Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Explanation Subsystem Case Specific Database User Interface User
Uploaded by
skaushik2410Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Explanation Subsystem Case Specific Database User Interface User
Uploaded by
skaushik2410Copyright:
Available Formats
Knowledge Based System
KBSs are computer systems that contains stored knowledge and solve problems like humans.
Their core components are -
• knowledge-base (rules, facts, meta-knowledge)
• inference engine (reasoning and search strategy for solution, other services)
characteristics of KBSs:
• intelligent information processing systems
• representation of domain of interest - > symbolic representation
• problem solving-> by symbol - manipulation
=> symbolic programs
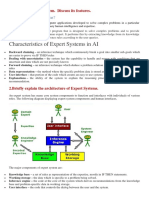
STRUCTURE
Explanation Case specific
subsystem database
User
User
interface
Inference
engine
Knowledge
base
Knowledge
Knowledge Developer's
acquisition
engineer interface
subsystem
knowledge-base (KB) : It contains knowledge about the field of interest (in natural language-
like formalism). It is a symbolically described system-specification. KNOWLEDGE-
REPRESENTATION METHOD!
inference engine: Its is an engine of problem solving (general problem solving knowledge)
and supports the operation of the other components. PROBLEM SOLVING METHOD!
case-specific database : It is an auxiliary component. It comprises of specific information
(information from outside, initial data of the concrete problem) and information obtained during
reasoning.
Explanation subsystem: It contains the explanation of system’s actions in case of user’s
request. Typical explanation facilities:
1. Explanation during problem solving:
• WHY... (explanative reasoning, intelligent help, tracing information about the
actual reasoning steps)
• WHAT IF... (hypothetical reasoning, conditional assignment and its
consequences, can be withdrawn)
• WHAT IS ... (gleaning in knowledge-base and case-specific database)
1. Explanation after problem solving:
• HOW ... (explanative reasoning, information about the way the result has been
found)
• WHY NOT ... (explanative reasoning, finding counter-examples)
• WHAT IS ... (gleaning in knowledge-base and case-specific database)
Knowledge acquisition subsystem: Its main tasks are:
• checking the syntax of knowledge elements
• checking the consistency of KB (verification, validation)
• knowledge extraction, building KB
• automatic logging and book-keeping of the changes of KB
• tracing facilities (handling breakpoints, automatic monitoring and reporting the values
of knowledge elements)
user interface (→ user) : dialogue on natural language (consultation/ suggestion)
Specially intefaces: comprises of database and other connections
Developer interface (→ knowledge engineer, human expert)
Knowledge engineer selects the knowledge representation method and reasoning strategy. He is
also responsible for the implementation of knowledge-based system.
Other tasks are -
• knowledge acquisition and design of KBS: determination, classification, refinement
and formalization of methods, thumb-rules and procedures
• verification and validation of KB
• KB maintenance
You might also like
- Project Communication MatrixDocument7 pagesProject Communication Matrixaldeto71No ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument30 pagesArtificial Intelligencevishnu m v100% (2)
- Indonesian SL Study DesignDocument61 pagesIndonesian SL Study DesignJase HarrisonNo ratings yet
- Security Survey, Security Inspection and Security InvestigationDocument5 pagesSecurity Survey, Security Inspection and Security InvestigationFrederick Eboña33% (3)
- Accounting Information Systems 3rd Edition Vernon Richardson Chengyee Chang Rod SmithDocument33 pagesAccounting Information Systems 3rd Edition Vernon Richardson Chengyee Chang Rod SmithDorothy Ashbaugh100% (31)
- Knowledge Based Expert SystemsDocument14 pagesKnowledge Based Expert Systemssuhani pandey100% (1)
- TAELLN411 Set 1 Written AssessmentDocument9 pagesTAELLN411 Set 1 Written Assessmentkiran seerooNo ratings yet
- AI & Expert SysDocument24 pagesAI & Expert SysNehaNo ratings yet
- The Law of The Squares - John SearlDocument3 pagesThe Law of The Squares - John Searlwatchman580% (1)
- Introduction To The Influence Model: ConfidentialDocument64 pagesIntroduction To The Influence Model: Confidentialkewang0429100% (3)
- Cs9152 DBT Unit V NotesDocument42 pagesCs9152 DBT Unit V NotesHema LathaNo ratings yet
- Knowledge-Based Systems: Rozália Lakner University of Veszprém Department of Computer ScienceDocument57 pagesKnowledge-Based Systems: Rozália Lakner University of Veszprém Department of Computer Sciencerak0249161No ratings yet
- Expert SystemsDocument9 pagesExpert SystemsmkNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 AiDocument48 pagesUnit 5 AiRamNo ratings yet
- Preserving and Applying Human Expertise: Knowledge-Based SystemsDocument74 pagesPreserving and Applying Human Expertise: Knowledge-Based SystemsbhuvijayNo ratings yet
- ExpertSystem 1Document18 pagesExpertSystem 1Dragon Ball SuperNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Knowledge and Expert SystemsDocument59 pagesLecture 5 - Knowledge and Expert SystemsBii PeterNo ratings yet
- IRS Unit-1Document14 pagesIRS Unit-1Nagendra MarisettiNo ratings yet
- Turban 12Document58 pagesTurban 12Ergalaxy ErgalaxyNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Based SystemsDocument18 pagesKnowledge Based SystemsMulika FatimaNo ratings yet
- AI-Knowledge Acquisition 6Document47 pagesAI-Knowledge Acquisition 6Mahmoud SolimanNo ratings yet
- AI Mod-4Document5 pagesAI Mod-4Shashank chowdary DaripineniNo ratings yet
- AI Mod-4Document5 pagesAI Mod-4Shashank chowdary DaripineniNo ratings yet
- Artifical Intelligence and Expert SystemsDocument62 pagesArtifical Intelligence and Expert SystemsLuyando HamasakaNo ratings yet
- Expert SystemDocument17 pagesExpert SystemkashishNo ratings yet
- Untitled PresentationDocument165 pagesUntitled PresentationDalia MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Expert Systems: Chapters 1-5Document13 pagesExpert Systems: Chapters 1-5Javed AhmadNo ratings yet
- Expert SystemDocument14 pagesExpert SystemSameer RijalNo ratings yet
- 1.4. General Approaches For Building Intelligent SystemsDocument21 pages1.4. General Approaches For Building Intelligent SystemsyagoencuestasNo ratings yet
- Presentation of AI ML Session 1Document131 pagesPresentation of AI ML Session 1ritu.agrawal31506No ratings yet
- Knowledge Based SystemsDocument70 pagesKnowledge Based SystemsSushma B SNo ratings yet
- Expert Systems IGCSEDocument6 pagesExpert Systems IGCSETeenage GirlNo ratings yet
- Expert SystemsDocument13 pagesExpert Systemsanand_seshamNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Based Expert SystemsDocument4 pagesKnowledge Based Expert SystemsLOOPY GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Business Intelligence (Bi) : Dr. P. Ravindra S de Silva Ravi@sjp - Ac.lk University of Sri JayawardenapuraDocument17 pagesBusiness Intelligence (Bi) : Dr. P. Ravindra S de Silva Ravi@sjp - Ac.lk University of Sri JayawardenapuraSupun BanupiyaNo ratings yet
- Ai R16 - Unit-5Document13 pagesAi R16 - Unit-5Simran Reyaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Wa0057.Document7 pagesWa0057.Chinnam RavitejaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1: Expert SystemsDocument29 pagesChapter-1: Expert SystemsEmran AljarrahNo ratings yet
- Inter CA EIS - Chapter 3Document80 pagesInter CA EIS - Chapter 3Ready 4 BooyahNo ratings yet
- Unit IV Part 111Document13 pagesUnit IV Part 111raghu RamNo ratings yet
- Structure of Management Information SystemsDocument71 pagesStructure of Management Information SystemsKochappen Ipe KumarNo ratings yet
- CS6659 Artificial Intelligence: Topic: Expert SystemsDocument24 pagesCS6659 Artificial Intelligence: Topic: Expert SystemsKhushi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Seminar 1Document19 pagesSeminar 1Hanis SNo ratings yet
- Executive Support Systems (Ess)Document38 pagesExecutive Support Systems (Ess)AshuNo ratings yet
- "Expert" Knowledge ModuleDocument67 pages"Expert" Knowledge ModuleRobert Hill100% (1)
- AI ApplicationsDocument165 pagesAI ApplicationsHosam HatimNo ratings yet
- Unit IV Part 1Document13 pagesUnit IV Part 1dheerajNo ratings yet
- BIS Chapter 4 ClassDocument31 pagesBIS Chapter 4 ClassareayaslassiebNo ratings yet
- Expert System: Xiu-Jun GONG (Ph. D)Document18 pagesExpert System: Xiu-Jun GONG (Ph. D)m291288No ratings yet
- AACS1304 04 - System Design 1 202005Document57 pagesAACS1304 04 - System Design 1 202005WIN YE KUANNo ratings yet
- 3.4 Unit 4 COMP4 The Computing Practical ProjectDocument3 pages3.4 Unit 4 COMP4 The Computing Practical ProjectdidaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document52 pagesLecture 1Rana GaballahNo ratings yet
- AI ApplicationsDocument165 pagesAI ApplicationsHosam HatimNo ratings yet
- Knowledge-Based Systems: Artificial Intelligence Knowledge BaseDocument4 pagesKnowledge-Based Systems: Artificial Intelligence Knowledge BaseRandika PereraNo ratings yet
- Chap 5.3OODesign222Document31 pagesChap 5.3OODesign222migadNo ratings yet
- 14 Lecture csc462Document47 pages14 Lecture csc462Hàssáñ YàsèéñNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 NotesDocument16 pagesUnit 4 NotesRamya F100% (2)
- Introduction To DBMS: Unit 1Document33 pagesIntroduction To DBMS: Unit 1Rajalaxmi Devagirkar KangokarNo ratings yet
- Expert SystemDocument54 pagesExpert SystemPooja DhanikNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization and Architecture (ECE2002)Document20 pagesComputer Organization and Architecture (ECE2002)Madhav Rav TripathiNo ratings yet
- Sie01introduction 180211173750Document77 pagesSie01introduction 180211173750maryamNo ratings yet
- Meet 03 - 04Document34 pagesMeet 03 - 04alma millaniaNo ratings yet
- Intelligence: Artificial Intelligence: "Can Machines Think?"Document11 pagesIntelligence: Artificial Intelligence: "Can Machines Think?"api-26830587No ratings yet
- Expert SystemDocument16 pagesExpert SystemASWATHY RAYIRATHNo ratings yet
- Module 1 & 2-MergedDocument147 pagesModule 1 & 2-MergedCaila PanerioNo ratings yet
- Automatic Image Annotation: Enhancing Visual Understanding through Automated TaggingFrom EverandAutomatic Image Annotation: Enhancing Visual Understanding through Automated TaggingNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Nursing InformaticsDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Nursing InformaticsEfjayNo ratings yet
- (Wilson, 1994) INFORMATION NEEDS AND USES: FIFTY YEARS OF PROGRESS?Document33 pages(Wilson, 1994) INFORMATION NEEDS AND USES: FIFTY YEARS OF PROGRESS?wan yong0% (1)
- UAE CST Framework PDFDocument280 pagesUAE CST Framework PDFChitra BharghavNo ratings yet
- Framework Answers - Berkeley 2017Document151 pagesFramework Answers - Berkeley 2017Andrew GrazianoNo ratings yet
- 1978 Caramazza Berndt PBDocument21 pages1978 Caramazza Berndt PBEddiesvoiceNo ratings yet
- STYLISTICS IntoDocument25 pagesSTYLISTICS IntoДжинси МілаNo ratings yet
- CMS CIO Policy Framework - 0Document24 pagesCMS CIO Policy Framework - 0jldtecnoNo ratings yet
- New PURCOM MODULE AY 2020 2021.separate With Cover PagedocxDocument36 pagesNew PURCOM MODULE AY 2020 2021.separate With Cover PagedocxSimon Benson FloresNo ratings yet
- 2020 Physics Subject Assessment AdviceDocument11 pages2020 Physics Subject Assessment AdviceMaan PatelNo ratings yet
- Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Academic LibrariesDocument6 pagesApplications of Artificial Intelligence in Academic LibrariesDaniel0% (1)
- Bryan Cahulogan DLP For English 3Document4 pagesBryan Cahulogan DLP For English 3Bryan Riños Cahulogan IINo ratings yet
- Can I Use Bullet Points in A Literature ReviewDocument6 pagesCan I Use Bullet Points in A Literature Reviewfohudenyfeh2100% (1)
- The History of Information Communication TechnologyDocument8 pagesThe History of Information Communication TechnologyRodolfo MondragonNo ratings yet
- Childers and Jass 2002 All Dressed Up With Something To Say Effects of TDocument15 pagesChilders and Jass 2002 All Dressed Up With Something To Say Effects of TȘtefania CucuNo ratings yet
- 3 29 2022 Ece Ug Detailed Hbook 21 22Document12 pages3 29 2022 Ece Ug Detailed Hbook 21 22vanoviNo ratings yet
- Design PortfolioDocument20 pagesDesign PortfolioArda ÖzdemirNo ratings yet
- Literature Review Physics ExampleDocument8 pagesLiterature Review Physics Exampleaflstquqx100% (1)
- TonmoyDocument2 pagesTonmoyTasnova Rebonya 201-15-14170No ratings yet
- Example of Scope and Limitation of The Study in Research PaperDocument5 pagesExample of Scope and Limitation of The Study in Research PaperrtggklrifNo ratings yet
- Accounting Information SystemDocument15 pagesAccounting Information SystemkanzamehmoodNo ratings yet
- Extended Literature Review Dissertation StructureDocument5 pagesExtended Literature Review Dissertation StructureBuyCheapPaperOnlineCanadaNo ratings yet
- Define Business CommunicationDocument3 pagesDefine Business CommunicationBul Bul Aw YusufNo ratings yet
- Solution Operations - Run SAP Like A FactoryDocument16 pagesSolution Operations - Run SAP Like A FactorykogaratsukeNo ratings yet