Professional Documents
Culture Documents
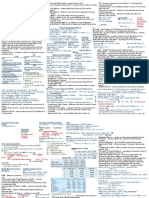
Accounting Cheat Sheet PDF
Accounting Cheat Sheet PDF
Uploaded by
SummerOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Accounting Cheat Sheet PDF
Accounting Cheat Sheet PDF
Uploaded by
SummerCopyright:
Available Formats
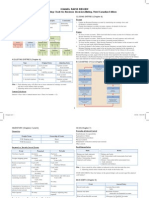
Lesson 6,
Bond interest: Two year semiannual bond w/ par value of $500 and STUDY GUIDE through
Financial stmts
Lesson 4 | Inventory & Payables Primary advantage
a stated rate of 7% was priced to yield 8%. Lesson 1 | Accounting Concepts Inventory costing methods LIFO & FIFO is tax benefit
cont... Footnotes
-Calc the issue price, find the pres value of both lump-sum principle pymt of $500 Purpose of accounting: 1) Provide financial information
Auditors's report INCOME Current, higher acquisition Px Older, lower acquisition Px
and the interest stream of $35 per year. - Pres val of principle = $427 about 2) Reporting entities
Basic financial Mgmt's discussion
STMT
mtchd w/ curr, higher sales px matched w/ higher sales Px
BEGINNING INTEREST INTEREST ENDING - Pres val of interest stream = $64 statements (FOUR) to 3) Primary users
PERIOD BALANCE EXPENSE PAYMENT BALANCE - Issue price = $491 & analysis (MD&A) BALANCE
Inventory is valued using Inventory is valued using
1 $491.00 $19.75 $17.50 $493.25 Income Statement Capital market Sole proprietors
SHEET
older lower acquisition Px current (higher) acquisition Px
Record bond proceeds
2 $493.25 $19.75 $17.50 $495.50
1
Cash Revenues Product market Partnerships
3 $495.50 $19.75 $17.50 $497.75 -Expenses Government Corporations ACCT for Inventory BALANCE SHEET INCOME STATEMENT
491.00 Net Income
4 $497.75 $19.75 $17.50 $500.00 Internal users - execs LLC's ASSETS = LIABILITIES + EQUITY REVENUE - EXPENSES = NET INCOME
Bonds Payable Inventory -500
EFFECTIVE STATED 500.00 Stmt of Retained Earnings
RATE = 4%
Record first semi-annual interest payment
RATE = 3.5% Disc on Bonds Pyble
9.00
Beginning RE
+ Net Income 2
Ending Retained Earnings Balance Sheet 4
COGS Expense
Cash +1,000
-500 -500 =-500
Sales Revenue +1,000 +1,000 =1,000
Cash Disc on Bonds Pyble Interest Expense Stmt of Cash Flows --Assets-- --Liabilities & Equity-- Totals +500 +500 +1,000 -500 =500
17.50 bal 9.00 19.75 Cash A/P
3
Beginning Cash
2.25 Inventory LT Debt Lower of Cost or Market
Operating Activities
BALANCE SHEET INCOME STATEMENT PPE Equity Other inventory issues
ASSETS = LIABILITIES + EQUITY REVENUE - EXPENSES = NET INCOME MY SIDE Investing Activities
Financing Activities
Total Total
When future revenue-producing ability < purch Px
the inventory asset write down will reflect loss
Interest Expense -19.75 -19.75 =-19.75
Cash -17.50 Trial Balance Form
Net Change in Cash
Ending Cash 1Info
Relevance
capable of making
Lesson 5 | Fixed
& Intangible Assets
-Ensures inventory is not overvalued
-Accelerates future losses to current Inc Stmt
Bonds Payable +2.25 Debit Credit Property, Plant, Compare historical cost (balance sheet value)
Asset Amount Qualitative characteristics | primary qualities (TWO) a difference in a decision to Market Value. Report the lower of the two.
& Equip
Liability Amount -Predictive value -Market value is cost to replace inventory today
Issue 3000 shares of common stock for $15,000
Cash 15,000 Equity Amount 2InfoReliability
strives to faithfully represent the
-Predict outcomes of past,
present, & future events
1
Straight-Line Depreciation
Common stock 15,000 Revenue Amount -Confirming value Depreciation Expense = Asset Cost - Salvage Value
economic situation example Estimated Useful Life
Common Expense Amount -Feedback can be used
Cash -Completeness $10k asset has salvage of $1k, use life is 3 years
Assets = Liabilities + Equity Stock Dividends Amount -Includes all info necessary for user to understand to set expectations
+15,000 +15,000 15k 15k Totals Total DRs Total CRs -Materiality =(10000 - 1000)/3 = 3000 per year
-Neutrality
-Info cannot be manipulated; free from bias -Inclusion/omission would BALANCE SHEET ASSETS INCOME STATEMENT
Receive $2,000 for future services Unearned -Freedom from Error
influence judgement PP& E ACCUM. DEPR DEPR. EXPENSE
Cash 2,000 Assets = Liabilities + Equity Cash Revenue -Contains no errors/omissions Acquire PP&E +10,000
For info to be relevant, it
Unearned Revenue 2,000 +2,000 +2,000 2k 2k -Does not require perfect accuracy should have predictive or Year 1 depreciation -3,000 -3,000
confirming value, & be Year 2 depreciation -3,000 -3,000
Pay $250 for advertising Advertising Year 3 depreciation -3,000 -3,000
material for the
Advertising Expense 250 Assets = Liabilities + Equity Cash Expense Balances +10,000 -9,000 -9,000
Reliability, or faithful representation, is a reporting entity.
Cash 250 -250 -250 250 250
necessity for individuals who neither have
Increase on the
2 Double Declining Balance
Depreciation Expense = Net Book Value * 2
Do work and leave an invoice for $3,500 the time nor the expertise to evaluate
Accounts Service Revenues increase Equity Credit Side Estimated Useful Life
Assets = Liabilities + Equity the factual content of the information. OR
Accounts Receivable 3,500 Receivable Revenue Expenses decrease Equity Debit Side
+3,500 +3,500 3.5k 3.5k Determine by taking the straight-line rate of depreciation and
Service Revenue 3,500 DOUBLE-ENTRY ACCOUNTING
DETAILED EXAMPLES
Lesson 2 | Accounting Building Blocks double it. Example: Asset w/ 4-year life = straight-line rate 25%,
Pay $1,500 in dividends Recording transactions accounting equation Assets = Liabilities + Equity calc'd by 100%/4years. The straight-line rate doubled = 50%.
Asset w/ a 5-year life would = 20% straight-line * 2 = 40%.
Dividends 1,500 Assets = Liabilities + Equity Cash Dividends Adjusting entries D C D C D C Doubled rate is then multiplied by Net Book Value:
-1,500 -1,500 1.5k 1.5k Accrual Cash
Cash 1,500 Recognizes economic Recognizes economic
Depreciation Expense = Depreciation rate * Net Book Value
events in the period events when cash has Ignores revenue recognition & matching principles -DO NOT REDUCE! cost by = (Straight-line rate *2)
Serviced pre-paid client ($2k) Unearned SVC salvage value * (Cost - Accumulated Depreciation)
in which they occur been exchanged Not in conformity with GAAP
Unearned Revenue 2,000 Assets = Liabilities + Equity Revenue Revenue -STOP DEPRECIATING
-2,000 +2,000 2k 2k DETAILED EXAMPLES when salvage value is reached
Service Revenue 2,000
Lesson 3 | Revenue & Receivables Realized example BALANCE SHEET ASSETS INCOME STATEMENT
Equipment depreciation of $600 per month Depreciation Accum Revenue recognition recognized/recorded when BOTH Seller has received cash or will at
PP& E ACCUM. DEPR DEPR. EXPENSE
Depreciation Expense 600 Assets = Liabilities + Equity Expense Deprec Acquire PP&E +10,000
some point in the future (AR)
Accumulated Depreciation 600 -600 -600 600 600 Earned Year 1 depreciation -6,667 -6,667
Goods/services are delivered & related obligs *General Rule Year 2 depreciation -2,222 -2,222
Balance sheet: Reports a company's resources & claims against @ a given point in time. are complete Recognition @ time of sale provides Year 3 depreciation -111 -111
Income Stmt: Rev & Exp over period. Stmt of RE: Shows RE over period. Stmt of Cash Flows: use of $$ Seller has performed duties under terms of a uniform/reasonable test Balances +10,000 -9,000 -9,000
sales agreement- title has passed to buyer Recognition Principle: Revenue should be
HANDY FORMULAS
Net income = Revenue - Expenses R=revenue
E=expense
Assets = Liabilities + Equity w/o right of return or contingencies recorded when a resource has been earned
Natural Resources
Net Book Value = $1,000
Intangible Assets
Retained Earnings = Net Income - Dividends
Receivable = Asset
D C D C D C -As extracted the asset is depleted -Lack physical existence
A=asset
Net sales = Credit sales - Sales returns & allowances L=liability
Receivables and transferred to inventory -Not financial instruments
Net Book Value = Cost - Accumulated Depreciation SE=Stock-
hld eq Net realizable value D C -As sold the expense is Xferred to -Normally classified as long-term
ITEMS, STATEMENTS, & ACCOUNTS Amount the company expects to collect (GAAP Requirement) income statement as COGS Exp assets
IS=income statement | RE=retained earnings | BS=balance sheet Income Stmt Balance Sheet
EXAMPLES Allowance method | Bad Debt Expense (BDE) Estimate results in Percentage of sales method Lesson 6
ITEM STATEMENT ACCOUNT Percentage % of current credit Allowance does not
Recognize BDE in the period of sale by estimating doubtful accounts Bad Debt Expense Bad debt is estimated as a % of credit sales that
Retained Earnings BS, RE SE sales is matched with necessarily reflect the
of credit current sales revenue receivables that are -Record estimate in contra-asset acct "Allowance for Doubtful Accts" occured during the period
Equipment BS A sales as bad debt expense -Estimate results in balance of -Percent is based on historical trends
uncollectible Aging of AR method allowable account
Common Stock BS SE Estimate how much of the ending balance of AR is bad debt & company policies
Unearned Revenue BS L Aging of Bad debt expense is a Allowance for Bad
-Amount becomes ending balance of Allowance for Bad DebtBALANCE SHEET
-Bad Debt Expense is a "plug"
EXAMPLES
plug to force Debts is calculated INCOME STATEMENT Effective/stated rates
Sales IS R Accounts allowance for bad based on balance in -Based on the age of account making up ending bal of AR ASSETS = LIABILITIES + EQUITY REVENUE - EXPENSES = NET INCOME -Effective = market rate, or yield
Rent Expense IS E Receivable debt to the proper Accounts Receivable Allow. for Bad Debt -4,500 -Stated = Specified on the face of
balance the bond.
Inventory BS A Bad Debt Exp -4,500
You might also like
- Accounting Cheat SheetDocument7 pagesAccounting Cheat Sheetopty100% (16)
- Cheat Sheet Exam 1Document1 pageCheat Sheet Exam 1Shashi Gavini Keil100% (2)
- Becker CPA BEC Review CheatsheetDocument6 pagesBecker CPA BEC Review CheatsheetGabrielNo ratings yet
- Basic Everyday Journal EntriesDocument2 pagesBasic Everyday Journal EntriesMary73% (15)
- Finance Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesFinance Cheat SheetMarc MNo ratings yet
- Inbm 110 - Accounts Study Sheet: Chapter 1 & 2Document5 pagesInbm 110 - Accounts Study Sheet: Chapter 1 & 2Laura TaiNo ratings yet
- Closing Journal EntriesDocument1 pageClosing Journal EntriesMary91% (11)
- Schaum's Outline of Bookkeeping and Accounting, Fourth EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Outline of Bookkeeping and Accounting, Fourth EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- General Accounting Cheat SheetDocument35 pagesGeneral Accounting Cheat SheetZee Drake100% (6)
- Final Report InternshipDocument17 pagesFinal Report InternshipSAMARTH UPADHYAYANo ratings yet
- CPA Review Notes 2019 - FAR (Financial Accounting and Reporting)From EverandCPA Review Notes 2019 - FAR (Financial Accounting and Reporting)Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (17)
- Cheat Sheet For AccountingDocument4 pagesCheat Sheet For AccountingshihuiNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet Final - FMVDocument3 pagesCheat Sheet Final - FMVhanifakih100% (2)
- CorpFinance Cheat Sheet v2.2Document2 pagesCorpFinance Cheat Sheet v2.2subtle69100% (4)
- Schaum's Outline of Principles of Accounting I, Fifth EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Outline of Principles of Accounting I, Fifth EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- What is Financial Accounting and BookkeepingFrom EverandWhat is Financial Accounting and BookkeepingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
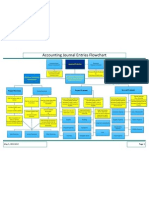
- Accounting Journal Entries Flowchart PDFDocument1 pageAccounting Journal Entries Flowchart PDFMary75% (4)
- Fnce 100 Final Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesFnce 100 Final Cheat SheetToby Arriaga100% (2)
- Intermediate Accounting 1: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideFrom EverandIntermediate Accounting 1: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting 2: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideFrom EverandIntermediate Accounting 2: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- Accounting and Finance Formulas: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandAccounting and Finance Formulas: A Simple IntroductionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (8)
- CheatDocument1 pageCheatIshmo KueedNo ratings yet
- Accounting Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesAccounting Cheat Sheetanoushes1100% (2)
- ACCT 101 Cheat SheetDocument1 pageACCT 101 Cheat SheetAndrea NingNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet For Financial AccountingDocument1 pageCheat Sheet For Financial Accountingmikewu101No ratings yet
- Accounting NotesDocument66 pagesAccounting NotesShashank Gadia71% (17)
- Fin Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesFin Cheat SheetChristina RomanoNo ratings yet
- FAR NotesDocument163 pagesFAR NotesClaire Antonette Limpangog100% (2)
- Learn Your Accounting Basics - A Step by Step Approach: Junior High School and beginners, #1From EverandLearn Your Accounting Basics - A Step by Step Approach: Junior High School and beginners, #1Rating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- General Accounting Cheat SheetDocument35 pagesGeneral Accounting Cheat Sheetazulceleste0_0100% (1)
- BEC Notes Chapter 3Document6 pagesBEC Notes Chapter 3cpacfa90% (10)
- Kelly's Finance Cheat Sheet V6Document2 pagesKelly's Finance Cheat Sheet V6Kelly Koh100% (4)
- Account ClassificationDocument2 pagesAccount ClassificationMary96% (23)
- Book of Facts by Isaac AsimovDocument158 pagesBook of Facts by Isaac AsimovMD. Monzurul Karim ShanchayNo ratings yet
- CPA Review Notes 2019 - BEC (Business Environment Concepts)From EverandCPA Review Notes 2019 - BEC (Business Environment Concepts)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- Accounting Cheat Sheet FinalsDocument5 pagesAccounting Cheat Sheet FinalsRahel Charikar100% (1)
- Accounting Cheat SheetsDocument4 pagesAccounting Cheat SheetsGreg BealNo ratings yet
- ACC1002X Cheat Sheet 2Document1 pageACC1002X Cheat Sheet 2jieboNo ratings yet
- Accouting Finals Cheat SheetDocument1 pageAccouting Finals Cheat SheetpinkrocketNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting: Tools For Business Decision-Making, Third Canadian EditionDocument6 pagesFinancial Accounting: Tools For Business Decision-Making, Third Canadian Editionapi-19743565100% (1)
- BEC CPA Formulas - November 2015 - Becker CPA ReviewDocument20 pagesBEC CPA Formulas - November 2015 - Becker CPA Reviewgavka100% (1)
- General Accounting Cheat SheetDocument35 pagesGeneral Accounting Cheat SheetHectorNo ratings yet
- Accounting Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesAccounting Cheat SheetvgirotraNo ratings yet
- Class of AccountsDocument5 pagesClass of AccountssalynnaNo ratings yet
- Accounting GuideDocument153 pagesAccounting Guidebam04100% (1)
- Basics of AccountingDocument20 pagesBasics of AccountingvirtualNo ratings yet
- Expressed As A Percentage of The Value of Revenue or Sales.: Balance Sheet: Reports What The Organization Owns and OwesDocument3 pagesExpressed As A Percentage of The Value of Revenue or Sales.: Balance Sheet: Reports What The Organization Owns and OwesDGNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet - Financial STDocument2 pagesCheat Sheet - Financial STMohammad DaulehNo ratings yet
- Basic Accounting Concepts - GE AccountingDocument62 pagesBasic Accounting Concepts - GE AccountingTarun ChawlaNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet - AccountingDocument2 pagesCheat Sheet - AccountingJeffery KaoNo ratings yet
- Midterm Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesMidterm Cheat SheetvikasNo ratings yet
- The Everything Accounting Book: Balance Your Budget, Manage Your Cash Flow, And Keep Your Books in the BlackFrom EverandThe Everything Accounting Book: Balance Your Budget, Manage Your Cash Flow, And Keep Your Books in the BlackRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- BEC Notes Chapter 3Document13 pagesBEC Notes Chapter 3bobby100% (1)
- Financial Accounting Is The Process of Preparing Financial Statements For A BusinessDocument11 pagesFinancial Accounting Is The Process of Preparing Financial Statements For A Businesshemanth727100% (1)
- The Holy AL-Quran (Bengali Translation)Document701 pagesThe Holy AL-Quran (Bengali Translation)MD. Monzurul Karim ShanchayNo ratings yet
- Best Stories of The Quran-Part 3Document244 pagesBest Stories of The Quran-Part 3MD. Monzurul Karim Shanchay100% (1)
- News Writting and Editing-Sikandar FayezDocument190 pagesNews Writting and Editing-Sikandar FayezMD. Monzurul Karim ShanchayNo ratings yet
- The Treasures of Good DeedsDocument24 pagesThe Treasures of Good DeedsMD. Monzurul Karim Shanchay100% (1)
- Mirza Galib's PoetryDocument93 pagesMirza Galib's PoetryMD. Monzurul Karim ShanchayNo ratings yet
- Regular Irregularities-Hanif SanketDocument75 pagesRegular Irregularities-Hanif SanketMD. Monzurul Karim ShanchayNo ratings yet
- Entire Travel-Humayun AhmedDocument360 pagesEntire Travel-Humayun AhmedMD. Monzurul Karim Shanchay100% (1)
- Bengali Grammar by Jyotibhusan ChakiDocument309 pagesBengali Grammar by Jyotibhusan ChakiMD. Monzurul Karim Shanchay100% (2)
- Thinking and Writing From Word To Sentence To Paragraph To EssayDocument238 pagesThinking and Writing From Word To Sentence To Paragraph To EssayMD. Monzurul Karim Shanchay50% (2)
- Sustho Deho Prashanto MonDocument210 pagesSustho Deho Prashanto MonmamunngsNo ratings yet
- Kidney DiseasesDocument136 pagesKidney DiseasesMD. Monzurul Karim ShanchayNo ratings yet
- Bengali Grammar-Exam. PreparationDocument43 pagesBengali Grammar-Exam. PreparationMD. Monzurul Karim Shanchay100% (2)
- Learning The Holy AL-QuranDocument128 pagesLearning The Holy AL-QuranMD. Monzurul Karim ShanchayNo ratings yet
- ShortCut MathDocument299 pagesShortCut MathMD. Monzurul Karim Shanchay100% (3)
- Allah's Names and AttributesDocument256 pagesAllah's Names and AttributesMD. Monzurul Karim ShanchayNo ratings yet
- Advanced Learner's Functional EnglishDocument448 pagesAdvanced Learner's Functional EnglishMD. Monzurul Karim Shanchay88% (8)
- Kalimatus ShahadahDocument98 pagesKalimatus ShahadahMD. Monzurul Karim Shanchay100% (1)
- Women's Prayer PDFDocument98 pagesWomen's Prayer PDFMD. Monzurul Karim ShanchayNo ratings yet
- Market Structure-Perfect CompetitionDocument72 pagesMarket Structure-Perfect CompetitionUtsav AaryaNo ratings yet
- Answer Key Far Assessment Questionairre 1Document22 pagesAnswer Key Far Assessment Questionairre 1Johnfree VallinasNo ratings yet
- ZAFRA Hannah Mae S. Income Statement and Balance Sheet Ferna CompanyDocument2 pagesZAFRA Hannah Mae S. Income Statement and Balance Sheet Ferna CompanyAngeliePanerioGonzagaNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Advanced Accounting 13Th Edition Beams Anthony Bettinghaus Smith 0134472144 9780134472140 Full Chapter PDFDocument30 pagesSolution Manual For Advanced Accounting 13Th Edition Beams Anthony Bettinghaus Smith 0134472144 9780134472140 Full Chapter PDFrose.carvin242100% (11)
- Ratio Analysis: Ratio Analysis Is The Process of Establishing and Interpreting Various RatiosDocument26 pagesRatio Analysis: Ratio Analysis Is The Process of Establishing and Interpreting Various RatiosTarpan Mannan100% (2)
- E-Commerce UNIT-1Document12 pagesE-Commerce UNIT-1Bhavan YadavNo ratings yet
- Intenship Project Omkar Sir Final 2Document20 pagesIntenship Project Omkar Sir Final 2Saurabh KumbharNo ratings yet
- Credit Memo - MH3M300182Document1 pageCredit Memo - MH3M300182AltafNo ratings yet
- Assignment Kinetic Honda Case Study Consumer Buying JourneyDocument3 pagesAssignment Kinetic Honda Case Study Consumer Buying JourneyAnnu ChandraNo ratings yet
- Revenue RecognitionDocument8 pagesRevenue RecognitionSedrick ChiongNo ratings yet
- Hul Lime IimiDocument25 pagesHul Lime Iimirsriram84No ratings yet
- Lat TakeDocument8 pagesLat TakeCamila Gail GumbanNo ratings yet
- Strategic ManagementDocument56 pagesStrategic Managementobsinan dejene100% (3)
- The Merit Corporation IDocument2 pagesThe Merit Corporation IMOHIT MALVIYA PGP 2020 BatchNo ratings yet
- A Construction Company Entered Into A FixedDocument40 pagesA Construction Company Entered Into A FixedDiaиa Diaz50% (2)
- Organization Chart - Marketing 2017 (Rev 5)Document2 pagesOrganization Chart - Marketing 2017 (Rev 5)Nam CHNo ratings yet
- Mas MCQDocument13 pagesMas MCQIm In TroubleNo ratings yet
- Main Cirque Du Soleil FinalDocument4 pagesMain Cirque Du Soleil FinalFarhan HossainNo ratings yet
- Connor Med SystemsDocument5 pagesConnor Med SystemsAndrii DutchakNo ratings yet
- Sample Client: CLS Investments, LLC Is Independent of Your Advisor's Broker/dealer And/or Registered Investment AdvisorDocument15 pagesSample Client: CLS Investments, LLC Is Independent of Your Advisor's Broker/dealer And/or Registered Investment AdvisorLaskar PejuangNo ratings yet
- Wellhead Procurement StrategyDocument2 pagesWellhead Procurement StrategyYougchu LuanNo ratings yet
- A Study On Customer Satisfaction of FMCG in Pathanjali ProductsDocument13 pagesA Study On Customer Satisfaction of FMCG in Pathanjali ProductseswariNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Advertising Imc Principles and Practice 10e by Moriarty 0133763536Document44 pagesTest Bank For Advertising Imc Principles and Practice 10e by Moriarty 0133763536JeremySotofmwa100% (43)
- Chapter 6 Test: InventoriesDocument129 pagesChapter 6 Test: InventoriesQueen Nikki MinajNo ratings yet
- A021221078 - Akuntansi Dasar Pekan 5Document2 pagesA021221078 - Akuntansi Dasar Pekan 5Nazwa AuliaNo ratings yet
- Absorption Vs Marginal CostingDocument24 pagesAbsorption Vs Marginal CostingPoint BlankNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 SolutionsDocument5 pagesQuiz 1 Solutionsgovt2No ratings yet
- 5 - DepreciationDocument22 pages5 - Depreciationnhel estalloNo ratings yet
- Marketing Plan TemplateDocument9 pagesMarketing Plan TemplateAzeb SeidNo ratings yet