Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Notebook 3
Uploaded by
api-3386617480 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesOriginal Title
notebook 3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesNotebook 3
Uploaded by
api-338661748Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Notebook 3
Sammy Puccini
Type of Radiation
Definitions
Properties
Particulate
Include high energy
electrons, protons, and
neutrons that produce
ionization in matter by
direct atomic collisions
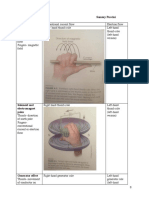
Alpha particles: two
protons and two
neutrons, equivalent to a
helium nucleus.
Beta: identical to
electrons except origin
Electromagnetic
produce ionization in matter by
other types of interactions.
x-ray and gamma rays: same
except their origin
photoelectric absorption and
Compton scattering
wave theory: electromagnetic
energy travels through space in the
form of waves, which are
disturbances in a medium. All
waves have a wavelength,
frequency, amplitude, and period
wavelength: distance between two
points on a wave
frequency: number of waves that
pass a particular point in given
time frame
amplitude: intensity of the wave,
height
and period: time required to
complete one cycle of wave
Originate
Alpha: emitted from the
nuclei of very heavy
elements as they
undergo radioactive
decay
Gamma ray emitted by nuclei of
radioactive material
X-rays: man made in x-ray tube
Beta: emitted rom the
nuclei of radioactive
material
Properties of x-rays:
1. Highly penetrating, invisible rays that are a form of electromagnetic radiation
2. Are electrically neutral, not affected by electric or magnetic fields
3. Produced by wide variety of energies and wavelengths
4. Release small amounts of heat passing through matter
5. Travel in straight lines
6. Travel at speed of light in a vacuum (3x10^8)
7. Can ionize matter
8. Cause emission of light in certain crystals
9. Cant be focused by a lens
10. Affect photographic film
11. Produce chemical and biological changes in matter through ionization and excitation
12. Produce secondary and scatter radiation
You might also like
- ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS: Exposure is not optional, no one can avoid itFrom EverandELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS: Exposure is not optional, no one can avoid itNo ratings yet
- Notebook 3Document3 pagesNotebook 3api-335583967No ratings yet
- Radioactive EmmissionDocument15 pagesRadioactive Emmissioneshabennie1No ratings yet
- Presented By-Aarzoo Pathak (Final YearDocument52 pagesPresented By-Aarzoo Pathak (Final YearSandeep VermaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Introduction To RadiationDocument36 pagesChapter 3 Introduction To Radiationhailemicael mesfinNo ratings yet
- Notebook 3Document2 pagesNotebook 3api-340425056No ratings yet
- Particulate ElectromagneticDocument2 pagesParticulate Electromagneticapi-356951570No ratings yet
- Radiation & Radioactivity and Half LifeDocument27 pagesRadiation & Radioactivity and Half LifedwyphyNo ratings yet
- Forms of Electromagnetic Waves and The em SpectrumDocument6 pagesForms of Electromagnetic Waves and The em SpectrumMicah TormonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02Document2 pagesChapter 02zahidNo ratings yet
- The Development of A New Atomic ModelDocument4 pagesThe Development of A New Atomic ModelanaNo ratings yet
- PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT yDocument17 pagesPHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT ynidhikoshaliaNo ratings yet
- Ionizing RadiationDocument5 pagesIonizing RadiationCristinaNo ratings yet
- Radiation Sources, Effects, and SolutionsDocument89 pagesRadiation Sources, Effects, and SolutionsCM NajitoNo ratings yet
- Radiation & Radioactivity: Department of Medical Biophysics and Informatics 3rd Medical Faculty of Charles UniversityDocument34 pagesRadiation & Radioactivity: Department of Medical Biophysics and Informatics 3rd Medical Faculty of Charles UniversityahkiaenaaaaNo ratings yet
- Natural and Induced Radioactivity: Prof - Dr. Mohamed Hasanein Gaber Professor of BiophysicsDocument51 pagesNatural and Induced Radioactivity: Prof - Dr. Mohamed Hasanein Gaber Professor of BiophysicsAhmedAmer1No ratings yet
- 4th Lecture Physics of Diagnostic X-RayDocument43 pages4th Lecture Physics of Diagnostic X-RayAsfoor gake1No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Spectrum: Learning OutcomesDocument7 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum: Learning OutcomesAbhishek KunalNo ratings yet
- Course: Introduction To Environmental Sciences Bs-Environmental Sciences Semester: Spring-2020 Department of Environmental SciencesDocument13 pagesCourse: Introduction To Environmental Sciences Bs-Environmental Sciences Semester: Spring-2020 Department of Environmental SciencesAwais HassanNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves Spectrum GuideDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic Waves Spectrum GuideJahleel TroupeNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Physics Chapter 12 Revision NotesDocument4 pagesClass 10 Physics Chapter 12 Revision NotesGAMING IN MOODNo ratings yet
- RADIOGRAPHY PRINCIPLESDocument63 pagesRADIOGRAPHY PRINCIPLESaasattiNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Radiography Using High Energy Radiation SystemsDocument25 pagesEvaluating Radiography Using High Energy Radiation SystemsMuthu SaravananNo ratings yet
- 1-Radiation Physics X Ray Machine Factors Affecting Qualitty 2Document168 pages1-Radiation Physics X Ray Machine Factors Affecting Qualitty 2zyad ahmedNo ratings yet
- Radiation Is Energy That Comes From A Source and Travels Through Some MaterialDocument9 pagesRadiation Is Energy That Comes From A Source and Travels Through Some MaterialmheljuNo ratings yet
- EMFT Assignment 5Document48 pagesEMFT Assignment 5M. HamzaNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry Notes Ch02 Structure of AtomDocument18 pages11 Chemistry Notes Ch02 Structure of AtomSayantanBanerjee0% (1)
- Structure and Properties of AtomsDocument10 pagesStructure and Properties of AtomsRishabh Garg33% (3)
- Scii 1Document6 pagesScii 1ReignNo ratings yet
- Rad PhysicsDocument109 pagesRad PhysicsRicardo EdanoNo ratings yet
- How scientists accelerate particles with electric fieldsDocument18 pagesHow scientists accelerate particles with electric fieldsHumaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.1: Introduction To Diagnostic Imaging and X-Ray FormationDocument9 pagesLesson 1.1: Introduction To Diagnostic Imaging and X-Ray FormationElah TapangNo ratings yet
- Hiro 1Document6 pagesHiro 1Aron JaroNo ratings yet
- Sunlight:: Sunlight Is A Portion of TheDocument8 pagesSunlight:: Sunlight Is A Portion of TheApu NayemNo ratings yet
- The Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument34 pagesThe Electromagnetic Spectrumsoha baigNo ratings yet
- 1-Biological Effects of RadiationsDocument18 pages1-Biological Effects of RadiationsAbdala M. Mostafa100% (1)
- Structure - of - Atom - Class 11 CbseDocument10 pagesStructure - of - Atom - Class 11 CbseAnshuman SinghNo ratings yet
- Introduction, History & Basic PhysicsDocument2 pagesIntroduction, History & Basic PhysicsAbo QadeerNo ratings yet
- Gamma Rays: Understanding the Penetrating Electromagnetic RadiationDocument6 pagesGamma Rays: Understanding the Penetrating Electromagnetic RadiationDairabiy AstarichNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics Hints: Atomic Structure, Spectra, Radiation, and MoreDocument21 pagesModern Physics Hints: Atomic Structure, Spectra, Radiation, and MoreOlajide HeritageNo ratings yet
- The Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument41 pagesThe Electromagnetic SpectrumNoel John UmallaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes Chap 2 Structure of An AtomDocument15 pagesChemistry Notes Chap 2 Structure of An AtomJo ParkerNo ratings yet
- History: Spectrum IsDocument23 pagesHistory: Spectrum IsMuhamad NurhudayahNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 7Document12 pagesChemistry Chapter 7Heather KieferNo ratings yet
- Act. 2 Natural Radioactive SeriesDocument2 pagesAct. 2 Natural Radioactive Seriesxiejie22590No ratings yet
- 1.1 Radiation: Interaction of Radiation With MatterDocument49 pages1.1 Radiation: Interaction of Radiation With MatterShiva KumarNo ratings yet
- Rad PhysDocument5 pagesRad PhysCarlos BustamanteNo ratings yet
- MODERN PHYSICS 1 Dual Nature and AtomsDocument4 pagesMODERN PHYSICS 1 Dual Nature and AtomsAkash tech. videoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Unit 2: Assignment 1 Analytical Methods and Separation TechniquesDocument30 pagesChemistry: Unit 2: Assignment 1 Analytical Methods and Separation TechniquesLorri - Ann Lamont100% (1)
- RadiationDocument31 pagesRadiationS RahmnNo ratings yet
- Electron Emission From Solids (I) : History & TheoryDocument6 pagesElectron Emission From Solids (I) : History & Theorydei_sandeep7994No ratings yet
- Physics - The Physics of The AtomDocument8 pagesPhysics - The Physics of The AtomNaomi JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Radiation PhysicsDocument61 pagesRadiation PhysicsfsdgfNo ratings yet
- Radiographic Testing Techniques and ApplicationsDocument99 pagesRadiographic Testing Techniques and ApplicationsThe Engineers EDGE, Coimbatore0% (1)
- High Voltage EngineeringDocument58 pagesHigh Voltage EngineeringDawood Najem Saleh100% (1)
- Lesson 2.2. Learning TimeDocument9 pagesLesson 2.2. Learning TimeCruella MajoNo ratings yet
- Dental Radiology Electron-Target InteractionDocument78 pagesDental Radiology Electron-Target InteractionbbnnnNo ratings yet
- Greg Herman Environmental Health and Safety Radiation Protection 814-865-6391 Gsh12@psu - EduDocument132 pagesGreg Herman Environmental Health and Safety Radiation Protection 814-865-6391 Gsh12@psu - EduSpoiled BratNo ratings yet
- Notebook 10Document7 pagesNotebook 10api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 7Document2 pagesNotebook 7api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 1Document4 pagesNotebook 1api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 12Document3 pagesNotebook 12api-338661748No ratings yet
- Test Tolerance Limits Frequency & Exceptions Performed by Explain Purpose Diagnostic Radiographic SystemsDocument5 pagesTest Tolerance Limits Frequency & Exceptions Performed by Explain Purpose Diagnostic Radiographic Systemsapi-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 8Document2 pagesNotebook 8api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 3Document2 pagesNotebook 3api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 5Document2 pagesNotebook 5api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 9 Sammy Puccini Artifact Causes Appearance Dirt On Optics (Lenses, Mirror, and Light Guide Not Cleaned Horizontal White LinesDocument4 pagesNotebook 9 Sammy Puccini Artifact Causes Appearance Dirt On Optics (Lenses, Mirror, and Light Guide Not Cleaned Horizontal White Linesapi-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 14Document2 pagesNotebook 14api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 4Document2 pagesNotebook 4api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 6Document2 pagesNotebook 6api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 10Document2 pagesNotebook 10api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 2Document4 pagesNotebook 2api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 15Document2 pagesNotebook 15api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 13Document1 pageNotebook 13api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 16Document3 pagesNotebook 16api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 8Document1 pageNotebook 8api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 11Document1 pageNotebook 11api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 9Document1 pageNotebook 9api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 12Document1 pageNotebook 12api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 2Document1 pageNotebook 2api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 7Document1 pageNotebook 7api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 1Document2 pagesNotebook 1api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 5Document3 pagesNotebook 5api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 4Document2 pagesNotebook 4api-338661748No ratings yet