Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science F3 Respiration
Uploaded by
Suntharan MuniandyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Science F3 Respiration
Uploaded by
Suntharan MuniandyCopyright:
Available Formats
http://mrsuntharanmuniandy.blogspot.
com
RESPIRATION
Chapter one
PMR
Chapter
Review:
Labeling
of
respiratory
system
Flow
of
air
in
and
out
of
lungs
Structure
and
functions
of
the
parts
in
respiratory
system
The
process
of
inhalation
and
exhalation
Function
of
blood
and
the
haemoglobin
How
gaseous
exchange
happens
Cellular
respiration
and
glucose
oxidation
Bell
Jar
model
experiment
Cigarette
smoking:-
What
it
contains
and
the
effect
of
smoking
Diseases
caused
by
cigarette
smoking
Effects
of
smoking
experiment
Pollution:-
what
it
contains
and
the
effect
of
smoking
Ways
to
improve
the
quality
of
air
http://mrsuntharanmuniandy.blogspot.com
Copyright
reserved
Prepared by Mr. Suntharan Muniandy 2012 edition
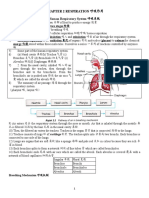
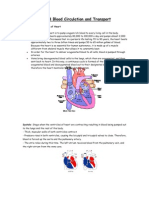
Human Respiratory system
Copyright reserved
Prepared by Mr. Suntharan Muniandy 2012 edition
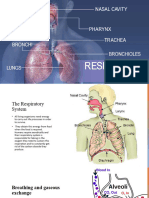
Airflow in and out of lungs Nasal Cavity Trachea Bronchus Bronchiole Alveolus
Inhalation Process: Air Taken in to lungs. External intercostal muscle contract, ribcage moves upward and inwards. Diaphragm contract and flattens, volume increase and pressure decrease. Atmospheric pressure forces outside air into lungs Exhalation Process: Air released out of lungs. Intercostal muscle contract , ribcage moves downwards and inwards. The diaphragm relaxes and curves upwards, volume decrease and pressure increase. Higher pressure in the lungs will force the air out of the lungs
http://mrsuntharanmuniandy.blogspot.com
Copyright reserved
Prepared by Mr. Suntharan Muniandy 2012 edition
RESPIRATION
Copyright
reserved
Function of important structure of respiratory system Nasal Cavity: Hair particles and mucus filters the air Trachea: Built with C-shape cartilage to prevent the trachea from collapsing during respiration. Alveolus: One cell thick, balloon shape and present in large number for large surface area, moist surface for easy diffusion of gaseous. Rib cage: Protects the lungs Diaphragm and Intercostal muscle: Contract and relax to expand and deflate the lungs
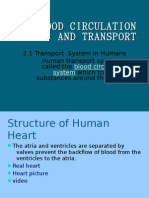
Prepared by Mr. Suntharan Muniandy 2012 edition Transport of oxygen in the human body
http://mrsuntharanmuniandy.blogspot.com
Oxygen diffuses in and carbon dioxide diffuses out. Oxygen moves in to Red Blood Cell (RBC) and binds with haemoglobin to form oxyhaemoglobin. Oxygenated blood is sent to heart and the heart pumps oxygentaed blood to the whole body. Oxygenated blood will release the oxygen from RBC to the body cell and receive carbon dioxide in return and becomes deoxygenated blood. Body cell will conduct cellular respiration. Food (Glucose) will be oxidized by using oxygen to produce energy, carbon dioxide and water. Carbon dioxide and water (water vapor) will be excreted out.
Pollution
Acidic gas from factories - Sulphur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide: Damages the breathing channels and lungs. Vehicle Fumes - Carbon monoxide: Competes with carbon dioxide for haemoglobin. Reduces the ability of blood to transport oxygen and causes death in severe cases. Burning forest or garbage (haze) - Damages the lungs, causes asthma Burning plastic materials: Corrodes the breathing channel.
Cigarette Smoking Tar - Darkens/blackens and thickens the lungs. Causes them less efficient for gaseous exchange Nicotine - A type of drug that causes addiction. Carbon dioxide - Acidic gas that corrodes alveolus wall - causes coughing, asthma, bronchitis and lung emphysema. Carcinogens - Causes cancer/tumor. Example: Lung cancer, throat cancer, mouth cancer. Heat - Dries the moist alveolus and causes difficulty in diffusion process Other symptoms are: breathing difficulty, tiredness and excessive coughing http://mrsuntharanmuniandy.blogspot.com
Copyright reserved
Prepared by Mr. Suntharan Muniandy 2012 edition
Bell Jar Experiment
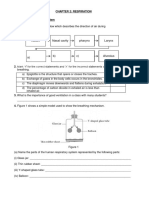
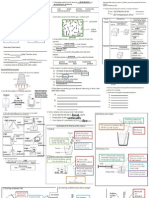
Aim: To study the action of the diaphragm in the breathing mechanism. ANALYSIS The parts in the human respiratory system that is analogous to the simple model in this experiment are as follows: - Rubber sheet: Diaphragm Copyright reserved - Bell jar: Thoracic cavity Prepared by Mr. Suntharan - Glass tube: Trachea Muniandy - Y-shaped tube: Bronchus 2012 edition - Balloon: Lungs The condition when the handle is pulled down represents inhalation in humans. When the rubber sheet is pulled down, the volume in the bell jar increases. This will result decrease of pressure in the bell jar The atmospheric pressure, which is more then the pressure in the bell jar will force the air to move in the bell jar. This will cause the balloon to inflate or expand. The condition when the handle is released represents exhalation in humans. When the rubber sheet is released or pushed up, the volume of the bell jar decrease. The pressure in the bell jar is more then the atmospheric pressure. This will cause the air forced out of the bell jar. This will cause the balloon to deflate. CONCLUSION: Inhalation takes place when the diaphragm is flat Exhalation takes place when the diaphragm curves
Cigarette Smoking Experiment
Aim: To study the effects of smoking on the human respiratory system. OBSERVATION: Materials Observation Thermometer The temperature rises White cotton wool Became darkish yellow Hydrogen carbonate indicator Changed form red to yellow ANALYSIS: The thermometer showed a change in temperature because cigarette smoke is hot. The white cotton wool became darkish yellow because of the presence of tobacco tar. The hydrogen carbonate indicator that changed from red to yellow shows that cigarette smoke is acidic. CONCLUSION: Smoking raises the lung temperature, blackens the lung and corrodes the lung cells.
RESPIRATION EXPERIMENTS
Copyright reserved
Prepared by Mr. Suntharan Muniandy 2012 edition
http://mrsuntharanmuniandy.blogspot.com
Copyright reserved Hydrogen Carbonate solution
The experiment above was not written in proper experimental procedure. This is just a simplified explanation. PLEASE DO NOT FOLLOW THIS PROCEDURE FOR YOUR SCHOOL REPORT
Prepared by Mr. Suntharan Muniandy 2012 edition
http://mrsuntharanmuniandy.blogspot.com Copyright reserved
Prepared by Mr. Suntharan Muniandy 2012 edition
You might also like
- Biodiversity Form 2 Science Chapter 3Document18 pagesBiodiversity Form 2 Science Chapter 3Angie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Respiratory SysteDocument5 pagesFunctions of The Respiratory SysteMohd FirdausNo ratings yet
- Science Form 3 Chapter 1 - Respiration (Notes)Document4 pagesScience Form 3 Chapter 1 - Respiration (Notes)Autumn JJ40% (5)
- Using The Words Given. Trachea Bronchus Lungs: Learning Objective: Human Breathing MechanismDocument3 pagesUsing The Words Given. Trachea Bronchus Lungs: Learning Objective: Human Breathing MechanismMp GopalNo ratings yet
- F3 Chapter 2 RespirationDocument13 pagesF3 Chapter 2 RespirationJue Hazea GoldshopNo ratings yet
- Activity Resources (Teacher's Edition) - 2 YearsDocument100 pagesActivity Resources (Teacher's Edition) - 2 YearsYenny Tiga100% (1)
- Remove Class Paper 1 PDF FreeDocument8 pagesRemove Class Paper 1 PDF Free劉心雅No ratings yet
- Blood Circulation and TransportDocument15 pagesBlood Circulation and Transportqas1727No ratings yet
- Module f3 SC Chapter 1Document26 pagesModule f3 SC Chapter 1HackqRNo ratings yet
- Math Chapter 1.1 Form 1 by KelvinDocument15 pagesMath Chapter 1.1 Form 1 by KelvinKelvin100% (1)
- Form 1 Chapter 7 HeatDocument4 pagesForm 1 Chapter 7 HeatJin TangNo ratings yet
- TB Science F1 Chapter 3Document35 pagesTB Science F1 Chapter 3wienna1987No ratings yet
- Form 2 Chapter 9 HeatDocument46 pagesForm 2 Chapter 9 HeatAmer MalekNo ratings yet
- F3 Chapter 3 TransportationDocument19 pagesF3 Chapter 3 TransportationJue Hazea GoldshopNo ratings yet
- Exam Form 2 March 2018Document10 pagesExam Form 2 March 2018AmetBasir100% (2)
- Science Form 3 Chapter 2 - Blood Circulation PDFDocument4 pagesScience Form 3 Chapter 2 - Blood Circulation PDFFarah Sofea Razali91% (11)
- Sci F1 T1 (E)Document7 pagesSci F1 T1 (E)Sylvia ChinNo ratings yet
- (Notes) Science Form 3 - Chapter 2 (Respiration)Document12 pages(Notes) Science Form 3 - Chapter 2 (Respiration)Aizzat BahiahNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 - Textbook ExerciseDocument8 pagesCHAPTER 2 - Textbook ExercisenoorNo ratings yet
- Science Chapter 2 Form 1Document23 pagesScience Chapter 2 Form 1Kelvin0% (1)
- Form 2 Science Air Pressure NotesDocument15 pagesForm 2 Science Air Pressure NotesAngie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- Sains Form1 Final ExamDocument10 pagesSains Form1 Final ExamNOR SUAKMA BT JAAFARNo ratings yet
- Science Form 2: ElectricityDocument32 pagesScience Form 2: ElectricityNurul HusnaNo ratings yet
- Modul Defra Ting 5 Guru FinalDocument34 pagesModul Defra Ting 5 Guru FinalWeenaNo ratings yet
- Nota PendekDocument9 pagesNota PendekBeevy GB71% (7)
- PMR 2012 Science 108 MantraDocument16 pagesPMR 2012 Science 108 MantraJun MingNo ratings yet
- Science Form 3 Blood Circulation and TransportDocument8 pagesScience Form 3 Blood Circulation and Transportkc_hani0% (1)
- Science-Form 3-Chapter 3 Excretion by KelvinDocument10 pagesScience-Form 3-Chapter 3 Excretion by KelvinKelvinNo ratings yet
- Industrial Wastewater Treatment Via PhotocatalysisDocument34 pagesIndustrial Wastewater Treatment Via PhotocatalysisAlok GargNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Chapter 10Document10 pagesForm 2 Chapter 10naza9775100% (7)
- Blood Circulation and Transport Learning Objective: 2.1 Understanding The Transport System in HumansDocument14 pagesBlood Circulation and Transport Learning Objective: 2.1 Understanding The Transport System in HumansJames WongNo ratings yet
- (2) 人文专业汉语读写 第10单元Document58 pages(2) 人文专业汉语读写 第10单元Дарья ИгнатьеваNo ratings yet
- Bio Form4 Chemical Composition in CellDocument11 pagesBio Form4 Chemical Composition in Celldebbycley86% (7)
- FORM 2, Chap 03-BiodiversityDocument15 pagesFORM 2, Chap 03-BiodiversitySyahrul100% (11)
- Mas SPM 2012Document218 pagesMas SPM 2012fizzykolaNo ratings yet
- Model Pt3Document30 pagesModel Pt3Sean Larson100% (4)
- Year 5 Science:HeatDocument7 pagesYear 5 Science:HeatRaj King50% (2)
- CHAPTER 3 Coordination ResponseDocument19 pagesCHAPTER 3 Coordination ResponseRozalina AzianNo ratings yet
- Science Form 3 Chapter 2Document31 pagesScience Form 3 Chapter 2rosya100% (5)
- Mathematics Form 3Document24 pagesMathematics Form 3Amal SufiahNo ratings yet
- Science Form 1 Chapter 1Document13 pagesScience Form 1 Chapter 1huisin100% (1)
- F3 Chapter 4 Reactivity of MetalsDocument11 pagesF3 Chapter 4 Reactivity of MetalsJue Hazea GoldshopNo ratings yet
- To Determine The Energy Content in The Sample of FoodDocument2 pagesTo Determine The Energy Content in The Sample of FoodnanarahmannaimNo ratings yet
- f1 Chapter 4 ReproductionDocument22 pagesf1 Chapter 4 ReproductionshshshchinNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Form 3Document24 pagesMathematics Form 3Amal SufiahNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4 Notes Chapter 7Document24 pagesBiology Form 4 Notes Chapter 7Nitya Dewi100% (2)
- Gas Exchange in Humans 1 QP PDFDocument9 pagesGas Exchange in Humans 1 QP PDFSyakir FahmieNo ratings yet
- Sains Tingkatan 3: Science Form 3Document27 pagesSains Tingkatan 3: Science Form 3Nadzirah RedzuanNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in Humans PDFDocument32 pagesGas Exchange in Humans PDFNaomi LimNo ratings yet
- S2 - Bio - RevisionNotes 1.1 To 1.4 - PreMidDocument7 pagesS2 - Bio - RevisionNotes 1.1 To 1.4 - PreMidKaung ThihaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: The Second HalfDocument35 pagesRespiratory System: The Second HalfnicopiiNo ratings yet
- F3 Chapter 1 Respiratory SystemDocument11 pagesF3 Chapter 1 Respiratory SystemFoh Lian HuaiNo ratings yet
- Respiration Form 3Document21 pagesRespiration Form 3zuereyda91% (11)
- Lecture 4 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEMDocument48 pagesLecture 4 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEMZara16No ratings yet
- Respiration Form 3Document19 pagesRespiration Form 3Akif FarhanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Uploaded On Dow PortalDocument52 pagesRespiratory System Uploaded On Dow PortalAyesha MasoodNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument24 pagesRespiratory SystemArjunNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument19 pagesRespiratory SystemMotiourNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: The Organs That Help To Get Oxygen From The Air Into Your Blood, and To Get Rid of Carbon DioxideDocument22 pagesRespiratory System: The Organs That Help To Get Oxygen From The Air Into Your Blood, and To Get Rid of Carbon DioxideTravel UnlimitedNo ratings yet
- Body Coordination Part 2Document22 pagesBody Coordination Part 2Suntharan MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Pt3 Science Seminar ModuleDocument28 pagesPt3 Science Seminar ModuleSuntharan Muniandy100% (5)
- Maths Upsr Sebenar 2002Document12 pagesMaths Upsr Sebenar 2002Anonymous xGCiF6oNo ratings yet
- 2019 Sains PT3Document25 pages2019 Sains PT3Suntharan MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Coordination and Response. PT3 2022Document3 pagesCoordination and Response. PT3 2022Suntharan MuniandyNo ratings yet
- PT3 Science Form 3 SEMINARDocument28 pagesPT3 Science Form 3 SEMINARSuntharan MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Science Chapter 7 PMRDocument10 pagesScience Chapter 7 PMRSuntharan MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Carrier Guidance BrochureDocument1 pageCarrier Guidance BrochureSuntharan MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Bio Essays f4 & f5Document23 pagesBio Essays f4 & f5Suntharan Muniandy100% (1)
- Expedition Booklet Taman Negara. Modified PenangDocument20 pagesExpedition Booklet Taman Negara. Modified PenangSuntharan MuniandyNo ratings yet
- ArtistDocument4 pagesArtistSuntharan MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Carrier Guidance BrochureDocument1 pageCarrier Guidance BrochureSuntharan MuniandyNo ratings yet
- ArtistDocument4 pagesArtistSuntharan MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Examiner Tips For IGCSE BiologyDocument12 pagesExaminer Tips For IGCSE BiologySunSun Hemnilrat42% (12)
- Greedy As A HumanDocument2 pagesGreedy As A HumanSuntharan MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument3 pagesCell DivisionSuntharan MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Stakeholder1 1Document2 pagesStakeholder1 1Suntharan MuniandyNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Math Question Paper 4 October/November 2007Document12 pagesIGCSE Math Question Paper 4 October/November 2007Mariam A.No ratings yet
- Seminar Pendidkan SPM Science: by MR Suntharan MuniandyDocument17 pagesSeminar Pendidkan SPM Science: by MR Suntharan MuniandySuntharan MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Favourite 3rd Party Transfer: SuccessfulDocument1 pageFavourite 3rd Party Transfer: SuccessfulSuntharan MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Convergence Project 1Document22 pagesConvergence Project 1Suntharan MuniandyNo ratings yet
- CH 7 Respiration StudentDocument25 pagesCH 7 Respiration StudentSuntharan MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Biotips 2013Document3 pagesBiotips 2013Suntharan MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument3 pagesCell DivisionSuntharan MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Organelles in CellsDocument3 pagesOrganelles in CellsSuntharan MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument3 pagesCell DivisionSuntharan MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Percubaan PMR 2013 Kedah Sains Paper 1Document26 pagesPercubaan PMR 2013 Kedah Sains Paper 1Chia Zhe LooNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan Phase 3 & 4Document18 pagesUnit Plan Phase 3 & 4Suntharan MuniandyNo ratings yet
- PMR Science Form 3 TipsDocument41 pagesPMR Science Form 3 TipsSuntharan MuniandyNo ratings yet
- g11 Sem1t1a2 FinalDocument8 pagesg11 Sem1t1a2 FinalSuntharan MuniandyNo ratings yet