Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ConceptMap (AML)
Uploaded by
CassandraOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ConceptMap (AML)
Uploaded by
CassandraCopyright:
Available Formats
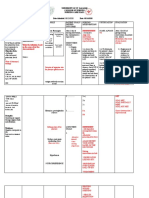
Rest and Activity
Diagnostic Tests: Interventions:
1. Adequate
• rest periods
Bone marrow Interventions:
1. Identify platelet counts. 1. Inspect buccal region/throat
2. PT w/ walker
examination for swelling and lesions daily.
2. Monitor VS Q4h and as needed.
3. Exercises for strengthening 2. Culture any oral lesions.
(Provides information 3. Avoid use of rectal
4. ROM thermometer/digital exam. 3. Assist with mouth care and
5. Callabout cells within
for assistance to getthe
up 4. Test all secretions and oral rinses.
marrow, the type of 4. Encourage soft bristle
erythropoieses, and the excretions.
toothbrush.
maturity of
5. Administer meds as ordered to
Goal # 1:
Labs: Pt will be free
CBC w/diff of signs and Goal #2:
Platelets. Labs / symptoms of Pt is free
bleeding.
Electrolytes Diagnosti from oral
Serum iron NSG Dx 2: inflammatio
cs Impaired oral n, oral
Total protein
Albumin NSG Dx 1: mucous bleeding,
Prealbumin Ineffective membranes and
protection R/T secondary to
reduced anemia and
Diet / Supplements: platelet count
Foods with low potential to reduced
cause nausea and vomiting (dry and risk for platelets. Goal # 3:
toast, crackers, ginger ale, cola, Pt states
popsicles, gelatin, baked or return of
boiled potatoes, and fresh or near-normal
canned fruit.) Serve meat in the activity
morning. Small frequent levels, and
nutritious meals.
achieves
tolerance of
Client’s Data: Interventions:
Dietary NSG Dx 3: 1. Assess
Considerati Fatigue specific
Medication
ons:
Consistent
Acute related to
anemia. 2.
cause of
fatigue.
Monitor
s: weighing is Hgb, Hct,
important to and RBC
Arsenic trioxide
levels.
(Trisenox) and ensure
all-trans
retinoic acid
accuracy in Myelocytic 3. Assess
current
activity
(ATRA) are level.
anti-cancer 4. Stress
drugs that can importance
be used alone
or in
combination
Leukemia NSG Dx 5.
of rest
periods.
Instruct
with 4:
chemotherapy Risk for
for remission Goal #
Medical infection
induction of a Risk 4:
certain subtype
Treatmen R/T
Pt has
of AML called t for Factors altered
reduced
promyelocytic Disease of WBC
risk of
leukemia. infection
These drugs
as
Common Increasing age
Interventions:
Treatments for 1. Monitor WBC
Disease Process: Sex (M or F) w/differential.
2. Assess for local or
Chemotherapy & systemic signs of
Previous cancer infection such as
Radiation
treatment fever, chills, malaise,
Single agent or combo swelling, and pain.
chemo is the treatment of 3. If pt is hospitalized
choice for most types of Exposure to put in private room
leukemia, with the goal of radiation and have pt on
eradicating leukemic cells reverse isolation.
4. Instruct pt to avoid
Dangerous contact with persons
chemical exposure have a cold or
infections.
You might also like
- Medical Medium Revised and Expanded Offers Immune Support and New RecipesDocument1 pageMedical Medium Revised and Expanded Offers Immune Support and New RecipesJordan Moyer0% (3)
- Maternal Newborn PDFDocument83 pagesMaternal Newborn PDFIya Katz33% (3)
- Teaching Plan Using "METHOD"Document6 pagesTeaching Plan Using "METHOD"Cassandra73% (11)
- STUDENT-Sickle - Cell-FUNDAMENTAL ReasoningDocument7 pagesSTUDENT-Sickle - Cell-FUNDAMENTAL ReasoningSharon Tanveer0% (1)
- System Do CopdDocument1 pageSystem Do CopdMarissa HambyNo ratings yet
- STI Chart (Maternity-Nursing)Document4 pagesSTI Chart (Maternity-Nursing)brittney bradyNo ratings yet
- ATI Acute ProctoredDocument6 pagesATI Acute Proctoredyoderjess425No ratings yet
- HA-RLE-WS # 10 Assessing Nutritional StatusDocument4 pagesHA-RLE-WS # 10 Assessing Nutritional StatusJULIE ANNE CORTEZNo ratings yet
- OB Meds WorksheetDocument18 pagesOB Meds WorksheetrickyandsheenaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of StrokeAqeel Al-Mahdaly0% (1)
- Learning Objective Content Teaching Strategy Time Alloted EvaluationDocument3 pagesLearning Objective Content Teaching Strategy Time Alloted EvaluationAmera DimatingcalNo ratings yet
- Acute PainDocument1 pageAcute Painnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Concept Map HypertensionDocument1 pageConcept Map Hypertensiongeorge pearson0% (1)
- Nursing Care for Chronic ConditionsDocument37 pagesNursing Care for Chronic ConditionsGracielaDaffodilYgay100% (1)
- Patho Physiology Bible: Over 70 Concept MapsDocument139 pagesPatho Physiology Bible: Over 70 Concept Mapslauramphs79100% (5)
- Medication Calculation - Commonly Used FormulasDocument1 pageMedication Calculation - Commonly Used FormulasAaron AntonioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Pharmacology Inflammation Study GuideDocument11 pagesNursing Pharmacology Inflammation Study GuideChelsea Smith100% (1)
- Pediatric Concept MapDocument12 pagesPediatric Concept Mapapi-352157080No ratings yet
- Herpes-Zoster Concept MapDocument5 pagesHerpes-Zoster Concept MapElleNo ratings yet
- Head to-Toe-Assessment Complete Guide - Nightingale CollegeDocument1 pageHead to-Toe-Assessment Complete Guide - Nightingale CollegeDabon RusselNo ratings yet
- Med Surg Week 6Document11 pagesMed Surg Week 6Eunice Cortés100% (1)
- Pku 3 Concept MapDocument3 pagesPku 3 Concept Mapnursing concept maps100% (1)
- ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATE: System DisorderDocument1 pageACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATE: System DisorderDeo FactuarNo ratings yet
- Template For NURSING NotesDocument2 pagesTemplate For NURSING Notesbngraham4No ratings yet
- Completed Concept MapDocument4 pagesCompleted Concept Mapapi-607361848No ratings yet
- PDF Ati Proctored Assessment DDDocument1 pagePDF Ati Proctored Assessment DDqwivy.com0% (2)
- Exam 1 Study Guide Summary Advanced Health AssessmentDocument27 pagesExam 1 Study Guide Summary Advanced Health AssessmentRhoda Mae Cubilla100% (1)
- Waiters Osteoarthritis PDFDocument1 pageWaiters Osteoarthritis PDFmp1757No ratings yet
- Mnemonics PDFDocument15 pagesMnemonics PDFbeingfiredNo ratings yet
- UTI Patient Concept Map Nursing Diagnosis Interventions OutcomesDocument1 pageUTI Patient Concept Map Nursing Diagnosis Interventions OutcomesDon Rieza100% (1)
- Concept MapDocument5 pagesConcept Mapapi-546509005No ratings yet
- COPD Concept MapDocument1 pageCOPD Concept MapSherree HayesNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaSystem DisorderDocument1 pagePneumoniaSystem DisorderAA DDNo ratings yet
- Pediatric CAP GuidelineDocument1 pagePediatric CAP GuidelineJohn Vincent Dy OcampoNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Nursing CareDocument78 pagesNervous System Nursing CareLouie ParillaNo ratings yet
- PN NCLEX PRACTICE TESTDocument75 pagesPN NCLEX PRACTICE TESTjedisay1100% (1)
- Pharm 1.11 Insulin Cheat SheetDocument1 pagePharm 1.11 Insulin Cheat SheetSanobar Charania100% (1)
- Medical Surgical: Nervous SystemDocument90 pagesMedical Surgical: Nervous SystemCatherine G. Borras100% (1)
- Head To Toe AssessmentDocument2 pagesHead To Toe Assessmentisapatrick8126No ratings yet
- BSN Concept MappingDocument36 pagesBSN Concept MappingMae Layug100% (1)
- ECG Interpretation: Learning The Basics: Presented byDocument65 pagesECG Interpretation: Learning The Basics: Presented bySherry DoddsNo ratings yet
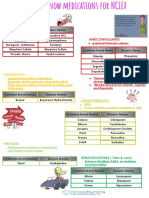
- 19-1 Need to know medications for NCLEXDocument8 pages19-1 Need to know medications for NCLEXGina Giammalvo100% (1)
- Hypertension Drugs and Pathophysiology ReviewDocument9 pagesHypertension Drugs and Pathophysiology ReviewChelsea SmithNo ratings yet
- COPD Care PLAN PDFDocument2 pagesCOPD Care PLAN PDFVanessaMUeller100% (1)
- POC and Concepts Maps Week 12Document23 pagesPOC and Concepts Maps Week 12Michelle CollinsNo ratings yet
- Clinical Concept MapDocument5 pagesClinical Concept MapMj FernandezNo ratings yet
- NUR129 Endocrine Concept Mapping InstructorDocument8 pagesNUR129 Endocrine Concept Mapping InstructorAmber EssmanNo ratings yet
- Concept Map TemplateDocument16 pagesConcept Map Templatenursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- NCLEX FundamentalsDocument13 pagesNCLEX FundamentalsSara Pirman100% (1)
- Basic Drug Cards 1Document13 pagesBasic Drug Cards 1Sara Sabra100% (1)
- Concept Map 2Document1 pageConcept Map 2lanrevoiceNo ratings yet
- Med Surg CardsDocument54 pagesMed Surg CardsIanne Merh100% (3)
- Sbar 2Document2 pagesSbar 2Nurse Betty100% (3)
- Medical Surgical ATI Review Flashcards - QuizletDocument27 pagesMedical Surgical ATI Review Flashcards - QuizletNursyNurseNo ratings yet
- Renal Concept MapDocument1 pageRenal Concept MapShaira Ann CalambaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric MedicationsDocument25 pagesPediatric MedicationsGloryJaneNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology For Nursing. Richard A. LehneDocument62 pagesPharmacology For Nursing. Richard A. LehneJC Ortiz-Carrillo50% (2)
- Complete Head-to-Toe Physical Assessment Cheat SheetDocument7 pagesComplete Head-to-Toe Physical Assessment Cheat SheetA C100% (1)
- Community Focused Nursing: Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandCommunity Focused Nursing: Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- ConceptMap AMLDocument1 pageConceptMap AMLnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- PATIENT CARE PLAN FOR DIARRHEADocument2 pagesPATIENT CARE PLAN FOR DIARRHEATimi Terpstra67% (3)
- Related To Vomiting As Evidence by Muscle Weakness and FatigueDocument3 pagesRelated To Vomiting As Evidence by Muscle Weakness and FatiguejuiceNo ratings yet
- Specific nursing interventions for Pernicious AnemiaDocument7 pagesSpecific nursing interventions for Pernicious AnemiaLeni YulisNo ratings yet
- Immunizations Teaching PlanDocument2 pagesImmunizations Teaching PlanCassandraNo ratings yet
- Teaching Plan Pain Management HandoutDocument1 pageTeaching Plan Pain Management HandoutCassandraNo ratings yet
- M E T H O D TEACHING PLAN Student: - Cassie WilliamsDocument4 pagesM E T H O D TEACHING PLAN Student: - Cassie WilliamsCassandra100% (1)
- Curs Prim Ajutor 2023 - MG An V - Șocul Hemoragic - English-1Document18 pagesCurs Prim Ajutor 2023 - MG An V - Șocul Hemoragic - English-1hulia jokoNo ratings yet
- CBU 5th Year Exam Paper 1 2017Document13 pagesCBU 5th Year Exam Paper 1 2017Homeground entertainment100% (3)
- Preeclampsia With HELLP SyndromeDocument8 pagesPreeclampsia With HELLP SyndromeWely Tiffani YpNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Acute Periodontal LesionsDocument14 pagesDiagnosis of Acute Periodontal Lesionsczarisse escalonaNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma: by Tekia BuntynDocument18 pagesGlaucoma: by Tekia BuntynTekia BuntynNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - LevothyroxineDocument1 pageDrug Study - LevothyroxineCarla Tongson Maravilla100% (1)
- Clinico-Etiological Spectrum of Pancytopenia in Hospitalized ChildrenDocument4 pagesClinico-Etiological Spectrum of Pancytopenia in Hospitalized ChildrenNurul Huda KowitaNo ratings yet
- Locally Endemic Diseases ControlhandoutDocument3 pagesLocally Endemic Diseases ControlhandoutEshiebel OrganistaNo ratings yet
- Salmonella in The CaribbeanDocument3 pagesSalmonella in The CaribbeanAlvin KiruiNo ratings yet
- BREESIDocument1 pageBREESIJulie MorenoNo ratings yet
- فندمنتل وظيفة رقم 2Document2 pagesفندمنتل وظيفة رقم 2Dental LecturesMMQNo ratings yet
- Screening Script and Procedure For Reception and SchedulingDocument3 pagesScreening Script and Procedure For Reception and SchedulingJobert NarvaezNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure BrochureDocument2 pagesHeart Failure Brochureapi-251155476No ratings yet
- Patient-Nurse DialogueDocument3 pagesPatient-Nurse Dialogueristy dian puspitaNo ratings yet
- DSM-5 and Neurocognitive DisordersDocument6 pagesDSM-5 and Neurocognitive DisordersluishelNo ratings yet
- Stool CultureDocument4 pagesStool CultureIzkandar RitzzneyNo ratings yet
- Cvspa01 Hypertension and AthrosclerosisDocument8 pagesCvspa01 Hypertension and AthrosclerosisRobert So JrNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics - Allergy & Immunology TopicsDocument40 pagesPediatrics - Allergy & Immunology TopicspreethamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 - Keith Conners PioneersDocument4 pagesChapter 20 - Keith Conners PioneersMaro KaNo ratings yet
- HSS International PDI Form - February 2023Document2 pagesHSS International PDI Form - February 2023wyzxy2793No ratings yet
- Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) Sample RequirementsDocument7 pagesCerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) Sample RequirementsDr.Nouf alhasawiNo ratings yet
- Herpes Zoster OticusDocument12 pagesHerpes Zoster Oticusraghad.bassalNo ratings yet
- E000675 FullDocument37 pagesE000675 Fullmartina silalahiNo ratings yet
- Peach and Green Organic Shapes Meditation Workshop Webinar Keynote PresentationDocument7 pagesPeach and Green Organic Shapes Meditation Workshop Webinar Keynote PresentationNicole Ivy GorimoNo ratings yet
- Vit DDocument36 pagesVit DConstantin MarioaraNo ratings yet
- MouthDocument12 pagesMouthRodolfo MartinezNo ratings yet