Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Controlling Fabric Pests: Clothes Moths & Carpet Beetles
Uploaded by
tostOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Controlling Fabric Pests: Clothes Moths & Carpet Beetles
Uploaded by
tostCopyright:
Available Formats
Clothes Moths & Carpet Beetles:
Controlling Fabric Pests
When you find an infestation: the larvae are undisturbed for long periods
of time, such as in stored clothing or carpet
Check carefully. Find everything that under heavy furniture.
is infested. Adult clothes moths (shown on page 2)
Clean, treat or get rid of infested items. are buff-colored insects about 1/2-inch long.
They have four wings, are weak flyers, and,
Clean and treat the closet, container since they avoid lighted areas, are seldom
or area. seen. Any small moths seen flying around
the room and toward lights are probably not
Store woolen and similar items prop-
clothes moths. Female clothes moths lay
erly to avoid future infestations. 100 to 300 eggs in a place where the larvae
will have plenty to eat when they hatch.
Only larvae feed on textile items; the moths
To prevent damage:
do not cause any direct feeding damage.
Clean and vacuum regularly. Dont After feeding on the clothes or carpets, the
neglect closets, upholstered furni- larvae spin cocoons from which the adult
moths emerge several days later.
ture, cracks and crevices and under The most prevalent clothes moth in North
furniture. Vacuum both sides of wool Carolina is the casemaking clothes moth.
rugs and rotate them periodically. The larva of this moth lives inside a fuzzy
case, which it spins from silk and pieces of
Store only freshly washed or dry- the fabric on which it is feeding. When it is
cleaned garments made of wool and full-grown, the larva crawls up and attaches
itself to the wall, ceiling or another high
other fabrics of animal origin in air-
place. The appearance of these cases alerts
tight containers with plenty of moth the homeowner to the fact that he has a
repellents. clothes moth problem. The color of the case
depends on the color of the fabric on which
Store furs professionally.
the larva has been feeding. Matching the
colors in the case with nearby stored suscep-
Clothes moths tible fabrics may lead the homeowner to the
Distributed in furtherance
Clothes moth larvae (shown on page 2) larval infestation.
of the Acts of Congress feed mostly on wool, fur, hair and feathers, Another type of moth, the webbing
of May 8 and June 30, 1914.
Employment and program and occasionally on leather, lint, mohair, clothes moth, does not make cases. They are
opportunities are offered to
all people regardless of
silk and similar materials. They are after usually found under silken webbing spread
race, color, national origin, keratin, a protein found only in animal- over the infested fabric. This moth is seldom
sex, age, or disability.
North Carolina State University, based materials. Fabric stained with food, found in North Carolina.
North Carolina A& T State perspiration and oils is especially vulner-
University, U.S. Department
of Agriculture, and local able. Most damage is done in areas where
governments cooperating.
Carpet beetles
Carpet beetle larvae (shown on page 3) feed on
animal materials like wool, fur, hair, feathers, glue,
book bindings, silk, horns, bone, leather and dead
insects. They attack cotton, linen and synthetic fibers if
they are soiled. (Some species also infest cereals, cake
mixes, spices, flour, powdered milk and pet foods, but
these are not the same species that attack fabrics.) Casemaking
Adult beetles and larvae live behind baseboards and Clothes Moth
moldings, in heating and cooling system ducts and Adult
vents, dresser drawers, carpets, clothing and uphol-
stered furniture. Adult beetles can feed on flower
pollen and nectar outdoors. Adults dont feed on fabric
and often are found at windows and on windowsills.
Adult carpet beetles (shown on page 3) are small,
1/16" to 3/16" long. They may be black or mottled
with white, gray and red. Adult female beetles lay
about 100 eggs where the larvae will have plenty to
eat. In one or two weeks, larvae emerge from the eggs.
They are somewhat oval, brownish-black, with bristles,
and they feed from nine months to three years before Casemaking
pupating into adult beetles. Clothes Moth
Larva
Habits of these pests
Once the insect gains entry, the larvae may crawl
The larvae of clothes moths and carpet beetles attack
from room to room, closet to closet, rug to rug, slowly
clothing and a wide range of household furnishings,
causing major fabric damage. An infestation usually
including blankets, comforters, rugs, carpets, draperies,
takes at least a year or two to reach major proportions,
pillows, natural bristle brushes and upholstery. Only
particularly if the homeowner does not watch for signs
animal-based materials that contain the protein keratin
of a clothes moth problem. These insects work and
are damaged. For the most part, synthetic and plant-
reproduce slowly, so the earlier you discover an
based fibers like cotton and linen are immune, espe-
infestation and the more quickly you react, the more
cially if they are clean when stored. Wool blends may
likely you are to prevent serious fabric damage.
be attacked. The larvae digest only the wool, but
damage other fibers as they feed. Textile articles soiled
with food, body oils, feces and urine are most suscep- Eliminating infestations
tible. Carpet beetle larvae tend to chew holes through Infested articles should be cleaned according to
fabric, while clothes moth larvae like to graze along the manufacturers directions or discarded. Remove all
surface, but they can make holes, too. items from the infested closet or container. Be careful
Larvae prefer dark, undisturbed areas and they can attack not to spread the infestation. Thoroughly brush or
an amazing array of items. In addition to clothes and carpets, vacuum items, giving special attention to seams,
they may attack mounted animal trophies, felts in seldom- pockets and cuffs. Then dry clean or launder using hot
used pianos, or a stored lock of babys hair. water, if it wont damage the fabric.
Some infestations occur when adult carpet beetles or Laundering and dry cleaning will kill insects in fabrics
clothes moths fly from one house to a nearby house. but will not protect against future infestations. Inspect your
Occasionally carpet beetles breed and feed outdoors in home to locate all sites of infestation. Unless all are found,
places such as bird and rodent nests and may enter the infestation cannot be eliminated.
homes from these locations or from floral bouquets If infested areas are cleaned thoroughly, it may not
picked outdoors. More commonly, the eggs or larvae be necessary to spray. If a pesticide is used, treat only
hitchhike into a home on articles containing wool or cracks, crevices and hidden surfaces with a residual
other animal fibers, particularly secondhand clothing, spray designed for use by homeowners. It is not
upholstered furniture and woolen scraps exchanged for necessary to treat walls, ceilings or storage shelf
making rugs or quilts. surfaces. Many of the household pesticides labeled for
North Carolina Cooperative Extension Service North Carolina State University
a month during the summer and every other month in other
seasons. Rotate rugs or rearrange furniture periodically to
expose different areas of the floor coverings.
Clean woolens and similar materials at the end of
the winter and place them into storage. Dry cleaning or
laundering in hot water kills all stages of insects. Store
furs commercially. In addition to protection from
insects, furs need controlled temperature and humidity.
Pesticides cannot take the place of cleanliness and
good storage practices. Few household insecticides can
Carpet Beetle Adult be sprayed on fabrics, and those that are labeled for
such use are not likely to provide more than six
months protection against fabric pests. If insecticides
are used to protect a carpet or other vulnerable item,
pyrethroids, such as tetramethrin, sumithrin, resmethrin
or permethrin, are among the best choices for home-
owners' use. Additional pyrethroids, with names often
ending in methrin, are under development and may
become available in the future.
Carpet Beetle Naphthalene or paradichlorobenzene (PDB) crystals,
Mature Larva balls or flakes can be used to treat air-tight containers.
As these chemicals evaporate, they produce vapors
which, in sufficient concentration, will repel and
ant and cockroach control are also labeled for fabric slowly kill insects. Place clean items in the container.
pests. However, most of these insecticides may be used Since the fumes are heavier than air, the insecticide
only on storage surfaces; only a few may be used should be placed as near the top of the storage con-
directly on fabrics. Before using an insecticide for any tainer as possible. Place mothballs, flakes or crystals
purpose, read the label thoroughly. Then follow the on a layer of paper on top of the items in the container.
directions carefully. Look for products with active They should not touch any plastic items, such as
buttons, zippers, hangers or the sides of the storage
ingredients such as permethrin, bifenthrin, cyfluthrin
boxes. Otherwise, the plastic may soften, melt and
and others ending in "thrin.
stick to the fabric. Since the insecticide vapors will
While the homeowner may control many infesta-
build up sufficiently only in an airtight container, seal
tions, professionals are able to treat hidden infestations
the storage box as tightly as possible, sealing any holes
in closets or rugs and carpets most effectively. Valu-
or cracks. If the lid does not fit tightly, seal it with tape
able items, such as expensive rugs, furs, carpets and
or wrap the entire container with heavy paper or plastic
pianos, definitely require the help of professionals. The
and seal it with tape.
homeowner who tries to treat such infestations may fail
Coats, suits and similar items may be stored in tight
to eliminate the problem and damage the item in the
garment bags with repellants suspended near the top in a
process. Also, pest control operators may use certain
small bag of netting. Small blocks or pouches of these
insecticides not available to the general public.
materials which have built-in hooks also are available.
Once a fabric pest infestation has been eliminated,
The fumes given off by naphthalene or PDB repel-
follow the advice given in the next section to prevent
lants should not harm people as long as the fumes are
new problems.
confined to the air-tight storage containers and people
are not exposed to them for extended periods. Before
Preventing infestations using stored items, air them out for a few days to get
Good housekeeping is the foundation of any good rid of any insecticide odor.
fabric pest prevention program. Thorough and frequent Plastic resin strips, such as "Pest Strips", contain
cleaning, taking special care with those hard-to-clean Vapona or DDVP, an insecticide that slowly vaporizes
areas, is important. Such cleaning removes debris deep and effectively kills small flying insects in confined
in rugs and carpets. Pay attention to areas under the areas. Hanging a strip in a seldom-opened closet will
edges of rugs and along the wall, under couches, sofas, help protect fabrics from adults, but it will have little
chairs and chests. Vacuum both sides of area rugs once effect on larvae already infesting materials. A strip
North Carolina Cooperative Extension Service North Carolina State University
should last for about six months. Some people dislike preferred food, check other possible food sources, such
the odor of DDVP, but it normally goes away after the as furs, feathers, leather, piano felts, tennis balls, hats,
item has been aired for one or two days. The strips gloves and boot liners.
should never be used in rooms where people are
exposed to the vapors for extended periods of time. Pesticide precautions
As always, when using any pesticide, read all the 1. Follow all the restrictions and precautions on
information on the label and follow instructions pesticide labels.
carefully and precisely. 2. Store all pesticides behind locked doors in original
Heat and cold destroy insects. Researchers have containers with labels intact.
found that temperatures of 120 degrees F. for 30 3. Use the correct dosage and intervals to avoid excessive
minutes or 0 degrees F. for four days or water tempera- pesticide residues and injury to plants and animals.
tures of 140 degrees F. along with soap or detergent in 4. Apply pesticides carefully to avoid drift.
the wash cycle usually will destroy all eggs, larvae, 5. Dispose of surplus pesticides and used pesticide
pupae and adult insects. Thorough cleaning removes containers properly.
some of the organic matter that larvae can eat. It also
removes some insects and eggs. Take special care in
What doesnt work
cleaning rugs, carpets, draperies, upholstered furniture,
Cedar wood storage chests and closets do not keep
closets, and hard-to-reach areas like corners, cracks,
woolens and furs safe from clothes moths and carpet
baseboards and behind radiators. Vacuum cleaning is
beetles for long periods. The mothproofing value of
best, but be sure to discard the bag contents promptly
cedar wood disappears after about two years. However,
so that reinfestation cannot occur.
most cedar closets and chests are carefully constructed
Items labeled moth resistant or mothproofed when
and make excellent storage containers, particularly
purchased were treated with a protective chemical when
when an insect repellant is used in them.
they were manufactured. Many woolens made in the United
Sunning items exposes the insects to heat, light and
States have this protection, which remains effective through
activity and upsets their lodging, but this may not be
many washings and dry cleanings.
enough to get rid of an infestation. Combine sunning
Some dry cleaning and rug and carpet cleaning
with vigorous brushing of the articles to dislodge insect
businesses offer fabric pest control services. They treat
eggs and larvae. This will help in controlling these pests.
cleaned fabric with a chemical that temporarily moth-
Herbs and spices placed in storage containers may
proofs the fabric for about six months. Many dry
provide some repelling effects, but they do not protect
cleaners no longer offer this service because they lack a
susceptible articles from fabric pests. Some of these
practical way to safely dispose of their waste materials.
plant products, if hung in closets, may actually attract
Check stored woolen items every month or two and
pantry pests such as cigarette and drugstore beetles.
replace repellant, as needed. Although woolens are the
The use of brand names in this publication does not imply endorsement of the products
or services named or criticism of similar ones not mentioned.
Prepared by
Michael Waldvogel, Extension Entomologist;
Judieth Mock, Extension Human Environment Specialist;
and R.C. Hillman, Extension Entomologist Emeritus
Much of the information in this publication originated in Clothes Moths and Carpet BeetlesFabric Insects,
a Georgia Cooperative Extension Service publication authored by Maxcy P. Nolan Jr., Extension Entomologist,
and Mary Lou Dixon, Extension Clothing and Textiles Specialist.
This document was issued in print by the North Carolina Cooperative Extension Service as HE-377 (April, 1993).
Published by
North Carolina Cooperative Extension Service
Electronic Publication Number HE-377 Revised - 2/2005 (MGW)
You might also like
- Beetles Infesting Woolens RreztqDocument3 pagesBeetles Infesting Woolens RreztqsmurfsiftNo ratings yet
- MODULE 5-Textile FiberDocument8 pagesMODULE 5-Textile FiberCarlo Tiburcio CapunoNo ratings yet
- Bed Bugs: by Michael F. Potter, Urban Entomologist University of Kentucky, Entomology DepartmentDocument11 pagesBed Bugs: by Michael F. Potter, Urban Entomologist University of Kentucky, Entomology DepartmentAndrea SallayNo ratings yet
- SericultureDocument37 pagesSericultureMuqadas Zahra lNo ratings yet
- IG080 Do1akgl6bnDocument7 pagesIG080 Do1akgl6bnice creaNo ratings yet
- Carpenter Ants: ENTFACT-603Document3 pagesCarpenter Ants: ENTFACT-603Sofia VioletaNo ratings yet
- Integrated Pest Management:: Rats and MiceDocument2 pagesIntegrated Pest Management:: Rats and MiceLionel TaneoNo ratings yet
- BedBugs MovingPreventionDocument8 pagesBedBugs MovingPreventiontestingpersonNo ratings yet
- W T D A H A: HAT O O Bout Ousehold NTSDocument9 pagesW T D A H A: HAT O O Bout Ousehold NTSRebel BlueNo ratings yet
- Bed Bug Fumigation Check List3Document3 pagesBed Bug Fumigation Check List3desibanda73No ratings yet
- Controlling Carpenter AntsDocument4 pagesControlling Carpenter AntsCullen CoxNo ratings yet
- BrochureDocument2 pagesBrochurewherrera6816No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Textiles: Learning ObjectivesDocument30 pagesFundamentals of Textiles: Learning ObjectiveskabuNo ratings yet
- Varroa Mites PMP2Document4 pagesVarroa Mites PMP2Ralf JonesNo ratings yet
- Wooly BearsDocument3 pagesWooly BearsyuniNo ratings yet
- 341 BB StepsDocument4 pages341 BB StepsSumedh WaradeNo ratings yet
- JJumping Worms-Accessible V2021 OPTIMIZEDDocument2 pagesJJumping Worms-Accessible V2021 OPTIMIZEDWDIV/ClickOnDetroitNo ratings yet
- Hawaii Rat FactsDocument2 pagesHawaii Rat FactsRebel BlueNo ratings yet
- North America Range: ProcyonDocument4 pagesNorth America Range: ProcyonIT MalurNo ratings yet
- Exp SC 6 - Chapter 03Document11 pagesExp SC 6 - Chapter 03megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- Spiders in Around HouseDocument5 pagesSpiders in Around HouseKen HusterNo ratings yet
- The Best Control For BatsDocument18 pagesThe Best Control For Batsflaviana17No ratings yet
- The Best Control For Bed BugsDocument10 pagesThe Best Control For Bed BugsHowPawNo ratings yet
- Lyme Fact SheetDocument2 pagesLyme Fact SheetAmanda MehallNo ratings yet
- SeriPaperIII PDFDocument100 pagesSeriPaperIII PDFMonuNo ratings yet
- P. G. Koehler, R. J. Vazquez, and R. M. PereiraDocument7 pagesP. G. Koehler, R. J. Vazquez, and R. M. PereiraStarcraft2shit 2sNo ratings yet
- Field Guide to Fabrics: The Complete Reference Tool to Understanding FabricFrom EverandField Guide to Fabrics: The Complete Reference Tool to Understanding FabricRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Facts About BatsDocument8 pagesFacts About BatsRAM KUMARNo ratings yet
- Production, Properties and Uses of Silk FiberDocument25 pagesProduction, Properties and Uses of Silk FibersandhyaRanimohantyNo ratings yet
- Cockroaches and Their Management (University of Florida, IG08200)Document18 pagesCockroaches and Their Management (University of Florida, IG08200)"Rufus"100% (1)
- Insect Pests Historic Houses PosterDocument1 pageInsect Pests Historic Houses PosterCristina Maria Dalla NoraNo ratings yet
- Encourage Ladybird Beetles To Stay in Your Garden: Use For Insect Pest ControlDocument2 pagesEncourage Ladybird Beetles To Stay in Your Garden: Use For Insect Pest ControlLibertad BaumNo ratings yet
- FTC Fact SheetDocument2 pagesFTC Fact SheetinforumdocsNo ratings yet
- Sericulture 1Document38 pagesSericulture 1AkNo ratings yet
- AlexyscorripagesDocument1 pageAlexyscorripagesalexysreneeeNo ratings yet
- Relationship Example Description: Salvia Leucphylla and Other S. Leucphylla SecretesDocument4 pagesRelationship Example Description: Salvia Leucphylla and Other S. Leucphylla SecretesAngelo Dela Cruz VillaromanNo ratings yet
- SymbiosisDocument14 pagesSymbiosislevi loretoNo ratings yet
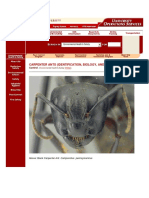
- Carpenter Ants (Identification, Biology, and Control)Document5 pagesCarpenter Ants (Identification, Biology, and Control)ViolintsarNo ratings yet
- 4.dermestid BeetleDocument2 pages4.dermestid Beetlevandv printsNo ratings yet
- 4.dermestid BeetleDocument2 pages4.dermestid Beetlevandv printsNo ratings yet
- 4.dermestid BeetleDocument2 pages4.dermestid Beetlevandv printsNo ratings yet
- Raccoon Fact SheetDocument2 pagesRaccoon Fact Sheetapi-652919626No ratings yet
- Silkworm and CocoonDocument4 pagesSilkworm and CocoonRemyaNo ratings yet
- Symbiosis: Plover BirdDocument14 pagesSymbiosis: Plover BirdSkyber TeachNo ratings yet
- Invading AntsDocument12 pagesInvading Antshamidreza mohseniNo ratings yet
- Urban Pest ControlDocument9 pagesUrban Pest ControlOonaghoneillNo ratings yet
- Nematodes Activity #3: AmericanusDocument7 pagesNematodes Activity #3: AmericanusVilllllNo ratings yet
- Fibre Crops, Bamboo, Timber - FinalDocument109 pagesFibre Crops, Bamboo, Timber - Finalsggdgd100% (1)
- CGTPaper IIDocument130 pagesCGTPaper IIMd. Humayun KabirNo ratings yet
- Fibre To Fabric Class 7 NotesDocument18 pagesFibre To Fabric Class 7 Notesshrutikashyap0003No ratings yet
- Economic Zoology: Learning ObjectivesDocument8 pagesEconomic Zoology: Learning ObjectiveshamzaNo ratings yet
- Managing Commensal: Rodent Rodent Rodent Rodent RodentDocument8 pagesManaging Commensal: Rodent Rodent Rodent Rodent RodentKashif AbrarNo ratings yet
- DalabuwaDocument2 pagesDalabuwaDeluka BandaraNo ratings yet
- Household & Public HealthDocument2 pagesHousehold & Public HealthmdollNo ratings yet
- Sample: Stool Chart/Bowel RecordDocument2 pagesSample: Stool Chart/Bowel RecordtostNo ratings yet
- Accessibility ChecklistDocument25 pagesAccessibility ChecklisttostNo ratings yet
- Events at The Goring: Beautifully Appointed Private SpacesDocument6 pagesEvents at The Goring: Beautifully Appointed Private SpacestostNo ratings yet
- Craap Worksheet PDFDocument1 pageCraap Worksheet PDFtostNo ratings yet
- 33 Mpact - of - The - Great - Earthquake-2015 - On - Hospitality PDFDocument30 pages33 Mpact - of - The - Great - Earthquake-2015 - On - Hospitality PDFJoannabelNo ratings yet
- 4th Semester Electrical Engg.Document19 pages4th Semester Electrical Engg.Bhojpuri entertainmentNo ratings yet
- 4 Pure BendingDocument42 pages4 Pure BendingOmarfirozNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Jun 2010 Mark Scheme Unit 3Document15 pagesChemistry Jun 2010 Mark Scheme Unit 3dylandonNo ratings yet
- Etl 213-1208.10 enDocument1 pageEtl 213-1208.10 enhossamNo ratings yet
- Moisture and Total Solids AnalysisDocument44 pagesMoisture and Total Solids AnalysisNicholas BoampongNo ratings yet
- Circle Theorem 1Document3 pagesCircle Theorem 1yaw197No ratings yet
- 2019 - High Levels of Polypharmacy in RheumatoidDocument7 pages2019 - High Levels of Polypharmacy in RheumatoidGustavo ResendeNo ratings yet
- Section 08630 Metal-Framed SkylightDocument4 pagesSection 08630 Metal-Framed SkylightMØhãmmed ØwięsNo ratings yet
- Annotated Bib-BirthingDocument3 pagesAnnotated Bib-Birthingapi-312719022No ratings yet
- Campa Cola - WikipediaDocument10 pagesCampa Cola - WikipediaPradeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument18 pagesLesson PlanYasmin Abigail AseriosNo ratings yet
- Veg Dum Biryani - Hyderabadi Veg Biryani Recipe - Hyderabadi Biryani - Hebbar's KitchenDocument2 pagesVeg Dum Biryani - Hyderabadi Veg Biryani Recipe - Hyderabadi Biryani - Hebbar's KitchenmusicalcarpetNo ratings yet
- List ToolingDocument10 pagesList Toolingyohanes adi saputroNo ratings yet
- The Common Reader-Virginia WoolfDocument216 pagesThe Common Reader-Virginia WoolfRusudan VardiashviliNo ratings yet
- Mechanism Design: A SeriesDocument3 pagesMechanism Design: A Seriesamirmasood kholojiniNo ratings yet
- Goal 6 Unesco Water SanatationDocument5 pagesGoal 6 Unesco Water Sanatationapi-644347009No ratings yet
- Practical 3.1 Determining The Specific Heat CapacityDocument3 pagesPractical 3.1 Determining The Specific Heat CapacityiAlex11No ratings yet
- Spina 2002Document10 pagesSpina 2002hasantapNo ratings yet
- ForewordDocument96 pagesForewordkkcmNo ratings yet
- Astm D974-97Document7 pagesAstm D974-97QcHeNo ratings yet
- Application of Eye Patch, Eye Shield and Pressure Dressing To The EyeDocument2 pagesApplication of Eye Patch, Eye Shield and Pressure Dressing To The EyeissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- Notice - Appeal Process List of Appeal Panel (Final 12.1.24)Document13 pagesNotice - Appeal Process List of Appeal Panel (Final 12.1.24)FyBerri InkNo ratings yet
- Ae 2 PerformanceDocument4 pagesAe 2 PerformanceankitNo ratings yet
- Library: Astrology and WisdomDocument13 pagesLibrary: Astrology and Wisdomalimuhammedkhan2115No ratings yet
- 1943 Dentures Consent FormDocument2 pages1943 Dentures Consent FormJitender ReddyNo ratings yet
- International Travel Insurance Policy: PreambleDocument20 pagesInternational Travel Insurance Policy: Preamblethakurankit212No ratings yet
- NDT Matrix 12-99-90-1710 - Rev.2 PDFDocument2 pagesNDT Matrix 12-99-90-1710 - Rev.2 PDFEPC NCCNo ratings yet
- South Valley University Faculty of Science Geology Department Dr. Mohamed Youssef AliDocument29 pagesSouth Valley University Faculty of Science Geology Department Dr. Mohamed Youssef AliHari Dante Cry100% (1)
- Anchor Chart-Describing Words-Descriptive Details of Setting and Character PDFDocument2 pagesAnchor Chart-Describing Words-Descriptive Details of Setting and Character PDFdellindiaNo ratings yet