Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Parts of A Computer
Parts of A Computer
Uploaded by
alucardcolomaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Parts of A Computer
Parts of A Computer
Uploaded by
alucardcolomaCopyright:
Available Formats
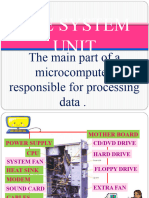
Random-access memory (RAM /rm/) is a form of computer data storage.
A random-access
memory device allows data items to be accessed (read or written) in almost the same amount of
time irrespective of the physical location of data inside the memory
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive or fixed disk[b] is a data storage device used for
storing and retrieving digitalinformation using one or more rigid rapidly rotating disks (platters)
coated with magnetic material.
A power supply unit (PSU) converts mains AC to low-voltage regulated DC power for the internal
components of a computer. Modern personal computers universally use switched-mode power
supplies.
A central processing unit (CPU) is the electronic circuitry within a computer that carries out
the instructions of a computer program by performing the basic arithmetic, logical, control
and input/output (I/O) operations specified by the instructions.
A motherboard (sometimes alternatively known as the mainboard, system
board, baseboard, planar board or logic board,[1] or colloquially, a mobo) is the main printed
circuit board (PCB) found in general purpose microcomputers and other expandable systems. It
holds and allows communication between many of the crucial electronic components of a system,
such as the central processing unit(CPU) and memory, and provides connectors for
other peripherals.
You might also like
- Hayat Ullah Lab WorkDocument47 pagesHayat Ullah Lab WorkHayat UllahNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware - WikipediaDocument51 pagesComputer Hardware - WikipediaNaniNo ratings yet
- Computer HardwareDocument37 pagesComputer HardwareTECH REALMNo ratings yet
- Write About Computer PartsDocument12 pagesWrite About Computer PartsThenaNo ratings yet
- CSS Ncii G 11 ReviewerDocument7 pagesCSS Ncii G 11 Reviewerjustin cabaneroNo ratings yet
- ReyesDocument17 pagesReyesMg EnopiaNo ratings yet
- Computer HardwareDocument1 pageComputer HardwareJenny Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- System Unit-The Main Part of A Microcomputer, Sometimes Called TheDocument6 pagesSystem Unit-The Main Part of A Microcomputer, Sometimes Called TheLarry RicoNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware - WikipediaDocument10 pagesComputer Hardware - Wikipediajustin time compilerNo ratings yet
- Abigail Gwyneth B. Bunao Jorwen BongcalotDocument18 pagesAbigail Gwyneth B. Bunao Jorwen BongcalotSalvador DominiqueNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware - WikipediaDocument35 pagesComputer Hardware - WikipediaAffif AbidNo ratings yet
- Computer DevicesDocument16 pagesComputer DevicesREYNEL BISTANo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computing Lab: Assignment On Assignment NameDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Computing Lab: Assignment On Assignment NameHamza KhanNo ratings yet
- Random-Access Memory (RAM) Is A Type of Computer DataDocument1 pageRandom-Access Memory (RAM) Is A Type of Computer DataasadNo ratings yet
- Computer HardwareDocument4 pagesComputer HardwareEhnan J LamitaNo ratings yet
- Cpu PartsDocument3 pagesCpu PartsJalil AzzadNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint IctDocument22 pagesPowerpoint IctAubreyNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Computer & Their UsesDocument21 pagesParts of The Computer & Their Usesgizelle heginaNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: Group 4Document13 pagesSubmitted By: Group 4Lorena TeofiloNo ratings yet
- The Computer System UnitDocument18 pagesThe Computer System UnitJohn Alfredo Koykoy VicioNo ratings yet
- Building A Computer SystemDocument4 pagesBuilding A Computer SystemKay LinnNo ratings yet
- CHS Set1 Week3-4Document3 pagesCHS Set1 Week3-4Omar Sharif CuyuganNo ratings yet
- IT 101 - Assignment Major Hardware ComponentsDocument2 pagesIT 101 - Assignment Major Hardware ComponentsJohn Clifford MantosNo ratings yet
- Major Hardware Components of A Computer SystemDocument9 pagesMajor Hardware Components of A Computer SystemMark anthony DuranNo ratings yet
- Computer InstallationDocument23 pagesComputer Installationkhatib mtumweniNo ratings yet
- Hardware Components of The System UnitDocument2 pagesHardware Components of The System UnitRebecca EjandraNo ratings yet
- Basic Set of Computer DevicesDocument22 pagesBasic Set of Computer DevicesLeah Pinili BlancoNo ratings yet
- مصطلحات وملحوظات مهمة لازم تعرفهاDocument8 pagesمصطلحات وملحوظات مهمة لازم تعرفهاmido.ezz05No ratings yet
- Parts of PCDocument2 pagesParts of PCAlex -No ratings yet
- Computer Hardware: (System Unit and Motherboard Parts)Document2 pagesComputer Hardware: (System Unit and Motherboard Parts)Gelo C. CondinatoNo ratings yet
- Internal HardwareDocument16 pagesInternal HardwareNathaniel GauranaNo ratings yet
- Computer Devices - ICT 9Document18 pagesComputer Devices - ICT 9Gerald TorrezNo ratings yet
- Wa0010.Document3 pagesWa0010.amanray2604No ratings yet
- Parts of The System Unit: Tle ClassDocument13 pagesParts of The System Unit: Tle ClassXavierNo ratings yet
- Hardware ComponentsDocument14 pagesHardware Componentsxxddariusxx19No ratings yet
- The Major Motherboard Components and Their FunctionsDocument9 pagesThe Major Motherboard Components and Their FunctionsJosekutty N Joseph75% (4)
- Computer Week 1Document13 pagesComputer Week 1Jan Paulo SantosNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document12 pagesPresentation 2Sanskar SethNo ratings yet
- Hardware PortfolioDocument5 pagesHardware Portfolioapi-417400228No ratings yet
- Computer PartsDocument2 pagesComputer PartsJayson MolejonNo ratings yet
- 1internal Parts of ComputerDocument53 pages1internal Parts of Computersheeshableangeline208No ratings yet
- Per Formance Task: Specifcation of Hard Disk Drive and Power Supply UnitDocument14 pagesPer Formance Task: Specifcation of Hard Disk Drive and Power Supply UnitSammy LibbyNo ratings yet
- Gomez Gimuel M. Assignment 3 CyberDocument1 pageGomez Gimuel M. Assignment 3 CyberSUNGA NIKKI KARENNo ratings yet
- System Unit and Storage DevicesDocument22 pagesSystem Unit and Storage DevicesJoyce Ann AmalangNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument6 pagesMotherboardGururajHudgiNo ratings yet
- Basic Parts of A ComputerDocument20 pagesBasic Parts of A ComputerHaru100% (1)
- Personal Computer HardwareDocument5 pagesPersonal Computer HardwareClaudia MarianaNo ratings yet
- Computer Unit 1Document6 pagesComputer Unit 1hindrixcatayas8No ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument2 pagesAssignmentMaon JulinaNo ratings yet
- MuntasirDocument1 pageMuntasirabdurahmonzodamuntasirNo ratings yet
- Personal Computer Parts: Central Processing UnitDocument3 pagesPersonal Computer Parts: Central Processing UnitEduardo CortesNo ratings yet
- Major Components of ComputerDocument29 pagesMajor Components of ComputerMary Jane Blanco FioNo ratings yet
- UC 1 Computer HardwareDocument27 pagesUC 1 Computer HardwareCorazon ReymarNo ratings yet
- Ict Assignment: Computer Componets and MemoryDocument3 pagesIct Assignment: Computer Componets and MemorySawrabNo ratings yet
- Read Me After Pre TestDocument4 pagesRead Me After Pre TestNa DzNo ratings yet
- Hardware and Software (Full Form)Document1 pageHardware and Software (Full Form)akaishamahadevanNo ratings yet
- Basicmachineorganization 170222183810Document9 pagesBasicmachineorganization 170222183810saira ramzanNo ratings yet
- Von Neumann ArchitectureDocument13 pagesVon Neumann ArchitectureKyla Claire BiñasNo ratings yet
- Student Handout 1 Hardware Components of A ComputerDocument4 pagesStudent Handout 1 Hardware Components of A ComputerLemuel Condes100% (1)