Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Future Simple (Futuro Simple)
Uploaded by
baterista99Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Future Simple (Futuro Simple)
Uploaded by
baterista99Copyright:
Available Formats
Future Simple (Futuro simple) Hay dos formas principales para expresar el futuro.
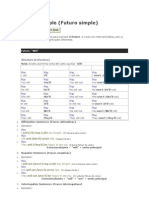
A veces son intercambiables, pero a menudo pueden tener significados diferentes. Future: "Will" Structure (Estructura) Nota: Existe una forma corta del verbo auxiliar "will". Afirmativo I will You will He will She will It will We will They will Forma corta I'll You'll He'll She'll It'll We'll They'll Negativo I will not You will not He will not She will not It will not We will not They will not Forma corta I won't (I'll not) You won't. You'll not He won't. He'll not. She won't. She'll not. It won't. It'll not. We won't (We'll not) They won't (They'll not)
1. Affirmative Sentences (Frases afirmativas) o Ejemplos: I will [I'll] ring (call) you tonight. (Te llamar esta noche.) She will [She'll] arrive late. (Llegar tarde.) They will [They'll] be happy to see you. (Estarn felices de verte.) Estructura Sujeto + "will" + verbo principal. 2. Negative Sentences (Frases negativas) o Ejemplos: I will not [won't] ring (call) you tonight. (No te llamar esta noche.) She will not [won't] arrive late. (No llegar tarde.)
They will not [won't] be happy to see you. (No estarn felices de verte.) Estructura Sujeto + "will" + "not" + verbo principal. 3. Interrogative Sentences (Frases interrogativas) o Ejemplos: Will you ring (call) me tonight? (Me llamars esta noche?) Will she arrive late? (Llegar tarde?) Will they be happy to see you? (Estarn felices de verte.) Estructura "Will" + sujeto + verbo principal. Future: "Going to" "Going to" se equivale a "ir a" en espaol. Structure (Estructura) 1. Affirmative Sentences (Frases afirmativas) o Ejemplos: I'm going to ring (call) you tonight. (Voy a llamarte esta noche.) She's going to arrive late. (Va a llegar tarde.) They're going to be happy to see you. (Van a estar felices de verte.) Estructura Sujeto + verbo auxiliar ("to be") + "going to" + verbo principal. 2. Negative Sentences (Frases negativas) o Ejemplos: I'm not going to ring (call) you tonight. (No voy a llamarte esta noche.) She's not going to arrive late. (No va a llegar tarde.)
They're not going to be happy to see you. (No van a estar felices de verte.) Estructura Sujeto + verbo auxiliar ("to be") + "not" + "going to" + verbo principal. 3. Interrogative Sentences (Frases interrogativas) o Ejemplos: Are you going to ring (call) me tonight? (Vas a llamarme esta noche?) Is she going to arrive late? (Va a llegar tarde?) Are they going to be happy to see you? (Van a estar felices de verte?) Estructura Verbo auxiliar ("to be") + sujeto + "going to" + verbo principal. Nota: Para acciones o eventos inminentes, podemos decir "about to" (a punto de). La estructura es el mismo de "going to."
Ejemplos: I'm about to leave. (Estoy a punto de irme.) The concert is about to begin. (El concierto est a punto de comenzar.)
Uses (Usos) Las formas "will" y "going to" se utilizan para el futuro, pero el uso de uno sobre el otro significa que la probabilidad de la accion futura pasar. El aspecto que lo diferencia del futuro "going to" con "will" es el sentido de "planificacin". En general, se usa "going to" para planes concretos, cuando tenemos la seguridad de que algo va a suceder. 1. Se usa "will" con acciones voluntarias. o Ejemplos: Will you help me move? (Me ayudars a mudarme?) They will clean their rooms. (Limpiarn sus habitaciones.) She won't work with Paul. (No trabajar con Paul.) 2. Se utiliza "will" para expresar una promesa. o Ejemplos: When I am president, I will lower taxes. (Cuando sea presidente, bajar los impuestos.)
He promises he will call when he arrives. (Le prometio llamar cuando llegue.) 3. Se usa "going to" para planes. Se indica la intencin a hacer algo. o Ejemplos: We're going to have a party tonight. (Vamos a dar una fiesta esta noche.) Richard's going to take an English class. (Richard va a realizar un clase de ingls.) Are Peter and you going to play football later? (Vas a jugar futbol luego?) 4. Se puede usar "will" o "going to" para predicciones porque el hablante no tiene control sobre el futuro. o Ejemplos: It will be a great party. / It's going to be a great party. (Ser una fiesta genial.) It won't rain. / It's not going to rain. (No va a llover.) Nota: Existen algunas situaciones en las que usamos el presente continuo o el presente simple para expresar acciones en el futuro. 1. Se puede usar el presente continuo para acciones en el futuro cercano. o Ejemplos: Sarah is arriving tonight. (Sarah llega esta noche.) I'm going to the doctor this afternoon. (Voy al mdico esta tarde.) 2. Se usa el presente simple para eventos programados en un futuro prximo. o Ejemplos: The party starts at 9pm. (La fiesta empieza a las 21h.) The train leaves at 10am. (El tren sale a las 10h.)
You might also like
- Spider SettingsDocument14 pagesSpider Settingsvandale38No ratings yet
- Cuadro Comparativo "Will" y "Going To"Document2 pagesCuadro Comparativo "Will" y "Going To"Erick Martinez Mariano75% (28)
- Faure Pavane PDFDocument13 pagesFaure Pavane PDFAnonymous ySVS7ANo ratings yet
- Music Theory Final ExamDocument7 pagesMusic Theory Final ExamIan Burns0% (1)
- Future WillDocument7 pagesFuture WillSamuel Tafur BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Future SimpleDocument25 pagesFuture SimpleCristhian Cruz TerronesNo ratings yet
- Future: "Will": Structure (Estructura)Document7 pagesFuture: "Will": Structure (Estructura)DEGARONo ratings yet
- How To Form The Simple Future: Form) Construction in Formal WritingDocument15 pagesHow To Form The Simple Future: Form) Construction in Formal WritingDiana Martinez E.No ratings yet
- Future Simple - Will + Going ToDocument4 pagesFuture Simple - Will + Going Toteacher.neusgiroNo ratings yet
- Class WorkshopDocument13 pagesClass WorkshopPipe RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Will y Going ToDocument3 pagesWill y Going ToLily SantosNo ratings yet
- Futuro Simple I y IIDocument18 pagesFuturo Simple I y IIJesusdavid CorderocovaNo ratings yet
- Future TenseDocument6 pagesFuture TenseMuhammad Ibnu LaksonoNo ratings yet
- FutureDocument21 pagesFutureEdna Margarita MeloNo ratings yet
- Future: "Will": StructureDocument5 pagesFuture: "Will": StructurekeilaNo ratings yet
- Grammar 1 (Future Time (Will and Going To)Document27 pagesGrammar 1 (Future Time (Will and Going To)Luis EnriqueNo ratings yet
- Uses Del Will y Going ToDocument2 pagesUses Del Will y Going ToYeraldine Johana Ramírez AdameNo ratings yet
- Guia de Estudio para Examen Extraordinario de InglesDocument6 pagesGuia de Estudio para Examen Extraordinario de InglesNohan OlivanderNo ratings yet
- Simple Future For Cmap ToolsDocument6 pagesSimple Future For Cmap Toolsapi-262708894No ratings yet
- Difference Between Will and Going ToDocument3 pagesDifference Between Will and Going ToemilillaNo ratings yet
- FutureDocument7 pagesFutureAndreiAlexandruNo ratings yet
- El FuturoDocument4 pagesEl FuturoMafe LunaNo ratings yet
- Future Simple (Will + Be Going ToDocument20 pagesFuture Simple (Will + Be Going ToMelanie GiovannettiNo ratings yet
- Fiuture and Future in The PastDocument11 pagesFiuture and Future in The PastElena PorceanuNo ratings yet
- Future Perfect TenseDocument18 pagesFuture Perfect TenseJasbir SinghNo ratings yet
- Simple Future: FORM WillDocument8 pagesSimple Future: FORM WillNong PhotiwongNo ratings yet
- Subject + Will + 1: 1 2 3 Go Went Gone Affirmative Negative InterrogativeDocument6 pagesSubject + Will + 1: 1 2 3 Go Went Gone Affirmative Negative InterrogativeИнженер Луис А. ГарсиаNo ratings yet
- Simple Future: Lendra Kerta Putra, SS., MMDocument11 pagesSimple Future: Lendra Kerta Putra, SS., MMyuliaNo ratings yet
- Future Forms: English As 2nd LanguageDocument4 pagesFuture Forms: English As 2nd LanguagecartuxaNo ratings yet
- Future: Will Verb (Base Form)Document4 pagesFuture: Will Verb (Base Form)Инженер Луис А. ГарсиаNo ratings yet
- Materi Tentang Can, CouldDocument6 pagesMateri Tentang Can, Couldfino harfalisNo ratings yet
- Simple Future Vs Idiomatic FutureDocument5 pagesSimple Future Vs Idiomatic FutureADOLFOASU23No ratings yet
- Theory - Simple and Continuous Present TensesDocument8 pagesTheory - Simple and Continuous Present TensesMiRella MaRiaNo ratings yet
- Tugas B.inggris Kelompok 5Document30 pagesTugas B.inggris Kelompok 5yanifitri7296No ratings yet
- Auxiliar Modal Verbo Auxiliar: EjemploDocument13 pagesAuxiliar Modal Verbo Auxiliar: EjemploFredNo ratings yet
- Tiempo Verbal Contracción Afirmación Estructura: I M, She SDocument28 pagesTiempo Verbal Contracción Afirmación Estructura: I M, She SEswin GarNo ratings yet
- Materi Ajar Modal Auxiliary Verb Can N WillDocument10 pagesMateri Ajar Modal Auxiliary Verb Can N WillZuliaNo ratings yet
- XauqueDocument25 pagesXauqueLindsey StokesNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 - Vocabulary & Will-Be Going ToDocument1 pageActivity 3 - Vocabulary & Will-Be Going ToJhonnyNo ratings yet
- Future TensesDocument20 pagesFuture TensesDaniel PopescuNo ratings yet
- Simple Future: FORM WillDocument5 pagesSimple Future: FORM WillMuhammad Rizam Hj BakriNo ratings yet
- This and TheseDocument4 pagesThis and ThesegiselleNo ratings yet
- Modals VerbsDocument8 pagesModals VerbsjsrkqsmjyjNo ratings yet
- Grammar Week 8 Future TenseDocument11 pagesGrammar Week 8 Future TenseSebastian PachecoNo ratings yet
- Future FormsDocument8 pagesFuture FormsAlaNo ratings yet
- The Simple Future - WillDocument4 pagesThe Simple Future - WillCindyNo ratings yet
- Disusun Oleh:: SMP Negeri 1 Pegajahan T.A 2018/2019Document9 pagesDisusun Oleh:: SMP Negeri 1 Pegajahan T.A 2018/2019riswanNo ratings yet
- The Future TensesDocument4 pagesThe Future TensesCélia ZENNOUCHENo ratings yet
- TrimestralDocument4 pagesTrimestralpaula muñozNo ratings yet
- Refers To A Time After The Current and Expresses Facts or CertaintiesDocument2 pagesRefers To A Time After The Current and Expresses Facts or CertaintiesCathy ArriazaNo ratings yet
- Future: Forms: 1. Basic Meanings of The FormsDocument5 pagesFuture: Forms: 1. Basic Meanings of The Formsalexferreire1No ratings yet
- Clase XII Futuro Simple Futuro ContinuoDocument30 pagesClase XII Futuro Simple Futuro ContinuoDenis CalleNo ratings yet
- Grammar Guide Inglés 2Document33 pagesGrammar Guide Inglés 2mavNo ratings yet
- Present Continuous TenseDocument4 pagesPresent Continuous TensesanmohdNo ratings yet
- Future Will & Be Going ToDocument8 pagesFuture Will & Be Going ToFitri HeldayetiNo ratings yet
- 1.simple Future TenseDocument18 pages1.simple Future TenseLiyan SusantoNo ratings yet
- Relative Clauses - Future TenseDocument6 pagesRelative Clauses - Future TenseJose Jaime SaldarriagaNo ratings yet
- Auxiliar Going ToDocument3 pagesAuxiliar Going ToCryz AjcucNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Fadly Nuralim (09320190175)Document4 pagesMuhammad Fadly Nuralim (09320190175)Muhammad Farhan AlimuddinNo ratings yet
- Future Simple Continuous PDFDocument2 pagesFuture Simple Continuous PDFGavril ApostolNo ratings yet
- Italian Irregular Verbs Fully Conjugated in all Tenses (Learn Italian Verbs Book 1)From EverandItalian Irregular Verbs Fully Conjugated in all Tenses (Learn Italian Verbs Book 1)No ratings yet
- How to Use the Word “Have” In English: A Comprehensive Guide to the Word “Have”From EverandHow to Use the Word “Have” In English: A Comprehensive Guide to the Word “Have”No ratings yet
- 84 P. Whats On Bristol Magazine March 2011Document84 pages84 P. Whats On Bristol Magazine March 2011whatsongroupNo ratings yet
- Patience (Acoustic) Guitar Tab by Guns N' Roses at XGuitar - ComDocument8 pagesPatience (Acoustic) Guitar Tab by Guns N' Roses at XGuitar - CompedubaNo ratings yet
- IELTS Reading - What Makes A Musical ExpertDocument1 pageIELTS Reading - What Makes A Musical ExpertKhánh LinhNo ratings yet
- Nazia Hassan Aap Jai Sa Koi Song Lyrics QurbaniDocument3 pagesNazia Hassan Aap Jai Sa Koi Song Lyrics QurbaniNarayanan MuthuswamyNo ratings yet
- Azu Etd 15461 Sip1 MDocument113 pagesAzu Etd 15461 Sip1 MsilviufiicrestinNo ratings yet
- Shelly As A Lyrical PoetDocument2 pagesShelly As A Lyrical PoetSr Chandrodaya JNo ratings yet
- Midterm - Marc Chagall TimelineDocument5 pagesMidterm - Marc Chagall TimelineHollyNo ratings yet
- LES MILLS THE TRIP 16 (THETRIP16ChoreographyNotes Row en App Print PDFDocument14 pagesLES MILLS THE TRIP 16 (THETRIP16ChoreographyNotes Row en App Print PDFDavid PulidoNo ratings yet
- Saxophone Trio - William PresserDocument13 pagesSaxophone Trio - William PresserVitor Bragança67% (3)
- Quizzes Questionnaires and PuzzlesDocument316 pagesQuizzes Questionnaires and PuzzlesDANIELA SIMONELLI100% (1)
- Menuet PDFDocument1 pageMenuet PDFPavao MasicNo ratings yet
- Ford SYNC With MyFord Touch HandbookDocument25 pagesFord SYNC With MyFord Touch HandbookFord Motor Company0% (1)
- Physical EducationDocument2 pagesPhysical EducationJules AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Catalogo KRKDocument12 pagesCatalogo KRKluz.negociosenlineaNo ratings yet
- Yakety Sax: PianoDocument3 pagesYakety Sax: PianomagnojazzmanNo ratings yet
- Homework 4 - Adriana UrrutiaDocument8 pagesHomework 4 - Adriana UrrutiaAdriana UrrutiaNo ratings yet
- Angela Ndalianis-Neo-Baroque Aesthetics and Contemporary Entertainment (Media in Transition) (2004)Document341 pagesAngela Ndalianis-Neo-Baroque Aesthetics and Contemporary Entertainment (Media in Transition) (2004)Radost Galonja Krtinić100% (2)
- Albert Einstein BiographyDocument1 pageAlbert Einstein Biographydewa putu dyakaNo ratings yet
- Mtima Woyera Catholic Tic RenewalDocument6 pagesMtima Woyera Catholic Tic Renewalmoseschelenga0% (1)
- Let It BeDocument5 pagesLet It BeItalian MappingNo ratings yet
- Fantasia Di Natale PianoforteDocument5 pagesFantasia Di Natale Pianofortefabio andrianòNo ratings yet
- Barrios Preludio en Do MenorDocument2 pagesBarrios Preludio en Do MenorMikeCook100% (2)
- Soal CaptionDocument5 pagesSoal CaptionNaufal Dhia PerwiraprasnaNo ratings yet
- A3 HigherDocument5 pagesA3 HigheriloveleeminhoNo ratings yet
- Carolyn Gage Portland, ME (207) 774-4231 Academic BackgroundDocument29 pagesCarolyn Gage Portland, ME (207) 774-4231 Academic Backgroundcarolyn6302No ratings yet
- Presonus Eureka ManualDocument26 pagesPresonus Eureka Manualkevin talloenNo ratings yet
- BC V Class NotificationDocument10 pagesBC V Class Notificationkuruba sairamNo ratings yet