Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 1 Electromagnetic Radiation and Antenna Fundamentals Two Mark Questions With Answers
Uploaded by
apecevsbOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 1 Electromagnetic Radiation and Antenna Fundamentals Two Mark Questions With Answers
Uploaded by
apecevsbCopyright:
Available Formats
UNIT 1 ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION AND ANTENNA FUNDAMENTALS Two Mark Questions with Answers
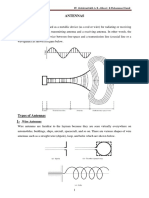
1. Define an antenna. Antenna is a transition device or a transducer between a guided wave and a free space wave or vice versa. Antenna is also said to be an impedance transforming device. 2. What is meant by radiation pattern? Radiation pattern is the relative distribution of radiated power as a function of distance in space .It is a graph which shows the variation in actual field strength of the EM wave at all points which are at equal distance from the antenna. The energy radiated in a particular direction by an antenna is measured in terms of FIELD STRENGTH. (E Volts/m) 3. Define Radiation intensity? The power radiated from an antenna per unit solid angle is called the radiation intensity U (watts per steradian or per square degree). The radiation intensity is independent of distance. 4. Define Beam efficiency? The total beam area (A) CONSISTS of main beam area (M) plus minor lobe area (m). Thus (A)= (M)+ (m). Beam efficiency =(M)/ (A) 5. Define Directivity? The directivity of an antenna is equal to them ratio of the maximum power density P(,f)max to its average value over a sphere as observed in the far field of an antenna. Directivity D= P(,f)max / P(,f)av 6. What is retarded current? Since current flowing through a short dipole is assumed to be constant throughout its length, the effect of current is not felt instantaneously at a distant point P, but only after an interval equal to the time required for the wave to propagate over distant r. This current is called retarded current. 7. Define hertzian dipole. Hertzian dipole is a defined as a short linear conductor or short electric dipole whose length is very short compared to wavelength (l<<) and current is assumed to be constant throughout its length l. 8. What are the two types of radiation pattern. (i) Field pattern: If the radiation from the antenna is expressed in terms of the field strength (either E or H), then the radiation pattern is called as field pattern.
(ii) Power pattern: If the radiation from the antenna is expressed in terms of power per unit area, then the resultant pattern is power pattern. 9. Distinguish between radian and steradian. The measure of a plane angle is radian. The measure of a solid angle is steradian. 1 steradian = 1 radian2 10.Define stray factor. The ratio of minor lobe area m to the beam area A is called stray factor. m = m/ A 11.Define different types of aperture.? Effective aperture(A). It is the area over which the power is extrated from the incident wave and delivered to the load is called effective aperture. Scattering aperture(Ae) It is the ratio of the reradiated power to the power density of the incident wave Loss aperture. (Aes). It is the area of the antenna which dissipates power as heat. Collecting aperture. (A). It is the addition of above three apertures. Physical aperture. (Ape). This aperture is a measure of the physical size of the antenna. 12. Define Aperture efficiency? The ratio of the effective aperture to the physical aperture is the aperture efficiency. i.e Aperture efficiency = ap = Ae / Ap (dimensionless). 13. What is meant by effective height? The effective height h of an antenna is the parameter related to the aperture.It may be defined as the ratio of the induced voltage to the incident field.i.e H= V / E. 14. Define FBR. Front to back ration is defined as the ratio of power radiated in desired direction to the power radiated in opposite direction. Higher the FBR , Better the antenna performance. 15. Define radiation resistance.
Antenna is a two terminal circuit element, as seen from the transmission line, having an impedence ZA=(Rr+RL) +jXA, where Rr is the radiation resistance. The resistance represents the amount of radiation by the antenna. 16. Define BWFN. Beam width between first nulls (BWFN) is defined as the angle between first nulls or the double the angle between first null and major lobe maximum directions. 17. What do you meant by self impedence? Self impedence is defined as the ratio of voltage to current at a pair of terminals Z11 = R11 + jX11. Where R11 Radiation resistance , X11 Self impedence. 18. What is mutual impedence? It is defined as the negative ratio of emf induced in one antenna to the current flowing in the other antenna. Mutual impedence , Z21 = -(V21/I1) 19. State reciprocity principle. If a current I1 at the terminals of antenna no.1 induces an emf E21 at the open terminals of antenna no.2 and a current I2 at the terminals of antenna no.2 induces an enf E 12 at the open terminals of antenna no.1 then E12 = E21 provided I1 = I2. 20. Define antenna temperature. The antenna temperature TA is defined as temperature of far field region of space and near surroundings which are coupled to the antenna through radiation resistance. 16 Mark questions 1. Explain the concept of vector potential. 2. Briefly explain about retarded vector potential. 3. Derive the fielde radiated from a hertzian dipole. Find the power radiated from the hertzian dipole. 4. Explain the following terms. a) Directivity b)Gain c)HPBW d)Radiation pattern e)Beam efficiency f)Directive gain g)Power gain. 5. What are the various types of aperatures? Find the effective aperature of a dipole antenna. 6. Derive relationship between directivity principle and effective aperature . 7. State and prove reciprocity principle with regard to antennas. 8. Explain the following. a) Vector effective length. b) Antenna temperature. 9. Explain how the solutions to wave equations are arrived. 10. Write short notes on a) Equivalence of radiation patterns. b) Equivalence of impedences.
You might also like
- Intensity of Electromagnetic Waves as a Function of Frequency, Source Distance and Aperture AngleFrom EverandIntensity of Electromagnetic Waves as a Function of Frequency, Source Distance and Aperture AngleNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- ANTENNA Term DefinitationDocument17 pagesANTENNA Term DefinitationShailendra Sapkota100% (1)
- Question Bank - 1741 - AntennasDocument11 pagesQuestion Bank - 1741 - AntennasPuthanial MariappanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document14 pagesChapter 1Varadharajan EswaramoorthiNo ratings yet
- EC1352 Antenna Wave PropagationDocument44 pagesEC1352 Antenna Wave Propagationjackdbomber100% (7)
- EC2353 ANTENNA AND WAVE PROPAGATION FUNDAMENTALSDocument56 pagesEC2353 ANTENNA AND WAVE PROPAGATION FUNDAMENTALSabinayageetha33% (3)
- Antenna DefinitionDocument3 pagesAntenna DefinitiondebabratalogonNo ratings yet
- 2 Marks With AnswerDocument9 pages2 Marks With AnswerMaha MurthyNo ratings yet
- EC2353 Antenna Fundamentals and Wave PropagationDocument55 pagesEC2353 Antenna Fundamentals and Wave PropagationAntonhy Raqui MarmanilloNo ratings yet
- Awp Questions PDFDocument43 pagesAwp Questions PDFJigar PatelNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Short Question-Answers On Antennas and Wave Propagation Class-Ece Iii ADocument14 pagesUnit 1: Short Question-Answers On Antennas and Wave Propagation Class-Ece Iii Appk100% (1)
- AWP Question BankDocument12 pagesAWP Question BankSuresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Ec2353 2 Marks PDFDocument15 pagesEc2353 2 Marks PDFpsjayakumarmeNo ratings yet
- Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering: Ec6602 - Antenna and Wave PropagationDocument17 pagesDepartment of Electronics and Communication Engineering: Ec6602 - Antenna and Wave PropagationSuresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Ec6602 2M Rejinpaul IiDocument20 pagesEc6602 2M Rejinpaul IiKumar RockyNo ratings yet
- EC1352 - Antenna Wave Propagation ConceptsDocument8 pagesEC1352 - Antenna Wave Propagation ConceptsAlexander JagannathanNo ratings yet
- Antennas and Wave Propagation-II MarksDocument33 pagesAntennas and Wave Propagation-II MarksBRINDHASHINEY100% (2)
- EC2353 – ANTENNA AND WAVE PROPAGATION NOTESDocument17 pagesEC2353 – ANTENNA AND WAVE PROPAGATION NOTESBachu Saee RamNo ratings yet
- AWP UNIT-1 (Vsem) - Merged-1Document76 pagesAWP UNIT-1 (Vsem) - Merged-1Pavan SaiNo ratings yet
- Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering: Ec6602 - Antenna and Wave PropagationDocument17 pagesDepartment of Electronics and Communication Engineering: Ec6602 - Antenna and Wave PropagationKumar RockyNo ratings yet
- Antenna fundamentals: RF transducer converts signals to EM wavesDocument12 pagesAntenna fundamentals: RF transducer converts signals to EM wavesAbdullah WalidNo ratings yet
- Antennas and Wave PropagationDocument107 pagesAntennas and Wave PropagationvivekanandaNo ratings yet
- Subject Code: 06es64 SUBJECT NAME: Antennas and PropagationDocument8 pagesSubject Code: 06es64 SUBJECT NAME: Antennas and PropagationShwetha B HegdeNo ratings yet
- EC6602Antennaandwavepropagation NotesDocument124 pagesEC6602Antennaandwavepropagation NotesGoh Chin HockNo ratings yet
- Antenna Parameters Wireless CommunicationsDocument5 pagesAntenna Parameters Wireless CommunicationsAdos OchiaNo ratings yet
- Antenna: Question 1. Define An Antenna?Document15 pagesAntenna: Question 1. Define An Antenna?Shreyas S RNo ratings yet
- Awp 2marksDocument8 pagesAwp 2marksHema Malini VggNo ratings yet
- Antenna BasicsDocument43 pagesAntenna BasicsSiddhartha OntelaNo ratings yet
- EC6602Antennaandwavepropagation NotesDocument124 pagesEC6602Antennaandwavepropagation NotesBaskaran SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Awp 2 MQDocument24 pagesAwp 2 MQrameshdurairajNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: 1. Explain The Radiation From Two-Wire. AnsDocument13 pagesUnit 1: 1. Explain The Radiation From Two-Wire. AnsRajaganapathi RajappanNo ratings yet
- Documentation On Proposed UWB AntennaDocument38 pagesDocumentation On Proposed UWB AntennaHaneesha ChelliNo ratings yet
- Antenna Objective QuestionsDocument8 pagesAntenna Objective QuestionsAkanksha Dixit ManodhyaNo ratings yet
- Antena Notes1Document9 pagesAntena Notes1Mahesh KolluriNo ratings yet
- EC2353 - Antenna and Wave PropagationDocument76 pagesEC2353 - Antenna and Wave PropagationTushar vaswaniNo ratings yet
- Cont. Parameters of Antennas: University of Gezira Faculty of Engineering & Technology Dept. of Electronics EngineeringDocument33 pagesCont. Parameters of Antennas: University of Gezira Faculty of Engineering & Technology Dept. of Electronics EngineeringGhshshehNo ratings yet
- Explain The Radiation From Two-Wire. Ans:: Unit 1Document13 pagesExplain The Radiation From Two-Wire. Ans:: Unit 1mohan inumarthiNo ratings yet
- 00 30 AntennaDocument93 pages00 30 AntennaBatuhan ALTINKÜPENo ratings yet
- EC2353 - Antenna and Wave Propagation IntroductionDocument76 pagesEC2353 - Antenna and Wave Propagation IntroductionSebastin SureshNo ratings yet
- Antennas: AnswerDocument18 pagesAntennas: AnswerAnonymous P2ZN8XNo ratings yet
- Antennas & Propagations Unit IDocument36 pagesAntennas & Propagations Unit IAdhra AllyNo ratings yet
- Antenna Theory Notes4Document62 pagesAntenna Theory Notes487kimeraNo ratings yet
- FUNDAMENTAL PARAMETERS AND FIGURES-OF-MERIT OF ANTENNAS - ch2&ch1Document21 pagesFUNDAMENTAL PARAMETERS AND FIGURES-OF-MERIT OF ANTENNAS - ch2&ch1Abdelrahman Shaban - 53No ratings yet
- Dhivya 2marksDocument4 pagesDhivya 2marksdhivyabharathyNo ratings yet
- Antenna Measurement TheoryDocument21 pagesAntenna Measurement Theorybrahmamtech100% (1)
- Module 2 - HandoutsDocument10 pagesModule 2 - HandoutsWondimu KenateNo ratings yet
- Antenna Input Impedance LectureDocument9 pagesAntenna Input Impedance Lectureمؤمل عبدالهاديNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: 1. Explain The Radiation From Two-Wire. AnsDocument13 pagesUnit 1: 1. Explain The Radiation From Two-Wire. AnsNallaManoharReddyNo ratings yet
- Antenna NOl PDFDocument77 pagesAntenna NOl PDFVenkataramanLakshminarayananNo ratings yet
- Antennas Lecture 9: Types, Length Calculations, and GainDocument29 pagesAntennas Lecture 9: Types, Length Calculations, and Gainmshri200658No ratings yet
- SECA1504Document71 pagesSECA1504SuganrajNo ratings yet
- Transmisi Gelombang Elektromagnetik: Radiasi, Polarisasi, dan Efisiensi AntenaDocument21 pagesTransmisi Gelombang Elektromagnetik: Radiasi, Polarisasi, dan Efisiensi AntenarizmanpebrianNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1No ratings yet
- Modern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsFrom EverandModern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Solid-State Circuits: Electrical Engineering DivisonFrom EverandSolid-State Circuits: Electrical Engineering DivisonRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)No ratings yet
- 1152EC120 - SATELLITE Communication: Dr. Saravanan M. Drsaravananm@veltech - Edu.inDocument10 pages1152EC120 - SATELLITE Communication: Dr. Saravanan M. Drsaravananm@veltech - Edu.inapecevsbNo ratings yet
- Orbital Mechanisms: Origin and Brief HistoryDocument15 pagesOrbital Mechanisms: Origin and Brief HistoryapecevsbNo ratings yet
- Poc 2 MarkDocument16 pagesPoc 2 MarkapecevsbNo ratings yet
- De Nitions of Terms For Earth-Orbiting SatellitesDocument9 pagesDe Nitions of Terms For Earth-Orbiting SatellitesapecevsbNo ratings yet
- 1152EC120 - SATELLITE Communication: Dr. Saravanan M. Drsaravananm@veltech - Edu.inDocument9 pages1152EC120 - SATELLITE Communication: Dr. Saravanan M. Drsaravananm@veltech - Edu.inapecevsb0% (1)
- Unit 1 Analog Communication (Adc)Document79 pagesUnit 1 Analog Communication (Adc)apecevsbNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document81 pagesUnit 2apecevsbNo ratings yet
- Department of Information Technology Question Bank Subject Name: Principles of Communication Year / Sem: II/III Unit - I Part-A (2 Marks)Document4 pagesDepartment of Information Technology Question Bank Subject Name: Principles of Communication Year / Sem: II/III Unit - I Part-A (2 Marks)apecevsbNo ratings yet
- Poc 2 MarkDocument16 pagesPoc 2 MarkapecevsbNo ratings yet
- Department of Information Technology Question Bank Subject Name: Principles of Communication Year / Sem: II/III Unit - I Part-A (2 Marks)Document4 pagesDepartment of Information Technology Question Bank Subject Name: Principles of Communication Year / Sem: II/III Unit - I Part-A (2 Marks)apecevsbNo ratings yet
- IT 2202 PocDocument41 pagesIT 2202 PocapecevsbNo ratings yet
- Poc 2 MarkDocument16 pagesPoc 2 MarkapecevsbNo ratings yet
- IT 2202 PocDocument41 pagesIT 2202 PocapecevsbNo ratings yet
- Adc Two Mark With Answer (1-4)Document21 pagesAdc Two Mark With Answer (1-4)apecevsbNo ratings yet
- Hfss Tutorial Design of A Loop InductorDocument23 pagesHfss Tutorial Design of A Loop InductorapecevsbNo ratings yet
- Adc Two Mark With Answer (1-4)Document21 pagesAdc Two Mark With Answer (1-4)apecevsbNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document13 pagesUnit 5apecevsbNo ratings yet
- Adc Two MarksDocument22 pagesAdc Two MarksapecevsbNo ratings yet
- Simulink BasicsDocument8 pagesSimulink BasicsapecevsbNo ratings yet
- Unit IvDocument47 pagesUnit IvapecevsbNo ratings yet
- Antennas and Propagation For Wireless Communication Systems, 2nd EdDocument553 pagesAntennas and Propagation For Wireless Communication Systems, 2nd Edthamtunhi130980% (5)
- Conditional Statements and LoopsDocument4 pagesConditional Statements and LoopsapecevsbNo ratings yet
- Simulink Modeling of Basic Modulation SystemsDocument7 pagesSimulink Modeling of Basic Modulation SystemsapecevsbNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MATLAB, MATLAB Help SystemDocument4 pagesIntroduction To MATLAB, MATLAB Help SystemapecevsbNo ratings yet
- Arrays, Multidimensional Arrays, OperationsDocument10 pagesArrays, Multidimensional Arrays, OperationsapecevsbNo ratings yet
- Generation of Various Signals and SequencesDocument6 pagesGeneration of Various Signals and Sequencesapecevsb0% (1)
- Plotting, Special Plotting: 3D PlottingDocument9 pagesPlotting, Special Plotting: 3D PlottingapecevsbNo ratings yet
- Editing and Debugging MATLAB ProgramsDocument4 pagesEditing and Debugging MATLAB ProgramsapecevsbNo ratings yet
- Matlab FunctionsDocument6 pagesMatlab FunctionsapecevsbNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic and Logical OperatorsDocument4 pagesArithmetic and Logical Operatorsapecevsb100% (1)
- Eight Steps or Principles For SMEDDocument3 pagesEight Steps or Principles For SMEDAlex SalazNo ratings yet
- Sample Apdf User InputDocument21 pagesSample Apdf User InputginjackNo ratings yet
- Mac Shortcut KeysDocument6 pagesMac Shortcut KeysJ. Peter SiriprakornNo ratings yet
- Letter of AuthorizationDocument1 pageLetter of Authorizationjheny farneubunNo ratings yet
- Drill Pipe Flow Chart PDFDocument1 pageDrill Pipe Flow Chart PDFairlinemembershipNo ratings yet
- Report On Modal Analysis of A Hollow CylinderDocument2 pagesReport On Modal Analysis of A Hollow CylinderkbhattacNo ratings yet
- Electrical CommissioningDocument19 pagesElectrical CommissioningLuis EnriqueNo ratings yet
- Python Date TimeDocument6 pagesPython Date TimeNataliaNo ratings yet
- Science Granting Councils Initiative (SGCI) in Sub-Saharan Africa-2019 Regional Meeting-Addis Ababa-EthiopiaDocument23 pagesScience Granting Councils Initiative (SGCI) in Sub-Saharan Africa-2019 Regional Meeting-Addis Ababa-EthiopiaSempiri Geoffery KasiwukiraNo ratings yet
- Catalogue Loc Camfil 2010-ResizeDocument159 pagesCatalogue Loc Camfil 2010-ResizeThanh Xuan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Automated BoreWelders make bore welding easierDocument1 pageAutomated BoreWelders make bore welding easierGeovanny SanjuanNo ratings yet
- A Framework For 21st Century Teaching and LearningDocument6 pagesA Framework For 21st Century Teaching and LearningFiorello Abenes100% (1)
- 8085 Microprocessor Trainer GuideDocument73 pages8085 Microprocessor Trainer GuideKuldeep Saini0% (1)
- Belmont Rapid Infuser Ri 2 Operation ManualDocument55 pagesBelmont Rapid Infuser Ri 2 Operation ManualColleen WalkerNo ratings yet
- Flutter Introduction and Dummy App WorkshopDocument27 pagesFlutter Introduction and Dummy App WorkshopubdNo ratings yet
- Owner's Manual: Öhlins Shock Absorber TPX/TTX44 AutomotiveDocument13 pagesOwner's Manual: Öhlins Shock Absorber TPX/TTX44 AutomotiveMauricio Xavier OjedaNo ratings yet
- ICR Composite Structural PresentationDocument20 pagesICR Composite Structural PresentationAmel RADJEFNo ratings yet
- Nptel SafetyDocument3 pagesNptel SafetySindhu ShijuNo ratings yet
- 802 11ah Overview Comm Soc r1Document15 pages802 11ah Overview Comm Soc r1l386543No ratings yet
- CWCT Curtain Wall Installation HandbookDocument34 pagesCWCT Curtain Wall Installation HandbookmoudshahineNo ratings yet
- Hawker perfect plus PzB-element technical data sheetDocument6 pagesHawker perfect plus PzB-element technical data sheetcrash2804No ratings yet
- Controls: Instruction ManualDocument16 pagesControls: Instruction ManualOG100% (1)
- Device Integration Cisco WLCDocument6 pagesDevice Integration Cisco WLCSpyman_pcNo ratings yet
- El Lector 1981 01 No 069Document50 pagesEl Lector 1981 01 No 069stzmakersNo ratings yet
- Pay at Your Bank Pay Online: Payment ReferenceDocument1 pagePay at Your Bank Pay Online: Payment ReferencesimplyrajuNo ratings yet
- (Riccardo Viale, Fondazione Rosselli) The Capitali (B-Ok - CC) PDFDocument364 pages(Riccardo Viale, Fondazione Rosselli) The Capitali (B-Ok - CC) PDFmarceloamaralNo ratings yet
- EIT062 Software TestingDocument190 pagesEIT062 Software TestingMayank SharmaNo ratings yet
- Oracle® Inventory: Consigned Inventory From Supplier Process Guide Release 12.1Document76 pagesOracle® Inventory: Consigned Inventory From Supplier Process Guide Release 12.1Guillermo ToddNo ratings yet
- ST 3000 Smart Transmitter Series 100 Remote Diaphragm Seals Models Specifications 34-ST-03-64 March 2013Document44 pagesST 3000 Smart Transmitter Series 100 Remote Diaphragm Seals Models Specifications 34-ST-03-64 March 2013ruzzo2003No ratings yet