Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Course Material (Question Bank)
Uploaded by
Saravana KumarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Course Material (Question Bank)
Uploaded by
Saravana KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
Course Material (Question Bank)
www.studentsfocus.com
CS6304 / Analog and Digital Communication
UNIT-V -- MULTI-USER RADIO COMMUNICATION
PART-A
1. Define orbit.
The satellite can be rotated around the earth through various paths. These paths are
called orbits of the satellite. These orbits are u-sed to cover the specific application areas.
2. What is a satellite system?
A satellite system consists of one or more satellite space vehicles, a ground
based station to control the operation of the system, and a user network of earth stations.
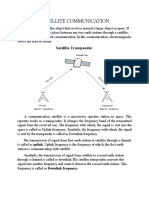
3. State the basic function of satellite transponder.
The t r a n s m i t t e r -receiver c o m b i n a t i o n i n t he s a t e l l i t e i s k now n as a
transponder. The basic function of a transponder is amplification and frequency translation.
4. List the satellite orbits.
Satellite orbits about the earth are either circular or elliptical. The satellite orbits are:
Inclined orbit, Polar orbit, Equatorial orbit
5. Define inclined orbit.
Inclined orbits are virtually all orbits except those that travel directly above the
equator or directly over the north and south poles.
6. Define polar orbit.
Satellite orbits with inclinations of 90are called polar orbit. Polar orbits are used for
special applications like navigational satellites.
7. Define geostationary orbit.
The circular equatorial orbit is exactly in the plane of equator on earth. All the points in
this orbit are at equal distance from earth surface, and a satellite in this orbit appears to be
stationary to the point of earth. Therefore this orbit is called geostationary orbit.
8. Define geosynchronous orbit.
When the inclination of the orbit is not zero and eccentricity is not zero, it is called as
geosynchronous orbit. The period of geosynchronous orbit is equal to the period of revolution
of earth with itself.
9. Define perigee and apogee.
The point in the orbit where the satellite is closest to the earth is called the perigee.
The point in the orbit where the satellite is farthest from the earth is called the apogee.
10. Define angle of inclination and angle of elevation.
Angle of inclination: It is the angle between the earths equatorial plane and the orbital plane
of a satellite measured counter clockwise at the point in the orbit where it crosses the
equatorial plane traveling from south to north.
Angle of elevation: It is the vertical angle formed between the direction of travel of an
electromagnetic wave radiated from an earth station antenna pointing directly toward a satellite
and the horizontal plane.
11. State the laws of planetary motion.
Keplers law may be simply stated as
CS6304 ADC UNIT 5
Page 1
www.studentsfocus.com
www.studentsfocus.com
Course Material (Question Bank)
(1) the planets move in ellipses with the sun at one focus,
(2) the line joining the sun and a planet sweeps out equal areas in equal intervals of time,
and
(3) the square of the time of revolution of a planet divided by the cube of its mean distance
form the sun gives a number that is the same for all planets.
12. How are satellites classified based on elevation?
i. Low earth orbit (LEO): 1 GHz -2.5 GHz
ii. Medium Earth orbit (MEO): 1.2GHz-1.66 GHz
iii. Geosynchronous earth orbit (GEO): 2 GHz -18 GHz
13. Define Azimuth angle.
It is defined as the horizontal pointing angle of an earth station antenna.
14. Define a transponder. What is its basic function?
A satellite radio repeater is called a transponder. It is an RF-RF repeater.
15. What is a footprint?
The geographical representation of a satellite antennas radiation pattern is called a
footprint or footprint map.
16. What is station keeping?
The process of maneuvering a satellite within a pre assigned window is called station
keeping.
17. State the uplink frequency and downlink frequency.
A typical uplink frequency is 6 GHz and a common downlink frequency is 4 GHz.
18. What are the techniques for increasing channel capacity?
Two of the techniques for increasing channel capacity are:
Frequency reuse
Spatial isolation
19. What are the major subsystems in a communication satellite?
The major subsystems in a communication satellite are
Communications subsystems
Power subsystems
Telemetry tracking and control (TTC) subsystems
Propulsion subsystems
Attitude stabilization subsystems
Antenna subsystems
20. What is the basic transponder configuration?
There are three basic transponder configurations used in communication systems. They
are
Single conversion transponder
Double conversion transponder
Regenerative transponder
21. State the major subsystems in a satellite earth station.
The major subsystems in a satellite earth station are:
Transmit subsystems
CS6304 ADC UNIT 5
Page 2
www.studentsfocus.com
Course Material (Question Bank)
www.studentsfocus.com
Receive subsystems
Power subsystems
Antenna subsystems
Telemetry tracking and control (TTC) subsystems
Ground control equipment (GCE) subsystems.
22. List the applications of a satellite
Some of the applications of a satellite are:
Surveillance or observation
Navigation
TV broadcast
Satellite telephones
23 What are the advantages of cellular systems?
Higher Capacity
Less transmission Power
Local interference only
Robustness
24. What are the disadvantages of cellular systems?
Infrastructure needed
Handover needed
Frequency Planning
25. Define Cluster
Cells are combined in cluster.
26. Define frequency management
Frequency management refers to designating set-up channels and voice Channels,
numbering the channels and grouping the voice channels into subsets.
27. What is channel assignment?
Channel assignment refers to the allocation of specific channels to cell sites and mobile
units.
28. Define Multiple Access and what are the major types of Multiple Accesses?
For high quality communication, many mobile users to share simultaneously a finite
amount of radio spectrum is called multiple Access. There are four major types of multiple
access. These are (i) Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) (ii) Time Division multiple
Access (iii) Space Division Multiple Access (iv) Code division Multiple Access.
29. Define CDMA.
Code Division Multiple Access systems use codes with certain characteristics to separate
different users. To enable access to the shared medium without interference, the users use the
same frequency and time to transmit data. The main problem is to find good codes and to
separate this signal from noise. The good code can be found the following 2 characteristic
Orthogonal &
Autocorrelation.
30. Define Attenuation
CS6304 ADC UNIT 5
Page 3
www.studentsfocus.com
www.studentsfocus.com
Course Material (Question Bank)
Whenever the output signal is lesser than the input signal it is called as loss.Any signal
passing through a device that is exhibiting loss has to experience attenuation. It is nothing but
reduction in signal strength mainly at higher frequency ranges, and at receiving end this
attenuated signal has reduced voltage levels.
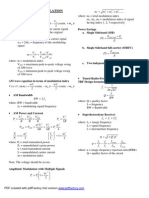
31. Define Data rate and Band width
The data rate in communication represents the speed at which the message is transmitted.
Bandwidth is the range of frequenices and represented as BW=f2-f1, where f1 and f2 are the first
and last frequenices of the signal graph.
32. What is the advantage of cell splitting concept?
In this technique the total number of users at a time will be increased so that traffic
congestion in the area can be avoided. Also a set of lowest power antennas can be used in place
of single antenna for the entire region so that the cellular coverage efficiency will be definitely
high.
33. What is frequency reuse?
The same carrier frequencies are reused in cellular communication for effective spectrum
utilization.
34. Define Handoff?
Handoff is the procedure for changing the assignment of a mobile unit from one BS to
another as the mobile unit moves from one cell to another. Handoff is the principle used to
continue that call established in mobile communication. When subscriber is towards the cell
boundary the signal strength reduces by which BTS of that cell handover the call to the net BTS
of another cell where the subscriber enters.
35. What is GSM?
The primary goal of GSM (Global System for Mobile communication) was provide a
mobile phone system that allows users to roam and provides voice services compatible to ISDN
and other PSTN systems.
36. Specify the security services offered by GSM.
Access control and authentication
Confidentiality
Anonymity
37. What is TDMA?
In time division multiple access, the time of the channel is shared by multiple
users. Complete bandwidth of the channel is available to the user in given time slot.
TDMA is in satellite communication.
38. What does CEPT stand for?
Conference of European Postal and Telecommunication Administrations (CEPT) is a
commonly used TDMA frame format for digital satellite systems.
39. What are the features of code division multiple accesses?
1. It does not require external synchronization networks.
2. CDMA offers gradual degradation in performance when the no. of users is
increased but it is easy to add new user to the system.
CS6304 ADC UNIT 5
Page 4
www.studentsfocus.com
Course Material (Question Bank)
www.studentsfocus.com
3. If offers an external interference rejection capability.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
PART-B
Write notes on satellite elevation categories and satellite orbital patterns.
Explain the satellite system with a neat block diagram.
State and explain the laws of planetary motion.
What is a geosynchronous satellite? Discuss its advantages and disadvantages.
Explain CDMA and also give the orthogonal condition of the signals in CDMA.
Explain about various multiple access schemes.
With neat sketch explain about cellular systems.
Draw and explain the architecture of GSM.
Write about AMPS.
CS6304 ADC UNIT 5
Page 5
www.studentsfocus.com
You might also like
- Radio Control for Model Ships, Boats and AircraftFrom EverandRadio Control for Model Ships, Boats and AircraftRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- EC1451 - Mobile CommunicationDocument18 pagesEC1451 - Mobile Communicationarivurp67% (3)
- Radio Propagation and Adaptive Antennas for Wireless Communication Networks: Terrestrial, Atmospheric, and IonosphericFrom EverandRadio Propagation and Adaptive Antennas for Wireless Communication Networks: Terrestrial, Atmospheric, and IonosphericNo ratings yet
- Unit IiDocument6 pagesUnit IimanoprabhaNo ratings yet
- Third Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesFrom EverandThird Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Ec 71 QBDocument16 pagesEc 71 QBepregithaNo ratings yet
- Radio Remote-Control and Telemetry and Their Application to MissilesFrom EverandRadio Remote-Control and Telemetry and Their Application to MissilesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Ec2401 - Wireless Communication - Question Bank Unit IDocument10 pagesEc2401 - Wireless Communication - Question Bank Unit ITrishul SampathNo ratings yet
- Cellular Networks, Satellite Communication 1 Satellite CommunicationDocument9 pagesCellular Networks, Satellite Communication 1 Satellite CommunicationSsk TempNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Wireless Mobile CommunicationsDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Wireless Mobile Communicationsrajesh053007No ratings yet
- Fifth Semester Wireless Communication Two Marks With Answers Regulation 2013Document12 pagesFifth Semester Wireless Communication Two Marks With Answers Regulation 2013PRIYA RAJI78% (9)
- Ec2401 - Wireless Communication - Question Bank Unit IDocument10 pagesEc2401 - Wireless Communication - Question Bank Unit Inazareth621No ratings yet
- Mobile CommunicationDocument16 pagesMobile CommunicationArun SampathNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communication 2 MarksDocument14 pagesWireless Communication 2 MarksBala Subramani100% (2)
- Satellite Communication Systems (SCSDocument27 pagesSatellite Communication Systems (SCSAmey GawdeNo ratings yet
- K. RAMAKRISHNAN COLLEGE EC6801 Wireless Communication Question Bank Part ADocument14 pagesK. RAMAKRISHNAN COLLEGE EC6801 Wireless Communication Question Bank Part Aهيثم محمد عبده قائد المخلافيNo ratings yet
- Midterm ReportDocument24 pagesMidterm ReportSrayee BanikNo ratings yet
- I. Ii. IIIDocument3 pagesI. Ii. IIIkarthick kumar.ANo ratings yet
- Chapter-XXII Satellite Communication SystemDocument13 pagesChapter-XXII Satellite Communication SystemFirdous AhmedNo ratings yet
- Mobile Computing Viva Voce QuestionsDocument10 pagesMobile Computing Viva Voce QuestionsMohamed Rafi100% (1)
- Major Satellite Comms SystemsDocument36 pagesMajor Satellite Comms SystemsMohammad Mostofa Kamal KowshikNo ratings yet
- CMC (2marks)Document9 pagesCMC (2marks)Prabhu PkNo ratings yet
- CMC Comp VivaDocument7 pagesCMC Comp VivadivinedinuNo ratings yet
- Orbital Parameters and Satellite Communication FundamentalsDocument45 pagesOrbital Parameters and Satellite Communication FundamentalsNahum SetuNo ratings yet
- EC 6801 - Wireless Communication QB (New One)Document20 pagesEC 6801 - Wireless Communication QB (New One)SamuelHericNo ratings yet
- Satellite Communication: Kalpesh B. Panchal Biren A - PatelDocument23 pagesSatellite Communication: Kalpesh B. Panchal Biren A - PatelSunil PillaiNo ratings yet
- CST64Document16 pagesCST64Thiagu RajivNo ratings yet
- Microwave, Radar and Satellite Communication Systems ExplainedDocument9 pagesMicrowave, Radar and Satellite Communication Systems ExplainedPatrick AfefohNo ratings yet
- SRS-Satellite CommunicationDocument13 pagesSRS-Satellite CommunicationVikrant Shimikeri100% (1)
- UntitledDocument184 pagesUntitledKathiravan ReddyNo ratings yet
- Ec1451 Mobile CommunicationDocument12 pagesEc1451 Mobile CommunicationainugiriNo ratings yet
- It1403 Mobile ComputingDocument15 pagesIt1403 Mobile Computingappsectesting3No ratings yet
- Satellite Communication Solutions (EC414)Document26 pagesSatellite Communication Solutions (EC414)Shaivi DewanganNo ratings yet
- StalliteDocument15 pagesStalliteحسين حيدر آلوس عباسNo ratings yet
- Satellite EclipseDocument22 pagesSatellite EclipseAma WeshNo ratings yet
- CS2402 Mobile Computing QuestionsDocument26 pagesCS2402 Mobile Computing QuestionsAnand KannanNo ratings yet
- Un It V - Part2-Satellite, Multiple Access, Satellite Acccess (Spade, Tdme), Spread SpectrumDocument67 pagesUn It V - Part2-Satellite, Multiple Access, Satellite Acccess (Spade, Tdme), Spread Spectrumsivagami nithyaNo ratings yet
- SatelliteDocument8 pagesSatelliteRifat ahmmedNo ratings yet
- Satellite Link Budget CalculationDocument64 pagesSatellite Link Budget CalculationHosam SaidNo ratings yet
- Satellite Communication An IntroductionDocument19 pagesSatellite Communication An IntroductionGolam Robbani RabbiNo ratings yet
- Satellite Communication 2 Marks AnswersDocument6 pagesSatellite Communication 2 Marks Answersvivek_ch87100% (5)
- 1.1. Introduction About Satellite CommunicationDocument4 pages1.1. Introduction About Satellite CommunicationChetna KauraNo ratings yet
- Notes Satellite Commn DR Umapathy ECEDocument118 pagesNotes Satellite Commn DR Umapathy ECERishikesh KumarNo ratings yet
- cs2402 2 Marks Question Bank-With AnswerDocument26 pagescs2402 2 Marks Question Bank-With AnswerFrousper29No ratings yet
- EC505Document87 pagesEC505kashi13No ratings yet
- Satellite Communication Systems ExplainedDocument55 pagesSatellite Communication Systems ExplainedIndraysh Vijay [EC - 76]No ratings yet
- UNIT 1 Satellite CommunicationDocument12 pagesUNIT 1 Satellite CommunicationRõçky StrâñgëNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communication Cellular ArchitectureDocument15 pagesWireless Communication Cellular ArchitectureTECH FROM ASHNo ratings yet
- Question Outline ICE-4103 Cellular and Mobile Communication 16-17Document4 pagesQuestion Outline ICE-4103 Cellular and Mobile Communication 16-17MD RAHATUL RABBINo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Microwave SystemsDocument53 pagesLecture 1 - Microwave SystemsAbdul SuboorNo ratings yet
- What Are Different Categories of Antenna and Give An Example of Each?Document8 pagesWhat Are Different Categories of Antenna and Give An Example of Each?Anonymous qYuxgojGe3No ratings yet
- Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering: 2 and 16 Mark Questions and AnswersDocument16 pagesDepartment of Electronics and Communication Engineering: 2 and 16 Mark Questions and Answersanjali9myneni100% (1)
- Sns College of Technology Sns College of Technology Sns College of Technology Sns College of TechnologyDocument33 pagesSns College of Technology Sns College of Technology Sns College of Technology Sns College of TechnologyakttripathiNo ratings yet
- EE4N L01-02 CCC OverviewDocument31 pagesEE4N L01-02 CCC OverviewMayar ZoNo ratings yet
- Komunikasi Satelite: Risanuri HidayatDocument21 pagesKomunikasi Satelite: Risanuri Hidayata_an687No ratings yet
- Ec1019-Radar and Navigational AidsDocument16 pagesEc1019-Radar and Navigational Aidsainugiri100% (2)
- K.S. School of Engineering and Management: ECE DepartmentDocument17 pagesK.S. School of Engineering and Management: ECE DepartmentParu RJNo ratings yet
- Satellite Communication Lecture Notes - Electronics and Communications Lecture NotesDocument8 pagesSatellite Communication Lecture Notes - Electronics and Communications Lecture NotesJoñalex N. MvamiNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Satellite CommunicationDocument19 pagesPresentation On Satellite Communicationalex sisayNo ratings yet
- Satellite Communication NotesDocument17 pagesSatellite Communication NotesAkhil RajuNo ratings yet
- SaraDocument7 pagesSaraSaravana KumarNo ratings yet
- AMPS system overviewDocument25 pagesAMPS system overviewSaravana KumarNo ratings yet
- AMPS system overviewDocument25 pagesAMPS system overviewSaravana KumarNo ratings yet
- Ec2357 Set2Document4 pagesEc2357 Set2VimalVengodiNo ratings yet
- Resume KalaivaniDocument3 pagesResume KalaivaniSaravana KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii - Part-A: Course Material (Question Bank)Document5 pagesUnit Iii - Part-A: Course Material (Question Bank)Saravana KumarNo ratings yet
- Course Material (Question Bank)Document5 pagesCourse Material (Question Bank)Saravana KumarNo ratings yet
- Course Material (Question Bank)Document4 pagesCourse Material (Question Bank)Saravana KumarNo ratings yet
- Course Material (Question Bank)Document4 pagesCourse Material (Question Bank)Saravana KumarNo ratings yet
- Ec2357 Set2Document4 pagesEc2357 Set2VimalVengodiNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii - Part-A: Course Material (Question Bank)Document5 pagesUnit Iii - Part-A: Course Material (Question Bank)Saravana KumarNo ratings yet
- Modulation Systems for MicrobroadcastingDocument110 pagesModulation Systems for MicrobroadcastingSaravana KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit I Fundamentals of Analog CommunicationDocument29 pagesUnit I Fundamentals of Analog CommunicationSaravana KumarNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal ProcessingDocument8 pagesDigital Signal ProcessingSaravana KumarNo ratings yet
- Optical CommunicationDocument14 pagesOptical CommunicationEr Akhilesh Singh100% (1)
- COMMUNICATIONS Formulas and ConceptsDocument24 pagesCOMMUNICATIONS Formulas and ConceptsAllan Paul Lorenzo Abando76% (17)
- Ion Thruster For Electric PropulsionDocument56 pagesIon Thruster For Electric Propulsionjidong jidongNo ratings yet
- (Studies in Space Policy) Annette Froehlich - Legal Aspects Around Satellite Constellations-ESPI - Springer (2019)Document110 pages(Studies in Space Policy) Annette Froehlich - Legal Aspects Around Satellite Constellations-ESPI - Springer (2019)Nebile Pelin MantıNo ratings yet
- Class Problems1Document2 pagesClass Problems1Arima ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Satellite Communication SystemsDocument164 pagesSatellite Communication SystemsSelva Raj50% (2)
- VasundharaDocument42 pagesVasundharaVarshareddie 2104No ratings yet
- C Band Ku Band For CATV Headend PDFDocument5 pagesC Band Ku Band For CATV Headend PDFMansour MashaeiNo ratings yet
- Nodia and Company: Gate Solved Paper Aerospace Engineering 2013Document13 pagesNodia and Company: Gate Solved Paper Aerospace Engineering 2013Ashok GopaleNo ratings yet
- Gordillo. 2020. Gravity, On The Primacy of Terrain. in Billé. Voluminous States...Document300 pagesGordillo. 2020. Gravity, On The Primacy of Terrain. in Billé. Voluminous States...LuisChaoNo ratings yet
- Communications Satellites DefinedDocument5 pagesCommunications Satellites DefinedGladys Merr DimapilisNo ratings yet
- Statellite Communication AssingnmentDocument23 pagesStatellite Communication AssingnmentAshfaq BurdiNo ratings yet
- Space Tech Achievements ApplicationsDocument88 pagesSpace Tech Achievements ApplicationsPrabhav JohariNo ratings yet
- Orbital Mechanics and LaunchersDocument42 pagesOrbital Mechanics and LaunchersidrishshaikNo ratings yet
- Orbital mechanics of satellites in space, Earth and topocentric framesDocument2 pagesOrbital mechanics of satellites in space, Earth and topocentric framesSamuel gultomNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics Notes on EM Waves and Communication SystemsDocument13 pagesClass 12 Physics Notes on EM Waves and Communication SystemsJaseela NaufalNo ratings yet
- Geostationary & Polar-Orbiting SatellitesDocument83 pagesGeostationary & Polar-Orbiting SatellitesAngelie LapeNo ratings yet
- Satellite Communications Presentation MaterialDocument90 pagesSatellite Communications Presentation MaterialJohn Dexter RealizoNo ratings yet
- Project Hope, Nasa Ames Space Settlement Contest 2018 ProjectDocument71 pagesProject Hope, Nasa Ames Space Settlement Contest 2018 ProjectSubhranshu Gupta67% (3)
- SpacetechnologyDocument138 pagesSpacetechnologyVaibhavNo ratings yet
- حل المسائل کتاب مقدمه ای بر اخترفیزیک مدرن بردلی کارولDocument5 pagesحل المسائل کتاب مقدمه ای بر اخترفیزیک مدرن بردلی کارولMA KhedriNo ratings yet
- DTH Set-Top-Box InstallerDocument79 pagesDTH Set-Top-Box InstallerRKT SOLUTION TP Help Desk100% (2)
- UNit-4 (Satellite Communication)Document15 pagesUNit-4 (Satellite Communication)Kunal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- 5 Satellite Orbit and PlatformDocument21 pages5 Satellite Orbit and Platformsureshkumar100% (1)
- Satellite IntrDocument35 pagesSatellite IntrjubairNo ratings yet
- Satellite Communications: PPT For Computer NetworksDocument47 pagesSatellite Communications: PPT For Computer NetworksQaisar Abbas QasimiNo ratings yet
- Ka-Band Vs Ku-Band Satellite SystemDocument2 pagesKa-Band Vs Ku-Band Satellite SystemOKORIE ChikezieNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Performance of Inter-Satellite Optical Link With Effect of Bit Rate and ApertureDocument4 pagesOptimization of Performance of Inter-Satellite Optical Link With Effect of Bit Rate and ApertureijsretNo ratings yet
- Comunicaciones Satelitales 2da Edicion Timothy Pratt, Charles W. Bostian, Jeremy E. AllnuttDocument143 pagesComunicaciones Satelitales 2da Edicion Timothy Pratt, Charles W. Bostian, Jeremy E. AllnutthackermasboNo ratings yet
- Satellite Network Hacking & Security AnalysisDocument48 pagesSatellite Network Hacking & Security AnalysisAI Coordinator - CSC JournalsNo ratings yet
- ITIL 4: Digital and IT strategy: Reference and study guideFrom EverandITIL 4: Digital and IT strategy: Reference and study guideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsFrom EverandMicrosoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- CCNA: 3 in 1- Beginner's Guide+ Tips on Taking the Exam+ Simple and Effective Strategies to Learn About CCNA (Cisco Certified Network Associate) Routing And Switching CertificationFrom EverandCCNA: 3 in 1- Beginner's Guide+ Tips on Taking the Exam+ Simple and Effective Strategies to Learn About CCNA (Cisco Certified Network Associate) Routing And Switching CertificationNo ratings yet
- The Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionFrom EverandThe Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Power of Habit: The Ultimate Guide to Forming Positive Daily Habits, Learn How to Effectively Break Your Bad Habits For Good and Start Creating Good OnesFrom EverandPower of Habit: The Ultimate Guide to Forming Positive Daily Habits, Learn How to Effectively Break Your Bad Habits For Good and Start Creating Good OnesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Study Guide: CLF-C01 ExamFrom EverandAWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Study Guide: CLF-C01 ExamRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The New 3D Layout for Oil & Gas Offshore Projects: How to ensure successFrom EverandThe New 3D Layout for Oil & Gas Offshore Projects: How to ensure successRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Nuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressFrom EverandNuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Computer Networking: The Complete Beginner's Guide to Learning the Basics of Network Security, Computer Architecture, Wireless Technology and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCENT, and CCNA)From EverandComputer Networking: The Complete Beginner's Guide to Learning the Basics of Network Security, Computer Architecture, Wireless Technology and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCENT, and CCNA)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Offshore Wind Energy Generation: Control, Protection, and Integration to Electrical SystemsFrom EverandOffshore Wind Energy Generation: Control, Protection, and Integration to Electrical SystemsNo ratings yet
- The Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialFrom EverandThe Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialNo ratings yet
- The CompTIA Network+ Computing Technology Industry Association Certification N10-008 Study Guide: Hi-Tech Edition: Proven Methods to Pass the Exam with Confidence - Practice Test with AnswersFrom EverandThe CompTIA Network+ Computing Technology Industry Association Certification N10-008 Study Guide: Hi-Tech Edition: Proven Methods to Pass the Exam with Confidence - Practice Test with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Computer Systems and Networking Guide: A Complete Guide to the Basic Concepts in Computer Systems, Networking, IP Subnetting and Network SecurityFrom EverandComputer Systems and Networking Guide: A Complete Guide to the Basic Concepts in Computer Systems, Networking, IP Subnetting and Network SecurityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- Renewable Energy: A Very Short IntroductionFrom EverandRenewable Energy: A Very Short IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- OFF-GRID PROJECTS: A Comprehensive Beginner's Guide to Learn All about OffGrid Living from A-Z and Live a Life of Self-SufficiencyFrom EverandOFF-GRID PROJECTS: A Comprehensive Beginner's Guide to Learn All about OffGrid Living from A-Z and Live a Life of Self-SufficiencyNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Kali Linux Book - Second Edition: Perform advanced penetration testing using Nmap, Metasploit, Aircrack-ng, and EmpireFrom EverandThe Ultimate Kali Linux Book - Second Edition: Perform advanced penetration testing using Nmap, Metasploit, Aircrack-ng, and EmpireNo ratings yet
- The Boy Who Harnessed the Wind: Creating Currents of Electricity and HopeFrom EverandThe Boy Who Harnessed the Wind: Creating Currents of Electricity and HopeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (130)
- Idaho Falls: The Untold Story of America's First Nuclear AccidentFrom EverandIdaho Falls: The Untold Story of America's First Nuclear AccidentRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Implementing an Integrated Management System (IMS): The strategic approachFrom EverandImplementing an Integrated Management System (IMS): The strategic approachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Computer Networking: The Complete Guide to Understanding Wireless Technology, Network Security, Computer Architecture and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCNA and CCENT)From EverandComputer Networking: The Complete Guide to Understanding Wireless Technology, Network Security, Computer Architecture and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCNA and CCENT)No ratings yet
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) Interview Questions and AnswersFrom EverandAmazon Web Services (AWS) Interview Questions and AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)