Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study
Uploaded by
Cee SanchezCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study
Uploaded by
Cee SanchezCopyright:
Available Formats
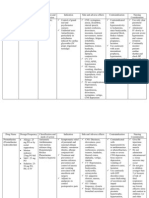
GENERIC NAME Levofloxac in 500mg/tab BID
BRAND NAME Levaqui n
CLASSIFICATI ON >Function classification: Antiinfective >Chemical classification: Fluoroquinolone
USES
ACTION
SIDE EFFECTS
CONTRAINDICATIO NS Hypersensitivity to quinolones, photosensitivity
>Acute sinusitis, acute chronic bronchitis, community acquired pneumonia, uncomplicate d skin infections, complicated UTI, cellulitis, PID, prostatitis, inhalational anthrax (postexposur e), acute pyelonephriti s, inhalation anthrax in children.
Interferes with conversion of intermediate DNA in bacteria; DNA gyrase inhibitor; inhibits topoisomera se IV.
CNS: headache, dizziness, insomnia, anxiety, seizures, encephalopathy, paresthesia CV: chest pain, palpitations, vasodilation, QT prolongation EENT: dry mouth, visual impairment GI: nausea, flatulence, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, pseudomembrano us colitis, hepatotoxicity GU: vaginitis, crystalluria HEMA: eosonophilia,
NURSING CONSIDERATIO NS Assess: >For previous sensitivity reaction Perform: Increase fluid intake to 2L/day to prevent crystalluria >For PO or IV dosing, reduce dose with impaired renal function. >Oral doses are given at least 2 hr before or 2 hr after antacids containing Mg or Al, as well as sucralfate, iron products, multivitamin preparations containing zinc, and didanosine (chewable/buffer ed tablets or pediatric powder for PO solution). >Store tablets in a
hemolytic anemia, lymphopenia INTEG: rash, pruritis, photosensitivity, epidermal necrosis MISC: hypoglycemia, hypersensitivity, tendinitis, tendon rupture RESP: pneumonitis SYST: anaphylaxis, multisystem organ failure
tight container at 15-30C.
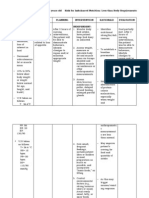
GENERIC NAME Clonidine 75 mcg SL now then every 15 min. x 3 doses
BRAND NAME Nu-clonidine
CLASSIFICATION Function classification: Antihypertensive Chemical classification: Central adrenergic agonist
USES Mild to moderate hypertension, used alone or in combination; severe pain in cancer patients (epidural)
ACTION Inhibits sympathetic vasomotor center in CNS, which reduces impulses in sympathetic nervous system; blood pressure, pulse rate, cardiac output decrease, prevents pain signal transmission in CNS by adrenergic receptor stimulation of spinal cord.
SIDE EFFECTS CNS: drowsiness, sedation, headache, fatigues, nightmares, insomnia, mental changes, anxiety, depression, hallucination, delirium CV: Orthostatic hypotension, palpitations, CHF, ECG abnormalities EENT: Taste change, parotid pain ENDO: Hyperglycemia GI: Nausea, vomiting, malaise, constipation, dry mouth GU: Impotence, dysuria,
CONTRAINDICATIONS NURSING CONSIDERATIONS Hypersensitivity; Assess: (epidural) bleeding >Renal studies: disorders, protein, BUN, anticoagulants creatinine; increased levels may indicate nephrotic syndrome >Baselines in renal, hepatic studies before therapy begins; potassium levels, although hyperkalemia rare >Renal symptoms: polyuria, oliguria, frequency
nocturia, gynecomastia INTEG: Rash, alopecia, facial pallor, pruritis, hives, edema, burning papules, excoriation (transdermal patches) MISC: Withdrawal symptoms MS: Muscle, joint pain; leg cramps
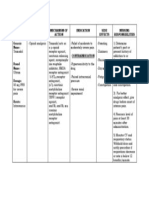
GENERIC NAME
BRAND NAME
CLASSIFICATION
USES
ACTION
SIDE EFFECTS
CONTRAINDICATIONS
NURSING CONSIDERATION S
tranexami c acid
Cyklokapro n
Antifibrinolytic antihemorrhagi c
Tranexamic acid is used to treat heavy menstrual bleeding in women. tranexamic acid may be used by teenage females, but is not recommende d before the start of menstruation .
Tranexamic acid is an antifibrinolyti c agent. It works by blocking the breakdown of blood clots, which prevents bleeding.
Tranexamic acid competitively inhibits activation of plasminogen thereby reducing conversion of plasminogen to plasmin (fibrinolysin), an enzyme that degrades fibrin clots, fibrinogen, and other plasma proteins, including the procoagulant factors V and VIII Tranexamic acid also directly inhibits plasmin activity, but higher doses are required
Anxiety blurred vision change in vision chest pain confusion cough dizziness or lightheaded ness fainting fast heartbeat greatly increased or decreased frequency of urination or amount of urine increased thirst loss of appetite nausea or vomiting numbness of the hands
Except under special circumstances, this medication should not be used when the following medical problem exists: Intravascular clotting, active (risk of serious, even fatal, thrombus formation) Risk-benefit should be considered when the following medical problems exist Defective color vision, acquired (condition precludes assessment of color vision, which may be required to determine toxicity) Hematuria of upper urinary tract origin (risk of intrarenal obstruction secondary to clot retention in the renal pelvis and ureters if hematuria is massive; also, if hematuria is associated with a
Before taking these medicine, ask first the patient if he or she is allergic to it or if he has other allergies
should not be administered concomitantly with Factor IX Complex concentrates or Antiinhibitor Coagulant concentrates, as the risk of thrombosis may be increased. The dose of CYKLOKAPRO N Injection should be reduced in patients with
than are needed to reduce plasmin formation. In vitro , the antifibrinolyti c potency of tranexamic acid is approximatel y 5 to 10 times that of aminocaproic acid In patients with hereditary angioedema, inhibition of the formation and activity of plasmin by tranexamic acid may prevent attacks of angioedema by decreasing plasmininduced activation of
pain, redness, or swelling in the arm or leg sudden shortness of breath or troubled breathing
disease of the renal parenchyma, intravascular precipitation of fibrin may occur and exacerbate the disease) Renal function impairment (medicati on may accumulate; dosage adjustment based on the degree of impairment is recommended) Thrombosis, predisposition to or history of (medication inhibits clot dissolution and may interfere with mechanisms for maintaining blood vessel patency; it is recommended that tranexamic acid be administered in conjunction with anticoagulant therapy, if at all)
renal insufficiency because of the risk of accumulation
the first complement protein
You might also like
- Drugs - Icu (Group)Document7 pagesDrugs - Icu (Group)Patricia LuceroNo ratings yet
- Pedia Ward Drug Study...Document12 pagesPedia Ward Drug Study...Sheena Arnoco ToraynoNo ratings yet
- Basic Life Support QuestionsDocument3 pagesBasic Life Support QuestionsCee Sanchez100% (11)
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug Studysarah1217No ratings yet
- Drug Study DengueDocument3 pagesDrug Study DengueiamELHIZANo ratings yet
- InvoiceDocument1 pageInvoiceKidambi SureshNo ratings yet
- CHN Drug StudyDocument10 pagesCHN Drug StudyJoshua Cyryll ComiaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study HydralazineDocument10 pagesDrug Study HydralazineLuige AvilaNo ratings yet
- HCVD NCPDocument5 pagesHCVD NCPCee Sanchez100% (1)
- HCVD NCPDocument5 pagesHCVD NCPCee Sanchez100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyHannah Philene D. CalubNo ratings yet
- ParacetamolDocument2 pagesParacetamolCee Sanchez92% (48)
- 13 Drug StudyDocument6 pages13 Drug StudyRachel Yvonne Cabacungan100% (1)
- Drug Study JrodDocument8 pagesDrug Study JrodGaez ﭢ UlpindoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study GuideDocument9 pagesDrug Study GuideSh3meeNo ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesPathophysiologyCee SanchezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Plant Physiology!!!!Document112 pagesIntroduction To Plant Physiology!!!!Bio SciencesNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationDocument1 pageName of Drug Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationCee SanchezNo ratings yet
- IVDocument2 pagesIVCee SanchezNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyLarah Mae AndogNo ratings yet
- Basic DWDM Components.Document16 pagesBasic DWDM Components.Pradeep Kumar SahuNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyAnn Therese C. GutierrezNo ratings yet
- WarfarinDocument10 pagesWarfarinMar Ordanza100% (1)
- Drug Study: Francisco Tampos JRDocument37 pagesDrug Study: Francisco Tampos JRCarlmeister Ambray JudillaNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesHypertension Nursing Care PlanCee SanchezNo ratings yet
- NCP 3A Nutritional Imbalance Less ThanDocument3 pagesNCP 3A Nutritional Imbalance Less ThanCee Sanchez100% (3)
- TramadolDocument1 pageTramadolCee Sanchez100% (2)
- Recruitment of Officers in Grade B' (General) - DR - By-2019Document2 pagesRecruitment of Officers in Grade B' (General) - DR - By-2019Shalom NaikNo ratings yet
- NGT Feeding ChecklistDocument4 pagesNGT Feeding ChecklistCee Sanchez100% (6)
- Drug StudiesDocument16 pagesDrug Studiesvitcloud23100% (2)
- Name of Drug Indications Action Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Side Effects Nursing ManagementDocument3 pagesName of Drug Indications Action Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Side Effects Nursing Managementjhappo31No ratings yet
- Drug Study (Mefenamic Acid, Beetab, Esomeprazole Aspirin, Citicoline Plavix)Document6 pagesDrug Study (Mefenamic Acid, Beetab, Esomeprazole Aspirin, Citicoline Plavix)Patricia LuceroNo ratings yet
- Stan Drug StudyDocument10 pagesStan Drug StudyIvan Louise Fajardo ManiquizNo ratings yet
- Case Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDocument12 pagesCase Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDanica May Galvez100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument22 pagesDrug StudyColleen Fretzie Laguardia NavarroNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - LeptospirosisDocument19 pagesDrug Study - LeptospirosisCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudytrinaLCNo ratings yet
- Jam (Drug Study)Document11 pagesJam (Drug Study)Vincent QuitorianoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyGail SantosNo ratings yet
- CefuroximeDocument11 pagesCefuroximeAlmira Ballesteros CestonaNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument5 pagesEmergency DrugsArra PlacidesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ArvinDocument6 pagesDrug Study ArvinArvin BeltranNo ratings yet
- Drug AnalysisDocument3 pagesDrug AnalysisAnn Aquino100% (1)
- Nicardipine (: ClassificationDocument14 pagesNicardipine (: ClassificationWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyMike Faustino SolangonNo ratings yet
- Drug MonographDocument7 pagesDrug Monographekram100% (1)
- Drug Study 1Document4 pagesDrug Study 1bibet_martijaNo ratings yet
- Indications For Ferrous Sulfate: Mechanism of ActionDocument4 pagesIndications For Ferrous Sulfate: Mechanism of ActionErelle John Vasquez EscaraNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic Acid Drug ProfileDocument3 pagesMefenamic Acid Drug ProfileAhmad WaliNo ratings yet
- Drug Analysis: Submitted By: GALICINAO, Gretta Shalou GDocument9 pagesDrug Analysis: Submitted By: GALICINAO, Gretta Shalou GggalicinaoNo ratings yet
- Genericcnamec Dosage G CCC Ñ Ndication Contraindication Adversec Effectc Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesGenericcnamec Dosage G CCC Ñ Ndication Contraindication Adversec Effectc Nursing ResponsibilitiesMark Genesis Sindol GorimoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluationthomasfinley44No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument28 pagesDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyShiara Ruth EdrosoloNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For TetanusDocument10 pagesDrug Study For TetanusMei PayumoNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Ceftriaxone Brand Name: (Kept Rix) IV, 1g, q12Document5 pagesGeneric Name: Ceftriaxone Brand Name: (Kept Rix) IV, 1g, q12De Sesto Rhys CarloNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument70 pagesDrug Studyjahmaicao50% (2)
- Drug FurosemideDocument3 pagesDrug FurosemideJicel Camille EdeaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyMaurence John Feliciano LuluquisenNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyKaloy KamaoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyJann Zaniel Allayne RiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyChickz HunterNo ratings yet
- Drug OrderDocument3 pagesDrug OrderSaima BataloNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument11 pagesDrugsClarence Lyndyll ToldingNo ratings yet
- Cortex Where Spread of SeizureDocument11 pagesCortex Where Spread of SeizureDustin JohnNo ratings yet
- Hemostan, Methergine CA Gluconate2Document4 pagesHemostan, Methergine CA Gluconate2Stacy MC PelitoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Cap RHPDocument7 pagesDrug Study Cap RHPJan DeeNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Indication Contraindication Drug Action Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: Brand Name: Classification: Route and DosageDocument6 pagesDrug Name Indication Contraindication Drug Action Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: Brand Name: Classification: Route and Dosageسبوكاي100% (1)
- Drug Study: OmeprazoleDocument5 pagesDrug Study: Omeprazoleclau_latojaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study QiDocument6 pagesDrug Study QiKevin Sam AguirreNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument13 pagesDrug StudyAldrin Ian Oraza AlpeNo ratings yet
- Activity Intolerance Related To Cognitve DeficitsDocument2 pagesActivity Intolerance Related To Cognitve DeficitsCee SanchezNo ratings yet
- Allen's TestDocument2 pagesAllen's TestCee SanchezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study RICUDocument6 pagesDrug Study RICUCee SanchezNo ratings yet
- Breast Milk Protein May Be Key To Protecting Babies From HIVDocument2 pagesBreast Milk Protein May Be Key To Protecting Babies From HIVCee SanchezNo ratings yet
- Disturbed Sleep Pattern Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesDisturbed Sleep Pattern Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationCee SanchezNo ratings yet
- Problem: Anemia: Name of Patient: L.G.C 68 Years OldDocument2 pagesProblem: Anemia: Name of Patient: L.G.C 68 Years OldCee SanchezNo ratings yet
- CiprofloxacinDocument2 pagesCiprofloxacinCee SanchezNo ratings yet
- Journal DengueDocument3 pagesJournal DengueCee SanchezNo ratings yet
- Thomas' SplintDocument2 pagesThomas' SplintCee SanchezNo ratings yet
- College of HealthDocument28 pagesCollege of HealthCee SanchezNo ratings yet
- Buerger's Raynaud'sDocument1 pageBuerger's Raynaud'sCee SanchezNo ratings yet
- User Guide: Echolife Hg520C Home GatewayDocument25 pagesUser Guide: Echolife Hg520C Home Gatewayluis PavilaNo ratings yet
- Colony Earth - Part X: The Myriad WorldsDocument7 pagesColony Earth - Part X: The Myriad WorldsV. Susan FergusonNo ratings yet
- Contemporary ArtsDocument16 pagesContemporary Artsantoinette100% (2)
- Harvester Main MenuDocument3 pagesHarvester Main MenuWonderboy DickinsonNo ratings yet
- Sari Sari Store in Tabango Leyte The Business Growth and Its Marketing Practices 124 PDF FreeDocument11 pagesSari Sari Store in Tabango Leyte The Business Growth and Its Marketing Practices 124 PDF FreeJim Ashter Laude SalogaolNo ratings yet
- Design Report of STOL Transport AircraftDocument64 pagesDesign Report of STOL Transport Aircrafthassan wastiNo ratings yet
- Robotech Hannibal Digital 114dpi V1.0Document119 pagesRobotech Hannibal Digital 114dpi V1.0nonfarb14thNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 3 Introduction To JqueryDocument88 pagesLecture # 3 Introduction To JqueryDanial AhmadNo ratings yet
- SOLIDWORKS 2022 Whitepaper UsingDesignAutomationtoReduceCostsIncreaseProfitability FinalDocument10 pagesSOLIDWORKS 2022 Whitepaper UsingDesignAutomationtoReduceCostsIncreaseProfitability FinalAlba R.No ratings yet
- Basic Customer Service SkillsDocument90 pagesBasic Customer Service SkillsGillian Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Product Management Software Director in Austin TX Resume Chad ThreetDocument2 pagesProduct Management Software Director in Austin TX Resume Chad ThreetChad ThreetNo ratings yet
- O RTIZDocument2 pagesO RTIZKhimberly Xylem OrtizNo ratings yet
- MAF 451 Suggested Solutions - A) I) Process 1Document9 pagesMAF 451 Suggested Solutions - A) I) Process 1anis izzatiNo ratings yet
- Caribbean Career Opportunity - Cayman Island Water Authority - Plant Operator Cayman Brac Plant Operator (Overseas)Document1 pageCaribbean Career Opportunity - Cayman Island Water Authority - Plant Operator Cayman Brac Plant Operator (Overseas)Cawasa St-LuciaNo ratings yet
- FFL/ A: Tutorial On Reed-Solomon Error Correction CodingDocument144 pagesFFL/ A: Tutorial On Reed-Solomon Error Correction Codingbatman chamkadarNo ratings yet
- Jackson R. Lanning: Profile StatementDocument1 pageJackson R. Lanning: Profile StatementJacksonLanningNo ratings yet
- Beamer Example: Ethan AltDocument13 pagesBeamer Example: Ethan AltManh Hoang VanNo ratings yet
- Request Please Only Students Who Are Willing To Join in Haryana in Any District Are Requested To Apply For JobDocument2 pagesRequest Please Only Students Who Are Willing To Join in Haryana in Any District Are Requested To Apply For JobUdayan KarnatakNo ratings yet
- Lagundi/Dangla (Vitex Negundo)Document2 pagesLagundi/Dangla (Vitex Negundo)Derrick Yson (Mangga Han)No ratings yet
- Vocabulary: ExileDocument5 pagesVocabulary: ExileWael MadyNo ratings yet
- Leading Airline Emirates Boosts Leisure Travel Sales - : Peakwork Case Study: EmiratesDocument3 pagesLeading Airline Emirates Boosts Leisure Travel Sales - : Peakwork Case Study: EmiratesAhmed AbboudNo ratings yet
- Swot Ananlysis of Fintech CompaniesDocument7 pagesSwot Ananlysis of Fintech CompaniesUyen Le VuNo ratings yet
- WestIntroToSSB PDFDocument100 pagesWestIntroToSSB PDFnaval_05No ratings yet
- GSM Rtu Controller Rtu5011 v2 PDFDocument27 pagesGSM Rtu Controller Rtu5011 v2 PDFAbdul GhaniNo ratings yet
- Ventilation WorksheetDocument1 pageVentilation WorksheetIskandar 'muda' AdeNo ratings yet
- Congenital Abnormalities of The Female Reproductive TractDocument14 pagesCongenital Abnormalities of The Female Reproductive TractMary SheshiraNo ratings yet