Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Trigonometric Identities Explained
Uploaded by
shaheerOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Trigonometric Identities Explained
Uploaded by
shaheerCopyright:
Available Formats
Trigonometry
There are six fundamental trigonometric identities called sine, cosecant, cosine,
secant, tangent and cotangent. To define these functions we use circular approach
which involves the unit circle.
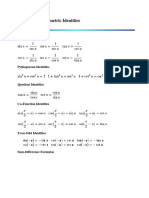
These identities are reciprocal to each other:
Sine=
1
cosecant
Cosine=
1
secant
Tangent=
Cosecant=
or
Secant =
or
1
cotangent
or
1
sine
1
cosine
Cotangent=
1
tangent
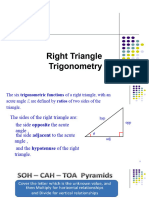
Where these identities in an angle are:
Cosine=
Sine=
Perpendicular
Hypotenuse
Secant =
Base
Hypotenuse
Tangent=
Hypotenuse
Perpendicular
Cosecant=
Perpendicular
Base
Cotangent=
Hypotenuse
Base
Base
Perpendicular
Pythagoras theorem
Hypotenuse=Base+Perpendicular
The other trignometric identities are
cos2 +sin2 =1
1+tan2 =sec2
Sec2 -tan2 =1
1+cot2 =cosec2
or cosec2 -cot2 =1
Signs of trignometric ratios in different quadrants
(i)
If
lies in first quadrant then a point P (x, y) on its terminal side has x
and y co-ordinate positive and in first quadrant all ratios will be
positive.
(ii)
lies in 2nd quadrant, then point P(x,y) on its terminal side has
If
negative x-coordinate and positive y-coordinate.
(iii)
When
lies in third quadrant, then a point P(x,y) on its terminal side
has negative x-coordinate and negative y-coordinate.
(iv)
When
Cos
lies in fourth quadrant then point P(x,y) on the terminal side of
has positive x-coordinate and y-coordinate.
0
1
30
45
1
2
2
Sin
tan
0
0
1
2
1/2
1
3
60
90
180
1/2
-1
3
2
You might also like
- Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument17 pagesTrigonometric Identitiesmaligaya evelynNo ratings yet
- Basic Trignometric NotesDocument2 pagesBasic Trignometric Notesakkisingh55555No ratings yet
- Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument14 pagesTrigonometric Identitiesthiamarie2007No ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument13 pagesTrigonometryjobmajuneNo ratings yet
- Maths Trigonometry IntroductionDocument4 pagesMaths Trigonometry IntroductionDivyaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric FunctionDocument4 pagesTrigonometric FunctionAna May BanielNo ratings yet
- TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES AND EQUATIONS_7f5357093db5654e2d349b9822bf2131Document22 pagesTRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES AND EQUATIONS_7f5357093db5654e2d349b9822bf2131mihlemgoduka22No ratings yet
- Reviewer in Pre-Calculus 11Document18 pagesReviewer in Pre-Calculus 11RJ Seva IIINo ratings yet
- The Trigonometric FunctionsDocument9 pagesThe Trigonometric Functionshenok12No ratings yet
- List of Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument16 pagesList of Trigonometric IdentitiesArnab NandiNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument36 pagesTrigonometryYoshika GNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument7 pagesTrigonometryRagav VijayNo ratings yet
- Trigonometri IdentitasDocument14 pagesTrigonometri IdentitasQonitah AdilahNo ratings yet
- List of Trigonometric Identities - wikiPEDIADocument26 pagesList of Trigonometric Identities - wikiPEDIAAmiya Ranjan MalikNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument101 pagesTrigonometryMarilyn LiconoNo ratings yet
- q391 Assignment LawrenzaquinoDocument50 pagesq391 Assignment LawrenzaquinoReuNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Formulas ListDocument6 pagesTrigonometry Formulas Listkarthik sivarajNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Functions - WikipediaDocument14 pagesTrigonometric Functions - WikipediaAlone EulerNo ratings yet
- 14-4 Trigonometry Ratios in Right TriangleDocument21 pages14-4 Trigonometry Ratios in Right Triangleapi-277585828No ratings yet
- Group-6-EDU-10-FCODocument6 pagesGroup-6-EDU-10-FCOJaishenne CastuloNo ratings yet
- Random LecturesDocument30 pagesRandom LecturesTrisha KayeNo ratings yet
- List of Trigonometric Identities: Wiki Loves Monuments: Photograph A Monument, Help Wikipedia and Win!Document43 pagesList of Trigonometric Identities: Wiki Loves Monuments: Photograph A Monument, Help Wikipedia and Win!rajeshkumar0243No ratings yet
- 11 MathematicsDocument10 pages11 MathematicsJoseph MukupaNo ratings yet
- TrignometryDocument12 pagesTrignometryVardaan ThakurNo ratings yet
- 4.3Document39 pages4.3Erjohn OcaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 13 - Trigonometry IDocument4 pagesLesson 13 - Trigonometry IAmmar RizwanNo ratings yet
- G9 Six Trigonometric Ratios (Autosaved)Document26 pagesG9 Six Trigonometric Ratios (Autosaved)anwa waNo ratings yet
- The Six Trigonometric RatiosDocument30 pagesThe Six Trigonometric Ratiosmaligaya evelynNo ratings yet
- TrigDocument14 pagesTrigSuyash PatilNo ratings yet
- 4-3 Right Triangle Trigonometry: Pre-CalculusDocument38 pages4-3 Right Triangle Trigonometry: Pre-CalculusMary Rose DavidNo ratings yet
- The Hexagon Trig Trick2Document6 pagesThe Hexagon Trig Trick2sh1k1_12No ratings yet
- In TrigonometryDocument2 pagesIn TrigonometryMJNo ratings yet
- Six TrigoDocument19 pagesSix TrigoJLacissej 117No ratings yet
- Basic Trigonometry ReviewerDocument6 pagesBasic Trigonometry ReviewerKarl Benedict Chua100% (1)
- 1Document4 pages1jaga022017No ratings yet
- Trig Identities Cheat SheetDocument15 pagesTrig Identities Cheat SheetEdward EceincoNo ratings yet
- Circular FunctionsDocument12 pagesCircular FunctionsCharlotte LladonesNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Notes, Definitions, and Formulae DefinitionsDocument6 pagesTrigonometry Notes, Definitions, and Formulae DefinitionsJulie Ailene AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Trygonometry Notes BilalgafDocument1 pageTrygonometry Notes Bilalgafcy.braylinNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric and Hyperbolic FunctionsDocument8 pagesTrigonometric and Hyperbolic FunctionsJpricarioNo ratings yet
- Advanced Trigonometry - PresentationDocument52 pagesAdvanced Trigonometry - Presentationtomas garciaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Ratios in Right TriangleDocument19 pagesTrigonometry Ratios in Right Trianglemicaela Jomil TizonNo ratings yet
- Day 38 Right Triangle TrigDocument32 pagesDay 38 Right Triangle TrigArchessNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document11 pagesPresentation 1james hardenNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Functions (Edustudy Point)_unlockedDocument4 pagesTrigonometric Functions (Edustudy Point)_unlockedsayantannandi9e1roll21No ratings yet
- The Six Trigonometric RatiosDocument30 pagesThe Six Trigonometric Ratiosmaligaya evelynNo ratings yet
- All The Trig That You Need To KnowDocument16 pagesAll The Trig That You Need To Knowapi-3755447No ratings yet
- Trigonometric FunctionsDocument10 pagesTrigonometric Functionsmaranoangela020No ratings yet
- Trigonometry FormulasDocument34 pagesTrigonometry FormulasAleksey KourbatovNo ratings yet
- Super Hexagon - Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument4 pagesSuper Hexagon - Trigonometric IdentitiesShaurya Mehta100% (1)
- Trigonometry Part 1 (Basic) VsDocument5 pagesTrigonometry Part 1 (Basic) VsLeng Kien YuenNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Functions and Identities ExplainedDocument1 pageTrigonometric Functions and Identities ExplainedmaxNo ratings yet
- IA 07trigonometric Functions37 40Document2 pagesIA 07trigonometric Functions37 40Madhu PriyaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 10 DLS 26-27Document6 pagesMathematics 10 DLS 26-27Ivan Miguel MariNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry: Lesson Two: Introduction To TrigonometryDocument11 pagesTrigonometry: Lesson Two: Introduction To TrigonometryTimothy S. San JuanNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry: Made By:-Suyash Agarwal X I - BDocument47 pagesTrigonometry: Made By:-Suyash Agarwal X I - BSuyash Agarwal100% (1)
- Basic Functions and The Right TriangleDocument15 pagesBasic Functions and The Right TriangleChetan Tolia100% (1)
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Democracy in The Modern World: United StatesDocument6 pagesDemocracy in The Modern World: United StatesshaheerNo ratings yet
- Cumulative Frequency TablesDocument5 pagesCumulative Frequency TablesshaheerNo ratings yet
- Grammar and CompositionDocument5 pagesGrammar and CompositionJohn miltonNo ratings yet
- AphroditeDocument1 pageAphroditeshaheerNo ratings yet
- Happy PrinceDocument7 pagesHappy PrinceshaheerNo ratings yet
- Compounding: Definition, Types, and Word FormationDocument2 pagesCompounding: Definition, Types, and Word FormationshaheerNo ratings yet
- Compounding: Definition, Types, and Word FormationDocument2 pagesCompounding: Definition, Types, and Word FormationshaheerNo ratings yet
- Freq PolygonDocument5 pagesFreq PolygonshaheerNo ratings yet
- University of Gujrat.: Faculty of CS & ITDocument3 pagesUniversity of Gujrat.: Faculty of CS & ITshaheerNo ratings yet
- University of Gujrat.: Faculty of CS & ITDocument3 pagesUniversity of Gujrat.: Faculty of CS & ITshaheerNo ratings yet
- ITC Lec 1Document27 pagesITC Lec 1shaheerNo ratings yet
- In The Name of ALLAH, The Most Beneficent, The Most MercifulDocument20 pagesIn The Name of ALLAH, The Most Beneficent, The Most MercifulshaheerNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Computer Applications and GenerationsDocument37 pagesIntroduction to Computer Applications and GenerationsjosephNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Muhammad Shaheer Inam Arshad Aizaz Ahmed Mirza Saad AhmedDocument4 pagesPresented By: Muhammad Shaheer Inam Arshad Aizaz Ahmed Mirza Saad AhmedshaheerNo ratings yet
- ITC Lec 11Document18 pagesITC Lec 11shaheerNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Applications: Lecture # 12Document19 pagesIntroduction To Computer Applications: Lecture # 12shaheerNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Applications: Lecture # 4Document21 pagesIntroduction To Computer Applications: Lecture # 4shaheerNo ratings yet
- IT101 Lecture8 PDFDocument31 pagesIT101 Lecture8 PDFshaheerNo ratings yet
- How To Hack Facebook by Just Doing Phishing 2016-2017 - ExtraTipsTricks (ETT)Document25 pagesHow To Hack Facebook by Just Doing Phishing 2016-2017 - ExtraTipsTricks (ETT)shaheer100% (5)
- Thish Is Sample OneDocument1 pageThish Is Sample OneshaheerNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Computer Applications Software and System SoftwareDocument25 pagesIntroduction to Computer Applications Software and System SoftwareshaheerNo ratings yet
- In The Name of ALLAH, The Most Beneficent, The Most MercifulDocument20 pagesIn The Name of ALLAH, The Most Beneficent, The Most MercifulshaheerNo ratings yet
- ITC Lec 1Document27 pagesITC Lec 1shaheerNo ratings yet
- SkimmingDocument2 pagesSkimmingapi-170611830No ratings yet
- Haifux Wireless HackingDocument70 pagesHaifux Wireless HackingTenchisanNo ratings yet
- Job Advice Reading ComprehensionDocument2 pagesJob Advice Reading ComprehensionSaima MalikNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer ApplicationsDocument31 pagesIntroduction To Computer ApplicationsshaheerNo ratings yet
- Form Method InstagramDocument1 pageForm Method InstagramIkra SukandhaaNo ratings yet
- RsDocument8 pagesRsshaheerNo ratings yet