Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IEC Categories Contactor PDF
Uploaded by
asalasv65Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IEC Categories Contactor PDF
Uploaded by
asalasv65Copyright:
Available Formats
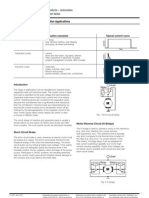
IEC Utilization Categories
(Explanation)
IEC Utilization Categories
Voltage Category Typical Applications
IEC
Product
Standard 3
AC-1
AC-2
AC-3
AC-4
AC-5a
AC-5b
AC-6a
AC-6b
AC-7a
AC-7b
AC-8a
AC-8b
AC-12
AC-13
AC-14
AC-15
AC-20
AC-21
AC-22
AC-23
A
B
DC-1
DC-3
DC-5
DC-6
DC-12
DC-13
DC-14
DC-20
DC-21
DC-22
DC-23
Non Industive or slightly inductive loads, example: resistive furnaces, Heaters
Slip-ring motors: switching off
Squirrel-cage motors: starting, swithces off motors during running time
Most typical industrial application for motors
Squirrel-cage motors: starting, plugging (1), inching (2)
Switching of electric discharge lamps
Switching of incandescent lamps
Switching of transfomers
Switching of capacitor banks
Slightly inductive loads in household appliances: examples: mixers, blenders
Motor-loads for household appliances: examples: fans, central vacuum
Hermetic refrigerant compressor motor control with manual resetting overloads
Hermetic refrigerant compressor motor control with automatic resetting overloads
Control of resisitive loads and solid state loads with opto-coupler isolation
Control of solid state loads with transformer isolation
Control of small electromagnetic loads
Control of A.C. electromagnetic loads
Connecting and disconnecting under no-load conditions
Switching of resistive loads, including moderate loads
Switching of mixed resistive and inductive loads, including moderate overloads
Switching of motor loads or other highly inductive loads
Protection of circuits, with no rated short-time withstand current
Protection of circuits, with a rated short-time withstand current
Non Inductive or slightly inductive loads, resistance furnaces, heaters
Shunt-motors, starting, plugging(1), inching(2), dynamic breaking of motors
Series-motors, starting, plugging(1), inching(2), dynamic breaking of motors
Switching of incandescent lamps
Control of resistive loads and solid state loads with opto-coupler isolation
Control of D.C. electromagnetics
Control of D.C. electromagnetic loads having economy resistors in the circuit
Connecting and disconnecting under no-load conditions
Switching of resistive loads, including moderate overloads
Switching of mixed resistive and inductive loads, including moderate overloads (i.e.
shunt motors)
Switching of highly inductive loads (i.e. series motors)
A.C.
A.C.
and
D.C.
D.C.
(1) Plugging - Stopping a motor rapidly by reversing the incoming power connections.
(2) Inching - Energizing a motor repeatedly for short periods to obtain small incremental movements.
947-4
947-5
947-3
947-2
947-4
947-5
947-3
p.21
You might also like
- Electric Circuits, Systems, and Motors - 3d PDFDocument415 pagesElectric Circuits, Systems, and Motors - 3d PDFray davisNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Safety Professionals Guide To Lockout Tagout EbookDocument33 pagesSafety Professionals Guide To Lockout Tagout EbookSebastian Mejia PuertaNo ratings yet
- Power ElectronicsDocument29 pagesPower ElectronicsMoiz Amjad50% (2)
- HID DatasheetDocument16 pagesHID DatasheetRomeo RubonalNo ratings yet
- CT VT Calculation Al AIN Rev.2Document43 pagesCT VT Calculation Al AIN Rev.2jm.mankavil623080% (5)
- Mitigating The Effect of Voltage Sags On Contactors in Industrial Plant and SubstationsDocument4 pagesMitigating The Effect of Voltage Sags On Contactors in Industrial Plant and SubstationsarisNo ratings yet
- IEC - Panel RegulationDocument20 pagesIEC - Panel RegulationAsith SavindaNo ratings yet
- Automatic Power Factor Controlling PanelDocument15 pagesAutomatic Power Factor Controlling PanelheruvalaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Paper Machine ControlDocument140 pagesFundamentals of Paper Machine ControlRizal Rivaldi100% (2)
- Ee 328 Lecture 1Document40 pagesEe 328 Lecture 1Hasan Hatice IlcalıNo ratings yet
- 2013 E.C. BASIC ELECTRICITY Entrance Exam For EEP.Document6 pages2013 E.C. BASIC ELECTRICITY Entrance Exam For EEP.Ziyad Mohammed100% (1)
- Low Voltage Switch Disconnectors for Photovoltaic SystemsDocument12 pagesLow Voltage Switch Disconnectors for Photovoltaic SystemswasinchaiNo ratings yet
- Self Switching Power Supply Regulates and Automatically Switches OffDocument20 pagesSelf Switching Power Supply Regulates and Automatically Switches OffPutra Purechk TokyoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Power Electronics SystemDocument41 pagesIntroduction To Power Electronics Systemrakesh_pal_3No ratings yet
- Astm E119-19Document37 pagesAstm E119-19Rodrigo Jeldes100% (2)
- Electrical Power Systems Quality Lecture 2Document43 pagesElectrical Power Systems Quality Lecture 2Carlnagum 123456789No ratings yet
- Ac Circuit Breaker: 2.1 What Is Circuit Breaker?Document13 pagesAc Circuit Breaker: 2.1 What Is Circuit Breaker?miguel itson100% (1)
- Duty VoltageDocument1 pageDuty VoltageNgoc NguyenNo ratings yet
- Categorias SeccionamentoDocument2 pagesCategorias SeccionamentoAlexandreNo ratings yet
- Ies Rule For Selection Switch GearDocument5 pagesIes Rule For Selection Switch Gearnikhil chandraNo ratings yet
- Contactor DutyDocument3 pagesContactor DutySteevan NelsonNo ratings yet
- AC Duty Contactors ExplainedDocument4 pagesAC Duty Contactors Explainedsowndarya balambikaNo ratings yet
- Utilization Categories: Utilization Typical Application CategoryDocument1 pageUtilization Categories: Utilization Typical Application CategorywizaarzNo ratings yet
- Overview and Power Devices PDFDocument48 pagesOverview and Power Devices PDFSebastian LangkahNo ratings yet
- Contactor by EE Controls PDFDocument10 pagesContactor by EE Controls PDFPaul MendozaNo ratings yet
- Utilization Categories For Contactors ITEM3Document3 pagesUtilization Categories For Contactors ITEM3Saravana Perumal KrishnasamyNo ratings yet
- Siemens - Contactor Utilization CategoriesDocument1 pageSiemens - Contactor Utilization CategoriesMiko QuijanoNo ratings yet
- 15EC73Document307 pages15EC73KN DEEPSHINo ratings yet
- Automotive Applications: Relay Products - Automotive Application NotesDocument3 pagesAutomotive Applications: Relay Products - Automotive Application NotesMarcel PozoNo ratings yet
- Contact orDocument5 pagesContact orZol MaksebNo ratings yet
- Electric Power and Power ElectronicsDocument144 pagesElectric Power and Power ElectronicsmnamkyNo ratings yet
- 1.chapter 1 Overview Power eDocument26 pages1.chapter 1 Overview Power eFarah AzlinaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Inverters: DC to AC ConversionDocument13 pagesIntroduction to Inverters: DC to AC ConversionEngrAneelKumarAkhaniNo ratings yet
- Serie R eDocument36 pagesSerie R ev5bw57b7tzNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Introduction: 1.0 Introduction To Power ElectronicsDocument30 pagesUnit-1 Introduction: 1.0 Introduction To Power ElectronicsAishwarya PKamatagiNo ratings yet
- LEARNING GUIDE 02 AC DC RectifierDocument27 pagesLEARNING GUIDE 02 AC DC Rectifiermeseret sisayNo ratings yet
- Fileadmin Catalog Literature Application Guidelines ADV P Application Information IEC 947 1 and 947 3 StandardsDocument1 pageFileadmin Catalog Literature Application Guidelines ADV P Application Information IEC 947 1 and 947 3 Standardsargari19No ratings yet
- 229 PE Innovative Practice 1Document2 pages229 PE Innovative Practice 1Sakshi BarapatreNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document30 pagesModule 1Sathya Prakash PNo ratings yet
- Nergy Conversions: University of TechnologyDocument9 pagesNergy Conversions: University of TechnologyFadhil A. HasanNo ratings yet
- Chap 12Document18 pagesChap 12Jarrett MathewsNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics EngineeringDocument30 pagesPower Electronics Engineeringiamjarvis990No ratings yet
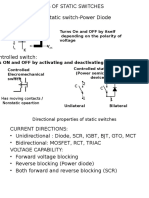
- Types of Static SwitchesDocument55 pagesTypes of Static SwitchesSubhash MurkuteNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Power ElectronicsDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Power ElectronicsNovie Ayub WindarkoNo ratings yet
- Introduction Unit1Document34 pagesIntroduction Unit1senthilku marNo ratings yet
- Power Semiconductor DevicesDocument6 pagesPower Semiconductor DevicesNassor Nassor ANo ratings yet
- Utilization CategoriesDocument4 pagesUtilization Categoriesanirban 007No ratings yet
- 1) Introduction 2018Document28 pages1) Introduction 2018Muhammad Anaz'sNo ratings yet
- Power Elecrtoincs and InstrumentationDocument119 pagesPower Elecrtoincs and InstrumentationMeenuNo ratings yet
- ADC3 en REVA 2009 Lift Magnet SupplyDocument2 pagesADC3 en REVA 2009 Lift Magnet Supplya2345No ratings yet
- Mini Project ModificatonsDocument30 pagesMini Project Modificatonsch manasaNo ratings yet
- Utilization Category 1Document2 pagesUtilization Category 1alageshvijayNo ratings yet
- 132 KV Substation Traning Report at HaldiaDocument31 pages132 KV Substation Traning Report at Haldiababli91No ratings yet
- Design Fabrication and Performance Analysis of Solar InverterDocument5 pagesDesign Fabrication and Performance Analysis of Solar InverterSyed ZadaaNo ratings yet
- Power ElectronicsDocument67 pagesPower ElectronicsJayarajan Jayarajan C NNo ratings yet
- Application of 4 Pole Switchgear DevicesDocument6 pagesApplication of 4 Pole Switchgear DevicesTigrilloNo ratings yet
- Application of 4pole Switchgear DevicesDocument5 pagesApplication of 4pole Switchgear Devicessaga2000cnNo ratings yet
- Power ElectronicsDocument264 pagesPower ElectronicsJayashree C RaoNo ratings yet
- ELG4139: Power Electronics Systems: Power Supplies and Motor Drives!Document25 pagesELG4139: Power Electronics Systems: Power Supplies and Motor Drives!bitew ayalewNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Power: Unit - 1 ElectronicsDocument41 pagesIntroduction To Power: Unit - 1 ElectronicsDevi Debora SiregarNo ratings yet
- U1 l1 Introduction To Power ElectronicsDocument5 pagesU1 l1 Introduction To Power ElectronicsRasedulIslamNo ratings yet
- A Power Supply Is A Device That Supplies Electric Power To An Electrical LoadDocument14 pagesA Power Supply Is A Device That Supplies Electric Power To An Electrical LoadElizabeth HarrisNo ratings yet
- Iare Pe Lecture NotesDocument177 pagesIare Pe Lecture NotesShewan DebretsionNo ratings yet
- Synchron Spec Sheet 0603407 CDocument2 pagesSynchron Spec Sheet 0603407 Capi-170472102No ratings yet
- DS Bu 16 @Document1 pageDS Bu 16 @asalasv65No ratings yet
- How Why GroundingDocument8 pagesHow Why GroundingReinerio Praxedes Castillo CespedesNo ratings yet
- Tektronix The Fundamentals of Three-Phase Power Measurements App NoteDocument8 pagesTektronix The Fundamentals of Three-Phase Power Measurements App Notesgshekar30No ratings yet
- Electroimanes Suspendidos Autolimpieza PDFDocument6 pagesElectroimanes Suspendidos Autolimpieza PDFasalasv65No ratings yet
- Fluke 19xC-2x5C: Getting StartedDocument18 pagesFluke 19xC-2x5C: Getting Startedasalasv65No ratings yet
- Synchrophasors: Definitions, Measurement and ApplicationDocument6 pagesSynchrophasors: Definitions, Measurement and ApplicationflaviograndoNo ratings yet
- Hwa - SPD - Ib - 8222-0012DDocument48 pagesHwa - SPD - Ib - 8222-0012Dasalasv65No ratings yet
- Fluke 192B - 196B/C - 199B/C: Getting StartedDocument20 pagesFluke 192B - 196B/C - 199B/C: Getting Startedasalasv65No ratings yet
- Fluke ScopeMeter Instrument SecurityDocument2 pagesFluke ScopeMeter Instrument Security15101980No ratings yet
- Glazier Wheat Pease Bartlett 06Document22 pagesGlazier Wheat Pease Bartlett 06asalasv65No ratings yet
- KN Atex 09-2013 NL GB PDFDocument12 pagesKN Atex 09-2013 NL GB PDFasalasv65No ratings yet
- Tableros ShafelDocument2 pagesTableros Shafelasalasv65No ratings yet
- INT-Terasaki Selection Guide 15-G00ENDocument32 pagesINT-Terasaki Selection Guide 15-G00ENasalasv65No ratings yet
- Optimize Power Quality and Reduce Costs with Metrel AnalyzersDocument12 pagesOptimize Power Quality and Reduce Costs with Metrel Analyzersasalasv65No ratings yet
- DC TC Tarif 906211399 GB BD PDFDocument3 pagesDC TC Tarif 906211399 GB BD PDFasalasv65No ratings yet
- 3-Lesson Notes Lec 15 DC Motors IDocument7 pages3-Lesson Notes Lec 15 DC Motors Iasalasv65No ratings yet
- UPS Handbook Rev D Low PDFDocument36 pagesUPS Handbook Rev D Low PDFAshwin DuhonarrainNo ratings yet
- UPS Theoretical ReviewDocument63 pagesUPS Theoretical ReviewAsad MadniNo ratings yet
- UPS Theoretical ReviewDocument63 pagesUPS Theoretical ReviewAsad MadniNo ratings yet
- EZine Volume 04 MarchDocument29 pagesEZine Volume 04 Marchasalasv65No ratings yet
- 3 Application Inductive SensorDocument3 pages3 Application Inductive Sensorasalasv65No ratings yet
- DC GB 906211239Document36 pagesDC GB 906211239Husnain AssociatesNo ratings yet
- Capacitor in The AC Circ... Gineering - ExperimentsDocument1 pageCapacitor in The AC Circ... Gineering - Experimentsasalasv65No ratings yet
- What Is Arc Flash - Mike HoltDocument10 pagesWhat Is Arc Flash - Mike Holtasalasv65No ratings yet
- BRADY-Arc Flash Labeling Whitepaper-NFPA 70E 2015Document5 pagesBRADY-Arc Flash Labeling Whitepaper-NFPA 70E 2015JOSE LUIS FALCON CHAVEZNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law With Cobra4 - ... Gineering - ExperimentsDocument1 pageOhm's Law With Cobra4 - ... Gineering - Experimentsasalasv65No ratings yet
- KN Atex 09-2013 NL GBDocument12 pagesKN Atex 09-2013 NL GBasalasv65No ratings yet
- How Why GroundingDocument8 pagesHow Why GroundingReinerio Praxedes Castillo CespedesNo ratings yet
- Reporte 2Document4 pagesReporte 2Nando_COBNo ratings yet
- GM 1927-16b Exhaust Pipe Bending Process AuditDocument4 pagesGM 1927-16b Exhaust Pipe Bending Process AuditJOHNNo ratings yet
- Level of Inquiry Wenning 2012Document10 pagesLevel of Inquiry Wenning 2012MeyisNo ratings yet
- RenaultDocument120 pagesRenaultcostinel iordachescuNo ratings yet
- Resistance and Ohm's Law: R and O2 Lo, Ia2i o 2Document1 pageResistance and Ohm's Law: R and O2 Lo, Ia2i o 2reymart cereneoNo ratings yet
- 125cc EFI ABS/PBS: DatasheetDocument2 pages125cc EFI ABS/PBS: DatasheetBart OszNo ratings yet
- Exp 1 For Electrical & Electronic Lab I MSUDocument8 pagesExp 1 For Electrical & Electronic Lab I MSUgogyoukageNo ratings yet
- Is 302 2 4 1993 PDFDocument15 pagesIs 302 2 4 1993 PDFInayat HathiariNo ratings yet
- FT Ultrasonic Repr IngDocument5 pagesFT Ultrasonic Repr IngYana LesmanaNo ratings yet
- Prac - Exam - Style - Paper - 6 2020Document11 pagesPrac - Exam - Style - Paper - 6 2020sybejoboNo ratings yet
- 1 DC Circuit PDFDocument119 pages1 DC Circuit PDFShivam PandeyNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Diodes IntroductionDocument23 pagesSemiconductor Diodes IntroductionSachinthaNo ratings yet
- D1878Document4 pagesD1878Catalin PancescuNo ratings yet
- Thermal Conductivity GuideDocument181 pagesThermal Conductivity GuideAl BNo ratings yet
- 614 CodeDocument20 pages614 CodeAdamNo ratings yet
- Saudi Aramco Grounding and Bonding Inspection PlanDocument12 pagesSaudi Aramco Grounding and Bonding Inspection PlanHatemS.MashaGbehNo ratings yet
- Aluminium Automotive Innovation BrochureDocument29 pagesAluminium Automotive Innovation BrochureMohamed NasrNo ratings yet
- Cmos PDFDocument61 pagesCmos PDFRamakrishna BoyapatiNo ratings yet
- Fire Resistant Coaxial CablesDocument38 pagesFire Resistant Coaxial Cablesrose chenNo ratings yet
- Current & Resistance: - Current and Current Density - Ohm's Law - Resistivity - ResistanceDocument17 pagesCurrent & Resistance: - Current and Current Density - Ohm's Law - Resistivity - ResistancePedroNo ratings yet
- Ical Panels MCB Cable Size Calculation 1.1.15Document65 pagesIcal Panels MCB Cable Size Calculation 1.1.15rushi_007No ratings yet
- About Fuses and Choosing The Appropriate Fuse For Your Mod (Mamu)Document4 pagesAbout Fuses and Choosing The Appropriate Fuse For Your Mod (Mamu)Jorge FarinhaNo ratings yet
- Physics Pre - Ig Yr9 Islam Abbas Notes (Elec&Magent)Document13 pagesPhysics Pre - Ig Yr9 Islam Abbas Notes (Elec&Magent)Saja Al-SultanNo ratings yet
- Upda-Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument39 pagesUpda-Multiple Choice QuestionsAnonymous GllSJsUNo ratings yet
- HMT Lab ManualDocument55 pagesHMT Lab ManualHarsha K100% (1)