Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drugs
Uploaded by
Jicel Camille EdeaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drugs
Uploaded by
Jicel Camille EdeaCopyright:
Available Formats
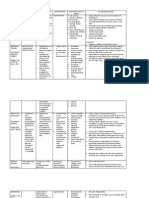
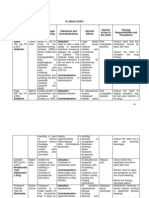
Name of Drug
Indication
Action
Furosem ide
Brand Name: Lasix
Acute pulmo nary edema Edema Hypert ension
A potent drug that inhibits sodium and chloride reabsorption at the proximal and distal tubules and the ascending loop of Henle
Dosage, Frequenc y and Route 200 mg TID
Contraindication
Adverse effect
Drug Interaction
Nursing Responsibilities To prevent nocturia, give P.O and I.M preparations in the morning. Give second dose in early afternoon. Monitor weight, blood pressure and pulse rate routinely with long term use during diuresis. Use can lead to profound water and electrolyte depletion. Monitor fluid intake and output and electrolyte Watch for signs of hypokalemi
Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to drug and in those with anuria. Use cautiously with patients with hepatic cirrhosis and in those allergic to sulfonamides
CNS: vertigo, headache, dizziness, paresthesia, weakness, restlessness, fever. CV: orthostatic hypotension, thrombophlebitis with IV administration EENT: transient deafness, blurred or yellowed vision, tinnitus Hepatic: hepatic dysfunction, jaundice GI: abdominal discomfort, diarrhea, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, constipation, pancreatitis Metabolic: volume depletion and dehydration Musculoskeletal: muscle spasm
Aminoglyc oside antibiotics cisplatin: May increase ototoxicity. Amphoteri cin B, corticoster oids, corticotropi n, May increase risk of hypokalem ia
a such as muscle weakness and cramps. Monitor for CNS, GI, Cardiovasc ular, Neurologic, Integument ary manifestatio ns of Hypocalce mia. Monitor for CNS, Neuromusc ular, GI, Cardiac manifestatio ns of Hypomagne semia. Monitor for CV, GI, Neurologic manifestatio ns of Hyponatre mia. Monitor for neurologic, respiratory manifestatio ns of hyperchlore mia.
Assess patient for tinnitus, hearing loss, ear pain, periodic testing of hearing is needed when high doses of this drug are given by IV route. Assess patients and familys knowledge of drug therapy.
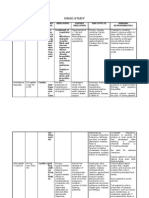
Name of Drug
Indication
Action
Folic Acid Brand Name: FOLATE
Treatment of megaloblastic anemias, nutritional deficiency
Required for nucleoprotein synthesis and maintenance of normal erythropoiesis
Dosage, Frequency and Route 1g 1tab Oral Drug, Once a day
Contraindication
Adverse effect
Drug Interaction Decreased serum phenytoin and increase in seizure activity with folic acid preparations Decreased absorption with sulfasalazine, aminosalicylic acid
Nursing Responsibilities Assess Allergy to folic acid preparations Physical: Skin lesions, hemoglobin serum folate levels Assess patients folic acid deficiency before starting therapy. Assess patient for (megaloblastic anemia), weakness, fatigue, dyspnea, shortness of breath and activity intolerance. Assess nutritional status: determine if high folic acid foods are missing from diet. Identify drugs currently taken: alcohol, oral contraceptive, glucocorticoids, estrogens, hydantoins and carbamazepine, These drugs may cause increased folic acid use by the body and contribute to the deficiency. Monitor folate levels (6-15 mcg/ml) Hgb, Hct and reticulocyte count before and throughout therapy.
Contraindicated with allergy to folic acid, pernicious, aplastic, normocytic anemias
Hypersensitivity: allergic reactions
Monitor for possible drug induced reactions: CNS: general malaise GI: bitter taste, anorexia, flatulence. Respiratory: bronchospasm Assess patients and familys knowledge on drug therapy.
You might also like
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyOdarp PradzNo ratings yet
- Hypophosphatemia, (Low Phosphate) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHypophosphatemia, (Low Phosphate) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological: Drug Features Therapeutic Effects Nursing Responsibilities Indication Contraindication Desired UntowardDocument7 pagesPharmacological: Drug Features Therapeutic Effects Nursing Responsibilities Indication Contraindication Desired UntowardyannahmaeNo ratings yet
- Mata Drug Study FurosemideDocument14 pagesMata Drug Study FurosemideNicole Keesha MataNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug Studyjanelee2824No ratings yet
- Medical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcFrom EverandMedical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcNo ratings yet
- FurosemideDocument2 pagesFurosemideJm RomancapNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Pseudohypoparathyroidism, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Pseudohypoparathyroidism, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For BronchiectasisDocument6 pagesDrug Study For BronchiectasisEdith AlegreNo ratings yet
- Drug Study On Emergency DrugsDocument34 pagesDrug Study On Emergency DrugsMei-mei ZhuangNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NewDocument4 pagesDrug Study NewJehannah Dayanara Berdan HayudiniNo ratings yet
- Epinephrine Classifications: Therapeutic: Antiasthmatics, Bronchodilators, Vasopressors Pharmacologic: Adrenergics IndicationsDocument14 pagesEpinephrine Classifications: Therapeutic: Antiasthmatics, Bronchodilators, Vasopressors Pharmacologic: Adrenergics IndicationsLindy Shane BoncalesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study On Emergency DrugsDocument14 pagesDrug Study On Emergency DrugsRene John FranciscoNo ratings yet
- EMERGENCY DRUGS: A Drug StudyDocument8 pagesEMERGENCY DRUGS: A Drug StudyShaine WolfeNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Classification and Mechanism of Action Indication/ Dosage/ Route Contraindicatio N Adverse Effects Nursing InterventionsDocument6 pagesDrug Name Classification and Mechanism of Action Indication/ Dosage/ Route Contraindicatio N Adverse Effects Nursing InterventionsVin LandichoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyAysaaa DCNo ratings yet
- EMERGENCY DRUGS: A Drug StudyDocument33 pagesEMERGENCY DRUGS: A Drug StudyNicole GarciaNo ratings yet
- Fusid®: TabletsDocument8 pagesFusid®: Tabletsddandan_2No ratings yet
- Clinical Medication ListDocument181 pagesClinical Medication Listsophia onu100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug Studyreanne_davidNo ratings yet
- ZafirlukastDocument3 pagesZafirlukastapi-379794167% (3)
- CVA Drug StudyDocument51 pagesCVA Drug StudyKarel LuNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug Studypaulkris_14100% (1)
- C C C Vertigo,: Electrolyte and Water Balance AgentDocument12 pagesC C C Vertigo,: Electrolyte and Water Balance AgentEarl Tony TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- 5th Draft DrugsDocument7 pages5th Draft DrugsShayne Jessemae AlmarioNo ratings yet
- Discharged PlanDocument6 pagesDischarged Planqueenieann100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument17 pagesDrug StudyKenneth ManalangNo ratings yet
- Drug Study TramadolDocument14 pagesDrug Study TramadolBianca Freya Porral85% (13)
- Furosemide HaloperidolDocument6 pagesFurosemide HaloperidolLady Lou ArmadaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyNajmah Saaban100% (1)
- Drug Study 68-75Document8 pagesDrug Study 68-75joshua_santiago_5No ratings yet
- Propylthiouracil DSDocument6 pagesPropylthiouracil DSAlexandrea MayNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyShane Arroyo100% (1)
- 1.) Generic Name: Gabapentin Brand Name Classification Dosage Route and Frequency Mechanism of ActionDocument15 pages1.) Generic Name: Gabapentin Brand Name Classification Dosage Route and Frequency Mechanism of ActionTyron ChuaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Medcor AguinaldoDocument6 pagesDrug Study Medcor AguinaldoYana PotNo ratings yet
- Pedia Drug StudyDocument11 pagesPedia Drug StudyPeetah PanNo ratings yet
- Amlodipine, Vit.b Complex, CombiventDocument6 pagesAmlodipine, Vit.b Complex, CombiventErickson Caisido GarciaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Acetylcyst e I N eDocument12 pagesDrug Study: Acetylcyst e I N eMarvin V ParahinogNo ratings yet
- Psych Drug StudyDocument5 pagesPsych Drug StudyLorina Lynne Apelacio100% (4)
- Generic Name: Albuterol Brand Name: Salbutamol, Proventil, Ventolin, Accuneb, Airet, Novo-SalbutamolDocument26 pagesGeneric Name: Albuterol Brand Name: Salbutamol, Proventil, Ventolin, Accuneb, Airet, Novo-SalbutamolAnna Joy Antone100% (1)
- Propylthiouracil Drug StudyDocument7 pagesPropylthiouracil Drug StudyAlexandrea MayNo ratings yet
- Propylthiouracil DSDocument7 pagesPropylthiouracil DSAlexandrea MayNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 1230913067634079 1Document4 pagesDrug Study 1230913067634079 1Jowel Cruz De LeonNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyDiana Laura LeiNo ratings yet
- Ciprofloxacin CiproDocument1 pageCiprofloxacin CiproKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument17 pagesDrugsRenzkie GeronimoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Medications ReviewerDocument4 pagesRespiratory Medications ReviewerKevin VillaranteNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyNedemar OcampoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug Studykcbabee0333% (3)
- w15 - Drug StudyDocument4 pagesw15 - Drug StudyGeneva LatorreNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyRoselle SorianoNo ratings yet
- DRUG StudyDocument6 pagesDRUG StudyJheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- I.Nutrition and Electrolytes A. Vitamins Classification: Fat Soluble Vitamin Generic Name: Vitamin E BRAND NAME: Aquasol EDocument176 pagesI.Nutrition and Electrolytes A. Vitamins Classification: Fat Soluble Vitamin Generic Name: Vitamin E BRAND NAME: Aquasol EFatima Doran PandaogNo ratings yet
- Nursing Responsibilities To:: Magnesium SulfateDocument13 pagesNursing Responsibilities To:: Magnesium SulfateabrokenheartedgirlNo ratings yet
- Drug Analysis (RN) - 3Document9 pagesDrug Analysis (RN) - 3Joannalyn Libo-on0% (1)
- Drug Name Dose, Route, Frequency Mechanism of Drug Indications Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument15 pagesDrug Name Dose, Route, Frequency Mechanism of Drug Indications Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitiesitsmechachaNo ratings yet
- Sleeping Pattern Among Students ReportDocument15 pagesSleeping Pattern Among Students ReportHazwani RahmanNo ratings yet
- Adult Friends Diaper (Thought Process)Document2 pagesAdult Friends Diaper (Thought Process)Rohan HiremathNo ratings yet
- Allianz Care Plus Brochure Update 19mar2015 FA R3 5Document11 pagesAllianz Care Plus Brochure Update 19mar2015 FA R3 5Leonard Yang0% (1)
- The Role of The Nurse in Health Promotion PDFDocument1 pageThe Role of The Nurse in Health Promotion PDFCie Ladd0% (1)
- PANCE Word Associations PDFDocument27 pagesPANCE Word Associations PDFkatNo ratings yet
- Brockton Police Log March 18Document20 pagesBrockton Police Log March 18BBNo ratings yet
- Vulnerable Patient Sop FinalDocument28 pagesVulnerable Patient Sop FinalManglemba Moirangthem100% (1)
- Assign Chem in EverydayLife 16Document1 pageAssign Chem in EverydayLife 16Shubham AsthanaNo ratings yet
- Sample RFPDocument7 pagesSample RFPrahul kNo ratings yet
- Article 257. Unintentional Abortion ElementsDocument3 pagesArticle 257. Unintentional Abortion ElementsJason ToddNo ratings yet
- Bulacan State University College of Nursing: Bulsu-Op-Con-23F15 Revision: 0Document6 pagesBulacan State University College of Nursing: Bulsu-Op-Con-23F15 Revision: 0Richmon SantosNo ratings yet
- Defination of FireDocument21 pagesDefination of FireVikas YamagarNo ratings yet
- Patient Care ConferenceDocument3 pagesPatient Care ConferenceValarmathiNo ratings yet
- Hiv Aids Laka Engtin Nge Kan Him Ang - Nuho TanDocument7 pagesHiv Aids Laka Engtin Nge Kan Him Ang - Nuho TanachungaNo ratings yet
- Mock Test January 2022-2Document17 pagesMock Test January 2022-2Ioana MandikNo ratings yet
- ECITB Approved Course Check List - MJIDocument5 pagesECITB Approved Course Check List - MJIZaw Htet WinNo ratings yet
- Letter To ParentsDocument4 pagesLetter To ParentsGary DetmanNo ratings yet
- An EUA For Casirivimab and ImdevimabDocument3 pagesAn EUA For Casirivimab and ImdevimabAllan FradiqueNo ratings yet
- Outreach Service in Selected Local in Lagos NigeriaDocument48 pagesOutreach Service in Selected Local in Lagos NigeriaDOYINSOLA ADENUGANo ratings yet
- (09032021) Press Release For Resumption of Selected Sports For NSG 2021 - MOEDocument2 pages(09032021) Press Release For Resumption of Selected Sports For NSG 2021 - MOEthesuperprogamer2 gamerNo ratings yet
- Temporomandibular Disorders: A Term Whose Time Has Passed!: PerspectivesDocument2 pagesTemporomandibular Disorders: A Term Whose Time Has Passed!: PerspectivesUmer HussainNo ratings yet
- C. Stages of Growth and Development - The LearnerDocument13 pagesC. Stages of Growth and Development - The Learner18shar_07No ratings yet
- List of Approvrd HospitalsDocument7 pagesList of Approvrd HospitalsTaresh MittalNo ratings yet
- Medic Shoes - Clinic Report - 25/10/2020Document49 pagesMedic Shoes - Clinic Report - 25/10/2020יפה גולןNo ratings yet
- Republic of The PhilippinesDocument24 pagesRepublic of The PhilippinesMarie France Suarin100% (1)
- What Is Alcohol2012AAlisherMDPhDDocument58 pagesWhat Is Alcohol2012AAlisherMDPhDAlisher AgzamovNo ratings yet
- HPLC Analysis of AlprazolamDocument8 pagesHPLC Analysis of AlprazolamJuan PerezNo ratings yet
- 2010 Integrated Updated Circulation ACLS Tachycardia AlgorithmDocument1 page2010 Integrated Updated Circulation ACLS Tachycardia AlgorithmRyggie ComelonNo ratings yet
- 26-06-21 S.B.L.D Ayurved Vishwa Bharti, Churu - MISPA VIVA - PM KitDocument4 pages26-06-21 S.B.L.D Ayurved Vishwa Bharti, Churu - MISPA VIVA - PM KitN. K. MandilNo ratings yet
- Announcement 01 Oct PDFDocument2 pagesAnnouncement 01 Oct PDFgaurav chauhanNo ratings yet