0% found this document useful (0 votes)
117 views4 pagesIntro to Electrical Circuits
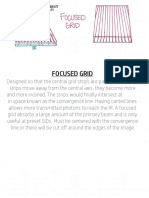
This document discusses the key components of an electrical circuit and their functions. It defines a basic electrical circuit as containing a power source, load, connectors, and switch. The power source provides energy and the load is the device being powered. It then lists and describes common circuit elements like resistors, capacitors, transformers, motors, conductors, diodes, fuses, circuit breakers, and batteries. Formulas for voltage, current, resistance, power, and power loss are also provided. References for further information on circuit components are listed at the end.
Uploaded by
api-335583967Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
117 views4 pagesIntro to Electrical Circuits
This document discusses the key components of an electrical circuit and their functions. It defines a basic electrical circuit as containing a power source, load, connectors, and switch. The power source provides energy and the load is the device being powered. It then lists and describes common circuit elements like resistors, capacitors, transformers, motors, conductors, diodes, fuses, circuit breakers, and batteries. Formulas for voltage, current, resistance, power, and power loss are also provided. References for further information on circuit components are listed at the end.
Uploaded by
api-335583967Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 4