Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Practica Seccion 2 Cap 6 Ciencia
Uploaded by
Araas AraasCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Practica Seccion 2 Cap 6 Ciencia
Uploaded by
Araas AraasCopyright:
Available Formats
Name
Date
Chapter
Class
Reinforcement and Study Guide
The Chemistry of Life, continued
Section 6.2 Water and Diffusion
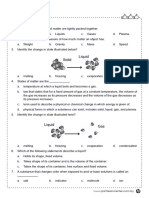
In your textbook, read about water and its importance.
For each statement below, write true or false.
false
____________________
1. In a water molecule, electrons are shared equally between the hydrogen
atoms and oxygen atom.
false
____________________
2. The attraction of opposite charges between hydrogen and oxygen forms
a weak oxygen bond.
true
____________________
3. Because of its polarity, water can move from the roots of a plant up to its leaves.
false
____________________
4. Water changes temperature easily.
true
____________________
5. Unlike most substances, water expands when it freezes.
Circle the letter of the choice that best completes the statement.
6. All objects in motion have
a. potential energy.
b. heat energy.
c. kinetic energy.
d. random energy.
Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
7. The first scientist to observe evidence of the random motion of molecules was
a. Brown.
b. Darwin.
c. Mendel.
d. Hooke.
8. The net movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower
concentration is called
a. dynamic equilibrium.
b. nonrandom movement.
c. concentration gradient.
d. diffusion.
9. Diffusion occurs because of
a. nonrandom movement of particles.
c. a chemical reaction between particles.
b. random movement of particles.
d. chemical energy.
10. When a few drops of colored corn syrup are added to a beaker of pure corn syrup, the color will
a. move from low concentration to high concentration.
b. form a polar bond.
c. start to diffuse.
d. remain on the bottom of the beaker.
11. Diffusion can be accelerated by
a. decreasing the pressure.
c. decreasing the movement of particles.
b. increasing the temperature.
d. increasing the dynamic equilibrium.
12. When materials pass into and out of a cell at equal rates, there is no net change in concentration
inside the cell. The cell is in a state of
a. dynamic equilibrium. b. metabolism.
c. imbalance.
d. inertia.
13. The difference in concentration of a substance across space is called
a. dynamic equilibrium.
b. concentration gradient.
c. diffusion.
d. Brownian movement.
REINFORCEMENT AND STUDY GUIDE
CHAPTER 6 BIOLOGY: The Dynamics of Life
27
You might also like
- Q1-WW in Gen Chem 2Document3 pagesQ1-WW in Gen Chem 2Jenny Vhie S. VinagreraNo ratings yet
- Midterm Genchem2Document5 pagesMidterm Genchem2MONTEALTO ALDRICH FAJARDONo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Science Summative TestDocument7 pagesGrade 8 Science Summative Testzerleigh dream pagal75% (4)
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDrew MalubagNo ratings yet
- Statement or Answers The Question. Write Your Answer On A Separate Sheet of PaperDocument4 pagesStatement or Answers The Question. Write Your Answer On A Separate Sheet of PaperJabsTheKnightNo ratings yet
- Monthly Assessment No. 1 General Chemistry IiDocument4 pagesMonthly Assessment No. 1 General Chemistry IiYesha Therese Eduarte MagsombolNo ratings yet
- MAP-Physical Science Worksheet 1 Matter Answer KeyDocument7 pagesMAP-Physical Science Worksheet 1 Matter Answer KeyEzra YoktaNo ratings yet
- Summative Test 1 Q 3 Gen - Chem 2 SY 2022 2023 Copy - Edited Copy - EditedDocument11 pagesSummative Test 1 Q 3 Gen - Chem 2 SY 2022 2023 Copy - Edited Copy - EditedJV Subang PatindolNo ratings yet
- 2324 - F3 - Sci Exam - Final (Roi) - AnsDocument8 pages2324 - F3 - Sci Exam - Final (Roi) - Anslmmlm0505No ratings yet
- Chapter Test A: Chapter: States of MatterDocument4 pagesChapter Test A: Chapter: States of MatterAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (Stem) : Vapn Condn Fusion FreezingDocument3 pagesScience, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (Stem) : Vapn Condn Fusion FreezingAlvin MontesNo ratings yet
- Is The Transition of A Substance Directly From The Solid To The Gas State, Without Passing Through The Liquid StateDocument5 pagesIs The Transition of A Substance Directly From The Solid To The Gas State, Without Passing Through The Liquid StateJerica BautNo ratings yet
- 78 11 12 Science Physics States of Matter 3Document3 pages78 11 12 Science Physics States of Matter 3Kung ThanyathornNo ratings yet
- Chem LHT 2 UnfinfihedDocument7 pagesChem LHT 2 Unfinfihederika sabelNo ratings yet
- 1 Atm 101.3 Kpa 1 Atm 760 MM HG or Torr: CH 13 and 14 Practice TestDocument11 pages1 Atm 101.3 Kpa 1 Atm 760 MM HG or Torr: CH 13 and 14 Practice Testيزن جانسيزNo ratings yet
- Education Gate International School 2: Name: - Grade: 6Document8 pagesEducation Gate International School 2: Name: - Grade: 6Lama AldailamiNo ratings yet
- Learning: Formation of Elements in The Universe and Properties of MatterDocument7 pagesLearning: Formation of Elements in The Universe and Properties of Matterrhiantics_kram11No ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Exam - Science 8Document4 pages3rd Quarter Exam - Science 8anon_29890413293% (98)
- Lab Sheet 5Document3 pagesLab Sheet 5MELISSA NANONGNo ratings yet
- A General Chemistry II 12 q1m1.3 Teacher Copy Final LayoutDocument21 pagesA General Chemistry II 12 q1m1.3 Teacher Copy Final LayoutCristine Mae MakinanoNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3 - W E E K 1: GradeDocument13 pagesQuarter 3 - W E E K 1: GradeAleesa RowanNo ratings yet
- SCI10 Q4 MOD1.3 Pages 15 23Document20 pagesSCI10 Q4 MOD1.3 Pages 15 23lotacaracasNo ratings yet
- Third Summative Test in Science 8Document5 pagesThird Summative Test in Science 8Sunny Amar100% (2)
- 3rd Unit Test in Science 8Document3 pages3rd Unit Test in Science 8Sophia Acer Artates0% (1)
- Science: Quarter 3: Module 2 Movement of MoleculesDocument11 pagesScience: Quarter 3: Module 2 Movement of MoleculesFriah Mae DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet General Chemistry 2 (Q2 - Wks. 1-2) Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument10 pagesLearning Activity Sheet General Chemistry 2 (Q2 - Wks. 1-2) Kinetic Molecular TheoryJeffrey YumangNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 Q1 Summative Test 1Document3 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Q1 Summative Test 1MA. HAZEL TEOLOGO100% (1)
- ch1 Test BankDocument9 pagesch1 Test BankshynggysNo ratings yet
- 7th Grade Science Calamity 2Document10 pages7th Grade Science Calamity 2Saima HoqueNo ratings yet
- T3Q1Document5 pagesT3Q1henni07.bwNo ratings yet
- Lesson Exemplar Forfood ChainDocument8 pagesLesson Exemplar Forfood ChainAngelita MenesesNo ratings yet
- Physicalscience q1 Mod6 Effectsofintermolecularforcesonpropertiesofsubstances v2Document35 pagesPhysicalscience q1 Mod6 Effectsofintermolecularforcesonpropertiesofsubstances v2Marivic Garvida0% (1)
- AP Practice Test Unit 1 2017Document7 pagesAP Practice Test Unit 1 2017김꽁쥬No ratings yet
- Gen Chem 2Document2 pagesGen Chem 2Trisha Camille MacarioNo ratings yet
- Jasmin-Week 7-Worksheets (Tests)Document18 pagesJasmin-Week 7-Worksheets (Tests)Abigail JasminNo ratings yet
- 3RD Quarter AssessmentsDocument6 pages3RD Quarter AssessmentsLorraine DonioNo ratings yet
- T F T T T: Name: - DateDocument5 pagesT F T T T: Name: - DateSamantha NortonNo ratings yet
- Sum 1, Phy SciDocument3 pagesSum 1, Phy SciJeclyn Filipinas100% (1)
- 3rd TQ-GENCHEM-2Document4 pages3rd TQ-GENCHEM-2Nazer M. LacaboNo ratings yet
- Science Quiz Grade: 8 Quiz 5: Do Not Turn The Page Until Instructed To Do SoDocument10 pagesScience Quiz Grade: 8 Quiz 5: Do Not Turn The Page Until Instructed To Do Soapi-238949685No ratings yet
- Science Worksheet 6Document2 pagesScience Worksheet 6Penelope RocesNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 Q3 Module 2Document16 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Q3 Module 2Jennylyn CariagaNo ratings yet
- Matter QuizDocument5 pagesMatter QuizduhyanNo ratings yet
- Final Study Guide (Science 7TH Grade)Document17 pagesFinal Study Guide (Science 7TH Grade)Sharon Miguel Clavijo AmarisNo ratings yet
- G8Document3 pagesG8Shaina Jandoc TalanginNo ratings yet
- Science 8 - Module 4 - Version 3 1Document16 pagesScience 8 - Module 4 - Version 3 1EdcheloNo ratings yet
- Physical-Science11 Q1 MODULE-6 Edited 08082020Document31 pagesPhysical-Science11 Q1 MODULE-6 Edited 08082020Roseman Tumaliuan100% (1)
- States of Matter Practice TestDocument14 pagesStates of Matter Practice TestBabeejay2No ratings yet
- Mogpog National Comprehensive High SchoolDocument3 pagesMogpog National Comprehensive High SchoolMyra Ramirez RamosNo ratings yet
- JCC Reviewer Nomenclature and Organic CompoundsDocument35 pagesJCC Reviewer Nomenclature and Organic CompoundsVel BascosNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 - Q3 - SLM3Document10 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 - Q3 - SLM3Jonnel RoqueNo ratings yet
- BIO CH02 L02 Properties of WaterDocument3 pagesBIO CH02 L02 Properties of WaterCamilo SepulvedaNo ratings yet
- Name: - Date: Section: Grade 11 - ScoreDocument3 pagesName: - Date: Section: Grade 11 - ScoreAnonymous Rwk3PgttIINo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Study GuideDocument8 pagesChapter 2 Study GuideportbluepicklesNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For 2010 Living in A Microbial World 1st Edition Study AidDocument37 pagesTest Bank For 2010 Living in A Microbial World 1st Edition Study Aidbrookemaxwellfhfpy100% (12)
- MatterDocument2 pagesMatterALEJANDRO CORTEZNo ratings yet
- Q1, Gen Chem 2 Sy 2022-2023Document4 pagesQ1, Gen Chem 2 Sy 2022-2023Jenny Vhie S. VinagreraNo ratings yet
- Phy Ex. 1.1 SolutionDocument3 pagesPhy Ex. 1.1 SolutionDilip deotaleNo ratings yet
- It's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingFrom EverandIt's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactFrom EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- AP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeFrom EverandAP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- Taste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodFrom EverandTaste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (20)
- Guidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsFrom EverandGuidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (90)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- AP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeFrom EverandAP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideFrom EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionFrom EverandThe Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Tribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsFrom EverandTribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Fundamentals of Chemistry: A Modern IntroductionFrom EverandFundamentals of Chemistry: A Modern IntroductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsFrom EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (146)
- Guidelines for Integrating Process Safety into Engineering ProjectsFrom EverandGuidelines for Integrating Process Safety into Engineering ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Formulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsFrom EverandFormulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactFrom EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNo ratings yet