Professional Documents
Culture Documents
UMTS Basic Refresher
Uploaded by
Joseph Kwafo MensahOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
UMTS Basic Refresher
Uploaded by
Joseph Kwafo MensahCopyright:
Available Formats
Signalling & interfaces Background
service user UE NAS/layer 3 Uu node B NBAP Iub Iur RRC RNC RNSAP RNC Iu RANAP service access point MSC/SGSN
Interface Application protocol Service related signalling
Application protocols Background
Allow communication (signalling: control plane) between different network elements Technology specific (e.g. UMTS) UMTS application protocols: RRC (Radio Resource Control) Runs over Uu and Iub interface, between UE and RNC NBAP (Node B Application Part) Used on Iub interface between node B and RNC
RANAP (Radio Access Network Application Part)
Used on Iucs/Iups interface between RNC and MSC/SGSN RNSAP (Radio Network Subsystem Application Part) Used on Iur interface between different RNCs Remark: only RRC application protocol will be studied in detail Can be captured on air interface during drive testing
Service related signalling Background
Used for service setup and release Between service user (UE) and service access point (MSC/SGSN) Service specific, but not technology specific UMTS service related signalling is different for voice call and PS data session 2G and 3G service related signalling can be the same for the same service type (e.g. voice call)
Control plane Background
UE
Iu Uu node B Iub Iur RNC
MSC/SGSN Iu signalling connection
RRC (signalling) connection RNC Only one RRC Connection in connected mode, no RRC Connection in idle mode RRC Connection consists of typically four signalling Radio Bearers (sRB) sRB1, sRB2, sRB3 and sRB4 Used for transport of RRC application protocol and NAS/layer 3 messages
Up to two Iu signalling connections in connected mode (to MSC and/or SGSN), none in idle mode
User plane Background
UE Radio Access Bearer (RAB) Uu node B Iub Iur Radio Bearer (RB) RNC RNC
Iu
MSC/SGSN Iu bearer
One RAB for each service type in connected mode (e.g. voice call, PS data service), no RAB in idle mode RAB consists of one or three RBs (depending on service) Voice call three RBs, all other services only one RB
One Iu bearer for every RAB used
Control/user plane flow during soft handover Background
One logical RRC Connection
UE Iu RNC node B Iub Iur Radio Link (RL) node B Iur Iub node B Signalling/data flow RNC MSC/SGSN
Serving RNC (SRNC)
Iub
RNC
Drift RNC (DRNC)
Drift RNC (DRNC)
Control plane vs. user plane bit pipe Background
C-plane SRNC RRC Connection Setup procedure RB Setup procedure UE U-plane
sRB 14 Control plane bit pipe (RRC Connection): Signalling transport (RRC, NAS)
RB 13
Typically 4 sRBs setup during RRC Connection Setup procedure User plane bit pipe: Transport of user data 1 or 3 RBs setup during RB Setup procedure
Control plane vs. user plane RRC procedures Background
UE RRC Connection Setup procedure SRNC Setup control plane bit pipe Setup user plane bit pipe
RB Setup procedure
RB Release procedure
Release user plane bit pipe Release control plane bit pipe
RRC Connection Release procedure
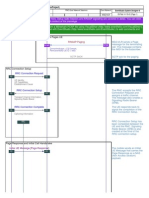
RRC Connection Setup procedure Background
UE RRC Connection Request (UL-CCCH) RRC Connection Setup (DL-CCCH) RRC Connection Setup Complete (UL-DCCH) RRC Connection Setup procedure: First step to go from idle mode to connected mode Establishment of RRC signalling connection Setup dedicated resources control plane (CCCH DCCH) RRC Connection Request: Used by UE to get access to network Retransmitted if no reaction from network Maximum # retransmissions: N300 (default: 3) Time between retransmissions: T300 (default: 1000ms) Parameters in System Information SRNC
RRC Connection Setup procedure Background
UE RRC Connection Request (UL-CCCH) RRC Connection Setup (DL-CCCH) RRC Connection Setup Complete (DL-DCCH) RRC Connection Setup: Contains downlink instructions regarding setup control plane bit pipe RRC Connection Setup Complete: Confirmation from UE indicating successful setup of control plane bit pipe Contains information on UE capabilities (e.g. HSDPA UE category) SRNC
RRC Connection Release procedure Background
UE RRC Connection Release (DL-DCCH) RRC Connection Release Complete (UL-DCCH) RRC Connection Release Complete (UL-DCCH) Used to release RRC signalling connection All sRBs released To go from connected mode to idle mode SRNC
RRC Connection Release complete: typically retransmitted several times
# retransmissions: N308 Time between retransmissions: T308
RRC Connection Setup failure Background
UE RRC Connection Request (UL-CCCH) RRC Connection Reject (DL-CCCH) SRNC
Indication of unsuccessful RRC Connection Setup procedure Reject cause, e.g. congestion Wait time: time needed before retry Optionally UE redirected to other carrier/RAT
RB Setup procedure Background
UE RB Setup RB Setup Complete SRNC
Setup dedicated resources/bit pipe user plane Consists of 1 or 3 RBs depending on requested service Triggered by RAB setup procedure (RANAP on Iu interface)
RB Release procedure Background
UE RB Release RB Release Complete SRNC
Release dedicated resources/bit pipe user plane Used for PS procedures Not used for CS procedures RBs released with RRC Connection Release procedure
CS vs. PS service Background
CS service
PS service
CS service No RB release procedure All RBs released implicitly with RRC Connection Release procedure
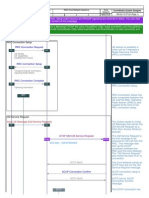
Initial Direct Transfer Background
UE Initial Direct Transfer (initial NAS message) SRNC
Used to setup Iu signalling connection between SRNC and MSC/SGSN
Carries the very first NAS message of the session from UE to SRNC
Contains CN domain: CS: Iu signalling connection needed to MSC PS: Iu signalling connection needed to SGSN Last step to go from idle mode to connected mode: 1) 2) RRC Connection Setup procedure (signalling connection UE-SRNC) Initial Direct Transfer (signalling connection UE-MSC/SGSN)
Uplink/Downlink Direct Transfer Background
UE Uplink Direct Transfer (NAS message) Downlink Direct Transfer (NAS message) SRNC
Used to carry NAS messages between UE and SRNC, once the Iu signalling connection exists Carries all NAS messages of the session except the initial NAS message
Mobile Originating Call part 1 Background
UE RRC Connection Request RRC Connection Setup RRC Connection Setup Complete Initial Direct Transfer (MM CM Service Request) Downlink Direct Transfer (MM Auth Req) Uplink Direct Transfer (MM Auth Resp) Security Mode Command Security Mode Complete Uplink Direct Transfer (CC Setup) Downlink Direct Transfer (CC Call Proceeding) RB Setup RB Setup Complete RB Setup procedure NAS signalling: service setup part 1 Security Mode procedure: ciphering Authentication procedure: double check UE id First NAS message SRNC RRC Connection Setup procedure
Mobile Originating Call part 2 Background
UE Downlink Direct Transfer (CC Alerting) Downlink Direct Transfer (CC Connect) Uplink Direct Transfer (CC Connect Ack) ACTIVE CALL Uplink Direct Transfer (CC Disconnect) Downlink Direct Transfer (CC Release) Uplink Direct Transfer (CC Release Complete) RRC Connection Release RRC Connection Release Complete RRC Connection Release Complete RRC Connection Release procedure NAS signalling: service release SRNC NAS signalling: service setup part 2
Intra-frequency soft handover Background
Iur RNC RNC
3G coverage f1
Soft handover area Handover between cells with same carrier Soft handover: UE connected simultaneously to multiple cells Iur interface needed if several RNCs involved Soft handover area: Overlapping cells with same quality
3G coverage f1
Intra-frequency soft handover area Background
2-cell soft handover area 3-cell soft handover area
Active Set (AS): all cells the UE is connected to in connected mode Typically Active Set is limited to maximum three cells Several possibilities for soft handover area: 2-cell soft handover area 3-cell soft handover area Soft handover causes redundancy, but results in reduction of transmitted power (SHO Gain)
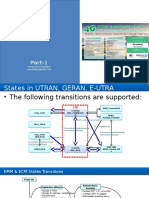
RRC state model main states Background
Connected mode
Idle mode
Two main states: Idle mode: no RRC connection Connected mode: one logical RRC connection
RRC state model - substates Background
Connected mode
URA-PCH
cell-PCH
cell-DCH
cell-FACH
Idle mode
Connected mode: four substates Cell-DCH: UE is allocated dedicated resources (e.g. codes from code tree) Cell-FACH: UE is using shared resources (common control channels RACH/FACH) Cell-PCH/URA-PCH UE in sleep mode, not using shared/dedicated resources from network Paging needed to wake up UE, resulting in transition to cell-FACH Location of UE known to network: cell (cell-PCH) or URA (URA-PCH)
Radio Bearer upgrade/downgrade Background
Switching between different data rates 64kbps 128kbps 384kbps By changing the uplink/downlink spreading factor Performed with Transport Channel Reconfiguration
Radio Bearer upgrade/downgrade Spreading Factor Background
Data rate (DL/UL) 64/64 64/128 64/384 128/64 128/128 128/384 384/64 384/128 384/384 SF DL 32 32 32 16 16 16 8 8 8 SF UL 16 8 4 16 8 4 16 8 4
Symmetrical service: SF DL is double of SF UL
Radio Bearer upgrade/downgrade logfile example Background
You might also like
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- WCDMA UTRAN Interfaces and Protocol StacksDocument94 pagesWCDMA UTRAN Interfaces and Protocol StacksAtul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Call Flow CSDocument17 pagesCall Flow CSAbdul Majeed KhanNo ratings yet
- 3G Protocals and ProcceduresDocument80 pages3G Protocals and ProccedureshohhoohNo ratings yet
- 3G Protocals and ProcceduresDocument80 pages3G Protocals and ProcceduresLotfi LotfibhNo ratings yet
- Call Flow PSDocument20 pagesCall Flow PSBhaskar KumarNo ratings yet
- Ue Nodeb RNC SGSN: RRC Connection Establishment - Cell DCH StateDocument20 pagesUe Nodeb RNC SGSN: RRC Connection Establishment - Cell DCH StateYogesh KumarNo ratings yet
- UMTS Interface Protocol: ZTE UniversityDocument57 pagesUMTS Interface Protocol: ZTE UniversityZahra ArshadNo ratings yet
- C WINDOWS TEMP Plugtmp-29 Plugin-Sprp501Document31 pagesC WINDOWS TEMP Plugtmp-29 Plugin-Sprp501Ekwere Wilfred UdohNo ratings yet
- Telkomsel Call Flow PSDocument20 pagesTelkomsel Call Flow PSPrabhakar SinghNo ratings yet
- WCDMA RAN Protocols and ProcedureDocument102 pagesWCDMA RAN Protocols and Proceduregsm_ibraNo ratings yet
- Radio Resource Con trol: 김민재 Kevin KimDocument30 pagesRadio Resource Con trol: 김민재 Kevin KimAMIT KUMAR DASNo ratings yet
- Lte L2 RLC MacDocument113 pagesLte L2 RLC MacShashank PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- RRC LayerDocument20 pagesRRC LayertargetpulsetradingNo ratings yet
- W-RNO Analysis Mate V1.0Document2,132 pagesW-RNO Analysis Mate V1.0Harold AquinoNo ratings yet
- Utran ConceptsDocument34 pagesUtran ConceptsUmar MirNo ratings yet
- 01 WO - SP2004 - E01 - 1 UMTS Interface Protocol-58Document58 pages01 WO - SP2004 - E01 - 1 UMTS Interface Protocol-58prabhum18100% (1)
- LTE L2 Introduction: Susan Sun Date: 2009.07.24Document116 pagesLTE L2 Introduction: Susan Sun Date: 2009.07.24Jawad AL-noaimi100% (3)
- Radio Interface ProtocolsDocument15 pagesRadio Interface ProtocolsGazal MittalNo ratings yet
- 3g Umts Terminating CallDocument5 pages3g Umts Terminating CallWalter MazibukoNo ratings yet
- 4 UMTS Signaling Flow-62Document57 pages4 UMTS Signaling Flow-62Camilo Bazan HerediaNo ratings yet
- UmtsDocument53 pagesUmtsNicholas WilsonNo ratings yet
- Uu InterfaceDocument5 pagesUu InterfaceSamira Shokry100% (1)
- WCDMA Radio Network Planning and Optimization: Song PengpengDocument56 pagesWCDMA Radio Network Planning and Optimization: Song PengpengAkhtar KhanNo ratings yet
- Introductions of UMTS Architecture, Call Flow Procedures and 3G EventsDocument68 pagesIntroductions of UMTS Architecture, Call Flow Procedures and 3G EventsRap PastidioNo ratings yet
- Umts Interface ProtocolDocument32 pagesUmts Interface ProtocolsirnateNo ratings yet
- RAN 3G Interfaces+ProtocolsDocument15 pagesRAN 3G Interfaces+Protocolsnavvicky082079No ratings yet
- Umts ProceduresDocument0 pagesUmts ProceduresUjjwal MaghaiyaNo ratings yet
- OWA310010 WCDMA Radio Interface Physical Layer ISSUE 1.10 (Compatibility Mode)Document64 pagesOWA310010 WCDMA Radio Interface Physical Layer ISSUE 1.10 (Compatibility Mode)nabsonNo ratings yet
- UMTS ... : 3G Technology and ConceptsDocument83 pagesUMTS ... : 3G Technology and Conceptssud_mishraNo ratings yet
- Lte L2 RLC MacDocument113 pagesLte L2 RLC MacRajeev KpNo ratings yet
- 4 Assumed UMTS Architecture: 5.1 Overall Protocol StructureDocument37 pages4 Assumed UMTS Architecture: 5.1 Overall Protocol StructureVivek KumarNo ratings yet
- Umts Radio Resource Control 3gpp Ts 25Document4 pagesUmts Radio Resource Control 3gpp Ts 25ismoilNo ratings yet
- 3g Umts Originating CallDocument6 pages3g Umts Originating Callk.naveedNo ratings yet
- 07-WCDMA UTRAN Signaling ProcedureDocument89 pages07-WCDMA UTRAN Signaling ProcedureMalik Pervaiz IqbalNo ratings yet
- 1.1 LTE RF Basic Module LTE Air InterfaceDocument43 pages1.1 LTE RF Basic Module LTE Air InterfaceJesus MartinezNo ratings yet
- 04 RN31584EN10GLA0 Paging+RRC ConnectionDocument70 pages04 RN31584EN10GLA0 Paging+RRC Connectionraghav_Sareen100% (1)
- 3 Generation Wcdma / Umts Wireless NetworkDocument39 pages3 Generation Wcdma / Umts Wireless Networkcarboneze9706No ratings yet
- WRAN Protocol Stack: Control Plane Between UE and RNCDocument2 pagesWRAN Protocol Stack: Control Plane Between UE and RNChamidboulahiaNo ratings yet
- LTE Deep Concept Part1Document26 pagesLTE Deep Concept Part1saifullahNo ratings yet
- 3g Umts Terminating Call RRC SignalingDocument2 pages3g Umts Terminating Call RRC SignalingDilmi MohamedNo ratings yet
- WCDMA Handover Principle and Power Control BasicsDocument26 pagesWCDMA Handover Principle and Power Control BasicsVishnu Kumar JayswalNo ratings yet
- UMTS ... : 3G Technology and ConceptsDocument83 pagesUMTS ... : 3G Technology and ConceptsAimad SadounNo ratings yet
- Call Flow: 1 © Nokia Siemens Networks Presentation / Author / Date Soc Classification LevelDocument47 pagesCall Flow: 1 © Nokia Siemens Networks Presentation / Author / Date Soc Classification Levelanban_mNo ratings yet
- WCMDA 04 Radio Connection SupervisionDocument19 pagesWCMDA 04 Radio Connection SupervisionHien Nguyen100% (1)
- 3 Generation Wcdma / Umts Wireless Network: Presentation by Tony Sung, MC Lab, IE CUHK 10th November 2003Document39 pages3 Generation Wcdma / Umts Wireless Network: Presentation by Tony Sung, MC Lab, IE CUHK 10th November 2003gayatridagarNo ratings yet
- UMTS System Architecture, Protocols: (Module 2)Document30 pagesUMTS System Architecture, Protocols: (Module 2)AhmedEL-NaggarNo ratings yet
- UMTSDocument170 pagesUMTSPraveen AnandNo ratings yet
- LTE Radio Access Network Protocols and ProceduresDocument151 pagesLTE Radio Access Network Protocols and ProceduresSuley Paterson0% (1)
- UMTS & HSDPA Fundamentals Version 4.0Document63 pagesUMTS & HSDPA Fundamentals Version 4.0Ravi_Vachhani_4636No ratings yet
- LTE Protocol Stack LayersDocument7 pagesLTE Protocol Stack Layersmd1234_1984No ratings yet
- Umts 3g Wcdma Call FlowsDocument98 pagesUmts 3g Wcdma Call FlowsNaveed Khan AbbuNo ratings yet
- 5 +procedures 1Document86 pages5 +procedures 1alquhaliNo ratings yet
- RADCOM - UMTS Iub and Iu InterfacesDocument26 pagesRADCOM - UMTS Iub and Iu InterfaceszhuqimingNo ratings yet
- Tabela de Faut Code GSM PortuguesDocument17 pagesTabela de Faut Code GSM PortuguesJefferson MotaNo ratings yet
- From GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandFrom EverandFrom GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandNo ratings yet
- Radio Control for Model Ships, Boats and AircraftFrom EverandRadio Control for Model Ships, Boats and AircraftRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Digital Signal Processing: Instant AccessFrom EverandDigital Signal Processing: Instant AccessRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Introduction Development Approach Questions - 095116Document2 pagesIntroduction Development Approach Questions - 095116Joseph Kwafo MensahNo ratings yet
- ExamTopics Questions - 092039Document1 pageExamTopics Questions - 092039Joseph Kwafo MensahNo ratings yet
- Agile Basic Questions and Answers - 092111Document42 pagesAgile Basic Questions and Answers - 092111Joseph Kwafo MensahNo ratings yet
- Project Code of Ethics and Professional Conduct Questions and Answers v1 - 095023Document11 pagesProject Code of Ethics and Professional Conduct Questions and Answers v1 - 095023Joseph Kwafo MensahNo ratings yet
- Agile Practice Guide Review 2 - 092040Document46 pagesAgile Practice Guide Review 2 - 092040Joseph Kwafo MensahNo ratings yet
- Acp Filla Final - 054341Document25 pagesAcp Filla Final - 054341Joseph Kwafo MensahNo ratings yet
- Quizlet Questions Missed Questions - 042313Document9 pagesQuizlet Questions Missed Questions - 042313Joseph Kwafo MensahNo ratings yet
- Managing Project Risks (2021 Update) - 042340Document11 pagesManaging Project Risks (2021 Update) - 042340Joseph Kwafo MensahNo ratings yet
- Virtual Team Article - 092030Document2 pagesVirtual Team Article - 092030Joseph Kwafo MensahNo ratings yet
- SH QuestionsDocument21 pagesSH QuestionsJoseph Kwafo MensahNo ratings yet
- PMP Alv Q PDFDocument11 pagesPMP Alv Q PDFJoseph Kwafo MensahNo ratings yet
- Delivering Project Quality (2021 Update) - 042333Document16 pagesDelivering Project Quality (2021 Update) - 042333Joseph Kwafo MensahNo ratings yet
- Understanding Agile Fundamentals (2021 Update) - 042329Document15 pagesUnderstanding Agile Fundamentals (2021 Update) - 042329Joseph Kwafo MensahNo ratings yet
- Establishing Quality Standards (2021 Update) - 042334Document20 pagesEstablishing Quality Standards (2021 Update) - 042334Joseph Kwafo MensahNo ratings yet
- Managing The Project Resources (2021 Update) - 042337Document11 pagesManaging The Project Resources (2021 Update) - 042337Joseph Kwafo MensahNo ratings yet
- Communicating Effectively (2021 Update) - 042343Document12 pagesCommunicating Effectively (2021 Update) - 042343Joseph Kwafo MensahNo ratings yet
- Performing Risk Analysis (2021 Update) - 042341Document16 pagesPerforming Risk Analysis (2021 Update) - 042341Joseph Kwafo MensahNo ratings yet
- Omf007004 GSM Cell Design Issue1.0Document81 pagesOmf007004 GSM Cell Design Issue1.0Houss HoussiNo ratings yet
- 3G Cluster Optimization by Drive TestingDocument43 pages3G Cluster Optimization by Drive Testingcorneliu.modilca71% (7)
- Selecting A Project Management Approach (2021 Update) - 042344Document19 pagesSelecting A Project Management Approach (2021 Update) - 042344Joseph Kwafo MensahNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management Project For MBA StudentsDocument393 pagesSupply Chain Management Project For MBA StudentsTaimoorAdilNo ratings yet
- Spurious EmissionDocument24 pagesSpurious EmissionJoseph Kwafo MensahNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument33 pagesQuestionsdeepeshkanungo100% (1)
- Research Process, Research Design and QuestionnairesDocument97 pagesResearch Process, Research Design and QuestionnairesJoseph Kwafo MensahNo ratings yet
- LTE Frequently Asked QuestionsDocument8 pagesLTE Frequently Asked QuestionsJoseph Kwafo Mensah100% (1)
- Oct, 2oo7: 1 © Nokia Siemens Networks Presentation / Author / Date For Internal UseDocument28 pagesOct, 2oo7: 1 © Nokia Siemens Networks Presentation / Author / Date For Internal UseJoseph Kwafo MensahNo ratings yet
- Accuview SeriesDocument18 pagesAccuview SeriestongaiNo ratings yet
- Dsa CheatsheetDocument28 pagesDsa CheatsheetRAJAN DUTTANo ratings yet
- Interview Qs On r12 p2pDocument15 pagesInterview Qs On r12 p2pAmitPradhanNo ratings yet
- Disk MagicDocument4 pagesDisk MagicMuhammad Javed SajidNo ratings yet
- A-Z Kali Linux CommandsDocument5 pagesA-Z Kali Linux CommandsGanteng Dewe100% (3)
- Quirino State University College of Information Technology and Computing Sciences Cabarroguis, QuirinoDocument3 pagesQuirino State University College of Information Technology and Computing Sciences Cabarroguis, Quirinochaddy rasilesNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Excel TutorialDocument90 pagesMicrosoft Excel Tutorialteacher.lexleo2782100% (1)
- Learning Activity Sheets (LAS) (For TLE/TVL CSS NCII)Document6 pagesLearning Activity Sheets (LAS) (For TLE/TVL CSS NCII)Jåy-ž ShìzhènNo ratings yet
- KeralaDocument514 pagesKeralaGayathriNo ratings yet
- Auditing Database Auditing Database System System: Chapter 4-HallDocument35 pagesAuditing Database Auditing Database System System: Chapter 4-HallElyssaNo ratings yet
- CT Series: OperationDocument1 pageCT Series: OperationcarlosorizabaNo ratings yet
- Acceptable Use AgreementDocument2 pagesAcceptable Use Agreementapi-325973069No ratings yet
- 3.4.4 Lab - Research Networking StandardsDocument5 pages3.4.4 Lab - Research Networking StandardsCT KHNo ratings yet
- Api Reference Guide PDFDocument440 pagesApi Reference Guide PDFpriyank31No ratings yet
- Godzilla: Seamless 2D and 3D Sketch Environment For Reflective and Creative Design WorkDocument8 pagesGodzilla: Seamless 2D and 3D Sketch Environment For Reflective and Creative Design Worksinghishpal24374No ratings yet
- Study of Advanced Current Control Strategies For Three-Phase Grid-Connected PWM Inverters For Distributed GenerationDocument6 pagesStudy of Advanced Current Control Strategies For Three-Phase Grid-Connected PWM Inverters For Distributed Generationapi-3826450100% (2)
- Supply Chain Version 2Document37 pagesSupply Chain Version 2Abdelhamid Harakat100% (1)
- AmpliTube X-GEAR User ManualDocument84 pagesAmpliTube X-GEAR User ManualToriano LampkinNo ratings yet
- AlvinDocument25 pagesAlvinAlvin AlexandriaNo ratings yet
- Tushar ResumeDocument2 pagesTushar ResumeDeepak PradhanNo ratings yet
- Quick Setup Guide: Terrasat Communications IBUC - Intelligent Block UpconverterDocument10 pagesQuick Setup Guide: Terrasat Communications IBUC - Intelligent Block UpconverterGenka BuchukuriNo ratings yet
- USACE Schedule SpecsDocument14 pagesUSACE Schedule SpecsAmgad FahmyNo ratings yet
- OCL TutorialDocument3 pagesOCL Tutorialshahid_abdullahNo ratings yet
- Learning SqlalchemyDocument19 pagesLearning SqlalchemyPushkar DeyNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of ANNDocument213 pagesFundamentals of ANNJosi MoNo ratings yet
- Detector de AmoniacoDocument4 pagesDetector de AmoniacoSegundo Teofilo Cadenillas CabanillasNo ratings yet
- Sip Series PDocument69 pagesSip Series PSyed Rahmath AliNo ratings yet
- Native InstallDocument64 pagesNative InstallSanthosh KrishnanNo ratings yet
- MR Cain Richard Mann: Curriculum VitaeDocument4 pagesMR Cain Richard Mann: Curriculum VitaeDoni MuharomNo ratings yet