Professional Documents
Culture Documents
(B) Titrimetric: Created by
Uploaded by
ak_thimiriOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
(B) Titrimetric: Created by
Uploaded by
ak_thimiriCopyright:
Available Formats
TEST METHOD OF HYDRAZINE
(B) TITRIMETRIC
1.
SCOPE
This method covers the estimation of hydrazine of high concentrations.
2.
APPLICATION
Boiler water during wet preservation and hydrazine solution as purchased.
3.
PRINCIPLE
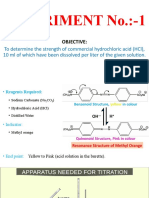
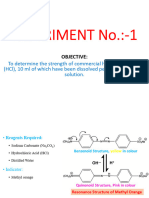
Hydrazine reacts with potassium iodate in strong acid medium as follows:
IO-3 + N2H4 + 2H+ + Cl- ICl + N2 + 3H2O
A known volume of hydrazine solution containing few ml of immiscible solvents like
chloroform or carbon tetra chloride is titrated with standard potassium iodate. The end
point is the disappearance of violet colour from the solvent.
4.
REAGENTS
(i)
(ii)
Potassium Iodate Solution 0.1M (0.4 N)
Weigh accurately 21.4 gm of pot. iodate, previously dried at 120 oC for 1
hour into a clean 1000 ml standard measuring flask. Dissolve and make up
to the mark with deionised water.
Potassium Iodate Solution (0.02 N)
Pipette out 25 ml of the above solution into a 500 ml standard measuring
flask and make up to the mark with deionised water.
(iii) Hydrochloric Acid A.R.(conc.)
(iv) Solvents CCl4 or CHCl3
5.
APPARATUS
Burette, Pipette, 250 ml reagent bottle or a narrow neck conical flask, etc.
6.
PROCEDURE
6.1 For Hydrazine Solution as Purchased
i)
Weigh out accurately about 5.0 gms of N2H4 solution into a 500 ml standard
measuring flask, make up to the mark and mix well.
Created by
KR.VEERAPPAN,LPS,SHARJAH,u.a.e./Asst.Manager,
TCPLKR.VEERAPPAN,LPS,SHARJAH,u.a.e./Asst.Manager,
TCPL
ii)
Pipette out 20 ml of sample into a 250 ml reagent bottle or conical flask.
iii) Add 30 ml of conc. HCl.
iv) Add 5 ml of CCl4 or CHCl3.
v)
Titrate against 0.4 N pot. iodate with gentle shaking until the organic layer is just
decolourised. Note down the titre value.
6.1.1 CALCULATIONS
% by wt. of N2H4 as N2H4 = V1 N1 x 8.011 x 100
V2 x W x 2
W = wt. of N2H4 solution taken, gram.
V1 = Titre value, ml.
V2 = Vol. of the N2H4 solution taken, ml.
N1 = Normality of KIO3.
The above eqn. can be written as:
V1 x 0.4 x 8.011 x 100 = V1 x 8.011
20 x 2 x W
W
6.2 For Boiler Wet Preservation Water
Follow steps ii to iv as in 6.1 and titrate against 0.02 N KIO 3 as described in
6.1(v).
6.2.1 CALCULATIONS
ppm N2H4 as N2H4 = V1 N1 x 8011
V2
V1 = Vol. of KIO3 , ml.
N1 = Normality of KIO3.
V2 = Vol. of boiler water taken , ml.
To report as N2H4.H2O multiply the N2H4 conc. by 1.56
REFERENCE
VOGELS Textbook of Quantitative Inorganic Analysis.
Note
The advantage of this method over the iodimetric method which is used at present, is
that the end point is sharp. Iodimetric method can still be used.
Created by
KR.VEERAPPAN,LPS,SHARJAH,u.a.e./Asst.Manager,
TCPLKR.VEERAPPAN,LPS,SHARJAH,u.a.e./Asst.Manager,
TCPL
You might also like
- API Piping Plans - FlowserveDocument56 pagesAPI Piping Plans - Flowservesachin ShindeNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Commercial Bleach LabDocument5 pagesAnalysis of Commercial Bleach Labsoccerprince2173% (11)
- Term SymbolDocument23 pagesTerm SymbolCyriac Mathew73% (11)
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisFrom EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Analytical Chem Questions 2Document59 pagesAnalytical Chem Questions 2Ash Yehia50% (2)
- Pall Gas Solid Separation SystemsDocument16 pagesPall Gas Solid Separation SystemsAndrew HillNo ratings yet
- Storage Tank Protection Using Aspen Hysys: Petroleum and Coal May 2019Document11 pagesStorage Tank Protection Using Aspen Hysys: Petroleum and Coal May 2019Elbahi DjaalabNo ratings yet
- CHM260 Lab Report SubmissionDocument38 pagesCHM260 Lab Report Submissionasta yuno100% (1)
- Standardization of Hydrochloric AcidDocument7 pagesStandardization of Hydrochloric AcidDenise Chow86% (21)
- Study of LDPE Hyper Compressor Lubrication: Engineering (Virtual) Internship ProgramDocument17 pagesStudy of LDPE Hyper Compressor Lubrication: Engineering (Virtual) Internship ProgramchanchalNo ratings yet
- Cathodic Protection ProcedureDocument5 pagesCathodic Protection ProcedureAjie Ekpere100% (1)
- Experiment 1Document4 pagesExperiment 1gajenraoNo ratings yet
- Unit V: Principles of Histology and HistochemistryDocument14 pagesUnit V: Principles of Histology and Histochemistryمروة صلاح0% (1)
- The Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresFrom EverandThe Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Standardization of HCLDocument9 pagesStandardization of HCLSuscyn CondrillonNo ratings yet
- Iodine Value of OilDocument3 pagesIodine Value of OilUsman Ghani100% (2)
- Peroxide ValueDocument6 pagesPeroxide ValueKrishna KalsekarNo ratings yet
- HRSG High Pressure Evaporator Sampling For Internal DepositDocument26 pagesHRSG High Pressure Evaporator Sampling For Internal Depositak_thimiriNo ratings yet
- Determination of Dissolved Oxygen in WaterDocument4 pagesDetermination of Dissolved Oxygen in WaterkuthappadyNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Dairy Products - A Chemical Analysis of Milk, Cream and ButterFrom EverandThe Chemistry of Dairy Products - A Chemical Analysis of Milk, Cream and ButterNo ratings yet
- High Pressure Boiler Water TreatmentDocument90 pagesHigh Pressure Boiler Water Treatmentak_thimiri100% (1)
- Experiment 2 - Analysis of An Unknown Vinegar SampleDocument8 pagesExperiment 2 - Analysis of An Unknown Vinegar SampleHanis Ridzuan100% (1)
- Glass RefractoryDocument52 pagesGlass RefractorySans Sen0% (1)
- Lab 6 TitrationDocument6 pagesLab 6 Titrationalextzhao1996No ratings yet
- Lab CHM 256 1Document5 pagesLab CHM 256 1kyungsoo studiesNo ratings yet
- Chlorine Thiosulfate Titration PDFDocument3 pagesChlorine Thiosulfate Titration PDFGregorio De La PeñaNo ratings yet
- Exp 1 PDFDocument3 pagesExp 1 PDFwaniNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Complete - 0Document8 pages4.2 Complete - 0Leo TaylorNo ratings yet
- PREPARATION AND STANDARDIZATION OF HCL SOLUTION WITH PRIMARY STANDARD Na CO SOLUTION (CHM256)Document10 pagesPREPARATION AND STANDARDIZATION OF HCL SOLUTION WITH PRIMARY STANDARD Na CO SOLUTION (CHM256)maisarah20salwaNo ratings yet
- CCC CC CCC CC CCC CCCDocument8 pagesCCC CC CCC CC CCC CCCfaznil100% (3)
- Chem ProjectDocument3 pagesChem ProjectSUDHARSHAN VIJAYNo ratings yet
- AnalysisDocument4 pagesAnalysisSubhash DhungelNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2 (Experiment 1)Document10 pagesPresentation 2 (Experiment 1)Rishabh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chlorine Thiosulfate TitrationDocument3 pagesChlorine Thiosulfate TitrationIbe CollinsNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2: Title:Preparation of Solutions. ObjectivesDocument4 pagesExperiment 2: Title:Preparation of Solutions. ObjectivesOromay Elias100% (1)
- Determination of Nickel in Trace LevelDocument2 pagesDetermination of Nickel in Trace LevelsatishNo ratings yet
- Report of Practical WorkDocument14 pagesReport of Practical WorkMuhammad abdur rehmanNo ratings yet
- Inky Pinky PonkyDocument4 pagesInky Pinky PonkyShruti TyagiNo ratings yet
- IOdoDocument2 pagesIOdoZeba HasanNo ratings yet
- Distribution CoefficientDocument5 pagesDistribution Coefficientaryajs2017No ratings yet
- Basic Analytical Chemistry Laboratory ReportDocument5 pagesBasic Analytical Chemistry Laboratory Reportfarah0% (1)
- Objective: The Objective of This Laboratory Is: - To Standardise of A Hydrochloric Acid (HCL) SolutionDocument12 pagesObjective: The Objective of This Laboratory Is: - To Standardise of A Hydrochloric Acid (HCL) SolutionShaker HusienNo ratings yet
- Lab Report CHM 256Document13 pagesLab Report CHM 256Khairul AnwarNo ratings yet
- SulfidaDocument3 pagesSulfidaFendi Setyo BudiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document6 pagesExperiment 2Rashmi RawatNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document10 pagesExperiment 1g googleNo ratings yet
- Theory:: Aim of ExperimentDocument9 pagesTheory:: Aim of ExperimentmuradNo ratings yet
- Acid Base TitrationDocument6 pagesAcid Base Titrationgunapranes15No ratings yet
- Laboratory Reports in Analytical ChemistryDocument10 pagesLaboratory Reports in Analytical ChemistryClyde Chloe D. TrayaNo ratings yet
- Exp 3-Reduction of Cyclohexanone With Sodium BorohydrideDocument11 pagesExp 3-Reduction of Cyclohexanone With Sodium Borohydrideakuserai100% (3)
- Chemistry 232 Determination of Vitamin C by An Iodometric TitrationDocument3 pagesChemistry 232 Determination of Vitamin C by An Iodometric TitrationHindami NugrohoNo ratings yet
- 4.4 Complete - 0Document9 pages4.4 Complete - 0Anna DixonNo ratings yet
- Chlorine Thiosulfate TitrationDocument3 pagesChlorine Thiosulfate Titrationskrim240No ratings yet
- Sodium Hypochlorite Prosedure AnalysisDocument2 pagesSodium Hypochlorite Prosedure AnalysisMarpuah PubieeNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6: Determination of Ascorbic Acid Using Iodometric Titration MethodDocument7 pagesExperiment 6: Determination of Ascorbic Acid Using Iodometric Titration MethodNurul AdNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7Document3 pagesExperiment 7Ana RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Solutions 2Document9 pagesPreparation of Solutions 2Louise Jiodielynne Salvador LandichoNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Experiment 1Document27 pagesLab Report Experiment 1zakwan murshidiNo ratings yet
- Analysis of An Unknown Vinegar SampleDocument8 pagesAnalysis of An Unknown Vinegar Samplearfanadib13No ratings yet
- Pre LabDocument3 pagesPre LabAlex XanderNo ratings yet
- Chem Prac Report 2Document5 pagesChem Prac Report 2AbdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- CHM 256 Experiment 2Document7 pagesCHM 256 Experiment 2Qistina NayliNo ratings yet
- Analysis of BleachDocument3 pagesAnalysis of BleachMatt VittingNo ratings yet
- CL in Bleaching PowderDocument2 pagesCL in Bleaching Powderlokesh_phantom110% (1)
- CHM 421 Analytical Chemistry Experiment 2: Analysis of An Unknown Vinegar SampleDocument14 pagesCHM 421 Analytical Chemistry Experiment 2: Analysis of An Unknown Vinegar SampleIntan SapuraNo ratings yet
- Lab Report chm256Document8 pagesLab Report chm256Wahida Amalin sofeaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report CHMDocument5 pagesLaboratory Report CHMhappy kuma50% (2)
- Lab ReportDocument9 pagesLab ReportmawarNo ratings yet
- Determination of The Alcohol LabDocument3 pagesDetermination of The Alcohol LabVIctoriakay100% (1)
- 521 Bench ChemicalDocument13 pages521 Bench ChemicalAnishah ChaudheryNo ratings yet
- Is.1448.16.1990 Density or API Gravity by Hydrometer Petroleum Produect PDFDocument10 pagesIs.1448.16.1990 Density or API Gravity by Hydrometer Petroleum Produect PDFak_thimiriNo ratings yet
- APPENDIX B: Short Cut Key FunctionsDocument2 pagesAPPENDIX B: Short Cut Key Functionsak_thimiriNo ratings yet
- Chemical Cleaning Procedure BdEU UNIT & AU Dahej SiteDocument24 pagesChemical Cleaning Procedure BdEU UNIT & AU Dahej Siteak_thimiriNo ratings yet
- AinDocument6 pagesAinak_thimiriNo ratings yet
- About ELGIDocument1 pageAbout ELGIak_thimiriNo ratings yet
- SAMSONType 3730 2 Electropneumatic Positioner & Type 3730 3 With HART Communication t83842Document8 pagesSAMSONType 3730 2 Electropneumatic Positioner & Type 3730 3 With HART Communication t83842ak_thimiriNo ratings yet
- 10HCB20AT160 LRSB While Retracting Power Cable and Cable Chain Link Damaged Due To Cable Chain JammedDocument4 pages10HCB20AT160 LRSB While Retracting Power Cable and Cable Chain Link Damaged Due To Cable Chain Jammedak_thimiriNo ratings yet
- Spray-Type Deaerator: Installation and Operating Service ManualDocument19 pagesSpray-Type Deaerator: Installation and Operating Service Manualak_thimiriNo ratings yet
- Pharmacist Syllabus DetailedDocument18 pagesPharmacist Syllabus DetailedHari Kamesh KiranNo ratings yet
- Brochure Armaflex Class 1 With FM ApprovedDocument6 pagesBrochure Armaflex Class 1 With FM ApprovedPT. PRIMAVERA TEHNIK ABADINo ratings yet
- Plastic AnalysisDocument10 pagesPlastic AnalysisSitiNo ratings yet
- 4 ReactorsDocument58 pages4 ReactorsKiran ShresthaNo ratings yet
- CIF-file and ValidationDocument25 pagesCIF-file and Validationbasco costasNo ratings yet
- DVGW Forschungsstelle at The Engler-Bunte-InstitutDocument1 pageDVGW Forschungsstelle at The Engler-Bunte-InstitutSetiono RachmanNo ratings yet
- Dirac Lecture PDFDocument6 pagesDirac Lecture PDFPuskesmas RawaloNo ratings yet
- LED ManufacturingDocument14 pagesLED ManufacturingsvishnuvNo ratings yet
- Cell, Cellular Components and Their FunctionDocument3 pagesCell, Cellular Components and Their FunctionNur SyahirahNo ratings yet
- Multi Layer Insulation Literature: 1. General OverviewDocument20 pagesMulti Layer Insulation Literature: 1. General OverviewJoan ReigNo ratings yet
- Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities of Pink Guava Leaves and SeedsDocument10 pagesAntioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities of Pink Guava Leaves and SeedsRobbyNo ratings yet
- Plate Fin Heat ExchangerDocument3 pagesPlate Fin Heat ExchangerRaju KalinthaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Structure of The Cu Au (1 1 1) Surface: Ch.E. Lekka, N. Bernstein, M.J. Mehl, D.A. PapaconstantopoulosDocument9 pagesElectronic Structure of The Cu Au (1 1 1) Surface: Ch.E. Lekka, N. Bernstein, M.J. Mehl, D.A. PapaconstantopoulosAmir Nazri KaibingNo ratings yet
- Catalogue 1524816Document18 pagesCatalogue 1524816webhareggebru06No ratings yet
- Cosmetic Allergen CertificateDocument1 pageCosmetic Allergen CertificateJeevan de SilvaNo ratings yet
- 1420Document31 pages1420LuciNo ratings yet
- Rajasthan VatDocument119 pagesRajasthan VatRakesh ParaliyaNo ratings yet
- Values of Selected Physical Constants: Quantity Symbol SI Units Cgs UnitsDocument1 pageValues of Selected Physical Constants: Quantity Symbol SI Units Cgs UnitsSAUDNo ratings yet
- Tubing ComparisonsDocument2 pagesTubing ComparisonsBrummerNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument24 pagesCambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationWENDY MENDIOLANo ratings yet
- Diemax L Die Springs: Made in AmericaDocument16 pagesDiemax L Die Springs: Made in AmericaHadi KoraniNo ratings yet