Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Abducting Muscle Groups
Uploaded by
D'restu PhysioCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Abducting Muscle Groups
Uploaded by
D'restu PhysioCopyright:
Available Formats
Abducting Muscle Groups
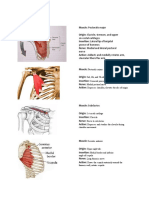
Muscles which Produce Scapular Abduction (Protraction) 1. Serratus Anterior Tendons Origin Insertion Function Nerve Artery : Outer surface of upper 8 or 9 ribs : Costal surface of vertebral border of the Scapula : Abducts scapula at the Scapulothoracic Joint; raises ribs when scapula is fixed : Long Thoracic Nerve : Lateral thoracic artery
2. Pectoralis Major Tendons Origin Insertion Function : Sternal half of the Clavicle, sternum to 7th rib, cartilages of true ribs, aponeurosis of external oblique : Lateral lip of bicipital groove of the Humerus : Adducts arm, extends arm, internal rotation of the shoulder along with other Muscles which produce shoulder Adduction Muscles which produce shoulder Extension Muscles which produce shoulder Internal (medial) Rotation Nerve Artery : dual innervation by the Medial Pectoral Nerve and the Lateral Pectoral Nerve : Pectoral branch of Thoracoacromial artery and the Internal Mammary artery
3. Pectoralis Minor Tendons Origin Insertion Function Nerve Artery : Outer suface and upper margin of 3rd 4th and 5th ribs : Coracoid process of the Scapula : Lowers angle of scapula, pulls shoulder forward at the Scapulothoracic Joint : Medial Pectoral Nerve : Pectoral branch of Thoracoacromial artery and the Lateral thoracic artery
Muscles which Produce Upward Rotation of Scapula 1. Trapezius (middle part) Tendons Origin Insertion Function Nerve Artery : External occipital protuberance, superior nuchal line of skull Nuchal ligament from spines of seventh cervical and all thoracic verebrae : Lateral third of the Clavicle, acromion and spine of the Scapula : Adducts scapula, tilts chin, draws back acromion, rotates scapula at the Scapulothoracic Joint : Spinal Accessory Nerve : Descending scapular artery
2. Serratus Anterior
Muscles which Produce Shoulder Abduction 1. Deltoid Tendons Origin Insertion Function Nerve Artery : Lateral third of the Clavicle, the upper surface of the acromion, and the spine of the Scapula : Deltoid tuberosity of the Humerus : Abducts the shoulder along with other Muscles which produce shoulder Abduction : Circumflex anterior and posterior brances of the Axillary Nerve : Posterior humeral circumflex artery Deltoid branch of Thoracoacromial artery 2. Supraspinatus Tendons Origin Insertion Function : Supraspinous fossa of the Scapula : Superior facet of greater tuberosity of the Humerus and the Glenohumeral Joint : Assists the deltoid in abducting the arm, fixes the head of the humerus in the glenoid fossa, and external rotation of the shoulder along with other Muscles
which produce shoulder Abduction and Muscles which produce shoulder External (lateral) Rotation Nerve Artery : Suprascapular Nerve : Suprascapular (transverse cervical) artery
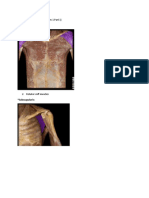
Muscles which Produce Wrist Radial Deviation 1. Abductor Pollicis Longus Tendons Origin : Posterior surface of the Ulna, the radioulnar interosseous membrane and the middle third of posterior surface of the Radius : Radial dorsal base of the Thumb Metacarpal, Variably the dorsal Trapezium and the radial surface of the Abductor pollicis longus muscle : Abducts the thumb basal joint, along with other muscles which radially abduct the thumb. Also radially deviates the wrist along with other mucles which produce wrist radial abduction : Posterior Interosseous Nerve : Posterior Interosseous artery
Insertion
Function
Nerve Artery
2. Flexor Carpi Radialis Tendons Origin : common forearm flexor origin from the medial epicondyle of the Humerus and the deep forearm fascia : Volar base of the Index Metacarpal and the Middle Metacarpal : flexion and radial deviation of the wrist, along with other muscles which flex the wrist and radially deviate the wrist, weak pronation of the forearm along with other muscles which pronate the forearm and weak flexion of the elbow along with other muscles which flex the elbow : Median Nerve : Muscular Branches of Radial Artery
Insertion Function
Nerve Artery
3. Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus Tendons Origin : Lower 1/3 of lateral supracondylar ridge of the Distal humerus and the lateral intermuscular septum : Dorsal base of the Index Metacarpal : Extends, radially deviates the Wrist : Radial : Muscular Branches of Radial Artery and the Radial Recurrent artery
Insertion Function Nerve Artery
4. Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis Tendons Origin : Common extensor tendon of the lateral epicondyle the radial collateral ligament of the elbow and the deep forearm fascia : Dorsal base of the Middle Metacarpal : Extends and radially deviates the Wrist. Weak elbow flexor. : Posterior Interosseous Nerve : Muscular Branches of Radial Artery Radial Recurrent artery
Insertion Function Nerve Artery
Muscles which Radial Abduct the Basal Joint 1. Abductor Pollicis Longus Tendons Origin : Posterior surface of the Ulna, the radioulnar interosseous membrane and the middle third of posterior surface of the Radius
Insertion : Radial dorsal base of the Thumb Metacarpal, Variably the dorsal Trapezium and the radial surface of the Abductor pollicis longus muscle
Function : Abducts the thumb basal joint, along with other muscles which radially abduct the thumb. Also radially deviates the wrist along with other mucles which produce wrist radial abduction Nerve Artery : Posterior Interosseous Nerve : Posterior Interosseous artery
2. Extensor Pollicis Brevis Tendons Origin Insertion Function : Posterior surface of the Radius and the radioulnar interosseous membrane : Dorsal base of the thumb proximal phalanx : Extends the thumb MCP joint and weakly abducts the thumb basal joint, along with other muscles which produce radial and palmar abduction : Posterior interosseous : Posterior interosseous
Nerve Artery
3. Opponens Pollicis Tendons Origin Insertion Function : transverse carpal ligament and the Trapezium : Volar radial aspect of the Thumb Metacarpal : flexes and pronates the basal joint along with other muscles which produce thumb opposition : Motor Branch of the Median Nerve : Superficial Volar Branch of Radial artery
Nerve Artery
You might also like
- Oina SummaryDocument37 pagesOina SummaryC1 - RAZALAN NICKA JOYNo ratings yet
- Discussion Topics IA1 AnatDocument9 pagesDiscussion Topics IA1 AnatPhysics TutionNo ratings yet
- Thumb Home Page: Anatomi JariDocument31 pagesThumb Home Page: Anatomi JaridesichNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb Anatomy Quiz: Questions AnswersDocument5 pagesUpper Limb Anatomy Quiz: Questions Answersapi-246259817No ratings yet
- Shoulder Anatomy SummaryDocument4 pagesShoulder Anatomy Summaryapi-246259817No ratings yet
- Summary Topographic Anatomy, Extras and Muscles To 1 Proof!!Document10 pagesSummary Topographic Anatomy, Extras and Muscles To 1 Proof!!Geovanna FernandesNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY: The Shoulder Girdle Shoulder Spaces Axilla The ArmDocument88 pagesANATOMY: The Shoulder Girdle Shoulder Spaces Axilla The ArmNur Liyana MohamadNo ratings yet
- Gross Anatomy of The Forearm: A CAL Package Designed By-Pratik SinhaDocument24 pagesGross Anatomy of The Forearm: A CAL Package Designed By-Pratik SinhaManvi JogiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Muscles of Upper LimbDocument61 pagesChapter 6 - Muscles of Upper LimbMahendran Jayaraman100% (1)
- MBBS MSK YR1 Muscles of Upper LimbDocument52 pagesMBBS MSK YR1 Muscles of Upper Limbcharlesy TNo ratings yet
- COMLEX OMM Shelf ReviewDocument373 pagesCOMLEX OMM Shelf ReviewJohn Doe60% (5)
- The Upper Extremity: Arm Muscles, Axilla, Brachial PlexusDocument37 pagesThe Upper Extremity: Arm Muscles, Axilla, Brachial Plexusbarang hajaNo ratings yet
- Muscles of Upper LimbsDocument6 pagesMuscles of Upper LimbsplanarshiftsNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb Anatomy TablesDocument8 pagesLower Limb Anatomy Tableskep1313No ratings yet
- 007superficial Back and Scapular & Deltoid RegionsDocument38 pages007superficial Back and Scapular & Deltoid RegionsEtsubNo ratings yet
- 10th Lec Muscles Posterior of ForearmDocument16 pages10th Lec Muscles Posterior of ForearmMudasir razaNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb Terms To KnowDocument7 pagesUpper Limb Terms To KnowKitziaColliardNo ratings yet
- The Upper Extremity: Arm Muscles, Axilla, Brachial PlexusDocument37 pagesThe Upper Extremity: Arm Muscles, Axilla, Brachial PlexusMicahMananguitNo ratings yet
- Muscle Origin/Insertion/Action/Innervation Chart Muscles of Upper Extremity Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action InnervationDocument9 pagesMuscle Origin/Insertion/Action/Innervation Chart Muscles of Upper Extremity Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action InnervationNurul Afiqah Fattin Amat100% (1)
- Posterior Compart. ForearmDocument12 pagesPosterior Compart. ForearmSyed NangyalNo ratings yet
- Tahilan Coaching Anatomy of The Elbow, Wrist and HandDocument63 pagesTahilan Coaching Anatomy of The Elbow, Wrist and HandJoymeeNo ratings yet
- (Ebook PDF) Pocket Atlas of Sectional Anatomy, Volume 3: Spine, Extremities, Joints: Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging 2Nd EditionDocument42 pages(Ebook PDF) Pocket Atlas of Sectional Anatomy, Volume 3: Spine, Extremities, Joints: Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging 2Nd Editiontim.garcia450100% (34)
- Anatomy Trans UPPER EXTREMITIESDocument9 pagesAnatomy Trans UPPER EXTREMITIESSan LapuhapuNo ratings yet
- 0608 Arm-1Document48 pages0608 Arm-1Jaeho LeeNo ratings yet
- Flexor Region of The ForearmDocument13 pagesFlexor Region of The ForearmNeil DolendoNo ratings yet
- Notes Jun 30, 2014 Anatomy Part 1Document37 pagesNotes Jun 30, 2014 Anatomy Part 1Diwakesh C BNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Nerves of UL 2022Document45 pagesAnatomy Nerves of UL 2022Malak AhmedNo ratings yet
- Posterior Aspect of The ForearmDocument17 pagesPosterior Aspect of The ForearmGuillaumeBanvilleNo ratings yet
- 2 Anatomy of The Shoulder Girdle OLUWADIYADocument39 pages2 Anatomy of The Shoulder Girdle OLUWADIYAADELAJA SAMUELNo ratings yet
- Cat Muscles and O.I.A.: Body Region Muscle Origin Insertion ActionDocument5 pagesCat Muscles and O.I.A.: Body Region Muscle Origin Insertion ActioneumarasiganNo ratings yet
- Muscle Upper LimbsDocument65 pagesMuscle Upper LimbsTom WuNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb FullDocument70 pagesUpper Limb FullSatrumin ShirimaNo ratings yet
- Cervical, Brachial PlexusDocument31 pagesCervical, Brachial PlexusSophy AhdyNo ratings yet
- Chick List 7 (Items For Lab Exam 1 Part 1) 1. Deltoid: SubscapularisDocument40 pagesChick List 7 (Items For Lab Exam 1 Part 1) 1. Deltoid: SubscapularisFranklinSappNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb Lecture 1Document45 pagesUpper Limb Lecture 1KhurshidbuyamayumNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb Lecture 1Document45 pagesUpper Limb Lecture 1fdjkvfjvNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb Lecture 1Document45 pagesUpper Limb Lecture 1RAHMADANI SAFITRINo ratings yet
- Front of ArmDocument23 pagesFront of ArmNicoleta PSNo ratings yet
- Arm - Anatomy - LecturioDocument17 pagesArm - Anatomy - LecturioElenaNo ratings yet
- Front of ForearmDocument19 pagesFront of ForearmAditya AnandNo ratings yet
- LG 8Document56 pagesLG 8Joo Se HyukNo ratings yet
- Elbow and Antebrachium NotesDocument8 pagesElbow and Antebrachium NoteschadNo ratings yet
- Muscles That Originate OnDocument7 pagesMuscles That Originate OnJoey TingNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lecture 5 Brachial PlexusDocument66 pagesAnatomy Lecture 5 Brachial PlexusSathvika ChallarapuNo ratings yet
- Revison For Upper LimbDocument55 pagesRevison For Upper LimbbEdo 0No ratings yet
- MHS1101 LECTURE 7 UPPER LIMB 2 - in Class VersionDocument52 pagesMHS1101 LECTURE 7 UPPER LIMB 2 - in Class VersionFlorence ManirambonaNo ratings yet
- Muscle of Upper LimbsDocument5 pagesMuscle of Upper LimbsFong Yu-heng100% (1)
- Origins and InsertionsDocument12 pagesOrigins and Insertionsking54591No ratings yet
- BRACHIAL PLEXUS (Autosaved)Document51 pagesBRACHIAL PLEXUS (Autosaved)Coy EnNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The BodyDocument86 pagesMuscles of The BodyFadhli Quzwain100% (2)
- Handount Limbs CompleteDocument67 pagesHandount Limbs CompletebigprogrammeramNo ratings yet
- Clinical Anat Upper and Lower LimbDocument36 pagesClinical Anat Upper and Lower Limbtri_purnamasari_1No ratings yet
- The Back of The Thigh & Popliteal Fossa-Tutorial PDFDocument17 pagesThe Back of The Thigh & Popliteal Fossa-Tutorial PDFChipego ChiyaamaNo ratings yet
- Rotator CuffDocument3 pagesRotator Cuffabiolad82No ratings yet
- Oral Anatomy: Upper LimbDocument3 pagesOral Anatomy: Upper LimbxcvdxNo ratings yet
- Chest Cavity, Vertebral Column and Back Muscles. Respiratory MusclesDocument35 pagesChest Cavity, Vertebral Column and Back Muscles. Respiratory MusclesOr100% (2)
- MSK IV: Upper Limb and Shoulder: Brachial PlexusDocument7 pagesMSK IV: Upper Limb and Shoulder: Brachial PlexusKevin Yixi RenNo ratings yet
- Forearm PostengDocument20 pagesForearm Postengaliqazal26No ratings yet
- Arm and Back - TabulatedDocument5 pagesArm and Back - TabulatedandiedeeNo ratings yet
- Muscle Grading and Testing Procedures 508 PDFDocument5 pagesMuscle Grading and Testing Procedures 508 PDFNanda Gusmaw BarcellioNo ratings yet
- Physiotherapy in Elderly People & Evidence Base PracticeDocument26 pagesPhysiotherapy in Elderly People & Evidence Base PracticeD'restu PhysioNo ratings yet
- Shoulder InstabilityDocument54 pagesShoulder InstabilityD'restu Physio100% (2)
- KlasifikasiDocument1 pageKlasifikasiD'restu PhysioNo ratings yet
- HydrotherapyDocument23 pagesHydrotherapy7e9oo9100% (1)
- 10 PP IllustratedDocument2 pages10 PP IllustratedD'restu PhysioNo ratings yet
- Rotator Cuff and Shoulder Conditioning ProgramDocument11 pagesRotator Cuff and Shoulder Conditioning ProgramD'restu PhysioNo ratings yet
- Natures Hidden Health MiracleDocument38 pagesNatures Hidden Health MiracleGorneau100% (2)
- Movement DisordersDocument10 pagesMovement DisordersAli 10No ratings yet
- Dna Replication, Translation, and TranscriptionDocument43 pagesDna Replication, Translation, and TranscriptionMaria VisitacionNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Molecular Biology and GeneticsDocument146 pagesIntroduction To Molecular Biology and GeneticsRedaGaafar100% (1)
- The Structure and Function of Proteins Chapter 5 (Continued)Document27 pagesThe Structure and Function of Proteins Chapter 5 (Continued)Rabi MehrNo ratings yet
- PathologyDocument36 pagesPathologySayeed KhanNo ratings yet
- Carbon Cycle PDFDocument9 pagesCarbon Cycle PDFheyitsmemuahNo ratings yet
- Anatomia de BufalosDocument24 pagesAnatomia de BufalosTrilce ClaroNo ratings yet
- Patient Monitoring and Telemetry Supplies ENGDocument154 pagesPatient Monitoring and Telemetry Supplies ENGĐức Đặng VũNo ratings yet
- The Inorganic Side of Chemical Biology: CommentaryDocument4 pagesThe Inorganic Side of Chemical Biology: CommentarySilloAntonioNo ratings yet
- Zinc and Immune Function PDFDocument17 pagesZinc and Immune Function PDF300r100% (1)
- Cortical Dipole and Clinical SignificanceDocument15 pagesCortical Dipole and Clinical SignificanceManamitaNo ratings yet
- Heat Stress in PlantsDocument22 pagesHeat Stress in PlantsPao GabrielNo ratings yet
- ALLOSTERISMDocument30 pagesALLOSTERISMFlora D Souza100% (1)
- The Whole Is Greater Than The Sum of Its PartsDocument12 pagesThe Whole Is Greater Than The Sum of Its PartsMabelPinesNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue Culture: Ms. Veena ShriramDocument38 pagesAnimal Tissue Culture: Ms. Veena Shriramw5waNo ratings yet
- It All Began With A Love BiteDocument17 pagesIt All Began With A Love Biteapi-262208234No ratings yet
- Cyanotic Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument58 pagesCyanotic Congenital Heart Diseasegolden37No ratings yet
- Easy EKGDocument45 pagesEasy EKGnov14No ratings yet
- Introduction To TheCourseDocument21 pagesIntroduction To TheCourseCharles SainzNo ratings yet
- The Welfare of Cattle Kept For Beef ProductionDocument150 pagesThe Welfare of Cattle Kept For Beef ProductionIsabel CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Lab 06 Classification and Dichotomous KeysDocument11 pagesLab 06 Classification and Dichotomous Keys13ucciNo ratings yet
- Midas VeniceDocument46 pagesMidas Venicemirescualin100% (1)
- Chakras Book FromDocument22 pagesChakras Book FromLindsey SpencerNo ratings yet
- Bio 130 Chapter 4 NotesDocument12 pagesBio 130 Chapter 4 Notesgilissa100% (1)
- Test Bank CardioDocument16 pagesTest Bank CardioLudwigJayBarayuga86% (7)
- Anatomy and Physiology: Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Circulatory SystemJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Equivalency ExaminationDocument26 pagesForeign Pharmacy Graduate Equivalency Examinationnewfakeemail100% (2)
- Centruroides Sculpturatus (Buthidae) and Diplocentrus Spitzeri (Diplocentridae) - J - ArachnolDocument12 pagesCentruroides Sculpturatus (Buthidae) and Diplocentrus Spitzeri (Diplocentridae) - J - ArachnoladriendrixNo ratings yet
- GENITOURINARYDocument24 pagesGENITOURINARYrlinaoNo ratings yet