Professional Documents
Culture Documents
#Disease of External Ear
Uploaded by
ameerabestCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
#Disease of External Ear
Uploaded by
ameerabestCopyright:
Available Formats
DISEASES OF THE EAR
Congenital EXTERNAL EAR 1. Meatal Atresia 2. Preauricular fistula/cyst 3. Microtia 4. Bifid lobule 5. Accessory auricle 1. Auricular Hematoma 2. Foreign Body MIDDLE EAR Ossicular anomalies *may be uni/bilateral INNER EAR Syndromic/ Nonsyndromic
Trauma
1. Traumatic rupture of tympanic membrane 2. Otitic Barotrauma (Aero-otitis) 1. Acute Otitis Media (OM) - Acute Suppurative (bacterial) OM (ASOM) - Acute Necrotizing OM - Acute Viral OM 2. Chronic Suppurative OM (CSOM) - Non-Specific Safe Tubo-tympanic Unsafe Attico-antral (Cholesteatoma) - Specific Tuberculous OM 3. Complications of Suppurative OM - Cranial Acute Mastoiditis Petrositis Labyrinthitis Facial paralysis - Intracranial Extradural Abscess *most common Meningitis (Leptomeningitis) Lateral Sinus Thrombosis Brain Abscess Otitic Hydrocephalus - Extra cranial 4. Chronic Non-suppurative OM OM with effusion Chronic Adhesive OM
1. Noise trauma 2. Mechanical trauma
Inflammation 1. Auricular - Herpes Zoster Oticus - Perichondritis 2. ECA - Acute Diffue Otitis Externa - Chronic Difusse Otitis Externa - Malignant Otitis Externa - Furunculosis - Otomycosis 3. Tympanic membrane
Inner Ear 1. Labyrinthitis 2. Menieres Disease (Endolymphatic Hydrops) 3. Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV) Internal Auditory Canal 4. Acute Vestibular Neuronitis 5. Acoustic Neuroma (Vestibular Schwannoma)
etc Tumor
Impacted wax 1. Auricular - Basal Cell Carcinoma - Squamous Cell Carcinoma 2. ECA - Exostosis & Osteoma - Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Otosclerosis Glomus tumor
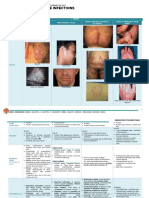
staphylococcal infection of hair follicles *limited to outer cartilaginous part of EAC *recurrent DM 1. Pain 2. HL (edema of EAC) 3. Purulent discharge (if rupture)
etiology
BACTERIAL INFECTION acute diffuse recurrent acute bacterial infection diffuse OE of the skin of EAC
severe pseudomonas infection of ext. ear * in elderly, uncontrolled DM patient *NOT a malignancy!
FUNGAL INFECTION Fungal infection of external ear - Aspergillus, Candida *predisposing factors - wetness of skin of ECA -excessive use of topical antibiotics 1. ITCHING, irritation 2. Mild pain 3. HL if blocked by fungal debris
BACTERIAL Usually following trauma
VIRAL INFECTION
1. Itching & irritation 2. Pain 3. Deafness if blocked by edema/discharge - Hyperemia, swelling & tenderness of EAC skin - Canal filled with debris & purulent exudates 1. Gentle cleaning 2. Topical antibiotics 3. Analgesics
symptoms
1. Itching, irritation 2. Blocked ear
infection in external ear parotid egionskull base facial & other CN palsies 1. Otagia 2. Purulent otorrhea - Granulation tissue at bony-cartilaginous junction of EAC - ESR
1. Severe pain 2. Fever (maybe)
1. Severe otalgia
Red tender soft swelling surrounded by hyperemia signs
- Narrowing of EAC - Scaling & fissures
Pale grayish fungal plug studded with dark spots (wet blotting paper)aspergillus Creamy coloured debris & musty odor - candida
Swollen tender auricle + loss or aurivular contour *uncontrolld infection + necrosis deform into CAULIFLOWER EAR 1. Systemic antibiotics 2. Drainage + irrigation with saline & local antibiotics
1. Herpetic vesicles 2.Ramsay-Hunt Syndrome - CN7-facial paralysis -CN8- SNHL, vertigo, tinnitus
treatment
* Differential diagnosis - Acute mastoiditis - Herpes Zoster oticus 1. Systemic antibiotics 2. Analgesics 3. Local antibiotic ear drops
1. Meticulous gentle cleaning 2. Local antibioticsteroid preparation 3. Control of predisposing factors ( eczema, allergy, Seborrheic state)
1. Control of diabetes 2. Antipseudomonas (quinolones ciprofloxacin)
1. Ear wash 2. Local antifungal preparations (clotrimazole)
1. Antiviral (acyclovir) 2. Systemic steroid 3. Symptomatic : - analgesics -labyrinthine sedative
CONGENITAL ANOMALIES
TRAUMA TO EXTERNAL EAR
TUMORS OF AURICLE
TUMORS OF EXTERNAL AUDITORY CANAL
IMPACTED WAX
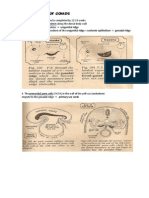
Ceruminous plug formed dt: 1. excessive secretion of wax 2. improper way of cleaning pushing the wax inwards *cartilaginous part of EAC! 1. Deafness (MCC of CHL in adults!) 2. Discomfort 3. Pain Brownish mass partially/ completely obstructing the EAC Blunt trauma/ accident accumulation of blood under perichondrium in children Types: -animate : flies,ants -inanimate : vegetable :beans,nuts non-vegetable :beads Discomfort
type of patient
etiology
- CHL surgical widening
SCC - elderly - fair skin long time exposure to sunlight
BCC any patient
* both in bony EAC! EXOSTOSIS OSTEOMA hyperostosis benign tumor! * most common tumor in EAC * in divers a.k.a. Surfers ear ivory bone
predisposing factor
symptoms
plastic surgery
Otalgia
CP
nodule, ulcer or protrusion
long time exposure to sunlight + irradiation typical malignant ulcer regional LN metastasis
cancellous bone unilateral single small pedicle
bilateral multiple wide base (sessile)
Soft bluish swelling on lateral surface of auricle *maybe deform into CAULIFLOWER EAR
FB in external ear *vegetable FB may absorb water grows OM *insects discomfort when moving 1. Ear wash, except in: - impacted FB - vegetable (absorbs water swell) - insects must be drowned first 2. Hooks (beads) 3. Suction
extension
signs
locally malignant * rare metastasis limited surgical excision with safety margin + plastic reconstruction
treatment
treatment
Ear wash *if impacted soften by glycerine bicarbonate etc *perforated TM electric suction machine
Drainage under strict aseptic condition + Pressure bandage
radical surgical excision with safety margin + radical neck dissection
treatment = - if obstructing EAC surgical excision - if NOT NO treatment
EAR WASH ^^,
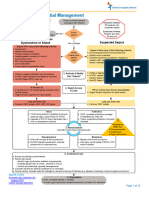
- by ear wash syringe - avoid directing water to the center of wax plug or tympanic membrane! INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS 1. WAX PLUG 1. Dry perforation of tympanic membrane avoid middle ear infection 2. FOREIGN BODIES *if not tightly impacted! 2. Recent trauma to ear/head (suspected skull base fracture) 3. OTOMYCOSIS 3. Impacted foreign bodies (esp vegetables) 4. Caloric test more impacted 4. Acute otitis externa painful COMPLICATIONS Physiological phenomena Cough & syncope stimulation of auricular br of vagus [vaso-vagal attack] - rough manipulation or cold water Vertigo, nausea, stimulation of lateral SCC [caloric stimulation of inner ear] vomiting - very cold (<30) or very hot (>44) water) Faulty techniques Traumatic rupture * with sharp pain in ear + slight bleeding + feeling of water of tympanic passing through the throat membrane treatment = keep ear dry + avoid nose blowing + antibiotics More wax impaction Trauma to the skin by syringe nozzle of EAC * also cause pain + bleeding, but INTACT TM! treatment = keep ear dry + antibiotics Faulty indications Otitis media ear wash in perforated TM Meningitis ear wash in skull base fracture Faulty after-care Otitis externa contaminated instruments Recurrence when etiology is untreated
You might also like
- #Acute & Chronic Otitis MediaDocument3 pages#Acute & Chronic Otitis MediaameerabestNo ratings yet
- ENT Emergency PresentationDocument135 pagesENT Emergency PresentationshahiruddinNo ratings yet
- Ryan Martin Ko, M.DDocument54 pagesRyan Martin Ko, M.DDhaval Makwana100% (2)
- Common Ent DisordersDocument20 pagesCommon Ent DisordersattaheeraNo ratings yet
- Cholesteatoma, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandCholesteatoma, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Glue Ear, (Otitis Media with Effusion) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandGlue Ear, (Otitis Media with Effusion) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Notes, 1/e: Acute and Chronic Inflammation of LarynxDocument23 pagesNotes, 1/e: Acute and Chronic Inflammation of LarynxvkNo ratings yet
- (Ent) 02 Endoscopy Applied Physiology EditedDocument5 pages(Ent) 02 Endoscopy Applied Physiology EditedKanako TakayaNo ratings yet
- ORL Interns NotesDocument15 pagesORL Interns NotesSandy Chiong MaganitoNo ratings yet
- Laryngitis: SpasmDocument13 pagesLaryngitis: Spasm44-Shruti paghdalNo ratings yet
- 14 OtosclerosisDocument76 pages14 OtosclerosisAatif_Saif_80No ratings yet
- Examination of Head and Neck SwellingsDocument22 pagesExamination of Head and Neck SwellingsObehi EromoseleNo ratings yet
- Notes EntDocument43 pagesNotes Entadriana azmanNo ratings yet
- Chhabhadiya Laxman (Ent)Document7 pagesChhabhadiya Laxman (Ent)Venkatesh GarikapatiNo ratings yet
- Pharyngeal Tumours2Document46 pagesPharyngeal Tumours2miramirajalalNo ratings yet
- RADIOLOGY 2.1e Skull FracturesDocument1 pageRADIOLOGY 2.1e Skull FracturesZazaNo ratings yet
- (ENT) 1.02 Middle Ear Diseases and Their Complications - DR - LlamanzaresDocument11 pages(ENT) 1.02 Middle Ear Diseases and Their Complications - DR - LlamanzaresDenise CedeñoNo ratings yet
- ENT Benign Laryngeal DisordersDocument6 pagesENT Benign Laryngeal DisordersLucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- Stridor in Children: By: Maj Vishal Gaurav Moderator: DR A SethiDocument33 pagesStridor in Children: By: Maj Vishal Gaurav Moderator: DR A SethiVishal GauravNo ratings yet
- X Ray SchemeDocument6 pagesX Ray SchemeIdiAmadouNo ratings yet
- Causes, Signs, Treatment of Acute Otitis MediaDocument19 pagesCauses, Signs, Treatment of Acute Otitis MediaRajesh Sharma100% (1)
- Problem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyFrom EverandProblem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyJohn N. PlevrisNo ratings yet
- Diseases of External EarDocument66 pagesDiseases of External Earalmazmulu76100% (1)
- ENT - Salivary Gland Diseases (Almazan)Document4 pagesENT - Salivary Gland Diseases (Almazan)Tj Kevin P-DoctorNo ratings yet
- Sailedinitis PDFDocument8 pagesSailedinitis PDFNavatha MorthaNo ratings yet
- Inflamed Trachea, (Tracheitis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandInflamed Trachea, (Tracheitis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Oral Cavity PharynxDocument9 pagesOral Cavity PharynxKezia MondonedoNo ratings yet
- Schreibman - Bone Tumors in 1 Simple ChartDocument31 pagesSchreibman - Bone Tumors in 1 Simple ChartborstNo ratings yet
- Eustachian Tube: Structure, Function, and Role in Middle-Ear Disease, 2eFrom EverandEustachian Tube: Structure, Function, and Role in Middle-Ear Disease, 2eNo ratings yet
- Ent Diseases of The Oral and Pharynx Dr. UyDocument7 pagesEnt Diseases of The Oral and Pharynx Dr. UyAileen EmyNo ratings yet
- Recurrent Ear Infection Diagnosis and Treatment ScenarioDocument23 pagesRecurrent Ear Infection Diagnosis and Treatment ScenarioAakashNo ratings yet
- Rhino SinusitisDocument57 pagesRhino SinusitisArif MohammedNo ratings yet
- Ent SignsDocument10 pagesEnt SignsPrasun Sit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Sex Development (DSD) DevelopmentDocument40 pagesDisorders of Sex Development (DSD) DevelopmentAndi AdityaNo ratings yet
- Enteral NutritionDocument18 pagesEnteral NutritionAbdullah YousefNo ratings yet
- External Ear Pathology - PresentationDocument25 pagesExternal Ear Pathology - PresentationNipun MalhotraNo ratings yet
- ENT Deferential Diagnosis MEDADDocument22 pagesENT Deferential Diagnosis MEDADReham AshourNo ratings yet
- Embryology of the Ear DevelopmentDocument3 pagesEmbryology of the Ear DevelopmentJem MontañaNo ratings yet
- Erb's PointDocument14 pagesErb's PointRohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- ENT 1.2 Diseases of The Nose, Paranasal Sinuses, and Face PDFDocument18 pagesENT 1.2 Diseases of The Nose, Paranasal Sinuses, and Face PDFZazaNo ratings yet
- Otitis Media With EffusionDocument3 pagesOtitis Media With EffusionAnish RajNo ratings yet
- RRM's Next - TraumaDocument284 pagesRRM's Next - TraumaRamkishan NekkantiNo ratings yet
- Nose & Respiration: IssueDocument52 pagesNose & Respiration: IssueIemima ȘtefanNo ratings yet
- ENT Teams A4 PDFDocument288 pagesENT Teams A4 PDFEbrahim JuniorNo ratings yet
- (DERMA) 03 TineasDocument9 pages(DERMA) 03 TineasJolaine ValloNo ratings yet
- Surgical Anatomy of NeckDocument37 pagesSurgical Anatomy of Neckaishwarya raviNo ratings yet
- Tonsillectomy Slides 050427Document62 pagesTonsillectomy Slides 050427Aidiel FikriNo ratings yet
- Distal To Ligament of Treitz: CausesDocument8 pagesDistal To Ligament of Treitz: CausesKiara GovenderNo ratings yet
- History and Examination in EntDocument71 pagesHistory and Examination in EntMuhammad Naquib AliNo ratings yet
- 4 PEDIA 8 - Bleeding DisordersDocument5 pages4 PEDIA 8 - Bleeding DisordersRainy Liony DuhNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Dr. AlbertoDocument10 pagesModule 6 Dr. AlbertoJASTHER LLOYD TOMANENGNo ratings yet
- Common Diseases of PharynxDocument72 pagesCommon Diseases of PharynxPinak DeNo ratings yet
- Otolaryngology PDA Toronto NotesDocument29 pagesOtolaryngology PDA Toronto NotesNor Aimi Abd Rahman100% (1)
- Classifying and Treating Sinonasal TumorsDocument25 pagesClassifying and Treating Sinonasal TumorsMariam QaisNo ratings yet
- Middle Ear AnatomyDocument17 pagesMiddle Ear AnatomyDr-Firas Nayf Al-ThawabiaNo ratings yet
- Tonsillitis BK (LR)Document57 pagesTonsillitis BK (LR)Tiffany NurzamanNo ratings yet
- Hernia Examination OSCE GuideDocument7 pagesHernia Examination OSCE GuideEssa AfridiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Larynx: General DescriptionDocument38 pagesAnatomy of The Larynx: General DescriptionDr-Firas Nayf Al-ThawabiaNo ratings yet
- CSOM of Middle Ear Part 1Document59 pagesCSOM of Middle Ear Part 1Anindya Nandi100% (1)
- @ovary Cyst ComparisonDocument2 pages@ovary Cyst ComparisonameerabestNo ratings yet
- Burn Injuries GuideDocument53 pagesBurn Injuries GuideHusna NadiaNo ratings yet
- @acute Nephrotic SyndromeDocument1 page@acute Nephrotic SyndromeameerabestNo ratings yet
- Cme Bronchial AsthmaDocument28 pagesCme Bronchial AsthmaameerabestNo ratings yet
- @acute Nephritic SyndromeDocument3 pages@acute Nephritic Syndromeameerabest100% (1)
- @hypothalamic HormonesDocument1 page@hypothalamic HormonesameerabestNo ratings yet
- @contraceptives DrugsDocument1 page@contraceptives DrugsameerabestNo ratings yet
- @ductal CarcinomaDocument1 page@ductal CarcinomaameerabestNo ratings yet
- E.coli, Klebsiella, Proteus EtcDocument3 pagesE.coli, Klebsiella, Proteus EtcameerabestNo ratings yet
- Genitourinarybacteria Comparisons PDFDocument7 pagesGenitourinarybacteria Comparisons PDFameerabest100% (1)
- @histology of Male Genital SystemDocument6 pages@histology of Male Genital SystemameerabestNo ratings yet
- @drugs Acting On Uterus and Erectile DysfunctionDocument2 pages@drugs Acting On Uterus and Erectile DysfunctionameerabestNo ratings yet
- @tumors of The Breast 1Document2 pages@tumors of The Breast 1ameerabestNo ratings yet
- @sex SteroidsDocument2 pages@sex SteroidsameerabestNo ratings yet
- @ovarian Tumors ComparisonDocument6 pages@ovarian Tumors ComparisonameerabestNo ratings yet
- @ovary Cyst ComparisonDocument2 pages@ovary Cyst ComparisonameerabestNo ratings yet
- @non Neoplastic Non Inflammatory Lesions of The BreastDocument2 pages@non Neoplastic Non Inflammatory Lesions of The BreastameerabestNo ratings yet
- Cardiac ExamDocument7 pagesCardiac ExamameerabestNo ratings yet
- @male PathoDocument8 pages@male Pathoameerabest100% (2)
- Anatomy of Male GenitaliaDocument4 pagesAnatomy of Male GenitaliaameerabestNo ratings yet
- Nota Patho PDFDocument8 pagesNota Patho PDFameerabestNo ratings yet
- Semen AnalysisDocument3 pagesSemen Analysisameerabest80% (5)
- Genitourinarybacteria Comparisons PDFDocument7 pagesGenitourinarybacteria Comparisons PDFameerabest100% (1)
- Patho Male BreastDocument1 pagePatho Male BreastameerabestNo ratings yet
- Genital EmbryologyDocument6 pagesGenital EmbryologyameerabestNo ratings yet
- OSCE DermaDocument8 pagesOSCE DermaameerabestNo ratings yet
- Histology Female PDFDocument5 pagesHistology Female PDFameerabestNo ratings yet
- Virology of Hepatitis ADocument33 pagesVirology of Hepatitis AameerabestNo ratings yet
- #Chest TraumasDocument4 pages#Chest Traumasameerabest100% (3)
- PleuraDocument6 pagesPleuraameerabest100% (1)
- 5th Year Pediatric Exam 2016Document14 pages5th Year Pediatric Exam 2016pal_pal_palNo ratings yet
- AW32150 - 30 - Surgical Guideline SYNCHRONY PIN - EN English - WebDocument64 pagesAW32150 - 30 - Surgical Guideline SYNCHRONY PIN - EN English - WebLong An DoNo ratings yet
- Burchum & Rosenthal: Lehne's Pharmacology For Nursing Care, 9th EditionDocument7 pagesBurchum & Rosenthal: Lehne's Pharmacology For Nursing Care, 9th Editionhockeyman1584No ratings yet
- Microbiology Key WordsDocument5 pagesMicrobiology Key Wordsmoilo86020% (1)
- Louisiana Department of Health Communicable Disease ChartDocument1 pageLouisiana Department of Health Communicable Disease ChartArlan AbraganNo ratings yet
- Stras Chapter 10-12Document17 pagesStras Chapter 10-12acer14appleNo ratings yet
- Neonatal InfectionsDocument18 pagesNeonatal InfectionsSanthosh.S.U100% (1)
- SepsisDocument10 pagesSepsisJessa MaeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of A Child With Physical AND Developmental ChallengesDocument9 pagesNursing Care of A Child With Physical AND Developmental ChallengesAngelo ArabejoNo ratings yet
- What You Need To Know: Rat Lungworm ParasiteDocument3 pagesWhat You Need To Know: Rat Lungworm ParasiteNational Content DeskNo ratings yet
- Orbital Cellulitis 2018Document20 pagesOrbital Cellulitis 2018María Alejandra Rojas MontenegroNo ratings yet
- Unusually Delayed Posttraumatic CSF RhinorrhoeaDocument2 pagesUnusually Delayed Posttraumatic CSF RhinorrhoeaPcrNo ratings yet
- Pediatric NeurologyDocument24 pagesPediatric NeurologyAndika GhifariNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Essentials of Pediatric Nursing 1st Edition Theresa KyleDocument13 pagesTest Bank For Essentials of Pediatric Nursing 1st Edition Theresa KyleAnthonyRiveraqion100% (32)
- Implementing NICE Guidance on Bacterial MeningitisDocument18 pagesImplementing NICE Guidance on Bacterial MeningitisZarwo Black UstadzNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Videos by DR RihamDocument31 pagesDermatology Videos by DR Rihamengr_shazzNo ratings yet
- NCLEX Practice Questions 2Document6 pagesNCLEX Practice Questions 2Filipino Nurses CentralNo ratings yet
- Clinical and Etiological Profile of Acute Febrile Encephalopathy in Eastern NepalDocument3 pagesClinical and Etiological Profile of Acute Febrile Encephalopathy in Eastern NepalNeha OberoiNo ratings yet
- Meningitis Beyond Neonatal AgeDocument57 pagesMeningitis Beyond Neonatal AgeTilahun Kegne100% (2)
- Diagnosis of Delirium and Confusional States - UpToDateDocument29 pagesDiagnosis of Delirium and Confusional States - UpToDateLilasNo ratings yet
- Divine Intervention Episode 45 Neurology Shelf Review Part 2Document11 pagesDivine Intervention Episode 45 Neurology Shelf Review Part 2hahaNo ratings yet
- IAMRmanualDocument84 pagesIAMRmanualDrashua Ashua100% (1)
- VT Quick Facts For NCLEX Pediatrics PDFDocument23 pagesVT Quick Facts For NCLEX Pediatrics PDFMerlande Remy90% (10)
- Nihms 1713249Document13 pagesNihms 1713249Achilles Fkundana18No ratings yet
- Pediatric 1Document13 pagesPediatric 1Doris Grace LagmanNo ratings yet
- Pembimbing: Dr. Partodji, SP - Rad Oleh: 1. Ira Rahmawati 2. Pradnya Ayu 3. LimastaniDocument32 pagesPembimbing: Dr. Partodji, SP - Rad Oleh: 1. Ira Rahmawati 2. Pradnya Ayu 3. Limastaniira rahmaNo ratings yet
- Gram Negative Bacteria of Medical Importance - PPTX, MONDAYDocument113 pagesGram Negative Bacteria of Medical Importance - PPTX, MONDAYGeorge C. KasondaNo ratings yet
- Perfect 2015Document6 pagesPerfect 2015windaNo ratings yet
- MRI findings in acute meningoencephalitis casesDocument10 pagesMRI findings in acute meningoencephalitis casesKriti KumariNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System: Key Points!!! FactsDocument18 pagesCentral Nervous System: Key Points!!! Factsjeron encaboNo ratings yet