Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Atropine
Uploaded by
Sarah BenjaminCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Atropine
Uploaded by
Sarah BenjaminCopyright:
Available Formats
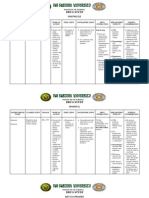
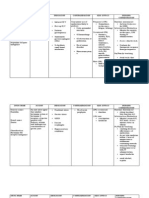
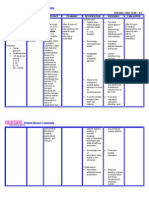
Brand Name/ Generic Dosage
Name
Classification
Indication
Contraindication
Side Effects
Nursing Interventions
Isopto
Atropine/Atropine
Sulfate
Anticholinergic
Antimuscarinic
Parasympatholytic
Antiparkinsonian
Antidote
Diagnostic agent
(ophthalmic
preparations)
Belladonna alkaloid
Antisialagogue for
preanesthetic
medication to prevent
or reduce respiratory
tract secretions
Treatment of
parkinsonism;
relieves tremor and
rigidity
Restoration of
cardiac rate and
arterial pressure
during anesthesia
when vagal
stimulation produced
by intra-abdominal
traction causes a
decrease in pulse rate,
lessening the degree
of AV block when
increased vagal tone
is a factor (eg, some
cases due to digitalis)
Relief of
bradycardia and
syncope due to
hyperactive carotid
sinus reflex
Relief of
pylorospasm,
hypertonicity of the
small intestine, and
hypermotility of the
colon
Relaxation of
the spasm of biliary
and ureteral colic and
Contraindicated with
hypersensitivity to
anticholinergic drugs.
Systemic
administration
Contraindicated
with glaucoma;
adhesions between
iris and lens;
stenosing peptic
ulcer; pyloroduodenal
obstruction; paralytic
ileus; intestinal atony;
severe ulcerative
colitis; toxic
megacolon;
symptomatic prostatic
hypertrophy; bladder
neck obstruction;
bronchial asthma;
COPD; cardiac
arrhythmias;
tachycardia;
myocardial ischemia;
impaired metabolic,
liver, or kidney
function; myasthenia
gravis.
Use cautiously
with Down syndrome,
brain damage,
spasticity,
hypertension,
hyperthyroidism,
lactation.
Ophthalmic solution
Contraindicated
dizziness, fainting,
new or increased eye
pressure/pain/swellin
g/discharge.Tell your
doctor immediately if
any of these rare but
very serious side
effects occur:
slow/shallow
breathing,
mental/mood changes
(e.g., confusion,
agitation),
fast/irregular
heartbeat.A very
serious allergic
reaction to this drug
is
rare, rash, itching/sw
elling (especially of
the
face/tongue/throat),
severe dizziness,
trouble breathing
Ensure adequate
hydration; provide
environmental control
(temperature) to
prevent hyperpyrexia.
Have patient
void before taking
medication if urinary
retention is a
problem.
adults vary from
around 0.5 mg to 1
mg (5 - 10 mL of the
0.1 mg/mL solution)
for antisialagogue
and other antivagal
effects, to 2 to 3 mg
(20 - 30 mL of the 0.1
mg/mL solution) as
an antidote for
organophosporous or
muscarinic mushroom
poisoning. When
used as an antidote,
the 2 to 3 mg dose
should be repeated no
less often that every
20 to 30 minutes until
signs of poisoning are
sufficiently lessened
or signs of atropine
poisoning
Teaching points
When used
preoperatively or in
other acute situations,
incorporate teaching
about the drug with
teaching about the
procedure; the
ophthalmic solution
is used mainly
acutely and will not
be self-administered
by the patient; the
following apply to
oral medication for
outpatients:
Take as
prescribed, 30 min
before meals; avoid
excessive dosage.
Avoid hot
environments; you
will be heat
intolerant, and
dangerous reactions
may occur.
You might also like
- Atropine Sulfate Drug StudyDocument4 pagesAtropine Sulfate Drug Studysandal_meenuNo ratings yet
- IbuprofenDocument3 pagesIbuprofenKristine Artes AguilarNo ratings yet
- Anesthetic DrugsDocument7 pagesAnesthetic DrugsAJ DalawampuNo ratings yet
- Aspirin: Anticoagulants Antiplatelets & Fibronolytic (Thrombolytics) Nonsteroid Anti-Inflamatory Drugs (Nsaids)Document3 pagesAspirin: Anticoagulants Antiplatelets & Fibronolytic (Thrombolytics) Nonsteroid Anti-Inflamatory Drugs (Nsaids)Acuña MonalyNo ratings yet
- Drug AnalysisDocument3 pagesDrug AnalysisAbby BorabienNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: OmeprazoleDocument5 pagesDrug Study: Omeprazoleclau_latojaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyMike Faustino SolangonNo ratings yet
- CefuroximeDocument11 pagesCefuroximeAlmira Ballesteros CestonaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ArvinDocument6 pagesDrug Study ArvinArvin BeltranNo ratings yet
- Name of The Drug Drug Classes Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilityDocument4 pagesName of The Drug Drug Classes Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilityKirstele Nicole QuijanoNo ratings yet
- Atropine Sulfate InjectionDocument4 pagesAtropine Sulfate InjectionIrawanMarlyNo ratings yet
- Brand Name:: VasopressinDocument3 pagesBrand Name:: VasopressinHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Atropine Sulfate (Drug Study)Document3 pagesAtropine Sulfate (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (1)
- Pharmacology ReviewDocument64 pagesPharmacology ReviewRichard BakerNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Francisco Tampos JRDocument37 pagesDrug Study: Francisco Tampos JRCarlmeister Ambray JudillaNo ratings yet
- Key Points (OTC DRUGS) : Cough, Cold, and AllergyDocument3 pagesKey Points (OTC DRUGS) : Cough, Cold, and Allergyann_michelle7No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument28 pagesDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyHelen ReonalNo ratings yet
- AnalgesicsDocument20 pagesAnalgesicsPamela Ria HensonNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Indications Action Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Side Effects Nursing ManagementDocument3 pagesName of Drug Indications Action Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Side Effects Nursing Managementjhappo31No ratings yet
- FINAL Drug StudyDocument9 pagesFINAL Drug StudyKristen Leigh MarianoNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument40 pagesEmergency Drugsmattheus101No ratings yet
- Drug RationaleDocument77 pagesDrug RationaleYolanda WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument22 pagesDrug StudyColleen Fretzie Laguardia NavarroNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyJannefer HernandezNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyCee SanchezNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic Acid Drug ProfileDocument3 pagesMefenamic Acid Drug ProfileAhmad WaliNo ratings yet
- Atropine SulfateDocument6 pagesAtropine SulfateManelle SingzonNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Frequent (10%) Baseline Assessment Antiemetic (Assess Intervention/EvaluationDocument11 pagesGeneric Name: Frequent (10%) Baseline Assessment Antiemetic (Assess Intervention/EvaluationIrene Soriano BayubayNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Mefenamic Acid, Beetab, Esomeprazole Aspirin, Citicoline Plavix)Document6 pagesDrug Study (Mefenamic Acid, Beetab, Esomeprazole Aspirin, Citicoline Plavix)Patricia LuceroNo ratings yet
- Drug Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing Considerations Ketorolac TromethamineDocument8 pagesDrug Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing Considerations Ketorolac TromethamineAiryn CanonNo ratings yet
- Nephrolithiasis - Drug StudyDocument5 pagesNephrolithiasis - Drug StudyAia JavierNo ratings yet
- Drug 1Document5 pagesDrug 1Jesamine MayNo ratings yet
- Carvedilol Drug Name Classifications Indications Contraindications Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationsDocument5 pagesCarvedilol Drug Name Classifications Indications Contraindications Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationsClaudette Sanvictores0% (1)
- Atropine Sulfate Drug STudyDocument2 pagesAtropine Sulfate Drug STudyLiway100% (1)
- Drug Study - LeptospirosisDocument19 pagesDrug Study - LeptospirosisCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive Pharmacologic Agents: Nr33 K Burger, Msed, MSN, RN, CneDocument28 pagesAntihypertensive Pharmacologic Agents: Nr33 K Burger, Msed, MSN, RN, CneLopez JoeNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument20 pagesDrugsLee Won100% (1)
- Drugs 1Document27 pagesDrugs 1vinaynagar1994No ratings yet
- Propanolol and Spironolactone Drug StudyDocument2 pagesPropanolol and Spironolactone Drug StudyLisette Castillo91% (11)
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- Final Drug StudyDocument22 pagesFinal Drug StudyPaula Xavier AlfalahiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyHannah Philene D. CalubNo ratings yet
- ASPIRIN Drug Study ERDocument1 pageASPIRIN Drug Study ERMargueretti Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Atorvastatin Side EffectsDocument5 pagesAtorvastatin Side EffectsNAVNEET BAGGANo ratings yet
- NCLEX Pharmacology LPDocument53 pagesNCLEX Pharmacology LPSara Pirman100% (1)
- Drug Study (FINAL)Document31 pagesDrug Study (FINAL)iamjenivicNo ratings yet
- CHF Drug StudyDocument4 pagesCHF Drug StudyAiza Apelada-NievaNo ratings yet
- S2 Skills Check Medication LSTDocument2 pagesS2 Skills Check Medication LSTshazel chiasaokwuNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyMaurence John Feliciano LuluquisenNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyFranco ObedozaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyNedemar OcampoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study GuideDocument9 pagesDrug Study GuideSh3meeNo ratings yet
- Top 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)From EverandTop 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Phytotherapy in the Management of Diabetes and Hypertension: Volume 2From EverandPhytotherapy in the Management of Diabetes and Hypertension: Volume 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 327Document5 pages327Sarah BenjaminNo ratings yet
- 327Document2 pages327Sarah BenjaminNo ratings yet
- Room 326Document7 pagesRoom 326Sarah BenjaminNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MetronidazoleDocument1 pageDrug Study MetronidazoleSarah Benjamin33% (3)
- Co AmoxiclavDocument2 pagesCo AmoxiclavKatrina Ponce92% (12)
- Room 326Document7 pagesRoom 326Sarah BenjaminNo ratings yet
- Date Activities Address Contact No.: Daily ItineraryDocument2 pagesDate Activities Address Contact No.: Daily ItinerarySarah BenjaminNo ratings yet
- Presenation Final CADDocument5 pagesPresenation Final CADSarah BenjaminNo ratings yet
- Percentage Distribution of Gender: Male - 48% Female - 52%Document10 pagesPercentage Distribution of Gender: Male - 48% Female - 52%Sarah BenjaminNo ratings yet
- NCP Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument2 pagesNCP Electrolyte ImbalanceSarah Benjamin100% (1)
- Trial Chapter 4Document3 pagesTrial Chapter 4Sarah BenjaminNo ratings yet
- Source of Information: TV - 78% Radio - 17% Newspaper - 1% Neighbors - 4%Document5 pagesSource of Information: TV - 78% Radio - 17% Newspaper - 1% Neighbors - 4%Sarah BenjaminNo ratings yet
- AcknowledgementDocument1 pageAcknowledgementSarah Benjamin100% (1)
- NCP For Case StudyDocument10 pagesNCP For Case StudySarah BenjaminNo ratings yet
- 3 Developmental Tasks of Later MaturityDocument3 pages3 Developmental Tasks of Later MaturitySarah BenjaminNo ratings yet
- Amebiasis NCPDocument3 pagesAmebiasis NCPSarah Benjamin0% (1)
- Disease ProcessDocument13 pagesDisease ProcessSarah BenjaminNo ratings yet
- Presenation Final CADDocument5 pagesPresenation Final CADSarah BenjaminNo ratings yet
- CHN Description of The StudyDocument2 pagesCHN Description of The StudySarah BenjaminNo ratings yet
- NCP - AgeDocument5 pagesNCP - Ageunsp3akabl386% (7)
- CHN Description of The StudyDocument2 pagesCHN Description of The StudySarah BenjaminNo ratings yet
- MethodologyDocument1 pageMethodologySarah BenjaminNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan CVADocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan CVAhermesdave175% (4)
- Presenation Final CADDocument5 pagesPresenation Final CADSarah BenjaminNo ratings yet
- Source of Information: TV - 78% Radio - 17% Newspaper - 1% Neighbors - 4%Document5 pagesSource of Information: TV - 78% Radio - 17% Newspaper - 1% Neighbors - 4%Sarah BenjaminNo ratings yet
- Final Reserach About TechnologyDocument72 pagesFinal Reserach About TechnologySarah BenjaminNo ratings yet
- AcknowledgementDocument1 pageAcknowledgementSarah Benjamin100% (1)
- Result, Analysis and InterpretationDocument1 pageResult, Analysis and InterpretationSarah BenjaminNo ratings yet
- Charlotte PDFDocument4 pagesCharlotte PDFSarah BenjaminNo ratings yet
- Technology and Its Impact On The Academic Performance ofDocument67 pagesTechnology and Its Impact On The Academic Performance ofSarah Benjamin71% (75)
- Introduction To Infection ControlDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Infection ControlLast YearNo ratings yet
- Auntminnie SignsDocument56 pagesAuntminnie SignsHey ReelNo ratings yet
- Cornea and External DiseaseDocument26 pagesCornea and External Diseaserajeshwari saravananNo ratings yet
- Infectios DiseasesDocument183 pagesInfectios DiseasesAnonymous eson90No ratings yet
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder Screener GAD7Document2 pagesGeneralized Anxiety Disorder Screener GAD7Indira Damar PangestuNo ratings yet
- WIDALDocument17 pagesWIDALNasti YL HardiansyahNo ratings yet
- Human Behavior Victimology 75 102 PDFDocument28 pagesHuman Behavior Victimology 75 102 PDFAndales Melbert G.No ratings yet
- GI Part 2 2016 StudentDocument131 pagesGI Part 2 2016 StudentDaniel RayNo ratings yet
- Hand Hygiene PPT 2020Document24 pagesHand Hygiene PPT 2020bevzie datuNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)deric95% (97)
- RHB en Cancer, GeneralidadesDocument12 pagesRHB en Cancer, GeneralidadesDaniela Fernanda Cruz GómezNo ratings yet
- Immunization FormDocument4 pagesImmunization FormSowmya RaghuNo ratings yet
- Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT)Document15 pagesHereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT)MarshallNo ratings yet
- Shock RosenDocument10 pagesShock RosenJuan GallegoNo ratings yet
- Articol Medicina de TrimisDocument19 pagesArticol Medicina de TrimisMoldovan TiberiuNo ratings yet
- PAINWeek Journal Vol 7, Q1Document78 pagesPAINWeek Journal Vol 7, Q1Apostolos T.No ratings yet
- Acupuncture - MeniereDocument4 pagesAcupuncture - MeniereTinnitus Man IndonesiaNo ratings yet
- Klemm 2001Document4 pagesKlemm 2001Krishna CaitanyaNo ratings yet
- GRTP Wallet Card FinalDocument2 pagesGRTP Wallet Card FinalIrish FroggyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For UTIDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For UTIbeatriceNo ratings yet
- Materi 1 - WS Exercise Stress TestDocument25 pagesMateri 1 - WS Exercise Stress TestMaria ulfahNo ratings yet
- Bursitis Hip Exercises For Pain ReliefDocument8 pagesBursitis Hip Exercises For Pain ReliefMark BeechNo ratings yet
- Entamoeba Coli: BackgroundDocument4 pagesEntamoeba Coli: BackgroundJam Pelario100% (1)
- Uterine AtonyDocument4 pagesUterine AtonyThirdie LacorteNo ratings yet
- Catangay Module 1Document3 pagesCatangay Module 1Kristen Althea CatangayNo ratings yet
- VAN HILTEN, Meindert Onno - Covid-19 and NCDs - PUBLISHED (23 March 2020) PDFDocument2 pagesVAN HILTEN, Meindert Onno - Covid-19 and NCDs - PUBLISHED (23 March 2020) PDFPriyanka BindaNo ratings yet
- Occupational Health and Safety Including PadamsDocument27 pagesOccupational Health and Safety Including PadamsFerlyn SanorjoNo ratings yet
- Ophtalmology Record Corneal Ulcer: Anggi Lewis R P Aruan 1161050113Document7 pagesOphtalmology Record Corneal Ulcer: Anggi Lewis R P Aruan 1161050113LewishoppusNo ratings yet
- Large CystDocument4 pagesLarge CystKin DacikinukNo ratings yet
- Operating Room LectureDocument12 pagesOperating Room LectureMARY GRACE SABAL100% (1)