Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FYP Casting
Uploaded by
أحمد فايز مد يونسOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
FYP Casting
Uploaded by
أحمد فايز مد يونسCopyright:
Available Formats
2.
3 Casting Processes
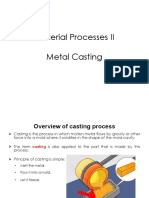
Casting process can be defined as a manufacturing process involves pouring of liquid metal into a mould cavity and then allowing it to solidify. The final shape of the metal was determined by the shape of the mould cavity. The solidified metal is also refers as a casting. The casting processes can be broadly classified by the type of mould used as illustrate in figure 8. The expandable mould is non reusable mould and usually destroyed to remove out the solidified cast. In contrast, the permanent can be reuse to make other casting.
Figure 8: Classifications of Casting Processes
In a basic casting process, the mould must be produce based on the desired shape. Followed by melting process where metal is heated in furnace until it changed into liquid form the molten metal is poured into mould cavity. Lastly, when the solidification process is finished, the mould is broke or opened to take out the product. The basic step for casting process presented as per below: Mould Cavity: A mould cavity must have the desired shape and size. It also must have a refractory character so that it will not be significantly affected by the molten metal that it must contain. There are two major types of mould which is expendable mould and non-expendable mould. The expendable mould only used for single process and new mould must be prepared for next casting. For the non-expendable mould usually made from strong material that withstand for using in repeated casting process. Melting Process: A melting process must be capable of providing molten material not only at the proper temperature, but also in the desired quantity, with an acceptable quality, and within a reasonable cost.[3]
Pouring Techniques: Before pouring process, provision should be made to permit the escape of all air or gases in the mould. The hot metal is poured into mould and then completely filled the cavity in fully dense and no defect. Solidification Process: Provision must be made so that the mould will not cause too much restraint to the shrinkage that accompanies the cooling of solidified metal. Otherwise, the casting will crack when it is still hot and its strength is low.[3] Mould Removal: Remove the casting from the mould is done after the solidification process finished. Usually the difficulty occurs while removal of the casting for permanent mould. Cleaning, Finishing and Inspection: Extraneous material that is attached where the metal entered the cavity, excesses at mould parting lines, and mould material that is attached to the casting surface must all be removed.
You might also like
- CH 7-Methods of CastingDocument44 pagesCH 7-Methods of CastingGosaye DesalegnNo ratings yet
- Types of Casting and InspectionDocument5 pagesTypes of Casting and InspectionSahal T YousephNo ratings yet
- Hofim: Hermetically-Sealed Motor-Compressor SystemDocument6 pagesHofim: Hermetically-Sealed Motor-Compressor Systemdvcher78No ratings yet
- Foundery Shop (Ch-6)Document121 pagesFoundery Shop (Ch-6)Shubham VermaNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Metal Forming Process and Casting ProcessDocument21 pagesDifferences Between Metal Forming Process and Casting ProcessFarhana Eyla75% (4)
- Equipment Design and Drawing: Project ReportDocument40 pagesEquipment Design and Drawing: Project Reportsurajagtap01No ratings yet
- MasoneilanDocument20 pagesMasoneilanJohn MarshalNo ratings yet
- Metal CastingDocument11 pagesMetal Castingআজিজুর রহমান চৌধুরীNo ratings yet
- Metal Casting Processes: 3.1 Introduction of Casting ProcessDocument14 pagesMetal Casting Processes: 3.1 Introduction of Casting Processharshita gupta100% (1)
- The Fabrication of Materials: Materials TechnologyFrom EverandThe Fabrication of Materials: Materials TechnologyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Quiz Name OxidationDocument3 pagesQuiz Name OxidationAnony MousNo ratings yet
- Concrete Technology HandoutDocument21 pagesConcrete Technology HandoutsainathNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment Plant Spesification PDFDocument8 pagesWater Treatment Plant Spesification PDFrando85100% (1)
- Casting PDFDocument40 pagesCasting PDFphani301100% (1)
- Die CastingDocument6 pagesDie Castingkutik3bugerNo ratings yet
- Solder Wiki Inc Solder Melting PointsDocument57 pagesSolder Wiki Inc Solder Melting PointsPJFNo ratings yet
- Dimethyl AnilineDocument68 pagesDimethyl Anilinemikelycan100% (1)
- Size ReductionDocument28 pagesSize Reductionchurvalooo100% (1)
- Week 2 Advanced Workshop PracticeDocument28 pagesWeek 2 Advanced Workshop PracticeBasit AliNo ratings yet
- Manuf ProcessDocument15 pagesManuf ProcessKaruppiah ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Casting ProcessDocument4 pages3.1 Casting Processزينب عبد الخالق كاملNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - METAL WORK, CASTING PROCESS AND HEAT TREATMENT ON STEELDocument21 pagesChapter 3 - METAL WORK, CASTING PROCESS AND HEAT TREATMENT ON STEELتاج نيسهاNo ratings yet
- Casting Processes: March 2020Document26 pagesCasting Processes: March 2020Bhavin DesaiNo ratings yet
- ( (Manufacturing) ) : Permanent Mold Casting ProcessesDocument15 pages( (Manufacturing) ) : Permanent Mold Casting ProcessesKarthikeyan MuthukumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Lec 2castingpdfDocument26 pagesLec 2castingpdfHải TrầnNo ratings yet
- 2nd Class Notes 17.01Document48 pages2nd Class Notes 17.01EDISON OCHIENGNo ratings yet
- Introduction 1.. FoundryDocument112 pagesIntroduction 1.. FoundryDhananjay Shimpi100% (1)
- TEKNOLOGI PEMBUATAN Lec 7Document14 pagesTEKNOLOGI PEMBUATAN Lec 7Wawa RusliNo ratings yet
- Casting Process: Steps of Casting AreDocument10 pagesCasting Process: Steps of Casting AreReham Emad Ezzat MohamedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11Document22 pagesLecture 11Huraira AbidNo ratings yet
- 1st Class 13.01.2020Document18 pages1st Class 13.01.2020EDISON OCHIENGNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Processes Manufacturing Processes ME ME - 222 222Document66 pagesManufacturing Processes Manufacturing Processes ME ME - 222 222shahnawaz875No ratings yet
- Types of Castings in Mechanical Engineering: Dharma Maheswara 2 1 0 5 1 4 6 1 9 2 1 3Document12 pagesTypes of Castings in Mechanical Engineering: Dharma Maheswara 2 1 0 5 1 4 6 1 9 2 1 3TM Dharma maheswaraNo ratings yet
- The Casting Process PlanningDocument1 pageThe Casting Process Planningأحمد فايز مد يونسNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 - Special Moulding Processes PART-2Document25 pagesUnit-3 - Special Moulding Processes PART-2mahammad kamaluddeenNo ratings yet
- CastingDocument25 pagesCastingAhsan RiazNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Technology - I Course ID: ME 222 (3-0-0-6)Document33 pagesManufacturing Technology - I Course ID: ME 222 (3-0-0-6)captain indiaNo ratings yet
- ME 212 Materials Processing-1Document15 pagesME 212 Materials Processing-1Favour LawrenceNo ratings yet
- Overview of Casting TechnologyDocument5 pagesOverview of Casting TechnologySK Kushwah RajputNo ratings yet
- ME 330 Manufacturing Processes Casting Processes (Cont.)Document39 pagesME 330 Manufacturing Processes Casting Processes (Cont.)Sibu SibuNo ratings yet
- Die Casting ProcessDocument23 pagesDie Casting ProcessshayarigurunitinNo ratings yet
- Types of CastingDocument14 pagesTypes of CastingRamoji Aditya Chary100% (1)
- DFM ch-2Document114 pagesDFM ch-2Trâp A NâtïøñNo ratings yet
- Metal Casting: AdvantagesDocument35 pagesMetal Casting: AdvantagesDida KhalingNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 6: Casting Is ADocument6 pagesExperiment No. 6: Casting Is AArun kumar rouniyarNo ratings yet
- Basic Engineering MaterialDocument14 pagesBasic Engineering MaterialNur Husnina NinaRamanNo ratings yet
- UNit 2 MEC 305Document32 pagesUNit 2 MEC 305Fuzzy is EasyNo ratings yet
- Unit - I Metal Casting Processes What Is Sand Casting?Document43 pagesUnit - I Metal Casting Processes What Is Sand Casting?Indumathiuuuijiio89i889 VelusamyxNo ratings yet
- Classification of Casting TechniquesDocument16 pagesClassification of Casting TechniquesRehan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document14 pagesChapter 5Phuc Truong DucNo ratings yet
- Man Tech Assignment 1Document6 pagesMan Tech Assignment 1trishNo ratings yet
- Foundry Asguest57564 Download: Share Add To Flagembed Views: 5846 Category: EducationDocument9 pagesFoundry Asguest57564 Download: Share Add To Flagembed Views: 5846 Category: EducationGurjinder SinghNo ratings yet
- MM Experiment ReportDocument10 pagesMM Experiment ReportAbdullah ArshadNo ratings yet
- Mce516 Lecture Note 1Document98 pagesMce516 Lecture Note 1Edward JNo ratings yet
- Lec 5Document39 pagesLec 5Omar AssalNo ratings yet
- Internship ReportDocument28 pagesInternship ReportCH.H.AWAIS RASOOLNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Metal Casting: Overview of Casting Technology Heating and Pouring Solidification and CoolingDocument40 pagesFundamentals of Metal Casting: Overview of Casting Technology Heating and Pouring Solidification and Coolingalemu170No ratings yet
- Permanent Mold CastingDocument10 pagesPermanent Mold Castingroronoa zoroNo ratings yet
- MGF Notes - 1Document79 pagesMGF Notes - 1A ABHISHEK MARSHALLNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 2Document21 pagesLab Report 2Cherif ChokeirNo ratings yet
- CastingDocument8 pagesCastingTody IsfitazliNo ratings yet
- A402072949 - 17676 - 17 - 2018 - Casting 2Document39 pagesA402072949 - 17676 - 17 - 2018 - Casting 2KushNo ratings yet
- CastingDocument12 pagesCastingS V Garata ReddyNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing DefectsDocument44 pagesManufacturing DefectsaliNo ratings yet
- Casting Notes2Document12 pagesCasting Notes2darksiderruvNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Metal Casting: Overview of Casting Technology Heating and Pouring Solidification and CoolingDocument37 pagesFundamentals of Metal Casting: Overview of Casting Technology Heating and Pouring Solidification and CoolingSachin RanaNo ratings yet
- Fire ProtectionDocument10 pagesFire ProtectionRasadnya SirNo ratings yet
- Molecules: Synthesis and Bioactivity of A-Aminophosphonates Containing FluorineDocument7 pagesMolecules: Synthesis and Bioactivity of A-Aminophosphonates Containing FluorineThomas CharmNo ratings yet
- Post Activity PrelimDocument91 pagesPost Activity PrelimWYATT ASTERISCONo ratings yet
- Unit 1: LNG Introduction and ProductionDocument39 pagesUnit 1: LNG Introduction and ProductionDeepak SharmaNo ratings yet
- Pra Un Ing 2013-Paket 7Document14 pagesPra Un Ing 2013-Paket 7adela_97lineNo ratings yet
- (Martin Moeller, Krzysztof Matyjaszewski) PolymerDocument1,052 pages(Martin Moeller, Krzysztof Matyjaszewski) PolymerGrayNo ratings yet
- Open Test Series - Paper-1 - (21-09-2021)Document31 pagesOpen Test Series - Paper-1 - (21-09-2021)Yogesh KhatriNo ratings yet
- CO Storage: 20 ASCO ISO Tank ContainersDocument5 pagesCO Storage: 20 ASCO ISO Tank ContainersMB ManyauNo ratings yet
- S3D Settings PETG EsunDocument4 pagesS3D Settings PETG Esunjose luis martinez martinezNo ratings yet
- Aphron Invasion Control System (ICS)Document8 pagesAphron Invasion Control System (ICS)LoganBohannonNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of MaterialsDocument24 pagesMechanical Properties of MaterialsMohannad sehwailNo ratings yet
- Bioinspiration and BiomimeticsDocument7 pagesBioinspiration and BiomimeticsAyush 100niNo ratings yet
- Foundation Chemistry 2811 June 2007Document12 pagesFoundation Chemistry 2811 June 2007M S RahmanNo ratings yet
- Protocol Hybridization Capture of Dna Libraries Using Xgen Lockdown Probes and Reagents Version 3Document16 pagesProtocol Hybridization Capture of Dna Libraries Using Xgen Lockdown Probes and Reagents Version 3Rodger12No ratings yet
- Maintenance Solutions For Hvac Systems: Belzona Protective Coatings and Engineering CompositesDocument12 pagesMaintenance Solutions For Hvac Systems: Belzona Protective Coatings and Engineering CompositesSUHEL NEVREKARNo ratings yet
- List of HW RecyclersDocument11 pagesList of HW RecyclersUnitedWork ServiceNo ratings yet
- Dowtherm sr-1Document16 pagesDowtherm sr-1Rafael LealNo ratings yet
- Websitecompanies NewDocument33 pagesWebsitecompanies NewRajiv JulakantiNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMDocument3 pagesBIOCHEMLeighRence BaltazarNo ratings yet
- PR-TR009-006 4 Table of ContentsDocument5 pagesPR-TR009-006 4 Table of Contentspushpak2312No ratings yet
- S - Amlo BesylateDocument20 pagesS - Amlo BesylateDrkrishnasarma pathyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document5 pagesLecture 2Quỳnh Anh TrầnNo ratings yet