Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Machine Tools: Lathe
Machine Tools: Lathe
Uploaded by
Ravichandran GOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Machine Tools: Lathe
Machine Tools: Lathe
Uploaded by
Ravichandran GCopyright:
Available Formats
Lathe
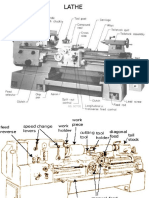
MACHINE TOOLS
LATHE
A Lathe is a general purpose machine tool which holds the work piece in a work holding device
and rotating it against a suitable cutting tool to remove excess metal from the work piece. It employs
single point cutting tool for various type of operation. The tool should be harder than material of work
piece. Lathe is also known as mother of all machine tools.
FUNCTIONS OF LATHE
1. To remove excess material from the work piece.
2. To produce cylindrical work piece.
3. To carryout the operations such as drilling, boring, grinding, milling etc.
PARTS OF LATHE
Bed:
It is the foundation part of the lathe and supports all its other parts. Its top surface is
machined to provide guide ways for carriage.
Basic Mechanical Engineering notes by Ravichandran G 1
Lathe
Carriage:
It supports the tool. It is composed of 5 main parts saddle, compound rest, tool post and
apron.
Saddle is sliding along the guide ways to provide the movement of the tool in a direction parallel to
the direction of work piece axis.
Cross slide is placed above the saddle and can be moved by hand wheel or by power feed.
Compound rest is mounted on cross slide. It is used to move the tool at an angle to the lathe axis.
Tool post is mounted on top of compound rest. It is used to hold the tool using tool holder.
Apron is a part used to house the carriage through gears and clutches.
Head Stock:
It is located at the left side of the Lathe. It contains driving mechanism of the spindle. A
stepped cone pulley is used in head stock to accommodate different speeds. Also headstock is used to
support one end of the work piece.
Tail Stock:
It is located at the right side of the Lathe. It is mounted on the base with adjusting screws. The
important function of tail stock are to support the free end of the work piece also to hold cutting tools
for performing certain machining operations like drilling, boring etc.
Feed box:
It is fitted directly below the head stock. It contains a number of different types of gears to
change the speed.
Feed rod:
It is a long shaft which supports the movement of the carriage throughout the lathe length.
Lead Screw:
It is a long threaded shaft. It is used when threads have to be cut. It is used to move the
carriage during thread cutting operation.
Chuck:
It is the element to hold the work piece.
Basic Mechanical Engineering notes by Ravichandran G 2
Lathe
Lathe Specification
1. Overall length of bed
It is the total space occupied by the Lathe.
2. Maximum diameter of work piece
It is also known as swing of Lathe. Swing is specified at two positions
a. Maximum swing diameter over the carriage
It is the largest diameter of the work piece which revolves over the carriage.
b. Maximum swing over bed
It is the largest diameter of work piece revolving over the bed.
3. Distance between centers
It indicates the maximum length of work piece that can be mounted between the centers.
Lathe Operations
1. Facing
Facing is an operation of machining the ends of a work piece
to produce a flat surface square with the axis. It is also used to cut
the work to the required length. The operation involves feeding the
tool perpendicular to the axis of rotation of the work piece.
A properly ground facing tool is mounted in the tool post. A regular
turning tool may also be used for facing a large work piece. The
cutting edge should be set at the same height as the center of the
work piece.
Basic Mechanical Engineering notes by Ravichandran G 3
Lathe
2. Plain Turning
It is an operation of removing excess material from the surface of
the cylindrical work piece. In this operation the work is held either in the
chuck or between centers and the longitudinal feed is given to the tool
either by hand or power. This operation is done to reduce the diameter of
work piece.
3. Step Turning
In this type of operation various steps of different diameters in
the work piece are produced. It is carried out in the similar way as plain
turning.
4. Drilling
It is an operation of producing a cylindrical hole in a work
piece by rotating cutting edge of a cutter known as the drill. For this
operation the work is held in a suitable device and the drill is held in
the sleeve or barrel of the tailstock. The drill is fed by hand by rotating
the hand wheel of the tailstock.
5. Threading
Threading is an operation of cutting helical grooves on the
external cylindrical surface of the work piece. In this operation the
work is held in a chuck or between centers and the threading tool is
fed longitudinally to the revolving work. The longitudinal feed is equal in
the pitch of the thread to be cut.
6. Knurling
It is an operation of embossing a diamond shaped pattern on the
surface of a work piece. The purpose of knurling is to provide an
effective gripping surface on a work piece to prevent it from slipping
when operated by hand.
Basic Mechanical Engineering notes by Ravichandran G 4
Lathe
The operation is performed by a special knurling tool which consists of one set of hardened steel
rollers in a holder with the teeth cut on their surface in a definite pattern. The tool is held rigidly on
the tool post and the rollers are pressed against the revolving work piece to squeeze the metal against
the multiple cutting edges, producing depressions in a regular pattern on the surface of the work
piece.
7. Taper Turning
A taper may be defined as an uniform increase or decrease in diameter of a piece of work
measured along its length.
Taper angle is given by
Dd
Tan = 2L
A = tan-1 [D2L d ]
Where D Large diameter of taper
d Small diameter of taper
L Length of tapered part
Half of taper angle
By setting over the tailstock center
This method is used for small taper only.
It is based upon the principle of shifting the axis
of rotation of the work piece at an angle to the
axis and feeding the tool parallel to the lathe
axis. The angle at which the axis rotation of
work piece is shifted is equal to half angle of
taper. This is done when the body of the
tailstock is made to slide on its base towards or
away from the operator by a set over screw.
By swiveling the compound rest
It is the best method as it doesnt affect
the centering of the job. In this method of taper
turning the work piece is rotated on the lathe
axis and the tool is fed at an angle to the axis of
rotation of the work piece. The tool mounted
Basic Mechanical Engineering notes by Ravichandran G 5
Lathe
on the compound rest is attached to the circular base, graduated in degrees which may be swiveled
and clamped at an desired angle.
Basic Mechanical Engineering notes by Ravichandran G 6
You might also like
- Making A Spur GearDocument9 pagesMaking A Spur GearHaraprasad DolaiNo ratings yet
- Up Workshop Manual 2020Document62 pagesUp Workshop Manual 2020Yash MittalNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 Locating Principles and DevicesDocument57 pagesChapter2 Locating Principles and DevicesAbhishek KulhariNo ratings yet
- Shaper MachineDocument18 pagesShaper MachineSanyam JainNo ratings yet
- Tools (Abril2015)Document48 pagesTools (Abril2015)Ricardo LopezNo ratings yet
- Practical 6Document7 pagesPractical 6Farid FazamyNo ratings yet
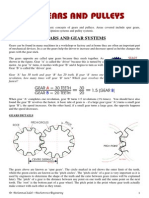
- Gears and PulleysDocument33 pagesGears and Pulleyskim haroldNo ratings yet
- Lathe DrillingDocument16 pagesLathe DrillingManjunatha EikilaNo ratings yet
- Milling NotesDocument20 pagesMilling NotesleoandresmessiNo ratings yet
- Lathe Part IDocument151 pagesLathe Part Ishiva100% (2)
- Workshop Technology Unit 1Document15 pagesWorkshop Technology Unit 1Chidu Devang0% (2)
- Lab Manual - FM and M LabDocument64 pagesLab Manual - FM and M LabRavichandran GNo ratings yet
- LatheDocument4 pagesLatheAnees Calicut100% (1)
- Production Technology (IV Sem)Document24 pagesProduction Technology (IV Sem)Shubham AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Lathes and Lathe Machining OperationsDocument11 pagesLathes and Lathe Machining OperationsJunayed HasanNo ratings yet
- Surface Grinding ReportDocument12 pagesSurface Grinding ReportyowiskieNo ratings yet
- Screw JackDocument14 pagesScrew JackSadeesh ManujaNo ratings yet
- Hand ToolsDocument44 pagesHand Toolsmarlito100% (1)
- 3-Limits Fits and TolerancesDocument22 pages3-Limits Fits and TolerancesAbhay Sharma100% (1)
- Chucks: Clamp Radial Symmetry Cylindrical Drill Bit Power Tool Bar Spindle LatheDocument14 pagesChucks: Clamp Radial Symmetry Cylindrical Drill Bit Power Tool Bar Spindle LatheIrtaza Husnain100% (1)
- Operations in TurningDocument8 pagesOperations in Turningcanavarsanayok100% (1)
- LatheDocument63 pagesLatheRandom100% (1)
- Lathe: GS, SctceDocument48 pagesLathe: GS, SctceGouthamPrasad100% (2)
- Lathe AccessoriesDocument4 pagesLathe AccessoriesBOT-X GAMING100% (1)
- Mvaj101 - Trip RelayDocument2 pagesMvaj101 - Trip Relayratheeshkumard100% (1)
- Lathe and Capstan & TurretDocument13 pagesLathe and Capstan & TurretNishit Parmar100% (1)
- CNC MillingDocument48 pagesCNC MillingEswaran ManakorNo ratings yet
- Pinagem Volvo Eecu Motor D6DDocument2 pagesPinagem Volvo Eecu Motor D6DJhecko Balbinot100% (1)
- Lathe Accessories and Attachments Lathe Accessories:: 1. Face PlateDocument7 pagesLathe Accessories and Attachments Lathe Accessories:: 1. Face PlateRohan SahaNo ratings yet
- Grinding MachineDocument9 pagesGrinding Machinejineesha p jNo ratings yet
- Generalized Kinematics of Five-Axis Serial Machines WithDocument47 pagesGeneralized Kinematics of Five-Axis Serial Machines WithJoss Joss100% (1)
- Metal Cutting and Production LAB Manual-New (ME452)Document58 pagesMetal Cutting and Production LAB Manual-New (ME452)Ravichandran GNo ratings yet
- Cutter Radius CompensationDocument2 pagesCutter Radius CompensationSivateja NallamothuNo ratings yet
- Tail Stock of LatheDocument7 pagesTail Stock of LatheKIÊN HOÀNG TRUNG100% (1)
- Secondary or Machining ProcessDocument49 pagesSecondary or Machining ProcessHar QuinNo ratings yet
- Shs Work Immersion Program Training PlanDocument5 pagesShs Work Immersion Program Training PlanAlfie LariosaNo ratings yet
- Rommel Chapter 1 & 2Document22 pagesRommel Chapter 1 & 2Erika DonglawenNo ratings yet
- Man Pro Lab Lab Exp No 6 - Introduction To Lathe OperationDocument8 pagesMan Pro Lab Lab Exp No 6 - Introduction To Lathe OperationfotickNo ratings yet
- Lathe Machine - All Parts and Functions With Diagrams and UsesDocument11 pagesLathe Machine - All Parts and Functions With Diagrams and UsesSATYANARAYANANo ratings yet
- AnacondaDocument4 pagesAnacondaDarshan PatelNo ratings yet
- ShaperDocument20 pagesShaperMilan SainiNo ratings yet
- Lathe Diagram With ExplanationDocument3 pagesLathe Diagram With ExplanationEnrico959No ratings yet
- 06 GearsDocument22 pages06 GearsTeaching ClubNo ratings yet
- H4CL T Operation Manual PDFDocument149 pagesH4CL T Operation Manual PDFNestor German PissoniNo ratings yet
- Milling MachineDocument43 pagesMilling MachineJUAN DAVID MOSQUERA GARCIANo ratings yet
- Unit - V: Manufacturing TechnologyDocument54 pagesUnit - V: Manufacturing TechnologyIjanSahrudinNo ratings yet
- The Indexing or Dividing Head For Milling MachineDocument4 pagesThe Indexing or Dividing Head For Milling MachineDion Adi PutraNo ratings yet
- Unit-II-Capstan & Turret LatheDocument101 pagesUnit-II-Capstan & Turret LatheRavichandran GNo ratings yet
- Name of The Experiment:: Study and Operation Bench Drilling MachineDocument5 pagesName of The Experiment:: Study and Operation Bench Drilling MachinemadNo ratings yet
- ThreadsDocument50 pagesThreadsSagar JathanNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument60 pagesLab Manualshahid_ahmed_28No ratings yet
- BME Lecture 5 ShaperDocument6 pagesBME Lecture 5 ShaperRoop LalNo ratings yet
- Study of Grinding MachinesDocument10 pagesStudy of Grinding Machinesdeepa82ece100% (1)
- Lathe MachineDocument5 pagesLathe Machinegunawan refiadiNo ratings yet
- Wabeco D2000 D24000 D3000 LatheDocument184 pagesWabeco D2000 D24000 D3000 LatheTAREQ_BELALNo ratings yet
- Lab Session Introduction To Lathe MachineDocument5 pagesLab Session Introduction To Lathe MachineAqib ZamanNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 TurningDocument12 pagesLab 2 TurningLuqman HakimNo ratings yet
- TurningDocument6 pagesTurningShivshankar Singh0% (1)
- Manufacturing of Spur Gear: Aim of The ExperimentDocument5 pagesManufacturing of Spur Gear: Aim of The ExperimentParameshwara MeenaNo ratings yet
- Design of Single Point Cutting ToolDocument11 pagesDesign of Single Point Cutting ToolSiddharth DubeyNo ratings yet
- Angle and Tilting Vice - SynopsisDocument6 pagesAngle and Tilting Vice - SynopsisTanvi Khurana100% (3)
- Experiment No 8: To Perform Boring Operation On Lathe: Theoretical BackgroundDocument3 pagesExperiment No 8: To Perform Boring Operation On Lathe: Theoretical BackgroundHasnain AshrafNo ratings yet
- End Mill and Cutting Tool Design Criteria and Technical FeaturesDocument4 pagesEnd Mill and Cutting Tool Design Criteria and Technical FeaturesdkkNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Lathe DrillingDocument16 pagesUnit 5 Lathe Drilling1994prdpNo ratings yet
- Unit 5: Lathe and Drilling MachinesDocument16 pagesUnit 5: Lathe and Drilling MachinesSHANKAREGOWDA K CNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Unit-5Document31 pagesEngineering Mechanics Unit-5ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Department of Petrochemical Engineering College of Technical Engineering University of Polytechnic-DuhokDocument21 pagesDepartment of Petrochemical Engineering College of Technical Engineering University of Polytechnic-DuhokWalid AdnanNo ratings yet
- Machine ShopDocument6 pagesMachine ShopAmarjeet Singh (Assistant Professor- Mechanical Engineer)No ratings yet
- Study On Basic Lathe Machining: AIM: To Study The Construction Details and Working Principle of Basic MachiningDocument12 pagesStudy On Basic Lathe Machining: AIM: To Study The Construction Details and Working Principle of Basic Machininggirma workuNo ratings yet
- CTP Journal PaperDocument7 pagesCTP Journal PaperRavichandran GNo ratings yet
- V Sem 'B' Section Ese Result Analysis FormatDocument3 pagesV Sem 'B' Section Ese Result Analysis FormatRavichandran GNo ratings yet
- Machine Vision and Metrology Workshop-08.09.2018Document2 pagesMachine Vision and Metrology Workshop-08.09.2018Ravichandran GNo ratings yet
- Elective List 7th SemDocument14 pagesElective List 7th SemRavichandran GNo ratings yet
- Computer Literacy: Centre For Social Actions (Csa) Program ONDocument2 pagesComputer Literacy: Centre For Social Actions (Csa) Program ONRavichandran GNo ratings yet
- 15eme14 PDFDocument5 pages15eme14 PDFRavichandran GNo ratings yet
- Workshop 09-2016 AerotrixDocument3 pagesWorkshop 09-2016 AerotrixRavichandran GNo ratings yet
- V SEM B LABDocument7 pagesV SEM B LABRavichandran GNo ratings yet
- ASEE04 (Peer Review) PDFDocument11 pagesASEE04 (Peer Review) PDFRavichandran GNo ratings yet
- Mom Tcs Team 2014-06Document3 pagesMom Tcs Team 2014-06Ravichandran GNo ratings yet
- Natonial Conference 2016-02 (Innovative Trends in Mechanical Engineering)Document16 pagesNatonial Conference 2016-02 (Innovative Trends in Mechanical Engineering)Ravichandran GNo ratings yet
- Guest Lecture 08-2016 Higher Studies in USADocument5 pagesGuest Lecture 08-2016 Higher Studies in USARavichandran GNo ratings yet
- Aculty of Engineering Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument2 pagesAculty of Engineering Department of Mechanical EngineeringRavichandran GNo ratings yet
- E 410 ContentDocument29 pagesE 410 ContentRavichandran GNo ratings yet
- Guest Lecture 2015-11 MR - Gnanaseelan (How A Mechanical Engineer Shapes Him To Tailor The Needs of The Software)Document4 pagesGuest Lecture 2015-11 MR - Gnanaseelan (How A Mechanical Engineer Shapes Him To Tailor The Needs of The Software)Ravichandran GNo ratings yet
- 9AKK108466A8095 S&P Recombiners Utility Scale IECDocument10 pages9AKK108466A8095 S&P Recombiners Utility Scale IECgastonmdqNo ratings yet
- IEC 61000-4-4 Burst Electrical Fast Transient / Burst Immunity TestDocument64 pagesIEC 61000-4-4 Burst Electrical Fast Transient / Burst Immunity TestopinzonNo ratings yet
- A Presentation On Summer Training at Assam Electricity Grid Corporation LTDDocument47 pagesA Presentation On Summer Training at Assam Electricity Grid Corporation LTDAshis karmakarNo ratings yet
- Manual de Partes Plataforma Genie Serie GSDocument186 pagesManual de Partes Plataforma Genie Serie GSVictorMoraUrrutiaNo ratings yet
- Tra Loi Cau Hoi - Energy SavingDocument11 pagesTra Loi Cau Hoi - Energy Savinghung Pham ThanhNo ratings yet
- CM1060 IB 11973 00 RevisedDocument28 pagesCM1060 IB 11973 00 Revised1V4NDragoNo ratings yet
- 3sty 6C ElectDocument59 pages3sty 6C ElectAhmad HamoudaNo ratings yet
- Indralogic L20 System DescriptionDocument124 pagesIndralogic L20 System DescriptionCristopher EntenaNo ratings yet
- Break The Bank Service Manual (ICE) - 11-01-07 - ADocument16 pagesBreak The Bank Service Manual (ICE) - 11-01-07 - AJorge De La FuenteNo ratings yet
- 555 Oscilador Datasheet PDFDocument6 pages555 Oscilador Datasheet PDFArlés GómezNo ratings yet
- Brocade 2800 ManualDocument72 pagesBrocade 2800 ManualjobabobNo ratings yet
- WIMA DC Link CapacitorsDocument16 pagesWIMA DC Link CapacitorsAkash GautamNo ratings yet
- Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K TrucksDocument259 pagesElectrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K TruckssaschaweissNo ratings yet
- Modbus - MP15 A.c72-M4-V65Document13 pagesModbus - MP15 A.c72-M4-V65ManelNo ratings yet
- Rotary Deck Bushing: Balls Make The Difference... Increased Drilling Production Proves ItDocument2 pagesRotary Deck Bushing: Balls Make The Difference... Increased Drilling Production Proves ItFedericoButronNo ratings yet
- Acez Sensing Green Mark Sensor Catalogue TE25Document5 pagesAcez Sensing Green Mark Sensor Catalogue TE25v6656100% (1)
- RC Toys Quotation List (NEW)Document13 pagesRC Toys Quotation List (NEW)Consignatie CampinaNo ratings yet
- 176 fc151Document3 pages176 fc151Hamilton MirandaNo ratings yet
- Rineer Hydraulics: GeneralDocument2 pagesRineer Hydraulics: Generalwilo100% (1)
- HFY3-3720-ELE-PD-0002 - 0 OHTL Installation and Test ProcedureDocument10 pagesHFY3-3720-ELE-PD-0002 - 0 OHTL Installation and Test ProcedureAli SalehNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Permit FormDocument4 pagesMechanical Permit FormJean TroncoNo ratings yet
- Comfort Was Never So Affordable: HBL Installment Plan at 0% Mark-UpDocument2 pagesComfort Was Never So Affordable: HBL Installment Plan at 0% Mark-UpSyedTasawarHussainNo ratings yet
- 14 My BedroomDocument1 page14 My Bedroommarie lucasNo ratings yet