Professional Documents
Culture Documents
B. For Voltage Clamping: The Power Diode 23
Uploaded by
Muhammad Siddiq0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageOriginal Title
asasd.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageB. For Voltage Clamping: The Power Diode 23
Uploaded by
Muhammad SiddiqCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
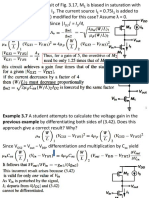
The Power Diode 23
D1
VS D2
D3
RL
D1, D2 Conducting
0ms 80ms 90ms
D3, D4 Conducting
D4
70ms
FIGURE 2.16 Full bridge rectifier and its output dc voltage.
The average rectifier output voltage:
Vdc = 2Vm
, where Vm is the peak input voltage
The rms rectifier output voltage:
Vrms = Vm
2
This rectifier is twice as efficient as compared to a single
phase one.
B. For voltage clamping
Figure 2.17 shows a voltage clamper. The negative pulse of the
sinusoidal input voltage charges the capacitor to its maximum
value in the direction shown. After charging, the capacitor
cannot discharge, since it is open circuited by the diode. Hence
the output voltage:
Vo = Vc + Vi = Vm(1 + sin(t ))
The output voltage is clamped between zero and 2Vm.
Vm cos( t)
Vo
2Vm Vo
Vc
Vi
Vm
0
FIGURE 2.17 Voltage clamping with diode.
C. As voltage multiplier
Connecting diode in a predetermined manner, an ac signal can
be doubled, tripled, and even quadrupled. This is shown in
Fig. 2.18. As evident, the circuit will yield a dc voltage equal to
2Vm. The capacitors are alternately charged to the maximum
value of the input voltage.
Quadrupler
Doubler
2Vm
Vm sin( t)
Vm 2Vm
2Vm
FIGURE 2.18 Voltage doubler and quadrupler circuit
You might also like
- Half Wave and Full Wave RectifierDocument8 pagesHalf Wave and Full Wave RectifierArun Jyothi82% (11)
- Half Wave and Full Wave RectifierDocument6 pagesHalf Wave and Full Wave RectifierBilal KhanNo ratings yet
- Frequency Response of A Single Stage RC Coupled AmplifierDocument26 pagesFrequency Response of A Single Stage RC Coupled AmplifierkanchankonwarNo ratings yet
- Ashfaq Hussain Electrical Machines PDF FreeDocument4 pagesAshfaq Hussain Electrical Machines PDF FreeShubham Oswal32% (25)
- Diode Clippers and ClampersDocument13 pagesDiode Clippers and ClampersVishnu Prasad0% (1)
- Diod RectifierDocument35 pagesDiod RectifierRizalNo ratings yet
- Clipping Problems and Solutions - 2 PDFDocument7 pagesClipping Problems and Solutions - 2 PDFIlham Santoso100% (1)
- Clamping CircuitsDocument9 pagesClamping Circuitsnikola CHECNo ratings yet
- Voltage Multipliers: Half-Wave Voltage DoublerDocument5 pagesVoltage Multipliers: Half-Wave Voltage DoublerKade Ben100% (1)
- Voltage Multipliers PDFDocument3 pagesVoltage Multipliers PDFlaltu adgiriNo ratings yet
- Diode ApplicationsDocument33 pagesDiode Applicationspransdom10No ratings yet
- ElectronicsDocument72 pagesElectronicszaidlateefNo ratings yet
- ABSTRAC1 MinDocument10 pagesABSTRAC1 MinGUMMADISANI RISHITHA 193T1A0417No ratings yet
- Part1 ElectronicsDocument48 pagesPart1 ElectronicsRalph NakadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Clippers, Clampers & Voltage MultipliersDocument6 pagesChapter 3 Clippers, Clampers & Voltage MultipliersTarisai DoroNo ratings yet
- Lec05 Ae Ms14Document27 pagesLec05 Ae Ms14Mohsin Abbas ZafarNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Limiting and Clamping CircuitsDocument7 pages1.1 Limiting and Clamping Circuitsdido rattNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12: Diode ClampersDocument4 pagesLecture 12: Diode ClampersChandru RamaswamyNo ratings yet
- Ec8351 Electronic Circuits 1 Unit 2 Solved WMRDocument11 pagesEc8351 Electronic Circuits 1 Unit 2 Solved WMRSaravanan MurugaiyanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Rectifiers-1Document43 pagesChapter 3 - Rectifiers-1CraigNo ratings yet
- Colour Coded ResistorsDocument28 pagesColour Coded ResistorsEd JudgeNo ratings yet
- Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University at RangsitDocument13 pagesSirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University at RangsitMohd Helmy Hakimie RozlanNo ratings yet
- Notes2 PDFDocument21 pagesNotes2 PDFJameelAhmedNo ratings yet
- Clipper Clamper CircuitsDocument15 pagesClipper Clamper CircuitsAnilaSaghirNo ratings yet
- Doubler, TriplerDocument3 pagesDoubler, TriplerARUNNo ratings yet
- Voltage Multipler: Half Wave Voltage DoublerDocument3 pagesVoltage Multipler: Half Wave Voltage DoublerAshik AhmedNo ratings yet
- In Voltage Multiplier Circuit Two or More Peak Rectifiers Are Cascaded To Produce A DDocument3 pagesIn Voltage Multiplier Circuit Two or More Peak Rectifiers Are Cascaded To Produce A DAmit GargNo ratings yet
- I, V, C MeasurementsDocument12 pagesI, V, C MeasurementsArpandip boruahNo ratings yet
- Voltagemultiplier 150406030541 Conversion Gate01Document15 pagesVoltagemultiplier 150406030541 Conversion Gate01Idris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- 1519292487one Indian Girl by Chetan BhagatDocument32 pages1519292487one Indian Girl by Chetan Bhagatabhishek kumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 01: PH. D FALL 2019Document5 pagesAssignment No. 01: PH. D FALL 2019Engr Rab Nawaz ButtNo ratings yet
- Lec 2Document17 pagesLec 2mezo4326No ratings yet
- Assignment1-Differential Amplifiers& Operational AmplifierDocument5 pagesAssignment1-Differential Amplifiers& Operational AmplifierAdithya ReddyNo ratings yet
- Clipper and Clamper: Amity School of EngineeringDocument38 pagesClipper and Clamper: Amity School of EngineeringRahul YadavNo ratings yet
- Diode Clamping CircuitsDocument7 pagesDiode Clamping Circuitsgayathri-eceNo ratings yet
- Direct Test Voltage: - Ripple FactorDocument9 pagesDirect Test Voltage: - Ripple Factorسرحان سويد عيسىNo ratings yet
- Arun Exp2 PrelabReportDocument5 pagesArun Exp2 PrelabReportLone WolfNo ratings yet
- T3 TugasDocument15 pagesT3 TugasSri rahayuNo ratings yet
- I-9 Power CircuitDocument7 pagesI-9 Power Circuitsulatt.nandar.mdyNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 - AC TO DC CONVERTER (Student Updated)Document60 pagesCHAPTER 2 - AC TO DC CONVERTER (Student Updated)Ct KhatijahNo ratings yet
- R and RC Firing CircuitsDocument3 pagesR and RC Firing CircuitsDeepa Mary Sobha70% (10)
- Lab#3A: Full-Wave Bridge Rectifier Circuit Without and With FilterDocument6 pagesLab#3A: Full-Wave Bridge Rectifier Circuit Without and With FilterSadil BatafNo ratings yet
- Voltagemultiplier 150406030541 Conversion Gate01Document15 pagesVoltagemultiplier 150406030541 Conversion Gate01rahabar azizNo ratings yet
- Diode Clamping CircuitsDocument7 pagesDiode Clamping CircuitsDeepak ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet: = 10 Ω and V = 0.7 V. The load /N = 10/1. If the primary isDocument3 pagesTutorial Sheet: = 10 Ω and V = 0.7 V. The load /N = 10/1. If the primary isDaniel EkassiNo ratings yet
- Diode Clamping CircuitsDocument4 pagesDiode Clamping CircuitsftafedeNo ratings yet
- Lab#2B: Half-Wave Rectifier Circuit Without and With FilterDocument5 pagesLab#2B: Half-Wave Rectifier Circuit Without and With FilterHemanth GedelaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices Experiment 4Document13 pagesElectronic Devices Experiment 4ArvinALNo ratings yet
- Rectifier Half WaveDocument15 pagesRectifier Half WaveFahrizaNo ratings yet
- Experiment #2 Diode Clipping and Clamping Circuits: Limiter (ClippeDocument7 pagesExperiment #2 Diode Clipping and Clamping Circuits: Limiter (ClippeSumeet KumarNo ratings yet
- High Bandwidth Low Noise Amplifier With Improved Stability Over Radio Frequency RangeDocument11 pagesHigh Bandwidth Low Noise Amplifier With Improved Stability Over Radio Frequency Rangesushil4056No ratings yet
- 3-A-Full Wave RectifierDocument6 pages3-A-Full Wave Rectifierbaig79No ratings yet
- PE 1ph VSI 5.sqprojDocument3 pagesPE 1ph VSI 5.sqprojPAVAN kumarNo ratings yet
- Diode Circuits or Uncontrolled Rectifier: EE 435-Electric Drives Dr. Ali M. EltamalyDocument21 pagesDiode Circuits or Uncontrolled Rectifier: EE 435-Electric Drives Dr. Ali M. EltamalyNaga Surya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Ec FinalDocument46 pagesEc FinalManjunath YadavNo ratings yet
- Wave Shaping CircuitsDocument7 pagesWave Shaping CircuitsMansi NanavatiNo ratings yet
- CH 02 - Diode ApplicationsDocument25 pagesCH 02 - Diode ApplicationsHatem DheerNo ratings yet
- A PWM Circuit Using Operational AmplifiersDocument7 pagesA PWM Circuit Using Operational Amplifiershamza abdo mohamoud100% (1)
- Half Wave RectifierDocument4 pagesHalf Wave RectifierrodinooNo ratings yet
- Full-Wave Rectifiers (Full-Wave Rectification)Document13 pagesFull-Wave Rectifiers (Full-Wave Rectification)مصطفى عدنان احمدNo ratings yet
- 2 The Power Diode 25: FIGURE 2.21 Variation of Peak Forward Voltage Drop With PeakDocument2 pages2 The Power Diode 25: FIGURE 2.21 Variation of Peak Forward Voltage Drop With PeakMuhammad SiddiqNo ratings yet
- 2.5 Snubber Circuits for Diode: dv dt τ RDocument1 page2.5 Snubber Circuits for Diode: dv dt τ RMuhammad SiddiqNo ratings yet
- List of Figures: Department of Electrical and Electronics IIIDocument1 pageList of Figures: Department of Electrical and Electronics IIIMuhammad SiddiqNo ratings yet