 0 and 750 ?
4. At what angle of projection did the object reach the maximum height?
5. Compare the height achieved by the object at 75 0, 450 and 300.
Make your conclusion:
How does the angle of projection affect the range and height of a projectile?
E. Engagement (Time Frame: _________)
Activity 2: Projectile Motion
Learning Competency:
Use examples derived from sports to show that the angle of release affects the range and height of a projectile;(S9FE-
IVa-35.4)
Objective:
Solve problems for projectiles launched horizontally and at various angles to the horizontal to
calculate maximum height, range, and overall time of flight of the projectile.
Procedure:
Complete the table below.
A football player kicked the ball at a speed of 27.0 m/s as shown in the figure. Determine the
range and the height achieved by the ball at a given angle. (Assume that the speeds are the same
at a different angle).
Angle Time of flight Height Range
20º 4.4 m
35º 3.2 s 71 m
45º 18.6 m
55º 6.2 s
70º 5.2 s
Questions:
1. What is the distance traveled by the ball at 20º?
2. How would you compare the distance travelled by the ball at angles of 35º to 55º?
3. At what angle of projection is the distance travelled maximum?
4. What is the height achieved by the ball that is projected at an angle of 70º?
5. Compare the height achieved by the ball projected at 35º to 55º.
Make your conclusion:
Explain the relationship between the angle of projection to the range and height of a projection
A. Assimilation (Time Frame: _________)
Read each statement below carefully and fill in the blank(s) with the correct answer. Answers may be more than one
word. Write your answer on a separate answer sheet.
1. As the angle of launch _______, the vertical displacement of the projectile will also ________.
2. The _________ is achieved if the projectile is fired at an angle of 45º with respect to the horizontal.
3. At the highest point, the vertical component of velocity is ________ and the time to reach the maximum height is _______
of the total time of flight.
4. An object launched at an angle of 15º will also be the same if it is launched at _____.
No copyright infringement intended. Ready-to-print
5. A ________________ is an example of projectile motion.
VALUING
Which should you prefer: playing computer games like Mobile legends, clash of clans, and Minecraft or playing
sports? Why?
To know more about the lesson, do Activity 3.
Activity 3: What is my Sport?
Learning Competency:
Use examples derived from sports to show that the angle of release affects the range and height of a projectile;(S9FE-
IVa-35.4)
Objective: Draw their favorite sport/s which observe projectile motion and they can explain it.
Materials:
Pen, coloring materials and short bond paper
Procedure:
Draw your favorite sport(s) which you can observe projectile motion and explain it in a short bond paper.
Make your conclusion:
What are the examples of sports that exhibits projectile motion?
V. ASSESSMENT (Time Frame: _________)
(Learning Activity Sheets for Enrichment, Remediation, or Assessment to be given on Weeks 3 and 6)
POSTTEST
Direction: Choose the letter of the correct answer. Write your answer on a separate answer sheet.
1. Four balls are thrown with the same initial velocity, but at different angles above the ground. Which
diagram represents the initial velocity of the projectile have the maximum range?
2. A basketball player throws the ball at
different angles. At which of the following angles will the ball achieve the maximum height?
A. 35.00 m B. 45.00 m C. 65.00 m D. 70.00m
For nos. 3 and 4
A Ping-Pong ball is projected from the ground at an angle of 35º from the horizontal with an initial velocity of 20 m/s.
3. What is the horizontal distance?
A. 13.78 m B. 19.66 m C. 27.55 m D. 39.31 m
4. What is the maximum height achieved by the ball?
A. 13.78 m B. 19.66m C. 27.55 m D. 39.31 m
5. Long jump sports require a firm body to be able to jump high and project their body perfectly to get the longest
distance for them to win. The following are some of the good qualities of a player except _______.
A. Good listener B. Cooperative C. Respectful D. Arrogant
VI. REFERENCES REFERENCE: Science – Grade 9 Quarter 4 – Self-Learning Module 6:
Projectile Motion ,First Edition, 2020
Published by the Department of Education Division of Pasig City
Prepared by: DIGNA DC. CLAVERIA Checked by: Shirley F. Ferrera
No copyright infringement intended. Ready-to-print
You might also like
- Science9 Q4 SLM6Document9 pagesScience9 Q4 SLM6Soliel RiegoNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE-9-Q4-SLM6_editedDocument7 pagesSCIENCE-9-Q4-SLM6_editedkerstinfsevilla777No ratings yet
- Projectile Motion in SportsDocument3 pagesProjectile Motion in SportsMira VeranoNo ratings yet
- Las No. 2Document8 pagesLas No. 2santos.johnandrei719No ratings yet
- P6 Projectile MotionDocument5 pagesP6 Projectile MotionKim ValdezNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion GuideDocument3 pagesProjectile Motion GuideKurt AntonioNo ratings yet
- VLab Projectile Motion 2017Document9 pagesVLab Projectile Motion 2017JenNo ratings yet
- Calculate Projectile Motion EquationsDocument6 pagesCalculate Projectile Motion EquationsKaterina TagleNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument19 pagesProjectile MotionJorge Rodríguez SedanoNo ratings yet
- Q4 Long TestDocument9 pagesQ4 Long TestMelanie Ibarra CarlosNo ratings yet
- Maximum Range ExplainedDocument4 pagesMaximum Range ExplainedNgan DoanNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion: How Angle of Release Affects Height and RangeDocument11 pagesProjectile Motion: How Angle of Release Affects Height and RangeTrevor James TjNo ratings yet
- Lab 3: Projectile MotionDocument12 pagesLab 3: Projectile MotionUdara Silva100% (1)
- Projectile Motion WorkbookDocument8 pagesProjectile Motion WorkbookLorieley EugenioNo ratings yet
- Bucio - Projectile WS 1Document3 pagesBucio - Projectile WS 1ZhaeNo ratings yet
- Projectile SimulationDocument5 pagesProjectile SimulationAamena GinwalaNo ratings yet
- Science: Learning Activity Sheet Quarter 4 Week 1 - 2Document5 pagesScience: Learning Activity Sheet Quarter 4 Week 1 - 2Ma.Kristine Ibarreta JazulNo ratings yet
- SCI19_Q4_M1_Projectile-MotionDocument14 pagesSCI19_Q4_M1_Projectile-MotionricorodriguezmolinaNo ratings yet
- Learning Plan 1: Projectile MotionDocument32 pagesLearning Plan 1: Projectile MotionErica KnowzNo ratings yet
- DocDocument7 pagesDocEmad90% (20)
- Measuring Acceleration Down an Inclined PlaneDocument3 pagesMeasuring Acceleration Down an Inclined PlaneRicky SerioNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion: Learning Activity Sheets (LAS)Document6 pagesProjectile Motion: Learning Activity Sheets (LAS)Franz Eugene Almodiente100% (3)
- Lesson Plan: A. Standard of Competency B. Basic CompetencyDocument5 pagesLesson Plan: A. Standard of Competency B. Basic CompetencyRevni Yusmeiniar PratiwiNo ratings yet
- 9 2D Motion - ProjectileDocument42 pages9 2D Motion - ProjectileBebe rhexaNo ratings yet
- 2d Motiontest - 5R Review - KEYDocument6 pages2d Motiontest - 5R Review - KEYKristel Jade MontaNo ratings yet
- Experiment# 3 Projectile MotionDocument18 pagesExperiment# 3 Projectile MotionHafiz MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Lathe Cutting Tool Displacement RankingDocument8 pagesLathe Cutting Tool Displacement RankingVogelNo ratings yet
- Q4-WEEK 2-Projectile Motion (Part 2)Document26 pagesQ4-WEEK 2-Projectile Motion (Part 2)Adonis SanielNo ratings yet
- Experiment# 3 Projectile Motion (Tasks 3 and 4)Document18 pagesExperiment# 3 Projectile Motion (Tasks 3 and 4)Hafiz MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Final Project Guidelines Amber GDocument4 pagesFinal Project Guidelines Amber GspreemouseNo ratings yet
- Golf Range SEDocument10 pagesGolf Range SENate KossNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion: Feu High SchoolDocument6 pagesProjectile Motion: Feu High SchoolRein Margaret RogelNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument3 pagesProjectile MotionnashrulNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Parabolic TrajectoryDocument7 pagesProjectile Motion Parabolic TrajectorydanielNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument8 pagesPhysicsShrushritha sriNo ratings yet
- Physics Report PROJECTILE MOTIONDocument9 pagesPhysics Report PROJECTILE MOTIONHulwan Mukhlis76% (25)
- Experiment No. 4 - PROJECTILE Using Phet SimulationDocument6 pagesExperiment No. 4 - PROJECTILE Using Phet SimulationMaica ElliNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE9_Q4_LAS_Week1Document8 pagesSCIENCE9_Q4_LAS_Week1Jinky AydallaNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1Document9 pagesSheet 1Tony AtefNo ratings yet
- Projectile at AngleDocument24 pagesProjectile at AngleappleNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Online LabDocument6 pagesProjectile Motion Online LabSarah PimentaNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument58 pagesProjectile Motionrain diapoletNo ratings yet
- Physics LabDocument9 pagesPhysics LabPau Dela PenaNo ratings yet
- We Generally View Objects As Either Moving or Not MovingDocument11 pagesWe Generally View Objects As Either Moving or Not MovingMarietoni D. QueseaNo ratings yet
- Kinematics and Dynamics Concepts ExplainedDocument51 pagesKinematics and Dynamics Concepts ExplainedArilSharilNo ratings yet
- 7.2 ProjectMotDocument3 pages7.2 ProjectMotSubramanyam Vangara100% (1)
- Unit 1 Golf RangeDocument8 pagesUnit 1 Golf RangeBruh Ster69No ratings yet
- Measuring Acceleration on an InclineDocument4 pagesMeasuring Acceleration on an InclineGuangyu GuNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument13 pagesProjectile MotionMajed SenbolNo ratings yet
- Mechanic 20152016 PDFDocument8 pagesMechanic 20152016 PDFANo ratings yet
- 2D Projectile Motion Practice IDocument2 pages2D Projectile Motion Practice IErin ChoiNo ratings yet
- Motion in Two DimensionsDocument43 pagesMotion in Two DimensionsJessiee YeoNo ratings yet
- Physics Project ProjectileDocument16 pagesPhysics Project ProjectileDIPESH BHUSAL100% (3)
- Projectile Motion: Lesson 08Document14 pagesProjectile Motion: Lesson 08Muhammad Muneeb ShahidNo ratings yet
- Q4-WEEK 1-Projectile Motion (Part 1)Document33 pagesQ4-WEEK 1-Projectile Motion (Part 1)Adonis SanielNo ratings yet
- Projectiles LabDocument2 pagesProjectiles LabBolting FNNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Honors PhysicsDocument29 pagesProjectile Motion Honors PhysicsDeepanshu GautamNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 Projectile: Learning OutcomesDocument10 pagesExperiment 2 Projectile: Learning Outcomes翁绍棠No ratings yet
- Seatwork in P.EDocument1 pageSeatwork in P.Edonamia quintanNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in MusicDocument26 pagesReviewer in Musicdonamia quintanNo ratings yet
- Quiz# 1 ArtsDocument1 pageQuiz# 1 Artsdonamia quintanNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 A-STEM Attendance and Performance SheetDocument5 pagesGrade 12 A-STEM Attendance and Performance Sheetdonamia quintanNo ratings yet
- g7 Arts 1 ST QuarterDocument19 pagesg7 Arts 1 ST Quarterdonamia quintan100% (2)
- Cooling Tower DesignDocument4 pagesCooling Tower DesignRavi KasaudhanNo ratings yet
- Unacademy Plus Trigonometry FormulaDocument4 pagesUnacademy Plus Trigonometry FormulabilalNo ratings yet
- Intro To CalculusDocument24 pagesIntro To CalculusCovenant AdeogoNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive Cooling Technologies For Thermal Management of AvionicsDocument10 pagesActive and Passive Cooling Technologies For Thermal Management of AvionicsdavidNo ratings yet
- Bis Is 9143 - 1979 (Reaffirmed 2021) - Method For The Determination of Unconfined Compressive Strength of Rock MaterialsDocument8 pagesBis Is 9143 - 1979 (Reaffirmed 2021) - Method For The Determination of Unconfined Compressive Strength of Rock MaterialsArpan NandyNo ratings yet
- Ce8511 Soil Mechanics LaboratoryDocument95 pagesCe8511 Soil Mechanics LaboratoryMaran100% (1)
- Fiitjee: Internal TestDocument3 pagesFiitjee: Internal TestVineet MadanNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 10 Activity 2.2Document3 pagesSCIENCE 10 Activity 2.2sheila GepigaNo ratings yet
- SmithMinton Calculus ET 5e C01 S01Document12 pagesSmithMinton Calculus ET 5e C01 S01maged wagehNo ratings yet
- The Endocrown - A Different Type of All-Ceramic Reconstruction For Molars - JcdaDocument10 pagesThe Endocrown - A Different Type of All-Ceramic Reconstruction For Molars - Jcdaabcder1234No ratings yet
- Materials 14 075402Document20 pagesMaterials 14 075402sahib mohammadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Coulomb's Law PDFDocument43 pagesChapter 1 Coulomb's Law PDFChitra Ashutosh Tembe50% (2)
- Gravity MethodDocument38 pagesGravity Methodzain828No ratings yet
- (Non-Periodic Signals) : Fourier TransformDocument33 pages(Non-Periodic Signals) : Fourier TransformPragya ChakshooNo ratings yet
- BIOBASE Low Speed Centrifuge BKC-TL6III User ManualDocument15 pagesBIOBASE Low Speed Centrifuge BKC-TL6III User Manualsoporte03No ratings yet
- Moocs Lecture On Experimental Stress Analysis by Prof.K.Ramesh, Iit Madras 27-1Document29 pagesMoocs Lecture On Experimental Stress Analysis by Prof.K.Ramesh, Iit Madras 27-1muhammad hamzaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Scattering Factors 1Document14 pagesAtomic Scattering Factors 1Soumajit DasNo ratings yet
- 1977 - Patankar - Journal of Heat Transfer - Periodic Flow in DuctsDocument7 pages1977 - Patankar - Journal of Heat Transfer - Periodic Flow in Ductsarif aktaşNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: WavesDocument10 pagesStudent Exploration: Wavesamber jenkinsNo ratings yet
- Science 8 3.3 Force in Circular MotionDocument23 pagesScience 8 3.3 Force in Circular MotionKrisha PoloanNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Momentum and Impulse QuizDocument5 pagesUnit 5 - Momentum and Impulse QuizJessica HainesNo ratings yet
- SFD & BMDDocument46 pagesSFD & BMDMominul Islam OpuNo ratings yet
- Black Holes A Very Short Introduction by Katherine BlundellDocument150 pagesBlack Holes A Very Short Introduction by Katherine BlundellSalman Ali100% (2)
- Embediment LengthDocument6 pagesEmbediment LengthkelvinNo ratings yet
- Statics 213 Module 3.1 AND 3.2 HCCDocument12 pagesStatics 213 Module 3.1 AND 3.2 HCCMark MagcalasNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and Electromagnetism ProblemsDocument9 pagesMagnetism and Electromagnetism ProblemsRabi KhanNo ratings yet
- Errata For Modern Quantum Mechanics 2nd Ed by Sakurai and NapolitanoDocument16 pagesErrata For Modern Quantum Mechanics 2nd Ed by Sakurai and Napolitanokevinchu021195No ratings yet
- Substantivul Cu ExercitiiDocument13 pagesSubstantivul Cu ExercitiiMihaela CrisanNo ratings yet
- FRQ Review 2 - W - Teacher NotesDocument5 pagesFRQ Review 2 - W - Teacher NotesNoor FarhanNo ratings yet
- An Intuitive Guide To Linear Algebra - BetterExplainedDocument25 pagesAn Intuitive Guide To Linear Algebra - BetterExplainedvkk intensiveNo ratings yet