0% found this document useful (0 votes)
103 views1 pageUnit 35: Measuring Volume
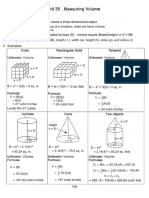
1. Volume refers to the space inside a three-dimensional object and is calculated using the object's base and height. The formula for volume is V=Bh, where B is the base and h is the height.
2. Examples of how to calculate the volume of different shapes are shown, including cubes, rectangular solids, pyramids, cylinders, cones, and multiple objects. Formulas for finding the volume of each shape are provided.
3. Volume calculations are worked through for sample objects like a cube with a base of 9 in^2 and height of 3 in, giving a volume of 27 cubic inches.
Uploaded by
weranCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
103 views1 pageUnit 35: Measuring Volume
1. Volume refers to the space inside a three-dimensional object and is calculated using the object's base and height. The formula for volume is V=Bh, where B is the base and h is the height.
2. Examples of how to calculate the volume of different shapes are shown, including cubes, rectangular solids, pyramids, cylinders, cones, and multiple objects. Formulas for finding the volume of each shape are provided.
3. Volume calculations are worked through for sample objects like a cube with a base of 9 in^2 and height of 3 in, giving a volume of 27 cubic inches.
Uploaded by
weranCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd