Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Taenia Saginata - Beef Tapeworm Diagnosis & Treatment
Uploaded by
Ecy Haqy Zhanah d'AphenOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Taenia Saginata - Beef Tapeworm Diagnosis & Treatment
Uploaded by
Ecy Haqy Zhanah d'AphenCopyright:
Available Formats
Taenia Saginata - Beef Tapeworm
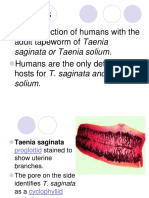
Taenia saginata is a large tapeworm that causes an infection called taeniasis. It is commonly known as the beef tapeworm or cattle tapeworm because it uses cows as intermediate hosts. Humans are the only definitive hosts. Taeniasis occurs worldwide and is relatively common in Africa, Eastern Europe, Latin America and the Philippines. The life cycle of Taenia saginata starts, when eggs are passed in the feces of an infected human in a container called a proglottid or a tapeworm segment. They can survive a few months out in the environment. If a cow (the intermediate host) feeds on contaminated vegetation, it ingests mature eggs or gravid proglottids. In the small intestine larvae called oncospheres hatch, penetrate the intestinal wall, enter the bloodstream and migrate to muscle tissue (rarely to liver or other organs), where they encyst into cysticerci. The pea-sized cysticerci can survive for years and still be infective when humans eat the meat. If the beef is not cooked properly, cysticerci excyst in the small intestine and develop into adults within two months. Adults attach to the intestinal wall with their scolex using four suckers. The scolex has a pear-shaped and cup-like appearance reaching 12 mm in diameter. It is attached to the neck which starts to produce proglottids that make up the flat, long, segmented body also known as strobila. The proglottids mature and grow bigger as they get further from the neck. They are about 1620 mm long and 57 mm wide and each proglottid has its own reproductive organs. They absorb nutrients through their membranes and produce up to 100 000 eggs per day. Proglottids break off from the tail and move with stool out of the human body. A full-grown Taenia saginata is whitish in colour and has about 10002000 proglottids and about six of them detach every day. The eggs usually stay inside the proglottids until they are out in the environment. When the proglottid dries up, it ruptures and releases the eggs. The eggs are embryonated, walnut brown and about 35 micrometers in diameter having a 6-hooked oncosphere inside its thick shell. If the feces land on grazing ground for cattle, a cow might accidentally ingest proglottids or eggs. Taenia saginata can live up to 25 years. It can grow up to 5 meters but in some cases can reach lengths of over 10 meters (coiled in the intestinal tract).
Taenia saginata - Beef cacing pita Taenia saginata adalah cacing pita besar yang menyebabkan infeksi yang disebut taeniasis. Hal ini umumnya dikenal sebagai cacing pita daging sapi atau ternak cacing pita karena menggunakan sapi sebagai host intermediate. Manusia adalah satu-satunya host definitif. Taeniasis terjadi di seluruh dunia dan relatif umum di Afrika, Eropa Timur, Amerika Latin dan Filipina. Siklus hidup Taenia saginata dimulai, ketika telur yang berlalu dalam tinja dari manusia yang terinfeksi dalam wadah yang disebut proglottid atau segmen cacing pita. Mereka dapat bertahan beberapa bulan keluar di lingkungan. Jika seekor sapi (host intermediate) memakan vegetasi yang terkontaminasi, itu ingests telur matang atau proglottids terkubur. Dalam larva usus kecil yang disebut oncospheres menetas, menembus dinding usus, memasuki aliran darah dan bermigrasi ke jaringan otot (jarang ke hati atau organ lain), di mana mereka encyst ke cysticerci. Para seukuran kacang cysticerci dapat bertahan selama bertahun-tahun dan masih menjadi infektif ketika manusia makan daging. Jika daging sapi yang tidak dimasak dengan benar, cysticerci excyst di usus kecil dan berkembang menjadi dewasa dalam waktu dua bulan. Dewasa menempel pada dinding usus
dengan scolex mereka menggunakan empat pengisap. Scolex ini memiliki penampilan yang berbentuk buah pir dan cangkir-seperti mencapai 1-2 mm. Hal ini melekat pada leher yang mulai memproduksi proglottids yang membentuk, datar panjang, tubuh tersegmentasi juga dikenal sebagai strobila. Para proglottids matang dan tumbuh lebih besar karena mereka mendapat lebih jauh dari leher. Mereka adalah sekitar 16-20 mm dan mm 5-7 lebar dan proglottid masing-masing memiliki organ reproduksi sendiri. Mereka menyerap nutrisi melalui membran mereka dan memproduksi hingga 100 000 telur per hari. Proglottids putus dari ekor dan bergerak dengan kotoran keluar dari tubuh manusia. Sebuah dewasa Taenia saginata adalah keputihan dalam warna dan memiliki sekitar 1000-2000 proglottids dan sekitar enam dari mereka melepaskan setiap hari. Telur-telur biasanya tinggal di dalam proglottids sampai mereka keluar di lingkungan. Ketika mengering proglottid, itu pecah dan melepaskan telur. Telur berembrio, kenari coklat dan sekitar 35 mikrometer diameter memiliki oncosphere 6-doyan dalam shell tebal. Jika kotoran tanah di tanah penggembalaan untuk ternak, sapi mungkin tidak sengaja menelan proglottids atau telur. Taenia saginata dapat hidup sampai 25 tahun. Hal ini dapat tumbuh hingga 5 meter namun dalam beberapa kasus bisa mencapai panjang lebih dari 10 meter (melingkar dalam saluran usus).
The disease is often asymptomatic. Taeniasis caused by Taenia saginata is more noticeable than taeniasis caused by Taenia solium (although T. solium is overall more dangerous because of the risk of cysticercosis). Heavy infection of Taenia saginata can cause some of the following symptoms:
allergic reactions chronic indigestion
constipation diarrhea dizziness headache loss of appetite nausea obstruction of the bowel stomach ache weight loss.
Migrating proglottids can cause:
inflammation of the appendix) inflammation of the bile duct) unpleasant surprise when seen in the feces.
Your health care provider makes the Taenia saginata diagnosis by identifying eggs or proglottids. Eggs and proglottids start appearing in the stool sample after three months of the start of the infection. During the first three months antibody detection methods can be used to find antibodies from a blood sample. All Taenia species have similar eggs so identification can only be done at the genus level. For educational purposes the specific species can be identified by examining gravid proglottids. The diagnosis can also be done during an endoscopic examination. Treatment is traditionally done with an oral drug called praziquantel. It causes paralysis of the worm by opening its membrane calcium channels. Then through peristaltic movements the tapeworm is defecated out. Alternatively niclosamide can be used. Both drugs have some side effects (especially praziquantel) that are similar to actual tapeworm infection symptoms. Endoscopic treatment is available in some areas. In the endoscopic treatment a drug is injected straight to the small intestine. This causes all nearby tapeworms to detach and come out whole. It the scolex (and neck) is left behind, it might produce new segments. To prevent infection:
Cook beef at or above 60 degrees Celsius until it is no longer pink inside. Alternatively freeze the meat at or below -5 degrees Celsius for a few days. Prevent cattle from eating in areas where vegetation might be contaminated with humans feces.
http://www.parasitesinhumans.org/taenia-saginata-beef-tapeworm.html
Penyakit ini sering tanpa gejala. Taeniasis akibat Taenia saginata lebih terlihat dari taeniasis disebabkan oleh Taenia solium (meskipun T. solium adalah keseluruhan lebih berbahaya karena risiko sistiserkosis). Infeksi berat dari Taenia saginata dapat menyebabkan beberapa gejala berikut: reaksi alergi gangguan pencernaan kronis sembelit diare pusing sakit kepala kehilangan nafsu makan mual Obstruksi usus sakit perut penurunan berat badan. Proglottids Migrasi dapat menyebabkan: radang usus buntu) radang saluran empedu) menyenangkan terkejut ketika terlihat di feses. Dokter membuat diagnosis Taenia saginata dengan mengidentifikasi telur atau proglottids. Telur dan proglottids mulai muncul dalam sampel feses setelah tiga bulan awal infeksi. Selama antibodi bulan pertama tiga metode deteksi dapat digunakan untuk mencari antibodi dari sampel darah. Semua spesies Taenia telah telur serupa sehingga identifikasi hanya dapat dilakukan pada tingkat genus. Untuk tujuan pendidikan spesies spesifik dapat diidentifikasi dengan memeriksa proglottids terkubur. Diagnosis juga dapat dilakukan selama pemeriksaan endoskopi. Pengobatan secara tradisional dilakukan dengan obat oral disebut praziquantel. Hal ini menyebabkan kelumpuhan cacing dengan membuka membran saluran kalsium.Kemudian melalui gerakan peristaltik cacing pita yang buang air besar keluar. Atau niclosamide dapat digunakan. Kedua obat memiliki efek samping (terutama praziquantel) yang mirip dengan gejala infeksi cacing pita yang sebenarnya. Perawatan endoskopik tersedia di beberapa daerah. Dalam perawatan endoskopik obat disuntikkan langsung ke usus kecil. Hal ini membuat seluruh cacing pita di dekatnya untuk melepaskan dan keluar utuh. Hal tersebut scolex (dan leher) yang tertinggal, mungkin menghasilkan segmen baru. Untuk mencegah infeksi: Masak daging sapi pada atau di atas 60 derajat Celcius sampai tidak lagi di dalam merah muda. Atau membekukan daging pada atau di bawah -5 derajat Celcius selama beberapa hari.
Mencegah ternak dari makan di daerah di mana vegetasi mungkin terkontaminasi dengan kotoran manusia.
You might also like
- Beef Tapeworm - Taenia SaginataDocument6 pagesBeef Tapeworm - Taenia SaginataAnonymous HXLczq3No ratings yet
- Taenia: Saima Ismail 2014-Ag - 2547 Iqra Aziz 2013-Ag-3776 M.Phil. (Parasitology) 3 SmesterDocument14 pagesTaenia: Saima Ismail 2014-Ag - 2547 Iqra Aziz 2013-Ag-3776 M.Phil. (Parasitology) 3 SmesterIqraAzizNo ratings yet
- CestodesDocument34 pagesCestodesمصطفي خندقاويNo ratings yet
- General Properties of CestodesDocument42 pagesGeneral Properties of CestodesNicole NipasNo ratings yet
- Siklus Hidup Taenia SaginataDocument2 pagesSiklus Hidup Taenia Saginatazahra apriyani pratiwiNo ratings yet
- Taenias IsDocument9 pagesTaenias IsFadeli100% (1)
- Taeniasis Infection Causes and SymptomsDocument18 pagesTaeniasis Infection Causes and SymptomsTea-yuhNo ratings yet
- Aeniasis Is The Infection of Humans With The Adult Tapeworm ofDocument18 pagesAeniasis Is The Infection of Humans With The Adult Tapeworm ofvivi maykasariNo ratings yet
- Other CestodesDocument9 pagesOther CestodesChristine BuenNo ratings yet
- Diphyllobothrium Latum, and Echinococcus Granulosus - Saginata (Known As The Beef Tapeworm), T. Solium (Pork Tapeworm) - Humans AreDocument6 pagesDiphyllobothrium Latum, and Echinococcus Granulosus - Saginata (Known As The Beef Tapeworm), T. Solium (Pork Tapeworm) - Humans AreBadur MohammedNo ratings yet
- Cestode SDocument26 pagesCestode SJustin Mutua100% (1)
- FA18-MZO-012 ParasytologyDocument7 pagesFA18-MZO-012 ParasytologySaba TanveerNo ratings yet
- Taenia saginata and solium: Pathogens Causing CysticercosisDocument20 pagesTaenia saginata and solium: Pathogens Causing CysticercosisfaradillaNo ratings yet
- Pork Tapeworm: Causes Taeniasis and CysticercosisDocument2 pagesPork Tapeworm: Causes Taeniasis and CysticercosisraphaelNo ratings yet
- Taenia Solium 2Document3 pagesTaenia Solium 2Otuko JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Cestodes Parasitology NotesDocument5 pagesCestodes Parasitology NotesKat SunicoNo ratings yet
- Cestodes & TrematodesDocument57 pagesCestodes & TrematodesCielo SanchezNo ratings yet
- General Parasitology L7Document17 pagesGeneral Parasitology L7kayse abtidoonNo ratings yet
- Medical Helminthology-CestodesDocument71 pagesMedical Helminthology-CestodesKAYISIRE EMERYNo ratings yet
- Ronald G. Daroya, M.DDocument72 pagesRonald G. Daroya, M.DJhenestka Joy SorianoNo ratings yet
- Draft NeurocysticercosisDocument1 pageDraft NeurocysticercosisMaria MarcellaNo ratings yet
- TaeniasisDocument66 pagesTaeniasisM Lutfi Fanani100% (1)
- Selma CestodesDocument23 pagesSelma CestodesAhmed EisaNo ratings yet
- Cestodes: Prepared By: Charriz A. AmoyanDocument37 pagesCestodes: Prepared By: Charriz A. AmoyanAudrie Allyson GabalesNo ratings yet
- Hymenolepis Nana Group 5 Write UpDocument7 pagesHymenolepis Nana Group 5 Write UpSusan GachukiaNo ratings yet
- PARASITOLOGYDocument13 pagesPARASITOLOGYJoel CabañasNo ratings yet
- Cestodes Lecture: Dr. Sulaiman LakohDocument53 pagesCestodes Lecture: Dr. Sulaiman LakohAbubakar JallohNo ratings yet
- Practical - Larval Stages of Taenia Solium - DR Roopa SamalDocument6 pagesPractical - Larval Stages of Taenia Solium - DR Roopa SamalAmishee SoodNo ratings yet
- Taenia SagitaDocument3 pagesTaenia SagitaNur LiyanaNo ratings yet
- Beef Tapeworm Infection GuideDocument39 pagesBeef Tapeworm Infection GuideMicah MatibagNo ratings yet
- Cestodes: Tapeworms and Their BiologyDocument70 pagesCestodes: Tapeworms and Their BiologyBlanche AltheaNo ratings yet
- Taenia Saginata and SoliumDocument46 pagesTaenia Saginata and SoliumKotilakshmanareddy TetaliNo ratings yet
- Helminth Infections (1) : Ni Putuwintariani S.Farm., M.Farm., AptDocument40 pagesHelminth Infections (1) : Ni Putuwintariani S.Farm., M.Farm., AptSurya PradnyaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology and Parasitology #1Document11 pagesMicrobiology and Parasitology #1Judy BaguiwenNo ratings yet
- Tapeworm InfectionsDocument4 pagesTapeworm InfectionsJayesh MahajanNo ratings yet
- TaeniasisDocument2 pagesTaeniasisSid QNo ratings yet
- Zoonotic DiseasesDocument96 pagesZoonotic DiseasesWakjira GemedaNo ratings yet
- Roundworms1 150412082717 Conversion Gate01Document37 pagesRoundworms1 150412082717 Conversion Gate01Wahed KabirNo ratings yet
- Cestodes ReportingDocument50 pagesCestodes ReportingEdwin GanadinNo ratings yet
- Beef and Pork Tapeworm Classification, Lifecycle and TreatmentDocument8 pagesBeef and Pork Tapeworm Classification, Lifecycle and TreatmentadhiNo ratings yet
- Helminthology Platyhelminthes CestodesDocument46 pagesHelminthology Platyhelminthes CestodesTutde SedanaNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Cestodes: Morphology, Life Cycles and TreatmentDocument9 pagesIntestinal Cestodes: Morphology, Life Cycles and Treatmentبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- Taenia SoliumDocument44 pagesTaenia SoliumRanti AgustiniNo ratings yet
- Baterial Infection (Taeniasis)Document8 pagesBaterial Infection (Taeniasis)Brijesh Singh YadavNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity - FecalysisDocument2 pagesLab Activity - FecalysisARRWEN DOMINIQUE YZABELLE TUAZONNo ratings yet
- Taenias IsDocument25 pagesTaenias Iszaid nabeelNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 - CESTODES GROUP 4 FINAL.Document9 pagesActivity 3 - CESTODES GROUP 4 FINAL.the someoneNo ratings yet
- 5 - Stephanurus, Heterakis and SpiruridsDocument78 pages5 - Stephanurus, Heterakis and Spiruridsaniel_bmNo ratings yet
- Cleanup Run Me FirstDocument12 pagesCleanup Run Me FirstJesus BerriosNo ratings yet
- Diphyllobothrium Latum: Morphology (Adults)Document11 pagesDiphyllobothrium Latum: Morphology (Adults)Sheana TmplNo ratings yet
- Ascaris Lumbricoides: MorphologyDocument7 pagesAscaris Lumbricoides: MorphologyIntan HaddadNo ratings yet
- Fascioliasis: (Assignment)Document6 pagesFascioliasis: (Assignment)adeelNo ratings yet
- Taenias IsDocument56 pagesTaenias Iseliwaja100% (1)
- Cestodes: Tapeworms and Their Life CyclesDocument18 pagesCestodes: Tapeworms and Their Life CyclesLaith BioNo ratings yet
- The Anatomy and Life Cycles of Common FlukesDocument29 pagesThe Anatomy and Life Cycles of Common FlukesBudi AfriyansyahNo ratings yet
- Taenia SoliumDocument10 pagesTaenia SoliumDorothyNo ratings yet
- RingwormsDocument5 pagesRingwormsCitrusNo ratings yet
- Cyclophyllidean CestodesDocument92 pagesCyclophyllidean CestodesPauline AñesNo ratings yet
- CestodaDocument57 pagesCestodaJingga TuasamuNo ratings yet