Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics of Sound and Motion Concepts
Uploaded by
JinYuenWongOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics of Sound and Motion Concepts
Uploaded by
JinYuenWongCopyright:
Available Formats
Class 1
Wednesday, January 14, 2015
10:07 PM
Distance - measurement from 1 point to another
Speed - distance covered in specific time. (distance/time)
Displacement - (shortest distance from the initial to the final position of a point P)
Mass - amount of matter
Acceleration - increase in speed
Velocity - speed with direction
Compression - reduction in volume
Rarefaction - increase in volume, decrease in pressure,
Attack - speed from no sound to peak.
Transient - movements/vibrations happen really quickly
Sustain - lasts for a longer duration
Decay - Amount of time taken for something to drop.
Frequency -Number of complete oscillation in 1 sec. ( 1Hz = 1 complete movement
in 1 sec)
Wavelength - Distance between 2 similar points (*inversely proportional to
frequency)
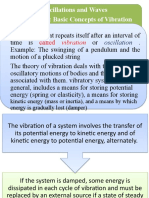
To have sound, you must have vibration. V ibration creates sound.
The quantity of sound contained in frequency is pitch.
Basic definition
Mass - the quantity of matter that a body contains, as measured by its acceleration
under the force exerted on it by a gravitational field.
Force - an influence tending to change the motion of a body or produce motion or
stress in a stationary body
Distance - an amount of space between two points or things. Usually measured in
meters ( m) or feet
Displacement - Change of position of a point or object in reference to its previous
position
Acceleration - the rate of change of velocity per unit of time
Velocity - rate of change of position or speed of something in a given direction. It is
measured in meters per second ( m/s). Both speed and direction is required to
define velocity
Acceleration - the rate of change of velocity per unit of time
Velocity - rate of change of position or speed of something in a given direction. It is
measured in meters per second ( m/s). Both speed and direction is required to
define velocity
Pressure - the continuous physical force exerted on or against an object by
something in contact with it. Defined as force per unit area applied to an object
Compression - reduction in volume causing an increase in pressure
Oscillation - move or swing back and forth at a regular speed
Attack - the initial transient of a musical note or the time taken for a sound to reach
its initial peak
Transient - a sound that is not sustained. Rapid attack and decay. Eg. Snare drum
Cycle - series of events that are regularly repeated in the same order
Pressure - the continuous physical force exerted on or against an object by
something in contact with it. Defined as force per unit area applied to an object
Compression - reduction in volume causing an increase in pressure
Rarefaction - the opposite of compression. Increase in volume causing reduction in
pressure
Sound
Sound is vibrations perceived by the sense of hearing
In more technical language, sound is an alternation in pressure, particle
displacement, or particle velocity propagated in an elastic material or series
of mechanical compressions and rarefactions or longitudinal waves that
successively propagate through a medium.
Sounds travels as longitudinal waves
Simple Harmonic motion (SHM)
Simple harmonic motion is neither driven nor damped and the motion is
periodic and repeats itself at standard intervals in a specific manner -
described as being sinusoidal or that of a sine function with constant
amplitude
A sine wave can be considered as the purest or simplest form of oscillatory
representation where as a common musical sound will contain complex
waveform with harmonic content
periodic and repeats itself at standard intervals in a specific manner -
described as being sinusoidal or that of a sine function with constant
amplitude
A sine wave can be considered as the purest or simplest form of oscillatory
representation where as a common musical sound will contain complex
waveform with harmonic content
You might also like
- Physics NotesDocument4 pagesPhysics Notesevelynkanuri86No ratings yet
- Physics Quiz ReviewerDocument7 pagesPhysics Quiz ReviewerJennylyn CariagaNo ratings yet
- Sound: Characteristics and PropagationDocument27 pagesSound: Characteristics and PropagationDevansh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sound EnergyDocument5 pagesSound EnergySherilyn ApostolNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument28 pagesSoundKunal100% (1)
- Properties of Sound: ACOUSTICSDocument51 pagesProperties of Sound: ACOUSTICSVeda DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Physics of Oscillations and Waves ChapterDocument36 pagesPhysics of Oscillations and Waves ChapterMerawi TilahunNo ratings yet
- 12. SoundDocument16 pages12. SoundRSNo ratings yet
- Sound 2nd JanDocument43 pagesSound 2nd JanKashish TilokaniNo ratings yet
- Motion: Change Its VelocityDocument3 pagesMotion: Change Its VelocityUmakishueNo ratings yet
- SHM Waves Chapter ReviewDocument6 pagesSHM Waves Chapter ReviewasdfNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Wave (Form 5)Document29 pagesChapter 1 - Wave (Form 5)kcnjojo91% (11)
- Frequency of Vibrating ForkDocument2 pagesFrequency of Vibrating ForkbaobeipandaNo ratings yet
- Wave NotesDocument6 pagesWave NotesVittorio ApidosNo ratings yet
- Sound and Its CharacteristicsDocument16 pagesSound and Its CharacteristicsGian Louise BarolaNo ratings yet
- Vibrations and WavesDocument44 pagesVibrations and Wavesحسن الدريديNo ratings yet
- Pitch and Frequency Intensity and The Decibel ScaleDocument3 pagesPitch and Frequency Intensity and The Decibel ScaleCatalina G. EnerioNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument23 pagesWavesAbdullah alifNo ratings yet
- Vibrations and WavesDocument2 pagesVibrations and WavesJonathanNo ratings yet
- Sound Grade 7Document1 pageSound Grade 7Bik BokNo ratings yet
- Physics NotesDocument12 pagesPhysics NotesBaseerArafaatNo ratings yet
- Physics Final NotesDocument15 pagesPhysics Final NotesalzainaNo ratings yet
- Longitudinal WaveDocument5 pagesLongitudinal WaveChristineNo ratings yet
- Study GuideDocument6 pagesStudy GuideIrene DimatulacNo ratings yet
- Acoustics - Module 1Document40 pagesAcoustics - Module 1Ashna AshrafNo ratings yet
- Waves NotesDocument7 pagesWaves Notesswhchang1No ratings yet
- WavesDocument37 pagesWavesmohammed issaNo ratings yet
- Sound NotesDocument5 pagesSound NotesumaNo ratings yet
- Sound: Wave That Carries EnergyDocument15 pagesSound: Wave That Carries EnergyJohn Lester TabianNo ratings yet
- Sound IXDocument35 pagesSound IXarpankrishna739No ratings yet
- 18 ARC 74 ACOUSTICSDocument25 pages18 ARC 74 ACOUSTICSsuryaa ksNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument21 pagesSounduma mishraNo ratings yet
- AccousticsDocument62 pagesAccousticsSahil MistryNo ratings yet
- 2312221519049139Document4 pages2312221519049139Shriya SNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 12 Sound NotesDocument3 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 12 Sound Notessanthoshsabarish4No ratings yet
- Acoustics PDFDocument28 pagesAcoustics PDFCharles Harvey Cabrezos DaabayNo ratings yet
- Sound SDocument23 pagesSound Spaul camitNo ratings yet
- BUILDING UTILITIES 2: SOUND THEORY FUNDAMENTALSDocument15 pagesBUILDING UTILITIES 2: SOUND THEORY FUNDAMENTALSIzzah LNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Waves NotesDocument23 pagesCharacteristics of Waves Notesapi-449002661No ratings yet
- 12 SoundDocument22 pages12 SoundAyush NayakNo ratings yet
- Vibration 1Document39 pagesVibration 1Jobin VargheseNo ratings yet
- Something About Sound Wave: Hui LeiDocument19 pagesSomething About Sound Wave: Hui Leimohan raoNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 12 Sound Revision NotesDocument6 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 12 Sound Revision NotesYogesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit-I (INTRODUTION)Document30 pagesUnit-I (INTRODUTION)GokulNo ratings yet
- Building Services Iii - Sar 1302: Unit - 1Document97 pagesBuilding Services Iii - Sar 1302: Unit - 1Mahamud MusaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Waves, Sound, Light Properties & InteractionsDocument63 pagesMechanical Waves, Sound, Light Properties & InteractionsJylle Vernie HembraNo ratings yet
- Week 8 - Sound and LightDocument68 pagesWeek 8 - Sound and LightGenel Yutuc100% (1)
- Course Outline About SoundsDocument1 pageCourse Outline About SoundsJayson PangibitanNo ratings yet
- Periodic MotionDocument15 pagesPeriodic MotionObogne, Lynn Clarisse C.No ratings yet
- Sound Amplitude PitchDocument19 pagesSound Amplitude PitchVase VaseskiNo ratings yet
- UT LEVEL 2 Part 1Document150 pagesUT LEVEL 2 Part 1RobertRoy100% (1)
- SOUNDDocument21 pagesSOUNDdav borlNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument36 pagesWavesjomelleann.pasolNo ratings yet
- Acoustics 1 (Sound Theory)Document21 pagesAcoustics 1 (Sound Theory)bishal dasNo ratings yet
- 09 Science Notes ch+12 Sound PDFDocument6 pages09 Science Notes ch+12 Sound PDFafhamNo ratings yet
- Physics PrinciplesDocument38 pagesPhysics PrinciplesShoSheetaNo ratings yet
- How Do Waves Behave? How Are They Measured? Physics Lessons for Kids | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandHow Do Waves Behave? How Are They Measured? Physics Lessons for Kids | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- 08 Longitudinal WavesDocument3 pages08 Longitudinal Wavesapi-235269401No ratings yet
- Physics Reviewer MotionDocument9 pagesPhysics Reviewer MotionCamaddu GelaicaNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer 3rd QuarterDocument13 pagesScience Reviewer 3rd Quartergenshingrinding2023No ratings yet
- Ching Chong - 1 - Full ScoreDocument3 pagesChing Chong - 1 - Full ScoreJinYuenWongNo ratings yet
- Titas Project: by Wong Jin YuenDocument8 pagesTitas Project: by Wong Jin YuenJinYuenWongNo ratings yet
- Slow Love Lead SheetDocument2 pagesSlow Love Lead SheetJinYuenWongNo ratings yet
- Blue Room DrumsDocument3 pagesBlue Room DrumsJinYuenWongNo ratings yet
- I Am The Walrus Lead SheetDocument2 pagesI Am The Walrus Lead SheetJinYuenWong0% (1)
- United States of EurasiaDocument3 pagesUnited States of EurasiaJinYuenWong100% (1)
- hw1 SolutionsDocument3 pageshw1 SolutionsFatih İnalNo ratings yet
- Specific Energy and Critical Depth Lec #1Document30 pagesSpecific Energy and Critical Depth Lec #1Shoaib FarooqNo ratings yet
- Axial & Radial ThrustDocument35 pagesAxial & Radial ThrustMohamed RadwanNo ratings yet
- Naca 64-012 PDFDocument38 pagesNaca 64-012 PDFLucía Ojer GuerraNo ratings yet
- Understanding Vibration Can Help Prevent Pump FailuresDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Vibration Can Help Prevent Pump FailuresvfrpilotNo ratings yet
- Homework #4 Due Date: 02/28/2020Document2 pagesHomework #4 Due Date: 02/28/2020Gaga852No ratings yet
- 환경유체역학 강의 1Document38 pages환경유체역학 강의 1HyunJoon, KimNo ratings yet
- Lab - Acceleration of Gravity - Ball Toss - OnlineDocument5 pagesLab - Acceleration of Gravity - Ball Toss - Onlineapi-356551305No ratings yet
- Flow Through Pipe Presentation by 4 StudentsDocument18 pagesFlow Through Pipe Presentation by 4 StudentsDurgesh KolheNo ratings yet
- fypANG, ENGR 62, StanfordDocument35 pagesfypANG, ENGR 62, StanfordsuudsfiinNo ratings yet
- Hydrodynamic Calculation Needle ValveDocument25 pagesHydrodynamic Calculation Needle ValveEng-CalculationsNo ratings yet
- PSV SIZING CALCULATIONSDocument3 pagesPSV SIZING CALCULATIONSAthiphap SrisupareerathNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 - Fluids - ปกติ - Google FormsDocument4 pagesQuiz 2 - Fluids - ปกติ - Google FormsVej JuttNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Class XI Laws of MotionDocument2 pagesWorksheet Class XI Laws of MotionroythomascNo ratings yet
- A Train Travelling at 40 M / S Takes 2.0 S To Pass The Man. What Is The Length of The Train? M MC 40 MD 80 MDocument4 pagesA Train Travelling at 40 M / S Takes 2.0 S To Pass The Man. What Is The Length of The Train? M MC 40 MD 80 MDaniel CannywoodNo ratings yet
- Drag CoefficientDocument61 pagesDrag CoefficientSaurabh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Visual AidDocument20 pagesVisual AidYhan Brotamonte BoneoNo ratings yet
- Aeromodelling Basics Dynamics PDFDocument20 pagesAeromodelling Basics Dynamics PDFmanoj100% (1)
- Topic T4: Pumps and Turbines AUTUMN 2013 Objectives: Laws To Calculate Pump Characteristics at Different SpeedsDocument19 pagesTopic T4: Pumps and Turbines AUTUMN 2013 Objectives: Laws To Calculate Pump Characteristics at Different SpeedsTeguh SetionoNo ratings yet
- Pumps and Pumping SystemsDocument20 pagesPumps and Pumping SystemsLailatin QodriyahNo ratings yet
- Suction Specific Speed FromDocument18 pagesSuction Specific Speed FromAlda EnglandNo ratings yet
- C-D Nozzle ExperimentDocument3 pagesC-D Nozzle ExperimentKarthick MurugesanNo ratings yet
- Physics 11 4thDocument2 pagesPhysics 11 4thArseniojakejr FloresNo ratings yet
- Liquid Line SizingDocument12 pagesLiquid Line Sizinglolofm25No ratings yet
- Phy101 SPDocument5 pagesPhy101 SPFatima Haider Fatima HaiderNo ratings yet
- PE VI-MEG347A-CFD Syllabus 2020Document5 pagesPE VI-MEG347A-CFD Syllabus 2020Vaibhav AnandNo ratings yet
- MKP 05 en IC LST 001 Instrument IndexDocument5 pagesMKP 05 en IC LST 001 Instrument Indexsugeng wahyudiNo ratings yet
- La Tech: Physics 201: Practice Exam 1Document8 pagesLa Tech: Physics 201: Practice Exam 1Q_TNo ratings yet
- PS2 Syllabus 2017 3Document3 pagesPS2 Syllabus 2017 3rayNo ratings yet
- Modul 8 Perhitungan Debit Menggunakan VenturimeterDocument7 pagesModul 8 Perhitungan Debit Menggunakan Venturimeter222021169 BAIZAL FIRMANSYAHNo ratings yet