Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PCHEM Definitions Exam 2
Uploaded by
TanyaTouché0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views6 pagesnotes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentnotes
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views6 pagesPCHEM Definitions Exam 2
Uploaded by
TanyaTouchénotes
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Phase is a form of matter that is uniform throughout the chemical
composition and physical state.
Allotrope is a particular molecular form of an element (O2 and O3)
Polymorph is one of a number of solid phases of an element or
compound.
Phase transition is the spontaneous conversion of one phase into
another phase, occurs at a characteristic temperature for a given
pressure.
Transition temperature (Ttrs) is the temperature at which the two
phases are in equilibrium and Gibbs energy is minimized at the
prevailing pressure.
Thermal analysis detects a phase transition by nothing temperature
does not change even though heat is being added/removed.
Metastable phases are thermodynamically unstable phases that
persist because the transition is kinetically hindered.
Chemical potential is a measure of the potential that a substance
has for undergoing change in a system.
Phase diagram of pure substance shows the regions of pressure and
temperature at which its various phases are thermodynamically stable.
Phase boundaries (coexistence curves) show the values of p and T
at which phases coexist in equilibrium and their chemical potentials
are equal.
Vapor pressure is pressure of vapor in equilibrium with the liquid.
Sublimation pressure vapor pressure of the solid phase.
Boiling is the condition of free vaporization throughout the liquid.
Boiling temperature is the temperature at which the vapor pressure
of a liquid is equal to the external pressure.
Normal boiling point (Tb) is temperature of boiling point at 1 atm.
Standard boiling point is the temperature of boiling point at 1 bar.
Critical temperature (Tc) is the temperature where the liquid phase
does not exist.
Critical pressure (Pc) is the vapor pressure at the critical
temperature.
Supercritical fluid occurs at and above the critical temperature as a
uniform phase.
Melting/freezing temperature is when the solid and liquid phase
coexist in equilibrium.
Normal/melting freezing point (Tf) is the temperature of
freezing/melting at 1 atm.
Standard freezing point is the temperature of freezing/melting at 1
bar.
Triple point is a point at which the three phase boundaries meet.
Component is chemically independent constituent of a system.
Constituent of a system is the chemical species that is present.
Variance of a system is the number of intensive variables that can be
changed independently without disturbing the number of phases in
equilibrium.
Bivariant two degrees of freedom.
Partial vapor pressure is pressure of substance when pressure is
exerted onto the condensed phase.
Gas solvation is the attachment of molecules to gas-phase species.
Ehrenfest classification uses the behavior of the chemical potential
to classify phase transitions into different types.
First-order phase transition is a transition for which first derivative
of chemical potential with respect to temperature is discontinuous. (H
changes by a finite amount for an infinitesimal change of
temperature.)
Second-order phase transition is a transition in which the first
derivative of chemical potential with respect to temperature is
continuous but its second derivative is discontinuous. Implies that
volume and entropy do not change at the transition.
Lambda transition
First derivatives of chemical potentials with respect to pressure and
temperature are discontinuous at transition
Binary mixtures are a mixture of 2 components A and B.
Molar concentration (molarity, [J], c) is the amount of solute divided
by the volume of the solution.
Molality (b) is the amount of solute divided by the mass of the
solvent.
Partial molar volume of a substance A in a mixture is the change in
volume per mole of A added to a large volume of the mixture.
Ideal solutions are mixtures that obey Raoults law throughout the
composition range from pure A to pure B. (structurally similar
components)
Ideal-dilute solutions are mixtures for which the solute B obeys
Henrys law and the solvent A obeys Raoults law.
Raoults law provides relation between vapor pressure of substance
and mole fraction in a mixture, basis of definition of ideal solution.
Henrys law provides relation between vapor pressure of solute and
its mole fraction in a mixture, basis of the definition of an ideal-dilute
solution.
Excess functions are the difference between the observed
thermodynamic function of mixing and the function for an ideal
solution.
Regular solution a solution for which excess H is not 0, but excess
S=0.
Colligative properties only dependent on the amount of solute
present.
Semipermeable membrane is a membrane that is permeable to the
solvent but not the solute.
Osmotic pressure is he pressure that must be applied to the solution
to stop the influx of solvent.
Osmometry is the determination of molar mass by the measurement
of osmotic pressure.
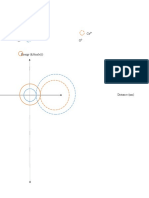
System under high pressure that it contains only liquid phase (applied
pressure is higher than the vapor pressure)
Points below the lower curve correspond to system under such low
pressure only contains a vapor phase (applied pressure is lower than
vapor pressure)
Starting from a and moving down isopleth, system consists of a single
liquid phase.
At a1 liquid exists in equilibrium with vapor, vapor has composition of
a1
At a1 composition of liquid is initially same as a, so at pressure p1
there is small amount of vapor present with the composition a1
If pressure is reduced to p2
Isopleth is a vertical line where changes to the system do not affect
the overall composition.
Tie lie is a horizontal line joining two points in equilibrium.
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Voltage Drop and Short CircuitDocument39 pagesVoltage Drop and Short CircuitMinerva Abanto100% (1)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Dimensional Analysis Worksheet 2Document4 pagesDimensional Analysis Worksheet 2German ToledoNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Margarine 12Document74 pagesMargarine 12the_gunners2004No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Units and VectorsDocument33 pagesChapter 1 Units and VectorslozzzzzNo ratings yet
- Column Design Prokon.Document16 pagesColumn Design Prokon.akankwasaNo ratings yet
- ANSYS FLUENT Population Balance Module ManualDocument80 pagesANSYS FLUENT Population Balance Module ManualGokul PrabuNo ratings yet
- Biochem ReactionsDocument1 pageBiochem ReactionsTanyaTouchéNo ratings yet
- L3 Heat CapacityDocument2 pagesL3 Heat CapacityTanyaTouchéNo ratings yet
- HelloDocument1 pageHelloTanyaTouchéNo ratings yet
- EthicsDocument8 pagesEthicsTanyaTouchéNo ratings yet
- Substrates&EnzymesDocument15 pagesSubstrates&EnzymesTanyaTouchéNo ratings yet
- SeparationsDocument11 pagesSeparationsTanyaTouchéNo ratings yet
- Substrates&EnzymesDocument15 pagesSubstrates&EnzymesTanyaTouchéNo ratings yet
- Kinetics of OxidationDocument9 pagesKinetics of OxidationTanyaTouchéNo ratings yet
- Kinetics of OxidationDocument9 pagesKinetics of OxidationTanyaTouchéNo ratings yet
- ExamDocument1 pageExamTanyaTouchéNo ratings yet
- THE GuidelinesDocument3 pagesTHE Guidelinesdanena88No ratings yet
- Chapter 16 - Chemical EquilibriumDocument2 pagesChapter 16 - Chemical EquilibriumTanyaTouchéNo ratings yet
- Transport HW and ExamplesDocument2 pagesTransport HW and ExamplesTanyaTouchéNo ratings yet
- Biopharmaceutical Regulatory ComplianceDocument1 pageBiopharmaceutical Regulatory ComplianceTanyaTouchéNo ratings yet
- Material Science FinaDocument1 pageMaterial Science FinaTanyaTouchéNo ratings yet
- Exam 3 NotesDocument4 pagesExam 3 NotesTanyaTouchéNo ratings yet
- P Ar T Temper Ature (°C) PH Ase Compo Sition Pha Se Amo UntDocument1 pageP Ar T Temper Ature (°C) PH Ase Compo Sition Pha Se Amo UntTanyaTouchéNo ratings yet
- Material Science FinaDocument1 pageMaterial Science FinaTanyaTouchéNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25Document1 pageChapter 25TanyaTouchéNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21Document2 pagesChapter 21TanyaTouchéNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2Document14 pagesChemistry 2TanyaTouchéNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25Document1 pageChapter 25TanyaTouchéNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer HW 1Document1 pageHeat Transfer HW 1TanyaTouchéNo ratings yet
- NaCaClO2EnergyDistanceDocument2 pagesNaCaClO2EnergyDistanceTanyaTouchéNo ratings yet
- ScheduleDocument1 pageScheduleTanyaTouchéNo ratings yet
- Homework FMEA 2017Document3 pagesHomework FMEA 2017TanyaTouchéNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Kinetics Study of Alcohol Dehydrogenase InhibitionDocument2 pagesEnzyme Kinetics Study of Alcohol Dehydrogenase InhibitionTanyaTouchéNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument1 pageBiochemistryTanyaTouchéNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument1 pageBiochemistryTanyaTouchéNo ratings yet
- Science Lesson Plan: Rubrics On Assessing The Performance of Group ActivityDocument1 pageScience Lesson Plan: Rubrics On Assessing The Performance of Group ActivityRowena Sta MariaNo ratings yet
- CK Osborne Reynolds PDFDocument4 pagesCK Osborne Reynolds PDFChaminduKrishanRupasingheNo ratings yet
- JJHJHHJHDocument6 pagesJJHJHHJHjayarNo ratings yet
- Metrix Px110 and Px120 Power Meter User ManualDocument21 pagesMetrix Px110 and Px120 Power Meter User ManualjcowNo ratings yet
- EquiprobabilityDocument2 pagesEquiprobabilitydanny222No ratings yet
- Shaft Critical SpeedDocument8 pagesShaft Critical SpeedkannanjuNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits & Networks Question BankDocument6 pagesElectrical Circuits & Networks Question BankMATHANKUMAR.S100% (1)
- Pressure-Grouted Soil Nails Improve Weathered Slope StabilityDocument11 pagesPressure-Grouted Soil Nails Improve Weathered Slope StabilityFrans van der MerweNo ratings yet
- ENCH4PP: Petroleum & Synthetic Fuel ProcessingDocument16 pagesENCH4PP: Petroleum & Synthetic Fuel ProcessingAshrafNo ratings yet
- Line-Scanning Laser Scattering System For Fast Defect Inspection of A Large Aperture SurfaceDocument10 pagesLine-Scanning Laser Scattering System For Fast Defect Inspection of A Large Aperture SurfaceAyman IsmailNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Dynamic Increment Component of Earth Pressure Behind The Retaining WallsDocument7 pagesEvaluation of Dynamic Increment Component of Earth Pressure Behind The Retaining WallsSivaramakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Paul FrictionDocument5 pagesPaul FrictionPaul Aldrin OlvezNo ratings yet
- Theory of Machines Lab Manual 10122015 030654AMDocument51 pagesTheory of Machines Lab Manual 10122015 030654AMAjay Kumar AgarwalNo ratings yet
- JNTU World Geotech Engineering ExamDocument4 pagesJNTU World Geotech Engineering ExamDp VisheshNo ratings yet
- Experimental study of four-point bending test on CLT deep beamsDocument6 pagesExperimental study of four-point bending test on CLT deep beamsFergus GardnerNo ratings yet
- Forane 22 Saturation Pressure Temperature DataDocument1 pageForane 22 Saturation Pressure Temperature Datavineeth100% (1)
- Applications Using The Partial Differential Equation ToolboxDocument11 pagesApplications Using The Partial Differential Equation ToolboxIgor WosniakNo ratings yet
- torque 정의Document40 pagestorque 정의valmaxjeonNo ratings yet
- Models - Mph.heat Transient AxiDocument6 pagesModels - Mph.heat Transient AxiAnonymous sAmJfcVNo ratings yet
- IME Micro ProjectDocument4 pagesIME Micro Projectshubhamghodekar76No ratings yet
- Nanometer Scale Multilayer Coatings Achieve Extreme HardnessDocument12 pagesNanometer Scale Multilayer Coatings Achieve Extreme HardnessBojan PodgornikNo ratings yet
- Experiment #3 / Unit 6 Calorimetry - Measuring Heat Changes During A Physical or Chemical ChangeDocument2 pagesExperiment #3 / Unit 6 Calorimetry - Measuring Heat Changes During A Physical or Chemical Changeapi-368121935No ratings yet
- FEA 2 McqsDocument26 pagesFEA 2 Mcqsrak RoyNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Plastic Bottle and Can Crusher For Recycling PurposeDocument3 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Plastic Bottle and Can Crusher For Recycling PurposeInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet