Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial 1 - Introduction To Signals and Systems
Uploaded by
Mirza DanishOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial 1 - Introduction To Signals and Systems
Uploaded by
Mirza DanishCopyright:
Available Formats
TUTORIAL 1
INTRODUCTION TO SIGNALS (CHAPTER 1) AND SYSTEMS (CHAPTER 2)
1.
Represent f(t) in terms of singularity function as shown.
f(t)
2
1
t
-3
-2
-1
-1
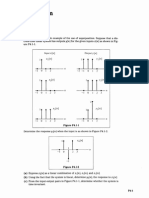
2. The signal x(t) is represent in terms of piecewise continuous functions as shown:
for 1 t 0
1,
t 1, for 0 t 1
x (t )
for 1 t 3
2,
0,
elsewhere
i)
ii)
Sketch x(t)
Determine wether signal x(t) is an energy, power or neither energy nor power.
Justify your answer.
3.
m(t)
1
t
-3
-1
1
-1
-2
i)
ii)
iii)
Sketch the derivative of m(t).
Sketch the integral of m(t).
Sketch the signal z(t) = 2m(-0.25t-5)
4. Define the following terms with an aid of diagram:
i)
Causal system
ii)
Time-variant system
iii)
Deterministic signal
iv) Aperiodic signal
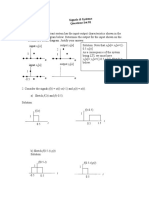
5. Consider the following piece-wise continuous function:
; 2 t 1
t 1
0
y (t ) t 2
2t 4
i)
ii)
iii)
; 1 t 1
; 1 t 2
;2t 3
;3t 4
Sketch y(t)
Represent y(t) in term of sum of singularity functions
Determine whether the signal y(t) is energy signal, power signal or neither
energy nor power signal. Justify your answer.
6. For the signal z(t) shown in Figure Q1 below:
i)
ii)
Sketch the integration of z(t)
Sketch the signal -3z(-0.5t+2)
z(t)
2
1
t
0
-1
-1
-2
Figure Q1
7.
Represent f(t) in terms of singularity function as shown.
f(t)
2
1
t
-3
-2
-1
-1
8.
The signal x(t) is represent in terms of piecewise continuous functions as
shown:
for 1 t 0
2,
t
1,
x (t ) 3
1,
0,
i)
ii)
for 0 t 3
for 3 t 4
elsewhere
Sketch x(t)
Determine whether signal x(t) is an energy, power or neither energy nor
power. Justify your answer.
9.
m(t)
1
t
-3
-2
-1
-1
-2
i)
ii)
iii)
Sketch the derivative of m(t).
Sketch the integral of m(t).
Sketch the signal z(t) = -2m(-0.5t+4)
TEST 1 JAN-MAY 2011
QUESTION 1
a) A signal can be said as a function of time that represents a physical variable that
carries information and commonly associated with a system.
i)
ii)
Briefly define the two (2) types of signal classification.
A signal
consists of a summation of two periodic signals,
and
where
whilst
. Determine whether the signal,
is a periodic signal or non-periodic signal and its new fundamental period if the
signal is said to be a periodic signal.
(4 marks)
b) Given a signal x(t) as shown in Figure Q1b. Sketch
i) Derivative of x(t)
ii)
Integration of x(t)
(4 marks)
x (t)
2
1
t
-3
-2
-1
-2
Figure Q1b
c) Refer to signal y t represented in Figure Q1c, sketch
i)
signal of zt if zt 3y 2 0.5t .
(4 marks)
y(t)
-4
-3
-2
-1
-1
-2
Figure Q1c
ii) Express the signal y t in Figure Q1c in terms of sum of singularity functions.
(3 marks)
2
iii) Given sin 4t 2 . (t 3) dt . Evaluate the given integral by using
3
properties of impulse function.
(1 mark)
d) i)
Give the definition of a system. Give ONE example of any relevant system
including its block diagram.
ii)
Determine whether the following system is with memory or without memory,
causal or non causal, time variant or time invariant and linear or non linear.
Justify your answers.
y (t ) tx (t 2 ) e 5t
(6 marks)
e) The signal x(t ) is represent in terms of piecewise continuous functions as shown:
4 t 2
2 ;
2t 4, 2 t 3
x (t )
3t 4
t 2,
0,
elsewhere
Determine whether signal x(t ) is an energy signal or power signal or neither energy
nor power. Justify your answer.
(3 marks)
You might also like
- Solution 1 - SignalsDocument3 pagesSolution 1 - SignalsRaja SNo ratings yet
- Increased VCSEL Output Power Under Pulsed ConditionsDocument10 pagesIncreased VCSEL Output Power Under Pulsed Conditionsvijila vargheseNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy Resource and Utilization Technologies: Dr. Ram ChandraDocument34 pagesSolar Energy Resource and Utilization Technologies: Dr. Ram ChandraPrashant KumarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics - Unit 1: EnergyDocument10 pagesChemical Engineering Thermodynamics - Unit 1: EnergyaargovindNo ratings yet
- Term Paper On Financial Performance AnalDocument41 pagesTerm Paper On Financial Performance AnalMd. Riyajul IslamNo ratings yet
- Mensuration Formula SheetDocument2 pagesMensuration Formula SheetDipin SuresanNo ratings yet
- Task1 - PP Interim PaymentDocument5 pagesTask1 - PP Interim Paymentillya amyra100% (1)
- BS 1881 Part 117 83 Spli Tensile StrengthDocument10 pagesBS 1881 Part 117 83 Spli Tensile Strengthrajeshji_000No ratings yet
- Liquidated and Unliquidated DamagesDocument6 pagesLiquidated and Unliquidated DamagesXinbby BeexinNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: NG Mei ShanDocument31 pagesPrepared By: NG Mei ShanAnis Syahirah FauziNo ratings yet
- AP1682E Calculator Isolated Flyback DesignDocument13 pagesAP1682E Calculator Isolated Flyback DesignAnonymous n30qTRQPoINo ratings yet
- BS873 - 4 Road Traffic Signs and Internally Illuminated BollardsDocument15 pagesBS873 - 4 Road Traffic Signs and Internally Illuminated BollardsPrasanna S Kulkarni100% (1)
- Design of Proposed Soil Protection For Cliff Soil in Balimbing, Tanay RizalDocument1 pageDesign of Proposed Soil Protection For Cliff Soil in Balimbing, Tanay RizalReiBañezNo ratings yet
- CSE 331 - Final - Assignment - v2Document5 pagesCSE 331 - Final - Assignment - v2S.M. Imam Jahed Hossain 1511500642No ratings yet
- 6.2c. Critical Parth Method (CPM)Document3 pages6.2c. Critical Parth Method (CPM)sokogi reksaciptaNo ratings yet
- Lattice Vibrations, Part I: Solid State Physics 355Document22 pagesLattice Vibrations, Part I: Solid State Physics 355Anonymous 9rJe2lOskxNo ratings yet
- Senior Class FormulaeDocument8 pagesSenior Class FormulaeOP GuptaNo ratings yet
- Programm of WorksDocument4 pagesProgramm of WorksLekins Sefiu YekiniNo ratings yet
- Signals and SystemsDocument17 pagesSignals and SystemsSanthosh Vegeta Goku GNo ratings yet
- ME2151Document6 pagesME2151Delroy JqNo ratings yet
- Sadiku 5th Ed Chapter 15Document74 pagesSadiku 5th Ed Chapter 15Lucas PlentzNo ratings yet
- Z-Transform: E) KT T (L Z eDocument23 pagesZ-Transform: E) KT T (L Z enenusakNo ratings yet
- Signal&systemDocument2 pagesSignal&systemJariey SallehNo ratings yet
- ELEG 3124 Fourier Series and Transforms AssignmentsDocument16 pagesELEG 3124 Fourier Series and Transforms AssignmentsNguyễn Văn ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Proakis ProblemsDocument4 pagesProakis ProblemsJoonsung Lee0% (1)
- Question Bank EE V S&SDocument10 pagesQuestion Bank EE V S&SAbhNo ratings yet
- Signals and Systems: Assignment-1 Monsoon 2020Document3 pagesSignals and Systems: Assignment-1 Monsoon 2020NishkarshNo ratings yet
- Assignment For Signal AnalysisDocument2 pagesAssignment For Signal AnalysisAhmed EwadaNo ratings yet
- Signals and Networks Assignment 2Document6 pagesSignals and Networks Assignment 2Avikalp SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Ect204 Signals and Systems, June 2022Document4 pagesEct204 Signals and Systems, June 2022instapc0210No ratings yet
- Midterm Exam Paper No.1: EE2001E: Signals and SystemsDocument2 pagesMidterm Exam Paper No.1: EE2001E: Signals and SystemsHưng NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam Paper No.1: EE2001E: Signals and SystemsDocument2 pagesMidterm Exam Paper No.1: EE2001E: Signals and SystemsHưng NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Question Bank ECE IV S&SDocument10 pagesQuestion Bank ECE IV S&SAbhNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 01Document2 pagesAssignment No 01mallikarjunbpatilNo ratings yet
- Nec 303Document4 pagesNec 303Jane MuliNo ratings yet
- Signals and Systems: 18EC45 Model Question Paper-2 With Effect From 2019-20 (CBCS Scheme)Document3 pagesSignals and Systems: 18EC45 Model Question Paper-2 With Effect From 2019-20 (CBCS Scheme)siddhu 2002No ratings yet
- Exercises For Signals and Systems (Part One)Document3 pagesExercises For Signals and Systems (Part One)Vincent YuchiNo ratings yet
- Ss QuetionsDocument7 pagesSs QuetionsSalai Kishwar JahanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 - Systems (Exercises)Document3 pagesTutorial 2 - Systems (Exercises)LEIDYDANNYTSNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document2 pagesTutorial 1HarshaNo ratings yet
- SS Dec 15Document4 pagesSS Dec 15SAURABH BHISENo ratings yet
- 2024_ELEC3004_Problem_Set_1Document4 pages2024_ELEC3004_Problem_Set_1songpengyuan123No ratings yet
- Signals & System Lecture by OppenheimDocument10 pagesSignals & System Lecture by OppenheimJeevith JeeviNo ratings yet
- Signals and Systems (ELE-202) RCS (EngineeringDuniya - Com)Document2 pagesSignals and Systems (ELE-202) RCS (EngineeringDuniya - Com)Sudhakar JoshiNo ratings yet
- Ec3354 Signals and SystemsDocument57 pagesEc3354 Signals and SystemsParanthaman GNo ratings yet
- Assignment-1: Signal & System (C2)Document2 pagesAssignment-1: Signal & System (C2)jeevan saiNo ratings yet
- EEB731 Signals and Systems: Tutorial 2 Q1Document2 pagesEEB731 Signals and Systems: Tutorial 2 Q1Prince RaynalNo ratings yet
- Mumbai University Signals and Systems University QuestionsDocument2 pagesMumbai University Signals and Systems University QuestionsshilpaNo ratings yet
- Sigsys 1Document3 pagesSigsys 1Rounak MandalNo ratings yet
- Exercises For Signals and Systems (Part Four)Document3 pagesExercises For Signals and Systems (Part Four)Vincent YuchiNo ratings yet
- Signals 1Document15 pagesSignals 1Rupesh SushirNo ratings yet
- Signals & Systems Questions Set 01Document13 pagesSignals & Systems Questions Set 01Sachin Singh NegiNo ratings yet
- Jntuworld: R09 Set No. 2Document8 pagesJntuworld: R09 Set No. 2Ysurya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Ec010403 Signals and Systems Questionbank PDFDocument16 pagesEc010403 Signals and Systems Questionbank PDFSriju RajanNo ratings yet
- Signals and Systems: Dr. MuayadDocument11 pagesSignals and Systems: Dr. MuayadallyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document2 pagesTutorial 3Prince RaynalNo ratings yet
- Integrated Dual Degree (B.Tech.+M.Tech.) Examination Electronics & Communication EngineeringDocument4 pagesIntegrated Dual Degree (B.Tech.+M.Tech.) Examination Electronics & Communication EngineeringNaresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document2 pagesTutorial 1joahua mickkinNo ratings yet
- ECE102 hw2Document5 pagesECE102 hw2Yi LinNo ratings yet
- Tables of Generalized Airy Functions for the Asymptotic Solution of the Differential Equation: Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTables of Generalized Airy Functions for the Asymptotic Solution of the Differential Equation: Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Ent300 - Business PlanDocument43 pagesEnt300 - Business PlanMirza Danish22% (18)
- Chapter 1 - Principles of ManagementDocument17 pagesChapter 1 - Principles of ManagementMirza DanishNo ratings yet
- ECE351 April 11'Document8 pagesECE351 April 11'Mirza DanishNo ratings yet
- ECG304 - Highway Engineering UiTM OCTDocument7 pagesECG304 - Highway Engineering UiTM OCTMirza DanishNo ratings yet
- ECG304 - Highway Engineering UiTM March2013Document7 pagesECG304 - Highway Engineering UiTM March2013Mirza DanishNo ratings yet
- Calculus 2 A Simplified Text in Integral CalculusDocument150 pagesCalculus 2 A Simplified Text in Integral CalculusRic NapusNo ratings yet
- OceanographyDocument114 pagesOceanographyJanus MalikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Application of DifferentiationDocument33 pagesChapter 3 Application of DifferentiationAdron LimNo ratings yet
- BC MC P1ansDocument17 pagesBC MC P1anssharon cha100% (1)
- BTech AEIE Syllabus June2019Document80 pagesBTech AEIE Syllabus June2019Buzz PriyanshuNo ratings yet
- A1 - Full Papers PS2 10355 2022Document11 pagesA1 - Full Papers PS2 10355 2022DmitryNo ratings yet
- Math 31 IB HL - SL (Areas - Volumes) With AnswersDocument4 pagesMath 31 IB HL - SL (Areas - Volumes) With AnswersKabir MehtaNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Programming For Engineers: Course Objectives Course OutcomesDocument2 pagesMathematical Programming For Engineers: Course Objectives Course Outcomeskishore_k777No ratings yet
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Engr3300.003.10f Taught by Arash Loloee (Axl018200)Document5 pagesUT Dallas Syllabus For Engr3300.003.10f Taught by Arash Loloee (Axl018200)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupNo ratings yet
- Mathematics MITDocument30 pagesMathematics MITSalwa NursyahidaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Harmonic AnalysisDocument33 pagesIntroduction to Harmonic AnalysisEram KhanNo ratings yet
- 12th Board Math Lecture PlannerDocument2 pages12th Board Math Lecture PlannerAditya Singh PatelNo ratings yet
- B.Tech CSE Curriculum Siddharth Institute of EngineeringDocument121 pagesB.Tech CSE Curriculum Siddharth Institute of EngineeringSureshNo ratings yet
- Mat 225 Business Calculus: Basic InformationDocument9 pagesMat 225 Business Calculus: Basic InformationCameronNo ratings yet
- Predicting The FutureDocument253 pagesPredicting The FuturemariozappaNo ratings yet
- Resolution of Singularities For Multi-Loop Integrals: Christian Bogner and Stefan WeinzierlDocument23 pagesResolution of Singularities For Multi-Loop Integrals: Christian Bogner and Stefan WeinzierlWiluam Rutherford BondNo ratings yet
- Direct Numerical Integration MethodsDocument19 pagesDirect Numerical Integration MethodsallentvmNo ratings yet
- DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS GUIDEDocument13 pagesDIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS GUIDECorina UrbinaNo ratings yet
- Integral Cryptanalysis (Extended Abstract)Document16 pagesIntegral Cryptanalysis (Extended Abstract)Ta Thanh DinhNo ratings yet
- JEE Advanced 2018: Physics SyllabusDocument13 pagesJEE Advanced 2018: Physics SyllabusBalaji Yaswanth VankalaNo ratings yet
- BSc-Phys-Hon-CBCS (2020) PDFDocument139 pagesBSc-Phys-Hon-CBCS (2020) PDFBikash DeyNo ratings yet
- Further Pure 2 and 3 For OcrDocument14 pagesFurther Pure 2 and 3 For Ocrmardel110% (2)
- Textile I & Ii PDFDocument22 pagesTextile I & Ii PDFRaja PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Putting Differentials Back Into CalculusDocument14 pagesPutting Differentials Back Into Calculus8310032914No ratings yet
- Jiao (2020 Berkeley) - Spectral Representation of Random ProcessesDocument5 pagesJiao (2020 Berkeley) - Spectral Representation of Random ProcessesconfinexNo ratings yet
- VTU SEM 1 Scheme of Evaluation and SyllabusDocument13 pagesVTU SEM 1 Scheme of Evaluation and SyllabusAdilHEngineerNo ratings yet
- Reducing IVPs and BVPs to Integral EquationsDocument17 pagesReducing IVPs and BVPs to Integral EquationsSyeda Tehmina100% (1)
- Ometry B098MMT32KDocument472 pagesOmetry B098MMT32KEh PhotographyNo ratings yet
- (Series - Graduate Texts in Mathematics, Vol. 153) William Fulton-Algebraic Topology - A First Course-Springer-Verlag (1995)Document449 pages(Series - Graduate Texts in Mathematics, Vol. 153) William Fulton-Algebraic Topology - A First Course-Springer-Verlag (1995)Nahuel García100% (3)