Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Individcollect Chart
Uploaded by
api-306867903Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Individcollect Chart
Uploaded by
api-306867903Copyright:
Available Formats
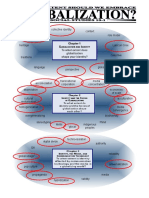
Individualism:
an ideology based on the primacy of individual freedom; values the freedom and worth of the
individual, sometimes over the security and welfare of the group. A supporter of the
principles of individualism might be referred to as an individualist.
Collectivism:
an ideology based on the primacy of collective welfare; values the goals of the group and the
common good over the goals of any one individual. A supporter of the principles of
collectivism might be referred to as a collectivist.
Major Components of Collectivism and Individualism
(Chart is adapted from Global Systems by K. Gilchrist)
Collectivism
The survival of the collective takes
precedence over that of the individual.
Personal potential is attained through
collective development.
Uniformity and conformity are the ideal.
Collective identity is defined by group
membership.
Conformity to group norms, obedience, and
harmony are expected.
The group is able and entitled to know
what its members do and think in private.
Collective responsibility is expected; the
entire group is responsible for the actions
of its members. Collective efforts are
believed to be superior.
Cooperation and conformity are the best
way to achieve goals.
The group assumes responsibility for the
well-being of its members.
Fulfilment of the group's obligations is
important; actions are guided by group
interests.
Sharing of wealth, egalitarianism, public or
collective ownership are important.
Rights of the group take precedence;
individual rights are secondary.
Individualism
Individual self-worth; ultimate moral
authority lies with the individual.
Personal potential is developed through
individual effort.
Each person is unique.
A person's identity is defined by personal
characteristics.
The individual makes independent decisions
and judgements.
The person has the right to privacy; people
should not interfere ill what another person
does and thinks.
The individual is morally and/or legally
responsible for personal actions.
Emphasis on individual initiative and
personal achievement.
Excellence attained and goals met through
competition.
The individual is responsible for personal
well-being.
Fulfilment of individual needs and
interests; actions guided by self-interest.
Material rewards and wealth are not
shared; property is held privately.
The individual's rights are paramount and
protected by laws.
You might also like
- Decoding Right from Wrong: 7 Key Strategies for Ethical Decision-MakingFrom EverandDecoding Right from Wrong: 7 Key Strategies for Ethical Decision-MakingNo ratings yet
- Major Components of Collectivism and IndividualismDocument1 pageMajor Components of Collectivism and IndividualismRaphael OcampoNo ratings yet
- Collective and IndividualismDocument3 pagesCollective and Individualismkerrbelches08No ratings yet
- The Utilitarian ApproachDocument4 pagesThe Utilitarian Approachanon_972987121No ratings yet
- 5 Ethical ApproachesDocument5 pages5 Ethical ApproachesPrasanna KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.1: Types of Moral Dilemmas: Ge 108: EthicsDocument3 pagesChapter 2.1: Types of Moral Dilemmas: Ge 108: EthicsHazel BorborNo ratings yet
- EthicsDocument29 pagesEthicsOscar Manlolo100% (1)
- ETHICS Lesson 1 & 2Document10 pagesETHICS Lesson 1 & 2AEHYUN YENVYNo ratings yet
- Overview of Ethics Written Report 1Document7 pagesOverview of Ethics Written Report 1Aron Jay MejiaNo ratings yet
- Universal ValuesDocument7 pagesUniversal ValuesBES BEBENo ratings yet
- Ethics and MoralityDocument23 pagesEthics and Moralitymikhil.muraliNo ratings yet
- Moral and Civic EducationDocument16 pagesMoral and Civic Educationtarekegn gezahegnNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1-3 ETHICSDocument61 pagesChapter-1-3 ETHICSjv100% (1)
- Ethics. Part 1 & 2.Document11 pagesEthics. Part 1 & 2.Yenelle Miranda Abuan100% (1)
- Social Responsibility and Managerial EthicsDocument11 pagesSocial Responsibility and Managerial EthicsMwangy PinchezNo ratings yet
- Civics AssignmentDocument14 pagesCivics AssignmentTeamireab Desta100% (1)
- BSAIS 2E Ethics and Morality GuideDocument4 pagesBSAIS 2E Ethics and Morality GuideWishNo ratings yet
- Ethics Prelim Lessons ActivitiesDocument8 pagesEthics Prelim Lessons Activitiesjohnmark gumbanNo ratings yet
- What Is Social GroupDocument5 pagesWhat Is Social GroupAsif BalochNo ratings yet
- Ethics (Gec 7) 1 SEM 2021-2022Document26 pagesEthics (Gec 7) 1 SEM 2021-2022Alyn Cabañal AlmazarNo ratings yet
- Professional Ethics and Human ValuesDocument41 pagesProfessional Ethics and Human Valuesvani100% (3)
- Thinking Ethically: 5 ApproachesDocument4 pagesThinking Ethically: 5 ApproachesMark Charle Mana IINo ratings yet
- 2ndquarter Lesson 1part 2 ChoicesDocument20 pages2ndquarter Lesson 1part 2 ChoicesJaira Mae Alyssa CortezNo ratings yet
- Consolidated ReportDocument4 pagesConsolidated ReportSczharmellagne R. SarahaniNo ratings yet
- ETHICS FGFDocument2 pagesETHICS FGFScar ShadowNo ratings yet
- Ethics: By: Neo, Nindi, Jazlyn, CharleneDocument12 pagesEthics: By: Neo, Nindi, Jazlyn, CharleneArsenia LotivoNo ratings yet
- Are we truly free_ _ Philo EssayDocument1 pageAre we truly free_ _ Philo EssayNeyarah SheynNo ratings yet
- Chapter Iii EroDocument17 pagesChapter Iii ErocandiefacuraNo ratings yet
- A Framework For Thinking EthicallyDocument30 pagesA Framework For Thinking EthicallyArmand NarcellesNo ratings yet
- Eastern and Westen Culture-UTSDocument9 pagesEastern and Westen Culture-UTSJerwin RafolNo ratings yet
- Islam, MD Lawahid Ul Ethics Mid TermDocument4 pagesIslam, MD Lawahid Ul Ethics Mid Termlawa islamNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Understanding Civics and Ethics 1.1. Defining Civics, Ethics and Morality 1.1.1. Civic EducationDocument12 pagesChapter One Understanding Civics and Ethics 1.1. Defining Civics, Ethics and Morality 1.1.1. Civic EducationNardos EshetuNo ratings yet
- SS 112 ReviewerDocument6 pagesSS 112 ReviewerHana MiNo ratings yet
- Ethics, Mores and Values ExplainedDocument12 pagesEthics, Mores and Values ExplainedCyj Kianj SoleroNo ratings yet
- Importance of FamilyDocument3 pagesImportance of FamilySel EscutinNo ratings yet
- Assignment in Phl/203: Submitted To: Asst. Prof. Emmanuel Domingo M.ADocument6 pagesAssignment in Phl/203: Submitted To: Asst. Prof. Emmanuel Domingo M.APatricia Ann JoseNo ratings yet
- Running Ethical Discussions 3Document8 pagesRunning Ethical Discussions 3martin pontNo ratings yet
- A Framework For Thinking EthicallyDocument30 pagesA Framework For Thinking EthicallyXainab AmirNo ratings yet
- Ethical Guidelines and Values in Decision MakingDocument2 pagesEthical Guidelines and Values in Decision MakingUzair HanifNo ratings yet
- Ethics PDFDocument13 pagesEthics PDFRick StantonNo ratings yet
- Foundation of MoralityDocument18 pagesFoundation of Moralityisaiah menesesNo ratings yet
- A Framework For Ethical Decision MakingDocument6 pagesA Framework For Ethical Decision MakingHaider AliNo ratings yet
- INDIVIDUALISMDocument4 pagesINDIVIDUALISMkoomifaithNo ratings yet
- IFUGAO STATE UNIVERSITY College of Criminal Justice Ethics ChapterDocument7 pagesIFUGAO STATE UNIVERSITY College of Criminal Justice Ethics ChapteriamysaaahhhNo ratings yet
- Ethics 1Document21 pagesEthics 1Rozweld GalangNo ratings yet
- Lists Alternate Ethics SystemDocument2 pagesLists Alternate Ethics SystemAsmaa ZairiNo ratings yet
- Normative Ethics Readings (19-20)Document27 pagesNormative Ethics Readings (19-20)Adrian BrillantesNo ratings yet
- Framework 2 - Thinking Critically - A Framework For Moral Decision Making - PDF Doc. 8-31-13Document2 pagesFramework 2 - Thinking Critically - A Framework For Moral Decision Making - PDF Doc. 8-31-13Danny ZapataNo ratings yet
- Normative Ethics Readings19 20 1Document27 pagesNormative Ethics Readings19 20 1JHUZELL DUMANJOGNo ratings yet
- UCSP Lesson11 STDocument44 pagesUCSP Lesson11 STLea SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Framework On Thinking EthicallyDocument3 pagesFramework On Thinking EthicallyLabingla VingyuuuNo ratings yet
- Groups & ProcessesDocument7 pagesGroups & Processessushil_bugalia7293No ratings yet
- Ethics and Management DecisionsDocument5 pagesEthics and Management DecisionsJenipher KalembelaNo ratings yet
- Nandan Ethics Lec-4Document16 pagesNandan Ethics Lec-4S SinghNo ratings yet
- Theories in Business EthicsDocument20 pagesTheories in Business EthicsJanu KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Ethics Prelim ReviewerDocument8 pagesEthics Prelim ReviewerRia Paula PacuanNo ratings yet
- Module 2 ReviewerDocument8 pagesModule 2 ReviewerElmeerajh JudavarNo ratings yet
- The Cognitive Basis of Institutions: A Synthesis of Behavioral and Institutional EconomicsFrom EverandThe Cognitive Basis of Institutions: A Synthesis of Behavioral and Institutional EconomicsNo ratings yet
- Ethics and Culture: Some Contemporary Indian ReflectionsFrom EverandEthics and Culture: Some Contemporary Indian ReflectionsNo ratings yet
- Sweden-Life Is A Shmorgasbord ArticleDocument3 pagesSweden-Life Is A Shmorgasbord Articleapi-306867903No ratings yet
- Vid2 Individualism Collectivism Understandcheck 1Document2 pagesVid2 Individualism Collectivism Understandcheck 1api-306867903No ratings yet
- Social Stuides 10-2 LRPDocument4 pagesSocial Stuides 10-2 LRPapi-306867903No ratings yet
- Economic Source Analysis AssignmentDocument6 pagesEconomic Source Analysis Assignmentapi-306867903No ratings yet
- 1 Ideology UnderstandcheckDocument2 pages1 Ideology Understandcheckapi-306867903No ratings yet
- IdeologynotesDocument6 pagesIdeologynotesapi-245696323No ratings yet
- Terminology Chapter 5Document1 pageTerminology Chapter 5api-306867903No ratings yet
- Course Outline 20Document2 pagesCourse Outline 20api-306867903No ratings yet
- 2-3 VisualDocument2 pages2-3 Visualapi-306867903No ratings yet
- PPGP 2015-2016Document8 pagesPPGP 2015-2016api-306867903No ratings yet
- 2-1 Brainstorming SheetbDocument2 pages2-1 Brainstorming Sheetbapi-306867903No ratings yet
- Course OutlineDocument2 pagesCourse Outlineapi-306867903No ratings yet
- Social 20 Unit-LrpDocument4 pagesSocial 20 Unit-Lrpapi-306867903No ratings yet
- Weekly AssignmentsDocument10 pagesWeekly Assignmentsapi-306867903No ratings yet
- Steps For Writing A ParagraphDocument2 pagesSteps For Writing A Paragraphapi-306867903No ratings yet
- Writing Sample Grade10 3Document2 pagesWriting Sample Grade10 3api-306867903No ratings yet
- Guidelines For Writing An Argumentative Essay in - 2: Opposing ViewsDocument5 pagesGuidelines For Writing An Argumentative Essay in - 2: Opposing Viewsapi-306867903No ratings yet
- Writing Sample Grade10 1Document2 pagesWriting Sample Grade10 1api-306867903No ratings yet
- Related Issue 1 Review Key TermsDocument2 pagesRelated Issue 1 Review Key Termsapi-306867903No ratings yet
- Writing Sample Grade10 5Document2 pagesWriting Sample Grade10 5api-306867903No ratings yet
- Related Issue 2 Review 2012Document6 pagesRelated Issue 2 Review 2012api-306867903No ratings yet
- r1 Terminology Social Studies 10Document1 pager1 Terminology Social Studies 10api-306867903No ratings yet
- Ri1 Sources To Study From 1Document7 pagesRi1 Sources To Study From 1api-306867903No ratings yet
- Talking Canadian Video Questions - DigitalDocument2 pagesTalking Canadian Video Questions - Digitalapi-306867903No ratings yet