Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Radio Bearers On UMTS System: The AS Provides The NAS
Uploaded by
manish_chaturvedi_19Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Radio Bearers On UMTS System: The AS Provides The NAS
Uploaded by
manish_chaturvedi_19Copyright:
Available Formats
B (Radio Bearer) signifies the connection between the MT and the RNC RAB (Radio Access Bearer) signifies
the connection between the MT and the Core Network after RAB_Assignment_Req being received in RNC, the RNC will start to build Radio Bearer in radio side (RNC<> UE), traffic radio bearer (TRB) and signaling radio bearer (SRB). thansk,
The AS provides the NAS with a service of information transfer between UE and the CN in what is named a Radio Access Bearer (RAB). RAB consists of two: 1. Radio bearer (RB) between the UE and RNC 2. Iu Bearer between RNC and CN RB is only for user data either in CS or PS mode. RB is for both user data and signaling.
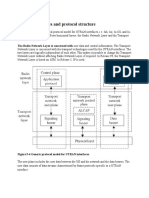
Radio Bearers on UMTS System
A radio bearer (RB) of a radio access bearer (RAB) carries the control plane signaling or user plane data of L3 between the UE and the UTRAN. RB is mapped onto logical channels through the radio link control (RLC) sublayer of L2. After RLC processing, RLC protocol data units (PDUs) are sent to the medium access control (MAC) sublayer through logical channels. Based on the traffic class and quality of service (QoS) required by the upper layer, the MAC selects appropriate transport channels and maps the logical channels onto the transport channels. The physical layer (L1) maps the transport channels onto one or more physical channels. After data processing, such as spreading and scrambling, the signaling or user data is sent through radio waves.
Especially for signaling purpose RB, we call it SRB: In the control plane, the signalling information is transfered through the Signaling Radio Bearer (SRB). However, RAB consists of Iu bearer and user data RB (not SRB).
About these ads
Radio Bearers on UMTS System
A radio bearer (RB) of a radio access bearer (RAB) carries the control plane signaling or user plane data of L3 between the UE and the UTRAN. RB is mapped onto logical channels through the radio link control (RLC) sublayer of L2. After RLC processing, RLC protocol data units (PDUs) are sent to the medium access control (MAC) sublayer through logical channels. Based on the traffic class and quality of service (QoS) required by the upper layer, the MAC selects appropriate transport channels and maps the logical channels onto the transport channels. The physical layer (L1) maps the transport channels onto one or more physical channels. After data processing, such as spreading and scrambling, the signaling or user data is sent through radio waves.
Radio Bearers on UMTS System
A radio bearer (RB) of a radio access bearer (RAB) carries the control plane signaling or user plane data of L3 between the UE and the UTRAN. RB is mapped onto logical channels through the radio link control (RLC) sublayer of L2. After RLC processing, RLC protocol data units (PDUs) are sent to the medium access control (MAC) sublayer through logical channels. Based on the traffic class and quality of service (QoS) required by the upper layer, the MAC selects appropriate transport channels and maps the logical channels onto the transport channels. The physical layer (L1) maps the transport channels onto one or more physical channels. After data processing, such as spreading and scrambling, the signaling or user data is sent through radio waves.
You might also like
- UMTS - RLC and MAC Layer in DetailDocument126 pagesUMTS - RLC and MAC Layer in DetailCaymennNo ratings yet
- Uu InterfaceDocument5 pagesUu InterfaceSamira Shokry100% (1)
- UMTS Interface Protocols ExplainedDocument32 pagesUMTS Interface Protocols ExplainedsirnateNo ratings yet
- 10 - Layer 2 (Mac, RLC, PDCP)Document34 pages10 - Layer 2 (Mac, RLC, PDCP)Kwangrok ChangNo ratings yet
- UMTS Chap7Document126 pagesUMTS Chap7John GarciaNo ratings yet
- WCDMA Channels & Channel SwitchingDocument26 pagesWCDMA Channels & Channel SwitchingDee OyeNo ratings yet
- 3G Protocals and ProcceduresDocument80 pages3G Protocals and ProccedureshohhoohNo ratings yet
- MAC in Umts ProtocolsDocument10 pagesMAC in Umts ProtocolsQasim Abbas AlviNo ratings yet
- Register 2 - Radio Protocol Architecture and Idle Mode TasksDocument60 pagesRegister 2 - Radio Protocol Architecture and Idle Mode TasksTrilok SaxenaNo ratings yet
- RRC Vs RABDocument3 pagesRRC Vs RABsurvivalofthepolyNo ratings yet
- UMTS ArchitectureDocument37 pagesUMTS ArchitectureVivek KumarNo ratings yet
- RRC Stands For Radio Resource Control. As We Know Whenever UE Needs Resources From UTRAN Network, ItDocument3 pagesRRC Stands For Radio Resource Control. As We Know Whenever UE Needs Resources From UTRAN Network, ItmosesNo ratings yet
- WCDMA Physical Layer GuideDocument64 pagesWCDMA Physical Layer GuidenabsonNo ratings yet
- The LTE Protocols Layer 2 MAC, RLC and PDCPDocument41 pagesThe LTE Protocols Layer 2 MAC, RLC and PDCPJJamesranNo ratings yet
- 3G Protocals and ProcceduresDocument80 pages3G Protocals and ProcceduresLotfi LotfibhNo ratings yet
- WRAN Protocol Stack: Control Plane Between UE and RNCDocument2 pagesWRAN Protocol Stack: Control Plane Between UE and RNChamidboulahiaNo ratings yet
- UTRAN Radio Interface ProtocolsDocument31 pagesUTRAN Radio Interface ProtocolsDpkKSinghNo ratings yet
- LTE Radio Interface Section 3Document80 pagesLTE Radio Interface Section 3Nikan AminiNo ratings yet
- LTE ChannelDocument11 pagesLTE ChannelNam Song Hau CTONo ratings yet
- Utran ConceptsDocument34 pagesUtran ConceptsUmar MirNo ratings yet
- Air Interface ProtocolsDocument22 pagesAir Interface ProtocolsmetootheskullNo ratings yet
- Tutorial: Medium Access Control (MAC) in 3G/UMTS Protocol StackDocument10 pagesTutorial: Medium Access Control (MAC) in 3G/UMTS Protocol StackbyamokeshNo ratings yet
- UTRAN Interface and Signaling Procedure GuideDocument90 pagesUTRAN Interface and Signaling Procedure GuideTrần Ngọc Bình100% (2)
- WCDMA RAN Protocols and ProcedureDocument102 pagesWCDMA RAN Protocols and Proceduregsm_ibraNo ratings yet
- 3Gpp Utran Signalling Protocol Node B RNC User Equipment IubDocument2 pages3Gpp Utran Signalling Protocol Node B RNC User Equipment IubNagendra BadamNo ratings yet
- Radio Interface ProtocolsDocument15 pagesRadio Interface ProtocolsGazal MittalNo ratings yet
- LTE Protocol Stack LayersDocument7 pagesLTE Protocol Stack Layersmd1234_1984No ratings yet
- Wireless LAN (2): HIPERLAN, Bluetooth, 802.11 StandardsDocument74 pagesWireless LAN (2): HIPERLAN, Bluetooth, 802.11 StandardsCynthia PlazaNo ratings yet
- UMTS Chap5Document170 pagesUMTS Chap5ManeeshSharmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture7 RadioInterfaceProtcolsDocument31 pagesLecture7 RadioInterfaceProtcolsRajveer SinghNo ratings yet
- LTE Channels: (Physical, Logical and Transport)Document34 pagesLTE Channels: (Physical, Logical and Transport)AsmaeNo ratings yet
- 02 Ra41232en05gla0 Lte ChannelsDocument37 pages02 Ra41232en05gla0 Lte ChannelsMuhammad Ali MalikNo ratings yet
- Wcdma Channel ConceptDocument18 pagesWcdma Channel Conceptneelachal100% (1)
- Lte 5GDocument10 pagesLte 5GRaghuram MahataNo ratings yet
- Next Generation Networks (The Radio Aspect)Document53 pagesNext Generation Networks (The Radio Aspect)omer449100% (1)
- Radio Access Network Architecture OverviewDocument170 pagesRadio Access Network Architecture OverviewhamidboulahiaNo ratings yet
- Wcdma Channels: by - Manish SrivastavaDocument19 pagesWcdma Channels: by - Manish SrivastavakikirnNo ratings yet
- Wcdma Channels: by - Manish SrivastavaDocument19 pagesWcdma Channels: by - Manish SrivastavaMostafizaktelNo ratings yet
- Wireless Cellular & LTE 4G Broadband: Packet Data Convergence Protocol (PDCP)Document11 pagesWireless Cellular & LTE 4G Broadband: Packet Data Convergence Protocol (PDCP)NavaneethNo ratings yet
- LTE L2 Introduction: Bearers, Channels, MAC & RLCDocument116 pagesLTE L2 Introduction: Bearers, Channels, MAC & RLCJawad AL-noaimi100% (3)
- MC NotesDocument109 pagesMC Notesprithwirajsrimani2No ratings yet
- Umts Ranap ProtocolDocument7 pagesUmts Ranap Protocolrahulsingh_2998No ratings yet
- 03.WCDMA RAN Signaling FlowDocument77 pages03.WCDMA RAN Signaling FlowKareem HaidarNo ratings yet
- LTE Protocol Stack Layers ExplainedDocument13 pagesLTE Protocol Stack Layers ExplainedDhyanendra SinghNo ratings yet
- UMTS Tutorial Session 1 - Introduction: Vikalp VeerDocument12 pagesUMTS Tutorial Session 1 - Introduction: Vikalp VeerVikalp VeerNo ratings yet
- LTE Logical Channels (What Info is TransferredDocument13 pagesLTE Logical Channels (What Info is TransferredAnshul GuptaNo ratings yet
- Medium Access Control (MAC) in 3GDocument8 pagesMedium Access Control (MAC) in 3Gsamtec32No ratings yet
- By - Manish SrivastavaDocument19 pagesBy - Manish SrivastavaRahul DubeyNo ratings yet
- Telecom Transmission & Switching Systems (EET-456) : Assignment 3Document4 pagesTelecom Transmission & Switching Systems (EET-456) : Assignment 3Isif SethiNo ratings yet
- UTRAN Interfaces and Protocol StructureDocument10 pagesUTRAN Interfaces and Protocol StructureBala Murugan VNo ratings yet
- Radio Access Network ArchitectureDocument170 pagesRadio Access Network Architecturethutihehe67% (3)
- LTE Channels Explained: Logical, Transport and Physical ChannelsDocument8 pagesLTE Channels Explained: Logical, Transport and Physical ChannelsFajar Aditya WNo ratings yet
- ROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL: RIP DYNAMIC ROUTING LAB CONFIGURATIONFrom EverandROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL: RIP DYNAMIC ROUTING LAB CONFIGURATIONNo ratings yet
- Radio Spectrum Management: Policies, Regulations and TechniquesFrom EverandRadio Spectrum Management: Policies, Regulations and TechniquesNo ratings yet
- From GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandFrom EverandFrom GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandNo ratings yet
- Agenda Item: Source: Title: Text Proposal For 25.213 On The Maximal Number of Physical Channels ForDocument2 pagesAgenda Item: Source: Title: Text Proposal For 25.213 On The Maximal Number of Physical Channels Formanish_chaturvedi_19No ratings yet
- Channelization Cbjkode and UsesDocument18 pagesChannelization Cbjkode and Usesmanish_chaturvedi_19No ratings yet
- NAS MessageDocument3 pagesNAS Messagemanish_chaturvedi_19No ratings yet
- Timers On The Mobile Station SideDocument6 pagesTimers On The Mobile Station Sidemanish_chaturvedi_19No ratings yet
- Secção de Sistemas de TelecomunicaçõesDocument21 pagesSecção de Sistemas de TelecomunicaçõesControl A60100% (1)
- NAS MessageDocument3 pagesNAS Messagemanish_chaturvedi_19No ratings yet
- 01 CV ManunpornwDocument4 pages01 CV Manunpornwmanish_chaturvedi_19No ratings yet
- Nbnfi Fe20021270Document120 pagesNbnfi Fe20021270Dinesh Raja MNo ratings yet
- Channelization CodeDocument1 pageChannelization Codemanish_chaturvedi_19No ratings yet
- Compress ModeDocument16 pagesCompress Modemanish_chaturvedi_19No ratings yet
- GPRS and GSM System Information DetailDocument62 pagesGPRS and GSM System Information Detailpham_chauNo ratings yet
- NAS MessageDocument3 pagesNAS Messagemanish_chaturvedi_19No ratings yet
- Opti This WeakDocument2 pagesOpti This Weakmanish_chaturvedi_19No ratings yet
- Compress ModeDocument16 pagesCompress Modemanish_chaturvedi_19No ratings yet
- Hosr PPT in EricssioDocument3 pagesHosr PPT in Ericssiomanish_chaturvedi_19No ratings yet
- GSM DT KpiDocument5 pagesGSM DT KpiKalpesh JesalpuraNo ratings yet
- PCHDocument3 pagesPCHmanish_chaturvedi_19No ratings yet
- Consistancy CheckDocument2,612 pagesConsistancy Checkmanish_chaturvedi_19No ratings yet
- BSC 13Document6 pagesBSC 13manish_chaturvedi_19No ratings yet
- Commmand 2decDocument25 pagesCommmand 2decmanish_chaturvedi_19No ratings yet
- 3g TimerDocument19 pages3g Timermanish_chaturvedi_19No ratings yet
- Cna Consistancy CheckDocument5 pagesCna Consistancy Checkmanish_chaturvedi_19No ratings yet
- BSC 13Document6 pagesBSC 13manish_chaturvedi_19No ratings yet
- Open Loop Power Control Is The Ability of The UE Transmitter To Sets Its OutputDocument2 pagesOpen Loop Power Control Is The Ability of The UE Transmitter To Sets Its Outputmanish_chaturvedi_19No ratings yet
- BSC Site - Name Site Id Cell Name Site Type Tower Typeantenna HT Antenna Typedir-PreDocument6 pagesBSC Site - Name Site Id Cell Name Site Type Tower Typeantenna HT Antenna Typedir-Premanish_chaturvedi_19No ratings yet
- BSC Site and Cell DetailsDocument2 pagesBSC Site and Cell Detailsmanish_chaturvedi_19No ratings yet
- Ashok Kumar Verma ResumeDocument2 pagesAshok Kumar Verma ResumeManish ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Ant HoppingDocument1 pageAnt Hoppingmanish_chaturvedi_19No ratings yet
- Book 3Document210 pagesBook 3manish_chaturvedi_19No ratings yet
- Good 3g ResumeDocument5 pagesGood 3g ResumeRaju KumarNo ratings yet
- TocDocument8 pagesTocshadi22No ratings yet
- Audio and Navi Control Unit DiagnosisDocument10 pagesAudio and Navi Control Unit DiagnosismihaimartonNo ratings yet
- A Software-Defined Radio For The MassesDocument40 pagesA Software-Defined Radio For The MassesLaFlibusteNo ratings yet
- Alarm Kebakaran Dengan Sensor Api Dan AsapDocument6 pagesAlarm Kebakaran Dengan Sensor Api Dan AsapDeny SetiadyNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes Class 12 Chapter 14 Semiconductor Electronics, Materials, Devices and Sample CircuitsDocument13 pagesPhysics Notes Class 12 Chapter 14 Semiconductor Electronics, Materials, Devices and Sample CircuitsAisha Agarwal50% (2)
- Test Questions of HandoverDocument4 pagesTest Questions of Handoverdayoladejo777No ratings yet
- MOSFET Lab Simulation CharacteristicsDocument13 pagesMOSFET Lab Simulation CharacteristicsFio MNo ratings yet
- Roland Fantom x6Document66 pagesRoland Fantom x6Blair Alward100% (1)
- 2006 A Generalized Memory Polynomial Model For Digital Predistortion of RF Power AmplifiersDocument9 pages2006 A Generalized Memory Polynomial Model For Digital Predistortion of RF Power Amplifiers9885842565No ratings yet
- Pepperl & Fuchs: Zone 1 Galvanic IsolatorsDocument1 pagePepperl & Fuchs: Zone 1 Galvanic IsolatorsRaj ChavanNo ratings yet
- A Simple Space Vector PWM Generation Scheme For Any General N-Level InverterDocument9 pagesA Simple Space Vector PWM Generation Scheme For Any General N-Level InverterAhmad MqdadNo ratings yet
- Terrestrial Trunked Radio Voice Plus Data P17 TETRA and DMO Subpart4 (ETSI TR 100 392-17-4)Document16 pagesTerrestrial Trunked Radio Voice Plus Data P17 TETRA and DMO Subpart4 (ETSI TR 100 392-17-4)Li XinNo ratings yet
- Gate 2007 Questions 1-20Document30 pagesGate 2007 Questions 1-20prabhjot singh1No ratings yet
- PCM, Differential Coding, DPCM, DM, ADPCM - Ze-Nian Li and Mark SDocument13 pagesPCM, Differential Coding, DPCM, DM, ADPCM - Ze-Nian Li and Mark SAkshay GireeshNo ratings yet
- AR9002AP-1S: AP/Router Solution Based On 802.11n 1-Stream SpecificationDocument2 pagesAR9002AP-1S: AP/Router Solution Based On 802.11n 1-Stream SpecificationAsep AcengNo ratings yet
- Hacking Your IrobotDocument123 pagesHacking Your IrobotHusam WadiNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Aperture Coupled Micro Strip Patch Antenna Forradar ApplicationsDocument7 pagesDesign and Analysis of Aperture Coupled Micro Strip Patch Antenna Forradar ApplicationsBrijesh SoniNo ratings yet
- CoaDocument11 pagesCoashubhampawar404043No ratings yet
- Conditions (IMC), Such As Low Ceilings or Reduced Visibility Due To Fog, Rain, or Blowing SnowDocument6 pagesConditions (IMC), Such As Low Ceilings or Reduced Visibility Due To Fog, Rain, or Blowing SnowJay ComajesNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: LC-42D64U LC-46D64U LC-52D64UDocument172 pagesService Manual: LC-42D64U LC-46D64U LC-52D64UJosue Hernandez GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Wireless Mobile Charger Report PDFDocument16 pagesWireless Mobile Charger Report PDFudaykanth3mudhiraj94% (18)
- Realtek Single Chip 16-PORT 10/100 ETHERNET Switch Controller With Embedded Memory RTL8316Document22 pagesRealtek Single Chip 16-PORT 10/100 ETHERNET Switch Controller With Embedded Memory RTL8316Vinicius ZanicheliNo ratings yet
- HD406VRH ON&OFF SpecificationDocument4 pagesHD406VRH ON&OFF SpecificationKarloff AutencioNo ratings yet
- LMD 2030WDocument2 pagesLMD 2030WPhong DoNo ratings yet
- Logic Gate Investigatory PDFDocument12 pagesLogic Gate Investigatory PDFGaurang MathurNo ratings yet
- Panasonic New Camera ProtocolDocument26 pagesPanasonic New Camera ProtocolMike MelgaNo ratings yet
- Panasonic KX-TCD 725 EDocument100 pagesPanasonic KX-TCD 725 EAleksandarRistićNo ratings yet
- EC201 Analog Circuits: Problem Set 1 SolutionsDocument2 pagesEC201 Analog Circuits: Problem Set 1 Solutionss_subbulakshmiNo ratings yet
- WEG 10004278046 13617810 r01 CFW700 Adenddum H1as1 en Es PTDocument2 pagesWEG 10004278046 13617810 r01 CFW700 Adenddum H1as1 en Es PTLuanNo ratings yet
- Acer LCD Monitor Quick Setup GuideDocument3 pagesAcer LCD Monitor Quick Setup GuideRymez2kNo ratings yet