Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Form 4: Chapter 9 (Differentiation) SPM Practice Fully Worked Solutions
Uploaded by
ruvenvishaliOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Form 4: Chapter 9 (Differentiation) SPM Practice Fully Worked Solutions
Uploaded by
ruvenvishaliCopyright:
Available Formats
30
1 (a) y = 15x(3 x)
= 45x 15x
2
dy
dx
= 45 30x
When
dy
dx
= 0,
45 30x = 0
x = 1.5
(b) When x = 1.5, y = 15(1.5)(3 1.5) = 33.75
d
2
y
dx
2
= 30 (negative)
Therefore, y is a maximum.
2
y
x
dy
dx
y
dy
dx
x
= (2x + 3) (2.01 2)
= (2 2 + 3) 0.01
= 0.07
3 y = 3x
3
(2x 1)
3
Let u = 3x
3
and v = (2x 1)
3
du
dx
= 9x
2
dv
dx
= 3(2x 1)
2
(2)
= 6(2x 1)
2
dy
dx
= u
dv
dx
+ v
du
dx
= 3x
3
[6(2x 1)
2
] + (2x 1)
3
(9x
2
)
= 18x
3
(2x 1)
2
+ 9x
2
(2x 1)
3
= 9x
2
(2x 1)
2
[2x + (2x 1)]
= 9x
2
(2x 1)
2
(4x 1)
4 y = 4x +
4
x
= 4x + 4x
1
dy
dx
= 4 4x
2
= 4
4
x
2
dx
dy
=
1
dy
dx
=
1
4
4
x
2
Rate of change of x:
dx
dt
=
dx
dy
dy
dt
=
1
4
4
x
2
2
=
1
4
4
3
2
2
=
9
16
units s
1
5 g(x) =
1
6(3x 4)
2
=
1
6
(3x 4)
2
g(x) =
2
6
(3x 4)
3
(3)
= (3x 4)
3
g(x) = 3(3x 4)
4
(3)
= 9(3x 4)
4
=
9
(3x 4)
4
g
1
3
=
9
3
1
3
4
4
=
1
9
6 V =
1
3
h
2
(21 h)
= 7h
2
1
3
h
3
dV
dh
= 14h h
2
dh
dV
=
1
14h h
2
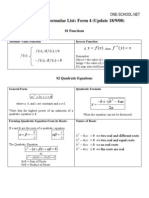
Form 4: Chapter 9 (Differentiation)
SPM Practice
Fully Worked Solutions
Paper 1
Rate of change of
y = 2 units
31
Rate of change of depth of water
=
dh
dt
=
dh
dV
dV
dt
=
1
14h h
2
9
=
1
14(3) (3)
2
9
=
3
11
cm s
1
7 y = (x + 3)
2
= x
2
+ 6x + 9
dy
dx
= 2x + 6
If the gradient of the normal is
1
6
, then the
gradient of the tangent is 6.
dy
dx
= 6
2x + 6 = 6
x = 0
When x = 0, y = (0 + 3)
2
= 9
Hence, the coordinates of point Q are (0, 9).
8 y =
1
3
u
6
=
1
3
(3x 6)
6
dy
dx
=
6
3
(3x 6)
5
(3)
= 6(3x 6)
5
9 (a) y = 3 + 14x 2x
3
dy
dx
= 14 6x
2
When x = 2,
dy
dx
= 14 6(2)
2
= 10
(b) y
dy
dx
x
= (10) [(2 + k) 2]
= 10k
10 Gradient = 4
dy
dx
= 4
2kx + 7 = 4
2k(1) + 7 = 4
2k = 3
k = 1
1
2
11 y = x
2
+ 16x 48
dy
dx
= 2x + 16
At a maximum point,
dy
dx
= 0
2x + 16 = 0
2k + 16 = 0
k = 8
12 y =
9
x
2
= 9x
2
dy
dx
= 18x
3
=
18
x
3
y
x
dy
dx
y
dy
dx
x
=
18
x
3
(u)
=
18
3
3
(u)
=
2
3
u
13 The normal to the curve y = x
2
7x at point L is
parallel to the straight line y = x 10.
L
y = x 10
y = x
2
7x
m (normal) = 1
m (tangent) =
1
(1)
= 1
dy
dx
= 1
2x 7 = 1
x = 4
When x = 4, y = 4
2
7(4) = 12
Hence, the equation of the normal at the point
L(4, 12) is
y (12) = 1(x 4)
y + 12 = x + 4
y = x 8
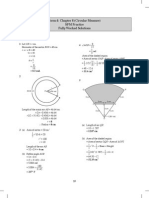
32
1
0.7 m
0.5 m
r m
h m
Using the concept of similar triangles,
r
0.5
=
h
0.7
r =
h
0.7
0.5
=
5
7
h
V =
1
3
r
2
h
=
1
3
5
7
h
2
h
=
25
147
h
3
dV
dh
=
25
147
(3h
2
)
dV
dh
=
25
49
h
2
dh
dV
=
49
25h
2
Rate of change of the height of the water level:
dh
dt
=
dh
dV
dV
dt
dh
dt
=
49
25h
2
0.1
14 (a) h9 (x) = 3kx
2
6x + 4
(b) h(x) = 6kx 6
When h(1) = 5,
6k(1) 6 = 5
k =
11
6
15 y = x
2
(3 + px)
y = 3x
2
+ px
3
dy
dx
= 6x + 3px
2
Gradient = 8 when x = 2:
6(2) + 3p(2)
2
= 8
12 + 12p = 8
12p = 20
p =
5
3
Paper 2
dh
dt
=
49
25(0.3)
2
0.1
dh
dt
=
49
25(3.142)(0.3)
2
0.1
= 0.6931 m s
1
2 y = 2x
3
3x
2
12x + 11
dy
dx
= 6x
2
6x 12
d
2
y
dx
2
= 12x 6
(a) At turning point,
dy
dx
= 0
6x
2
6x 12 = 0
x
2
x 2 = 0
(x + 1)(x 2) = 0
x = 1 or 2
When x = 1,
y = 2(1)
3
3(1)
2
12(1) + 11
= 18
(1, 18) is a turning point.
When x = 1,
d
2
y
dx
2
= 12(1) 6 = 18 (negative)
(1, 18) is a maximum point.
When x = 2,
y = 2(2)
3
3(2)
2
12(2) + 11
= 9
(2, 9) is a turning point.
When x = 2,
d
2
y
dx
2
= 12(2) 6 = 18 (positive)
(2, 9) is a minimum point.
Rate of increase of the volume of water:
dV
dt
= 0.1 m
3
s
1
33
(b) At point (3, 2),
dy
dx
= 6(3)
2
6(3) 12
= 24
m
tangent
= 24
m
normal
=
1
24
The equation of normal is
y 2 =
1
24
(x 3)
24(y 2) = (x 3)
24y 48 = x + 3
24y = x + 51
At the x-axis, y = 0.
24(0) = x + 51
x = 51
P is point (51, 0).
3 (a)
dy
dx
= 3x
2
18x + 24
Gradient at A(3, 3)
= 3(3)
2
18(3) + 24
= 3
(b) Gradient of normal at A =
1
3
Equation of normal at A is
y 3 =
1
3
(x 3)
3y 9 = x 3
3y = x + 6
(c) At turning points,
dy
dx
= 0
3x
2
18x + 24 = 0
x
2
6x + 8 = 0
(x 2)(x 4) = 0
x = 2 or 4
x = 2 is not accepted.
x = 4
When x = 4,
y = 4
3
9(4)
2
+ 24(4) 15
= 1
The coordinates of point Q are (4, 1).
d
2
y
dx
2
= 6x 18
When x = 4,
d
2
y
dx
2
= 6(4) 18 = 6 (positive)
Hence, Q is a minimum point.
You might also like
- Soalan DifferentiationDocument9 pagesSoalan DifferentiationKhairuddin MuhamadNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Add Math DifferentiationDocument9 pagesForm 4 Add Math DifferentiationYouwer WeiNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- f4 c9 Differentiation NewDocument9 pagesf4 c9 Differentiation NewlinusshyNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- DeterminantDocument6 pagesDeterminantr55088299No ratings yet
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Answers Are You Ready For CalculusDocument6 pagesAnswers Are You Ready For CalculusKevin HsiehNo ratings yet
- Test Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsFrom EverandTest Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument9 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- JC2 Prelim H2 Math Solution Paper 1Document10 pagesJC2 Prelim H2 Math Solution Paper 1Huixin LimNo ratings yet
- A LEVEL DifferentiationDocument15 pagesA LEVEL DifferentiationKizitoNo ratings yet
- De-Lecture 9 by Engineer MarcosDocument5 pagesDe-Lecture 9 by Engineer Marcosmelenyo tuqueroNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli SDocument5 pagesBernoulli SkennethNo ratings yet
- © Science Exam Papers: Worked Solutions Edexcel C4 Paper DDocument3 pages© Science Exam Papers: Worked Solutions Edexcel C4 Paper DPa GesNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5A: Dy DX 2 1Document11 pagesExercise 5A: Dy DX 2 1kamaldinho11No ratings yet
- 2007 Ajc h2 Prelims Paper 1 SolutionsDocument9 pages2007 Ajc h2 Prelims Paper 1 Solutionsvincesee85No ratings yet
- 10 04 Angle Between Two Curves PDFDocument15 pages10 04 Angle Between Two Curves PDFSri DNo ratings yet
- Add Maths DifferentiationDocument44 pagesAdd Maths DifferentiationTANG PEI PEI92% (12)
- Worksheet A: IfferentiationDocument11 pagesWorksheet A: IfferentiationPhilip ImarhiagbeNo ratings yet
- Bab Xiii Integral: 13. 1 DefinisiDocument25 pagesBab Xiii Integral: 13. 1 DefinisiDeazzy AndriyaniNo ratings yet
- 1 Direct Solution To Poisson Equation Using Green's FunctionDocument2 pages1 Direct Solution To Poisson Equation Using Green's Functionpvn251No ratings yet
- Krisna Mutiara Putri Xi - Ipa.5Document24 pagesKrisna Mutiara Putri Xi - Ipa.5Devi indah pratiwiNo ratings yet
- VJ Integrali PDFDocument52 pagesVJ Integrali PDFAgrif.bg-fovkaNo ratings yet
- Differentiation RevisionDocument4 pagesDifferentiation RevisionMavakise CalvinNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli Equation. Example 1, 2, 3Document4 pagesBernoulli Equation. Example 1, 2, 3harabassNo ratings yet
- Answers - Worksheet F: IfferentiationDocument2 pagesAnswers - Worksheet F: IfferentiationMohammed Jawad AyubNo ratings yet
- Integral Calculus - ExercisesDocument34 pagesIntegral Calculus - ExercisesVillamorchard0% (2)
- + 1 Sea U X + 1 Du 2xdx Entonces: Integrales IndefinidasDocument7 pages+ 1 Sea U X + 1 Du 2xdx Entonces: Integrales IndefinidasTrankiloChicoTrankiloNo ratings yet
- + 1 Sea U X + 1 Du 2xdx Entonces: Integrales IndefinidasDocument7 pages+ 1 Sea U X + 1 Du 2xdx Entonces: Integrales IndefinidasTrankiloChicoTrankiloNo ratings yet
- + 1 Sea U X + 1 Du 2xdx Entonces: Integrales IndefinidasDocument7 pages+ 1 Sea U X + 1 Du 2xdx Entonces: Integrales IndefinidasTrankiloChicoTrankiloNo ratings yet
- + 1 Sea U X + 1 Du 2xdx Entonces: Integrales IndefinidasDocument7 pages+ 1 Sea U X + 1 Du 2xdx Entonces: Integrales IndefinidasTrankiloChicoTrankiloNo ratings yet
- + 1 Sea U X + 1 Du 2xdx Entonces: Integrales IndefinidasDocument7 pages+ 1 Sea U X + 1 Du 2xdx Entonces: Integrales IndefinidasTrankiloChicoTrankiloNo ratings yet
- + 1 Sea U X + 1 Du 2xdx Entonces: Integrales IndefinidasDocument7 pages+ 1 Sea U X + 1 Du 2xdx Entonces: Integrales IndefinidasTrankiloChicoTrankiloNo ratings yet
- + 1 Sea U X + 1 Du 2xdx Entonces: Integrales IndefinidasDocument7 pages+ 1 Sea U X + 1 Du 2xdx Entonces: Integrales IndefinidasTrankiloChicoTrankiloNo ratings yet
- 2010 DHS Paper 1solDocument10 pages2010 DHS Paper 1solnothingtodo1992No ratings yet
- Integral Indefinida-Resueltos en WordDocument7 pagesIntegral Indefinida-Resueltos en WordTrankiloChicoTrankiloNo ratings yet
- + 1 Sea U X + 1 Du 2xdx Entonces: Integrales IndefinidasDocument7 pages+ 1 Sea U X + 1 Du 2xdx Entonces: Integrales IndefinidasTrankiloChicoTrankiloNo ratings yet
- Calculus: Differentiation RulesDocument17 pagesCalculus: Differentiation RulesAoSd' TikmanNo ratings yet
- Pure Mathematics: For CAPEDocument11 pagesPure Mathematics: For CAPERonaldoNo ratings yet
- AB AB: 1. (A) One-To-OneDocument9 pagesAB AB: 1. (A) One-To-OneSeanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 Differential Equations: Exercise 17Document9 pagesChapter 17 Differential Equations: Exercise 17ZaleNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Chapter 17 Answers PDFDocument9 pagesUnit 1 Chapter 17 Answers PDFEggBread12No ratings yet
- 2011 IJC Prelims P1 SolnDocument15 pages2011 IJC Prelims P1 Solnmath3matics3No ratings yet
- AIEEE Mock Solved: Sol. (A) Sol. (B)Document7 pagesAIEEE Mock Solved: Sol. (A) Sol. (B)kishangopi123No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Differential EquationsDocument22 pagesChapter 10 Differential EquationsAloysius Raj67% (3)
- AP Calc AB/BC Review SheetDocument2 pagesAP Calc AB/BC Review Sheetmhayolo69100% (1)
- Integral Calculus Finals ReviewerDocument12 pagesIntegral Calculus Finals ReviewerJaimee Navarro50% (2)
- Avaliações 2009-1 - GabaritoDocument13 pagesAvaliações 2009-1 - GabaritoEduardobelloNo ratings yet
- SAT ACT EquationsDocument18 pagesSAT ACT EquationsYb Andik Adi CahyonoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Conclusion Proposition ProofDocument12 pagesMathematics Conclusion Proposition ProofPrasen RajNo ratings yet
- 9 Differentiation: 1. (A) Lim 2. Gradient of The Chord ABDocument23 pages9 Differentiation: 1. (A) Lim 2. Gradient of The Chord ABSeanNo ratings yet
- AP Calc - Instructor Solutions - Chapter 3Document43 pagesAP Calc - Instructor Solutions - Chapter 3Ishaan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Solutions For Exam # 3: F (X) X 9x + 24x F F F F XDocument4 pagesSolutions For Exam # 3: F (X) X 9x + 24x F F F F XparcaperuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Quadratic Expressions and EquationsDocument91 pagesChapter 2 Quadratic Expressions and Equationsjuriah binti ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bab-I & Bab IiDocument28 pagesTugas Bab-I & Bab IiblackzmillianNo ratings yet
- SPM Add Maths Formula List Form4 PDFDocument16 pagesSPM Add Maths Formula List Form4 PDFNicholas Rogers80% (5)
- Form 5: Chapter 21 (Linear Programming) SPM Practice Fully Worked SolutionsDocument4 pagesForm 5: Chapter 21 (Linear Programming) SPM Practice Fully Worked SolutionsruvenvishaliNo ratings yet
- Probability DistributionDocument5 pagesProbability DistributionMichael JohnNo ratings yet
- Form 5: Chapter 18 (Probability) SPM Practice Fully Worked SolutionsDocument1 pageForm 5: Chapter 18 (Probability) SPM Practice Fully Worked SolutionsruvenvishaliNo ratings yet
- Form 5: Chapter 20 (Motion Along A Straight Line) SPM Practice Fully Worked SolutionsDocument5 pagesForm 5: Chapter 20 (Motion Along A Straight Line) SPM Practice Fully Worked SolutionsruvenvishaliNo ratings yet
- Form 5: Chapter 16 (Trigonometric Functions) SPM Practice Fully Worked SolutionsDocument5 pagesForm 5: Chapter 16 (Trigonometric Functions) SPM Practice Fully Worked SolutionsruvenvishaliNo ratings yet
- Form 5: Chapter 17 (Permutations and Combinations) SPM Practice Fully Worked SolutionsDocument2 pagesForm 5: Chapter 17 (Permutations and Combinations) SPM Practice Fully Worked SolutionsruvenvishaliNo ratings yet
- Form 5: Chapter 15 (Vectors) SPM Practice Fully Worked SolutionsDocument7 pagesForm 5: Chapter 15 (Vectors) SPM Practice Fully Worked SolutionsruvenvishaliNo ratings yet
- ACEAM Web F514 (53 59)Document7 pagesACEAM Web F514 (53 59)ruvenvishaliNo ratings yet
- Form 5: Chapter 12 (Progressions) SPM Practice Fully Worked SolutionsDocument4 pagesForm 5: Chapter 12 (Progressions) SPM Practice Fully Worked SolutionsruvenvishaliNo ratings yet
- Form 4: Chapter 11 (Index Numbers) SPM Practice Fully Worked SolutionsDocument4 pagesForm 4: Chapter 11 (Index Numbers) SPM Practice Fully Worked SolutionsruvenvishaliNo ratings yet
- ACEAM Web F513 (47 52)Document6 pagesACEAM Web F513 (47 52)ruvenvishaliNo ratings yet
- ACEAM Web F410 (34-38)Document5 pagesACEAM Web F410 (34-38)ruvenvishaliNo ratings yet
- ACEAM Web F408 (25-29)Document5 pagesACEAM Web F408 (25-29)ruvenvishaliNo ratings yet
- Form 4: Chapter 1 (Functions) SPM Practice Fully Worked SolutionsDocument4 pagesForm 4: Chapter 1 (Functions) SPM Practice Fully Worked SolutionsLuculus LeeNo ratings yet
- AC 23-8B Flight Test Guide App 1Document22 pagesAC 23-8B Flight Test Guide App 1Ladislao PazmanyNo ratings yet
- Shortcuts For Ellipses and HyperBolaDocument3 pagesShortcuts For Ellipses and HyperBolaChristian Simon D. SOLINAPNo ratings yet
- Technical Analysis 1: Lg/Med Track ExcavatorsDocument6 pagesTechnical Analysis 1: Lg/Med Track ExcavatorsKang AdingNo ratings yet
- ISCSI OptimizationDocument28 pagesISCSI OptimizationrahulhclNo ratings yet
- Game of SultansDocument268 pagesGame of Sultansmnz gmz100% (1)
- Windows Forms in VBNET Tutorial With Example CodeDocument12 pagesWindows Forms in VBNET Tutorial With Example CodeLubadri LmNo ratings yet
- Linear ProgrammingDocument29 pagesLinear ProgrammingBrejohn McCrary100% (1)
- Article - Designing Sand Cores and ToolingDocument4 pagesArticle - Designing Sand Cores and ToolingroyhanNo ratings yet
- Lehmann Et Al 2013 PDFDocument13 pagesLehmann Et Al 2013 PDFJack HamiltonNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme: June 2018Document12 pagesMark Scheme: June 2018BethanyNo ratings yet
- SIGGRAPH2022 Advances Lumen Wright Et AlDocument199 pagesSIGGRAPH2022 Advances Lumen Wright Et AlmhazaniNo ratings yet
- Interpretations of The IMO Gas Code: International Association of Classification SocietiesDocument53 pagesInterpretations of The IMO Gas Code: International Association of Classification SocietiesAlkaNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument4 pagesLab ReportSyafiq MTNo ratings yet
- Surgical Sutures: Suture SizeDocument7 pagesSurgical Sutures: Suture SizeMei PayumoNo ratings yet
- GusekDocument177 pagesGusekAitorAlbertoBaezNo ratings yet
- SQL Interview QuestionsDocument2 pagesSQL Interview QuestionscourpediaNo ratings yet
- Aptitude Questions and Answers Sample Test 1Document11 pagesAptitude Questions and Answers Sample Test 1Udaya Kumar100% (1)
- 1 Routing Tables ExplainedDocument8 pages1 Routing Tables ExplainedallandonaldNo ratings yet
- Cam Less Engine.1Document15 pagesCam Less Engine.1Pradeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Mounting Systems For Solar TechnologyDocument24 pagesMounting Systems For Solar TechnologyArianit ZeqiriNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The AtomDocument26 pagesThe Structure of The AtomUnknownKidNo ratings yet
- Condensatoare MLCC-1837944Document130 pagesCondensatoare MLCC-1837944gigiNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Generators - 2 Marks Questions and AnswersDocument3 pagesSynchronous Generators - 2 Marks Questions and AnswersJoseph Harindranath67% (3)
- Advantage of Oil CoolingDocument2 pagesAdvantage of Oil CoolingYin ThoNo ratings yet
- Surveying 2 Final ExamDocument3 pagesSurveying 2 Final ExamRodin James GabrilloNo ratings yet
- GCSE Higher Student Book Unit Test AnswersDocument26 pagesGCSE Higher Student Book Unit Test Answersswiftmessi100% (5)
- Nitrosyl Complexes of RutheniumDocument26 pagesNitrosyl Complexes of RutheniumBenjamín Marc Ridgway de SassouNo ratings yet
- Site Preparation, Layout, Installation, and Hydration of Geosynthetic Cementitious Composite MatsDocument8 pagesSite Preparation, Layout, Installation, and Hydration of Geosynthetic Cementitious Composite Matsomar TahaNo ratings yet
- Iteration: Chapter GoalsDocument46 pagesIteration: Chapter GoalsAni AniNo ratings yet
- LSMW Carga SapDocument7 pagesLSMW Carga SapMario A. AvilaNo ratings yet
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceFrom EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldFrom EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (64)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1395)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessFrom EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (410)
- The Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectFrom EverandThe Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (20)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeFrom EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeNo ratings yet
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldFrom EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (60)
- Too Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldFrom EverandToo Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowFrom EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (49)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldFrom EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (54)
- Infinite Powers: How Calculus Reveals the Secrets of the UniverseFrom EverandInfinite Powers: How Calculus Reveals the Secrets of the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (126)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayFrom EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (125)
- The Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityFrom EverandThe Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (76)
- Strange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsFrom EverandStrange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (94)
- The Universe: The book of the BBC TV series presented by Professor Brian CoxFrom EverandThe Universe: The book of the BBC TV series presented by Professor Brian CoxRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (27)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismFrom EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (500)
- Chasing Heisenberg: The Race for the Atom BombFrom EverandChasing Heisenberg: The Race for the Atom BombRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Mastering Logical Fallacies: The Definitive Guide to Flawless Rhetoric and Bulletproof LogicFrom EverandMastering Logical Fallacies: The Definitive Guide to Flawless Rhetoric and Bulletproof LogicRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (91)