Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fueling Tactics by Dave Ellis
Uploaded by
Chris RudicelOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fueling Tactics by Dave Ellis
Uploaded by
Chris RudicelCopyright:
Available Formats
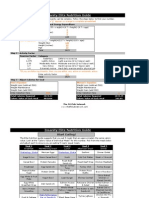
Fueling Tactics - 3 Step System
Dave Ellis - The Fundamental Fueling Tactics: Sports Nutrition System Jon Torine - Former Colts Strength Coach: Body Composition and Nutrition
STEP 1 FOODS - FRESH PRODUCE AND HEALTHY OILS
Highlight items in each category These items represent the choices you are most likely to consume Attempt to make these "highlighted-items" regular selections in your diet This group of foods will help improve resiliency to stress EXTREMELY important for the adolescent age-group Improves immune system function More colorful food choices will produce greater benefits ALWAYS select fresh foods over frozen Frozen foods are preferred to canned foods This group of foods also possesses natural anti-inflammatory properties (Advil/Tylenol) This decreases the effects of constant inflammation that comes along with competing in athletics and weight training A basic multi-vitamin will not replace these foods Many Cathedral High School student-athletes do not get adequate amounts of sleep This lack of sleep occurs during competitive seasons and also in the off-season due to academic requirements It is know that anything that disrupts sleep will increase inflammation and decrease immune system function This INCREASES the importance of this group of foods Nuts, seeds, avocados (healthy fats) can also help improve focus, and improve bone mineral density (BMD)
STEP 1 FOODS - FRESH PRODUCE AND HEALTHY OILS
Vitamin C & Carotenoids
Fruits: Cantaloupe, Oranges, Mango, Cayenne Cherries Vegetables: Sweet Potatoes, Red Bell Peppers, Squash, Broccoli, Asparagus, Spaghetti Sauce, Marinara Sauce, Tomato Juice, V8, Tomatoes Dark Salad Greens: Spinach, Turnips, Beets, Kale Herbs & Spices: Paprika, Pesto, Chili Powder, Basil, Parsley, Cilantro, Chives, Curry
Vitamin C
Fruits: Kiwi, Oranges, Strawberries, Pineapples, Grapefruit, Peaches, Honeydew Melon, Most Fruit Juices, Blackberries, Apricot, Cranberries, Blueberries Vegetables: Green & Yellow Peppers, Cauliflower, Red & Green Cabbage, Zucchini, Green Onions, Turnips, Green Beans, Baked Potato Skins, Sauerkraut Herbs & Spices: Cinnamon, Black & White Pepper, Garlic Powder, Yellow Mustard Seed
Carotenoids
Fruits: Prunes, Apricots Vegetables: Carrots, Pumpkins, Yellow Squash, Vegetable Soups, Seafood Cocktail Sauce
Vitamin E
Vitamin E: Corn Oil, Sunflower Seeds and Oil, Blue Cheese Salad Dressings, Almonds, Peanut Oil, Canola Oil, Rice & Wheat Bran, Cashews, Peanuts & Peanut Butter, Wild Rice, Pistachio Nuts, Caesar Salad Dressing, Pecans, Soybeans, Egg Yolk, Avocado or Guacamole
Complimentary Antioxidants
Complimentary Antioxidants: Apples, Celery, Cucumber, Garlic, Grapes, Mustard, Onions, Pears, Plums
STEP 2 FOODS- CARBOHYDRATES & FIBER: ENERGY CRITICAL FOR QUALITY WORK
Highlight items in each category These items represent the choices you are most likely to consume Attempt to make these "highlighted-items" regular selections in your diet Glycemic index - smaller # = slower digestion rate Smaller # = more fiber and won't raise blood sugar rapidly Higher # = less fiber and faster acting Preferred following practice, games, and workouts There is a time and place for both high and low glycemic carbohydrates 1/2 of a plate of food should be carbohydrate on active days HARD-WORKING ATHLETES NEED MORE CARBS! Muscles that don't have enough carbohydrate can NOT generate as much force Decreased force leads to reduction in speed, strength, and your ability to be explosive on the field Muscles low on carbohydrate are also much slower to relax, which makes them more vulnerable to pulls, cramps, and tears Only if activity levels are reduced (at least 2-consecutive inactive days) should you back off carbohydrate intake slightly Reduce high-glycemic carbohydrates first (higher #'s) Reduce from 1/2 of plate to 1/4 of plate Consuming adequate carbohydrates is critical for high school athletes Carbohydrates do NOT turn into fat with the high activity levels associated with athletics Athletes should prepare for in-game nutrition all week before contest You can't start this process on game-day or the day before the game
STEP 2 FOODS- CARBOHYDRATES & FIBER: ENERGY CRITICAL FOR QUALITY WORK
Slow Digesting Carbohydrates (Low Glycemic)
Vegetables: Cooked Carrots, Grits, Carrot Juice Potatoes: Boiled Potatoes, Sweet Potatoes, Steamed Potatoes Beans/Peas/Nuts: Peanuts, Soy Beans, Baked Beans, Green Peas Soups: Tomato Soup, Black Bean Soup Pasta: Fettuccini, Ravioli with Meat and Cheese, White Spaghetti, Macaroni, Linguine, Gnocchi Grains/Rice: Uncle Ben's Brown Rice, Sweet Corn, Wild Rice, Cornmeal Breads/Rolls: Mixed Grain Breads, Oat Bran Breads, Pumpernickel Bread, Sourdough Bread, Ground Wheat Bread, Pita Bread, Biscuits, Croissants, Taco Shells, High Fiber Wheat Bread Crackers/Snack Chips: Fried Potato Chips, Popcorn, Wheat Crackers, Wheat Thins Cereal: Plain Oatmeal, Oat Bran, Special K, Frosted Flakes, Nutri-Grain, Shredded Wheat, Fruit Loops Fruits: Cherries, Grapefruit, Pears, Apples, Plums, Apple Juice, Peaches, Oranges, Grapes, Pineapple Juice, Canned Peaches, Grapefruit Juice, Cranberry Juice, Orange Juice, Kiwi, Bananas, Fruit Cocktail, Mangos, Apricots, Raisins, Cantaloupe, Pineapple Sweets: Sweetened Yogurt, CHOCOLATE MILK, Fruit Flavored Yogurt, Puddings, Apple Cinnamon Muffin, Banana Bread, Oatmeal Cookies, Blueberry Muffin, Granola Bar, Sports Drinks
Fast Digesting Carbohydrates (High Glycemic)
Potatoes: Stuffing, French Fries, Pumpkin, Hash browns, Instant Mashed Potatoes Crackers/Snack Chips: Corn Chips, Graham Crackers, Cheese Puffs, Rice Cakes, Pretzels Grains/Rice: Corn Pasta, Quick Rice, Instant White Rice, White Bread Bread/Breakfast Items: Toast, Pop Tarts, Bread Sticks, Plain Bagel, Kaiser Rolls, Dark Rye, Doughnuts, English Muffin, Waffles, Crepes, Pancakes Cereal: Golden Grahams, Coco Pops, Cheerios, Cocoa Krispies, Corn Pops, Rice Krispies, Corn Flakes, Most Cartoon Character Cereals Fruits/Sweets: Sweetened Soft Drinks, Teas, Skittles, Cup Cakes, Dried Fruits
STEP 3 - DIVERSIFY PROTEIN SOURCES AND LOW-FAT SOURCES Highlight items in each category These items represent the choices you are most likely to consume Attempt to make these "highlighted-items" regular selections in your diet Quality protein consumption and appropriate timing (post-workout) can decrease muscle soreness and improve recovery time Protein at every meal will enhance recovery Active athletes can get away with medium-fat protein sources Male athletes have approximately a 25% higher protein requirement than females Lean Protein Sources - 1/2 as much fat compared to protein Medium Sources - fat and protein are equivalent High Fat Sources - more fat than protein Consuming BOTH carbohydrates and protein following a workout is 2x better than just having a regular sports drink Drinking only a sports drink will not help quickly rebuild broken-down muscle Drinking a protein powder mixed with water will not successfully refuel carbohydrate levels YOU MUST HAVE BOTH! Effective post-workout nutrition = Gatorade + Chocolate Milk
STEP 3 - DIVERSIFY PROTEIN SOURCES AND LOW-FAT SOURCES
Lean Protein Sources
Eggs/Beef/Game: Egg Whites, 95% Lean Ground Beef, Ground Round, Flank Steak, Tenderloin, Lean Deli Roast Beef, Porterhouse, Buffalo Pork/Lamb: Ham, Canadian Bacon, Tenderloin, Lean Deli Ham, Lamb Roast, Chop, or Leg Poultry: Chicken, Turkey, Cornish Hen, Duck, Goose, Lean Deli Meats Fish/Shellfish: Clam, Crab, Lobster, Scallops, Shrimp, Cod, Trout, Fresh/Canned Tuna in Water, Salmon, Oysters Dairy Sources: Skim-1% Milk, Fat Free Cottage Cheese, Parmesan Cheese, Yogurt from Skim Vegetable Sources: Peas, Soy Milk, Soy Burgers
Medium-Fat Protein Sources
Eggs/Beef: Regular Eggs, 85% Lean Ground Beef, Prime Rib, Rib-Eye Steak, Corned Beef, Short Ribs, Fried Veal Pork/Lamb: Top Loin, Lamb Chop, Boston Butt Poultry: Ground Turkey, Fried Chicken Fish/Shellfish: Any Fried Fish or Seafood, Canned Tuna in Oil Dairy Sources: 2% Reduced Fat Milk, Cottage Cheese, White Cheese, Provolone, Mozzarella, Plain Low-Fat Yogurt Vegetable Sources: Tofu, Soy Yogurt, Boiled Green Soybeans, Soy Milk
High-Fat Protein Sources
Beef: 75% Lean Ground Beef, Beef Ribs Pork: Spareribs, Ground Pork, Bacon, Bratwurst, Italian Sausage, Polish Sausage Dairy Sources: Whole Milk, Cottage Cheese, Yellow Cheeses such as American, Cheddar, Monterey Jack, Swiss Vegetable Sources: Peanut Butter, Soy Cheese
MANAGING WEIGHT On inactive days, one should reduce and/or eliminate: Medium-fat proteins High-fat proteins Fast digesting carbohydrates (high glycemic) It is recommended to feed athletes at least every 4 hours Example: breakfast, lunch, post-workout, dinner, late snack You MUST plan ahead to make this happen during a regular school day This schedule helps to reduce over-eating, as another meal is always coming PRE-GAME NUTRITION Pregame - typically eat last solid meal 3-4 hours prior to activity Liquid meals/snacks can be consumed 1-2 hours pre-activity Lots of high-water foods from Step-1 food list Select slower digesting carbohydrates (low glycemic) Small amounts of lean protein SUPPLEMENTS May do no harm, but are they harmless? Supplements are NOT regulated by the Food & Drug Administration (FDA) Ingredient lists are not tested for accuracy Results are not proven DIETARY PATTERNS WILL ALWAYS BE MORE POWERFUL AND INFLENTIAL THAN SUPPLEMENTS! You do NOT need any form of supplementation Addressing all controllable issues will produce real results 1) Do you consistently eat from each of the 3 steps above? 2) Do you consistently eat adequate amounts from the 3 steps above? 3) Do you consistently (3-4 months) train HARD without missing workouts? 4) Do you consistently get enough sleep? 5) Do you consistently use the post-workout nutrition outlined above?
IMPORTANCE OF SLEEP Good quality sleep in adequate amounts allows us to perform at our optimum, both physically and mentally: Physically: Enables the body to significantly recuperate and restore energy Enables the body to repair itself Helps our immune system to work at its best Mentally: Lack of sleep can lead to anxiety Crucial in our memory retention and the learning of new motor skills Ideally, you should get at least 7.5 - 9 hours per night Naps should be 15-20 minutes in length FINAL RECOMMENDATIONS AND RECORDING Every meal and snack should include foods from ALL 3 steps Only make changes in your diet that will be consistent Consistently making small improvements over time is more likely to yield success Small changes over time will become habit and eventually apart of your daily routine Making too many changes in a short time is unlikely to yield success Big changes in a short time period are difficult to maintain in the long term Take your nutrition seriously; it is a critical factor in movement, speed, change-ofdirection, endurance, and reducing injuries of fatigue and force
Breakfast Step 1 Foods Step 2 Foods Step 3 Foods
Snack
Lunch
Snack
Dinner
You might also like
- The Essential Bodybuilder's Cookbook - Fuel Your Gains with Delicious RecipesFrom EverandThe Essential Bodybuilder's Cookbook - Fuel Your Gains with Delicious RecipesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Soccer Sports Nutrition Presentation U11 U14Document11 pagesSoccer Sports Nutrition Presentation U11 U14giannidietNo ratings yet
- Weight Loss Survival Guide: Insulin Resistance Diet, Adrenal Fatigue Diet, GAPS Diet, Negative Calorie Diet, Get Your Dream Body, Detox Your System, Zero Belly Recipes, Quit SugarFrom EverandWeight Loss Survival Guide: Insulin Resistance Diet, Adrenal Fatigue Diet, GAPS Diet, Negative Calorie Diet, Get Your Dream Body, Detox Your System, Zero Belly Recipes, Quit SugarNo ratings yet
- 21: Eating Post-Surgery: FundamentalsDocument14 pages21: Eating Post-Surgery: FundamentalsNume PrenumeNo ratings yet
- Welcome To The Center For Young Women's Health Project Healthy LifestyleDocument31 pagesWelcome To The Center For Young Women's Health Project Healthy LifestyleSajad Ahmad100% (1)
- Clean Eating 4-Week Meal Plan: Clean Eating Beginners Guide With A 28-Day Clean Eating Meal PlanFrom EverandClean Eating 4-Week Meal Plan: Clean Eating Beginners Guide With A 28-Day Clean Eating Meal PlanNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Plan For The Serious Basketball Player: Food ChoicesDocument2 pagesNutrition Plan For The Serious Basketball Player: Food Choicesbetsi ozunaNo ratings yet
- Low Carb Mediterranean Diet Cookbook: Beginner Low Card Mediterranean Feasts for a Healthier LifestyleFrom EverandLow Carb Mediterranean Diet Cookbook: Beginner Low Card Mediterranean Feasts for a Healthier LifestyleNo ratings yet
- Hormone Balance DietDocument3 pagesHormone Balance DietEstefanie AyalaNo ratings yet
- Sport Smoothies: More Than 65 Recipes to Boost Your Workouts & RecoveryFrom EverandSport Smoothies: More Than 65 Recipes to Boost Your Workouts & RecoveryNo ratings yet
- NutritionDocument4 pagesNutritionalmaforma100% (1)
- Demo For College Emily Edison - 'Eat 2 Win With Cutting Edge Nutrition Science'Document39 pagesDemo For College Emily Edison - 'Eat 2 Win With Cutting Edge Nutrition Science'Sylvester Avila GustoNo ratings yet
- LTSD Plan - Academy Sport Nutrition Guide UpdateDocument20 pagesLTSD Plan - Academy Sport Nutrition Guide Updateapi-246218373No ratings yet
- The Atkins Diet Is A 4-Phase Plan: Low-Carb VegetablesDocument28 pagesThe Atkins Diet Is A 4-Phase Plan: Low-Carb VegetablesElena AlinaNo ratings yet
- MacMurray Football Post Season WorkoutsDocument18 pagesMacMurray Football Post Season Workoutsmartiny67No ratings yet
- Nutrition - Fueling For Optimal PerformanceDocument18 pagesNutrition - Fueling For Optimal Performancethat/niggaNo ratings yet
- Gastric Bypass Diet Manual: Advanced Laparoscopic Specialists, LLCDocument7 pagesGastric Bypass Diet Manual: Advanced Laparoscopic Specialists, LLCKaren PowersNo ratings yet
- NUTRITIONDocument32 pagesNUTRITIONlimberg arandiaNo ratings yet
- NutritionDocument39 pagesNutritionapi-263861419No ratings yet
- MacMurray Football Off Season WorkoutsDocument35 pagesMacMurray Football Off Season Workoutsmartiny67100% (2)
- Meal PlanningDocument4 pagesMeal Planningvega100% (1)
- Performance Nutrition Manual: University of WashingtonDocument25 pagesPerformance Nutrition Manual: University of WashingtonHakimAliouaNo ratings yet
- Nutritional PlanDocument20 pagesNutritional Planapi-259457599No ratings yet
- Basic Nutrition For AthletesDocument3 pagesBasic Nutrition For AthletesherkamayaNo ratings yet
- Camp Nutrition InfoDocument7 pagesCamp Nutrition InfoWes GearyNo ratings yet
- Nutrition PlanDocument2 pagesNutrition PlanBogdan BurcaNo ratings yet
- Football Nutrition ManualDocument12 pagesFootball Nutrition ManualrontraubNo ratings yet
- NutritionbookletDocument22 pagesNutritionbookletapi-252780946No ratings yet
- Lovelylesh Carb CycleDocument27 pagesLovelylesh Carb CycleAlejandraNo ratings yet
- Power Back DietDocument26 pagesPower Back DietAnthony Bonafide DakushNo ratings yet
- Crohns Disease Nutrition PDFDocument4 pagesCrohns Disease Nutrition PDFSher Lee HoNo ratings yet
- W E G D R: HAT TO AT FOR AME AY AND EcoveryDocument2 pagesW E G D R: HAT TO AT FOR AME AY AND EcoveryViolintsarNo ratings yet
- Diabetes LatestDocument11 pagesDiabetes LatestThaila Renay RampershadNo ratings yet
- Nutrition MacroDocument36 pagesNutrition Macroapi-261745434No ratings yet
- 8 DAYS - Weight GainDocument22 pages8 DAYS - Weight Gainilekachristelle100% (1)
- Bland Diet: Making A Lifestyle Change?Document5 pagesBland Diet: Making A Lifestyle Change?Wushuuu PabatangNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Plan To Put Weight On PDFDocument7 pagesNutrition Plan To Put Weight On PDFaghorbanzadehNo ratings yet
- Eating Strategies To Gain Weight: Sheri Barke, MPH, RD COC, Student Health & Wellness Center Rev. 2004Document5 pagesEating Strategies To Gain Weight: Sheri Barke, MPH, RD COC, Student Health & Wellness Center Rev. 2004aghorbanzadehNo ratings yet
- Wild Fire Cookbook Full DetailDocument10 pagesWild Fire Cookbook Full DetailLuca DiFlavioNo ratings yet
- LiverDocument6 pagesLivertejasviniNo ratings yet
- Control Diabetes Ebook by Guru MannDocument8 pagesControl Diabetes Ebook by Guru MannGaurav Sharma100% (1)
- Twice The Speed Nutrition GuidelinesDocument7 pagesTwice The Speed Nutrition Guidelinesshinsei40100% (1)
- MacMurray Football Pre Season WorkoutsDocument106 pagesMacMurray Football Pre Season Workoutsmartiny67No ratings yet
- MacMurray Football Pre Season WorkoutsDocument106 pagesMacMurray Football Pre Season Workoutskc016No ratings yet
- Sports Nutrition For High School AthletesDocument16 pagesSports Nutrition For High School Athletesevan markle100% (1)
- 20231213-A Low Carbohydrates, High Protein Diet Using Meal Replacements - EnglishDocument10 pages20231213-A Low Carbohydrates, High Protein Diet Using Meal Replacements - Englishwhalet74No ratings yet
- New York Cycle Club April 2016 - Reyna Franco Nutrition PresentationDocument29 pagesNew York Cycle Club April 2016 - Reyna Franco Nutrition PresentationBrian Van NieuwenhovenNo ratings yet
- Calories in Fruits Per 100 GramsDocument11 pagesCalories in Fruits Per 100 Gramsnehakothari_1985No ratings yet
- Calories in Fruits Per 100 GramsDocument11 pagesCalories in Fruits Per 100 Gramsnehakothari_1985No ratings yet
- 6 Week ProgramDocument22 pages6 Week ProgramValerie Najjuma100% (4)
- Dietary Chart For DiabeticsDocument5 pagesDietary Chart For DiabeticsYogeswara Rao VeeravalliNo ratings yet
- Basic Nutrition Guide For Basketball Players PDFDocument5 pagesBasic Nutrition Guide For Basketball Players PDFLi An RillNo ratings yet
- Lovely Lesh Gains Meal Guide 1Document24 pagesLovely Lesh Gains Meal Guide 1Tanner Rhodes100% (2)
- Football NutritionDocument52 pagesFootball NutritionJalil AtaieNo ratings yet
- 31 Blender DrinksDocument18 pages31 Blender DrinksAishwarya KrishnanNo ratings yet
- DetoxmanualDocument12 pagesDetoxmanualgungi1950No ratings yet
- Weight Gain Tips For Athletes: Cooperative ExtensionDocument2 pagesWeight Gain Tips For Athletes: Cooperative ExtensionWilly FoldismNo ratings yet
- Insanity Elite Nutrition GuideDocument3 pagesInsanity Elite Nutrition GuideJainesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Basic Eating Plan Weeks 1-6: GET IN TimeDocument8 pagesBasic Eating Plan Weeks 1-6: GET IN Timebri113No ratings yet
- RT-650 Provisional Manual - April 2008Document32 pagesRT-650 Provisional Manual - April 2008lula6894No ratings yet
- Jennifers Karaoke Songlist by TitleDocument10 pagesJennifers Karaoke Songlist by Titleapi-664681961No ratings yet
- FOLKDocument6 pagesFOLKcrisNo ratings yet
- Ives Charles Schoffman Nachum Serialism in The Work ofDocument13 pagesIves Charles Schoffman Nachum Serialism in The Work ofEsteban De Boeck100% (1)
- Choose The Present Perfect or Past SimpleDocument2 pagesChoose The Present Perfect or Past Simplememolkan100% (1)
- Openings ListDocument48 pagesOpenings ListJhonny CehNo ratings yet
- 5K by Jeff GallowayDocument2 pages5K by Jeff GallowaySas ParakNo ratings yet
- Bios 7SDV PDFDocument2 pagesBios 7SDV PDFneuzasilva.k16No ratings yet
- 3051 VOG Brochure 2015 WEBDocument33 pages3051 VOG Brochure 2015 WEBNelson Correa DíazNo ratings yet
- Low Anode 2Document3 pagesLow Anode 2dusan1962No ratings yet
- B2B Brand Management: Philip Kotler Waldemar PföertschDocument21 pagesB2B Brand Management: Philip Kotler Waldemar PföertschIrma NosadseNo ratings yet
- Julius Caesar SummaryDocument2 pagesJulius Caesar SummaryAmAr MoHit Jaiswal100% (1)
- Review, Summery & Evaluation of - Music Beyond Boundries - Hindi Film Songs SUBMISSIONDocument16 pagesReview, Summery & Evaluation of - Music Beyond Boundries - Hindi Film Songs SUBMISSIONAnil Pundlik GokhaleNo ratings yet
- V14 Series Spare Parts - Parker PDFDocument12 pagesV14 Series Spare Parts - Parker PDFeddyvegaNo ratings yet
- Amadeus Quick Reference - Reservation by Iata Travel ConsultanceDocument6 pagesAmadeus Quick Reference - Reservation by Iata Travel ConsultanceLEO OrtizNo ratings yet
- I Thank God-Maverick City Music-Move Your Heart.GDocument5 pagesI Thank God-Maverick City Music-Move Your Heart.Gemmapowell2007No ratings yet
- TDB013 ManualDocument9 pagesTDB013 ManualKALILNo ratings yet
- Book Review Kapt ZumazliDocument3 pagesBook Review Kapt Zumazliafiq_ismail_2No ratings yet
- Pioneer M-L11Document26 pagesPioneer M-L11adriangtamas1983No ratings yet
- Vaddio Catalog 2017-A4Document43 pagesVaddio Catalog 2017-A4Alina ManduNo ratings yet
- Body Work University Malaysia Sarawak Dr. Mastika Bin Lamat Lmastika@unimas - MyDocument1 pageBody Work University Malaysia Sarawak Dr. Mastika Bin Lamat Lmastika@unimas - MyharwezelNo ratings yet
- Fare Tool and Fare IntroductionDocument11 pagesFare Tool and Fare IntroductionkingxyzgNo ratings yet
- Young September-October 2011Document4 pagesYoung September-October 2011Straight Talk FoundationNo ratings yet
- Marketing Final TermDocument9 pagesMarketing Final TermClarice TorresNo ratings yet
- CharactersDocument2 pagesCharactersSi TepekNo ratings yet
- GM Bluetooth Starter Guide PDFDocument5 pagesGM Bluetooth Starter Guide PDFTin_AmoNo ratings yet
- Dgcis Report Kolkata PDFDocument12 pagesDgcis Report Kolkata PDFABCDNo ratings yet
- Anushka GNM YmtDocument3 pagesAnushka GNM YmtPreetam ParabNo ratings yet
- Card Encoding Engine Card Personalization SoftwareDocument10 pagesCard Encoding Engine Card Personalization SoftwareMagabata GoguNo ratings yet
- Notka Biograficzna ENG Katarzyna ŁukawskaDocument1 pageNotka Biograficzna ENG Katarzyna ŁukawskaKasia ŁukawskaNo ratings yet
- Forever Strong: A New, Science-Based Strategy for Aging WellFrom EverandForever Strong: A New, Science-Based Strategy for Aging WellNo ratings yet
- Summary of Mary Claire Haver's The Galveston DietFrom EverandSummary of Mary Claire Haver's The Galveston DietRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)From EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (378)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- The Encyclopedia of Spices & Herbs: An Essential Guide to the Flavors of the WorldFrom EverandThe Encyclopedia of Spices & Herbs: An Essential Guide to the Flavors of the WorldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (5)
- Summary: Fast Like a Girl: A Woman’s Guide to Using the Healing Power of Fasting to Burn Fat, Boost Energy, and Balance Hormones: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Fast Like a Girl: A Woman’s Guide to Using the Healing Power of Fasting to Burn Fat, Boost Energy, and Balance Hormones: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Instant Loss On a Budget: Super-Affordable Recipes for the Health-Conscious CookFrom EverandInstant Loss On a Budget: Super-Affordable Recipes for the Health-Conscious CookRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Not That Fancy: Simple Lessons on Living, Loving, Eating, and Dusting Off Your BootsFrom EverandNot That Fancy: Simple Lessons on Living, Loving, Eating, and Dusting Off Your BootsNo ratings yet
- Waiter Rant: Thanks for the Tip—Confessions of a Cynical WaiterFrom EverandWaiter Rant: Thanks for the Tip—Confessions of a Cynical WaiterRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (487)
- Mostly Plants: 101 Delicious Flexitarian Recipes from the Pollan FamilyFrom EverandMostly Plants: 101 Delicious Flexitarian Recipes from the Pollan FamilyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Metabolism Revolution: Lose 14 Pounds in 14 Days and Keep It Off for LifeFrom EverandMetabolism Revolution: Lose 14 Pounds in 14 Days and Keep It Off for LifeNo ratings yet
- Saved By Soup: More Than 100 Delicious Low-Fat Soups To Eat And Enjoy Every DayFrom EverandSaved By Soup: More Than 100 Delicious Low-Fat Soups To Eat And Enjoy Every DayRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- The Body Book: The Law of Hunger, the Science of Strength, and Other Ways to Love Your Amazing BodyFrom EverandThe Body Book: The Law of Hunger, the Science of Strength, and Other Ways to Love Your Amazing BodyNo ratings yet
- The Food Lover's Cleanse: 140 Delicious, Nourishing Recipes That Will Tempt You Back into Healthful EatingFrom EverandThe Food Lover's Cleanse: 140 Delicious, Nourishing Recipes That Will Tempt You Back into Healthful EatingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Surprise-Inside Cakes: Amazing Cakes for Every Occasion—with a Little Something Extra InsideFrom EverandSurprise-Inside Cakes: Amazing Cakes for Every Occasion—with a Little Something Extra InsideRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Instant Pot Miracle 6 Ingredients Or Less: 100 No-Fuss Recipes for Easy Meals Every DayFrom EverandInstant Pot Miracle 6 Ingredients Or Less: 100 No-Fuss Recipes for Easy Meals Every DayRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Sugar Crush: How to Reduce Inflammation, Reverse Nerve Damage, and Reclaim Good HealthFrom EverandSugar Crush: How to Reduce Inflammation, Reverse Nerve Damage, and Reclaim Good HealthRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- The Beck Diet Solution Weight Loss Workbook: The 6-Week Plan to Train Your Brain to Think Like a Thin PersonFrom EverandThe Beck Diet Solution Weight Loss Workbook: The 6-Week Plan to Train Your Brain to Think Like a Thin PersonRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (33)
- How Not to Die by Michael Greger MD, Gene Stone - Book Summary: Discover the Foods Scientifically Proven to Prevent and Reverse DiseaseFrom EverandHow Not to Die by Michael Greger MD, Gene Stone - Book Summary: Discover the Foods Scientifically Proven to Prevent and Reverse DiseaseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (83)
- Secrets From the Eating Lab: The Science of Weight Loss, the Myth of Willpower, and Why You Should Never Diet AgainFrom EverandSecrets From the Eating Lab: The Science of Weight Loss, the Myth of Willpower, and Why You Should Never Diet AgainRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (38)
- The Diabetes Code: Prevent and Reverse Type 2 Diabetes NaturallyFrom EverandThe Diabetes Code: Prevent and Reverse Type 2 Diabetes NaturallyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Pati's Mexican Table: The Secrets of Real Mexican Home CookingFrom EverandPati's Mexican Table: The Secrets of Real Mexican Home CookingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- The Stark Naked 21-Day Metabolic Reset: Effortless Weight Loss, Rejuvenating Sleep, Limitless Energy, More MojoFrom EverandThe Stark Naked 21-Day Metabolic Reset: Effortless Weight Loss, Rejuvenating Sleep, Limitless Energy, More MojoNo ratings yet