Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Prob 3
Uploaded by
Dinesh KumarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Prob 3
Uploaded by
Dinesh KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
11/28/14
propability tutorial | quantitative aptitude probability questions | probability aptitude
Quantitative Aptitude
Read propability tutorial, quantitative aptitude probability
questions, get basic probability aptitude problems, Probability
questions with solutions, campus placement papers on
probability, probability questions asked in TCS, Wipro, Accenture,
Infosys
Probability Part 3:
Probability-4
Next-
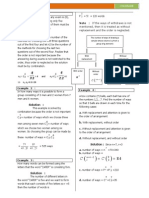
Ex. A card is drawn at random from a pack of 52 cards, What is
the probability that it is
(a) A card of Red Suit ?
Solution : There are 26 cards of Red Suit
(b) An honour card of Black suit ?
Solution : There are 16 honour cards out of which 8 are of Black
suit and 8 are of Red Suit. So n(E) = 8 , n(S)=52
(c) A card is drawn and its number is multiple of 2
Solution : E = 4 (2)'s + 4 (4)'s + 4 (6)'s + 4 (8)'s + 4 (10)'s
So, n(E) = 20, n (S) = 52
(d) A king or a queen ?
Solution : There are 4 kings and 4 Queens in 52 cards
www.vidyatutorial.com/Probability-3.html
1/4
11/28/14
propability tutorial | quantitative aptitude probability questions | probability aptitude
(e) A king of black suit ?
Solution : There are 2 kings in black suit ( King of Spade and King
of Club )
Ex. A bag contains 4 red, 3 yellow and 5 green balls. 3 balls are
drawn randomly. What is the probability that balls drawn contain
(a) Balls of different colors ?
Solution : Toatal numbers of balls = 12
(b) Exactly two Red Balls ?
Solution : Here only three balls are to be drawn out of which
condition is of Exactly two Red balls,
(c) No Red balls ?
Solution : Now three balls can be selected from 3 Y + 5 G balls
Ex. A bag contains 4 Red balls and 5 Green balls. Two balls are
drawn at random. Find the probability that they are of the same
colour ?
Solution : Let S be the sample space and E be the event, so
n(E) = ( Number of ways of drawing 2 balls of Red ) OR ( Number
of ways of drawing 2 balls of Green )
www.vidyatutorial.com/Probability-3.html
2/4
11/28/14
propability tutorial | quantitative aptitude probability questions | probability aptitude
Ex. A three-digit number is formed with the digits 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 at
random. What is probability that number formed is
(a) Divisible by 2
Solution : From the given digits 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 numbers formed is :
For divisibility with 2, even number or 0 should appear at unit
place, here 2, 4 are even numbers and can occupy unit place in 2
! ways, Rest 2 place can be filled in :
Ex. Not divisible by 2 ?
Solution : P (Not divisible by 2 ) = 1 - P (Divisible by 2 )
Ex. Divisible by 5 ?
Solution : A number ends with 5, 0 then the number will be
divisible by 5
Here only 5 is present, end place will be fixed by 5 so,
Ex. The letters of the word CASTIGATION is arranged in different
ways randomly. What is the chance that vowels occupy the even
places ?
Solution : Vowels are A I A I O,
C A S T I G A T I O N
(O)(E)(O)(E)(O)(E)(O)(E)(O)(E)(O)
So there are 5 even places in which five vowels can be arranged
and in rest of 6 places 6 constants can be arranged as follows :
www.vidyatutorial.com/Probability-3.html
3/4
11/28/14
propability tutorial | quantitative aptitude probability questions | probability aptitude
Next-
Probability-4
All copyrights reserved@VidyaTutorial2012
Home
About Us
www.vidyatutorial.com/Probability-3.html
Contact Us
Feedback
4/4
You might also like
- Mathematical Snacks: A Collection of Interesting Ideas to Fill Those Spare MomentsFrom EverandMathematical Snacks: A Collection of Interesting Ideas to Fill Those Spare MomentsNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 15Document9 pagesChapter - 15inba673No ratings yet
- Maths Mania # 073: DIRECTIONS: For The Following Questions, Four Options Are Given. Choose The Correct OptionDocument5 pagesMaths Mania # 073: DIRECTIONS: For The Following Questions, Four Options Are Given. Choose The Correct OptionTUSHAR JALANNo ratings yet
- Permutations and CombinationsDocument5 pagesPermutations and CombinationsNat RajaNo ratings yet
- ChutiyabanayaphirseDocument9 pagesChutiyabanayaphirseLallu Singh YadavNo ratings yet
- Geometry Snacks: Bite Size Problems and How to Solve ThemFrom EverandGeometry Snacks: Bite Size Problems and How to Solve ThemRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chapter 06Document6 pagesChapter 06Jose D. Elvena Jr.No ratings yet
- Permutation: CombinationDocument36 pagesPermutation: CombinationHassam BashirNo ratings yet
- Discrete Math Chapter 2Document12 pagesDiscrete Math Chapter 2kumar_anup11No ratings yet
- Probability Questions With SolutionsDocument16 pagesProbability Questions With Solutionskrackyournut100% (1)
- PermutationDocument25 pagesPermutationprasrikumarNo ratings yet
- Experime NT:: Probability Problems With Solutions Important FormulasDocument11 pagesExperime NT:: Probability Problems With Solutions Important FormulasbhargatejaNo ratings yet
- #1 Counting TechniquessDocument17 pages#1 Counting TechniquessPatricia Nicole MonderinNo ratings yet
- Typical Test ProblemsDocument11 pagesTypical Test ProblemsDISCOVERYNo ratings yet
- MathptDocument10 pagesMathptAilyn Grace SullanoNo ratings yet
- Solution:: 11th GRADEDocument7 pagesSolution:: 11th GRADEHammersteinJimNo ratings yet
- Places: No. of Choices: 1 2 3 4 5: Example: 1Document17 pagesPlaces: No. of Choices: 1 2 3 4 5: Example: 1Sarvesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Question & Answer On ProbabilityDocument5 pagesQuestion & Answer On ProbabilityRustam SalamNo ratings yet
- Business StatisticsDocument2 pagesBusiness StatisticsjustinatorNo ratings yet
- Eg. in How Many Ways Can and Be Arranged On A Bench If A) There Are No Restrictions?Document24 pagesEg. in How Many Ways Can and Be Arranged On A Bench If A) There Are No Restrictions?shri1980No ratings yet
- Module 2: COUNTING TECHNIQUESDocument18 pagesModule 2: COUNTING TECHNIQUESrinobiNo ratings yet
- Module 4,5,6,7Document71 pagesModule 4,5,6,7karen perrerasNo ratings yet
- Probabl It yDocument13 pagesProbabl It yUTKARSH TRIPATHI (RA1811004010394)No ratings yet
- Combinatorics 6 Solutions UHSMCDocument5 pagesCombinatorics 6 Solutions UHSMCWalker KroubalkianNo ratings yet
- Puzzles For FreshersDocument33 pagesPuzzles For FreshersAvi KapoorNo ratings yet
- Tut 28 POYO & HQ & Supplementary Qns (Solutions)Document9 pagesTut 28 POYO & HQ & Supplementary Qns (Solutions)Lim Kew ChongNo ratings yet
- EE 302 Division 1. Homework 3 SolutionsDocument9 pagesEE 302 Division 1. Homework 3 Solutionserwin rosumanNo ratings yet
- 85 More Probability Questions: Prob-Stats (Math 3350)Document10 pages85 More Probability Questions: Prob-Stats (Math 3350)BarakaNo ratings yet
- Probability PDFDocument10 pagesProbability PDFImtiaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Black Probability 1 and 2 PDFDocument15 pagesBlack Probability 1 and 2 PDFRishav Shiv RanjanNo ratings yet
- Combinations and PermutationsDocument16 pagesCombinations and PermutationsShaik FarooqNo ratings yet
- Puzzles For Freshers..........Document32 pagesPuzzles For Freshers..........api-3806986100% (1)
- Set Theory Permutations Combinations and Probability Review 1Document3 pagesSet Theory Permutations Combinations and Probability Review 1api-718784549No ratings yet
- Practice - Permutations and Combinations Problems - Ncert Chapter 7 Solutions Part - 50 SolutionsDocument14 pagesPractice - Permutations and Combinations Problems - Ncert Chapter 7 Solutions Part - 50 Solutionsalroy dcruzNo ratings yet
- TCS Latest Pattern Questions With Solutions - 16Document3 pagesTCS Latest Pattern Questions With Solutions - 16bhslegion1498No ratings yet
- Concepts of ProbabilityDocument18 pagesConcepts of ProbabilityKenjie Mariano JimenezNo ratings yet
- Probability: Probability of Event To Happen P (E) Number of Favorable Outcomes/total Number of OutcomesDocument7 pagesProbability: Probability of Event To Happen P (E) Number of Favorable Outcomes/total Number of Outcomesolid mahmoodNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Home Practice Test-5/Mathematics: Permutation and Combination HWT - 1Document10 pagesSolutions To Home Practice Test-5/Mathematics: Permutation and Combination HWT - 1varunkohliinNo ratings yet
- VTAMPS Session 3 - Primary 1Document7 pagesVTAMPS Session 3 - Primary 1Mark FoxNo ratings yet
- Probability Questions MEMODocument29 pagesProbability Questions MEMObanathi nkosiNo ratings yet
- Probability Notes and ProblemsDocument41 pagesProbability Notes and Problemsamul65No ratings yet
- Probability - Solved RxamplesDocument6 pagesProbability - Solved RxamplesUmer KhanNo ratings yet
- Permutation & Combination-02 - Solved ExampleDocument13 pagesPermutation & Combination-02 - Solved ExampleRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- WMO Practice Set For Level 1 Answer KeyDocument5 pagesWMO Practice Set For Level 1 Answer KeyJomar EjedioNo ratings yet
- Short Question Ch07 FSC Part1 Akhtar AbbasDocument2 pagesShort Question Ch07 FSC Part1 Akhtar Abbas2020gu2935No ratings yet
- Kuliahke 1 Tambahan PermutasidankombinasiDocument55 pagesKuliahke 1 Tambahan PermutasidankombinasiHeri HadiantoNo ratings yet
- ProbabilityDocument8 pagesProbabilityVimal KrNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Ability 15: P & C and ProbabilityDocument4 pagesQuantitative Ability 15: P & C and ProbabilityRimple DhillonNo ratings yet
- 2002 AMC8 Solutions NiceDocument5 pages2002 AMC8 Solutions NiceAddux ParagonNo ratings yet
- MATH1081 Test 4 SolutionsDocument13 pagesMATH1081 Test 4 SolutionsIsha DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Probability of Compound EventsDocument9 pagesMathematics: Probability of Compound EventsJess Anthony EfondoNo ratings yet
- Permutation and CombinationDocument50 pagesPermutation and CombinationPurplesmilezNo ratings yet
- ProbabilityDocument18 pagesProbabilityRekha TandonNo ratings yet
- Immaculate Conception Academy : High School Department SHS Grade 12 Handout #2 Statistics and Probability ProbabilityDocument6 pagesImmaculate Conception Academy : High School Department SHS Grade 12 Handout #2 Statistics and Probability ProbabilityElysia BalodNo ratings yet
- Combinatorics 1 Solutions UHSMCDocument7 pagesCombinatorics 1 Solutions UHSMCWalker KroubalkianNo ratings yet
- Combinatorial Problems SolDocument5 pagesCombinatorial Problems SolMin Fong HsuNo ratings yet
- Permutation and CombinationDocument42 pagesPermutation and CombinationPUNAM THAPANo ratings yet
- Ibps - Pos Exam Model Paper: Computer KnowledgeDocument1 pageIbps - Pos Exam Model Paper: Computer KnowledgeDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- 19 - Sep - 2017J. Box Leaflet With 18gauge115Document2 pages19 - Sep - 2017J. Box Leaflet With 18gauge115Dinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Etapro V2.0: Electrical Interview QuestionsDocument4 pagesEtapro V2.0: Electrical Interview QuestionsDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- FGGHHDocument2 pagesFGGHHDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Priority) : WWW - Webthunders.tkDocument5 pagesPriority) : WWW - Webthunders.tkDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- DSP Sorted Bits (TheWebEagles)Document3 pagesDSP Sorted Bits (TheWebEagles)Dinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- FGGHHDocument2 pagesFGGHHDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Change Log Functionality: This Is Applicable Only For The Masters Having The UI (Front End)Document2 pagesChange Log Functionality: This Is Applicable Only For The Masters Having The UI (Front End)Dinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Example of Runtime PolymorphismDocument3 pagesExample of Runtime PolymorphismDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Hibernate: Simple - Example: Vinay@careeraxis - inDocument6 pagesHibernate: Simple - Example: Vinay@careeraxis - inDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- How To Create Partition in SOA - Weblogic EM ConsoleDocument1 pageHow To Create Partition in SOA - Weblogic EM ConsoleDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Steps: @e:/shilpa/changelog - Trig - SQLDocument3 pagesSteps: @e:/shilpa/changelog - Trig - SQLDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Hibernate: Simple - Example: Part One - The Example StepsDocument5 pagesHibernate: Simple - Example: Part One - The Example StepsDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- 6 Tourist Information Office PDFDocument7 pages6 Tourist Information Office PDFMaría Luján PorcelliNo ratings yet
- Thirsty Sword Lesbians - Advanced Lovers Lesbians TablesDocument14 pagesThirsty Sword Lesbians - Advanced Lovers Lesbians TablesJaceNo ratings yet
- Reinforcement PlacementDocument3 pagesReinforcement PlacementRomani Noel S. Chavez Jr.No ratings yet
- Crossword Puzzle - NumbersDocument1 pageCrossword Puzzle - NumbersVahid UzunlarNo ratings yet
- Family and Relatives - TextDocument4 pagesFamily and Relatives - TextАнастасия tarasovaNo ratings yet
- Khawas Ji Ki HaveliDocument2 pagesKhawas Ji Ki HaveliAayushi GoyalNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes Chapter - 13 Sound: Sound: Vibrations That Travel Through The Air or Another Medium and Can Be Heard WhenDocument5 pagesRevision Notes Chapter - 13 Sound: Sound: Vibrations That Travel Through The Air or Another Medium and Can Be Heard WhenAarush SharmaNo ratings yet
- 3dboxx w4880 SeriesDocument2 pages3dboxx w4880 SeriesSaud AhmedNo ratings yet
- Hockeydraft PoolsheetDocument1 pageHockeydraft Poolsheeta_bummer338349No ratings yet
- ListofaprovedprojectsDocument22 pagesListofaprovedprojectsMahend RanNo ratings yet
- Instrucciones Pictureka Juego de Cartas en FrancésDocument2 pagesInstrucciones Pictureka Juego de Cartas en FrancésALEJANDRO LOPEZ ZEPEDANo ratings yet
- Knave Barrowmaze Optimized - 1 Sheet - 2 Pages (Slimmed Down and Adjusted Rules With Barrowmaze Restock Table)Document2 pagesKnave Barrowmaze Optimized - 1 Sheet - 2 Pages (Slimmed Down and Adjusted Rules With Barrowmaze Restock Table)max quayle0% (1)
- Adiff - Clothing System Top ExtDocument14 pagesAdiff - Clothing System Top ExtsoledadNo ratings yet
- Past Simple and Past ContinuousDocument4 pagesPast Simple and Past ContinuousRosa Sousa100% (1)
- Blackout - ScriptDocument9 pagesBlackout - Scriptapi-295129288No ratings yet
- Basic DialoguesDocument131 pagesBasic DialoguesElizabeth Simão MiguensNo ratings yet
- 0471 w12 Ms 2 PDFDocument9 pages0471 w12 Ms 2 PDFMuhammad Talha Yousuf SyedNo ratings yet
- An Irish BlessingDocument1 pageAn Irish BlessingNele-D0% (1)
- The Abington Journal 05-25-2011Document28 pagesThe Abington Journal 05-25-2011The Times LeaderNo ratings yet
- Recreation and LeisureDocument42 pagesRecreation and LeisureGina del Mar75% (4)
- Created by Jesus, Guardiola Date of Configuration: 26th September, 2019Document12 pagesCreated by Jesus, Guardiola Date of Configuration: 26th September, 2019Rob CasterNo ratings yet
- Music, Arts, Pe & HealthDocument7 pagesMusic, Arts, Pe & HealthKesh AceraNo ratings yet
- Identity TheotherDocument4 pagesIdentity Theotherapi-282750167No ratings yet
- Cutting Edge STARTER Final TestDocument12 pagesCutting Edge STARTER Final TestprofaderomanaNo ratings yet
- Atg Worksheet Subjectobjpron PDFDocument2 pagesAtg Worksheet Subjectobjpron PDFbunhuot100% (2)
- Sportech - Current & Future Scenario in India, FIICI & Ministry of Textiles Seminar, Dec 2010 PDFDocument37 pagesSportech - Current & Future Scenario in India, FIICI & Ministry of Textiles Seminar, Dec 2010 PDFKapsno1No ratings yet
- Wireless Pan: Wireless Usb, Irda, Blue-Tooth, Ultra-Wide-Band (Uwb), Zig-Bee, and SimilarDocument5 pagesWireless Pan: Wireless Usb, Irda, Blue-Tooth, Ultra-Wide-Band (Uwb), Zig-Bee, and SimilarSaman Nilantha PereraNo ratings yet
- Hes 386 Poster Breanna CrockettDocument2 pagesHes 386 Poster Breanna CrockettManuel FerreiraNo ratings yet
- SAILOR 6004 Control Panel: Installation GuideDocument2 pagesSAILOR 6004 Control Panel: Installation GuideRomeish KelaartNo ratings yet
- Apax EnglishDocument4 pagesApax EnglishJayzNo ratings yet