Professional Documents
Culture Documents
How To Perfrom PN Diode Characteristics
Uploaded by
krishnaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
How To Perfrom PN Diode Characteristics
Uploaded by
krishnaCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
PN - JUNCTION DIODE CHARACTERISTICS
AIM:
a) To Plot V-I characteristics of PN junction diode both in Forward Bias and Reverse
Bias.
b) To calculate the Forward Static and dynamic resistance of the diode at a particular
operating point.
Apparatus Required:
S.No
1
2
3
5
6
7
8
Name of the
Equipment/ Component
Diode
Resistor
Transistor regulated power
Supply
Voltmeter
Ammeter
Connecting wires
Bread board
Specifications:
For silicon diode IN4007:
Max. Forward current
= 1A
Max. Reverse current = 30A
Max. Forward voltage
= 0.8V
Max. Reverse voltage
= 1000V
Max. Power Dissipation = 30mW
Temperature
Circuit Diagrams:
= -65 to 2000 c
Number/range
Quantity
IN4007
100
1
1
(0-30)V,1A
(0-2)V, (0-50)V
(0-100)mA,( 0-100)A
---
1
1
1
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUIT LAB
DEPARTMENT
ECE
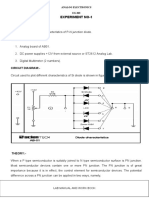
Fig.a .PN junction diode forward bias
Fig.b. PN junction diode reverse bias
Procedure:
a) Forward Bias:
1.
Connect the circuit as shown in Fig A.
2.
Apply the supply voltage, VIN in steps of 0.2V from 0V to 1V, after then vary
VIN in steps of 1v and note down the voltage at which current starts. Also note
the exact voltage at which current starts .ie cut-in voltage.
3.
Measure the voltage across the diode (Vd) from voltmeter and current through
the diode (Id) from ammeter for different steps of applied voltage, Vin.
b) Reverse Bias:
4.
Connect the circuit as shown in Fig B.
5.
Apply the supply voltage, Vin in steps of 2V from 0V to 30V.
ENGINEERING COLLEGE
Page 2
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUIT LAB
DEPARTMENT
6.
ECE
Measure the voltage across the diode (Vd) from voltmeter and current through
the diode (Id) from ammeter for different steps of applied voltage, Vin.
7.
Draw a graph between the voltage and current for both forward bias and
reverse bias.
8.
Identify the linear region of the forward bias curve and fix the operating point
at the center, calculate the static, dynamic resistances of the diode. Also find
reverse resistance from the reverse bias curve.
Tabular Forms:
a) Forward Bias:
S. No.
Diode Voltage
Vd (Volts)
Diode Current
Id (mA )
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
b) Reverse Bias:
S.NO
Diode Voltage
Diode Current
Vd (Volts)
Id(A)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
ENGINEERING COLLEGE
Page 3
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUIT LAB
DEPARTMENT
ECE
Model Graph:
Calculations:
1. Static Forward Resistance ,R =Vf/If=
2. Dynamic Forward Resistance, r =Vf/If=
3. Reverse Resistance=Vr/Ir=
4. Cut-in Voltage of diode=
Result:
ENGINEERING COLLEGE
Page 4
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUIT LAB
DEPARTMENT
ENGINEERING COLLEGE
ECE
Page 5
You might also like
- Lab 2 - Diode CharacteristicsDocument7 pagesLab 2 - Diode CharacteristicsFasil EndalamawNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 Wave Shaping CircuitsDocument9 pagesExperiment 2 Wave Shaping CircuitsMaria Abia Lapena50% (2)
- Full Wave Rectifier Characteristics LabDocument36 pagesFull Wave Rectifier Characteristics LabTushar Kush100% (4)
- PN Junction Diode Characteristics: Experiment No: 1Document4 pagesPN Junction Diode Characteristics: Experiment No: 1ramunagatiNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 1 FinalDocument6 pagesExperiment No 1 Finaldipesh mandaviNo ratings yet
- Osmania University BE 2/4 Electronic Devices Lab ManualDocument88 pagesOsmania University BE 2/4 Electronic Devices Lab ManualAbdulShehzadNo ratings yet
- Aero Lab Manual 2014-2015Document23 pagesAero Lab Manual 2014-2015Muthyala AkhilNo ratings yet
- EDC Lab I ManualsDocument101 pagesEDC Lab I ManualskattaswamyNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Devices and Circuits LaboratoryDocument53 pagesSemiconductor Devices and Circuits LaboratoryKaryampudi RushendrababuNo ratings yet
- Ee LabDocument28 pagesEe LabBalajiNo ratings yet
- EeeeDocument20 pagesEeeeমজুমদার অলিনNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.2: Objective: Study of Characteristics of Silicon DiodeDocument5 pagesExperiment No.2: Objective: Study of Characteristics of Silicon DiodeUday BhartiyaNo ratings yet
- Diode ExperimentDocument4 pagesDiode ExperimentShubham GoelNo ratings yet
- STP 211 Practical-1-1-1-1-1Document25 pagesSTP 211 Practical-1-1-1-1-1Abdulaziz MuhammedNo ratings yet
- Light Bulb and Diode CurvesDocument1 pageLight Bulb and Diode CurvesIbrahim BtNo ratings yet
- KEC151P - Lab - Experiments - UPDATED ONEDocument34 pagesKEC151P - Lab - Experiments - UPDATED ONEAkshat GuptaNo ratings yet
- Experiment NoDocument54 pagesExperiment Nohemant rathodNo ratings yet
- Plot V-I Characteristics of Zener DiodeDocument4 pagesPlot V-I Characteristics of Zener DioderamunagatiNo ratings yet
- List of Experiments: Diode Forward CharacteristicDocument22 pagesList of Experiments: Diode Forward CharacteristicrajeshNo ratings yet
- Electronics 1Document42 pagesElectronics 1Shanti Emmanuelle EscabarteNo ratings yet
- Diode, BJT, Zener, MosfetDocument10 pagesDiode, BJT, Zener, MosfetSundar Krishna MoorthyNo ratings yet
- ECCE4466: Power Electronics Student Lab Manual: Department of Electrical and Computer EngineeringDocument20 pagesECCE4466: Power Electronics Student Lab Manual: Department of Electrical and Computer Engineeringsenpai_mendozaNo ratings yet
- Automatic Power Factor Detection and CorDocument53 pagesAutomatic Power Factor Detection and CorAshritaNo ratings yet
- Ex 305Document51 pagesEx 305DineshKumarCholkarNo ratings yet
- Diode Characteristics PDFDocument16 pagesDiode Characteristics PDFJOECELLE ABLEGINANo ratings yet
- Characteristics of P-N Junction DiodeDocument38 pagesCharacteristics of P-N Junction Diodeanon_450523292No ratings yet
- SDC- Important Questions for Semiconductor Diodes and CircuitsDocument5 pagesSDC- Important Questions for Semiconductor Diodes and CircuitsInstagramNo ratings yet
- Principle of Electronics EnggDocument47 pagesPrinciple of Electronics EnggNilabh KumarNo ratings yet
- SDC Lab Manual - PDFDocument41 pagesSDC Lab Manual - PDFRonitNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronic Circuits Assignment QuestionsDocument6 pagesAnalog Electronic Circuits Assignment QuestionschaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law Verification on Diodes Lab (EEE 3100Document9 pagesOhm's Law Verification on Diodes Lab (EEE 3100tengyanNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument17 pagesLab ManualSatyam Govila100% (1)
- Edc Lab ManualDocument70 pagesEdc Lab ManualreneeshczNo ratings yet
- Expt 3 - Diode CharaDocument5 pagesExpt 3 - Diode Charaokay gNo ratings yet
- Ele456 1. DeneyDocument6 pagesEle456 1. Deneyjackal571No ratings yet
- Edc Manual RoseDocument48 pagesEdc Manual RoseRagabindu GuruNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 Circuit ElementsDocument8 pagesLab 1 Circuit ElementsDawood SulemanNo ratings yet
- FullDocument67 pagesFullKalaiselvan PunniyamoorthyNo ratings yet
- EDC 3rd SemDocument52 pagesEDC 3rd Semvijay kumar100% (1)
- Ecb 2182 Electronics and Microprocessors Lab Manual: S.Sadhish Prabhu, Ap/EceDocument63 pagesEcb 2182 Electronics and Microprocessors Lab Manual: S.Sadhish Prabhu, Ap/EceNeoNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual EE552Document50 pagesLab Manual EE552s.r.No ratings yet
- Electronic Devices & Circuits: Laboratory ManualDocument61 pagesElectronic Devices & Circuits: Laboratory ManualFadila IsmailNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual: Electrical Engineering Materials & Semiconductor Devices Lab (EC-317-F)Document41 pagesLab Manual: Electrical Engineering Materials & Semiconductor Devices Lab (EC-317-F)Ilavarasan TamizhNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument41 pagesLab ManualSyaoran7Li80% (5)
- Diod RectifierDocument35 pagesDiod RectifierRizalNo ratings yet
- Experiment # 1: P-N Junction Diode: TheoryDocument9 pagesExperiment # 1: P-N Junction Diode: Theorypoonginithi040% (1)
- Basic Electronics Half Wave Rectification LabDocument13 pagesBasic Electronics Half Wave Rectification LabPaa Kwesi ArhinfulNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices - Circuits Lab ManualDocument77 pagesElectronic Devices - Circuits Lab ManualpdnkiranNo ratings yet
- BEC - ASSIGNMENT I and IIDocument6 pagesBEC - ASSIGNMENT I and IIMansi BhatiaNo ratings yet
- ECAD2 Complete ManualDocument37 pagesECAD2 Complete ManualJeremy HensleyNo ratings yet
- Harrisob Laboratory No.1Document4 pagesHarrisob Laboratory No.1Harrison VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Experiment-No 2Document5 pagesExperiment-No 2carloNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1: Aim: TheoryDocument13 pagesExperiment No. 1: Aim: TheoryAyushiNo ratings yet
- Diode Characteristics LabDocument8 pagesDiode Characteristics LabFaisal KhalilNo ratings yet
- Elce221 Lab 1Document6 pagesElce221 Lab 1Little VoiceNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronic Devices and Circuits Lab ExperimentsDocument45 pagesBasic Electronic Devices and Circuits Lab ExperimentsChirag Sachdeva100% (2)
- EDC Lab ManualDocument68 pagesEDC Lab ManualRocky AdityaNo ratings yet
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsFrom EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsNo ratings yet