Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Doctor and Public Health
Uploaded by
sarguss14Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Doctor and Public Health
Uploaded by
sarguss14Copyright:
Available Formats
AGARIN ALDEMITA ALVEZ ANSON ASPERAS BALMEO BARTOLOME BAWALAN BERNARD BINAG BISAREZ BOOL CABIGTIN
O G
CASTELO CLOSA CO COMO CONDE CRUZ DELA CRUZ DELA DIAZ DOMING EVANGELIST GABUYO GALANG
BATCH 2010 Pamantasan ng Lungsod ng Maynila –effort
College of Medicine
ROSA
whether
O
done by a voluntary or a
A
FCM 3 - THE DOCTOR andgovernment
PUBLIC HEALTH
agency by Dra. Cruz
13-june-08
GENEBLAZ ILAGAN ISANAN JAMORALIN JOSE LAGAS LAZARO LIBIRAN LINTAG LUZA MAGSAKAY MALLARE MANZAN
O O
MATIAS MENDING MOZO NAGUIT ODEVILLAS PATIGAS PRELIGERA QUIBULUE RAMOS REAŇO REQUINTA RODRIGUEZ SALVADO
R
SOMBILLA SOSA TOLED UBALDE VEGO VERGAR VILLANUEVA VILORIA
O A
SESSION OBJECTIVES: ROLES OF A PUBLIC HEALTH DOCTOR
1. To define Preventive Medicine and Public Health 1. Healer
2. To discuss the roles of a public health doctor 2. Educator
3. To discuss the concept, approach and goal of 3. Administrator
PHC 4. Researcher
4. To discuss Health for All in the 21st Century 5. Social mobilizer
based on the ff:
a. Policy objectives 1970s – growing demand for improved health
b. Goals WHO’s answer was expressed in the
c. Global Health targets to 2020 slogan
Health for All by the Year 2000
PREVENTIVE MEDICINE
- the science & art of preventing disease, 1978 – Alma Alta Conference on PHC
prolonging life & promoting Physical and Mental > jointly sponsored by the WHO and
Health and efficiency UNICEF
> discussed PHC as one of the ways to
bring about the
Medical Practitioner Public goal of HFA
Health Practitioner
dealing w/ individuals dealing w/
groups of
& families
individuals in a community
WHAT IS PRIMARY HEALTH CARE?
Clinical Practice Types of PHC:
Public Health hospital or clinic-based
community-based
PUBLIC HEALTH community managed
- the science & art of preventing disease,
prolonging life & promoting physical & mental THE CONCEPT
health & efficiency thru:
PHILOSOPHY based on values
Organized Community Effort for: Health as fundamental human right
the sanitation of the environment Health as individual collective responsibility
the control of community infections Health as equal opportunity
the education of the individual in principles of Health as an essential element of socio-
personal hygiene economic development
the organization of medical services for the - productivity of the people no socio-
early diagnosis and economic dev’t
treatment of diseases
the development of a social machinery which STRUCTURE that is part of the health care
will ensure a standard of living adequate for system that takes place in the community
the maintenance of health
SERVICES that include:
The Agencies set to carry out organized Education
community health activities: Food supply and nutrition
1. Voluntary – private, supported wholly or in large Safe water and sanitation
part by non-tax MCH and Family Planning
funds
ex. NGOs, private clinics, private Immunization
foundations Disease Prevention and Control
2. Governmental – health work carried on thru Treatment of common diseases
organized community Essential Drugs
by: goldi ^_^, adi,, buff, ezrah
THE APPROACH b. combat poverty as a reflection of PHC’s concern
Partnership with the community for social justice
Intersectoral Coordination c. promote equity in access to health care
Intrasectoral – DOH w/ other health care d. build partnerships to include families,
systems such as communities & their organizations
district hospitals, clinics e. reorient health systems towards promotion of
w/in the Health Sector health & prevention of disease
Intersectoral – DOH with other government
agencies or GOALS OF HFA
institutions such as the LGU, An increase in the life expectancy & in the
NGOs, etc. quality of life for all
Appropriate Technology Improved equity in health between and within
a. practical – simple to use by the countries
community under local Access for all to sustainable health systems &
conditions services
b. scientifically sound – produces side
effects with minimal GLOBAL HFA TARGETS to 2020
harm
c. acceptable to the community TARGET 1: By 2005, health equity indices will be
Suitable Manpower used within & between countries as a basis for
Self-reliance promoting & monitoring equity in health
Equitable distribution of health resources equity will be assessed on the basis of a
- based on needs measure of child growth
Appropriate health system infrastructure The percentage of children under 5 yrs who are
stunted should be less than 20% in all
THE GOAL countries and in all specific subgroups within
TO ACHIEVE HEALTH FOR ALL THAT IS countries by 2020
Accesible to everyone
TARGET 2: By 2020, the targets agreed at world
Acceptable and affordable to everyone
conferences for MMR (maternal mortality rate),
Based in the community or workplace
under-five or child mortality rate (CMR) and life
expectancy will be met
MMR – less than 100 / 100,000 live births
CMR – less than 45 / 1000 live births
Life expectancy at birth – over 70 yrs for all
HEALTH FOR ALL IN THE 21ST CENTURY
countries
- aims to help realize the vision of Health for All
Optional indicators: infant, neonatal, and adult
launched at the Alma Alta Conference in 1978
mortality rates
- it sets out for the first 2 decades of the 21st
century, global priorities and targets w/c will
TARGET 3: By 20202, the worldwide burden of
create conditions for people worldwide to reach
disease will be substantially decreased
and maintain the highest attainable level of health
achieved thru disease control programs aimed
throughout their lives
at reversing
- HFA in the 21st Century is a continuation of the
current trends of increasing incidence and
HFA process
disability caused by:
TB, HIV/AIDS, Malaria, Tobacco related diseases,
Keys to Achieving HFA: Lessons and
and violence
Progress
and trauma
a. PHC as an approach has provided impetus and
energy to progress towards HFA impact will be quantified in terms of premature
b. Some progress has been made in ensuring death and disability
access to the original 8 PHC elements
c. PHC remains valid as the point of entry into a
comprehensive health care system
d. Intersectoral action for health has not been fully
achieved TARGET 4: Eradicate and Eliminate certain
e. Reorientation of health services & personnel to diseases
PHC principles remains elusive Measles will be eradicated by 2020
f. Community participation takes time and Lymphatic filariasis will be eliminated by 2020
dedication Transmission of Chagas disease will be
interrupted by 2010
POLICY OBJECTIVES Leprosy will be eliminated by 2010
a. make health central to development & enhance Trachoma will be eliminate by 2020
prospects for intersectoral action
by: goldi ^_^, adi,, buff, ezrah
Vitamin A and iodine deficiencies will be - owari -
eliminated by 2020
TARGET 5: By 2020, all countries through
intersectoral action, will have made proper
progress in making available safe drinking water,
adequate sanitation, foord and shelter in sufficient
quantity and quality
Proportion of households/people:
with regular access to sufficient and safe
drinking water
with adequate sanitation facilities
living in shelter that is structurally safe & sited
on safe land
with access to sufficient and safe food
TARGET 6: By 2020, all countries will have
introduced & be actively managing and monitoring
strategies that strengthen health-enhancing
lifestyles & weaken health damaging ones through
a combination of regulatory, economic,
educational, organizational, and community-based
programmes
TARGET 7: By 2005, all member states will have
operational mechanisms for developing,
implementing and monitoring policies that are
consistent with this HFA policy
Indicators should be applied to measure:
the quality of community involvement
existence of a policy as reflected in terms of
national legislation
resource allocation in line with the policy
technical cooperation
TARGET 8: By 2010, all people will have access
throughout their lives to comprehensive, essential,
quality health care, supported by essential public
health functions
provide sustainable financing for PHC
invest in human & institutional capacity for
health
optimize private and public sector support
strengthen research to support & advance PHC
implement global, national, and local
surveillance and monitoring systems
TARGET 9: by 2010, appropriate global and
national health information, surveillance & alert
systems will be established
enable countries to monitor & evaluate their
health situation, performance of their services
& impact of their policies
TARGET 10: By 2010, research policies and
institutional mechanisms will be operational at
global, regional, and country level
all countries need to define their research
priorities and ensure that research is funded
and managed
by: goldi ^_^, adi,, buff, ezrah
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Hotel Design Planning and DevelopmentDocument30 pagesHotel Design Planning and DevelopmentTio Yogatma Yudha14% (7)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- World Gastroenterology Organization Global GuidelineDocument29 pagesWorld Gastroenterology Organization Global GuidelineRizky Rachmania AmandaNo ratings yet
- Preoperative EvaluationDocument25 pagesPreoperative Evaluationsarguss14No ratings yet
- Male PelvisDocument8 pagesMale Pelvissarguss14100% (1)
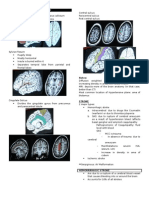
- NeuroradiologyDocument11 pagesNeuroradiologysarguss14100% (2)
- Small BowelDocument4 pagesSmall Bowelsarguss14100% (1)
- Kidney, Ureter, BladderDocument12 pagesKidney, Ureter, Bladdersarguss14100% (1)
- Axial Arthritis: Degenerative Annular DiseaseDocument18 pagesAxial Arthritis: Degenerative Annular Diseasesarguss14100% (1)
- Inhalational Anesthetics: Patigas, Requinta, ResuelloDocument88 pagesInhalational Anesthetics: Patigas, Requinta, Resuellosarguss140% (1)
- Epidural and Spinal AnesthesiaDocument86 pagesEpidural and Spinal Anesthesiasarguss1471% (7)
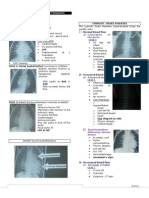
- Cyanotic Congenital Heart Diseases, Etc.Document12 pagesCyanotic Congenital Heart Diseases, Etc.sarguss14100% (2)
- Pediatric GI RadiologyDocument6 pagesPediatric GI Radiologysarguss14No ratings yet
- Stage 1: Dorsal Induction: Pediatric NeuroradiologyDocument8 pagesStage 1: Dorsal Induction: Pediatric Neuroradiologysarguss14100% (1)
- Introduction To RadiologyDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Radiologysarguss14No ratings yet
- Male Genital TractDocument7 pagesMale Genital Tractsarguss14No ratings yet
- Gallbladder, Liver, Pancreas and SpleenDocument19 pagesGallbladder, Liver, Pancreas and Spleensarguss14100% (3)
- Genitourinary SystemDocument8 pagesGenitourinary Systemsarguss14100% (1)
- Extracerebral Hemorrhage, Etc.Document14 pagesExtracerebral Hemorrhage, Etc.sarguss14No ratings yet
- From Doc Bandong's Own Words:: Shar 1 of 20Document20 pagesFrom Doc Bandong's Own Words:: Shar 1 of 20sarguss14100% (1)
- CNS Tumors and Infections Part3Document6 pagesCNS Tumors and Infections Part3sarguss14100% (1)
- CNS Tumors and Infections Part2Document2 pagesCNS Tumors and Infections Part2sarguss14No ratings yet
- Bone TumorsDocument15 pagesBone Tumorssarguss1450% (2)
- CNS Tumors and Infections Part1Document2 pagesCNS Tumors and Infections Part1sarguss14100% (1)
- Congenital Cystic Adenomatoid Malformation (CCAM)Document7 pagesCongenital Cystic Adenomatoid Malformation (CCAM)sarguss14No ratings yet
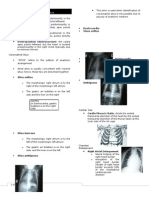
- Chest RadiologyDocument3 pagesChest Radiologysarguss14No ratings yet
- ArthritisDocument9 pagesArthritissarguss14100% (1)
- Genitourinary SystemDocument8 pagesGenitourinary Systemsarguss14100% (1)
- Cardiac ImagingDocument7 pagesCardiac Imagingsarguss14No ratings yet
- Pleura and MediastinumDocument16 pagesPleura and Mediastinumsarguss14100% (1)
- NeuroradiologyDocument25 pagesNeuroradiologysarguss14100% (2)
- Introduction To RadiologyDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Radiologysarguss14No ratings yet
- Ipo Exam Revised SyllabusDocument1 pageIpo Exam Revised Syllabusজ্যোতিৰ্ময় বসুমতাৰীNo ratings yet
- National Products Classification Code For Services in IndiaDocument92 pagesNational Products Classification Code For Services in Indiakalanemi0% (2)
- Principles of Cost Accounting 1Document6 pagesPrinciples of Cost Accounting 1Alimamy KamaraNo ratings yet
- MSC Euribia - 2023-06-01Document2 pagesMSC Euribia - 2023-06-01蔡國懷No ratings yet
- Chemical Cleaning Products Are Destroying The Ecosystem and Your Septic Tank - Organica BiotechDocument14 pagesChemical Cleaning Products Are Destroying The Ecosystem and Your Septic Tank - Organica BiotechKrispin FongNo ratings yet
- Strain Gauge Sensor PDFDocument12 pagesStrain Gauge Sensor PDFMario Eduardo Santos MartinsNo ratings yet
- E PortfolioDocument76 pagesE PortfolioMAGALLON ANDREWNo ratings yet
- What Is Rack Chock SystemDocument7 pagesWhat Is Rack Chock SystemSarah Perez100% (1)
- PowerhouseDocument10 pagesPowerhouseRanjan DhungelNo ratings yet
- SQL 1: Basic Statements: Yufei TaoDocument24 pagesSQL 1: Basic Statements: Yufei TaoHui Ka HoNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School: Class: XI Subject: Assignment No. 3Document1 pageDelhi Public School: Class: XI Subject: Assignment No. 3Aman Kumar BhagatNo ratings yet
- Aircraft ChecksDocument10 pagesAircraft ChecksAshirbad RathaNo ratings yet
- Scholars of Hadith Methodology in Dealing With The Two Sahihs: The Criticized Ahadith As A Model. Ammar Ahmad Al-HaririDocument37 pagesScholars of Hadith Methodology in Dealing With The Two Sahihs: The Criticized Ahadith As A Model. Ammar Ahmad Al-HaririSalah KhanNo ratings yet
- Call SANROCCO 11 HappybirthdayBramanteDocument8 pagesCall SANROCCO 11 HappybirthdayBramanterod57No ratings yet
- COT EnglishDocument4 pagesCOT EnglishTypie ZapNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Questions & AnswersDocument161 pagesMechanical Questions & AnswersTobaNo ratings yet
- Startups Helping - India Go GreenDocument13 pagesStartups Helping - India Go Greensimran kNo ratings yet
- SOP for Troubleshooting LT ACB IssuesDocument9 pagesSOP for Troubleshooting LT ACB IssuesAkhilesh Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Tugas B InggrisDocument6 pagesTugas B Inggrisiqbal baleNo ratings yet
- Rescue Triangle PDFDocument18 pagesRescue Triangle PDFrabas_No ratings yet
- Electronic Harassment Strahlenfolter - A Short History of Sound Weapons Pt2 - InfrasoundDocument10 pagesElectronic Harassment Strahlenfolter - A Short History of Sound Weapons Pt2 - InfrasoundFrank-BoenischNo ratings yet
- Motivations for Leaving Public Accounting FirmsDocument33 pagesMotivations for Leaving Public Accounting Firmsran0786No ratings yet
- Analysis of VariancesDocument40 pagesAnalysis of VariancesSameer MalhotraNo ratings yet
- STERNOL Specification ToolDocument15 pagesSTERNOL Specification ToolMahdyZargarNo ratings yet
- 3 Steel Grating Catalogue 2010 - SERIES 1 PDFDocument6 pages3 Steel Grating Catalogue 2010 - SERIES 1 PDFPablo MatrakaNo ratings yet
- Models of Health BehaviorDocument81 pagesModels of Health BehaviorFrench Pastolero-ManaloNo ratings yet
- EMMS SpecificationsDocument18 pagesEMMS SpecificationsAnonymous dJtVwACc100% (2)
- Research Paper Theory of Mind 2Document15 pagesResearch Paper Theory of Mind 2api-529331295No ratings yet