Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Solid State Properties and Types
Uploaded by
HaRryOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Solid State Properties and Types
Uploaded by
HaRryCopyright:
Available Formats
Solid State
1.
1.1
1.2
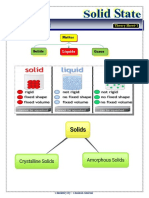
SOLIDS
Solids are characterised by the state of matter in which particles are closely packed and held together by strong
inter molecular attractive force.
Properties of solids
(a)
In solid state the particles are not able to move randomly.
(b)
They have definite shape and volume.
(c)
Solids have high density..
(d)
Solids have high and sharp melting point which is depend on the strength or value of binding energy.
(f)
They are very low compressible.
(g)
They show very slow diffusion.
Types of Solids
Solids
(c)
(d)
(e)
Crystalline Solids
Amorphous Solids
Crystalline solids
In this type of solids the atoms or molecule are arranged in a regular pattern in the three dimensional network.
They havewell defined geometrical pattern, sharp melting point, definite heat of fusion and anisotropic nature.
Anisotropic means they exhibit different physical properties in all directions.
eg. The electrical and thermal conductivities are different in different directions.
They are generally incompressible.
.
The general examples of crystalline solids are as Quartz, diamond etc.
Amorphous Solids
In this type of solids, the arrangement of-building constituents is not regular.
They are regarded as super cooled liquids with high viscosity in which the force of attraction holding the molecules together are so great, that the material becomes rigid but there is no regularity in structure.
They do not have sharp melting points.
They are isotropic as they exhibit same physical properties in all the directions.
The general examples of this solids are as glass, Rubber, plastics etc.
1.3
Difference between crystalline and amorphous solids
1. 2.1
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
1.2.2
(a)
(b)
S.No Property
1
Shape
Crystalline solids
They have definite and regular geometrical form.
Amorphus solids
They do not have definite and regular
geometrical form.
Melting point
They have definite melting point.
They do not have definite melting point.
Heat of fusion
They have a definite heat of fusion.
They do not have definite heat of fusion
Compressibility They are rigid and incompressible.
Cutting with a
Sharp edged
tool
They are given cleavage i.e. they
break into two pieces with plane
surfaces.
These may be compressed to any
appreciable extent.
They are given irregular cleavage i.e.
they break into two pieces with
irregular surface.
Isotropy and
Anisotropy
They are anisotropic.
They are isotropic.
You might also like
- Solid-State 01Document1 pageSolid-State 01javeed akthaar sNo ratings yet
- Solid State Structure and PropertiesDocument36 pagesSolid State Structure and PropertiesVedant BiyaniNo ratings yet
- Genchem2 q3m2b Solids-And-imf FinalDocument50 pagesGenchem2 q3m2b Solids-And-imf Finalroxtonandrada8No ratings yet
- LP - GC - Nature of SolidsDocument9 pagesLP - GC - Nature of SolidsAllyza SobosoboNo ratings yet
- 5921apni KakshaDocument109 pages5921apni KakshaVimal PrasadNo ratings yet
- LP - GP - Coulomb's LawDocument9 pagesLP - GP - Coulomb's LawAllyza SobosoboNo ratings yet
- SheetDocument108 pagesSheetPinkyNo ratings yet
- CH-1 (Xii)Document11 pagesCH-1 (Xii)Vijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Noo Xii Ch01 Solid StateDocument51 pagesNoo Xii Ch01 Solid StateG boiNo ratings yet
- ES Module 3 - Quarter 1 - Types of SolidsDocument13 pagesES Module 3 - Quarter 1 - Types of SolidsAnalynAsuncionAtaydeNo ratings yet
- Solidstate Part 1Document35 pagesSolidstate Part 1Gopikrishna ThirunavukarasuNo ratings yet
- 1. The Solid StateDocument41 pages1. The Solid StateComedy BoyNo ratings yet
- Nature of CrystalDocument24 pagesNature of CrystalYeh I'mBreadNo ratings yet
- 1.solid StateDocument33 pages1.solid StateBHAVITH SD VNS 06No ratings yet
- Solid StateDocument41 pagesSolid State45 XI A Subham SharmaNo ratings yet
- A premium institute for CBSE, NEET & JEEDocument25 pagesA premium institute for CBSE, NEET & JEEDigvijay SolankiNo ratings yet
- Solid StateDocument17 pagesSolid Statenoorunnisa0184No ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 - Q3 - SLM4Document11 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 - Q3 - SLM4Jonnel RoqueNo ratings yet
- Solid State Chemistry Maharashtra State BoardDocument27 pagesSolid State Chemistry Maharashtra State BoardPankaj JindamNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-01 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (The Solid State) Topic: Solids and Their ClassificationDocument4 pagesCbse Test Paper-01 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (The Solid State) Topic: Solids and Their ClassificationAtashImranNo ratings yet
- Solid State Typed Notes STUDY RATEDocument25 pagesSolid State Typed Notes STUDY RATEYASH SONARNo ratings yet
- Rizal General Chemistry 2 q3 Slm4Document12 pagesRizal General Chemistry 2 q3 Slm4Darlene OpeñaNo ratings yet
- SOLID STATE (School)Document36 pagesSOLID STATE (School)CHIRAG VOHRANo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Class - 12 SubjectDocument7 pagesChemistry: Class - 12 SubjectHemant YadavNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER-solid State Part 1Document2 pagesCHAPTER-solid State Part 1Arpandeep KaurNo ratings yet
- Solid State Day 1Document8 pagesSolid State Day 1Rakesh SenNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 Quarter 3: Week 2 - Module 2B Intermolecular Forces of Liquids and Solids Solids and Their PropertiesDocument20 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Quarter 3: Week 2 - Module 2B Intermolecular Forces of Liquids and Solids Solids and Their PropertiesJessicaNo ratings yet
- Modul 6 The Solid StateDocument31 pagesModul 6 The Solid StateACHMAD ZULFAN ALMAHDY 1No ratings yet
- 1 Solid State 25Document25 pages1 Solid State 25Aryan POONIANo ratings yet
- Classification and Properties of Crystalline and Amorphous SolidsDocument3 pagesClassification and Properties of Crystalline and Amorphous Solidsmillinagi95No ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Intermolecular Forces of Liquids and Solids - Solids and TheirDocument24 pagesLesson 3 Intermolecular Forces of Liquids and Solids - Solids and TheirLyndy PantaoNo ratings yet
- Us To Make Solids of Desired PurposeDocument5 pagesUs To Make Solids of Desired PurposeSam JonesNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Crystalline and Amorphous SolidsDocument3 pagesModule 5 - Crystalline and Amorphous Solidsmm.vince21No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Solid State Study NotesDocument414 pagesCBSE Class 12 Solid State Study Notespranav kudesiaNo ratings yet
- Amorphous and Crystalline SolidsDocument8 pagesAmorphous and Crystalline SolidsAli ImranNo ratings yet
- Solid StateDocument25 pagesSolid StateMohit KumarNo ratings yet
- Solid StateDocument37 pagesSolid StateSai Sasivardhan GampaNo ratings yet
- Target Publications Pvt. Ltd. Chapter 01: Classification of SolidsDocument14 pagesTarget Publications Pvt. Ltd. Chapter 01: Classification of SolidsSayyed SohelNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 - LAS 2 LEARNING CAPSULEDocument5 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 - LAS 2 LEARNING CAPSULEMark RazNo ratings yet
- Solids 150702201407 Lva1 App6892Document9 pagesSolids 150702201407 Lva1 App6892Samina ZaibNo ratings yet
- By Prin Ces Ir: He Olid TateDocument49 pagesBy Prin Ces Ir: He Olid TateVinayNo ratings yet
- Squid Dame PPDocument27 pagesSquid Dame PPJaier DojolesNo ratings yet
- Solid States NotesDocument34 pagesSolid States NotesTNo ratings yet
- SolidsDocument2 pagesSolidsNimz StudioNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 Q3 Week 2Document2 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Q3 Week 2jcjimz259No ratings yet
- Physical ChemistryDocument5 pagesPhysical ChemistryJothi KNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solid States (Typed Notes)Document12 pagesClass 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solid States (Typed Notes)Shaku JoshiNo ratings yet
- JEE Advanced 2023 Solid State Revision Notes - Free PDF DownloadDocument11 pagesJEE Advanced 2023 Solid State Revision Notes - Free PDF Downloadhishamkalliyath19No ratings yet
- Aerospce Batch 3 PHY 4201 Lecture 1Document26 pagesAerospce Batch 3 PHY 4201 Lecture 1Rasel khanNo ratings yet
- GCHEM2_Q3_LAS_WK1_DAY5Document2 pagesGCHEM2_Q3_LAS_WK1_DAY5mae.joan.reposposaNo ratings yet
- Solid StateDocument49 pagesSolid Statekishangopi123No ratings yet
- Hbse Revision CapsuleDocument18 pagesHbse Revision CapsuleS.S. Tutorials Radaur OfficialNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document9 pagesChapter 3JeromeNo ratings yet
- CRYSTALDocument28 pagesCRYSTALakinlangsigyuuuNo ratings yet
- Solid State Notes PDFDocument36 pagesSolid State Notes PDFGyanendra Gs100% (1)
- The Solid State GuideDocument75 pagesThe Solid State GuideNishali SamNo ratings yet
- Structure and Properties of Solids Helps Us To Make Solids of Desired PurposeDocument37 pagesStructure and Properties of Solids Helps Us To Make Solids of Desired PurposeSam JonesNo ratings yet
- Children Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeFrom EverandChildren Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- AIIMS MBBS 2013 Question PaperDocument14 pagesAIIMS MBBS 2013 Question PaperElla BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Gta San Andreas All CheatsDocument3 pagesGta San Andreas All CheatsLupoaie MihaiNo ratings yet
- Solutions AIATS Medical-2017 Test-3 (Code-A B) (18!12!2016)Document24 pagesSolutions AIATS Medical-2017 Test-3 (Code-A B) (18!12!2016)HaRry0% (1)
- 11 Biology Exemplar Chapter 10Document5 pages11 Biology Exemplar Chapter 10HaRryNo ratings yet
- Iit Jee BNHBDocument1 pageIit Jee BNHBHaRryNo ratings yet
- Beneficiary CertificateDocument1 pageBeneficiary CertificateHaRryNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Summer Assignment 2014Document3 pagesAP Biology Summer Assignment 2014HaRryNo ratings yet
- SC/ST certificate guideDocument13 pagesSC/ST certificate guideHaRryNo ratings yet
- Gta San Andreas All CheatsDocument3 pagesGta San Andreas All CheatsLupoaie MihaiNo ratings yet
- Aipmt Pre 2000Document15 pagesAipmt Pre 2000HaRryNo ratings yet
- Spring Force (PG by AA) 635526663296751304Document4 pagesSpring Force (PG by AA) 635526663296751304Hrithik GoyalNo ratings yet
- Updated ListDocument1 pageUpdated ListHaRryNo ratings yet
- PG Brainstormer - 9c (Mechanics) 635526719868222666Document5 pagesPG Brainstormer - 9c (Mechanics) 635526719868222666mahmood_810357066No ratings yet
- B. Sc. Second Semester: Zoology Paper - VI Genetics - IDocument2 pagesB. Sc. Second Semester: Zoology Paper - VI Genetics - IHaRryNo ratings yet
- IPU CET MBBS 2016 How To Fill Application Form PDFDocument13 pagesIPU CET MBBS 2016 How To Fill Application Form PDFsurendra thakurNo ratings yet
- Analysis Aipmt Neet 6Document4 pagesAnalysis Aipmt Neet 6Ritik ShuklaNo ratings yet
- VCI AIPVT 2016 NoticeDocument1 pageVCI AIPVT 2016 NoticeHaRryNo ratings yet
- Advertisement PDFDocument1 pageAdvertisement PDFHaRryNo ratings yet
- Full Mechanics - Question PaperDocument7 pagesFull Mechanics - Question PaperharwinderNo ratings yet
- AIPVT 2016 Admit Card Download InstructionsDocument1 pageAIPVT 2016 Admit Card Download InstructionsHaRryNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Field and Magnetic Effects of Current: Assignment 2Document2 pagesMagnetic Field and Magnetic Effects of Current: Assignment 2HaRryNo ratings yet
- Harru Saab IttytuytDocument3 pagesHarru Saab IttytuytHaRryNo ratings yet
- Central Board of Secondary Education: National Eligibility Cum Entrance Test-Ii (Ug) Admission NoticeDocument1 pageCentral Board of Secondary Education: National Eligibility Cum Entrance Test-Ii (Ug) Admission NoticeHaRryNo ratings yet
- Physics IitDocument233 pagesPhysics IitHaRry50% (2)
- 22 7 131Document5 pages22 7 131HaRryNo ratings yet
- ShowPdf 2Document3 pagesShowPdf 2HaRryNo ratings yet
- Central Board of Secondary Education: All India Pre-Medical/Pre-Dental Test UnitDocument1 pageCentral Board of Secondary Education: All India Pre-Medical/Pre-Dental Test UnitHaRryNo ratings yet
- Iitggfdgdfagsghghgfhs Ew87y Whuiorqh0hpDocument3 pagesIitggfdgdfagsghghgfhs Ew87y Whuiorqh0hpHaRryNo ratings yet
- Shiftingcmch PDFDocument1 pageShiftingcmch PDFHaRryNo ratings yet